




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 32-44.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0235
刘盼1( ), 高珊1, 李浩宇2, 王翼2, 尹宝重2, 郭进考3, 甄文超1,4,5(
), 高珊1, 李浩宇2, 王翼2, 尹宝重2, 郭进考3, 甄文超1,4,5( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-28
接受日期:2023-04-12
出版日期:2023-04-01
发布日期:2023-06-26
通讯作者:
甄文超
作者简介:刘盼 E-mail:liupan198612@163.com;
基金资助:
Pan LIU1( ), Shan GAO1, Haoyu LI2, Yi WANG2, Baozhong YIN2, Jinkao GUO3, Wenchao ZHEN1,4,5(
), Shan GAO1, Haoyu LI2, Yi WANG2, Baozhong YIN2, Jinkao GUO3, Wenchao ZHEN1,4,5( )
)
Received:2023-03-28
Accepted:2023-04-12
Online:2023-04-01
Published:2023-06-26
Contact:
Wenchao ZHEN
摘要:
为明确缩行匀株(row space reduction and plant space expansion,RRPE)对冬小麦分蘖的影响及其生理机制,于2019-2021年小麦种植季,以‘马兰1号’为供试品种,设置2个行距和3个播期,研究RRPE处理对小麦冬前分蘖数和生物量的影响,及分蘖节内源激素和蔗糖对RRPE的响应特征。结果表明,RRPE处理能促进小麦冬前分蘖数(tillers number,TN)和生物量,平均增加14.5%和20.9%,并增加≥3叶的分蘖数;RRPE处理降低了3叶期至越冬期小麦分蘖节吲哚乙酸(indoleacetic acid,IAA)、独脚金内酯(strigolactones,SLs)、赤霉素(gibberellin,GA)和油菜素甾醇(brassinosterol,BR)含量,分别平均降低19.4%、17.5%、11.4%和13.6%;RRPE处理显著提高了玉米素核苷(zeatin nucleoside,ZR)、细胞分裂素(cytokinin,CTK)和蔗糖(saccharose,SA)含量,平均提高13.1%、54.4%和15.2%。RRPE处理还降低了IAA/ZR、BR/SL和BR/CTK,但提高了SLs/GA。相关分析表明,CTK、BR与冬前TN显著相关,相关系数平均为0.65。BR对TN的正向贡献最高;GA、BR/CTK对TN的负向贡献较高;IAA/ZR通过GA和IAA对TN的负向贡献较高。综上所述,RRPE处理可以促进小麦冬前分蘖、增加生物量,这与BR、GA含量,以及BR/CTK的直接作用、IAA/ZR通过GA和IAA的间接作用关系密切。
中图分类号:
刘盼, 高珊, 李浩宇, 王翼, 尹宝重, 郭进考, 甄文超. 缩行匀株对小麦分蘖的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 32-44.
Pan LIU, Shan GAO, Haoyu LI, Yi WANG, Baozhong YIN, Jinkao GUO, Wenchao ZHEN. Effects of Row Space Reduction and Plant Space Expansion on Tillers Number in Wheat and Its Physiological Mechanism[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 32-44.
| 处理Treatment | 2019—2020 | 2020—2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播前 Before sowing | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 播前 Before sowing | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 开花期 Anthei stage | ||
| 15.0RS | SD1 | 538.5 | 873.0 | 384.0 | 631.5 | 826.5 |
| SD2 | 552.0 | 852.0 | 412.5 | 606.0 | 831.0 | |
| SD3 | 580.5 | 798.0 | 423.0 | 568.5 | 790.5 | |
| 7.5RS | SD1 | 568.5 | 822.0 | 336.0 | 591.0 | 756.0 |
| SD2 | 594.0 | 766.5 | 388.5 | 564.0 | 733.5 | |
| SD3 | 550.5 | 723.0 | 393.0 | 525.0 | 678.0 | |
表1 不同处理下各生育期的灌水量 (m3·hm-2)
Table 1 Irrigation amount of wheat fields under different treatments in different periods
| 处理Treatment | 2019—2020 | 2020—2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播前 Before sowing | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 播前 Before sowing | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 开花期 Anthei stage | ||
| 15.0RS | SD1 | 538.5 | 873.0 | 384.0 | 631.5 | 826.5 |
| SD2 | 552.0 | 852.0 | 412.5 | 606.0 | 831.0 | |
| SD3 | 580.5 | 798.0 | 423.0 | 568.5 | 790.5 | |
| 7.5RS | SD1 | 568.5 | 822.0 | 336.0 | 591.0 | 756.0 |
| SD2 | 594.0 | 766.5 | 388.5 | 564.0 | 733.5 | |
| SD3 | 550.5 | 723.0 | 393.0 | 525.0 | 678.0 | |
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 苗数 Seedling number/(104·hm-2) | 分蘖数Tillers number | 生物量Biomass | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
单株 Per plant | ≥3叶 ≥3 leaf | ≥3叶占比 ≥3 leaf ratio/% | 单株 Per plant/g | 分蘖 Tiller/g | 分蘖占比 Ratio of tiller/% | ||||
| 2019 | SD1 | 15.0RS | 342.0 | 2.7 b | 1.9 b | 70.6 a | 0.39 b | 0.19 b | 48.8 b |
