




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 155-163.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0681
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
阿什日轨( ), 张荣萍(
), 张荣萍( ), 周宁宁, 冯婷煜, 周林, 马鹏, 阿尔力色, 廖雪环, 张坷塬
), 周宁宁, 冯婷煜, 周林, 马鹏, 阿尔力色, 廖雪环, 张坷塬
收稿日期:2022-08-17
接受日期:2022-09-24
出版日期:2024-03-15
发布日期:2024-03-07
通讯作者:
张荣萍
作者简介:阿什日轨 E-mail:1397706720@qq.com;
基金资助:
Rigui ASHEN( ), Rongping ZHANG(
), Rongping ZHANG( ), Ningning ZHOU, Tingyu FENG, Lin ZHOU, Peng MA, Lise AER, Xuehuan LIAO, Keyuan ZHANG
), Ningning ZHOU, Tingyu FENG, Lin ZHOU, Peng MA, Lise AER, Xuehuan LIAO, Keyuan ZHANG
Received:2022-08-17
Accepted:2022-09-24
Online:2024-03-15
Published:2024-03-07
Contact:
Rongping ZHANG
摘要:
为研究硅钙钾镁肥及栽培密度对杂交稻分蘖特性、物质积累和产量形成等的影响,以‘晶两优534’为供试品种,试验采用裂区设计,主区设置不施硅钙钾镁肥和增施硅钙钾镁肥(G)2个肥料处理,副区设置19.3万(M1)、16.0万(M2)、13.0万(M3)和10.04万株·hm-2(M4)共4个移栽密度。通过连续2年田间定位试验,调查水稻产量及其构成因素、干物质积累、分蘖动态及成穗结构,分析增施硅钙钾镁肥和密度处理对水稻生长和产量的影响。结果表明,硅钙钾镁肥和移栽密度共同影响水稻产量。在相同施氮量和硅钙钾镁肥下,移栽密度的增加可显著提高水稻有效穗数、群体干物质生产量和分蘖数,增加水稻产量,M2处理下有效穗数较M1、M3和M4处理2年平均提高5.83%、13.69%和12.50%;相同密度下增施硅钙钾镁肥能显著提高有效穗数,增加水稻干物质积累,提高水稻生育后期叶面积指数,增施硅钙钾镁肥较不施硅钙钾镁肥2年平均增产8.30%~12.56%。综合硅钙钾镁肥和移栽密度的互作效应,本试验条件下,在施纯氮量150 kg·hm-2时增施硅钙钾镁肥300 kg·hm-2、移栽密度16.0×104株·hm-2时,‘晶两优534’干物质生产量最大,产量最高。研究结果可为四川水稻高产高效栽培提供参考。
中图分类号:
阿什日轨, 张荣萍, 周宁宁, 冯婷煜, 周林, 马鹏, 阿尔力色, 廖雪环, 张坷塬. 硅钙钾镁肥和密度对水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 155-163.
Rigui ASHEN, Rongping ZHANG, Ningning ZHOU, Tingyu FENG, Lin ZHOU, Peng MA, Lise AER, Xuehuan LIAO, Keyuan ZHANG. Effects of Silicon, Calcium, Potassium and Magnesium Fertilizer and Density on Rice Yield Formation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 155-163.
