




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 171-180.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0627
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-07-26
接受日期:2022-09-21
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-04
通讯作者:
唐红琴
作者简介:李忠义E-mail:lizhongyi2007@163.com;
基金资助:
Zhongyi LI( ), Hongqin TANG(
), Hongqin TANG( ), Wenbin DONG, Caihui WEI, Tieguang HE
), Wenbin DONG, Caihui WEI, Tieguang HE
Received:2022-07-26
Accepted:2022-09-21
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
Hongqin TANG
摘要:
为评价稻秸-紫云英联合还田对水稻光合特性、产量及稻米品质的影响,采用田间随机试验,以不施氮肥为对照(CK),设置常规氮肥(N)、稻秸还田+常规氮肥(RN)、紫云英还田+常规氮肥(MN)、稻秸还田+紫云英还田+常规氮肥(MRN)、稻秸还田+紫云英还田+60%氮肥(MRN60%),共计6个处理。对不同处理下的叶绿素含量(SPAD值)、净光合速率(net photosynthetic rate,Pn)、气孔导度(stomatal conductance,Gs)、胞间CO2浓度(intercellular CO2 concentration,Ci)、蒸腾速率(transpiration rate,Tr)和干物质积累量、产量及稻米品质进行比较。结果表明,与CK相比,N、RN、MN、MRN和MRN60%处理均可显著提高水稻剑叶的SPAD值、Pn、Gs、稻谷产量及稻米糙米率、整精米率和蛋白含量,并显著降低直链淀粉含量。与N处理相比,在光合特性方面,MRN处理剑叶的SPAD值、净光合速率、气孔导度分别显著提高2.36%、5.95%、7.80%;在干物质积累量方面,MRN处理分蘖期、孕穗期、乳熟期的干物质积累量分别显著提高14.77%、3.52%、4.95%;在产量及构成因素方面,MRN处理的有效穗数、穗粒数、稻谷产量分别显著提高7.38%、3.08%、15.96%;在稻米品质方面,MRN处理的整精米率显著提高4.63%,直链淀粉含量显著降低6.54%。与N处理相比,MN处理仅净光合速率显著提高4.75%;MRN60%处理仅直链淀粉含量显著降低7.00%。相关分析结果表明,剑叶SPAD值、Pn和Gs均与有效穗数、穗粒数、产量、糙米率、整精米率呈极显著正相关,与直链淀粉含量呈极显著负相关;SPAD值和Pn与蛋白含量呈极显著正相关;Gs与蛋白含量呈显著正相关。综上,在常规施氮下,稻秸-紫云英联合还田可显著提高水稻剑叶的SPAD值、Pn、Gs等光合指标及水稻产量和蒸煮品质;在60%氮肥施用下,稻秸-紫云英联合还田有利于稳定水稻剑叶光合特性,保持水稻增产和品质特征,可应用于优质水稻生产。
中图分类号:
李忠义, 唐红琴, 董文斌, 韦彩会, 何铁光. 稻秸-紫云英联合还田对水稻光合特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 171-180.
Zhongyi LI, Hongqin TANG, Wenbin DONG, Caihui WEI, Tieguang HE. Effects of Co-incorporation of Rice Straw and Chinese Milk Vetch on Photosynthetic Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 171-180.
处理 Treatment | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度Gs/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 40.64±1.33 c | 23.02±0.89 d | 0.83±0.04 d | 328.77±1.61 a | 8.24±0.28 a |
| N | 42.52±0.92 b | 24.42±0.88 c | 0.94±0.02 bc | 327.51±1.55 a | 8.34±0.43 a |
| RN | 42.69±1.08 b | 24.79±0.83 c | 0.94±0.02 bc | 327.57±1.90 a | 8.45±0.32 a |
| MN | 43.14±1.51 ab | 25.58±0.46 ab | 0.98±0.04 ab | 327.22±1.89 a | 8.48±0.26 a |
| MRN | 43.52±1.62 a | 25.87±0.37 a | 1.01±0.05 a | 327.09±1.98 a | 8.53±0.09 a |
| MRN60% | 42.56±0.96 b | 24.87±0.68 bc | 0.92±0.04 c | 327.14±1.77 a | 8.42±0.34 a |
表1 不同施肥处理下水稻叶绿素含量及光合特性
Table 1 Chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics of rice under different fertilization treatments
处理 Treatment | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度Gs/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 40.64±1.33 c | 23.02±0.89 d | 0.83±0.04 d | 328.77±1.61 a | 8.24±0.28 a |
| N | 42.52±0.92 b | 24.42±0.88 c | 0.94±0.02 bc | 327.51±1.55 a | 8.34±0.43 a |
| RN | 42.69±1.08 b | 24.79±0.83 c | 0.94±0.02 bc | 327.57±1.90 a | 8.45±0.32 a |
| MN | 43.14±1.51 ab | 25.58±0.46 ab | 0.98±0.04 ab | 327.22±1.89 a | 8.48±0.26 a |
| MRN | 43.52±1.62 a | 25.87±0.37 a | 1.01±0.05 a | 327.09±1.98 a | 8.53±0.09 a |
| MRN60% | 42.56±0.96 b | 24.87±0.68 bc | 0.92±0.04 c | 327.14±1.77 a | 8.42±0.34 a |
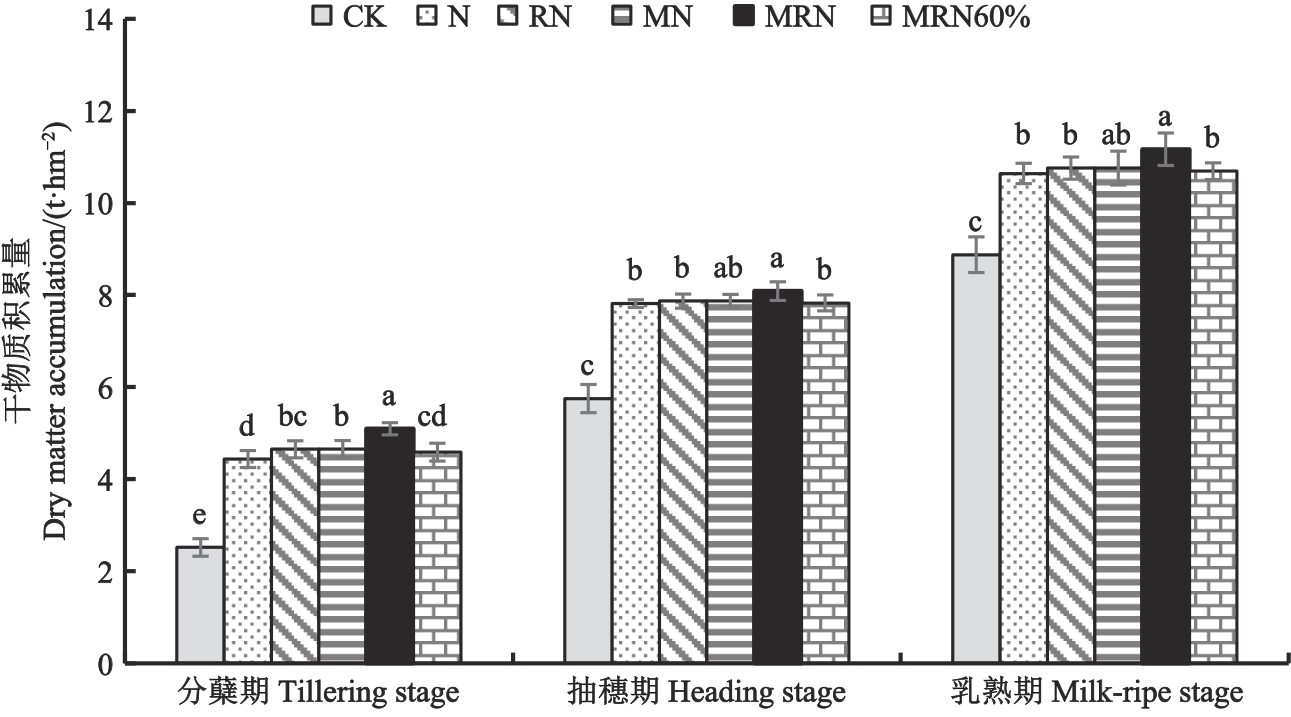
图1 不同施肥处理下水稻干物质积累量注:不同小写字母表示同一时期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Dry matter accumulation of rice under different fertilization treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same stage at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective spikes/(104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1 000-grain weigh/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 213.75±15.09 c | 153.67±6.55 d | 25.12±0.39 a | 81.64±4.78 a |
| N | 223.50±12.90 b | 162.20±2.91 bc | 25.23±0.28 a | 81.48±2.56 a |
| RN | 227.25±17.76 b | 163.40±4.00 bc | 25.17±0.29 a | 80.68±3.73 a |
| MN | 231.75±20.25 ab | 165.27±3.86 ab | 25.21±0.43 a | 82.93±2.69 a |
| MRN | 240.00±18.67 a | 167.20±3.43 a | 25.32±0.46 a | 82.60±3.82 a |
| MRN60% | 229.50±14.70 b | 161.80±3.53 c | 25.22±0.23 a | 81.73±2.20 a |
表2 不同施肥处理下水稻产量性状
Table2 Rice yield traits under different fertilization treatments
处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective spikes/(104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1 000-grain weigh/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 213.75±15.09 c | 153.67±6.55 d | 25.12±0.39 a | 81.64±4.78 a |
| N | 223.50±12.90 b | 162.20±2.91 bc | 25.23±0.28 a | 81.48±2.56 a |
| RN | 227.25±17.76 b | 163.40±4.00 bc | 25.17±0.29 a | 80.68±3.73 a |
| MN | 231.75±20.25 ab | 165.27±3.86 ab | 25.21±0.43 a | 82.93±2.69 a |
| MRN | 240.00±18.67 a | 167.20±3.43 a | 25.32±0.46 a | 82.60±3.82 a |
| MRN60% | 229.50±14.70 b | 161.80±3.53 c | 25.22±0.23 a | 81.73±2.20 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 增产率Increase rate/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 较CK Compare with CK | 较N处理 Compare with N treatment | ||
| CK | 4 869.10±470.83 c | — | -22.96 |
| N | 6 319.83±398.90 b | 29.79 | — |
| RN | 6 644.99±255.49 b | 36.47 | 5.15 |
| MN | 6 953.48±350.17 ab | 42.81 | 10.03 |
| MRN | 7 328.66±288.46 a | 50.51 | 15.96 |
| MRN60% | 6 536.60±364.47 b | 34.25 | 3.43 |
表3 不同施肥处理下水稻产量
Table 3 Effects of different fertilization treatments on rice yield
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 增产率Increase rate/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 较CK Compare with CK | 较N处理 Compare with N treatment | ||
| CK | 4 869.10±470.83 c | — | -22.96 |
| N | 6 319.83±398.90 b | 29.79 | — |
| RN | 6 644.99±255.49 b | 36.47 | 5.15 |
| MN | 6 953.48±350.17 ab | 42.81 | 10.03 |
| MRN | 7 328.66±288.46 a | 50.51 | 15.96 |
| MRN60% | 6 536.60±364.47 b | 34.25 | 3.43 |
处理 Treatment | 加工品质 Milling quality | 外观品质 Appearance quality | 蒸煮品质 Cooking quality | 营养品质 Nutritional quality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalk degree/% | 垩白粒率 Chalk grain rate/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylase content/% | 蛋白含量 Protein content/% | |
| CK | 77.85±0.71 b | 57.83±0.59 c | 1.65±0.09 a | 7.10±0.25 a | 16.91±0.41 a | 7.40±0.34 b |
| N | 80.17±0.65 a | 59.30±0.62 b | 1.78±0.10 a | 7.52±0.33 a | 15.71±0.57 b | 8.30±0.33 a |
| RN | 80.32±0.72 a | 59.62±0.78 ab | 1.74±0.13 a | 7.74±0.75 a | 15.44±0.27 bc | 8.34±0.52 a |
| MN | 80.43±0.21 a | 60.17±0.31 ab | 1.76±0.07 a | 7.57±0.43 a | 15.14±0.68 bc | 8.56±0.58 a |
| MRN | 80.73±0.60 a | 60.51±0.73 a | 1.77±0.07 a | 7.55±0.41 a | 14.68±0.57 c | 8.75±0.34 a |
| MRN60% | 79.98±0.69 a | 59.40±0.20 ab | 1.75±0.07 a | 7.67±0.50 a | 14.61±0.27 c | 8.33±0.69 a |
表4 不同施肥处理下稻米品质特征
Table 4 Rrice quality under different fertilization treatments
处理 Treatment | 加工品质 Milling quality | 外观品质 Appearance quality | 蒸煮品质 Cooking quality | 营养品质 Nutritional quality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalk degree/% | 垩白粒率 Chalk grain rate/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylase content/% | 蛋白含量 Protein content/% | |
| CK | 77.85±0.71 b | 57.83±0.59 c | 1.65±0.09 a | 7.10±0.25 a | 16.91±0.41 a | 7.40±0.34 b |
| N | 80.17±0.65 a | 59.30±0.62 b | 1.78±0.10 a | 7.52±0.33 a | 15.71±0.57 b | 8.30±0.33 a |
| RN | 80.32±0.72 a | 59.62±0.78 ab | 1.74±0.13 a | 7.74±0.75 a | 15.44±0.27 bc | 8.34±0.52 a |
| MN | 80.43±0.21 a | 60.17±0.31 ab | 1.76±0.07 a | 7.57±0.43 a | 15.14±0.68 bc | 8.56±0.58 a |
| MRN | 80.73±0.60 a | 60.51±0.73 a | 1.77±0.07 a | 7.55±0.41 a | 14.68±0.57 c | 8.75±0.34 a |
| MRN60% | 79.98±0.69 a | 59.40±0.20 ab | 1.75±0.07 a | 7.67±0.50 a | 14.61±0.27 c | 8.33±0.69 a |
指标 Index | 有效穗数 Effective spikes | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1 000-grain weigh | 结实率 Seed setting rate | 产量 Yield | 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 整精 米率 Head rice rate | 垩白度 Chalk degree | 垩白 粒率 Chalk grain rate | 直链淀粉含量 Amylase content | 蛋白 含量 Protein content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAD值 SPAD value | 0.666** | 0.887** | 0.201 | 0.094 | 0.826** | 0.831** | 0.856** | 0.393 | 0.457 | -0.623** | 0.658** |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.804** | 0.891** | 0.375 | 0.294 | 0.897** | 0.712** | 0.817** | 0.45 | 0.24 | -0.687** | 0.687** |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.767** | 0.881** | 0.174 | 0.188 | 0.875** | 0.886** | 0.819** | 0.398 | 0.316 | -0.669** | 0.571* |
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.382 | -0.381 | -0.348 | -0.39 | -0.447 | -0.595** | -0.46 | 0.064 | -0.293 | 0.628** | -0.422 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.575* | 0.515* | -0.042 | 0.155 | 0.425 | 0.526* | 0.394 | 0.195 | 0.36 | -0.446 | 0.246 |
表5 水稻光合特性与产量和稻米品质的相关性
Table 5 Correlation of photosynthetic characteristics,yield and quality in rice
指标 Index | 有效穗数 Effective spikes | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1 000-grain weigh | 结实率 Seed setting rate | 产量 Yield | 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 整精 米率 Head rice rate | 垩白度 Chalk degree | 垩白 粒率 Chalk grain rate | 直链淀粉含量 Amylase content | 蛋白 含量 Protein content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAD值 SPAD value | 0.666** | 0.887** | 0.201 | 0.094 | 0.826** | 0.831** | 0.856** | 0.393 | 0.457 | -0.623** | 0.658** |
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.804** | 0.891** | 0.375 | 0.294 | 0.897** | 0.712** | 0.817** | 0.45 | 0.24 | -0.687** | 0.687** |
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.767** | 0.881** | 0.174 | 0.188 | 0.875** | 0.886** | 0.819** | 0.398 | 0.316 | -0.669** | 0.571* |
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.382 | -0.381 | -0.348 | -0.39 | -0.447 | -0.595** | -0.46 | 0.064 | -0.293 | 0.628** | -0.422 |
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.575* | 0.515* | -0.042 | 0.155 | 0.425 | 0.526* | 0.394 | 0.195 | 0.36 | -0.446 | 0.246 |
| 1 | 唐先干,谢金水,徐昌旭,等.红壤性稻田紫云英与化肥减施对早稻品质与养分吸收的影响[J].中国水稻科学,2021,35(5):466-474. |
| TANG X G, XIE J S, XU C X, et al.. Effects of Chinese milk vetch and reduced chemical fertilizer application on quality and nutrient uptake of early rice in red soil paddy field [J]. Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2021, 35(5):466-474. | |
| 2 | 方克明,沈慧芳,双巧云,等.水稻化肥使用量增长问题与零增长对策[J].中国农学通报,2016,32(9):200-204. |
| FANG K M, SHEN H F, SHUANG Q Y, et al.. Problem of fertilizer application increase in rice and countermeasures of “zero increase” [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 32(9):200-204. | |
| 3 | 曹卫东,包兴国,徐昌旭,等.中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(6):1444-1455. |
| CAO W D, BAO X G, XU C X, et al.. Reviews and prospect on science and technology of green manure in China [J]. J Plant Nutr. Fert., 2017, 23(6):1444-1455. | |
| 4 | 杨德生,黄冠军,李勇,等.水稻氮高效栽培技术、品种改良和生理机制研究进展[J].华中农业大学学报,2022,41(1):62-75. |
| YANG D S, HUANG G J, LI Y, et al.. Progress on cultivation technologies, variety improvements and physiological mechanisms of rice with high nitrogen utilization efficiency [J]. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ., 2022, 41(1):62-75. | |
| 5 | 彭志芸,丁峰,谌洁,等.麦油稻轮作秸秆还田与施氮对水稻光合特性及产量的影响[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,46(3):253-261. |
| PENG Z Y, DING F, SHEN J, et al.. Effects of straw mulching and nitrogen management on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of direct seeding rice under wheat rape rice rotation [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2020, 46(3):253-261. | |
| 6 | 周丁香,曾莹,许晓萱,等.不同早稻品种净光合速率对产量和群体特性的影响[J/OL].分子植物育种,2021:1-11[2023-06-06]. . |
| ZHOU D X, ZENG Y, XU X X, et al.. Effects of net photosynthetic rate on yield and population characteristics of different early rice varieties [J/OL]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2021:1-11 [2023-06-06]. . | |
| 7 | 吕伟生,曾勇军,石庆华,等.合理氮肥运筹提高双季机插稻产量及氮肥利用率[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(6):259-268. |
| LYU W S, ZENG Y J, SHI Q H, et al.. Proper nitrogen fertilizer application improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency of machine transplanted double rice [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2018, 32(6):259-268. | |
| 8 | 梁琴,周泽弘,马雪清,等.绿肥翻压与氮肥减施对水稻产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(10):124-130. |
| LIANG Q, ZHOU Z H, MA X Q, et al.. Effects of green manure turning over and nitrogen reducing on rice yield, quality and soil fertility [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(10):124-130. | |
| 9 | 吴建富,曾研华,潘晓华,等.稻草还田方式对双季水稻产量和土壤碳库管理指数的影响[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(6):1572-1578. |
| WU J F, ZENG Y H, PAN X H, et al.. Effects of rice straw returning mode on rice grain yield and soil carbon pool management index in double rice-cropping system [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2013, 24(6):1572-1578. | |
| 10 | CHOUDHURY A T, KENNEDY L R. Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2004, 39(4):219-227. |
| 11 | 宋大利,侯胜鹏,王秀斌,等.中国秸秆养分资源数量及替代化肥潜力[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(1):1-21. |
| SONG D L, HOU S P, WANG X B, et al.. