




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 59-70.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0986
收稿日期:2021-11-20
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-06-01
发布日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
李培英
作者简介:张一龙 E-mail:871298780@qq.com;
基金资助:
Yilong ZHANG( ), Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI(
), Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI( ), Zongjiu SUN
), Zongjiu SUN
Received:2021-11-20
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-06-01
Published:2023-07-28
Contact:
Peiying LI
摘要:
为揭示狗牙根抗旱生理机制,筛选不同干旱胁迫下影响其抗旱性的关键指标, 探明不同抗旱性狗牙根对干旱胁迫的响应差异,以2种类型不同抗旱性狗牙根(Cynodon dactylon)种质(敏旱种质:C10和C32;抗旱种质:C118和C138)为供试材料,研究其在渐进式缓慢干旱胁迫下叶片相对含水量、相对电导率、光合色素含量、抗氧化酶活性及渗调物质含量等的变化规律。结果表明,随着土壤含水量降低、干旱胁迫加剧,供试狗牙根叶片的相对含水量不断下降,相对电导率及丙二醛、可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸含量呈升高趋势,光合色素含量及3种抗氧化酶活性呈现先升后降趋势。与敏旱材料相比,抗旱狗牙根种质在中、重度干旱胁迫下能够维持较高的抗氧化酶活性,积累更多的脯氨酸和可溶性蛋白,导致其相对电导率及丙二醛含量增加缓慢。即使同为抗旱类型,不同种质对干旱的响应机制也存在差异,C118具有较高的叶绿素含量,而C138维持较高的类胡萝卜素含量。灰色关联分析表明,中度干旱下,相对电导率、类胡萝卜素含量及超氧化物歧化酶活性受狗牙根的抗旱性影响较大;而重度干旱下,脯氨酸和可溶性蛋白含量与抗旱性的关联度更高。以上结果明确了不同抗旱性狗牙根种质的干旱生理响应机制,为选育耐旱草种及节水技术奠定基础。
中图分类号:
张一龙, 孙晓梵, 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根种质的抗旱生理响应差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 59-70.