| 7.5RS | 327.0 | 3.5 a | 2.4 a | 67.9 a | 0.48 a | 0.26 a | 53.9 a | ||
| SD2 | 15.0RS | 370.5 | 2.1 b | 1.5 b | 71.9 b | 0.33 b | 0.14 b | 40.5 b | |
| 7.5RS | 361.5 | 2.8 a | 2.3 a | 81.9 a | 0.40 a | 0.19 a | 48.9 a | ||
| SD3 | 15.0RS | 409.5 | 1.5 b | 0.9 b | 61.7 b | 0.22 b | 0.07 b | 31.6 b | |
| 7.5RS | 423.0 | 1.8 a | 1.4 a | 75.8 a | 0.26 a | 0.11 a | 42.6 a | ||
| 2020 | SD1 | 15.0RS | 328.5 | 2.9 b | 2.1 b | 71.3 a | 0.43 b | 0.21 b | 49.1 b |
| 7.5RS | 339.0 | 3.6 a | 2.6 a | 71.8 a | 0.49 a | 0.27 a | 55.9 a | ||
| SD2 | 15.0RS | 369.0 | 2.3 b | 1.8 b | 78.2 b | 0.36 b | 0.16 b | 43.4 b | |
| 7.5RS | 366.0 | 2.9 a | 2.4 a | 84.0 a | 0.43 a | 0.22 a | 49.5 a | ||
| SD3 | 15.0RS | 403.5 | 1.2 b | 0.8 b | 64.2 b | 0.23 b | 0.08 b | 33.5 b | |
| 7.5RS | 409.5 | 1.7 a | 1.3 a | 75.0 a | 0.28 a | 0.11 a | 39.5 a | ||
| 年份 Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ||
| 播期 SD | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 行距 RS | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×播期Y×SD | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×行距Y×RS | ns | ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 播期×行距SD×RS | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×播期×行距Y×SD×RS | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
表2 不同处理下小麦的茎(蘖)数量及生物量
Table 2 Tillers number and biomass under different treatments
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 苗数 Seedling number/(104·hm-2) | 分蘖数Tillers number | 生物量Biomass | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
单株 Per plant | ≥3叶 ≥3 leaf | ≥3叶占比 ≥3 leaf ratio/% | 单株 Per plant/g | 分蘖 Tiller/g | 分蘖占比 Ratio of tiller/% | ||||
| 2019 | SD1 | 15.0RS | 342.0 | 2.7 b | 1.9 b | 70.6 a | 0.39 b | 0.19 b | 48.8 b |
| 7.5RS | 327.0 | 3.5 a | 2.4 a | 67.9 a | 0.48 a | 0.26 a | 53.9 a | ||
| SD2 | 15.0RS | 370.5 | 2.1 b | 1.5 b | 71.9 b | 0.33 b | 0.14 b | 40.5 b | |
| 7.5RS | 361.5 | 2.8 a | 2.3 a | 81.9 a | 0.40 a | 0.19 a | 48.9 a | ||
| SD3 | 15.0RS | 409.5 | 1.5 b | 0.9 b | 61.7 b | 0.22 b | 0.07 b | 31.6 b | |
| 7.5RS | 423.0 | 1.8 a | 1.4 a | 75.8 a | 0.26 a | 0.11 a | 42.6 a | ||
| 2020 | SD1 | 15.0RS | 328.5 | 2.9 b | 2.1 b | 71.3 a | 0.43 b | 0.21 b | 49.1 b |
| 7.5RS | 339.0 | 3.6 a | 2.6 a | 71.8 a | 0.49 a | 0.27 a | 55.9 a | ||
| SD2 | 15.0RS | 369.0 | 2.3 b | 1.8 b | 78.2 b | 0.36 b | 0.16 b | 43.4 b | |
| 7.5RS | 366.0 | 2.9 a | 2.4 a | 84.0 a | 0.43 a | 0.22 a | 49.5 a | ||
| SD3 | 15.0RS | 403.5 | 1.2 b | 0.8 b | 64.2 b | 0.23 b | 0.08 b | 33.5 b | |
| 7.5RS | 409.5 | 1.7 a | 1.3 a | 75.0 a | 0.28 a | 0.11 a | 39.5 a | ||
| 年份 Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ||
| 播期 SD | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 行距 RS | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份×播期Y×SD | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×行距Y×RS | ns | ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 播期×行距SD×RS | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 年份×播期×行距Y×SD×RS | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||

图1 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的吲哚乙酸与玉米素核苷含量注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示含量分布。
Fig. 1 Contents of IAA and ZR in wheat tiller nodes under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of content.
