




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 28-39.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0558
邓玉荣1( ), 韩联1, 王金龙1, 韦兴翰1, 王旭东1, 赵颖1,2, 魏小红1,2(
), 韩联1, 王金龙1, 韦兴翰1, 王旭东1, 赵颖1,2, 魏小红1,2( ), 李朝周1(
), 李朝周1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-05
接受日期:2022-10-08
出版日期:2024-01-15
发布日期:2024-01-08
通讯作者:
魏小红,李朝周
作者简介:邓玉荣 E-mail:2940834096@qq.com
基金资助:
Yurong DENG1( ), Lian HAN1, Jinlong WANG1, Xinghan WEI1, Xudong WANG1, Ying ZHAO1,2, Xiaohong WEI1,2(
), Lian HAN1, Jinlong WANG1, Xinghan WEI1, Xudong WANG1, Ying ZHAO1,2, Xiaohong WEI1,2( ), Chaozhou LI1(
), Chaozhou LI1( )
)
Received:2022-07-05
Accepted:2022-10-08
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Xiaohong WEI,Chaozhou LI
摘要:
超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)是植物抗氧化系统的关键酶,在保护植物免受生物和非生物胁迫方面发挥重要作用。以拟南芥SOD为基础,通过序列比对在藜麦基因组中鉴定出12个SOD基因,分别定位于细胞核、微体及线粒体,在11条染色体上不均匀分布,其编码蛋白质三级结构显示Cu/Zn-SODs与Fe-SODs为同源二聚体,Mn-SODs为同源四聚体。CqSOD基因内含子/外显子分布模式不尽相同,内含子数介于4~7个,保守基序差异明显。系统发育关系显示,SOD蛋白可分为Cu/Zn-SODs、Fe-SODs及Mn-SODs 3个亚族。此外,所有的CqFe-SODs及CqMn-SODs启动子区都含有脱落酸激素反应顺式元件,CqSOD12与11个CqSOD蛋白及4个CqCAT蛋白存在相互作用。表达谱分析表明,12个CqSOD基因对混合盐碱及硝普钠均有较强响应。研究结果为SOD基因在植物发育和胁迫响应中的作用及分子机制研究奠定基础。
中图分类号:
邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39.
Yurong DENG, Lian HAN, Jinlong WANG, Xinghan WEI, Xudong WANG, Ying ZHAO, Xiaohong WEI, Chaozhou LI. Identification of SOD Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa and Their Response to Mixed Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 28-39.
处理 Treatment | 盐分组成Salt composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化钠NaCl/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 硫酸钠Na2SO4/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸氢钠NaHCO3/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸钠Na2CO3/(200 mmol·L-1) | 硝普纳SNP/ (150 μmol·L-1) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - |
| B | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - |
| C | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | - |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| E | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | - |
| CK+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| A+ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | + |
| B+ | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | + |
| C+ | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | + |
| D+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | + |
| E+ | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | + |
表1 各处理盐分组成及摩尔比
Table 1 Salt composition and molar ratio of different treatment
处理 Treatment | 盐分组成Salt composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化钠NaCl/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 硫酸钠Na2SO4/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸氢钠NaHCO3/ (200 mmol·L-1) | 碳酸钠Na2CO3/(200 mmol·L-1) | 硝普纳SNP/ (150 μmol·L-1) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - |
| B | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - |
| C | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | - |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| E | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | - |
| CK+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| A+ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | + |
| B+ | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | + |
| C+ | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 | + |
| D+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | + |
| E+ | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 | + |
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) | 退火温度 Tm/℃ | 产物长度 Amplicon size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqActin | CCCTCACCACTTTCCGATCT | TCCTCACCCTCACCCATTTT | 62.6 | 62 |
