




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 96-105.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0411
周世莹1,2( ), 刘晏辰2(
), 刘晏辰2( ), 张洋1, 杨雪松1, 关伟军2, 高扬1(
), 张洋1, 杨雪松1, 关伟军2, 高扬1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-30
接受日期:2023-07-04
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-07
通讯作者:
高扬
作者简介:周世莹 E-mail:643135130@qq.com基金资助:
Shiying ZHOU1,2( ), Yanchen LIU2(
), Yanchen LIU2( ), Yang ZHANG1, Xuesong YANG1, Weijun GUAN2, Yang GAO1(
), Yang ZHANG1, Xuesong YANG1, Weijun GUAN2, Yang GAO1( )
)
Received:2023-05-30
Accepted:2023-07-04
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-07
Contact:
Yang GAO
摘要:
骨髓间充质干细胞(bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, BMSCs) 来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,作为干细胞中的种子细胞,具有强大的自我复制和更新能力,并对治疗、修复、补充受损或缺损的肝、肌肉等组织有修复和治疗作用。为了研究BMSCs的生物学特性和多化潜能,对日本大耳白兔BMSCs进行体外分离培养及生物学鉴定研究。取日本大耳白胎兔骨髓组织,采用全骨髓贴壁法分离纯化、体外培养,鉴定日本大耳白兔BMSCs生物学特性,并进行细胞形态学观察、生长动力学检测及其成骨、成软骨、成脂肪能力鉴定。结果表明,采用全骨髓贴壁法成功从日本大耳白胎兔骨髓中分离得到生长状态良好的大耳白兔BMSCs,细胞形态为长梭形,生长曲线呈典型“S”形;免疫荧光和RT-PCR结果显示,大耳白兔BMSCs表达CD29、CD44、CD73、CD105间充质干细胞表面标记物基因,但不表达原始造血祖细胞标志物CD45;经特异性染色和RT-PCR分析表明,分离的细胞是间充质干细胞;体外诱导大耳白兔BMSCs能够分化为骨骼细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞。建立了大耳白兔BMSCs体外分离培养体系,为利用骨髓间充质干细胞进行组织与工程学研究和动物遗传资源保存研究奠定了一定的理论基础。
中图分类号:
周世莹, 刘晏辰, 张洋, 杨雪松, 关伟军, 高扬. 大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养与生物学鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 96-105.
Shiying ZHOU, Yanchen LIU, Yang ZHANG, Xuesong YANG, Weijun GUAN, Yang GAO. Isolational Culture and Biological Identification of Japanese Large Ear White Rabbit Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 96-105.
基因 Gene | 引物序列(3’-5’) Primer sequence(3’-5’) | 退火温度 Anneal temperature/℃ | 产物长度 Product length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F:ACTATGGACGTAGAGCTGGTCCCTGA | 61.00 | 492 |
| R:TCCAGGCAGGCCCCAATTGTGGGTG | |||