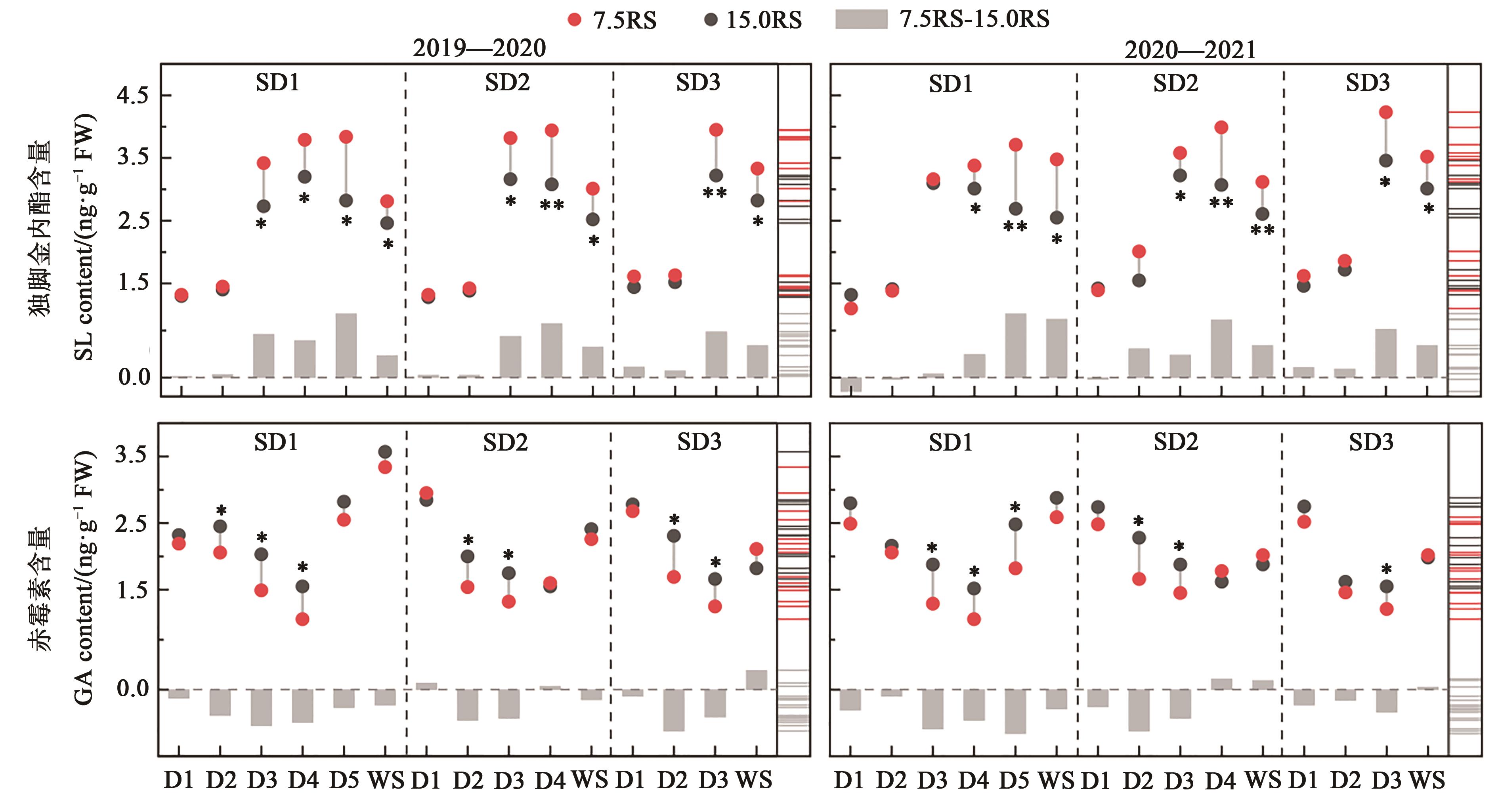
图2 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的独角金内酯和赤霉素含量注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05 和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示含量分布。
Fig. 2 Contents of SLs and GA in wheat tillers node under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of content.
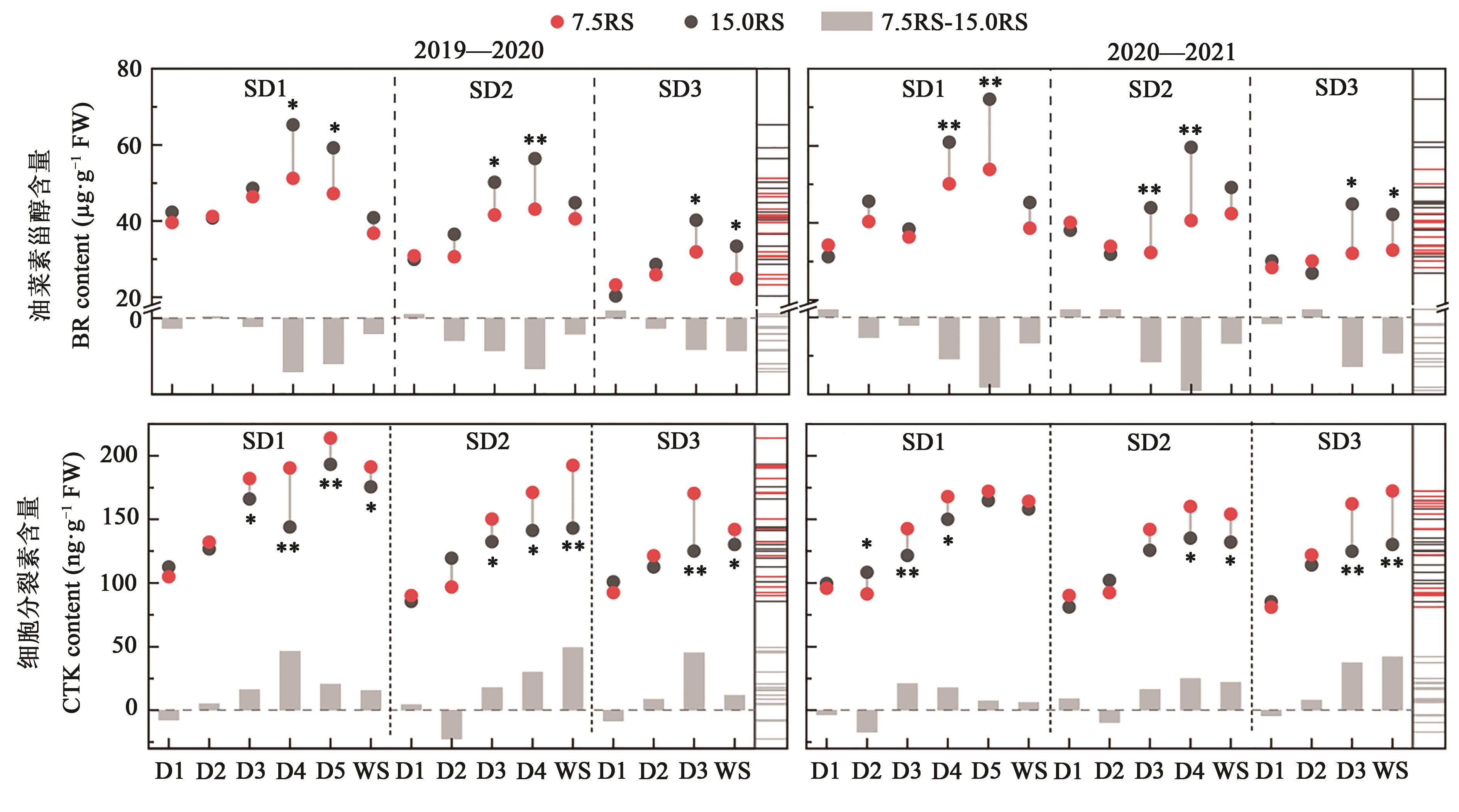
图3 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的油菜素甾醇和细胞分裂素含量注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示含量分布。
