




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 178-188.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0228
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
郑淑琳1,2( ), 石玉涛1(
), 石玉涛1( ), 王飞权1, 吴邦强3, 李远华1, 张渤1, 叶乃兴2(
), 王飞权1, 吴邦强3, 李远华1, 张渤1, 叶乃兴2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-25
接受日期:2022-05-07
出版日期:2023-04-01
发布日期:2023-06-26
通讯作者:
石玉涛,叶乃兴
作者简介:郑淑琳 E-mail: zsl@wuyiu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shulin ZHENG1,2( ), Yutao SHI1(
), Yutao SHI1( ), Feiquan WANG1, Bangqiang WU3, Yuanhua LI1, Bo ZHANG1, Naixing YE2(
), Feiquan WANG1, Bangqiang WU3, Yuanhua LI1, Bo ZHANG1, Naixing YE2( )
)
Received:2022-03-25
Accepted:2022-05-07
Online:2023-04-01
Published:2023-06-26
Contact:
Yutao SHI,Naixing YE
摘要:
为综合评价不同茶树种质资源花器的矿质营养品质差异,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪法测定了23份茶树种质资源花器中18种矿质元素含量,并对其进行相关性分析、聚类热图分析和主成分分析。结果表明,茶树种质资源花器中18种矿质元素含量具有较为丰富的多样性,变异系数为11.86%~48.96%,遗传多样性指数为1.19~2.19;钾、钙、镁、磷、硫、铝、硼、钡、铬、铜、铁、锰、钛13种元素含量呈正态分布,钠、钴、镍、锌4种元素含量呈正偏态分布,硒含量呈负偏态分布;聚类热图分析将23份茶树种质资源花器分为3个类群;经主成分分析,矿质营养品质综合得分排在前5位的茶树种质资源花器材料依次为‘平阳特早茶’‘巴渝特早’‘黄金芽’‘名山早311’和‘大红袍’,可作为优先开发利用的材料。研究结果可为茶树种质资源的创新利用和茶树花产品的开发提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188.
Shulin ZHENG, Yutao SHI, Feiquan WANG, Bangqiang WU, Yuanhua LI, Bo ZHANG, Naixing YE. Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation of Content of Mineral Elements in Flowers of Different Tea Germplasm Resources[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 178-188.
样品编号 Sample No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Origin | 样品编号 Sample No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF01 | 巴渝特早 Bayutezao | 重庆Chongqing | TF13 | 名山白毫131 Mingshanbaihao 131 | 四川Sichuan |
| TF02 | 白鸡冠 Baijiguan | 福建Fujian | TF14 | 名山早311 Mingshanzao 311 | 四川Sichuan |
| TF03 | 半天妖 Bantianyao | 福建Fujian | TF15 | 平阳特早茶 Pingyangtezaocha | 浙江Zhejiang |
| TF04 | 北斗 Beidou | 福建Fujian | TF16 | 奇曲 Qiqu | 福建Fujian |
| TF05 | 春闺 Chungui | 福建Fujian | TF17 | 千年雪 Qiannianxue | 浙江Zhejiang |
| TF06 | 大红袍 Dahongpao | 福建Fujian | TF18 | 青心乌龙 Qingxinwulong | 台湾Taiwan |
| TF07 | 丹桂 Dangui | 福建Fujian | TF19 | 秋香 Qiuxiang | 福建Fujian |
| TF08 | 黄金芽 Huangjinya | 浙江Zhejiang | TF20 | 肉桂 Rougui | 福建Fujian |
| TF09 | 金凤凰 Jinfenghuang | 福建Fujian | TF21 | 玉麒麟 Yuqilin | 福建Fujian |
| TF10 | 涟源奇曲 Lianyuanqiqu | 湖南Hunan | TF22 | 紫红袍 Zihongpao | 福建Fujian |
| TF11 | 龙井43 Longjing 43 | 浙江Zhejiang | TF23 | 紫娟 Zijuan | 云南Yunnan |
| TF12 | 蒙山11号 Mengshan 11 | 四川Sichuan |
表1 供试茶树种质资源基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of tea germplasms for testing
样品编号 Sample No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Origin | 样品编号 Sample No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF01 | 巴渝特早 Bayutezao | 重庆Chongqing | TF13 | 名山白毫131 Mingshanbaihao 131 | 四川Sichuan |
| TF02 | 白鸡冠 Baijiguan | 福建Fujian | TF14 | 名山早311 Mingshanzao 311 | 四川Sichuan |