| CqSOD01 | ACTGGGAATGTCTCGGGTCT | GTAGCGGTACCATCATCCCC | 61.6 | 141 |
| CqSOD02 | AGGAGATGGCCCAACAACTG | GGCGAACTTCGTCTTCAGGA | 61.8 | 89 |
| CqSOD03 | TGCTGGTGGAAGATTGGCTT | TGTGGTGACTCGGTGAACTG | 62.7 | 107 |
| CqSOD04 | CGGAAGATGAAGTCCGGCAT | CACAAGGGCTCTACCGACAA | 61.9 | 138 |
| CqSOD05 | TTCAGAGAGACATGCGGGTG | CAGCATGCACCACAATAGCC | 62.3 | 111 |
| CqSOD06 | TCATCTCCGGCGCCAATAAC | GCCATGAAGACCAGGAGTGA | 62.0 | 87 |
| CqSOD07 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 63.1 | 125 |
| CqSOD08 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | CGGCTCCAAGGCATCAAATG | 63.5 | 86 |
| CqSOD09 | GGAGTCACATTGGGGAGAGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 62.2 | 90 |
| CqSOD10 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | ACATGACCTCCGCCATTGAA | 61.4 | 118 |
| CqSOD11 | GCTGGGCTTGGCTTGTTTAC | TGCTCCCAAACGTCGATAGT | 63.5 | 140 |
| CqSOD12 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | GATTCACATGACCTCCGCCA | 63.2 | 114 |
表2 CqSODs的qRT-PCR引物
Table 2 qRT-PCR primers of CqSODs
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) | 退火温度 Tm/℃ | 产物长度 Amplicon size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqActin | CCCTCACCACTTTCCGATCT | TCCTCACCCTCACCCATTTT | 62.6 | 62 |
| CqSOD01 | ACTGGGAATGTCTCGGGTCT | GTAGCGGTACCATCATCCCC | 61.6 | 141 |
| CqSOD02 | AGGAGATGGCCCAACAACTG | GGCGAACTTCGTCTTCAGGA | 61.8 | 89 |
| CqSOD03 | TGCTGGTGGAAGATTGGCTT | TGTGGTGACTCGGTGAACTG | 62.7 | 107 |
| CqSOD04 | CGGAAGATGAAGTCCGGCAT | CACAAGGGCTCTACCGACAA | 61.9 | 138 |
| CqSOD05 | TTCAGAGAGACATGCGGGTG | CAGCATGCACCACAATAGCC | 62.3 | 111 |
| CqSOD06 | TCATCTCCGGCGCCAATAAC | GCCATGAAGACCAGGAGTGA | 62.0 | 87 |
| CqSOD07 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 63.1 | 125 |
| CqSOD08 | GGGGCCTAAACACTTTTCGC | CGGCTCCAAGGCATCAAATG | 63.5 | 86 |
| CqSOD09 | GGAGTCACATTGGGGAGAGC | TCCAGGTTGCATGGATTCCC | 62.2 | 90 |
| CqSOD10 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | ACATGACCTCCGCCATTGAA | 61.4 | 118 |
| CqSOD11 | GCTGGGCTTGGCTTGTTTAC | TGCTCCCAAACGTCGATAGT | 63.5 | 140 |
| CqSOD12 | CGTACGACTATGGCGCTCTT | GATTCACATGACCTCCGCCA | 63.2 | 114 |
基因登录号 Gene accession No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸数 Size/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /kD | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数Instability index | 脂肪酸指数Aliphatic index | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点数量Phosphorylation site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUR62000929 | CqSOD01 | 152 | 15.26 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 14 |
| AUR62005041 | CqSOD02 | 152 | 15.27 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 |
| AUR62014976 | CqSOD03 | 287 | 29.96 | 8.34 | 41.28 | 78.61 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 77 |
| AUR62029152 | CqSOD04 | 246 | 25.26 | 6.02 | 28.11 | 85.28 | -0.01 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 56 |
| AUR62032030 | CqSOD05 | 157 | 16.01 | 6.38 | 22.92 | 87.52 | -0.18 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62032721 | CqSOD06 | 130 | 13.41 | 6.33 | 16.19 | 89.23 | -0.16 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62001685 | CqSOD07 | 262 | 29.89 | 8.33 | 38.29 | 81.15 | -0.35 | 微体Microbody | 36 |
| AUR62010480 | CqSOD08 | 280 | 31.65 | 6.19 | 35.50 | 69.71 | -0.46 | 微体Microbody | 25 |
| AUR62020097 | CqSOD09 | 262 | 30.00 | 7.73 | 39.44 | 82.63 | -0.33 | 微体Microbody | 34 |
| AUR62030413 | CqSOD10 | 281 | 31.66 | 6.40 | 36.42 | 70.85 | -0.47 | 微体Microbody | 31 |
| AUR62024917 | CqSOD11 | 295 | 32.43 | 8.80 | 37.17 | 93.63 | -0.12 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 46 |