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective spikes/(104·hm-²) | 每穗总粒数 Total grains per panicle | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | M1 | 220.47 d | 186.14 ab | 87.28 ab | 24.13 d | 8.69 cd |
| M2 | 228.93 c | 187.66 a | 85.79 bc | 24.19 d | 8.88 c | |
| M3 | 211.07 e | 180.74 bcd | 83.54 cd | 24.72 ab | 7.81 e | |
| M4 | 200.20 f | 183.44 abc | 85.15 bcd | 24.35 cd | 7.61 e | |
| GM1 | 266.09 a | 175.15 de | 82.07 d | 24.92 a | 9.53 b | |
| GM2 | 263.91 a | 177.82 cde | 89.52 a | 24.64 abc | 10.35 a | |
| GM3 | 247.10 b | 171.36 e | 87.50 ab | 24.58 bc | 9.11 bc | |
| GM4 | 222.22 d | 178.93 cd | 86.53 abc | 24.43 bcd | 8.40 d | |
| G | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | |
| G×M | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | |
| 2021 | M1 | 228.08 d | 216.66 a | 93.57 a | 22.14 b | 10.35 c |
| M2 | 245.89 b | 212.29 a | 94.23 a | 22.35 ab | 11.00 b | |
| M3 | 206.78 f | 212.55 a | 94.92 a | 22.54 ab | 9.40 d | |
| M4 | 222.22 de | 209.23 a | 93.13 a | 22.57 ab | 9.78 d | |
| GM1 | 243.28 bc | 215.46 a | 93.29 a | 22.63 a | 11.07 b | |
| GM2 | 256.49 a | 218.56 a | 94.98 a | 22.40 ab | 11.93 a | |
| GM3 | 216.22 e | 217.33 a | 94.72 a | 22.63 a | 10.12 c | |
| GM4 | 236.24 c | 215.23 a | 93.84 a | 22.48 ab | 10.73 bc | |
| G | ** | ns | ns | * | ** | |
| M | ** | ns | * | ns | ** | |
| Y | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| G×M | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Y×M | * | ** | ** | * | ** |
表1 硅钙钾镁肥和密度处理下水稻产量及产量构成
Table 1 Yield and yield components of rice under application of silicon, calcium, potassium, and magnesium fertilizer and density treatment
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective spikes/(104·hm-²) | 每穗总粒数 Total grains per panicle | 结实率 Grain filling/% | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | M1 | 220.47 d | 186.14 ab | 87.28 ab | 24.13 d | 8.69 cd |
| M2 | 228.93 c | 187.66 a | 85.79 bc | 24.19 d | 8.88 c | |
| M3 | 211.07 e | 180.74 bcd | 83.54 cd | 24.72 ab | 7.81 e | |
| M4 | 200.20 f | 183.44 abc | 85.15 bcd | 24.35 cd | 7.61 e | |
| GM1 | 266.09 a | 175.15 de | 82.07 d | 24.92 a | 9.53 b | |
| GM2 | 263.91 a | 177.82 cde | 89.52 a | 24.64 abc | 10.35 a | |
| GM3 | 247.10 b | 171.36 e | 87.50 ab | 24.58 bc | 9.11 bc | |
| GM4 | 222.22 d | 178.93 cd | 86.53 abc | 24.43 bcd | 8.40 d | |
| G | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | |
| G×M | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | |
| 2021 | M1 | 228.08 d | 216.66 a | 93.57 a | 22.14 b | 10.35 c |
| M2 | 245.89 b | 212.29 a | 94.23 a | 22.35 ab | 11.00 b | |
| M3 | 206.78 f | 212.55 a | 94.92 a | 22.54 ab | 9.40 d | |
| M4 | 222.22 de | 209.23 a | 93.13 a | 22.57 ab | 9.78 d | |
| GM1 | 243.28 bc | 215.46 a | 93.29 a | 22.63 a | 11.07 b | |
| GM2 | 256.49 a | 218.56 a | 94.98 a | 22.40 ab | 11.93 a | |
| GM3 | 216.22 e | 217.33 a | 94.72 a | 22.63 a | 10.12 c | |
| GM4 | 236.24 c | 215.23 a | 93.84 a | 22.48 ab | 10.73 bc | |
| G | ** | ns | ns | * | ** | |
| M | ** | ns | * | ns | ** | |
| Y | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| G×M | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Y×M | * | ** | ** | * | ** |
| 年份Year | 处理 Treatment | 拔节期 Jointing period | 齐穗期 Full head stage | 成熟期 Mature stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | ||
| 2020 | M1 | 3 103.74 e | 2 170.52 c | 7 648.15 b | 2 797.10 de | 1 825.24 b | 4 840.92 e | 2 174.54 cd | 8 848.93 ab |
| M2 | 3 601.05 c | 2 412.25 bc | 7 330.62 cd | 2 929.05 cd | 1 638.39 c | 4 998.37 d | 2 156.97 d | 8 930.79 ab | |
| M3 | 4 489.33 a | 2 280.63 c | 7 214.58 d | 2 829.67 de | 1 544.40 d | 4 387.65 g | 1 887.89 f | 7 368.41 e | |
| M4 | 2 875.68 f | 2 057.44 d | 7 423.85 bcd | 2 748.36 e | 1 877.46 b | 5 488.95 a | 1 978.23 e | 8 494.18 c | |
| GM1 | 3 753.12 c | 2 553.19 ab | 8 761.93 a | 3 471.83 a | 2 019.10 a | 5 074.91 c | 2 296.81 b | 9 011.33 a | |
| GM2 | 3 974.37 b | 2 787.18 a | 7 556.22 bc | 3 193.05 b | 1 860.79 b | 5 195.35 b | 2 544.16 a | 8 657.36 bc | |
| GM3 | 3 377.40 d | 2 662.40 ab | 7 310.34 d | 3 045.47 bc | 2 055.30 a | 4 652.99 f | 2 171.15 cd | 7 983.60 d | |
| GM4 | 3 009.00 ef | 2 180.76 c | 6 429.96 e | 2 542.39 f | 1 718.14 c | 4 157.32 h | 2 190.32 c | 8 641.38 bc | |
| G | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| G×M | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 2021 | M1 | 4 365.56 c | 2 304.27 c | 7 044.16 d | 2 415.30 e | 1 872.23 d | 3 687.35 e | 1 614.64 d | 9 685.32 c |
| M2 | 4 898.98 b | 2 394.05 bc | 8 552.69 a | 3 005.49 b | 2 202.68 b | 5 416.07 b | 1 698.38 c | 10 619.97 bc | |
| M3 | 4 075.71 d | 2 276.08 cd | 6 263.43 e | 2 210.24 d | 1 647.17 e | 4 951.06 c | 1 432.78 e | 7 752.08 d | |
| M4 | 4 405.40 c | 2 044.04 e | 7 524.19 c | 2 675.67 d | 2 061.40 c | 5 546.21 b | 1 661.63 c | 10 161.50 bc | |
| GM1 | 4 012.18 d | 2 173.58 d | 8 054.18 b | 3 132.85 b | 1 982.62 c | 5 197.94 c | 2 304.28 a | 11 105.82 b | |