| TF03 | 半天妖 Bantianyao | 福建Fujian | TF15 | 平阳特早茶 Pingyangtezaocha | 浙江Zhejiang |
| TF04 | 北斗 Beidou | 福建Fujian | TF16 | 奇曲 Qiqu | 福建Fujian |
| TF05 | 春闺 Chungui | 福建Fujian | TF17 | 千年雪 Qiannianxue | 浙江Zhejiang |
| TF06 | 大红袍 Dahongpao | 福建Fujian | TF18 | 青心乌龙 Qingxinwulong | 台湾Taiwan |
| TF07 | 丹桂 Dangui | 福建Fujian | TF19 | 秋香 Qiuxiang | 福建Fujian |
| TF08 | 黄金芽 Huangjinya | 浙江Zhejiang | TF20 | 肉桂 Rougui | 福建Fujian |
| TF09 | 金凤凰 Jinfenghuang | 福建Fujian | TF21 | 玉麒麟 Yuqilin | 福建Fujian |
| TF10 | 涟源奇曲 Lianyuanqiqu | 湖南Hunan | TF22 | 紫红袍 Zihongpao | 福建Fujian |
| TF11 | 龙井43 Longjing 43 | 浙江Zhejiang | TF23 | 紫娟 Zijuan | 云南Yunnan |
| TF12 | 蒙山11号 Mengshan 11 | 四川Sichuan |
元素 Element | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 最大值 Maximum value/(mg·kg-1) | 最小值 Minimum value/(mg·kg-1) | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 遗传多样性指数 H' |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 8 139.44 | 10 169.54 | 5 614.87 | 1 055.13 | 12.96 | 1.93 |
| Ca | 1 727.96 | 2 600.14 | 1 148.81 | 333.25 | 19.29 | 1.19 |
| P | 1 011.08 | 1 300.50 | 686.00 | 137.70 | 13.62 | 2.02 |
| Mg | 794.35 | 1 013.86 | 560.02 | 109.06 | 13.73 | 2.05 |
| Mn | 701.42 | 1 032.77 | 456.10 | 122.89 | 17.52 | 1.91 |
| S | 172.83 | 208.41 | 132.26 | 20.50 | 11.86 | 2.19 |
| Al | 131.61 | 214.93 | 88.41 | 30.03 | 22.81 | 2.04 |
| B | 43.99 | 80.01 | 18.72 | 18.38 | 41.78 | 2.13 |
| Ba | 30.36 | 51.87 | 13.60 | 10.24 | 33.73 | 2.17 |
| Fe | 22.71 | 42.60 | 13.11 | 5.92 | 26.08 | 1.78 |
| Na | 21.47 | 33.36 | 15.20 | 4.62 | 21.53 | 1.90 |
| Zn | 9.37 | 15.29 | 6.77 | 2.08 | 22.16 | 1.83 |
| Cu | 3.53 | 5.39 | 2.19 | 0.77 | 21.76 | 1.92 |
| Ti | 1.83 | 3.11 | 1.02 | 0.54 | 29.51 | 2.04 |
| Ni | 0.70 | 1.73 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 48.96 | 1.65 |
| Cr | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 37.42 | 1.99 |
| Se | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 15.88 | 1.73 |
| Co | 0.37 | 0.81 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 38.71 | 1.79 |
表2 23份茶树种质资源花器18种矿质元素含量的差异
Table 2 Characteristic statistic parameters of 18 mineral elements in 23 tea flower samples
元素 Element | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 最大值 Maximum value/(mg·kg-1) | 最小值 Minimum value/(mg·kg-1) | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 遗传多样性指数 H' |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 8 139.44 | 10 169.54 | 5 614.87 | 1 055.13 | 12.96 | 1.93 |
| Ca | 1 727.96 | 2 600.14 | 1 148.81 | 333.25 | 19.29 | 1.19 |
| P | 1 011.08 | 1 300.50 | 686.00 | 137.70 | 13.62 | 2.02 |
| Mg | 794.35 | 1 013.86 | 560.02 | 109.06 | 13.73 | 2.05 |
| Mn | 701.42 | 1 032.77 | 456.10 | 122.89 | 17.52 | 1.91 |
| S | 172.83 | 208.41 | 132.26 | 20.50 | 11.86 | 2.19 |
| Al | 131.61 | 214.93 | 88.41 | 30.03 | 22.81 | 2.04 |
| B | 43.99 | 80.01 | 18.72 | 18.38 | 41.78 | 2.13 |
| Ba | 30.36 | 51.87 | 13.60 | 10.24 | 33.73 | 2.17 |
| Fe | 22.71 | 42.60 | 13.11 | 5.92 | 26.08 | 1.78 |
