




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 226-233.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0513
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
裴薇薇1,2( ), 杨喆3, 王云英1,2, 王新1,2, 杜岩功1,2(
), 杨喆3, 王云英1,2, 王新1,2, 杜岩功1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-22
接受日期:2022-07-23
出版日期:2024-01-15
发布日期:2024-01-08
通讯作者:
杜岩功
作者简介:裴薇薇 E-mail: peiweiwei@nwipb.cas.cn;
基金资助:
Weiwei PEI1,2( ), Zhe YANG3, Yunying WANG1,2, Xin WANG1,2, Yangong DU1,2(
), Zhe YANG3, Yunying WANG1,2, Xin WANG1,2, Yangong DU1,2( )
)
Received:2022-06-22
Accepted:2022-07-23
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Yangong DU
摘要:
祁连山区是我国西部重要的生态安全屏障和固碳场所。为准确评估祁连山区青海云杉林生态系统生长季碳汇特征,利用涡度相关技术并结合增强回归树模型与结构方程模型,研究生长季其碳通量变化特征及其环境影响机制。结果表明,青海云杉林生长季净生态系统碳交换(net ecosystem carbon exchange, NEE)日变化呈“V”型,CO2通量变化范围在-0.71~0.08 mg CO2·m-2·s-1,季节尺度NEE变化范围在-20.93~11.75 g C·m-2,月均碳吸收量(188.27±17.85) g·m-2,生长季累积碳吸收941.34 g·m-2。增强回归树模型揭示植被指数对净生态系统碳交换量相对贡献率最高,为50.3%,其次是净辐射,为15.9%。结构方程模型表明,植被指数与相对湿度对净生态系统碳交换量的直接作用系数分别为0.61与-0.17。多元逐步回归模型表明植被指数与相对湿度对NEE具有显著影响(R2=0.74, P<0.01)。随着植被指数增加,祁连山森林生态系统碳汇功能显著增强。结果为准确评估祁连山区青海云杉林生态系统碳汇能力提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
裴薇薇, 杨喆, 王云英, 王新, 杜岩功. 祁连山区青海云杉林碳汇特征及调控因子[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 226-233.
Weiwei PEI, Zhe YANG, Yunying WANG, Xin WANG, Yangong DU. Carbon Sink Characteristics and Regulatory Factors of Qinghai Spruce Forests in the Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 226-233.
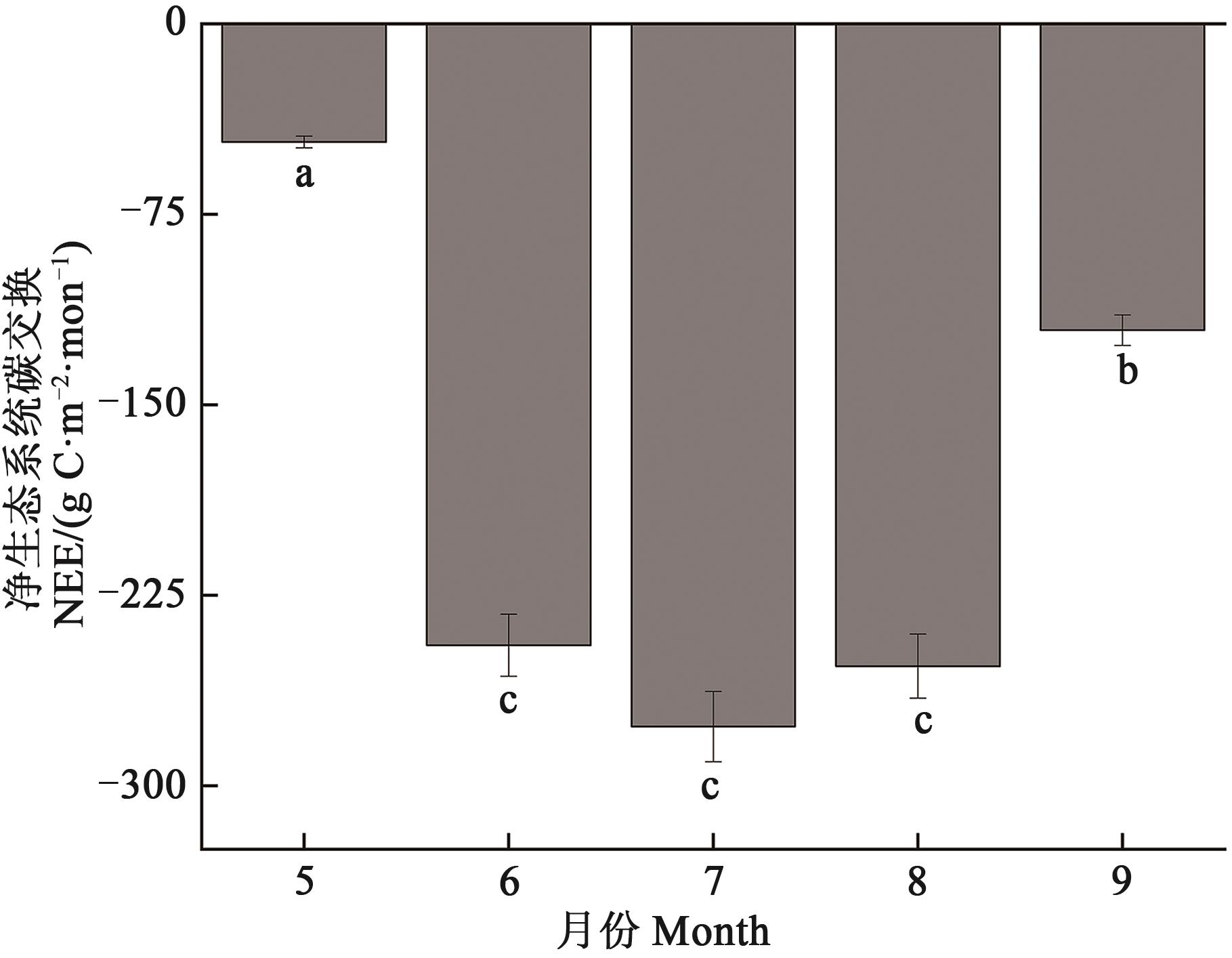
图3 青海云杉林生长季NEE月累积变化特征注:不同小写字母表示不同月份间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Characteristics of monthly cumulative changes of NEE in the growing season of Qinghai spruce forestNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different months at P<0.05 level.

图5 气象因素对生长季青海云杉林NEE影响特征注:箭头上的数值代表作用系数及其大小,实线代表正作用,虚线代表负作用,间接效应中只显示达到显著效果的结果值。**和***分别表示在P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 5 Effects of meteorological factors on NEE of Qinghai spruce forest in growing seasonNote: The values on the arrows represent the coefficient of action and its size, the solid line represents the positive action, the dashed line represents the negative effect, and the indirect effect only shows the result value that achieves a significant effect. ** and *** indicate significance at P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels,respectively.
| 1 | 杨长进, 田永, 许鲜. 实现碳达峰、碳中和的价税机制进路[J].价格理论与实践, 2021(1):20-26, 65. |
| YANG C J, TIAN Y, XU X. The path of price and tax mechanism to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality [J]. Price Theory Pract., 2021(1):20-26, 65. | |
| 2 | 王国胜, 孙涛, 昝国盛, 等. 陆地生态系统碳汇在实现“双碳”目标中的作用和建议[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4):13-19. |
| WANG G S, SUN T, ZAN G S, et al.. Roles and suggestions of terrestrial ecosystem carbon sink in achieving carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality in China [J]. Geol. Surv. Chin., 2021, 8(4):13-19. | |