| AUR62030627 | CqSOD12 | 233 | 25.89 | 6.79 | 39.36 | 87.98 | -0.35 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 30 |
表3 藜麦CqSOD蛋白基本理化性质
Table 3 Basic physicochemical properties of CqSOD proteins
基因登录号 Gene accession No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸数 Size/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /kD | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数Instability index | 脂肪酸指数Aliphatic index | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点数量Phosphorylation site number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUR62000929 | CqSOD01 | 152 | 15.26 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 14 |
| AUR62005041 | CqSOD02 | 152 | 15.27 | 5.28 | 15.37 | 76.91 | -0.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 |
| AUR62014976 | CqSOD03 | 287 | 29.96 | 8.34 | 41.28 | 78.61 | -0.19 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 77 |
| AUR62029152 | CqSOD04 | 246 | 25.26 | 6.02 | 28.11 | 85.28 | -0.01 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 56 |
| AUR62032030 | CqSOD05 | 157 | 16.01 | 6.38 | 22.92 | 87.52 | -0.18 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62032721 | CqSOD06 | 130 | 13.41 | 6.33 | 16.19 | 89.23 | -0.16 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 16 |
| AUR62001685 | CqSOD07 | 262 | 29.89 | 8.33 | 38.29 | 81.15 | -0.35 | 微体Microbody | 36 |
| AUR62010480 | CqSOD08 | 280 | 31.65 | 6.19 | 35.50 | 69.71 | -0.46 | 微体Microbody | 25 |
| AUR62020097 | CqSOD09 | 262 | 30.00 | 7.73 | 39.44 | 82.63 | -0.33 | 微体Microbody | 34 |
| AUR62030413 | CqSOD10 | 281 | 31.66 | 6.40 | 36.42 | 70.85 | -0.47 | 微体Microbody | 31 |
| AUR62024917 | CqSOD11 | 295 | 32.43 | 8.80 | 37.17 | 93.63 | -0.12 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 46 |
| AUR62030627 | CqSOD12 | 233 | 25.89 | 6.79 | 39.36 | 87.98 | -0.35 | 线粒体Mitochondrial | 30 |
基因 Gene | 蛋白质二级结构Secondary structure of protein | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α螺旋α helix | 延伸链Extension chain | 无规则卷曲Random coil | ||
| CqSOD01 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr12 |
| CqSOD02 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr05 |
| CqSOD03 | 86 | 46 | 155 | Chr15 |
| CqSOD04 | 47 | 55 | 144 | Chr00 |
| CqSOD05 | 0 | 55 | 102 | Chr11 |
| CqSOD06 | 4 | 42 | 84 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD07 | 71 | 61 | 130 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD08 | 93 | 49 | 138 | Chr13 |
| CqSOD09 | 93 | 48 | 121 | Chr18 |
| CqSOD10 | 94 | 51 | 136 | Chr16 |
| CqSOD11 | 96 | 49 | 150 | Chr01 |
| CqSOD12 | 89 | 43 | 101 | Chr04 |
表4 二级结构与染色体定位
Table 4 Secondary structure and chromosomal localization
基因 Gene | 蛋白质二级结构Secondary structure of protein | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α螺旋α helix | 延伸链Extension chain | 无规则卷曲Random coil | ||
| CqSOD01 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr12 |
| CqSOD02 | 4 | 57 | 91 | Chr05 |
| CqSOD03 | 86 | 46 | 155 | Chr15 |
| CqSOD04 | 47 | 55 | 144 | Chr00 |
| CqSOD05 | 0 | 55 | 102 | Chr11 |
| CqSOD06 | 4 | 42 | 84 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD07 | 71 | 61 | 130 | Chr07 |
| CqSOD08 | 93 | 49 | 138 | Chr13 |
| CqSOD09 | 93 | 48 | 121 | Chr18 |
| CqSOD10 | 94 | 51 | 136 | Chr16 |
| CqSOD11 | 96 | 49 | 150 | Chr01 |
| CqSOD12 | 89 | 43 | 101 | Chr04 |

图3 藜麦与拟南芥、棉花、水稻、番茄、小麦SOD蛋白的系统发育树注: At—拟南芥;Ta—小麦;Sl—番茄;Cq—藜麦;Gh—陆地棉;Os—水稻。
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic of SOD proteins from quinoa and other plantsNote: At—Arabidopsis; Ta—Triticum aestivum; Sl—Solanum lycopersicum;Cq-Chenopodium quinoa; Gh-Gossypium hirsutum; Os-Oryza sativa.