| Na | 21.47 | 33.36 | 15.20 | 4.62 | 21.53 | 1.90 |
| Zn | 9.37 | 15.29 | 6.77 | 2.08 | 22.16 | 1.83 |
| Cu | 3.53 | 5.39 | 2.19 | 0.77 | 21.76 | 1.92 |
| Ti | 1.83 | 3.11 | 1.02 | 0.54 | 29.51 | 2.04 |
| Ni | 0.70 | 1.73 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 48.96 | 1.65 |
| Cr | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 37.42 | 1.99 |
| Se | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 15.88 | 1.73 |
| Co | 0.37 | 0.81 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 38.71 | 1.79 |
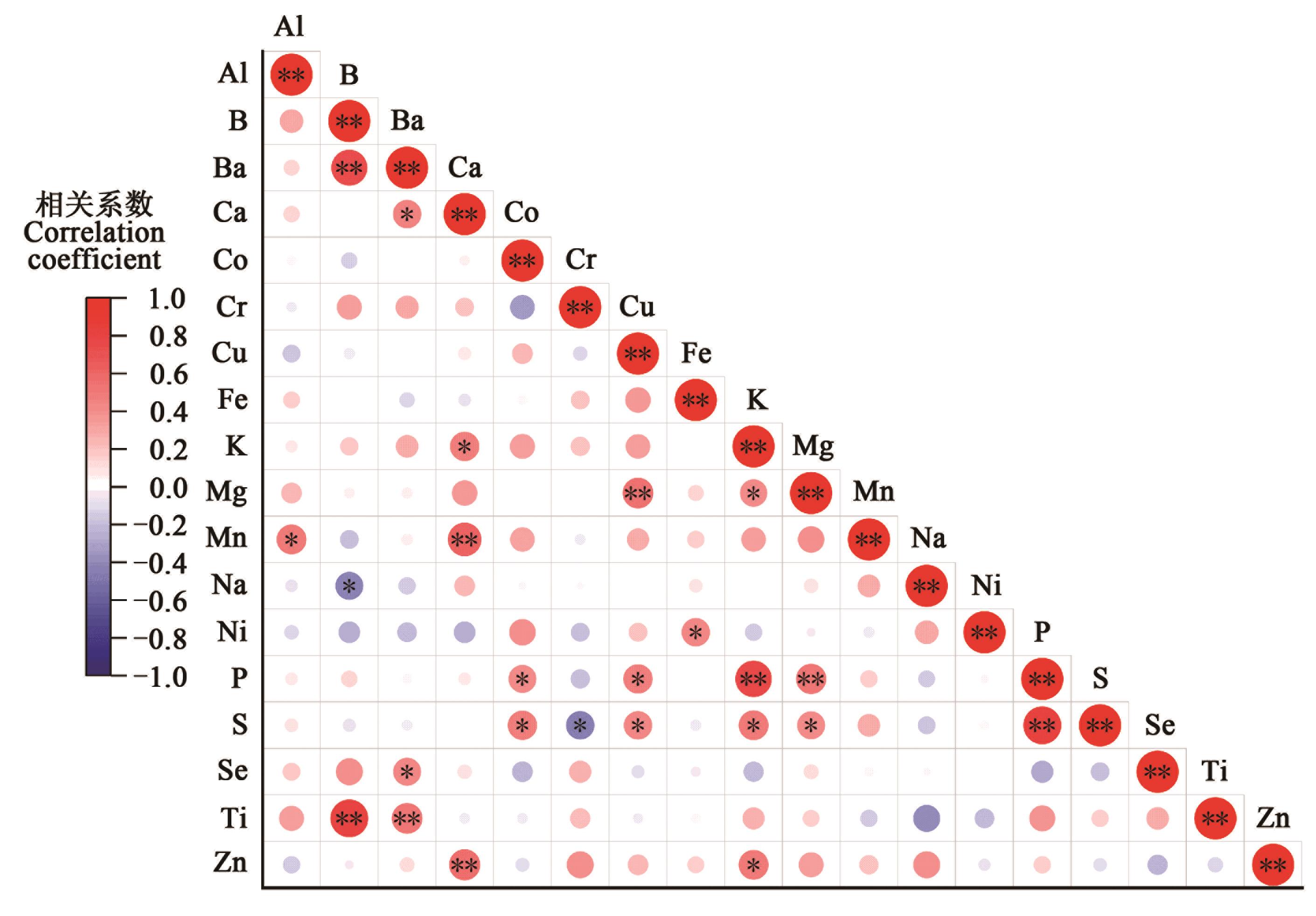
图 1 茶树种质资源花器中18种矿质元素含量相关性注:*和**分别表示相关在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 1 Correlation among 18 mineral elements in tea flower samplesNote: * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
矿质元素 Mineral element | 主成分Principal component | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | |
| Al (X1) | 0.137 | 0.162 | -0.061 | 0.395 | -0.388 | -0.262 | -0.396 |
| B (X2) | 0.095 | 0.474 | -0.141 | 0.078 | 0.145 | 0.088 | -0.040 |
| Ba (X3) | 0.157 | 0.398 | 0.061 | 0.022 | -0.030 | 0.417 | 0.199 |
| Ca (X4) | 0.264 | 0.082 | 0.401 | -0.070 | -0.279 | 0.183 | 0.055 |
| Co (X5) | 0.213 | -0.224 | -0.213 | 0.113 | -0.094 | 0.569 | -0.174 |
| Cr (X6) | -0.010 | 0.293 | 0.318 | -0.035 | 0.307 | 0.014 | -0.209 |
| Cu (X7) | 0.294 | -0.169 | -0.015 | 0.104 | 0.321 | -0.107 | 0.346 |
| Fe (X8) | 0.071 | -0.074 | 0.088 | 0.481 | 0.423 | -0.149 | -0.348 |
| K (X9) | 0.422 | 0.035 | 0.053 | -0.226 | 0.095 | 0.148 | -0.211 |
| Mg (X10) | 0.354 | -0.008 | 0.089 | 0.117 | 0.034 | -0.429 | 0.332 |
| Mn (X11) | 0.287 | -0.101 | 0.222 | 0.263 | -0.407 | -0.026 | -0.114 |
| Na (X12) | 0.000 | -0.224 | 0.393 | 0.138 | -0.037 | 0.092 | 0.109 |
| Ni (X13) | -0.044 | -0.260 | -0.049 | 0.451 | 0.285 | 0.362 | 0.070 |
| P (X14) | 0.411 | -0.062 | -0.256 | -0.157 | 0.117 | -0.053 | -0.019 |
| S (X15) | 0.339 | -0.167 | -0.332 | -0.061 | -0.088 | -0.060 | 0.139 |
| Se (X16) | -0.050 | 0.306 | 0.058 | 0.373 | -0.089 | 0.060 | 0.510 |
| Ti (X17) | 0.154 | 0.397 | -0.251 | 0.073 | 0.128 | -0.037 | -0.100 |
| Zn (X18) | 0.207 | -0.023 | 0.446 | -0.218 | 0.245 | -0.009 | -0.100 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 4.055 | 3.420 | 2.560 | 1.697 | 1.638 | 1.097 | 1.045 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 22.529 | 19.002 | 14.221 | 9.429 | 9.101 | 6.093 | 5.805 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 22.529 | 41.531 | 55.751 | 65.181 | 74.281 | 80.374 | 86.179 |
表3 23份茶树种质资源花器18种矿质元素含量的主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis of the content of 18 mineral elements in 23 tea flower samples
矿质元素 Mineral element | 主成分Principal component | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | |
| Al (X1) | 0.137 | 0.162 | -0.061 | 0.395 | -0.388 | -0.262 | -0.396 |
| B (X2) | 0.095 | 0.474 | -0.141 | 0.078 | 0.145 | 0.088 | -0.040 |
| Ba (X3) | 0.157 | 0.398 | 0.061 | 0.022 | -0.030 | 0.417 | 0.199 |
