




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 28-41.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0817
张会芳1( ), 张建红2, 刘海礁1, 孙岩3, 齐红志1, 王楠1, 段俊枝1, 郭燕1(
), 张建红2, 刘海礁1, 孙岩3, 齐红志1, 王楠1, 段俊枝1, 郭燕1( ), 尹海燕3
), 尹海燕3
收稿日期:2022-09-25
接受日期:2022-12-05
出版日期:2023-11-15
发布日期:2023-11-20
通讯作者:
郭燕
作者简介:张会芳 E-mail:hfzh2005@126.com;
基金资助:
Huifang ZHANG1( ), Jianhong ZHANG2, Haijiao LIU1, Yan SUN3, Hongzhi QI1, Nan WANG1, Junzhi DUAN1, Yan GUO1(
), Jianhong ZHANG2, Haijiao LIU1, Yan SUN3, Hongzhi QI1, Nan WANG1, Junzhi DUAN1, Yan GUO1( ), Haiyan YIN3
), Haiyan YIN3
Received:2022-09-25
Accepted:2022-12-05
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Yan GUO
摘要:
为研究黄淮冬麦区南片小麦种质性状演变,以黄淮冬麦区南片近20年育成的小麦品种为材料,通过Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(
中图分类号:
张会芳, 张建红, 刘海礁, 孙岩, 齐红志, 王楠, 段俊枝, 郭燕, 尹海燕. 近20年黄淮冬麦区南片小麦种质性状演变及其育种价值评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 28-41.
Huifang ZHANG, Jianhong ZHANG, Haijiao LIU, Yan SUN, Hongzhi QI, Nan WANG, Junzhi DUAN, Yan GUO, Haiyan YIN. Evolution of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Germplasm Traits and Evaluation of Breeding Value in Southern Huang-Huai Winter Wheat Region in Recent 20 Years[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 28-41.
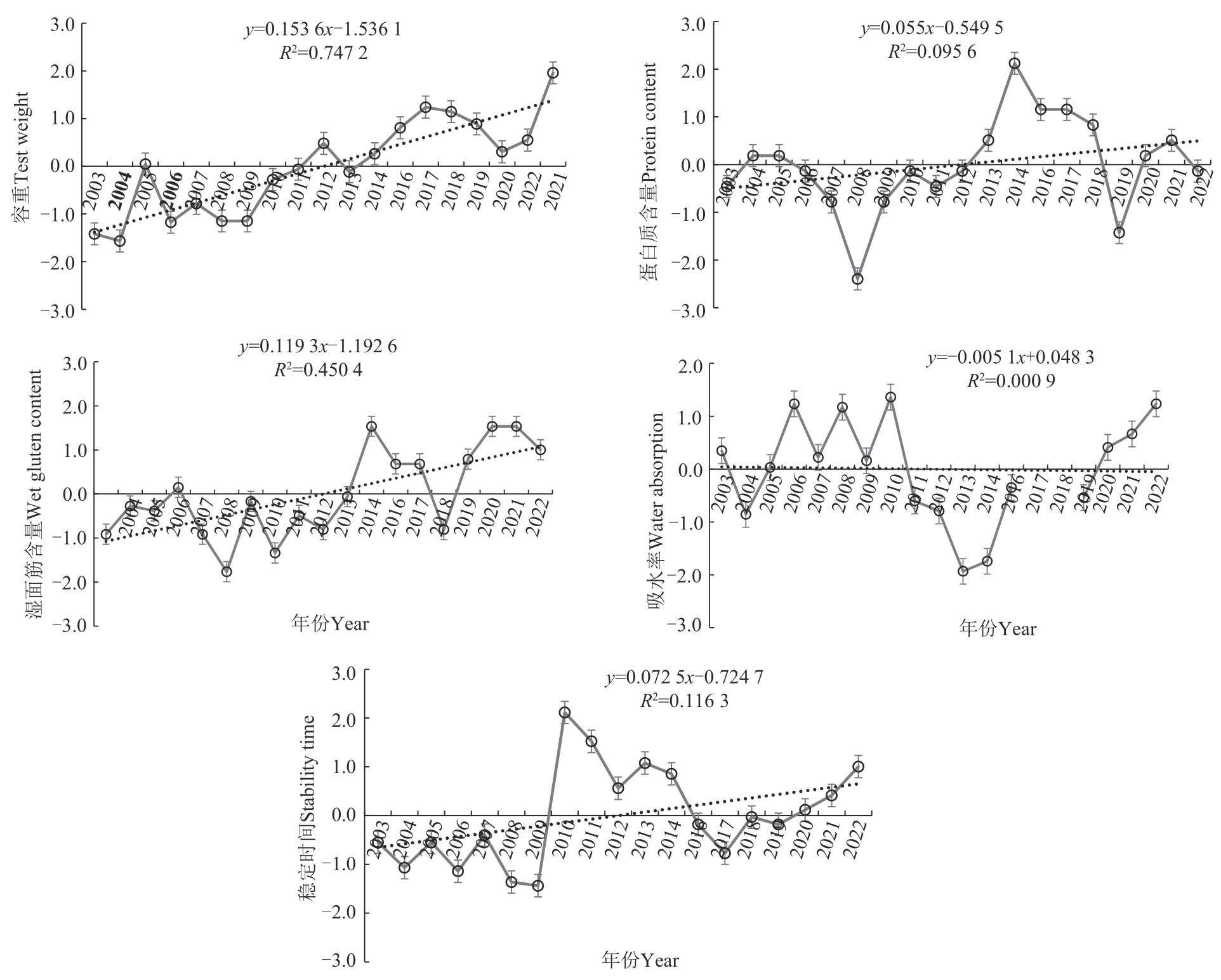
图3 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦品质性状演变注:2017—2018年无吸水率数据。
Fig. 3 Evolution of quality traits of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022Note: No water absorption data from 2017 to 2018.