Yilong ZHANG, Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI, Zongjiu SUN. Physiological Response of Different Drought-resistant Cynodon dactylon Germplasm to Drought[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 59-70.
| 编号Code | 采集地点 Collection location | 抗旱类型 Drought resistance type |
|---|---|---|
| C10 | 莎车县Shache county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C32 | 托克逊县Tuokexun county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C118 | 莎车县Shache county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
| C138 | 疏勒县Shule county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
表1 供试材料来源及抗旱性
Table 1 Origins and drought resistances of test materials
| 编号Code | 采集地点 Collection location | 抗旱类型 Drought resistance type |
|---|---|---|
| C10 | 莎车县Shache county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C32 | 托克逊县Tuokexun county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C118 | 莎车县Shache county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
| C138 | 疏勒县Shule county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |

图1 干旱胁迫下不同狗牙根的土壤含水量和叶片相对含水量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理时间不同材料间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示同一材料不同处理时间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Soil water content and relative leaf water content of different bermudagrass under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
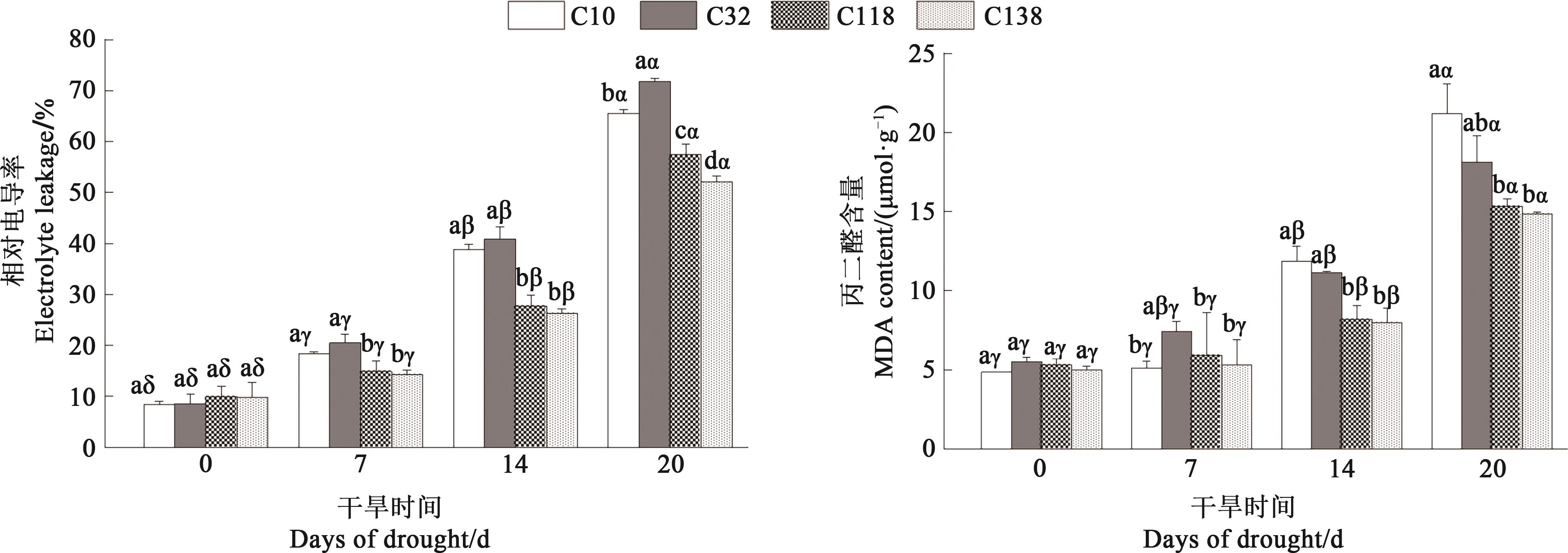
图2 干旱胁迫下不同狗牙根叶片相对电导率和丙二醛含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理时间不同材料间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示同一材料不同处理时间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Relative electrical conductivity and malondialdehyde content of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
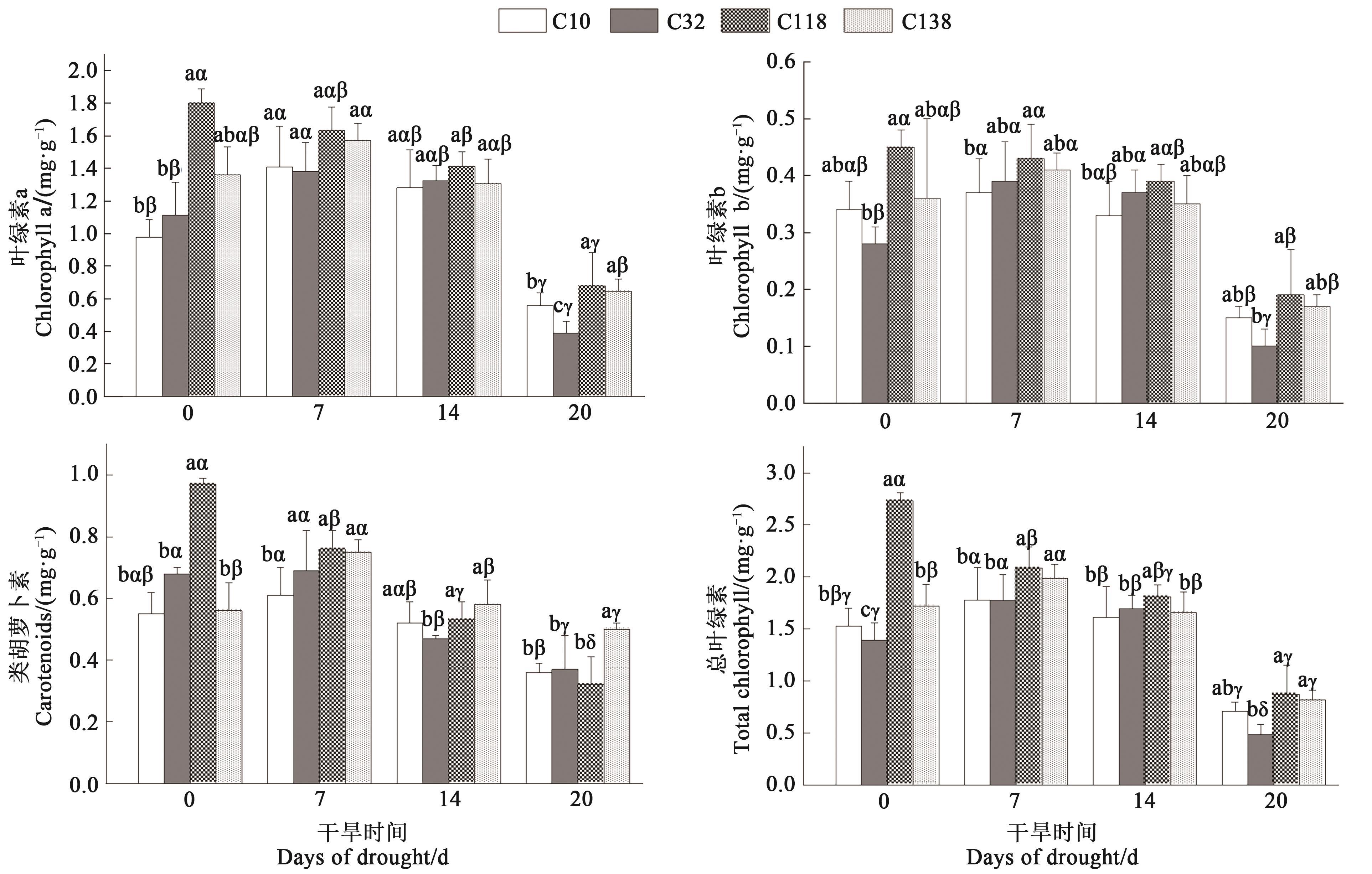
图3 干旱胁迫下不同狗牙根光合色素含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理时间不同材料间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示同一材料不同处理时间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Photosynthetic pigment content of different bermudagrass under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
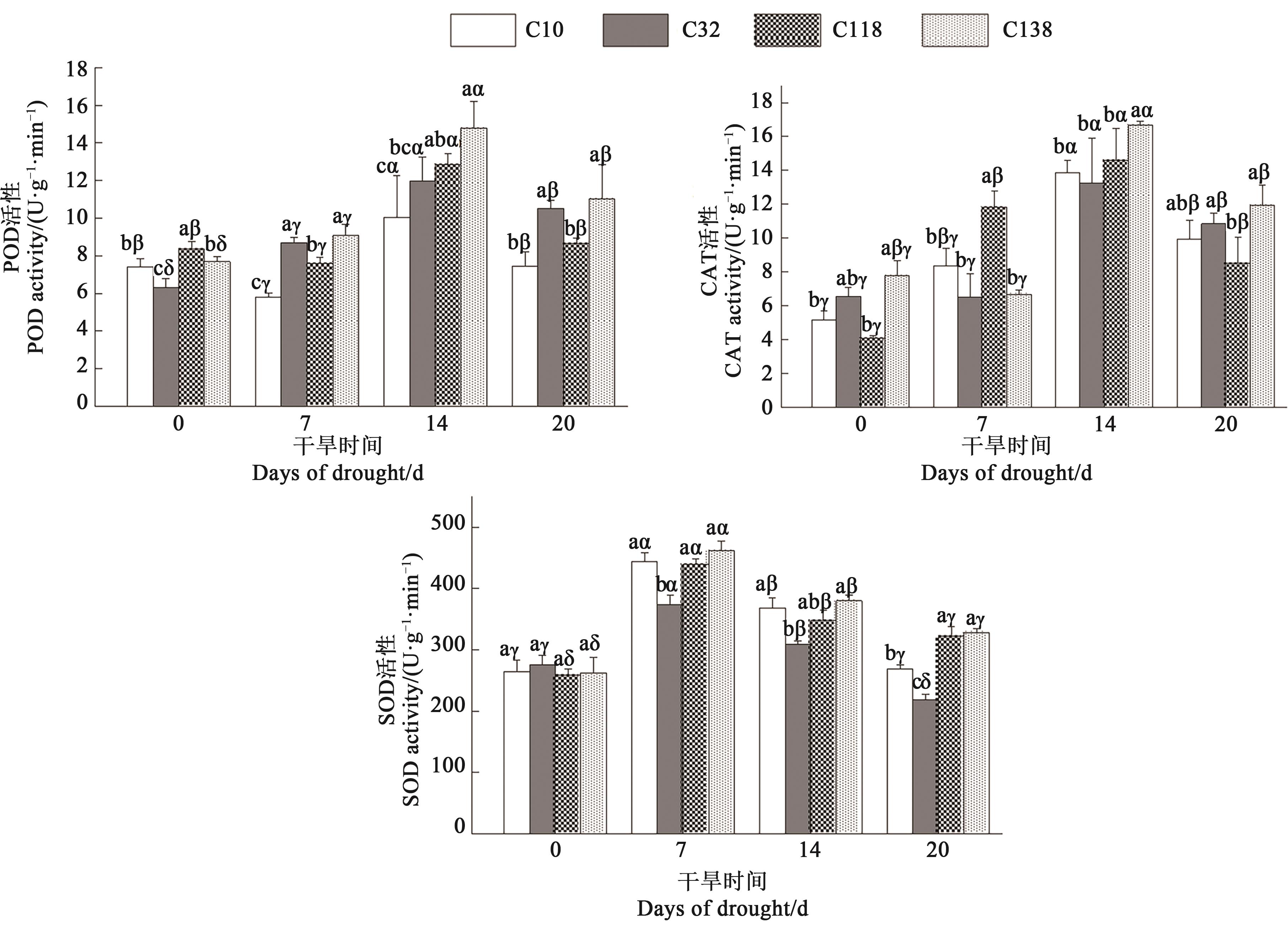
图4 干旱胁迫下不同狗牙根叶片抗氧化酶活性注:不同英文字母表示同一处理时间不同材料间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示同一材料不同处理时间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Antioxidant enzyme activities of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.