| Ca (X4) | 0.264 | 0.082 | 0.401 | -0.070 | -0.279 | 0.183 | 0.055 |
| Co (X5) | 0.213 | -0.224 | -0.213 | 0.113 | -0.094 | 0.569 | -0.174 |
| Cr (X6) | -0.010 | 0.293 | 0.318 | -0.035 | 0.307 | 0.014 | -0.209 |
| Cu (X7) | 0.294 | -0.169 | -0.015 | 0.104 | 0.321 | -0.107 | 0.346 |
| Fe (X8) | 0.071 | -0.074 | 0.088 | 0.481 | 0.423 | -0.149 | -0.348 |
| K (X9) | 0.422 | 0.035 | 0.053 | -0.226 | 0.095 | 0.148 | -0.211 |
| Mg (X10) | 0.354 | -0.008 | 0.089 | 0.117 | 0.034 | -0.429 | 0.332 |
| Mn (X11) | 0.287 | -0.101 | 0.222 | 0.263 | -0.407 | -0.026 | -0.114 |
| Na (X12) | 0.000 | -0.224 | 0.393 | 0.138 | -0.037 | 0.092 | 0.109 |
| Ni (X13) | -0.044 | -0.260 | -0.049 | 0.451 | 0.285 | 0.362 | 0.070 |
| P (X14) | 0.411 | -0.062 | -0.256 | -0.157 | 0.117 | -0.053 | -0.019 |
| S (X15) | 0.339 | -0.167 | -0.332 | -0.061 | -0.088 | -0.060 | 0.139 |
| Se (X16) | -0.050 | 0.306 | 0.058 | 0.373 | -0.089 | 0.060 | 0.510 |
| Ti (X17) | 0.154 | 0.397 | -0.251 | 0.073 | 0.128 | -0.037 | -0.100 |
| Zn (X18) | 0.207 | -0.023 | 0.446 | -0.218 | 0.245 | -0.009 | -0.100 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 4.055 | 3.420 | 2.560 | 1.697 | 1.638 | 1.097 | 1.045 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 22.529 | 19.002 | 14.221 | 9.429 | 9.101 | 6.093 | 5.805 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 22.529 | 41.531 | 55.751 | 65.181 | 74.281 | 80.374 | 86.179 |
样品编号 Sample No. | 主成分得分Principal component score | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | |||
| TF01 | 2.140 | 0.044 | 4.785 | -0.100 | -0.011 | 0.977 | 1.539 | 1.518 | 2 |
| TF02 | 0.550 | -1.288 | -0.600 | -1.740 | -1.342 | -0.981 | 2.091 | -0.500 | 16 |
| TF03 | -0.698 | -2.012 | 0.034 | 0.991 | -0.035 | 1.329 | 0.870 | -0.623 | 18 |
| TF04 | -0.030 | 1.379 | -0.520 | 0.212 | 1.001 | -0.752 | 0.281 | 0.305 | 9 |
| TF05 | 0.189 | -3.938 | -0.605 | 3.244 | 2.660 | -0.351 | 0.558 | -0.269 | 15 |
| TF06 | 1.427 | 2.395 | -2.881 | 0.737 | -0.807 | 0.296 | 1.773 | 0.559 | 5 |
| TF07 | -4.851 | -0.656 | 1.150 | -0.149 | 0.139 | 0.067 | 0.322 | -1.196 | 22 |
| TF08 | 2.395 | 1.165 | -0.261 | 0.184 | 0.101 | -2.013 | 0.211 | 0.740 | 3 |
| TF09 | -2.474 | 1.824 | -0.271 | 0.359 | 0.621 | 1.377 | -0.902 | -0.147 | 13 |
| TF10 | -2.729 | 0.793 | -0.728 | -0.686 | 0.749 | 0.139 | 0.171 | -0.632 | 19 |
| TF11 | 2.030 | -2.443 | 0.432 | 0.432 | -2.627 | 0.111 | -0.374 | -0.185 | 14 |
| TF12 | 0.380 | -0.750 | 0.999 | -1.748 | 0.009 | 0.553 | -0.274 | -0.070 | 11 |
| TF13 | 0.590 | -1.981 | 0.102 | -2.947 | 1.202 | -0.588 | -1.559 | -0.605 | 17 |
| TF14 | 0.840 | 2.683 | -0.801 | -0.528 | 1.139 | -0.032 | -0.724 | 0.690 | 4 |
| TF15 | 1.718 | 3.074 | 1.384 | -0.157 | 1.876 | 0.965 | -0.034 | 1.601 | 1 |
| TF16 | -2.980 | -0.300 | -1.120 | -0.329 | -2.105 | 0.840 | -0.536 | -1.264 | 23 |
| TF17 | 2.143 | -0.213 | -0.832 | 0.366 | -0.163 | 0.679 | 0.235 | 0.462 | 6 |