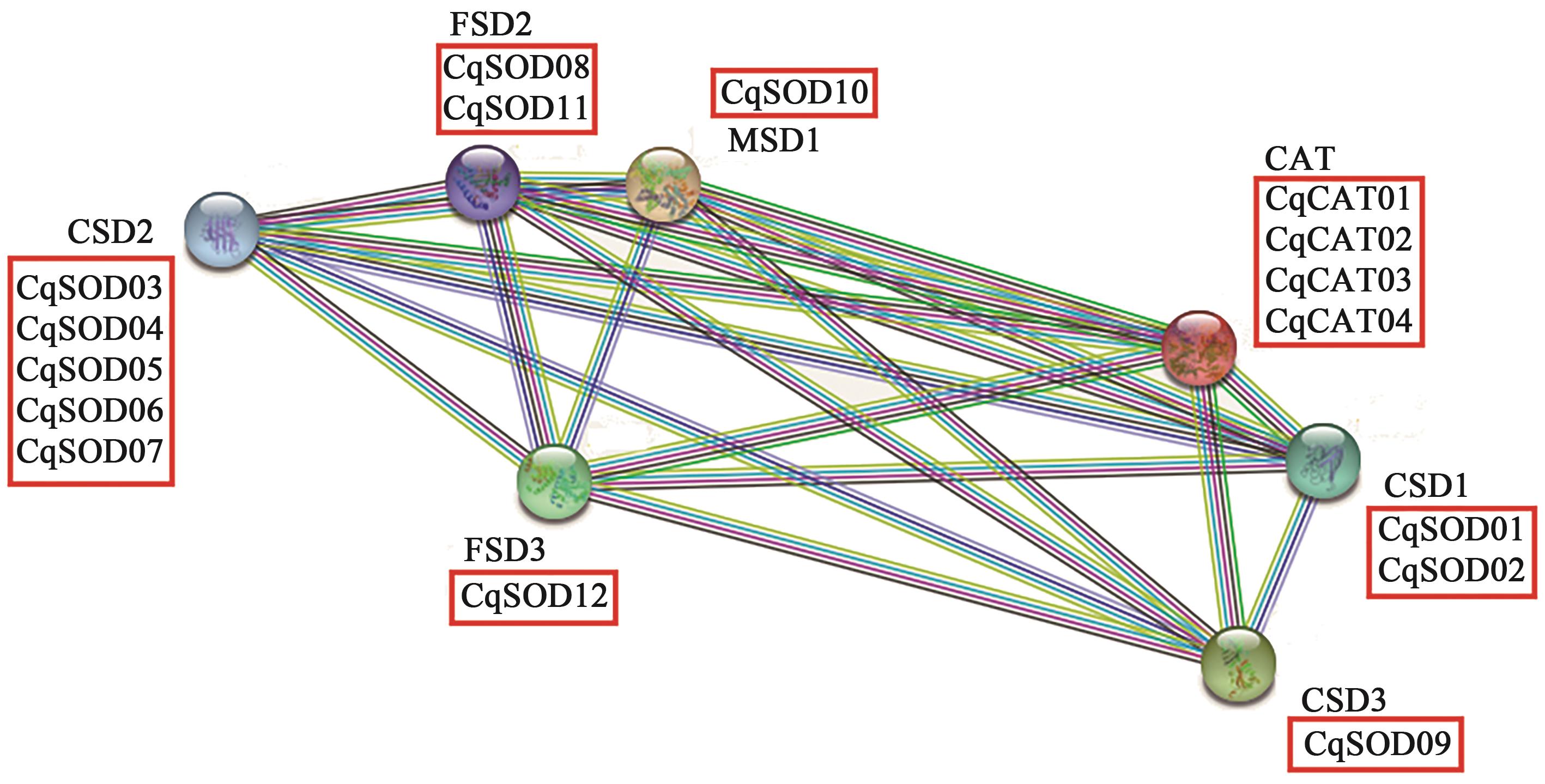
图4 基于拟南芥中的同源蛋白预测CqSOD蛋白的互作网络
Fig. 4 Prediction of the interaction network of CqSOD proteins based on the interactions of their orthologs in Arabidopsis
基因 Gene | 激素响应元件 Phytohormone responsiveness element | 压力响应元件 Stress responsiveness element | 组织特异性表达元件 Tissue-specific expression element | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ABA响应元件 ABRE | CGTCA 基序 CGTCA-motif | P盒 P-box | TATC盒TATC-box | TCA 元件 TCA-element | TGACG基序TGACG-motif | TGA 元件 TGA-element | 低温应答元件 LTR | MYB结合位点 MBS | 富含TC的重复序列 TC-rich repeats | 厌氧诱导作用元件 ARE | CAT盒CAT-box | MYB 结合位点MBSI | O2位点 O2-site | |
| CqSOD01 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD02 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD03 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
| CqSOD04 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| CqSOD05 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| CqSOD06 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| CqSOD07 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD08 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD10 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD11 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
表5 藜麦SOD基因启动子区顺式作用元件
Table 5 Cis-acting elements in the promoter region of CqSOD genes
基因 Gene | 激素响应元件 Phytohormone responsiveness element | 压力响应元件 Stress responsiveness element | 组织特异性表达元件 Tissue-specific expression element | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ABA响应元件 ABRE | CGTCA 基序 CGTCA-motif | P盒 P-box | TATC盒TATC-box | TCA 元件 TCA-element | TGACG基序TGACG-motif | TGA 元件 TGA-element | 低温应答元件 LTR | MYB结合位点 MBS | 富含TC的重复序列 TC-rich repeats | 厌氧诱导作用元件 ARE | CAT盒CAT-box | MYB 结合位点MBSI | O2位点 O2-site | |
| CqSOD01 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD02 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD03 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
| CqSOD04 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| CqSOD05 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| CqSOD06 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| CqSOD07 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD08 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CqSOD09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD10 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| CqSOD11 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| CqSOD12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
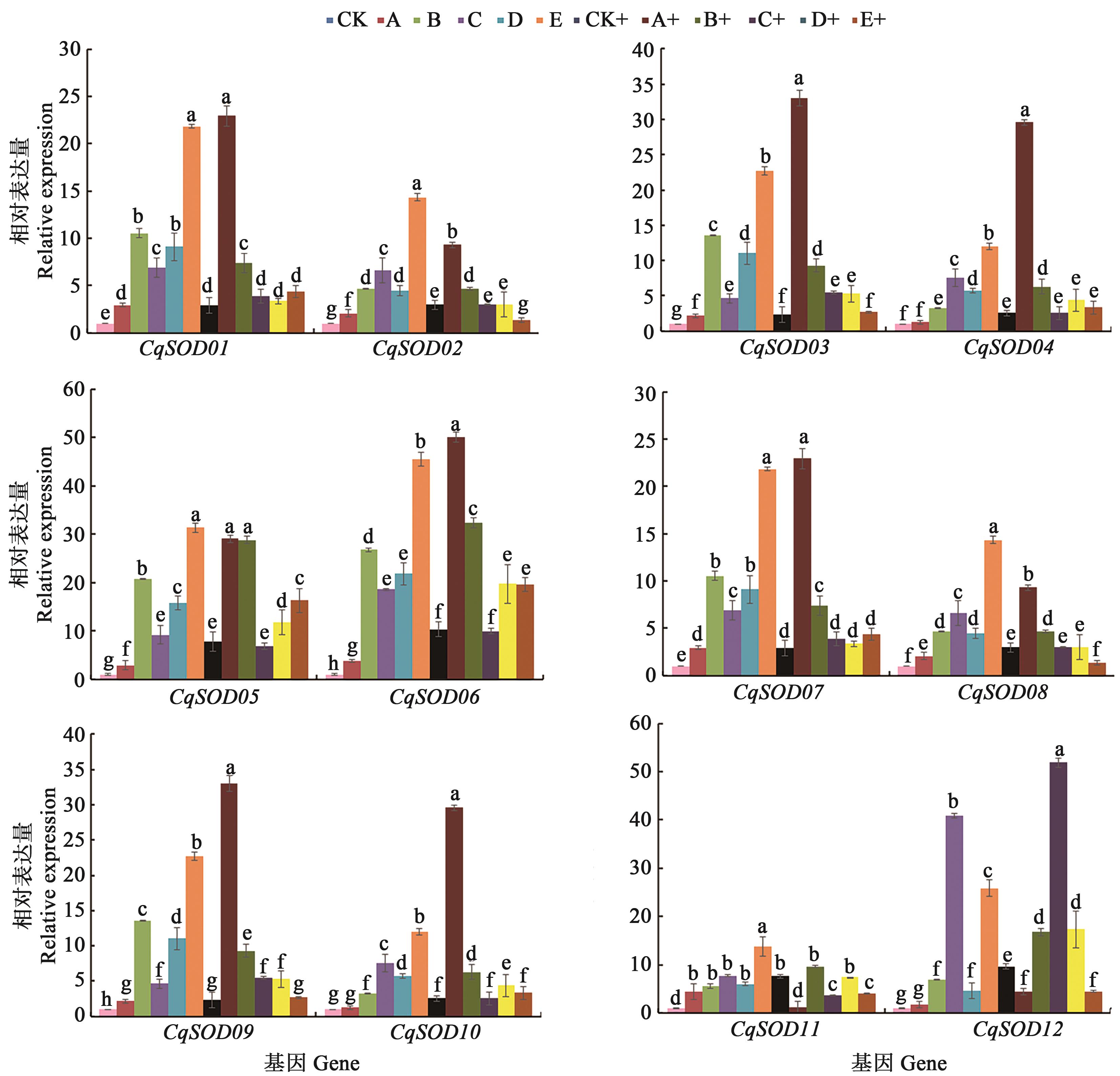
图5 混合盐碱胁迫下CqSODs的qRT-PCR注: 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 5 qRT-PCR of CqSODs in response to mixed saline-alkali stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | MILLER A. Superoxide dismutases: ancient enzymes and new insights [J]. FEBS Lett., 2012, 586(5): 585-595. |
| 2 | MITTLER R. ROS are good [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2017, 22(1):11-19. |
| 3 | BAFANA A, DUTT S, KUMAR S, et al.. Superoxide dismutase: an industrial perspective [J]. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2011, 31(1):65-76. |
| 4 | ZELKO I N, MARIANI T J, FOLZ R J. Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression [J]. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2002, 33(3):337-349. |
| 5 | TEPPERMAN J M, DUNSMUIR P. Transformed plants with elevated levels of chloroplastic SOD are not more resistant to superoxide toxicity [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 1990, 14(4): 501-511. |
| 6 | SU W, RAZA A, GAO A, et al.. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under different hormones and abiotic stress conditions [J/OL]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 10(8): 1182 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 7 | ABREU I A, CABELLI D E. Superoxide dismutases-a review of the metal-associated mechanistic variations [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2010, 1804(2): 263-274. |
| 8 | SONG J, ZENG L, CHEN R, et al.. In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula [J/OL]. 3 Biotech., 2018, 8(8): 348 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 9 | 魏婧, 徐畅, 李可欣, 等. 超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展与植物抗逆性[J].植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2571-2584. |
| WEI J, XU C, LI K X, et al.. Progress on superoxide dismutase and plant stress resistance [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2020, 56(12):2571-2584. | |
| 10 | ASENSIO A C, GIL-MONREAL M, PIRES L, et al.. Two Fe-superoxide dismutase families respond differently to stress and senescence in legumes [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, 169(13):1253-1260. |
| 11 | HAN L M, HUA W P, CAO X Y, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza [J/OL]. Gene, 2020, 742:144603[2022-06-03]. . |
| 12 | ZHANG X, ZHANG L T, CHEN Y Y, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the SOD gene family and expression analysis under drought and salt stress in barley [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2021, 94(1): 49-60. |
| 13 | FENG K, YU J H, CHENG Y, et al.. The SOD gene family in tomato: identification, phylogenetic relationships, and expression patterns [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016(7): 1279 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 14 | ZHOU Y, HU L F, WU H, et al.. Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of cucumber superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in response to various abiotic stresses [J/OL]. Int. J. Genomics, 2017, 2017: 7243973 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 15 | MOLINA-RUEDA J J, TSAI C J, KIRBY E G. The Populus superoxide dismutase gene family and its responses to drought stress in transgenic poplar overexpressing a pine cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GS1a) [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56421 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 16 | ZURITA-SILVA A, FUENTES F, ZAMORA P, et al.. Breeding quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): potential and perspectives [J]. Mol. Breed., 2014, 34(1): 13-30. |
| 17 | 赵颖, 魏小红, 李桃桃. 外源NO对混合盐碱胁迫下藜麦种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 92-101. |
| ZHAO Y, WEI X H, LI T T. Efferts of exogenous nitric oxide on seed Emination and seedling growth of Chenopodium quinoa under complex saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(4): 92-101. | |
| 18 | 刘文瑜, 杨发荣, 黄杰, 等. NaCl 胁迫对藜麦幼苗生长和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2017, 37(9): 1797-1804. |
| LIU W Y, YANG F R, HUANG J, et al.. Response of seedling growth and the activities of antioxidant enzymes of Chenopodium quinoa to salt stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2017, 37(9):1797-1804. | |
| 19 | RUIZ K B, BIONDI S, MARTÍNEZ E A, et al.. Quinoa-a model crop for understanding salt-tolerance mechanisms in halophytes [J]. Plant Biosyst., 2016, 150(2): 357-371. |
| 20 | 李美丽, 宿俊吉, 杨永林, 等. 陆地棉COI家族基因鉴定及在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析[J].中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4):63-74. |
| LI M L, SU J J, YANG Y L, et al.. Identification of COl family genes and their expression in Gossypium hirsutum L. under drought and salt stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(4): 63-74. | |
| 21 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real-time quantitative PCR [J]. Methods, 2002, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 22 | WANG T, SONG H, ZHANG B H, et al.. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) [J/OL]. 3 Biotech., 2018, 8(12): 486 [2022-06-03].. |
| 23 | DEHURY B, SARMA K, SARMAH R, et al.. In silico analyses of superoxide dismutases (SODs) of rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2013, 22(1): 150-156. |
| 24 | GOSAVI G U, JADHAV A S, KALE A A, et al.. Effect of heat stress on proline, chlorophyll content, heat shock proteins and antioxidant enzyme activity in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) at seedlings stage [J]. Indian J. Biotechnol., 2014, 13(13): 356-363. |
| 25 | XMHA B, QXC B, QI Y B, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of superoxide dismutase genes in Larix kaempferi [J]. Gene, 2019, 686: 29-36. |
| 26 | TANG Y H, BAO X X, ZHI Y L, et al.. Overexpression of a MYB family gene, OsMYB6, increases drought and salinity stress tolerance in transgenic rice [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019(10): 168 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 27 | LIN Y L, LAI Z X. Superoxide dismutase multigene family in longan somatic embryos: a comparison of CuZn-SOD, Fe-SOD, and Mn-SOD gene structure, splicing, phylogeny, and expression [J]. Mol. Breeding, 2013, 32(3): 595-615. |
| 28 | WANG W, ZHANG X, DENG F, et al.. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in Gossypium hirsutum [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2017,18(1):376 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 29 | FINK R C, SCANDALIOS J G. Molecular evolution and structure-function relationships of the superoxide dismutase gene families in angiosperms and their relationship to other eukaryotic and prokaryotic superoxide dismutases [J]. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2002, 399(1): 19-36. |
| 30 | XU G X, GUO C C, SHAN H Y, et al.. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109(4): 1187-1192. |
| 31 | GILL S S, TUTEJA N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2010, 48(12): 909-930. |
| 32 | FENG X, LAI Z X, LIN Y L, et al.. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the superoxide dismutase gene family in Musa acuminata cv.Tianbaojiao (AAA group)[J/OL]. BCM Genomics, 2015, 16:823 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 33 | HU X X, HAO C Y, CHENG Z M, et al.. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the grapevine superoxide dismutase (SOD) family [J/OL]. Int. J.Genomics, 2019:7350414 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 34 | PILON M, RAVET K, TAPKEN W. The biogenesis and physiological function of chloroplast superoxide dismutases [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2011, 1807(8): 989-998. |
| [1] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [2] | 孙鲁鹏, 杨洋, 王卫超, 傅廷栋, 周广生, 张凤华. 油菜苗期对盐碱胁迫的离子响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 46-54. |
| [3] | 张曼, 王志城, 刘正文, 王国宁, 王省芬, 张艳. 陆地棉BGLU基因家族成员的全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 48-59. |
| [4] | 梁培鑫, 唐榕, 刘建国. 混合盐碱胁迫对油莎豆光合生理及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 195-204. |
| [5] | 陈秋静, 杨招娣, 王仕玉, 郭凤根, 赵小雪, 陈凡, 丰扬. 植物生长延缓剂对藜麦抗倒伏能力及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 42-48. |
| [6] | 崔宏亮, 宋晓晓, 姚庆, 安万刚, 邢宝, 秦培友. 伊犁河谷不同藜麦品种对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 32-45. |
| [7] | 齐天明, 李志坚, 秦培友, 任贵兴, 周帮伟. 藜麦栽培技术研究与应用展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 157-165. |
| [8] | 万何平, 张浩, 余忆, 陈敬东, 曾长立, 赵伦, 文静, 沈金雄, 傅廷栋. 油菜耐盐碱研究与应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 59-67. |
| [9] | 赵晋锋, 余爱丽, 李颜方, 杜艳伟, 王高鸿, 王振华. 谷子SiCBL3对非生物胁迫响应特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| [10] | 王琴琴, 陈修贵, 陆许可, 王帅, 张悦新, 范亚朋, 陈全家, 叶武威. 陆地棉GhPKE1的生物信息学分析及功能验证[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 38-45. |
| [11] | 刘正文, 王省芬, 孟成生, 张艳, 孙正文, 吴立强, 马峙英, 张桂寅. 海岛棉GH9基因家族成员鉴定及分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 30-45. |
| [12] | 蒲全明, 杨鹏, 雍磊, 邓榆川, 何自涵, 林邦民, 施松梅, 向承勇, 方芳. 萝卜紫红叶色突变体的色素含量及光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| [13] | 崔江慧§,杨溥原§,常金华*. 高粱GRF基因家族鉴定及在非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 37-46. |
| [14] | 李媛媛1,陈博2,姚立蓉2,翟雪婷1,司二静2,汪军成2,马小乐2,孟亚雄2,王化俊2,李葆春1*,杨亮1. 283份小麦品种(系)萌发期耐盐碱性评价及种质筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 25-33. |
| [15] | 关思静, 王楠, 徐蓉蓉, 葛甜甜, 高静, 颜永刚, 张岗, 陈莹, 张明英. 甘草PRR基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 66-75. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号