图5 干旱胁迫下不同狗牙根叶片可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理时间不同材料间在P<0.05水平差异显著;不同希腊字母表示同一材料不同处理时间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Soluble protein and proline content of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
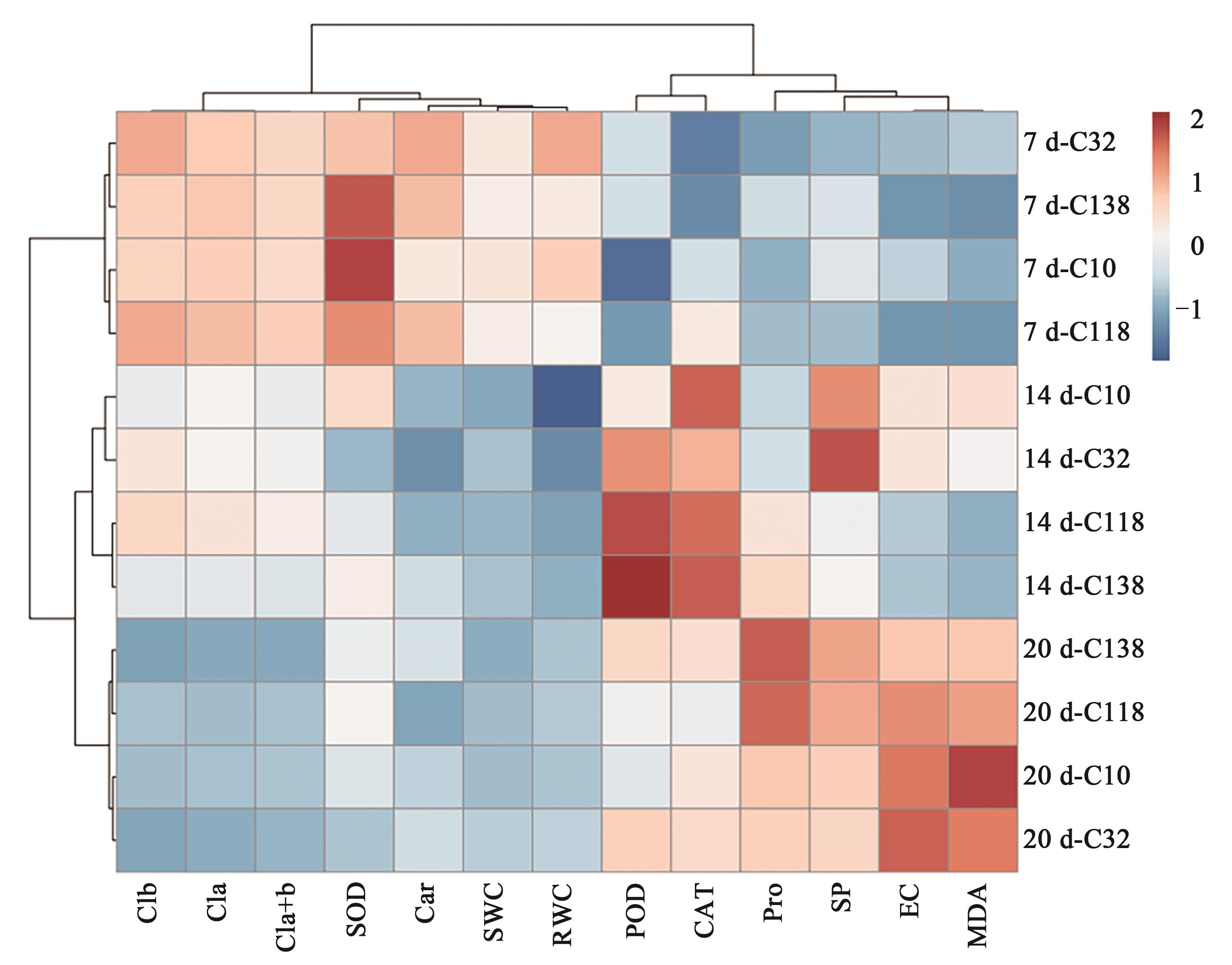
图6 4份狗牙根干旱处理7~20 d时各指标的热图聚类分析注:Clb—叶绿素b含量;Cla—叶绿素a含量;Cl(a+b)—叶绿素(a+b)含量;SOD—超氧化物歧化酶活性;Car—类胡萝卜素含量;SWC—土壤水分含量;RWC—叶片相对水分含量;POD—过氧化物酶活性;CAT—过氧化氢酶活性;Pro—脯氨酸含量;SP—可溶性蛋白含量;EC—相对电导率;MDA—丙二醛含量;7 d、14 d、20 d表示干旱处理时间。
Fig. 6 Heat map cluster analysis of each index of 4 bermudagrass under drought treatment for 7~20 dNote: Clb—Chlorophyll b content;Cla—Chlorophyll a content;Cl(a+b)—Chlorophyll (a+b) content;SOD—Superoxide dismutase activity;Car—Carotenoid content;SWC—Soil water content;RWC—Relative water content in leaf;POD—Peroxidase activity;CAT—Catalase activity;Pro—Proline content;SP—Soluble protein content;EC—electrical conductivity;MDA—Malondialdehyde content; and 7 d, 14 d, 20 d represent the drought treatment time.