| TF18 | -0.748 | 0.383 | 2.997 | 0.658 | -0.236 | -0.224 | -0.834 | 0.359 | 8 |
| TF19 | -0.387 | 2.779 | 0.426 | 0.921 | -2.194 | -0.133 | -0.228 | 0.424 | 7 |
| TF20 | 0.191 | -1.838 | -0.191 | -1.079 | -0.308 | -1.642 | -0.312 | -0.674 | 21 |
| TF21 | 3.413 | -1.344 | -1.917 | 0.228 | -0.129 | 1.890 | -1.856 | 0.300 | 10 |
| TF22 | -1.336 | -0.225 | -1.870 | -1.163 | 1.272 | -0.339 | 1.031 | -0.654 | 20 |
| TF23 | -0.773 | 0.468 | 0.288 | 2.290 | -0.814 | -2.168 | -1.448 | -0.139 | 12 |
表4 23份茶树种质资源花器主成分得分
Table 4 Score of principal components of 23 tea flower samples
样品编号 Sample No. | 主成分得分Principal component score | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | |||
| TF01 | 2.140 | 0.044 | 4.785 | -0.100 | -0.011 | 0.977 | 1.539 | 1.518 | 2 |
| TF02 | 0.550 | -1.288 | -0.600 | -1.740 | -1.342 | -0.981 | 2.091 | -0.500 | 16 |
| TF03 | -0.698 | -2.012 | 0.034 | 0.991 | -0.035 | 1.329 | 0.870 | -0.623 | 18 |
| TF04 | -0.030 | 1.379 | -0.520 | 0.212 | 1.001 | -0.752 | 0.281 | 0.305 | 9 |
| TF05 | 0.189 | -3.938 | -0.605 | 3.244 | 2.660 | -0.351 | 0.558 | -0.269 | 15 |
| TF06 | 1.427 | 2.395 | -2.881 | 0.737 | -0.807 | 0.296 | 1.773 | 0.559 | 5 |
| TF07 | -4.851 | -0.656 | 1.150 | -0.149 | 0.139 | 0.067 | 0.322 | -1.196 | 22 |
| TF08 | 2.395 | 1.165 | -0.261 | 0.184 | 0.101 | -2.013 | 0.211 | 0.740 | 3 |
| TF09 | -2.474 | 1.824 | -0.271 | 0.359 | 0.621 | 1.377 | -0.902 | -0.147 | 13 |
| TF10 | -2.729 | 0.793 | -0.728 | -0.686 | 0.749 | 0.139 | 0.171 | -0.632 | 19 |
| TF11 | 2.030 | -2.443 | 0.432 | 0.432 | -2.627 | 0.111 | -0.374 | -0.185 | 14 |
| TF12 | 0.380 | -0.750 | 0.999 | -1.748 | 0.009 | 0.553 | -0.274 | -0.070 | 11 |
| TF13 | 0.590 | -1.981 | 0.102 | -2.947 | 1.202 | -0.588 | -1.559 | -0.605 | 17 |
| TF14 | 0.840 | 2.683 | -0.801 | -0.528 | 1.139 | -0.032 | -0.724 | 0.690 | 4 |
| TF15 | 1.718 | 3.074 | 1.384 | -0.157 | 1.876 | 0.965 | -0.034 | 1.601 | 1 |
| TF16 | -2.980 | -0.300 | -1.120 | -0.329 | -2.105 | 0.840 | -0.536 | -1.264 | 23 |
| TF17 | 2.143 | -0.213 | -0.832 | 0.366 | -0.163 | 0.679 | 0.235 | 0.462 | 6 |
| TF18 | -0.748 | 0.383 | 2.997 | 0.658 | -0.236 | -0.224 | -0.834 | 0.359 | 8 |
| TF19 | -0.387 | 2.779 | 0.426 | 0.921 | -2.194 | -0.133 | -0.228 | 0.424 | 7 |
| TF20 | 0.191 | -1.838 | -0.191 | -1.079 | -0.308 | -1.642 | -0.312 | -0.674 | 21 |
| TF21 | 3.413 | -1.344 | -1.917 | 0.228 | -0.129 | 1.890 | -1.856 | 0.300 | 10 |
| TF22 | -1.336 | -0.225 | -1.870 | -1.163 | 1.272 | -0.339 | 1.031 | -0.654 | 20 |
| TF23 | -0.773 | 0.468 | 0.288 | 2.290 | -0.814 | -2.168 | -1.448 | -0.139 | 12 |
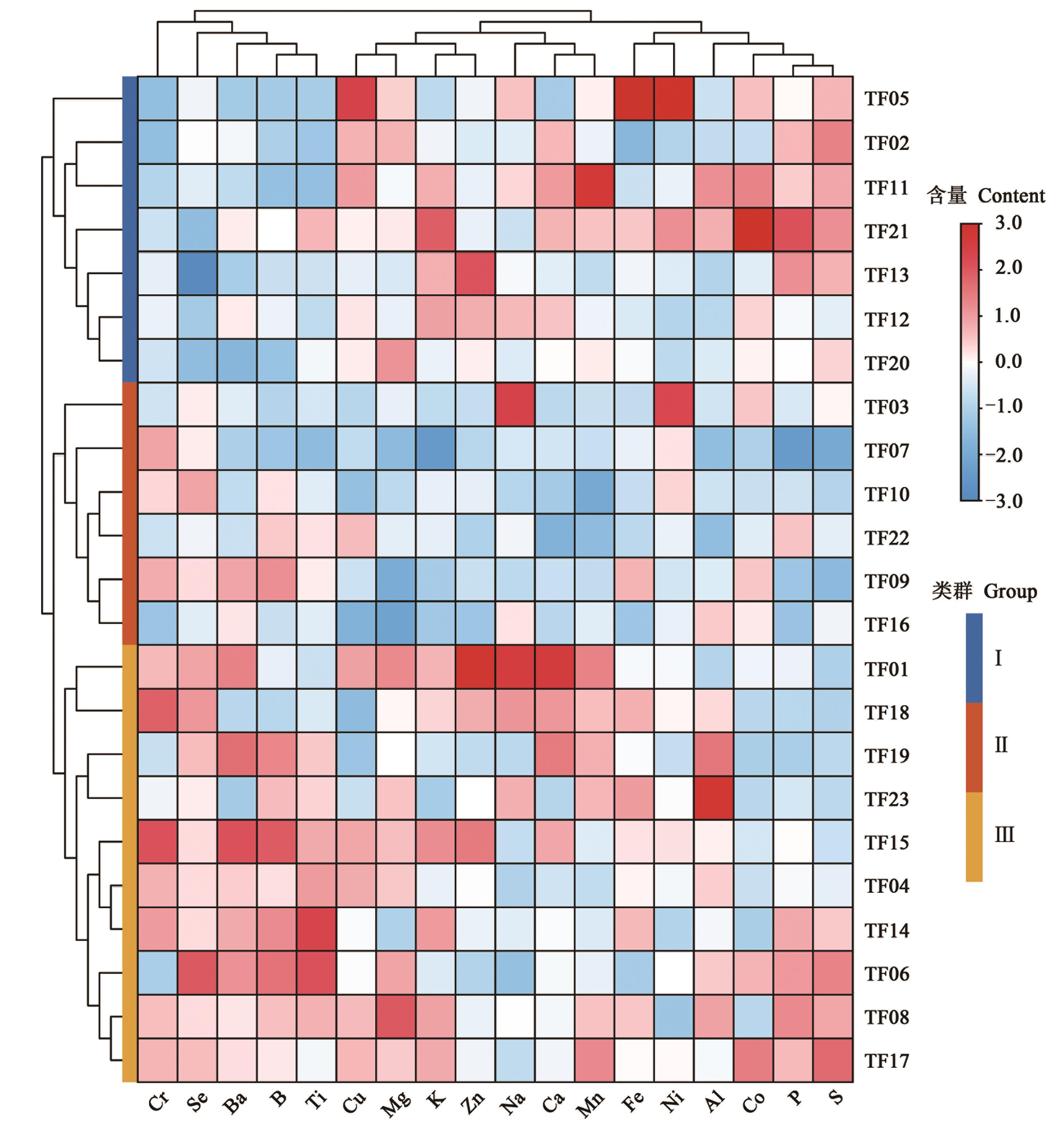
图2 23份茶树种质资源花器18种矿质元素含量的聚类热图注:热图颜色代表矿质元素含量归一化数值,颜色由蓝到红,代表含量由低到高;样品编号同表1。
Fig. 2 Cluster heatmap of 23 tea flower samples based on the content 18 mineral elementsNote:The color of the heatmap represents the normalized value of the mineral element content, with the color going from blue to red, representing low to high content; sample No. is same to Table 1.