| CD29 | F: CGATGTGATGACTTAGAAGCCTTG | 60.85 | 471 |
| R:CAGAGACATAAAGAAAAATAAGA | |||
| CD44 | F:GGAGGATATCACTCAGATCCAGCCA | 60.60 | 373 |
| R: GTTGAAGTTCAAGCGTGCTGAAGAC | |||
| CD73 | F:AAGATGATCTGGAGAACGTCAAGA | 61.65 | 623 |
| R: ACTTCCGAATTGGGTTTGGCTCCTT | |||
| CD105 | F: GCTCAAGAACCCTTGCACGAGTGAG | 60.35 | 550 |
| R: ACAGACAGAGGGGAGGAGTTCAACG | |||
| Collage typeⅠ | F: CCAACGATGGACAGTGCCACCTGG | 59.30 | 425 |
| R: GCCCACCTCGTCCAGAAACTCAG | |||
| osteopontin | F: CCTGTTTACAAGGAACTGAAAAAC | 59.00 | 512 |
| R: AATGTCATCCAGCTGATCATTGATG | |||
| LPL | F:GCCAGAAGGAGTAACGATAAATA | 54.50 | 486 |
| R:GAAGGAAGTGCTCCAATATCTCCAT | |||
| PPAR-γ | F: GCAAACTAACTGGCTATGGTCCT | 60.10 | 473 |
| R: ATTAAGTGTCACCCAGGATGTGC | |||
| ACAN | F:CACGTTTGAGTGTGGGGCTTGCAG | 60.50 | 464 |
| R:GGGAGTGCGTCTGTGGGCAGTGTT | |||
| SOX9 | F: CCTATTAATAATTTCAAGAATCCAA | 60.70 | 507 |
| R: ACTATGGACGTAGAGCTGGTCCCTGA | |||
| CD45 | F: ATGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTGAACGG | 60.40 | 304 |
| R: ATTTGGCCGCATTGGGCGCCTGGT |
表1 引物信息
Table 1 Primer information
基因 Gene | 引物序列(3’-5’) Primer sequence(3’-5’) | 退火温度 Anneal temperature/℃ | 产物长度 Product length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F:ACTATGGACGTAGAGCTGGTCCCTGA | 61.00 | 492 |
| R:TCCAGGCAGGCCCCAATTGTGGGTG | |||
| CD29 | F: CGATGTGATGACTTAGAAGCCTTG | 60.85 | 471 |
| R:CAGAGACATAAAGAAAAATAAGA | |||
| CD44 | F:GGAGGATATCACTCAGATCCAGCCA | 60.60 | 373 |
| R: GTTGAAGTTCAAGCGTGCTGAAGAC | |||
| CD73 | F:AAGATGATCTGGAGAACGTCAAGA | 61.65 | 623 |
| R: ACTTCCGAATTGGGTTTGGCTCCTT | |||
| CD105 | F: GCTCAAGAACCCTTGCACGAGTGAG | 60.35 | 550 |
| R: ACAGACAGAGGGGAGGAGTTCAACG | |||
| Collage typeⅠ | F: CCAACGATGGACAGTGCCACCTGG | 59.30 | 425 |
| R: GCCCACCTCGTCCAGAAACTCAG | |||
| osteopontin | F: CCTGTTTACAAGGAACTGAAAAAC | 59.00 | 512 |
| R: AATGTCATCCAGCTGATCATTGATG | |||
| LPL | F:GCCAGAAGGAGTAACGATAAATA | 54.50 | 486 |