材料 Accession | 7 d | 14 d | 20 d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | |
| C10 | 0.482 2 | 4 | 0.435 9 | 3 | 0.268 4 | 4 |
| C32 | 0.575 7 | 1 | 0.372 3 | 4 | 0.396 6 | 3 |
| C118 | 0.483 5 | 3 | 0.510 5 | 2 | 0.538 6 | 2 |
| C138 | 0.562 6 | 2 | 0.677 2 | 1 | 0.807 2 | 1 |
表2 干旱胁迫下狗牙根的隶属函数D值及排序
Table 2 Membership function D value and ranking of bermudagrass under drought stress
材料 Accession | 7 d | 14 d | 20 d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | |
| C10 | 0.482 2 | 4 | 0.435 9 | 3 | 0.268 4 | 4 |
| C32 | 0.575 7 | 1 | 0.372 3 | 4 | 0.396 6 | 3 |
| C118 | 0.483 5 | 3 | 0.510 5 | 2 | 0.538 6 | 2 |
| C138 | 0.562 6 | 2 | 0.677 2 | 1 | 0.807 2 | 1 |
干旱胁迫时间 Days after drought treatment/d | 特征向量 Eigen vector | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | ΨC10 | 0.624 0 | 0.514 5 | 0.516 6 | 0.508 5 | 0.648 0 | 0.520 7 | 0.569 8 | 0.754 3 | 0.577 8 | 0.839 2 | 0.614 4 | 0.512 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.620 0 | 0.510 3 | 0.734 0 | 0.624 1 | 0.550 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.749 1 | 0.500 2 | 0.972 4 | 0.729 6 | 0.571 6 | 0.748 5 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.644 0 | 0.710 8 | 0.734 1 | 0.551 8 | 0.589 4 | 0.677 2 | 0.563 3 | 0.667 2 | 0.345 7 | 0.893 1 | 0.654 5 | 0.504 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.635 1 | 0.787 5 | 0.520 9 | 0.834 0 | 0.564 7 | 0.653 7 | 0.583 1 | 0.569 4 | 0.555 0 | 0.785 0 | 0.597 0 | 0.559 0 | |
| 关联度Relevance | 0.630 8 | 0.630 8 | 0.626 4 | 0.629 6 | 0.588 0 | 0.614 1 | 0.616 3 | 0.622 8 | 0.612 7 | 0.811 7 | 0.609 4 | 0.580 9 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 12 | |
| 14 | ΨC10 | 0.606 9 | 0.409 4 | 0.428 3 | 0.369 4 | 0.498 0 | 0.357 1 | 0.663 0 | 0.615 3 | 0.488 5 | 0.396 0 | 0.530 1 | 0.729 2 |
| ΨC32 | 0.503 6 | 0.379 1 | 0.512 2 | 0.535 2 | 0.479 2 | 0.465 1 | 0.551 4 | 0.424 8 | 0.594 8 | 0.449 1 | 0.372 0 | 0.517 2 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.623 7 | 0.725 0 | 0.731 2 | 0.653 8 | 0.564 3 | 0.653 6 | 0.533 2 | 0.591 0 | 0.392 0 | 0.670 0 | 0.674 0 | 0.429 2 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.573 5 | 0.978 9 | 0.547 6 | 0.727 0 | 0.619 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.584 1 | 0.552 8 | 0.832 6 | 0.808 8 | 0.703 0 | 0.541 8 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.576 9 | 0.623 1 | 0.554 8 | 0.571 3 | 0.540 3 | 0.618 9 | 0.582 9 | 0.545 9 | 0.577 0 | 0.581 0 | 0.569 8 | 0.554 3 | |
| 排序Ranking | 6 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 10 | |
| 20 | ΨC10 | 0.658 0 | 0.666 0 | 0.369 5 | 0.376 1 | 0.448 5 | 0.490 2 | 0.453 9 | 0.525 1 | 0.409 3 | 0.350 4 | 0.611 1 | 0.657 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.563 9 | 0.400 6 | 0.734 5 | 0.504 1 | 0.472 0 | 0.466 7 | 0.633 7 | 0.381 3 | 0.522 0 | 0.494 4 | 0.645 0 | 0.562 8 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.649 0 | 0.657 6 | 0.664 6 | 0.637 9 | 0.573 2 | 0.591 6 | 0.475 7 | 0.591 0 | 0.474 8 | 0.651 0 | 0.606 7 | 0.687 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.582 7 | 0.668 0 | 0.519 4 | 0.776 7 | 0.711 7 | 0.615 5 | 0.619 4 | 0.655 6 | 0.569 0 | 0.921 2 | 0.672 7 | 0.643 6 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.613 4 | 0.598 0 | 0.572 0 | 0.573 7 | 0.551 3 | 0.541 0 | 0.545 7 | 0.538 3 | 0.493 7 | 0.604 2 | 0.633 9 | 0.637 6 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
表3 不同干旱时间下各指标与狗牙根抗旱的关联度
Table 3 Correlations between various indicators and bermudagrass drought resistance under different drought times
干旱胁迫时间 Days after drought treatment/d | 特征向量 Eigen vector | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | ΨC10 | 0.624 0 | 0.514 5 | 0.516 6 | 0.508 5 | 0.648 0 | 0.520 7 | 0.569 8 | 0.754 3 | 0.577 8 | 0.839 2 | 0.614 4 | 0.512 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.620 0 | 0.510 3 | 0.734 0 | 0.624 1 | 0.550 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.749 1 | 0.500 2 | 0.972 4 | 0.729 6 | 0.571 6 | 0.748 5 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.644 0 | 0.710 8 | 0.734 1 | 0.551 8 | 0.589 4 | 0.677 2 | 0.563 3 | 0.667 2 | 0.345 7 | 0.893 1 | 0.654 5 | 0.504 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.635 1 | 0.787 5 | 0.520 9 | 0.834 0 | 0.564 7 | 0.653 7 | 0.583 1 | 0.569 4 | 0.555 0 | 0.785 0 | 0.597 0 | 0.559 0 | |
| 关联度Relevance | 0.630 8 | 0.630 8 | 0.626 4 | 0.629 6 | 0.588 0 | 0.614 1 | 0.616 3 | 0.622 8 | 0.612 7 | 0.811 7 | 0.609 4 | 0.580 9 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 12 | |
| 14 | ΨC10 | 0.606 9 | 0.409 4 | 0.428 3 | 0.369 4 | 0.498 0 | 0.357 1 | 0.663 0 | 0.615 3 | 0.488 5 | 0.396 0 | 0.530 1 | 0.729 2 |
| ΨC32 | 0.503 6 | 0.379 1 | 0.512 2 | 0.535 2 | 0.479 2 | 0.465 1 | 0.551 4 | 0.424 8 | 0.594 8 | 0.449 1 | 0.372 0 | 0.517 2 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.623 7 | 0.725 0 | 0.731 2 | 0.653 8 | 0.564 3 | 0.653 6 | 0.533 2 | 0.591 0 | 0.392 0 | 0.670 0 | 0.674 0 | 0.429 2 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.573 5 | 0.978 9 | 0.547 6 | 0.727 0 | 0.619 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.584 1 | 0.552 8 | 0.832 6 | 0.808 8 | 0.703 0 | 0.541 8 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.576 9 | 0.623 1 | 0.554 8 | 0.571 3 | 0.540 3 | 0.618 9 | 0.582 9 | 0.545 9 | 0.577 0 | 0.581 0 | 0.569 8 | 0.554 3 | |
| 排序Ranking | 6 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 10 | |
| 20 | ΨC10 | 0.658 0 | 0.666 0 | 0.369 5 | 0.376 1 | 0.448 5 | 0.490 2 | 0.453 9 | 0.525 1 | 0.409 3 | 0.350 4 | 0.611 1 | 0.657 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.563 9 | 0.400 6 | 0.734 5 | 0.504 1 | 0.472 0 | 0.466 7 | 0.633 7 | 0.381 3 | 0.522 0 | 0.494 4 | 0.645 0 | 0.562 8 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.649 0 | 0.657 6 | 0.664 6 | 0.637 9 | 0.573 2 | 0.591 6 | 0.475 7 | 0.591 0 | 0.474 8 | 0.651 0 | 0.606 7 | 0.687 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.582 7 | 0.668 0 | 0.519 4 | 0.776 7 | 0.711 7 | 0.615 5 | 0.619 4 | 0.655 6 | 0.569 0 | 0.921 2 | 0.672 7 | 0.643 6 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.613 4 | 0.598 0 | 0.572 0 | 0.573 7 | 0.551 3 | 0.541 0 | 0.545 7 | 0.538 3 | 0.493 7 | 0.604 2 | 0.633 9 | 0.637 6 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | FENG Q, SHINOZAKIKAZUO, KAZUKO Y S. Achievements and challenges in understanding plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2011, 52(9):1569-1582. |
| 2 | 朱烨,刘懿,王文,等.基于土壤含水率的骤发干旱和缓慢干旱时空特征分析[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(2):114-122. |
| ZHU Y, LIU Y, WANG W, et al.. Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics of flash drought and slowly-evolving drought using soil moisture percentile [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2021, 37(2):114-122. | |
| 3 | 温琦,赵文博,张幽静,等.植物干旱胁迫响应的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(12):11-15. |
| WEN Q, ZHAO W B, ZHANG Y J, et al.. Research progress of plant response to drought stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(12):11-15. | |
| 4 | ANJUM S A, XIE Y. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress [J]. AFR JAGR Res., 2011, 6(9):2026-2032. |
| 5 | 宋娅丽,王莎,王克勤,等.3种冷季型草坪草苗期对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J].草原与草坪,2018,38(3):9-16. |
| SONG Y L, WANG S, WANG K Q, et al.. Physiological and ecological responses of three cool-season turfgrasses to drought stress at seedling stage [J]. Grassland Turf, 2018, 38(3): 9-16. | |
| 6 | 孙明伟,徐月乔,王贵,等.松嫩草地两种生态型羊草根际效应和光合生理对干旱胁迫的响应[J].中国草地学报, 2021,43(5):8-17. |
| SUN M W, XU Y Q, WANG G, et al.. Responses of the rhizosphere effect and photosynthetic physiology of two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis to drought stress in Songnen grassland [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2021, 43(5):8-17. | |
| 7 | 张娜.不同抗旱性燕麦品种对水分胁迫的生理响应机制研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2012. |
| ZHANG N. Drought resistance of different oat cultivars to water stress physiological response mechanism [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 8 | KATUWAL K B, SCHWARTZ B, JESPERSEN D. Desiccation avoidance and drought tolerance strategies in bermudagrasses [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2019, 171(10):39-47. |
| 9 | ZHOU Y, LAMBRIDES C J, FUKAI S. Drought resistance of bermudagrass (Cynodon spp) ecotypes collected from different climatic zones [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2013, 85:22-29. |
| 10 | 段敏敏,张向向,孙宗玖,等.水分胁迫下两种抗旱类型狗牙根种质的生理生态响应差异[J].中国草地学报,2018,40(3):8-13. |
| DUAN M M, ZHANG X X, SUN Z J, et al.. Response resistance difference in physiology and ecology of two drought resistance type Cynodon dactylon germplasm to water stress [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2018, 40(3):8-13. | |
| 11 | AJTAHED S S, REZAEI A, TAFRESHI S. Identifying superior drought-tolerant bermudagrass accessions and their defensive responses to mild and severe drought conditions [J]. Euphytica, 2021, 217(1):2-21. |
| 12 | 曾令霜,李培英,孙晓梵,等.新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J].草业学报,2020,29(8):155-169. |
| ZENG L S, LI P Y, SUN X F, et al.. A multi-trait evaluation of drought resistance of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) germplasm from different habitats in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(8):155-169. | |
| 13 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:1-275. |
| 14 | ALAN R W. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as will as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophoto meters of different resolution[J]. Plant Physiol., 1994, 144(3):307-313. |
| 15 | 王永军.超高产夏玉米群体质量与个体生理功能研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2008. |
| WANG Y J. Study on population quality and individual physiology function of super high-yielding maize (Zea mays) [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2008. | |
| 16 | 王燕凌.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2014:1-287. |
| 17 | 刘一明,郇恒福,丁西朋,等. 55份不同生态型假俭草的耐盐性评价[J].草业科学,2017,34(11):2261-2271. |
| LIU Y M, HUAN H F, DING X P,et al.. Evaluation of salinity tolerance of 55 centipedegrass ecotypes [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2017, 34(11):2261-2271. | |
| 18 | 伏兵哲,高雪芹,高永发,等. 21个苜蓿品种主要农艺性状关联分析与综合评价[J].草业学报,2015,24(11):174-182. |
| FU B Z, GAO X Q, GAO Y F, et al.. Correlation analysis of the main agronomic traits and performance of 21 alfalfa varieties [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2015, 24(11):174-182. | |
| 19 | CAUDLE K L, JOHNSON L C, BAER S G, et al.. A comparison of seasonal foliar chlorophyll change among ecotypes and cultivars of Andropogon gerardii (Poaceae) by using nondestructive and destructive methods [J]. Photosynthetica, 2014, 52(4):511-518. |
| 20 | 王平,王沛,孙万斌,等. 8份披碱草属牧草苗期抗旱性综合评价[J].草地学报,2020,28(2):109-116. |
| WANG P, WANG P, SUN W B, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of eight Elymus germplasms at seedling stage [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2020, 28(2): 397-404. | |
| 21 | 胡杨,李钢铁,李星,等.干旱胁迫对细穗柽柳幼苗生长和生理生化指标的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021, 23(6):43-50. |
| HU Y, LI G T, LI X, et al.. Growth and physiological index of tamarix leptostachys bunge seedlings under soil drought stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(6):43-50. | |
| 22 | 杨喜珍,杨利,覃亚,等.PEG-8000模拟干旱胁迫对马铃薯组培苗叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量的影响[J].中国马铃薯,2019,33(4):193-202. |
| YANG X Z, YANG L, QIN Y, et al.. Effects of PEG-8000 strees on carotenoid of potato contents of chlorophyll and plantlets in vitro [J]. Chin. Potato J., 2019, 33(4):193-202. | |
| 23 | 王凯悦, 陈芳泉, 黄五星. 植物干旱胁迫响应机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 19-25. |
| WANG K Y, CHEN F Q, HUANG W X. Research advance on drought stress response mechanism in plants [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(2):19-25. | |
| 24 | 张然,李佳缙,王铭,等. 11份草地早熟禾种质材料对PEG-6000胁迫的生理响应和耐旱性评价[J].草原与草坪,2021,41(2):113-121. |
| ZHANG R, LI J J, WANG M, et al.. Physiological kentucky responses to drought stress in 11 different bluegrass germplasm and the evaluation of their drought tolerance [J]. Grassland Turf, 2021, 41(2):113-121. | |
| 25 | 张翠梅,师尚礼,吴芳.干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系生长及生理特性影响[J].中国农业科学,2018,51(5):868-882. |
| ZHANG C M, SHI S L, WU F. Effects of drought stress on root and physiological responses of different drought-tolerant Alfalfa varieties [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2018, 51(5):868-882. | |
| 26 | 赵春程,李晓宁,张寅坤,等.4个多年生黑麦草品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J].草业科学,2020,37(4):669-677. |
| ZHAO C C, LI X N, ZHANG Y K, et al.. Physiological correspondence of four varieties of perennial ryegrass to drought stress [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2020, 37(4):669-677. | |
| 27 | 李州,彭燕,苏星源.不同叶型白三叶抗氧化保护及渗透调节生理对干旱胁迫的响应[J].草业学报,2013,22(2):257-263. |
| LI Z, PENG Y, SU X Y. Physiological responses of white clover by different leaf types associated with anti-oxidative enzyme protection and osmotic adjustment under drought stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2013, 22(2):257-263. | |
| 28 | 赵福庚,孙诚,刘友良.盐胁迫激活大麦幼苗脯氨酸合成的鸟氨酸途径[J].植物学报,2001,43(1):36-40. |
| ZHAO F G, SUN C, LIU Y L. Ornithine pathway in proline biosynthesis activated by salt stress in barley seedlings [J]. J. Acta Bot. Sin., 2001, 43(1):36-40. | |
| 29 | 郭郁频,米福贵,闫利军,等.不同早熟禾品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价[J].草业学报,2014,23(4):220-228. |
| GU Y P, MI F G, YAN L J, et al.. Physiological response to drought stresses and drought resistances evaluation of different Kentucky bluegrass varieties [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2014, 23(4):220-228. | |
| 30 | 李江艳,张鲜花,袁小强.鸭茅种质资源苗期抗旱指标筛选及抗旱评价[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,11(1):215-226. |
| LI J Y, ZHANG X H, YUAN X Q. Drought resistance index screening and drought resistance evaluation of Dactylis glomerata germplasm resources during seedling [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 11(1):215-226. | |
| 31 | 田小霞,许明爽,郑明利,等.黄花草木樨苗期抗旱性鉴定及抗旱指标筛选[J].干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(10):120-127. |
| TIAN X X, XU M S, ZHENG M L, et al.. Drought resistance identification and drought resistance index screening of melilotus officinalis seedling [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, 35(10):120-127. |
| [1] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [2] | 陆青, 梁婷, 王伟伟, 汪德州, 吴娴, 王小燕, 唐益苗. 小麦热激蛋白基因TaHSP90-1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [3] | 王莉莉, 殷丛培, 李峰, 杨志敏, 刘芳明, 林柏松, 刘晓静, 刘海军, 孙靖, 单东东, 崔江慧, 张振清. 马铃薯根际土壤细菌群落结构及其对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 58-69. |
| [4] | 王方玲, 张明月, 周亚茹, 管庆林, 李欣燕, 钟秋, 赵铭钦. 干旱胁迫下TS-PAA保水剂对雪茄烟生长发育和光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [5] | 李江艳, 张鲜花, 袁小强. 鸭茅种质资源苗期抗旱指标筛选及抗旱评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 84-94. |
| [6] | 孙晓春, 黄文静, 李铂. 水杨酸对干旱胁迫下桔梗幼苗生理生化指标及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 63-70. |
| [7] | 刘源, 张秀妍, 徐妙云, 郑红艳, 邹俊杰, 张兰, 王磊. 水稻干旱胁迫的small RNA转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 23-32. |
| [8] | 胡杨, 李钢铁, 李星, 贾守义. 干旱胁迫对细穗柽柳幼苗生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 43-50. |
| [9] | 孙艳, 蒲文宣, 吴长征, 黄平俊, 孙铭雪, 宋德安, 刘来华. 植物响应亚适低温的生长发育及分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 18-26. |
| [10] | 张豪洋,金伊楠,孙燕鑫,李子玮,郭笑恒,许自成*. 植物microRNAs在干旱胁迫响应中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 27-36. |
| [11] | 王得运1,2,刘培培1,陈云婷1,徐月莹1,周丽1,罗光明1*. 干旱胁迫对栀子内源激素含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 58-63. |
| [12] | 张茂,徐彦红,席溢*,裴应杰,黄本用,杨克超,李金孟. 铅、锌、镉胁迫对多年生黑麦草生长及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 41-50. |
| [13] | 苏雨萌§,张旭婷§,特日格乐,田敏,尚晓蕊,李国婧,王瑞刚*. 高通量测序鉴定中间锦鸡儿干旱条件下的microRNA[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 51-57. |
| [14] | 张璐翔1,陈思蒙1,郑聪2,金伊楠1,韩艺3,许自成1,黄五星1,邵惠芳1*. 脱驯化时长对烟草幼苗抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 57-64. |
| [15] | 杨瑞萍1,刘瑞香1,马迎梅1*,郭占斌2,张宏武2,白宇1,赵新宇1. 不同藜麦资源的抗旱性评价及渗透调节剂对其抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号