Fig. 3 Contents of BR and CTK in wheat tillers node under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of content.

图4 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的IAA/ZR和SLs/GA注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示比值分布。
Fig. 4 IAA/ZR and SLs/GA of wheat tillers node different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of ratio.
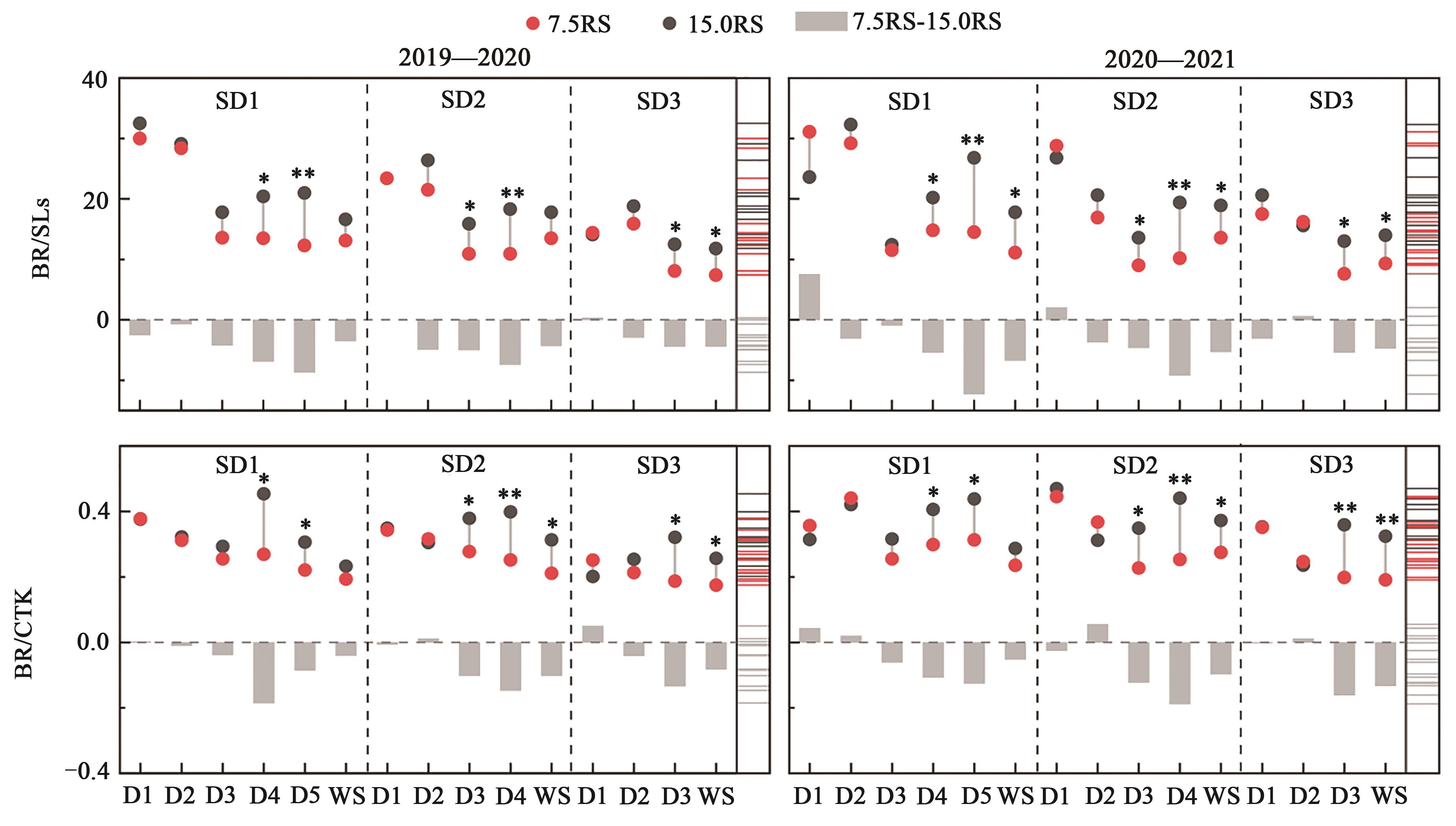
图5 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的BR/SLs和BR/CTK注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示比值分布。