矿质元素 Mineral element | 类群ⅠGroupⅠ | 类群Ⅱ GroupⅡ | 类群Ⅲ Group Ⅲ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| Al | 124.93 ab | 26.22 | 112.24 b | 33.52 | 147.91 a | 30.85 |
| B | 29.09 b | 18.83 | 41.23 ab | 6.77 | 56.08 a | 8.18 |
| Ba | 23.82 b | 29.96 | 27.64 ab | 25.97 | 36.57 a | 29.05 |
| Ca | 1 801.73 a | 33.90 | 1 413.42 b | 41.33 | 1 865.04 a | 28.71 |
| Co | 0.46 b | 26.24 | 0.35 b | 20.46 | 0.32 b | 24.21 |
| Cr | 0.37 b | 17.36 | 0.50 ab | 21.17 | 0.63 a | 19.65 |
| Cu | 4.00 a | 7.44 | 2.93 b | 13.23 | 3.56 ab | 10.10 |
| Fe | 23.53 b | 11.19 | 19.78 b | 11.72 | 23.90 b | 9.90 |
| K | 8 624.30 a | 18.73 | 7 084.04 b | 8.79 | 8 433.29 a | 23.82 |
| Mg | 818.93 a | 10.71 | 668.35 b | 26.09 | 852.74 a | 26.06 |
| Mn | 742.43 a | 13.66 | 582.42 b | 10.38 | 744.12 a | 19.19 |
| Na | 21.55 b | 18.46 | 21.75 b | 13.39 | 21.25 b | 12.20 |
| Ni | 0.75 b | 39.27 | 0.80 b | 20.08 | 0.60 b | 14.67 |
| P | 1 095.88 a | 67.07 | 887.31 b | 43.50 | 1 025.98 a | 28.19 |
| S | 187.18 a | 20.27 | 156.33 b | 19.22 | 172.70 ab | 20.71 |
| Se | 0.33 b | 39.44 | 0.41 a | 24.91 | 0.44 a | 36.94 |
| Ti | 1.48 b | 10.01 | 1.62 b | 15.17 | 2.19 a | 10.77 |
| Zn | 9.94 a | 6.07 | 7.75 b | 10.71 | 9.95 a | 12.19 |
平均值 Mean value | 23.05 | 20.35 | 20.30 | |||
表5 3个类群间矿质元素含量差异
Table 5 Comparison of mineral element content among three clusters
矿质元素 Mineral element | 类群ⅠGroupⅠ | 类群Ⅱ GroupⅡ | 类群Ⅲ Group Ⅲ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | 平均值 Mean value/(mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| Al | 124.93 ab | 26.22 | 112.24 b | 33.52 | 147.91 a | 30.85 |
| B | 29.09 b | 18.83 | 41.23 ab | 6.77 | 56.08 a | 8.18 |
| Ba | 23.82 b | 29.96 | 27.64 ab | 25.97 | 36.57 a | 29.05 |
| Ca | 1 801.73 a | 33.90 | 1 413.42 b | 41.33 | 1 865.04 a | 28.71 |
| Co | 0.46 b | 26.24 | 0.35 b | 20.46 | 0.32 b | 24.21 |
| Cr | 0.37 b | 17.36 | 0.50 ab | 21.17 | 0.63 a | 19.65 |
| Cu | 4.00 a | 7.44 | 2.93 b | 13.23 | 3.56 ab | 10.10 |
| Fe | 23.53 b | 11.19 | 19.78 b | 11.72 | 23.90 b | 9.90 |
| K | 8 624.30 a | 18.73 | 7 084.04 b | 8.79 | 8 433.29 a | 23.82 |
| Mg | 818.93 a | 10.71 | 668.35 b | 26.09 | 852.74 a | 26.06 |
| Mn | 742.43 a | 13.66 | 582.42 b | 10.38 | 744.12 a | 19.19 |
| Na | 21.55 b | 18.46 | 21.75 b | 13.39 | 21.25 b | 12.20 |
| Ni | 0.75 b | 39.27 | 0.80 b | 20.08 | 0.60 b | 14.67 |
| P | 1 095.88 a | 67.07 | 887.31 b | 43.50 | 1 025.98 a | 28.19 |
| S | 187.18 a | 20.27 | 156.33 b | 19.22 | 172.70 ab | 20.71 |
| Se | 0.33 b | 39.44 | 0.41 a | 24.91 | 0.44 a | 36.94 |
| Ti | 1.48 b | 10.01 | 1.62 b | 15.17 | 2.19 a | 10.77 |
| Zn | 9.94 a | 6.07 | 7.75 b | 10.71 | 9.95 a | 12.19 |
平均值 Mean value | 23.05 | 20.35 | 20.30 | |||
| 1 | XIA E H, TONG W, WU Q, et al.. Tea plant genomics: achievements, challenges, and perspectives [J/OL]. Hortic. Res., 2020, 7(7): 0225-4 [2022-03-24]. . |
| 2 | YANG Y, SUN M, LI S, et al.. Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: a systematic review [J/OL]. Hortic. Res., 2020, 7(1): 0332-2 [2022-03-24]. . |
| 3 | 金基强,张晨禹,马建强, 等.茶树种质资源研究“十三五”进展及“十四五”发展方向[J].中国茶叶,2021,43(9):42-49, 76. |
| JIN J Q, ZHANG C Y, MA J Q, et al.. Research progress on tea germplasms during the 13th five-year plan period and development direction in the 14th five-year plan period [J]. China Tea J., 2021,43(9):42-49, 76. | |
| 4 | SOETAN K O, OLAIYA C O, OYEWOLE O E. The importance of mineral elements for humans, domestic animals, and plants-a review [J]. African J. Food sci., 2010, 4(5): 200-222. |
| 5 | 齐冰洁,王敏,张智勇,等.燕麦种质资源矿质元素的多样性分析[J].作物杂志,2020(4):72-78. |
| QI B J, WANG M, ZHANG Z Y, et al.. Diversity analysis of mineral elements in oat germplasm resources [J]. Crops, 2020(4):72-78. | |
| 6 | MATSUDA H, NAKAMURA S, MORIKAWA T, et al.. New biofunctional effects of the flower buds of Camellia sinensis and its bioactive acylated oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides [J]. J. Nat. Med., 2016, 70(4):689-701. |
| 7 | CHEN D, CHEN G, DING Y, et al.. Polysaccharides from the flowers of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) modulate gut health and ameliorate cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression [J/OL]. J. Funct. Foods, 2019, 61: 103470 [2022-03-24]. . |
| 8 | CHEN Y, FU X, MEI X, et al.. Characterization of functional proteases from flowers of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants [J]. J. Funct. Foods, 2016, 25: 149-159. |
| 9 | CHEN D, CHEN G, SUN Y, et al.. Physiological genetics, chemical composition, health benefits and toxicology of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) flower: a review [J/OL]. Food Res. Int., 2020, 137: 109584 [2022-03-24]. . |