| GM2 | 5 649.02 a | 2 909.00 a | 8 103.31 b | 3 795.51 a | 2 688.84 a | 6 404.39 a | 2 284.24 a | 13 260.30 a | |
| GM3 | 5 055.44 b | 2 499.13 b | 6 875.44 d | 2 486.57 e | 1 623.79 e | 4 587.23 d | 1 774.52 c | 8 120.24 d | |
| GM4 | 4 047.71 d | 2 324.32 c | 6 874.21 d | 2 837.84 c | 1 591.92 e | 4 914.92 c | 1 960.96 b | 10 572.91 bc | |
| G | ns | * | * | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | |
| G×M | * | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | |
表2 硅钙钾镁肥和密度处理下水稻主要生育时期干物质积累 (kg·hm-2)
Table 2 Dry matter accumulation in the main growth period of rice under application of silicon, calcium, potassium, and magnesium fertilizer and density treatment
| 年份Year | 处理 Treatment | 拔节期 Jointing period | 齐穗期 Full head stage | 成熟期 Mature stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | 茎鞘Stem | 叶Leaf | 穗Panicle | ||
| 2020 | M1 | 3 103.74 e | 2 170.52 c | 7 648.15 b | 2 797.10 de | 1 825.24 b | 4 840.92 e | 2 174.54 cd | 8 848.93 ab |
| M2 | 3 601.05 c | 2 412.25 bc | 7 330.62 cd | 2 929.05 cd | 1 638.39 c | 4 998.37 d | 2 156.97 d | 8 930.79 ab | |
| M3 | 4 489.33 a | 2 280.63 c | 7 214.58 d | 2 829.67 de | 1 544.40 d | 4 387.65 g | 1 887.89 f | 7 368.41 e | |
| M4 | 2 875.68 f | 2 057.44 d | 7 423.85 bcd | 2 748.36 e | 1 877.46 b | 5 488.95 a | 1 978.23 e | 8 494.18 c | |
| GM1 | 3 753.12 c | 2 553.19 ab | 8 761.93 a | 3 471.83 a | 2 019.10 a | 5 074.91 c | 2 296.81 b | 9 011.33 a | |
| GM2 | 3 974.37 b | 2 787.18 a | 7 556.22 bc | 3 193.05 b | 1 860.79 b | 5 195.35 b | 2 544.16 a | 8 657.36 bc | |
| GM3 | 3 377.40 d | 2 662.40 ab | 7 310.34 d | 3 045.47 bc | 2 055.30 a | 4 652.99 f | 2 171.15 cd | 7 983.60 d | |
| GM4 | 3 009.00 ef | 2 180.76 c | 6 429.96 e | 2 542.39 f | 1 718.14 c | 4 157.32 h | 2 190.32 c | 8 641.38 bc | |
| G | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| G×M | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 2021 | M1 | 4 365.56 c | 2 304.27 c | 7 044.16 d | 2 415.30 e | 1 872.23 d | 3 687.35 e | 1 614.64 d | 9 685.32 c |
| M2 | 4 898.98 b | 2 394.05 bc | 8 552.69 a | 3 005.49 b | 2 202.68 b | 5 416.07 b | 1 698.38 c | 10 619.97 bc | |
| M3 | 4 075.71 d | 2 276.08 cd | 6 263.43 e | 2 210.24 d | 1 647.17 e | 4 951.06 c | 1 432.78 e | 7 752.08 d | |
| M4 | 4 405.40 c | 2 044.04 e | 7 524.19 c | 2 675.67 d | 2 061.40 c | 5 546.21 b | 1 661.63 c | 10 161.50 bc | |
| GM1 | 4 012.18 d | 2 173.58 d | 8 054.18 b | 3 132.85 b | 1 982.62 c | 5 197.94 c | 2 304.28 a | 11 105.82 b | |