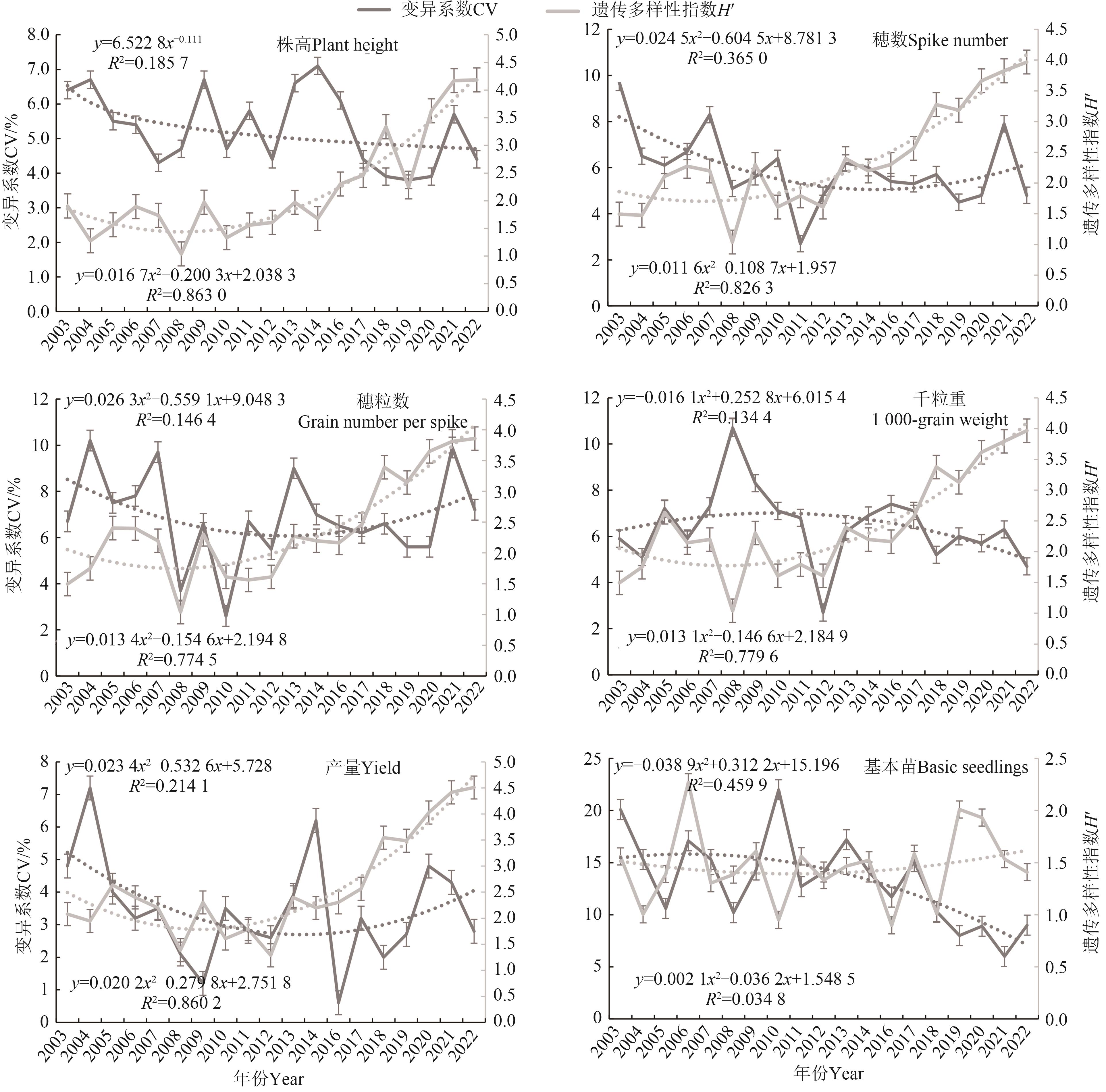
图4 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦农艺性状遗传多样性演变
Fig. 4 Evolution of H′ of agronomic traits of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022

图5 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦品质性状遗传多样性演变
Fig. 5 Evolution of H′ of quality traits of wheat cultivars in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022
年份 Year | 强筋小麦 Strong gluten wheat | 中强筋小麦 Medium strong gluten wheat | 中筋小麦 Medium gluten wheat | 弱筋小麦 Weak gluten wheat | 优质专用麦 High-quality special wheat | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion /% | |
数量合计/ 占比平均 Total number/average portion | 31 | 7.0 | 72 | 16.3 | 339 | 76.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 104 | 23.5 |
| 2003 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 7 | 87.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 12.5 |
| 2004 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 42.9 | 3 | 42.9 | 1 | 14.3 | 4 | 57.1 |
| 2005 | 2 | 14.3 | 1 | 7.1 | 11 | 78.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 21.4 |
| 2006 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 9.1 | 10 | 90.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 9.1 |
| 2007 | 1 | 11.1 | 1 | 11.1 | 7 | 77.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 22.2 |
| 2008 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2009 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 9 | 90.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 |
| 2010 | 1 | 20.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 20.0 |
| 2011 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 16.7 | 5 | 83.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 16.7 |
| 2012 | 1 | 20.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 20.0 |
| 2013 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 11 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2014 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 9 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2016 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 20.0 | 8 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 20.0 |
| 2017 | 1 | 7.7 | 1 | 7.7 | 11 | 84.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 15.4 |
| 2018 | 4 | 11.1 | 3 | 8.3 | 29 | 80.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 7 | 19.4 |
| 2019 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 14.7 | 29 | 85.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 14.7 |
| 2020 | 5 | 7.8 | 11 | 17.2 | 48 | 75.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 16 | 25.0 |
| 2021 | 8 | 9.5 | 16 | 19.0 | 60 | 71.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 24 | 28.6 |
| 2022 | 8 | 7.8 | 25 | 24.3 | 70 | 68.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 33 | 32.0 |
表1 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦不同类型占比
Table 1 Proportion of different types of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022
年份 Year | 强筋小麦 Strong gluten wheat | 中强筋小麦 Medium strong gluten wheat | 中筋小麦 Medium gluten wheat | 弱筋小麦 Weak gluten wheat | 优质专用麦 High-quality special wheat | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion/% | 数量Number | 占比 Proportion /% | |
数量合计/ 占比平均 Total number/average portion | 31 | 7.0 | 72 | 16.3 | 339 | 76.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 104 | 23.5 |
| 2003 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 7 | 87.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 12.5 |
| 2004 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 42.9 | 3 | 42.9 | 1 | 14.3 | 4 | 57.1 |
| 2005 | 2 | 14.3 | 1 | 7.1 | 11 | 78.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 21.4 |
| 2006 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 9.1 | 10 | 90.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 9.1 |
| 2007 | 1 | 11.1 | 1 | 11.1 | 7 | 77.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 22.2 |
| 2008 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2009 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 9 | 90.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 10.0 |