| R:GAAGGAAGTGCTCCAATATCTCCAT | |||
| PPAR-γ | F: GCAAACTAACTGGCTATGGTCCT | 60.10 | 473 |
| R: ATTAAGTGTCACCCAGGATGTGC | |||
| ACAN | F:CACGTTTGAGTGTGGGGCTTGCAG | 60.50 | 464 |
| R:GGGAGTGCGTCTGTGGGCAGTGTT | |||
| SOX9 | F: CCTATTAATAATTTCAAGAATCCAA | 60.70 | 507 |
| R: ACTATGGACGTAGAGCTGGTCCCTGA | |||
| CD45 | F: ATGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTGAACGG | 60.40 | 304 |
| R: ATTTGGCCGCATTGGGCGCCTGGT |
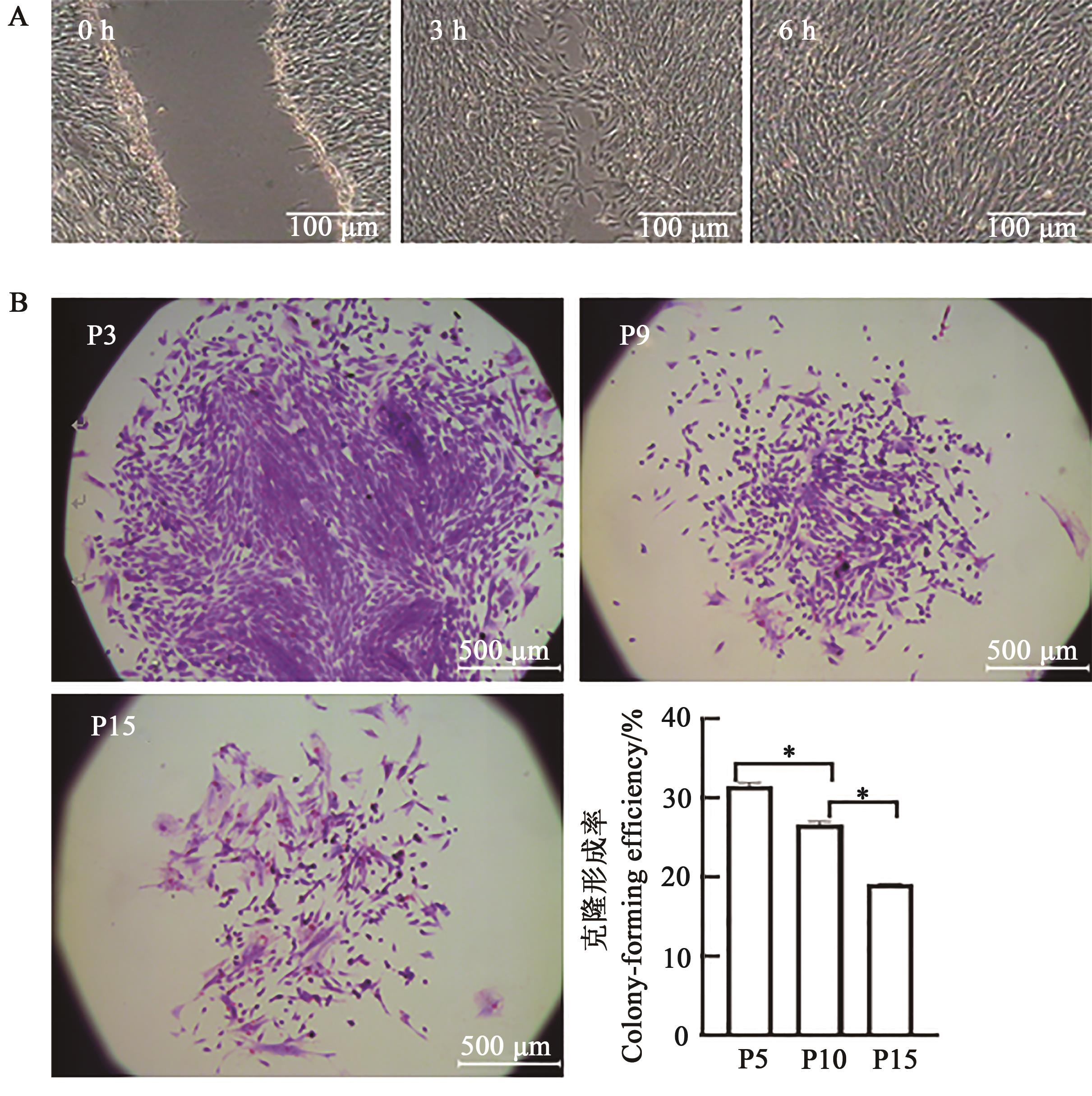
图4 日本大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞划痕试验及不同代次克隆形成能力A: 6 h划痕试验;B: P3、P9、P15克隆团及克隆形成率,*表示差异在P<0.05水平显著
Fig. 4 Scratching experiment and clonogenic ability of Japanese large ear white rabbits BMSCsA: 6 h scratch test;B: P3, P9, P15 clone groups and the cloning rate, * indicates significant difference at P<0.05 level.
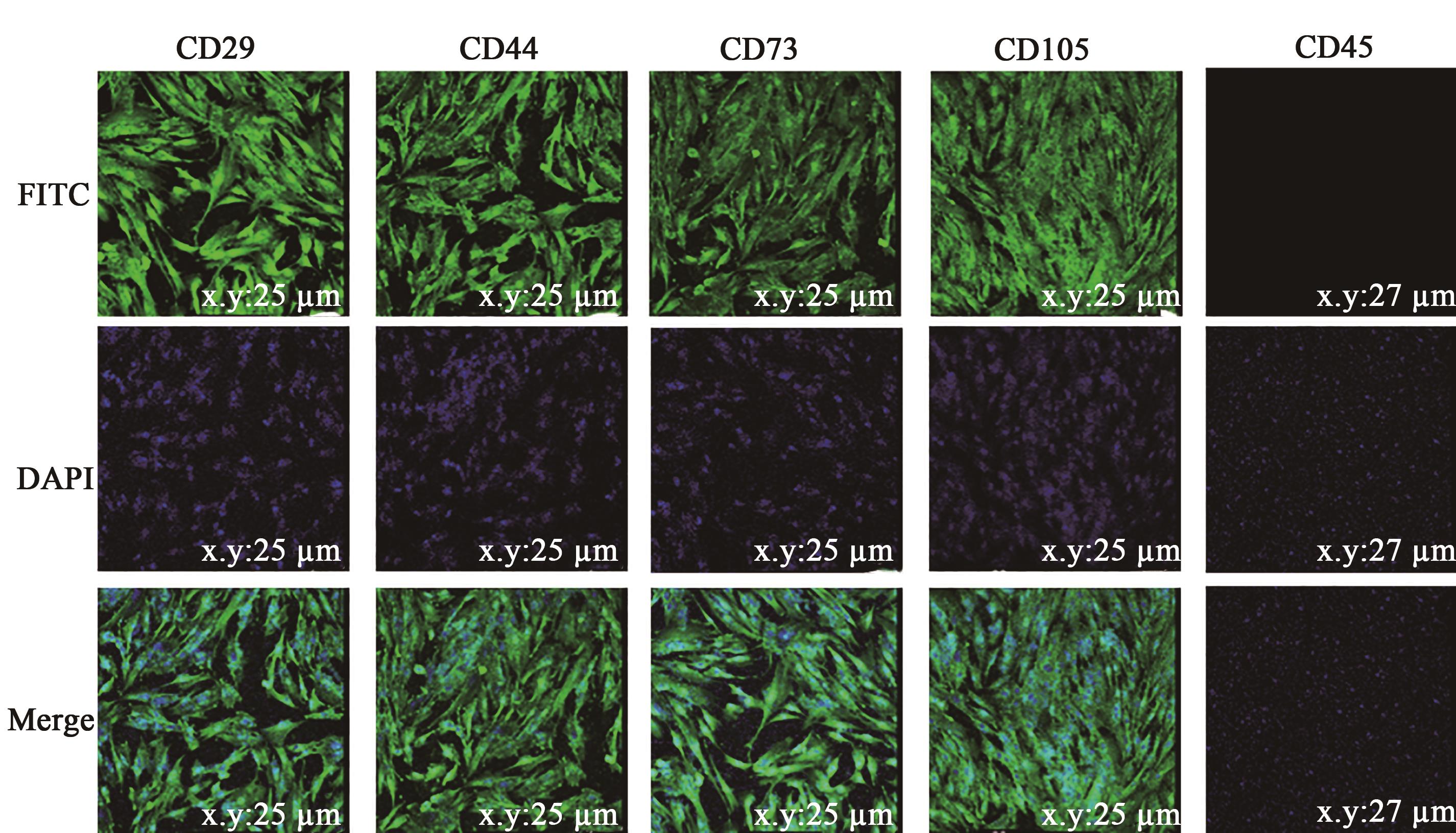
图5 日本大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞免疫荧光注:DAPI—核染;FITC—免疫荧光;Merge—DAPI和FITC图叠加。
Fig. 5 Immunofluorescence of Japanese large ear white rabbits BMSCsNote: DAPI—Nuclear staining;FITC—Immunofluorescence;Merge—Overlay of DAPI and FITC images.
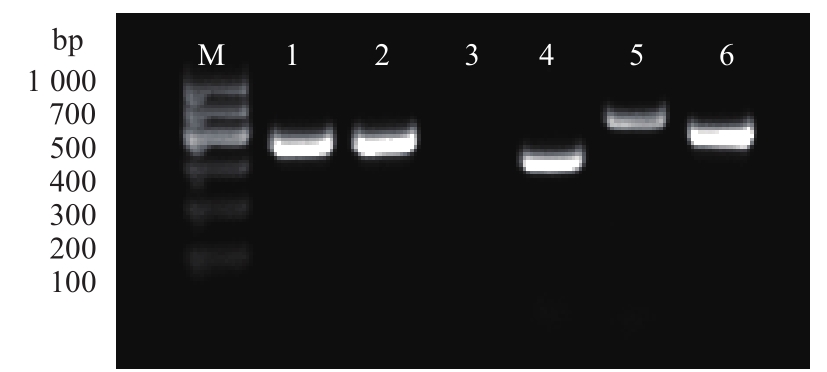
图6 表面标记物RT-PCR检测注:M为DNA Marker;1~6分别为GAPDH、CD29、CD45、CD44、CD73和CD105。
Fig. 6 RT-PCR result of marker genesNote: M shows DNA Marker;1~6 represent GAPDH,CD29,CD45,CD44,CD73 and CD105,respectively.
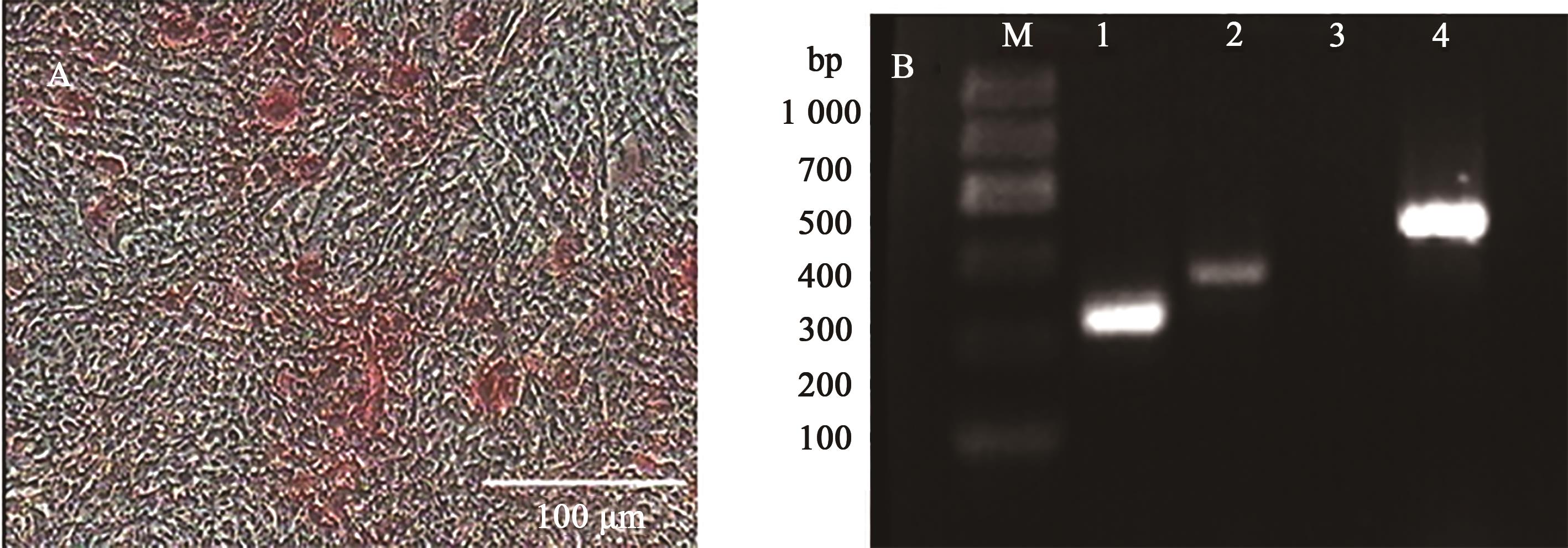
图7 日本大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化钙沉积茜素红染色和RT-PCR检测A:成骨诱导形态;B:成骨诱导后的RT-PCR检测;M为DNA Marker,1为GAPDH,2、4为诱导组,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和骨桥蛋白基因为阳性;3为阴性对照组,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白基因为阴性
Fig. 7 Detection of calcium deposition in osteoblastic differentiation of Japanese large ear white rabbits BMSCs using alizarin red and RT-PCRA: Osteogenic induction morphology; B: RT-PCR after osteogenic induction;M shows DNA Marker; 1 shows GAPDH; 2 and 4 show the induction group, collagen type I and osteopontin gene are positive;3 show negative control group, collagen type I is negative