| GM2 | 5 649.02 a | 2 909.00 a | 8 103.31 b | 3 795.51 a | 2 688.84 a | 6 404.39 a | 2 284.24 a | 13 260.30 a | |
| GM3 | 5 055.44 b | 2 499.13 b | 6 875.44 d | 2 486.57 e | 1 623.79 e | 4 587.23 d | 1 774.52 c | 8 120.24 d | |
| GM4 | 4 047.71 d | 2 324.32 c | 6 874.21 d | 2 837.84 c | 1 591.92 e | 4 914.92 c | 1 960.96 b | 10 572.91 bc | |
| G | ns | * | * | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | |
| M | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | |
| G×M | * | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | |

图2 硅钙钾镁肥和密度处理下水稻单株分蘖动态和群体分蘖动态
Fig. 2 Tillering dynamics per plant and population tillering dynamics of rice under application of silicon,calcium,potassium and magnesium fertilizer and density treatment
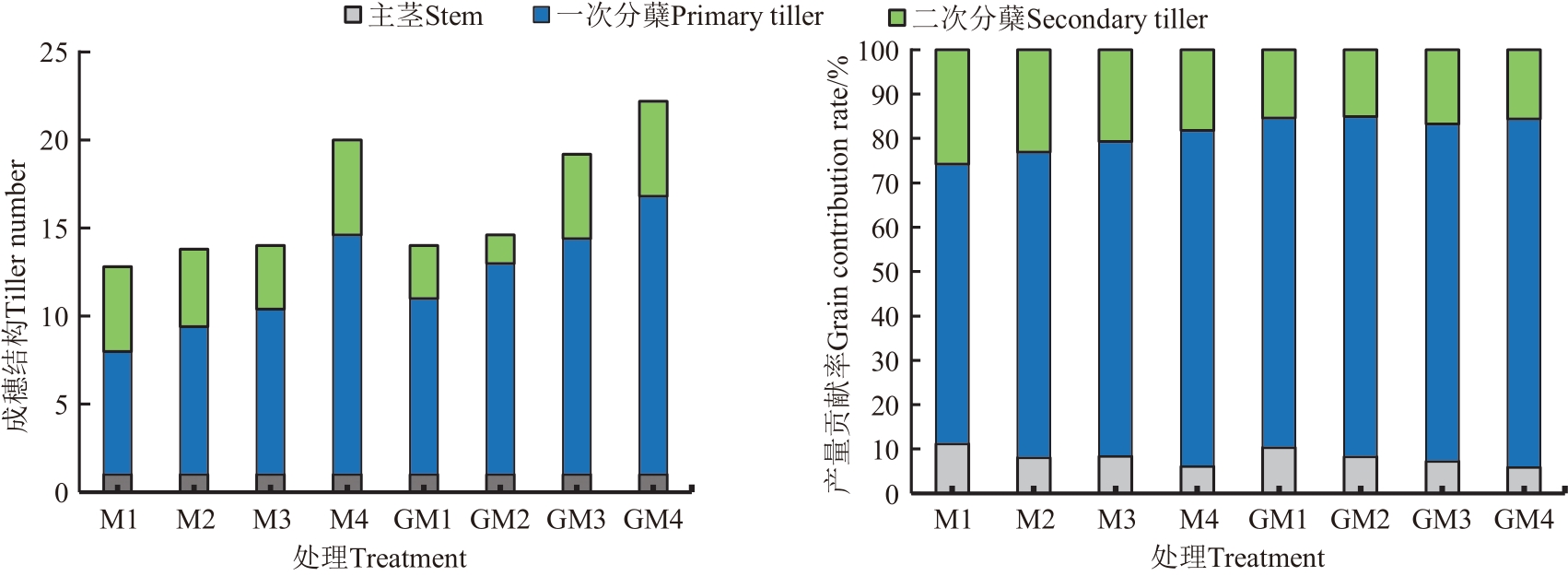
图3 硅钙钾镁肥和密度处理下‘晶两优534’的成穗结构及其对籽粒产量的贡献率
Fig. 3 Ear structure and the contribution rate to grain yield of ‘Jingliangyou 534’ under application of silicon, calcium, potassium and magnesium fertilizer and density treatment
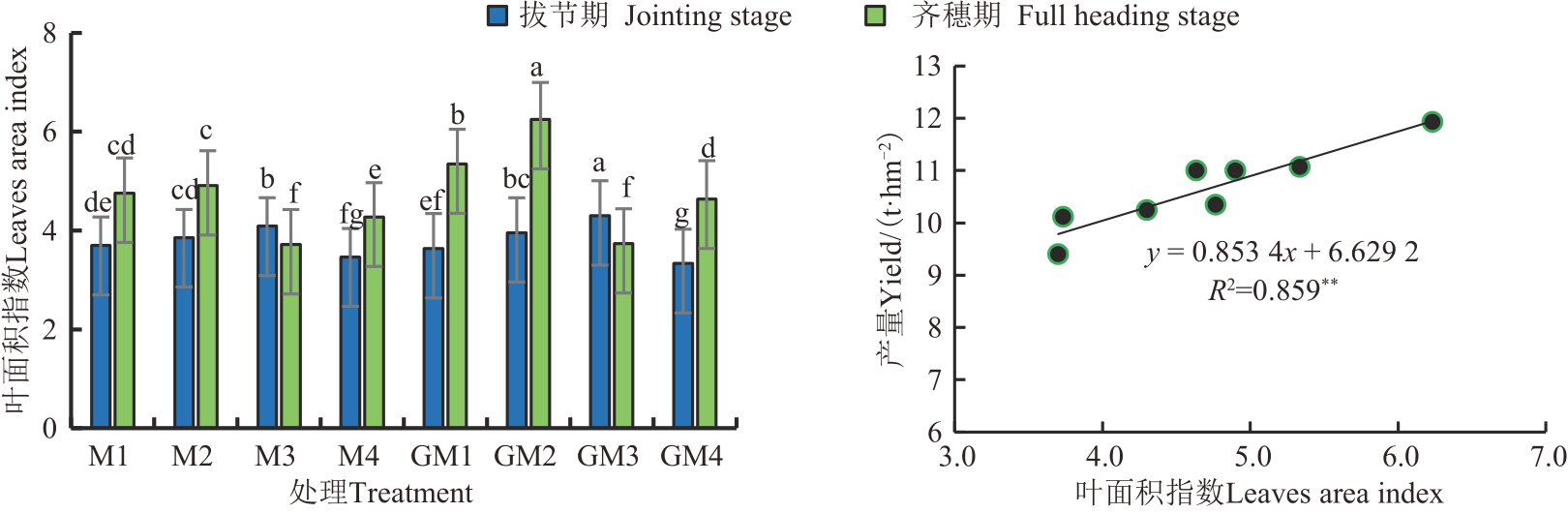
图4 拔节期及齐穗期叶面积指数和齐穗期叶面积指数与产量的关系注:同一时期不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。**表示P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 4 Relationship between leaf area index at jointing stage and full heading stage and leaf area index at full heading stage and yieldNote: Different lowercase letters in the same period indicate significant differentces between different treatments at P<0.05 level. ** indicates significance at P<0.01 level.
| 1 | ZHANG H, YU C, KONG X, et al.. Progressive integrative crop managements increase grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and irrigation water productivity in rice [J]. Field Crops Res., 2018, 215:1-11. |
| 2 | LIU Q, CHEN S, ZHOU L, et al.. Characteristics of population quality and rice quality of Semi-Waxy japonica rice varieties with different grain yields [J/OL]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(2): 241[2022-07-16]. . |
| 3 | 马均,徐富贤,郑家国,等.四川盆地杂交水稻资源利用与高产优质高效关键技术研究与应用[C]//中国作物学会.2018中国作物学会学术年会论文摘要集.北京:中国作物学会, 2018:35. |
| 4 | HUANG M, YANG C, JI Q, et al.. Tillering responses of rice to plant density and nitrogen rate in a subtropical environment of southern China [J]. Field Crops Res., 2013, 149: 187-192. |
| 5 | 田广丽,周毅,孙博,等.氮素及栽培密度影响水稻分蘖动态的机制[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(4):896-904. |
| TIAN G L, ZHOU Y, SUN B,et al.. Effects of nitrogen and transplanting density on the mechanisms of tillering dynamic of rice [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sic., 2018, 24(4):896-904. | |
| 6 | ZHOU C C, HUANG Y C, JIA B Y, et al.. Optimization of nitrogen rate and planting density for improving the grain yield of different rice genotypes in northeast China [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(9):555 [2022-07-16]. . |
| 7 | 冀建华,李絮花,刘秀梅,等.硅钙钾镁肥对南方稻田土壤酸度的改良作用[J].土壤学报,2019,56(4):895-906. |
| JI J H, LI X H, LIU X M, et al.. Improvement effect of fertilizer of silicon calcium potassium magnesium on soil acidity in southern paddy fields [J]. Acta pedol. Sin., 2019, 56(4): 895-906. | |
| 8 | 韩科峰,陈余平,胡铁军,等.硅钙钾镁肥对浙江省酸性水稻土壤的改良效果[J].浙江农业学报,2018,30(1):117-122. |
| HAN K F, CHEN Y P, HU T J, et al.. Improvement effect of fertilizer of silicon calcium potassium magnesium on acid rice soil in Zhejiang province [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(1): 117-122. | |
| 9 | 解秋,曾详忠,李小燕,等.不同硅钙钾镁肥用量对四川平原地区水稻生长及养分吸收利用的影响[J].广西农学报,2020,35(6):5-10. |
| XIE Q, ZENG X Z, LI X Y, et al.. Effects of different amounts of fertilizer of silicon,calcium,potassium and magnesium on rice growth and nutrient utilization in sichuan plain area [J]. J. Guangxi Agric., 2020, 35(6): 5-10. | |
| 10 | 林洪鑫,潘晓华,石庆华,等.施氮量与栽插密度对超级早稻中早22产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2011,17(1):22-28. |
| LIN H X, PAN X H, SHI Q H, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate and planting density on yield of super early rice Zhongzao 22 [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sic., 2011,17(1):22-28. | |
| 11 | 柯健,陈婷婷,吴周,等.沿江双季稻北缘区晚稻适宜品种类型及高产群体特征[J].作物学报,2022,48(4):1005-1016. |
| KE J, CHEN T T, WU Z, et al.. Suitable varieties and high-yielding population characteristics of late season rice in the northern margin area of double-cropping rice along the Yangtze River [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2022,48(4):1005-1016. | |
| 12 | 王海月,殷尧翥,孙永健,等.不同株距和缓释氮肥配施量下机插杂交稻的产量及光合特性[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(4):843-855. |
| WANG H Y, YIN Y Z, SUN Y J, et al.. Yield and photosynthetic characteristics of machine-transplanted hybrid rice under different plant spacing and application rate of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sic., 2017,23(4):843-855. | |
| 13 | PENG B, FENG G N, ZHEN Q, et al.. Effects of ozone and density interaction on the growth, development and yield formation of rice [J]. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res., 2018, 16(4): 4199-4215. |