| 2010 | 1 | 20.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 20.0 |
| 2011 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 16.7 | 5 | 83.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 16.7 |
| 2012 | 1 | 20.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 20.0 |
| 2013 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 11 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2014 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 9 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2016 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 20.0 | 8 | 80.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 20.0 |
| 2017 | 1 | 7.7 | 1 | 7.7 | 11 | 84.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 15.4 |
| 2018 | 4 | 11.1 | 3 | 8.3 | 29 | 80.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 7 | 19.4 |
| 2019 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 14.7 | 29 | 85.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 14.7 |
| 2020 | 5 | 7.8 | 11 | 17.2 | 48 | 75.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 16 | 25.0 |
| 2021 | 8 | 9.5 | 16 | 19.0 | 60 | 71.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 24 | 28.6 |
| 2022 | 8 | 7.8 | 25 | 24.3 | 70 | 68.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 33 | 32.0 |
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | 第3主成分 PC3 | 第4主成分 PC4 | 第5主成分 PC5 | 第6主成分 PC6 | 第7主成分 PC7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
特征向量 Eigenvector | 株高Plant height | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | -0.10 | -0.27 |
| 穗数Spike number | 0.33 | 0.03 | -0.32 | 0.32 | -0.11 | -0.19 | 0.07 | |
| 穗粒数Grain number per spike | -0.01 | -0.05 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.00 | -0.41 | |
| 千粒重1 000-grain weight | -0.05 | 0.28 | -0.46 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.54 | -0.07 | |
| 产量Yield | 0.17 | 0.24 | -0.55 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.02 | -0.15 | |
| 基本苗Basic seedlings | -0.09 | -0.17 | 0.18 | 0.49 | -0.23 | 0.50 | 0.32 | |
| 容重Test weight | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.18 | -0.49 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.11 | |
| 蛋白质含量Protein content | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.19 | -0.49 | -0.39 | -0.05 | |
| 湿面筋含量Wet gluten content | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.30 | -0.22 | -0.05 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| 吸水率Water absorption | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.30 | -0.28 | 0.33 | -0.27 | |
| 稳定时间Stability time | 0.40 | -0.34 | -0.06 | -0.06 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.95 | 2.25 | 1.64 | 1.40 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 0.71 | |
| 贡献率Contribution rate/% | 28.22 | 16.09 | 11.73 | 9.99 | 7.69 | 7.01 | 5.07 | |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/% | 28.22 | 44.32 | 56.05 | 66.04 | 73.73 | 80.75 | 85.81 | |
| 权重Index weight | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
表2 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦前7个主成分的特征向量、特征值、贡献率及累计贡献率
Table 2 Eigenvectors, eigenvalues, contribution rates and cumulative contribution rates of the first 7 principal components of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022
项目 Item | 性状 Trait | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | 第3主成分 PC3 | 第4主成分 PC4 | 第5主成分 PC5 | 第6主成分 PC6 | 第7主成分 PC7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
特征向量 Eigenvector | 株高Plant height | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | -0.10 | -0.27 |
| 穗数Spike number | 0.33 | 0.03 | -0.32 | 0.32 | -0.11 | -0.19 | 0.07 | |
| 穗粒数Grain number per spike | -0.01 | -0.05 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.00 | -0.41 | |
| 千粒重1 000-grain weight | -0.05 | 0.28 | -0.46 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.54 | -0.07 | |
| 产量Yield | 0.17 | 0.24 | -0.55 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.02 | -0.15 | |
| 基本苗Basic seedlings | -0.09 | -0.17 | 0.18 | 0.49 | -0.23 | 0.50 | 0.32 | |
| 容重Test weight | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.18 | -0.49 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.11 | |
| 蛋白质含量Protein content | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.19 | -0.49 | -0.39 | -0.05 | |
| 湿面筋含量Wet gluten content | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.30 | -0.22 | -0.05 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| 吸水率Water absorption | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.30 | -0.28 | 0.33 | -0.27 | |
| 稳定时间Stability time | 0.40 | -0.34 | -0.06 | -0.06 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.95 | 2.25 | 1.64 | 1.40 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 0.71 | |
| 贡献率Contribution rate/% | 28.22 | 16.09 | 11.73 | 9.99 | 7.69 | 7.01 | 5.07 | |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/% | 28.22 | 44.32 | 56.05 | 66.04 | 73.73 | 80.75 | 85.81 | |
| 权重Index weight | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking | 品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
稷麦336 Jimai 336 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.738 | 1 | 华伟306 Huawei 306 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 22 |
安科1801 Anke 1801 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.738 | 2 | 瑞华麦502 Ruihuamai 502 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 23 |
济麦44 Jimai 44 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.731 | 3 | 安科1803 Anke 1803 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 24 |
谷神麦19 Gushenmai 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.730 | 4 | 皖宿1510 Wansu 1510 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.673 | 25 |
华伟305 Huawei 305 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.721 | 5 | 科大1026 Keda 1026 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.672 | 26 |
西农20 Xinong 20 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.711 | 6 | 皖宿0313 Wansu 0313 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.671 | 27 |
新麦45 Xinmai 45 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.704 | 7 | 华垦麦7号 Huakenmai 7 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.671 | 28 |
| 金诚麦19号 Jinchengmai 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.702 | 8 | 中麦578 Zhongmai 578 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 29 |
山农41号 Shannong 41 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.696 | 9 | 淮麦45 Huaimai 45 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 30 |
新世纪878 Xinshiji 878 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.691 | 10 | 山农116 Shannong 116 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 31 |
新麦38 Xinmai 38 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.690 | 11 | 西农364 Xinong 364 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.669 | 32 |
安科157 Anke 157 | 中强筋 Medium strong gluten wheat | 0.689 | 12 | 中研麦688 Zhongyanmai 688 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.669 | 33 |
| 郑品优9号 Zhengpinyou 9 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.683 | 13 | 墩麦88 Dunmai 88 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.668 | 34 |
德宏福麦11 Dehongfumai 11 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.683 | 14 | 濮麦053 Pumai 053 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.667 | 35 |
宛1204 Wan 1204 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.682 | 15 | 华成865 Huacheng 865 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.667 | 36 |
商道29 Shangdao 29 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.681 | 16 | 徐麦44 Xumai 44 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.666 | 37 |
安科1701 Anke 1701 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.679 | 17 | 新麦26 Xinmai 26 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 38 |
富麦118 Fumai 118 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.678 | 18 | 漯麦40 Luomai 40 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 39 |
郑麦1835 Zhengmai 1835 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.677 | 19 | 徽研1722 Huiyan 1722 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 40 |
新世纪169 Xinshiji 169 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.677 | 20 | 涡麦1211 Womai 1211 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 41 |
囤麦257 Tunmai 257 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.675 | 21 | 航宇19 Hangyu 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.663 | 42 |
表3 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦综合得分前50的品种名称及品质分类
Table 3 Comprehensive scores and quality classification of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022
品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking | 品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
稷麦336 Jimai 336 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.738 | 1 | 华伟306 Huawei 306 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 22 |
安科1801 Anke 1801 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.738 | 2 | 瑞华麦502 Ruihuamai 502 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 23 |
济麦44 Jimai 44 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.731 | 3 | 安科1803 Anke 1803 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.674 | 24 |
谷神麦19 Gushenmai 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.730 | 4 | 皖宿1510 Wansu 1510 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.673 | 25 |
华伟305 Huawei 305 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.721 | 5 | 科大1026 Keda 1026 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.672 | 26 |
西农20 Xinong 20 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.711 | 6 | 皖宿0313 Wansu 0313 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.671 | 27 |
新麦45 Xinmai 45 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.704 | 7 | 华垦麦7号 Huakenmai 7 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.671 | 28 |
| 金诚麦19号 Jinchengmai 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.702 | 8 | 中麦578 Zhongmai 578 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 29 |
山农41号 Shannong 41 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.696 | 9 | 淮麦45 Huaimai 45 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 30 |
新世纪878 Xinshiji 878 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.691 | 10 | 山农116 Shannong 116 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.670 | 31 |
新麦38 Xinmai 38 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.690 | 11 | 西农364 Xinong 364 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.669 | 32 |
安科157 Anke 157 | 中强筋 Medium strong gluten wheat | 0.689 | 12 | 中研麦688 Zhongyanmai 688 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.669 | 33 |
| 郑品优9号 Zhengpinyou 9 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.683 | 13 | 墩麦88 Dunmai 88 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.668 | 34 |
德宏福麦11 Dehongfumai 11 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.683 | 14 | 濮麦053 Pumai 053 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.667 | 35 |
宛1204 Wan 1204 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.682 | 15 | 华成865 Huacheng 865 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.667 | 36 |
商道29 Shangdao 29 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.681 | 16 | 徐麦44 Xumai 44 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.666 | 37 |
安科1701 Anke 1701 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.679 | 17 | 新麦26 Xinmai 26 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 38 |
富麦118 Fumai 118 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.678 | 18 | 漯麦40 Luomai 40 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 39 |
郑麦1835 Zhengmai 1835 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.677 | 19 | 徽研1722 Huiyan 1722 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.664 | 40 |
新世纪169 Xinshiji 169 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.677 | 20 | 涡麦1211 Womai 1211 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 41 |
囤麦257 Tunmai 257 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.675 | 21 | 航宇19 Hangyu 19 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.663 | 42 |
| 指标Index | 株高 Plant height | 穗数 Spike number | 穗粒数 Grain number per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight | 产量 Yield | 基本苗 Basic seedlings | 容重 Test weight | 蛋白质含量 Protein content | 湿面筋含量 Wet gluten content | 吸水率 Water absorption | 稳定时间 Stability time | 品质分类 Quality classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D´ | 0.019 | 0.417** | -0.098 | 0.026 | 0.580** | 0.038 | 0.636** | 0.361** | 0.330** | 0.637** | 0.407** | 0.520** |
表4 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦性状、品质分类与D′相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between traits, quality classification and D' of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai wheat winter region from 2003 to 2022
| 指标Index | 株高 Plant height | 穗数 Spike number | 穗粒数 Grain number per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight | 产量 Yield | 基本苗 Basic seedlings | 容重 Test weight | 蛋白质含量 Protein content | 湿面筋含量 Wet gluten content | 吸水率 Water absorption | 稳定时间 Stability time | 品质分类 Quality classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D´ | 0.019 | 0.417** | -0.098 | 0.026 | 0.580** | 0.038 | 0.636** | 0.361** | 0.330** | 0.637** | 0.407** | 0.520** |
品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking | 品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
漯麦49 Luomai 49 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 43 | 万丰269 Wanfeng 269 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.662 | 47 |
皖垦麦1702 Wankenmai 1702 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 44 | 安科1602 Anke 1602 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.662 | 48 |
国禾麦3号 Guohemai 3 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 45 | 农麦168 Nongmai 168 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.661 | 49 |
国鑫麦188 Guoxinmai 188 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 46 | 西农172 Xinong 172 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.660 | 50 |
表3 2003—2022年黄淮冬麦区南片育成小麦综合得分前50的品种名称及品质分类 (续表Continued)
Table 3 Comprehensive scores and quality classification of wheat varieties in southern Huang-Huai winter wheat region from 2003 to 2022
品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking | 品种名称 Variety name | 品质分类 Quality classification | 得分 Score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
漯麦49 Luomai 49 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 43 | 万丰269 Wanfeng 269 | 中强筋 Medium-strong gluten wheat | 0.662 | 47 |
皖垦麦1702 Wankenmai 1702 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 44 | 安科1602 Anke 1602 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.662 | 48 |
国禾麦3号 Guohemai 3 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 45 | 农麦168 Nongmai 168 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.661 | 49 |
国鑫麦188 Guoxinmai 188 | 中筋 Medium gluten wheat | 0.663 | 46 | 西农172 Xinong 172 | 强筋 Strong gluten wheat | 0.660 | 50 |
| 1 | 杨建波,王莉,张萍丽,等.河南省粮食主产区中低产田分区综合整治研究[J].中国农业资源与区划,2015,36(1):79-85. |
| YANG J B, WANG L, ZHANG L P, et al.. Comprehensive improvement on the medium-low yield fields of the major grain production areas in Henan Province [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan., 2015, 36(1):79-85. | |
| 2 | 蒋永穆,卢洋,张晓磊.新中国成立70年来中国特色农业现代化内涵演进特征探析[J].当代经济研究,2019(8):9-18, 113. |
| JIANG Y M, LU Y, ZHANG X L. Analysis of the characteristics of connotation evolution of agricultural modernization with Chinese characteristics in the 70 years since the founding of new China [J]. Contemp. Econ. Res., 2019 (8):9-18, 113. | |
| 3 | 杜思梦,刘涛.基于新发展理念的农业高质量发展:内涵、问题及举措[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(3):18-24. |
| DU S M, LIU T. High-quality development of agriculture based on new development concept: connotation, problems and measures [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(3):18-24. | |
| 4 | 张勇,郝元峰,张艳,等.小麦营养和健康品质研究进展[J].中国农业科学,2016,49(22):4284-4298. |
| ZHANG Y, HAO Y F, ZHANG Y, et al.. Progress in research on genetic improvement of nutrition and health qualities in wheat [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2016, 49(22):4284-4298. | |
| 5 | 王洪新,胡志昂.植物的繁育系统、遗传结构和遗传多样性保护[J].生物多样性,1996,4(2):32-36. |
| WANG H X, HU Z A. Plant breeding system, genetic structure and conservation of genetic diversity [J]. Biodiversity Sci., 1996, 4(2):32-36. | |
| 6 | 丁明亮,林丽萍,李明菊,等.云南育成小麦品种(系)品质性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J].南方农业学报,2020,51(2):255-266. |
| DING M L, LIN L P, LI M J, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of quality traits of wheat varieties (lines) bred in Yunnan [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2020, 51(2):255-266. | |
| 7 | 许娜丽,王新华,马冬花,等.251份小麦种质资源的主要农艺与品质性状遗传多样性分析[J].南方农业学报,2021,5(9):2404-2416. |
| XU N L, WANG X H, MA D H, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis of main agronomic and quality traits of 251 wheat germplasm resources [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2021, 5(9):2404-2416. | |
| 8 | 胡卫国,赵虹,王西成,等.黄淮冬麦区小麦品种品质改良现状分析[J].麦类作物学报,2010,30(5):936-943. |
| HU W G, ZHAO H, WANG X C, et al.. Quality improvement of winter wheat in Yellow and Huai River wheat zone [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2010, 30(5):936-943. | |
| 9 | 赵广才.中国小麦种植区划研究(一)[J].麦类作物学报,2010,30(5):886-895. |
| ZHAO G C. Study on Chinese wheat planting regionalization (Ⅰ) [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2010, 30(5):886-895. | |
| 10 | 中华人民共和国农业部.专用小麦优势区域发展规划[EB/OL].(2003-05-26)[2022-06-11].. |
| 11 | 江涛,于艳玲,江楠,等.黄淮麦区85个小麦品种(系)农艺性状的聚类分析[J].山东农业科学,2009(10):14-17, 21. |
| JIANG T, YU Y L, JIANG N, et al.. Cluster analysis of 85 wheat varieties in Huang-Huai wheat area based on agronomic traits [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2009 (10):14-17, 21. | |
| 12 | 姚盟,张玲丽,冯毅,等.黄淮麦区小麦新品系主要农艺性状变异分析[J].种子,2015,34(9):66-70. |
| YAO M, ZHANG L L, FENG Y, et al.. Analysis of the main agronomic traits variation of new wheat lines in Huang Huai wheat growing region [J]. Seed, 2015, 34(9):66-70. | |
| 13 | 马艳明,范玉顶,李斯深,等.黄淮麦区小麦品种(系)品质性状多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2004,5(2):133-138. |
| MA Y M, FAN Y D, LI S S, et al.. Diversity of quality traits using wheat varieties of the Huang-Huai winter wheat area [J]. J. Plant Genetic. Resour., 2004, 5(2):133-138. | |
| 14 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 小麦品种品质分类: [S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2013. |
| 15 | 唐如玉,徐鹏,余迪求.水稻轮回选择群体XTBG-HP1表型遗传多样性分析[J].广西植物,2020,40(2):159-172. |
| TANG R Y, XU P, YU D Q. Phenotypic diversity analysis of rice recurrent selection population XTBG-HP1 [J]. Guihaia, 2020, 40(2):159-172. | |
| 16 | 武松,潘发明.SPSS统计分析大全[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2014:318-320. |
| 17 | 封婷.综合评价中一种凹性指数型功效函数[J].统计与信息论坛,2016,31(7):16-21. |
| FENG T. A concave exponential efficacy function in comprehensive evaluation [J]. Statistics Inform. Forum, 2016, 31(7):16-21. | |
| 18 | 李岚涛,张铎,盛开,等.施氮量对菊芋块茎产量、品质与植株生理特性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(3):496-506. |
| LI L T, ZHANG D, SHENG K, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rates on tuber yield, quality and plant physiological activities of Helianthus tuberosus L. [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2022, 28(3):496-506. | |
| 19 | 许昊,吴宏玥,王占军,等.立地条件对宁夏中部干旱风沙区柠条生物量分配格局的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2020,42(12):91-100. |
| XU H, WU H Y, WANG Z J, et al.. Effects of site conditions on biomass allocation patterns of Caragana korshinskii in arid aeolian sand regions, middle area of Ningxia of northwestern China [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2020, 42(12):91-100. | |
| 20 | 代顺冬,叶鹏盛,黄玲,等.四川烤烟区试新品种综合分析与评价[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(19):6601-6612. |
| DAI S D, YE P S, HUANG L, et al.. Comprehensive analysis and evaluation of new flue-cured tobacco varieties in Sichuan regional trials [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(19):6601-6612. | |
| 21 | 张雨晴,于海业,刘爽,等.玉米叶片净光合速率快速检测方法研究[J].农机化研究,2019,41(4):182-185. |
| ZHANG Y Q, YU H Y, LIU S, et al.. Study on rapid detection method of net photosynthetic rate of maize leaves [J]. J. Agric. Mech. Res., 2019, 41(4):182-185. | |
| 22 | 张淑文,梁森苗,郑锡良,等.杨梅优株果实品质的主成分分析及综合评价[J].果树学报,2018,35(8):977-986. |
| ZHANG S W, LIANG S M, ZHENG X L, et al.. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality in some advanced selections of Chinese bayberry [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2018, 35(8):977-986. | |
| 23 | 盖钧镒.试验统计方法[M].4版.北京:中国农业出版社,2013:173. |
| 24 | 成广雷,邱军,王晓光,等.我国青贮玉米组合(品种)的农艺性状、生物产量和品质变化[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(4):30-37. |
| CHENG G L, QIU J, WANG X G, et al.. Changes of agronomic traits, biomass yield and quality of national silage maize combinations (varieties) [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(4):30-37. | |
| 25 | 伍维模,李世清.小麦品种演变过程中性状遗传改良规律综述[J].塔里木大学学报,2006,18(1):43-47. |
| WU W M, LI S Q. A summary of genetic improvement of characters during wheat cultivars evolvement [J]. J. Tarim Univ., 2006, 18(1):43-47. | |
| 26 | 郭瑞,李正玲,张煜,等.30a来河南省不同类型小麦品种产量和农艺性状演变规律[J].河南农业科学,2018,47(4):15-20. |
| GUO R, LI Z L, ZHANG Y, et al.. Evolution rule of agronomic and yield traits of different types of wheat varieties in Henan Province in past 30 years [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2018, 47(4):15-20. | |
| 27 | 胡学旭,周桂英,吴丽娜,等.2006—2014年我国小麦品质在年度和品质区之间的变化[J].麦类作物学报,2016,36(3):292-301. |
| HU X X, ZHOU G Y, WU L N, et al.. Variation of wheat quality in wheat-producing regions in China from 2006 to 2014 [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2016, 36(3):292-301. | |
| 28 | 张文通,董伟.SPSS统计分析高级教程[M].3版.北京:高等教育出版社,2018:239. |
| 29 | 刘彤彤,李宁,魏良迪,等.山西省主推小麦品种芽期及苗期耐盐性的综合评价[J].中国农业大学学报,2022,27(2):22-33. |
| LIU T T, LI N, WEI L D, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance of wheat varieties in Shanxi Province during germination and seedling stages [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2022, 27(2) : 22-23. | |
| 30 | 刘孟宜,田博宇,王滢颖,等.基于主成分分析的不同小麦品种制作的韧性饼干品质评价[J].食品研究与开发,2021,42(10):44-53. |
| LIU M Y, TIAN B Y, WANG Y Y, et al.. Quality evaluation of tough biscuits made from different wheat varieties based on principal component analysis [J]. Food Res. Dev., 2021, 42(10):44-53. | |
| 31 | 宋晓,张珂珂,黄晨晨,等.基于主成分分析的氮高效小麦品种的筛选[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(12):10-16. |
| SONG X, ZHANG K K, HUANG C C, et al.. Selection of nitrogen-efficient wheat varieties based on principal component analysis [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2020, 49(12):10-16. | |
| 32 | 张会芳,齐红志,孙岩,等.黄淮冬麦区不同来源地新育成小麦品种性状多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2023,24(3):719-731. |
| ZHANG H F, QI H Z, SUN Y, et al.. Character diversity analysis of new wheat varieties from different origins in Huang-Huai winter wheat region [J]. J. Plant Genetic. Resour., 2023, 24(3):719-731. |
| [1] | 姜雪敏, 陈向前, 李红燕, 姜奇彦. 小麦盐胁迫响应的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [2] | 赵明宇, 贾浩, 石晓宇, 潘义, 黄妤韵, 王凯澄, 褚庆全. 近30年黄淮海农作区冬小麦水足迹分布变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 138-147. |
| [3] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [4] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [5] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [6] | 张力方, 李志元, 刘宇翔, 张红丽, 秦勇. 不同复合基质对盆栽芫荽生长状况的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 204-214. |
| [7] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [8] | 郭梓沣, 黄雷, 李奎. 畜禽种质资源的创新与利用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 14-22. |
| [9] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [10] | 郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188. |
| [11] | 刘盼, 高珊, 李浩宇, 王翼, 尹宝重, 郭进考, 甄文超. 缩行匀株对小麦分蘖的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 32-44. |
| [12] | 许娜丽, 余慧霞, 姚明明, 王彦青, 李清峰, 刘彩霞, 孙刚, 陈佳静, 龙姣卉, 王掌军. 基于SSR和SRAP标记小麦资源遗传多样性及农艺性状分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 30-46. |
| [13] | 郑童童, 杨雯迪, 王宁, 马俊杰, 刘龙, 郭庆元. 小麦叶枯病病原菌的形态学与多基因系统学鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 111-118. |
| [14] | 梁婷, 左静红, 陆青, 杨东, 唐益苗, 郭春曼, 汪德州, 王伟伟. 小麦IQM基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 27-37. |
| [15] | 郭胜微, 边思文, 丁建文, 张晓辰, 杨兴, 杜锦, 向春阳. 糯玉米萌发期耐低温品种资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号