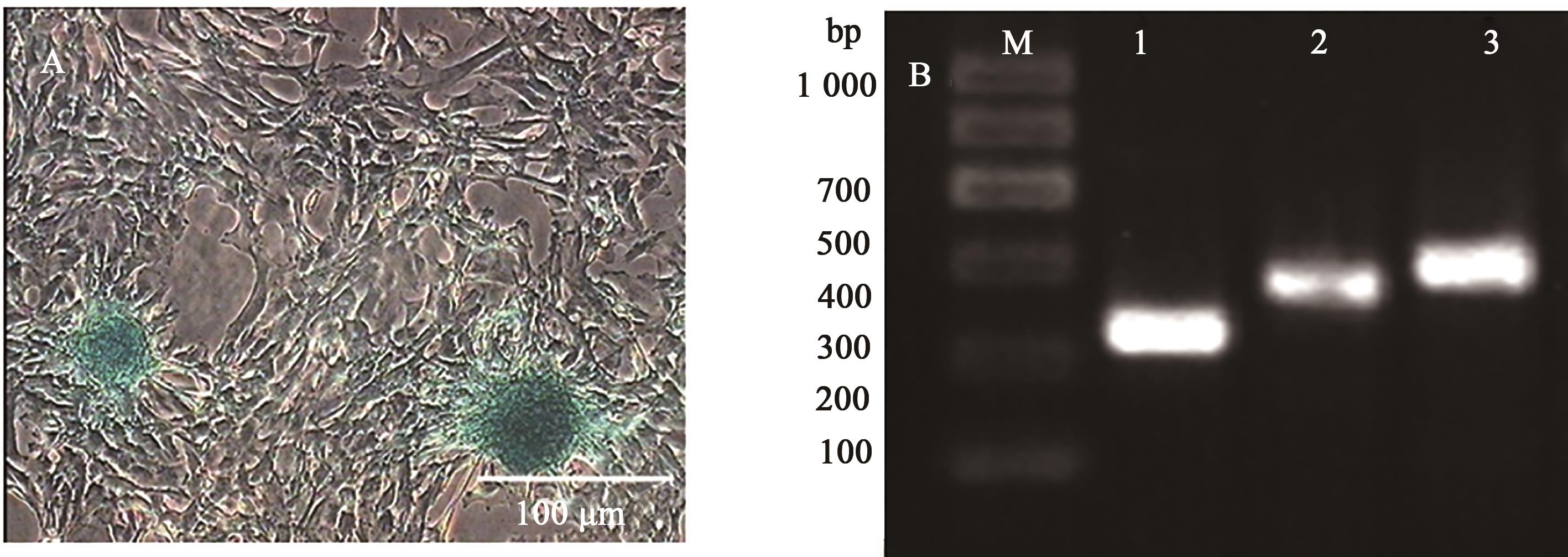
图8 日本大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化阿利新蓝染色和RT-PCR检测A:成软骨诱导形态;B:成软骨诱导后的RT-PCR检测;M为1 000 DNA Marker,1为GAPDH,2和3为诱导组,SOX9、ACAN为阳性
Fig. 8 Detection of chondrogenic differentiation of Japanese large ear white rabbits BMSCs using Alixin blue and RT-PCRA: Chondrogenic induction morphology; B: RT-PCR after chondrogenic induction;M shows 1 000 DNA Marker,1 shows GAPDH,2 and 3 show the induction group, SOX9 and ACAN are positive
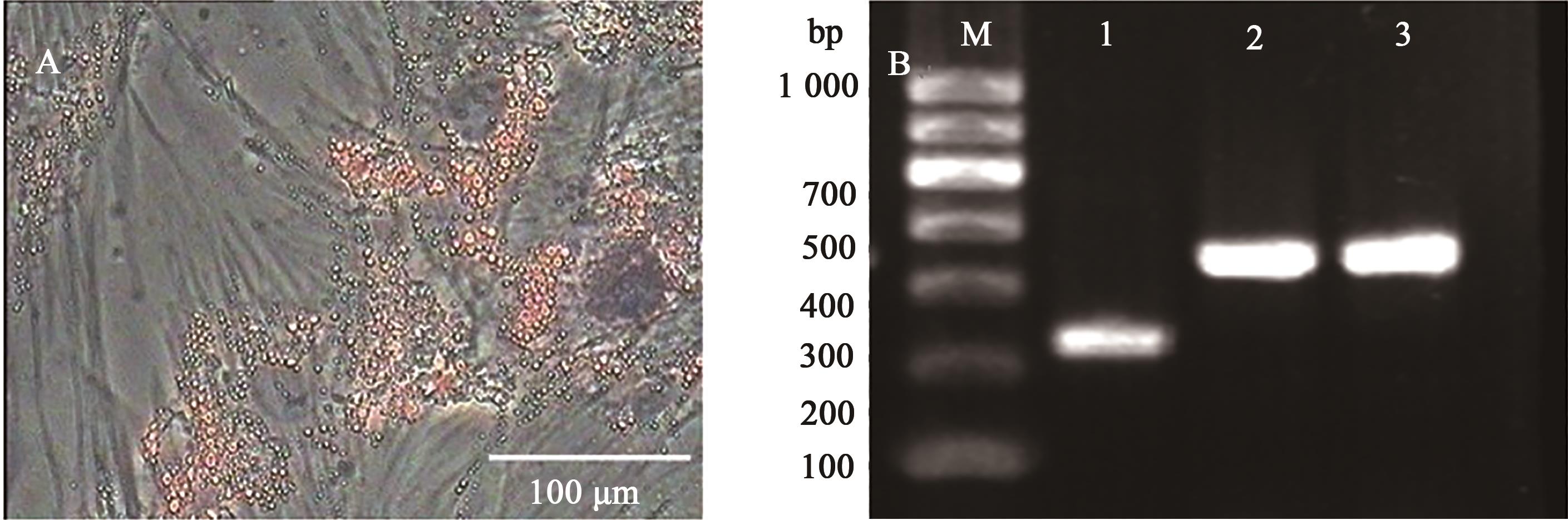
图9 日本大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化油红O染色和RT-PCR检测A:成脂诱导后形态; B:成脂诱导后RT-PCR检测;M为1 000 DNA Marker,1为GAPDH,2和3为诱导组,LPL、PPAR-γ为阳性
Fig.9 Oil red O staining and RT-PCR detection of adipogenic differentiation of Japanese large ear white rabbits BMSCsA: Lipogenic induction morphology; B: RT-PCR after induction of adipogenesis;M shows 1 000 DNA Marker,1 shows GAPDH,2 and 3 show the induction group,LPL and PPAR-γ are positive
| 1 | TRAVLOS G S. Normal structure, function, and histology of the bone marrow [J]. Toxicol. Pathol., 2006, 34(5): 548-565 |
| 2 | KIM S, LEE S, LIM J, et al.. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells play a role as a vascular pericyte in the reconstruction of human BBB on the angiogenesis microfluidic chip [J/OL]. Biomaterials, 2021, 279: 121210 [2023-04-21]. . |
| 3 | LIN C B, SHEN M R, CHEN W P, et al.. Isolation and purification of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells using an optimized protocol [J]. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim., 2015, 51(10): 1102-1108. |
| 4 | CHU D T, PHUONG T N T, TIEN N L B, et al.. An update on the progress of isolation, culture, storage, and clinical application of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(3): 708[20213-04-21]. . |