Fig. 5 BR/SLs and BR/CTK of wheat tillers node under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of ratio.
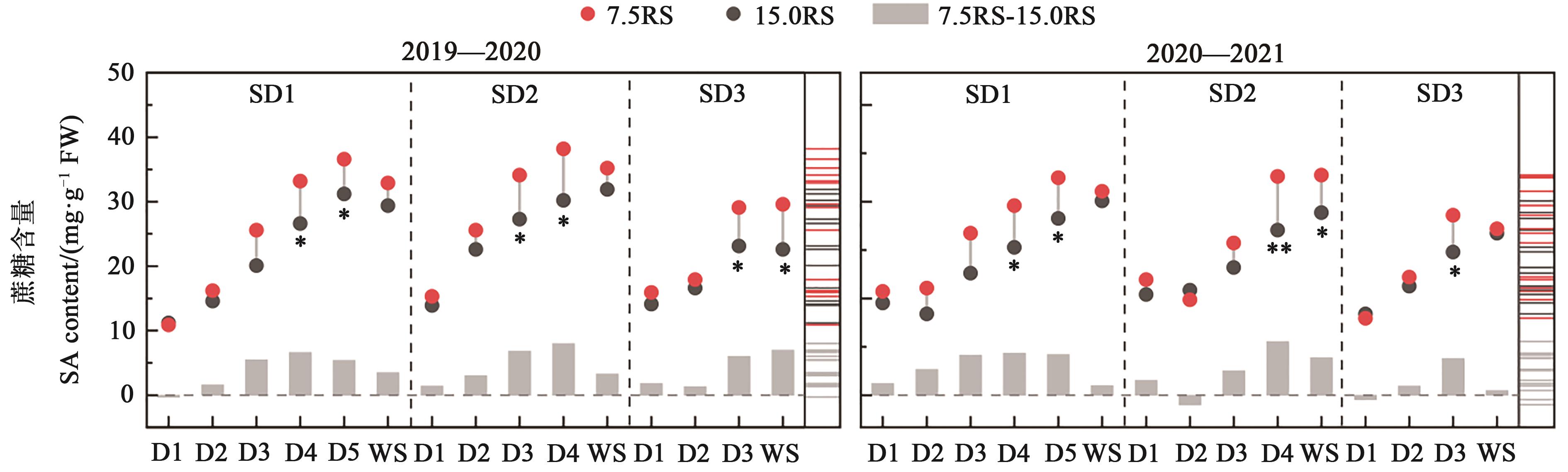
图6 不同处理下冬小麦分蘖节的蔗糖含量注:*和**分别表示7.5RS与15.0RS处理间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著;7.5RS-15.0RS表示7.5RS和15.0RS处理间的差值;图中不同颜色横线表示含量分布。
Fig. 6 Content of SA in wheat tillers node under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; 7.5RS-15.0RS represents difference value between 7.5RS and 15.0RS treatments; different color lines in the figure indicate the distribution of content.
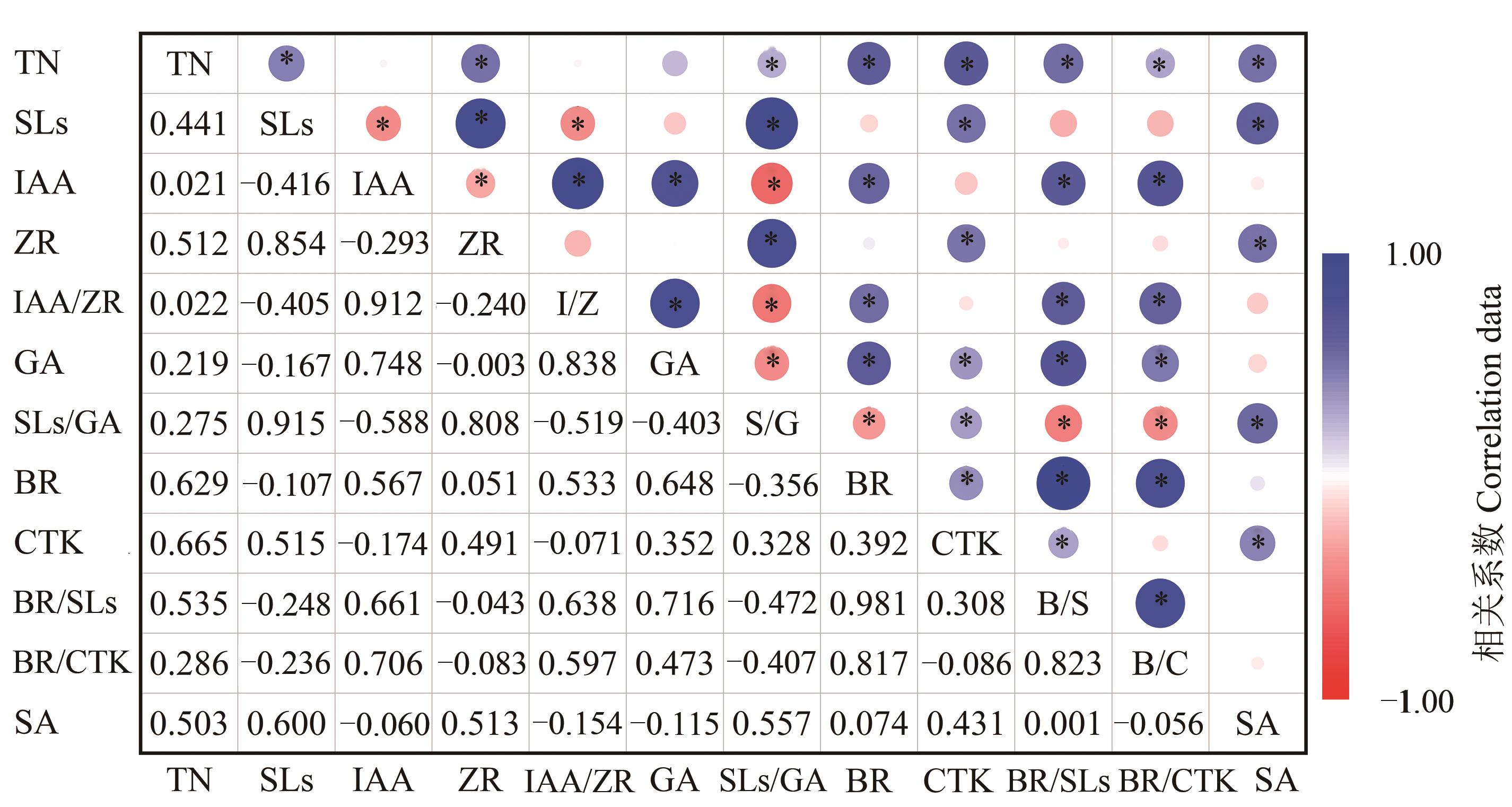
图7 缩行匀株条件下小麦分蘖数与分蘖节激素、蔗糖含量的相关性注:*表示在P<0.05水平显著相关。
Fig. 7 Correlation between tillers number and phytohormone, SA content of wheat tillers node under RRPE treatmentNote:* indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | ASSUERO S, LORENZO M, PÉREZ RAMÍREZ N, et al.. Tillering promotion by paclobutrazol in wheat and its relationship with plant carbohydrate status [J]. New Zealand J. Agric. Res., 2012, 55(4):347-358. |
| 2 | ZHUANG L L, GE Y, WANG J, et al.. Gibberellic acid inhibition of tillering in tall fescue involving crosstalks with cytokinins and transcriptional regulation of genes controlling axillary bud outgrowth [J/OL]. Plant. Sci., 2019, 287:110168 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 3 | BARBIER F F, DUN E A, KERR S C, et al.. An update on the signals controlling shoot branching [J]. Trends Plant. Sci., 2019, 24(3):220-236. |
| 4 | WANG Y, MIAO F, YAN L L. Branching shoots and spikes from lateral meristems in bread wheat [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(3):e0151656 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 5 | WANG G, RÖMHELD V, LI C, et al.. Involvement of auxin and CKs in boron deficiency induced changes in apical dominance of pea plants (Pisum sativum L.) [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2006, 163(6):591-600. |
| 6 | SHIMIZU-SATO S, TANAKA M, MORI H. Auxin-cytokinin interactions in the control of shoot branching [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2008, 69(4):429-435. |
| 7 | CAI T, MENG X P, LIU X L, et al.. Exogenous hormonal application regulates the occurrence of wheat tillers by changing endogenous hormones [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2018, 9(12):1-17. |
| 8 | LIU Y, DING Y F, WANG Q S, et al.. Effect of plant growth regulators on growth of rice tiller bud and changes of endogenous hormones [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2011, 37(4):670-676. |
| 9 | LIU R F, HOU J, LI H F, et al.. Association of Ta D14-4D, a gene involved in strigolactone signaling, with yield contributing traits in wheat [J/OL]. Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2021, 22(7):3748 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 10 | KENROM T H, BRUTNELL T P, FINLASON S A. Suppression of sorghum axillary bud outgrowth by shade, phyB and defoliation signalling pathways [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2010, 33(1): 48-58. |
| 11 | SHANG Q S, WANG Y P, TANG H, et al.. Genetic, hormonal, and environmental control of tillering in wheat [J]. Crop. J., 2021, 9(5):986-991. |
| 12 | YU H, YANG J, CUI H, et al.. Effects of plant density on tillering in the weed grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. and its phytohormonal regulation [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2020, 157(1):70-78. |
| 13 | BASTOS L M, CARCIOCHI W, LOLLATO R P, et al.. Winter wheat yield response to plant density as a function of yield environment and tillering potential: a review and field studies [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11(3):1-17. |
| 14 | ALI M, SHABBIR A, MAHMOOD Z, et al.. Case study: the effect of wheat density and cultivar on growth and reproduction of burr medic (Medicago polymorpha L.), wheat growth, and yield [J]. Weed Biol. Manag., 2021,22(1):3-12. |
| 15 | WALEY J M, SPARKES D L, FOULKES M J, et al.. The physiological response of winter wheat to reductions in plant density [J]. Ann. Appl. Biol., 2000, 137(2):165-177. |
| 16 | LIU X J, YIN B Z, HU Z H, et al.. Physiological response of flag leaf and yield formation of winter wheat under different spring restrictive irrigation regimes in the Haihe Plain, China [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2021, 20(9):2343-2359. |
| 17 | YIN B Z, LIU P, HU Z H, et al.. Soil physical properties, nutrients, and crop yield with two-year tillage rotations under a winter wheat-summer maize double cropping system [J]. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng., 2022, 15(1):172-181. |
| 18 | LIU G B, ZHAO J Z, LIAO T, et al.. Histological dissection of cutting-inducible adventitious rooting in Platycladus orientalis reveals developmental endogenous hormonal homeostasis [J/OL]. Ind. Crop. Prod., 2021, 170:113817 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 19 | MAO Y X, CHAI X R, ZHONG M, et al.. Effects of nitrogen and magnesium nutrient on the plant growth, quality, photosynthetic characteristics, antioxidant metabolism, and endogenous hormone of Chinese kale (Brassica albograbra Bailey) [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2022, 303:111243 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 20 | WANG W Q, HAO Q Q, TIAN F X, et al.. Cytokinin-regulated sucrose metabolism in stay-green wheat phenotype [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(8):e0161351[2023-02-20]. . |
| 21 | MUSTROPH A, BOAMFA E I, LAARHOVEN L J J, et al.. Organ-specific analysis of the anaerobic primary metabolism in rice and wheat seedlings. I: dark ethanol production is dominated by the shoots [J]. Planta, 2006, 225(1):103-114. |
| 22 | HUSSAIN M Z, MEHMOOD M B, KHANN S F, et al.. Narrow row spacing ensures higher productivity of low tillering wheat cultivars [J]. Int. J. Agric. Biol., 2012, 14(3):413-418. |
| 23 | TILLEY M S, HEINIGER R W, CROZIER C R. Tiller initiation and its effects on yield and yield components in winter wheat [J]. Agron. J., 2019, 111(3):1323-1332. |
| 24 | FISCHER R A, MORENO RAMOS O H, ORYIZ MONASTERIO I, et al.. Yield response to plant density, row spacing and raised beds in low latitude spring wheat with ample soil resources: an update [J]. Field Crops. Res., 2019, 232:95-105. |
| 25 | ABICHOU M, DE SOLAN B, ANDRIEU B. Architectural response of wheat cultivars to row spacing reveals altered perception of plant density [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019, 10(8):1-14. |
| 26 | DE VITA P, COLECCHIA S A, PECORELLA I, et al.. Reduced inter-row distance improves yield and competition against weeds in a semi-dwarf durum wheat variety [J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2017, 85:69-77. |
| 27 | HILTBRUNNER J, LIEDGENS M, STAMP P, et al.. Effects of row spacing and liquid manure on directly drilled winter wheat in organic farming [J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2005, 22(4):441-447. |
| 28 | DWYER L M, STEWART D W, TOLLENAAR M. Changes in plant density dependence of leaf photosynthesis of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids, 1959 to 1988 [J]. Can. J. Plant Sci., 1991, 71(1):1-11. |
| 29 | 董立强,王术,高光杰,等.直播条件下行距对不同穗型粳稻产量及倒伏性状的影响[J].华北农学报,2017,32(4):169-175. |
| DONG L Q, WANG S, GAO G J, et al.. Effect of row distances on yields and lodging resistance of japonica rice cultivars with different panicle types under drill seeding [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2017,32(4):169-175. | |
| 30 | BALLARÉ C L. Keeping up with the neighbours: phytochrome sensing and other signalling mechanisms [J].Trends Plant Sci., 1999, 4(5):97-102. |
| 31 | MCSTEEN P. Hormonal regulation of branching in grasses [J]. Plant Physiol., 2009, 149(1):46-55. |
| 32 | SAXENA P, HUANG B, BONOS S A, et al.. Photoperiod and temperature effects on rhizome production and tillering rate in tall fescue [Lolium arundinaceum (Schreb.) Darby.] [J]. Crop Sci., 2014, 54(3):1205-1210. |
| 33 | ALAM M M, HAMMER G L, VAN OOSTEROM E J, et al.. A physiological framework to explain genetic and environmental regulation of tillering in sorghum [J]. New Phytol., 2014, 203(1):155-167. |
| 34 | RAMEAU C, BERTHELOOT J, LEDUC N, et al.. Multiple pathways regulate shoot branching [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 5(1):1-15. |
| 35 | YIN Y H, WANG Z Y, MORA-GARCIA S, et al.. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation [J]. Cell, 2002, 109(2):181-191. |
| 36 | BREWER P B, DUN E A, FERGUSON B J, et al.. Strigolactone acts downstream of auxin to regulate bud outgrowth in pea and arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2009, 150(1):482-493. |
| 37 | LO S F, YANG S Y, CHEN K T, et al.. A novel class of gibberellin 2-oxidases control semidwarfism, tillering, and root development in rice [J]. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10):2603-2618. |
| 38 | DUGGAN B L, RICHARDS R A, TSUYUZAKI H. Environmental effects on stunting and the expression of a tiller inhibition (tin) gene in wheat [J]. Func. Plant Biol., 2002, 29(1):45-53. |
| 39 | ROLLAND F, BAENA-GONZALEZ E, SHEEN J. Sugar sensing and sinaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2006, 57(1):675-709. |
| 40 | RABOT A, HENRY C, BAAZIZ K BEN, et al.. Insight into the role of sugars in bud burst under light in the rose [J]. Plant Cell. Physiol., 2012, 53(6):1068-1082. |
| 41 | LIU J, CHENG X L, LIU P, et al.. miR156-targeted SBP-Box transcription factors interact with DWARF53 to regulate TEOSINTE BRANCHED1 and BARREN STALK1 expression in bread wheat [J]. Plant Physiol., 2017, 174(3):1931-1948. |
| 42 | FANG Z M, JI Y Y, HU J, et al.. Strigolactones and brassinosteroids antagonistically regulate the stability of the D53-OsBZR1 complex to determine FC1 expression in rice tillering [J]. Mol. Plant, 2020, 13(4):586-597. |
| [1] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [2] | 许娜丽, 余慧霞, 姚明明, 王彦青, 李清峰, 刘彩霞, 孙刚, 陈佳静, 龙姣卉, 王掌军. 基于SSR和SRAP标记小麦资源遗传多样性及农艺性状分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 30-46. |
| [3] | 郑童童, 杨雯迪, 王宁, 马俊杰, 刘龙, 郭庆元. 小麦叶枯病病原菌的形态学与多基因系统学鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 111-118. |
| [4] | 梁婷, 左静红, 陆青, 杨东, 唐益苗, 郭春曼, 汪德州, 王伟伟. 小麦IQM基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 27-37. |
| [5] | 赵文昊, 姬江涛, 马淏, 金鑫, 李雪, 马海港. 基于改进K-means算法的冬小麦覆盖度提取研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 83-91. |
| [6] | 贾睿琪, 郭子昂, 姚晨, 李璞, 腊贵晓, 陆夏梓, 郭虹妤, 李烜桢. 低磷胁迫对小麦镉吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 154-160. |
| [7] | 陆青, 梁婷, 王伟伟, 汪德州, 吴娴, 王小燕, 唐益苗. 小麦热激蛋白基因TaHSP90-1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [8] | 张文麒, 吴升, 郭新宇, 温维亮, 卢宪菊, 赵春江. 植株自旋转多视角重建技术在小麦植株三维表型获取中的应用评估[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 87-98. |
| [9] | 刘雪静, 鲍晓远, 候晓阳, 甄文超. 海河平原春季限水灌溉下冬小麦农田水分动态及产量形成特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 167-176. |
| [10] | 易媛, 张会云, 刘立伟, 王静, 朱雪成, 赵娜, 冯国华. 活性腐殖酸缓释肥替代尿素对徐麦新品种产量和群体质量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 144-153. |
| [11] | 许鑫, 马兆务, 熊淑萍, 马新明, 程涛, 李海洋, 赵锦鹏. 基于气候年型的河南省冬小麦产量预测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 136-144. |
| [12] | 曹世勤, 王万军, 贾秋珍, 鲁清林, 张耀辉, 张勃, 孙振宇, 白斌, 黄瑾, 王宏康. 甘肃省冬小麦抗条锈病育种现状及对策[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 109-124. |
| [13] | 陈昱利, 杨平, 李华伟. 种植密度和播期对冬小麦籽粒品质影响的模拟研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 143-153. |
| [14] | 王健, 许爱玲, 卫晓东, 席吉龙, 杨娜, 王珂, 席天元, 张建诚. 运城盆地不同播期小麦春季冻害风险评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 137-147. |
| [15] | 蒋赟, 张丽丽, 薛平, 王秀东. 我国小麦产业发展情况及国际经验借鉴[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号