| 14 | 梁传斌,李建国,沈枫,等.移栽密度和施用生物炭对水稻产量的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2021(2):240-247. |
| LIANG C B, LI J G, SHEN F, et al.. Effects of transplanting density and application of biochar on rice yield [J]. China Soil Fert., 2021(2):240-247. | |
| 15 | 龙旭,马均,许凤英,等.水稻强化栽培的适宜秧龄和栽植密度研究[J].四川农业大学学报,2005,23(3):368-373. |
| LONG X, MA J, XU F Y, et al.. Research on suitable seedling age and planting density for rice intensive cultivation [J]. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ., 2005,23(3):368-373. | |
| 16 | 徐新朋,周卫,梁国庆,等.氮肥用量和密度对双季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(3):763-772. |
| XU X P, ZHOU W, LIANG G Q, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer dosage and density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-cropping rice [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2015, 21(3):763-772. | |
| 17 | 樊红柱,曾祥忠,吕世华.水稻不同移栽密度的氮肥效应及氮素去向[J].核农学报,2009,23(4):681-685. |
| FAN H Z, ZENG X Z, LYU S H. Nitrogen fertilizer effect and nitrogen fate of different transplanting densities of rice [J]. Acta. Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2009,23(4):681-685. | |
| 18 | 秦俭,蒋开锋,张涛,等.施氮量和移栽密度对重穗型杂交稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].中国稻米,2017,23(4):94-98. |
| QIN J, JIANG K F, ZHANG T, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate and transplanting density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of heavy-spike hybrid rice [J].China Rice, 2017,23(4):94-98. | |
| 19 | 陈海飞,冯洋,蔡红梅,等.氮肥与移栽密度互作对低产田水稻群体结构及产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2014,20(6):1319-1328. |
| CHEN H F, FENG Y, CAI H M, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and transplanting density interaction on rice population structure and yield in low-yield fields [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2014,20(6):1319-1328. | |
| 20 | 刘红江,郭智,张岳芳,等.移栽密度及氮肥投入量对水稻氮素利用效率的协同效应[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(12):3952-3960. |
| LIU H J, GUO Z, ZHANG Y F, et al.. Synergistic effect of transplanting density and nitrogen fertilizer input on nitrogen use efficiency of rice [J]. J. Ecol., 2021, 40(12): 3952-3960. | |
| 21 | MASSCHENLEYN P H, DCLAUNE R D, PATRICK W H J R. Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol.,1991, 25(8):1414-1419. |
| 22 | 宁东峰,刘战东,肖俊夫,等.水稻土施用钢渣硅钙肥对土壤硅素形态和水稻生长的影响[J].灌溉排水学报,2016,35(8):42-46. |