| 5 | 孙凤. MRI体外定量测定SPIO标记兔骨髓间充质干细胞[D]. 南充:川北医学院,2014. |
| SUN F. MRI quantitatively measurement of SPIO-labeled mesenchymal stem cells in experimental rabbits in vitro [D]. Nanchong:North Sichuan Medical College,2014. | |
| 6 | ZHANG L, PENG L P, WU N, et al.. Development of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture in vitro [J]. Chin. Med. J., 2012, 125(9): 1650-1655. |
| 7 | HW J G, LI H R, LI B B, et al.. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing GATA-4 improve cardiac function following myocardial infarction [J]. Perfusion, 2019, 34(8): 696-704. |
| 8 | JENA D, KHARCHE S D, SINGH S P, et al.. Growth and proliferation of caprine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different culture media [J/OL]. Tissue Cell, 2020, 67: 101446 [2023-04-21]. . |
| 9 | DONG C L, LIU X H, WU L. Research and development of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. China J. Orthopaedics Traumatol., 2019, 32(3): 288-292. |
| 10 | LI K D, WANG Y, SUN Q, et al.. Rabbit umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new option for tissue engineering [J/OL]. J. Gene Med., 2021, 23(1): e3282[2023-04-21]. . |
| 11 | 吴月,王育南,宋哈楠,等. 固始鸡脐带间充质干细胞原代培养及其诱导分化潜能研究[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(9):79-87. |
| WU Y, WANG Y N, SONG H N, et al.. Primary culture and differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells from Gushi chicken umbilical cord [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022,24(9):79-87. | |
| 12 | PANG M J, HUANG Y H, MENG F S, et al.. Application of bacterial cellulose in skin and bone tissue engineering [J/OL]. European Polymer J., 2020, 122: 109365 [2023-04-21]. . |
| 13 | 张浩, 廖伟雄, 李冀, 等. 兔骨髓栓来源的间充质干细胞的分离培养及其生物学特性的研究[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2015, 23(2): 500-505. |
| ZHANG H, LIAO W X, LI J, et al. Isolation and biological characteristics of rabbit bone marrow plug-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. J. Exper. Hematol., 2015, 23(2): 500-505. | |
| 14 | BAI C, HOU L, MA Y, et al.. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from chicken bone marrow [J]. Cell Tissue Bank., 2013, 14: 437-451. |
| 15 | 杨金娟. 间充质干细胞生物学特性研究及肌腱损伤和肌肉损伤动物模型的构建[D].厦门:集美大学, 2016. |
| YANG J J. Research of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells and the construction of tendon injuries and muscle injuries in animal model [D]. Xiamen: Jimei Univercity, 2016. | |
| 16 | SONG N, SCHOLTEMEIJER M, SHAH K. Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: mechanisms and therapeutic potential [J]. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 2020, 41(9): 653-664. |
| 17 | 李佩霖,朱恒. 间充质干细胞生物学特性的可塑性研究进展[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2021, 29(2): 629-632. |
| LI P L, ZHU H. Research advances in plasticity of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells—review [J]. J. Exper. Hematol., 2021, 29(2): 629-632. | |
| 18 | WENG Z, WANG Y, OUCHI T, et al.. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell senescence: hallmarks, mechanisms, and combating strategies [J]. Stem Cells Translat. Med., 2022, 11(4): 356-371. |
| 19 | LEE D K, SONG S U. Immunomodulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications [J]. Cell. Immunol., 2018, 326: 68-76. |
| 20 | WANG L, LIAN J, XIA Y J, et al.. A study on in vitro and in vivo bioactivity of silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide composite scaffolds with directional channels [J/OL]. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2022, 652: 129886[2023-04-21]. . |
| 21 | 刘康, 白亦光, 冯刚, 等. 生长分化因子 5 诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨细胞的实验研究[J]. 西部医学, 2013, 25(8): 1128-1131. |
| LIU K, BAI Y G, FENG G, et al.. Experrimental study on growth and differentiationfactor 5 promoting chondrogenesis of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell [J]. Med. J. West China, 2013, 25(8): 1128-1131. | |
| 22 | FAJARDO-ORDUNA G R, MAYANI H, MONTESINOS J J. Hematopoietic support capacity of mesenchymal stem cells: biology and clinical potential [J]. Arch. Med. Res., 2015, 46(8): 589-596. |
| 23 | LIU Y L, LIU Y, YIE S M, et al.. Characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from bone marrow of giant panda [J]. Stem Cells Dev., 2013, 22(17): 2394-2401. |
| 24 | CALLE A, ZAMORA-CEBALLOS M, BARCENA J, et al.. Comparison of biological features of wild European rabbit mesenchymal stem cells derived from different tissues [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(12): 6420 [2023-04-21]. . |
| 25 | RAJAGOPAL K, MADHURI V. Comparing the chondrogenic potential of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells derived from the infrapatellar fat pad, periosteum & bone marrow [J]. Indian J. Med. Res., 2021, 154(5): 732-742. |
| 26 | BERNINGER M T, RODRIGUEZ-CONZALEZ P, SCHILLING F, et al.. Bifunctional labeling of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for mr imaging and fluorescence microscopy [J]. Mol. Imag. Biol., 2020, 22: 303-312. |
| 27 | FENG G J, ZHANG Z P, DANG M, et al.. Nanofibrous spongy microspheres to deliver rabbit mesenchymal stem cells and anti-miR-199a to regenerate nucleus pulposus and prevent calcification [J/OL]. Biomaterials, 2020, 256: 120213 [2023-04-21]. . |
| 28 | LIU H, WEI L K, JIAN X F, et al.. Isolation, culture and induced differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Exper. Therapeutic Med., 2018, 15(4): 3715-3724. |
| 29 | FU H D, WANG H R, LI D H. BMP-7 accelerates the differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells into cartilage through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [J]. Exper. Therapeutic Med., 2017, 14(6): 5424-5428. |
| 30 | LIN C, SHEN M, CHEN W, et al.. Isolation and purification of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells using an optimized protocol [J]. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim., 2015, 51: 1102-1108. |
| [1] | 王鑫慈, 李军乔, 李晨芹, 田甜, 曲俊儒. 一株乳突赤壳属蕨麻致病菌的鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 87-95. |
| [2] | 许鑫, 孟昆, 蔡红英, 杨培龙, 蒋显仁. 乳酸菌在猪生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 19-26. |
| [3] | 吴月, 王育南, 宋哈楠, 关伟军, 李楠. 固始鸡脐带间充质干细胞原代培养及其诱导分化潜能研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 79-87. |
| [4] | 霍佳欢, 温晓蕾, 李双民, 冯丽娜, 兰淑慧, 董立新, 郭思柔, 栗佳宁, 王建华, 齐慧霞. 北苍术根腐病病原鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 137-144. |
| [5] | 孙华, 郭宁, 郑晓娟, 石洁, 张立荣, 闫红飞. 玉米穗腐病病原菌新知镰孢的鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [6] | 张娜娜§, 李双民§, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 王俊凤, 杨文杰, 霍佳欢, 兰淑慧, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 板栗红粉病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [7] | 温晓蕾1,2,齐慧霞1*,孙伟明1,刘一健1,冯丽娜1,孟童瑶3,韩志玲1,曹佳1,王俊凤1. 北苍术枝枯病病原菌(Fusarium equiseti)的鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 115-121. |
| [8] | 梁峻1,张涛1*,李婷婷2. 北京鸭肝上皮样干细胞生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 107-114. |
| [9] | 王宝莲1,2,樊庆琦1,李永波1,曲志才2,楚秀生1. 甲羟戊酸激酶基因研究进展[J]. , 2011, 13(3): 17-25. |
| [10] | 唐海明,汤文光,肖小平,汤海涛,杨光立. 冬季覆盖作物对南方稻田水稻生物学特性及产量性状的影响[J]. , 2010, 12(3): 108-113. |
| [11] | 熊格生 陈金湘 唐海明. 棉花漂浮育苗法对棉苗生物学特性及移栽棉产量构成因素的影响[J]. , 2007, 9(5): 105-109. |
| [12] | 姜培增 李宏园 陈铁保. 淡紫拟青霉防治植物线虫研究进展[J]. , 2006, 8(6): 38-41. |
| [13] | 关伟军[1] 马月辉[1] 周雪雁[2] 刘桂林[2] 刘学东[1]. 太行黑山羊成纤维细胞系建立与生物学特性研究[J]. , 2005, 7(5): 25-33. |
| [14] | 盛晋华[1] 翟志席[2] 杨太新[2] 郭玉海[2]. 肉苁蓉寄生生物学的研究[J]. , 2004, 6(1): 57-62. |
| [15] | 刘筠 刘少军 孙远东 张纯 冯浩 刘季芳 郭新红 周工健 张轩杰. 多倍体鲫鲤[J]. , 2003, 5(6): 3-6. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号