| 10 | LI B, JIN Y, XU Y, et al.. Safety evaluation of tea (Camellia sinensis) flower extract: assessment of mutagenicity, and acute and subchronic toxicity in rats [J]. J. Ethnopharmacol., 2011, 133(2): 583-590. |
| 11 | 朱建新,程福建,林全女,等.茶树花资源综合利用及保健功效研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2021,49(6):7-9. |
| ZHU J X, CHENG F J, LIN Q N, et al.. Research progress on the comprehensive utilization and health efficacy of tea flower resources [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2021,49(6):7-9. | |
| 12 | 王泽涵,于文涛,王鹏杰,等.茶树花不同发育时期的转录组分析[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2022,51(1):46-52. |
| WANG Z H, YU W T, WANG P J, et al.. Transcriptome analysis at different flowering developmental stages of tea plant [J]. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2022,51(1):46-52. | |
| 13 | 李金,陈莲芙,金恩惠,等.不同茶树品种的茶树花黄酮苷研究[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2019,45(6):707-714. |
| LI J, CHEN L F, JIN E H, et al.. Research on flavonoid glycosides of tea flower in different tea plant cultivars [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2019,45(6):707-714. | |
| 14 | 黄艳,商虎,朱嘉威,等.加工工艺对茶树花品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J].食品科学,2020,41(11):165-170. |
| HUANG Y, SHANG H, ZHU J W, et al.. Effects of processing treatments on quality and antioxidant activity of tea plant flower [J]. Food Sci., 2020,41(11):165-170. | |
| 15 | CHEN D, DING Y, CHEN G, et al.. Components identification and nutritional value exploration of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) flower extract: evidence for functional food [J/OL]. Food Res. Int., 2020, 132: 109100 [2022-03-24]. . |
| 16 | 许兰,张丹,仝团团,等.茶树花提取物的抑菌和美白功效评价[J].天然产物研究与开发,2018,30(8):1287-1293. |
| XU L, ZHANG D, TONG T T, et al.. Assessment on antibacterial and whitening effect of tea (Camellia sinensis) flower extraction [J]. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev., 2018,30(8):1287-1293. | |
| 17 | 郑淑琳,石玉涛,王飞权,等.乌龙茶种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析与评价[J].福建农业学报,2020,35(2):150-160. |
| ZHENG S L, SHI Y T, WANG F Q, et al.. Minerals in oolong tea germplasms [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2020,35(2):150-160. | |
| 18 | 石玉涛,郑淑琳,王飞权,等.武夷名丛茶树种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(7):37-50. |
| SHI Y T, ZHENG S L, WANG F Q, et al.. Characteristics analysis of mineral element contents in Wuyi Mingcong tea plant germplasm resources [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020,22(7):37-50. | |
| 19 | 徐桂妹,陈泉宾.武夷岩茶产区的气候条件分析[J].茶叶科学技术,2009(3): 36-38. |
| 20 | 叶江华,张奇,林生,等.大红袍茶树生长及鲜叶品质与土壤特性的相关性[J].森林与环境学报,2019,39(5):488-496. |
| YE J H, ZHANG Q, LIN S, et al.. Correlation of growth and fresh leaf quality of Dahongpao tea tree with soil characteristics [J]. J. For. Environ., 2019,39(5):488-496. | |
| 21 | 叶宏萌,郑茂钟,李国平,等.武夷岩茶主产区土壤及茶叶微量元素分布特征[J].森林与环境学报,2016,36(4):423-428. |
| YE H M, ZHENG M Z, LI G P, et al.. Distribution characteristics of trace elements in the soils and tea leaves in Wuyi Yan tea provenance [J]. J. For. Environ., 2016,36(4):423-428. | |
| 22 | JIA S, WANG Y, HU J, et al.. Mineral and metabolic profiles in tea leaves and flowers during flower development [J]. Plant Physiol. Bioch., 2016, 106: 316-326. |
| 23 | 王洁,石元值,张群峰,等.基于矿物元素指纹的龙井茶产地溯源[J].核农学报,2017,31(3):547-558. |
| WANG J, SHI Y Z, ZHANG Q F, et al.. Geographical origin discriminant of Longjing tea based on mineral element fingerprints [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2017, 31(3):547-558. | |
| 24 | 黄月琴,方荣,陈学军,等.茄子种质资源表型性状分析与遗传多样性评价[J].热带作物学报,2021,42(7):1896-1904. |
| HUANG Y Q, FANG R, CHEN X J, et al.. Analysis of phenotypic traits and evaluation genetic diversity of eggplant germplasm resources [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2021,42(7):1896-1904. | |
| 25 | CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al.. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Mol. Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 26 | 刘伟,张群,李志坚,等.不同品种黄花菜游离氨基酸组成的主成分分析及聚类分析[J].食品科学,2019,40(10):243-250. |
| LIU W, ZHANG Q, LI Z J, et al.. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for evaluating free amino acids of different cultivars of daylily buds [J]. Food Sci., 2019,40(10):243-250. | |
| 27 | 马小卫, 马永利, 武红霞,等. 基于因子分析和聚类分析的杧果种质矿质元素含量评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(7):1371-1381. |
| MA X W, MA Y L, WU H X, et al.. Assessment of mineral elements contents at the mango germplasm level based on factor analysis and cluster analysis [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2018, 45(7):1371-1381. | |
| 28 | 张正仁, 宋长铣.土壤环境和植物基因型与土壤中微量元素的关系[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版),1992,28(3):472-478. |
| ZHANG Z R, SONG C X. The relationship between micronutrients in soil, and soil environments and plant genotypes [J]. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 1992,28(3):472-478. | |
| 29 | 杨雪梅,张锦超,邓光华,等.不同石榴品种籽粒矿质营养元素含量综合评价[J].山东农业科学,2022,54(2):63-68. |
| YANG X M, ZHANG J C, DENG G H, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of mineral elements contents in arils of different pomegranate varieties [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci.,2022,54(2):63-68. | |
| 30 | 陈昌婕,苗玉焕,方艳,等.不同艾种质资源矿质元素含量及其与品质的关系[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(4):880-888. |
| CHEN C J, MIAO Y H, FANG Y, et al.. Content of mineral elements in different Artemisia argyi germplasms and their relationship with quality properties [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2022,47(4):880-888. | |
| 31 | 薛晓芳,赵爱玲,王永康,等.不同枣品种果实矿质元素含量分析[J].山西农业科学,2016,44(6):741-745. |
| XUE X F, ZHAO A L, WANG Y K, et al.. Analysis on mineral element contents of fruits in different Chinese jujube varieties [J]. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2016,44(6):741-745. | |
| 32 | 项越,赵淑婷,吴昊,等.虎尾草不同器官矿质元素含量对碱化环境的响应[J].草业科学,2022,39(3):511-519. |
| XIANG Y, ZHAO S T, WU H, et al.. Effects of alkali stress on the content of mineral elements in different organs of Chloris virgata [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2022,39(3):511-519. | |
| 33 | 杨波,车玉红,徐叶挺,等.不同扁桃品种花和叶片矿质营养元素含量分析[J].新疆农业科学,2013,50(3):466-470. |
| YANG B, CHE Y H, XU Y T, et al.. Analysis of mineral nutrient content of flowers and leaves of different varieties of almond (Oblate Peach) [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2013,50(3):466-470. | |
| 34 | 王健胜,吴政卿,周正富,等.国内外小麦种质主要矿质元素含量的评价分析[J].分子植物育种,2018,16(22):7550-7557. |
| WANG J S, WU Z Q, ZHOU Z F, et al.. Evaluation and analysis of major mineral elements content in domestic and foreign wheat germplasm [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2018, 16(22):7550-7557. | |
| 35 | 严学成, 马艳兰, 孙治旭, 等. 茶叶中铬、镉、汞、砷及氟化物限量: [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003. |
| 36 | 刘新, 汪庆华, 张宪, 等. 绿色食品 茶叶: [S].北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018. |
| 37 | 张祺悦,张健,李赫,等.硒蛋白结构与营养功能研究进展[J].食品研究与开发,2021,42(3):196-201. |
| ZHANG Q Y, ZHANG J, LI H, et al.. Research progress of selenoprotein structure and nutritional function [J]. Food Res. Dev., 2021,42(3):196-201. | |
| 38 | 李传友, 吕宗浩, 黄辉, 等. 富硒茶: [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002. |
| [1] | 郭梓沣, 黄雷, 李奎. 畜禽种质资源的创新与利用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 14-22. |
| [2] | 郭胜微, 边思文, 丁建文, 张晓辰, 杨兴, 杜锦, 向春阳. 糯玉米萌发期耐低温品种资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| [3] | 李志元, 江虹, 马艳, 姜秀梅, 张力方, 梁志国, 王泽鹏, 唐亮, 梁肖, 秦勇. 氮水平对雪菊幼苗中黄酮类化合物和矿质营养累积的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 208-216. |
| [4] | 柴冠群, 刘桂华, 周玮, 张秀锦, 李龙品, 范成五. 贵州乌蒙山区设施土壤重金属污染风险评估与来源解析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 144-153. |
| [5] | 刘声传, 许应芬, 魏杰, 鄢东海, 陈智雄, 徐霖, 刘燕, 周玉锋. 基于2b-RAD技术分析白化茶树品种(系)遗传多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 65-73. |
| [6] | 李夏夏, 张思语, 程智慧. 中国优质大蒜品种区域试验评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 58-68. |
| [7] | 伊六喜, 萨如拉, 范鑫, 赵灿, 李茹, 斯钦巴特尔. 油用亚麻主要品质和农艺性状的变异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 56-67. |
| [8] | 崔晨珂, 林涛, 安艳波, 崔鹏. 不同类型甘薯品种遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 68-75. |
| [9] | 朱鹏, 许轲, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 杨郁文, 张保龙, 裘实. 稻麦轮作体系下抗除草剂稻麦种质资源的挖掘与利用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 142-152. |
| [10] | 温赛群, 刘灵娣, 田伟, 谢晓亮, 贾东升, 刘铭, 温春秀, 姜涛. 药食兼用型叶用紫苏种质鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 62-70. |
| [11] | 李俊杰, 杜蒲芳, 石婷瑞, 侯沛佳, 柴新宇, 赵瑞, 汪妤, 李红霞. 不同基因型小麦苗期耐低氮性评价及筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 21-32. |
| [12] | 叶江华, 刘德发, 刘国英, 刘扬, 张奇, 徐斌, 吴林春, 贾小丽. 不同等级武夷水仙茶品质和矿质元素差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 105-112. |
| [13] | 王颖1,喻阳华2*. 中国农业可持续发展水平多尺度时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 8-17. |
| [14] | 罗立娜1,韩树全1*,王代谷1,李茂富2,马蔚红3,张正学1,刘小翠1. 油梨果实品质的差异分析与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 105-113. |
| [15] | 王平. 我国种业发展的主要问题及对策探析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 7-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号