| NING D F, LIU Z D, XIAO J F, et al.. Effects of application of steel slag silicon and calcium fertilizer on paddy soil on soil silicon form and rice growth [J]. J. Irrig. Drain., 2016,35(8):42-46. | |
| 23 | LIU X, ZHANG A, JI C, et al.. Biochar's effect on crop productivity and the dependence on experimental conditions—a meta-analysis of literature data [J]. Plant Soil, 2013, 373(1): 583-594. |
| 24 | 叶建海,陈余平,孙文岳,等. 硅钙镁磷钾肥3年定位试验对早稻产量及性状的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2017,58(5):752-753, 757. |
| YE J H, CHEN Y P, SUN W Y, et al.. Effects of 3-year positioning experiment of silicon calcium magnesium phosphorus potassium fertilizer on yield and characters of early rice [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2017, 58(5): 752-753, 757. | |
| 25 | 凌启鸿,张洪程,蔡建中,等.水稻高产群体质量及其优化控制探讨[J].中国农业科学, 1993, 26(6): 1-11. |
| LING Q H, ZHANG H C, CAI J Z, et al.. Inrestigation on the population quality high yield and its optimizing control programme in rice [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 1993, 26(6): 1-11. |
| [1] | 李忠义, 唐红琴, 董文斌, 韦彩会, 何铁光. 稻秸-紫云英联合还田对水稻光合特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 171-180. |
| [2] | 王辉, 付虹雨, 岳云开, 崔国贤, 佘玮. 基于气候变量的苎麻产量SSA-BP预测模型[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 110-118. |
| [3] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [4] | 段媛媛, 刘晓洪, 唐涛, 王帆帆, 游景茂, 郭晓亮, 郭杰. 种植密度对湖北贝母生长及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [5] | 周影, 李京咏, 戴林秀, 敖弟彩, 李梓逸, 杨帆, 顾军伟, 徐强, 窦志, 高辉. 稻虾共作模式下喷施褪黑素对水稻产量形成和抗倒伏特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 34-42. |
| [6] | 王为, 赵强, 穆妮热·阿卜杜艾尼, 阿里木·阿木力null, 李欣欣, 田阳青. 烯效唑复配不同外源物质对棉花化学封顶及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [7] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [8] | 郑志刚, 向丽, 刘功义, 徐彩, 覃斌, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 唐启源. 施氮量和密度对有序机抛早稻生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [9] | 孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [10] | 周文, 郭笑恒, 徐锐, 王晓丽, 牛慧伟, 韩丹, 邵惠芳. 烤烟间作半夏对烤烟生长及产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 161-169. |
| [11] | 陈登龙, 张雨翔, 宋佳佳, 陈鹏宇, 温祥珍, 李亚灵. 火山石沉积对鱼菜共生系统运行的探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 207-214. |
| [12] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [13] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [14] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [15] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号