| 3 | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations(FAO). Global forest resources assessment(2020) [EB/OL].[2022-05-22 ] . . |
| 4 | 尹晶萍, 张煜星, 付尧, 等. 中国碳排放与森林植被碳吸收潜力研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2021(3):53-61. |
| YIN J P, ZHANG Y X, FU Y, et al.. The research of carbon emission and carbon sequestration potential of forest vegetation in China [J]. For. Resour. Manage., 2021(3):53-61. | |
| 5 | 谭丽萍, 刘苏峡, 莫兴国, 等. 华北人工林水热碳通量环境影响因子分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(8):773-784. |
| TAN L P, LIU S X, MO X G, et al.. Environmental controls over energy, water and carbon fluxes in a plantation in Northern China [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2015, 39(8):773-784. | |
| 6 | AHLSTRÖM A, RAUPACH M R, SCHURGERS G, et al.. The dominant role of semi-arid ecosystems in the trend and variability of the land CO2 sink [J]. Science, 2015, 348(6237):895-899. |
| 7 | 国家林业和草原局. 中国森林资源报告(2014—2018) [M]. 北京:中国林业出版社, 2019. |
| 8 | TANG X L, ZHAO X, BAI Y F, et al.. Carbon pools in China’s terrestrial ecosystems:new estimates based on an intensive field survey [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2018, 115(16):4021-4026. |
| 9 | NAVE L E, SWANSTON C W, MISHRA U, et al.. Afforestation effects on soil carbon storage in the United States: a synthesis [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2013, 77(3):1035-1047. |
| 10 | MAKKONEN M, HUTTUNEN S, PRIMMER E, et al.. Policy coherence in climate change mitigation: an ecosystem service approach to forests as carbon sinks and bioenergy sources [J]. For. Policy Econ., 2015, 50:153-162. |
| 11 | 周晓宇, 张称意, 郭广芬. 气候变化对森林土壤有机碳贮藏影响的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010,21(7):1867-1874. |
| ZHOU X Y, ZHANG C Y, GUO G F. Effects of climate change on forest soil organic carbon storage: a review [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2010, 21(7):1867-1874. | |
| 12 | 范叶青, 周国模, 施拥军, 等. 地形条件对毛竹林分结构和植被碳储量的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(11):177-182. |
| FAN Y Q, ZHOU G M, SHI Y J, et al.. Effects of terrain on stand structure and vegetation carbon storage of Phyllostachys edulis forest [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2013, 49(11):177-182. | |
| 13 | PUGH T A M, LINDESKOG M, SMITH B, et al.. Role of forest regrowth in global carbon sink dynamics [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2019, 116(10):4382-4387. |
| 14 | BERENGUER E, LENNOX G D, FERREIRA J, et al.. Tracking the impacts of El Niño drought and fire in human-modified Amazonian forests [J/OL]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2021, 118(30):2019377118 [2022-04-22]. . |
| 15 | 李小梅, 张秋良. 兴安落叶松林生长季碳通量特征及其影响因素[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(6):121-128. |
| LI X M, ZHANG Q L. Carbon flux and its impact factors of larix gmelinii forest ecosystem during growing season [J]. J. Northwest. A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2015, 43(6):121-128. | |
| 16 | MCEWAN R W, LIN Y C, SUN I F, et al.. Topographic and biotic regulation of aboveground carbon storage in subtropical broad-leaved forests of Taiwan [J]. For. Ecol. Manag., 2011, 262(9):1817-1825. |
| 17 | 魏红, 满秀玲. 中国寒温带不同林龄白桦林碳储量及分配特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(10):843-852. |
| WEI H, MAN X L. Carbon storage and its allocation in Betula platyphylla forests of different ages in cold temperate zone of China [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 43(10):843-852. | |
| 18 | 刘建泉, 李进军, 郝虎, 等. 祁连山青海云杉林生物量与碳储量及其影响因素分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2017(12):140-143, 146. |
| LIU J Q, LI J J, HAO H, et al.. Analysis on biomass and carbon storage of Picea crassifolia forest in Qilian mountains and its influence factors [J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2017(12):140-143, 146. | |
| 19 | 马剑, 金铭, 敬文茂, 等. 祁连山中段典型植被土壤有机碳密度研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(8):99-105. |
| MA J, JIN M, JING W M, et al.. Study on soil organic carbon density of typical vegetation in the middle Qilian mountains [J]. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol., 2020, 40(8):99-105. | |
| 20 | WANG H, LI X, XIAO J, et al.. Carbon fluxes across alpine, oasis, and desert ecosystems in northwestern China:the importance of water availability [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 697:133978[2022-04-22]. . |
| 21 | 周宇, 黄辉, 张劲松, 等. 森林生态系统涡度相关法碳通量长时间连续性缺失数据插补方法的比较[J]. 中国农业气象, 2021, 42(4):330-343. |
| ZHOU Y, HUANG H, ZHANG J S, et al.. Comparison of gap-filling methods for long-term continuous missing data in carbon flux observation by eddy covariance method of forest ecosystem [J]. Chin. J. Agro. Meteorol., 2021, 42(4):330-343. | |
| 22 | 牛晓栋, 江洪, 张金梦, 等. 浙江天目山老龄森林生态系统CO2通量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1):1-8. |
| NIU X D, JIANG H, ZHANG J M, et al.. Characteristics of CO2 flux in an old growth mixed forest in Tianmu mountain, Zhejiang, China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2016, 27(1):1-8. | |
| 23 | 李润东, 范雅倩, 冯沛, 等. 北京松山天然落叶阔叶林生态系统净碳交换特征及其影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(11):3621-3630. |
| LI R D, FAN Y Q, FENG P, et al.. Net ecosystem carbon exchange and its affecting factors in a deciduous broad-leaved forest in Songshan, Beijing, China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020,31(11):3621-3630. | |
| 24 | 王倩, 王云琦, 马超, 等. 缙云山针阔混交林碳通量变化特征及影响因子研究 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(3):565-576. |
| WANG Q, WANG Y Q, MA C, et al.. The characteristics and influencing factors of carbon fluxes in coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests in Jinyun mountain [J]. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(3):565-576. | |
| 25 | 纪小芳, 鲁建兵, 杨军, 等. 凤阳山针阔混交林碳通量变化特征及其影响因子[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(3):49-55. |
| JI X F, LU J B, YANG J, et al.. Carbon flux variation characteristics and its influencing factors in conifero us and broad-leaved mixed forest in Fengyang mountain [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2019, 47(3):49-55. | |
| 26 | 吴振云, 李进军, 李娜, 等. 祁连山青海云杉林生长状况及固碳潜力空间分异研究[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(6):749-754. |
| WU Z Y, LI J J, LI N, et al.. Growth status of Qinghai spruce forest and its potential distribution of biomass C stock in Qilian mountains, Northwestern China [J]. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2020, 56(6):749-754. | |
| 27 | 冯源, 朱建华, 肖文发, 等. 干扰及林龄影响下迪庆州云杉老龄林生态系统碳储量动态[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(9):1465-1472. |
| FENG Y, ZHU J H, XIAO W F, et al.. Disturbances and ageing affected carbon dynamics in old-growth spruce forest in Diqing prefecture [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2017, 26(9):1465-1472. | |
| 28 | 张颖, 李晓格, 温亚利. 碳达峰碳中和背景下中国森林碳汇潜力分析研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(1):38-47. |
| ZHANG Y, LI X G, WEN Y L. Forest carbon sequestration potential in China under the background of carbon emission peak and carbon neutralization [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2022, 44(1):38-47. | |
| 29 | 张静茹, 同小娟, 孟平, 等. 基于植被指数、叶绿素荧光和碳通量的华北山地人工林物候对比研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(11):17-26. |
| ZHANG J R, TONG X J, MENG P, et al.. Comparative study on phenology in a mountainous plantation in northern China based on vegetation index, chlorophyll fluorescence and carbon flux [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2020, 42(11):17-26. | |
| 30 | 田风霞, 赵传燕, 冯兆东, 等. 祁连山青海云杉林冠生态水文效应及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4):62-72. |
| TIAN F X, ZHAO C Y, FENG Z D, et al.. Eco-hydrological effects of Qinghai spruce (Picea crassifolia) canopy and its influence factors in thw Qilian mountains [J]. Acta. Ecol. Sin., 2012, 32(4):62-72. | |
| 31 | 张艳丽, 费世民, 李智勇, 等. 成都市沙河主要绿化树种固碳释氧和降温增湿效益[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(12):3878-3887. |
| ZHANG Y L, FEI S M, LI Z Y, et al.. Carbon sequestration and oxygen release as well as cooling and humidification efficiency of the main greening tree species of Sha River, Chengdu [J]. Acta. Ecol. Sin., 2013,33(12):3878-3887. | |
| 32 | 刘志理. 东北典型森林叶面积指数的时空动态[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2015. |
| LIU Z L. Spatial and temporal dynamics of forests in northeastern China [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2015. | |
| 33 | 徐勇峰, 季淮, 韩建刚, 等. 洪泽湖湿地杨树林生长季碳通量变化特征及其影响因子[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(2):322-331. |
| XU Y F, JI H, HAN J G, et al.. Variation of net ecosystem carbon flux in growing season and its driving factors in a poplar plantation from Hung-tse Lake wetland [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2018, 37(2):322-331. | |
| 34 | 刘佳. 太阳辐射对黄河小浪底人工混交林生态系统碳、水交换的影响[D]. 北京:北京林业大学, 2014. |
| LIU J. Impacts of solar radiation on net ecosystem carbon and water exchange in a mixed plantation in the Xiaolangdi area [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2014. | |
| 35 | 陈月明. 北美洲阔叶林与针叶林生态系统碳水通量驱动因素分析[D]. 广州:华南农业大学, 2018. |
| CHEN Y M. Main drivers of carbon and water flux at temperature deciduous forests and evergreen needleleaf forests in North American [D]. Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 36 | 赵仲辉. 亚热带杉木林生态系统与大气间的碳通量研究[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学, 2011. |
| ZHAO Z H. A study on carbon flux between Chinese fir planations and atmosphere in subtropical belts [D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2011. | |
| 37 | 栾金凯, 刘登峰, 刘慧, 等. 汉江流域上游植被指数变化的影响因素分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(1):46-54. |
| LUAN J K, LIU D F, LIU H, et al.. Analysis of the effecting factors of vegetation index change in the upper reach of Hanjiang River basin [J]. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci.), 2019, 40(1):46-54. | |
| 38 | LU E, TAKLE E S. Spatial variabilities and their relationships of the trends of temperature, water vapor, and precipitation in the North American regional reanalysis [J/OL]. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos., 2010, 115, D06110 [2022-05-22]. . |
| [1] | 甄琦, 闫广泽, 塔娜, 赵志勇, 于慧敏. 不同二氧化碳含量对马铃薯贮藏室内温度分布的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 154-165. |
| [2] | 文双雅, 石楠, 陈崇怡, 胡海燕, 高志强. 基于涡度相关法的水稻光能利用率研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 159-166. |
| [3] | 白思琦, 邹晓荣, 丁鹏, 林铭. 基于环境因子的东南太平洋智利竹筴鱼剩余产量模型建立[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 197-204. |
| [4] | 张标, 张冬梅, 张浪, 冯仲科, 孙林豪. 树干液流监测系统的研制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 121-129. |
| [5] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 天山北坡典型草地土壤呼吸特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 189-199. |
| [6] | 王檬檬1,党宏忠2*,李钢铁1,冯金超2,闫晶秋子1,胡杨1,李星1,杨超1. 晋西黄土区苹果树液流特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 140-147. |
| [7] | 黄雅茹1,李永华2*,辛智鸣1,马迎宾1,董雪1,李新乐1,段瑞兵1,罗凤敏1,边凯1. 乌兰布和沙漠人工梭梭夏季茎干液流变化特征及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 155-165. |
| [8] | 马鑫,秦富仓*,李龙,高天,黎英华. 黄土丘陵区山杏人工林蒸腾速率与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(12): 146-154. |
| [9] | 魏娜,次顿,张唐伟. 西藏高原地理与气候因子对青稞功能性成分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(12): 115-121. |
| [10] | 陈庆根,王磊,程式华*. 中国水稻生产环境与条件因子对产量的影响研究——湖南、浙江、黑龙江三省1 540农户实证调查[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(8): 1-8. |
| [11] | 颜建辉,陈崇成*,魏一丁,唐丽玉. 基于ZigBee无线传感器网络的林区局地环境监测系统[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(6): 72-82. |
| [12] | 王树键1,2,申国明1,高林1,王瑞3,王英旗2,周传哲2,. 采收期烟田生态系统碳通量的变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(10): 82-88. |
| [13] | 李亚迪,苗腾,朱超,纪建伟*. 北方日光温室智能监控系统的设计与实现[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(5): 94-101. |
| [14] | 句荣辉 沈佐锐. 环境因子与小动物的自动监测系统[J]. , 2004, 6(2): 54-56. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号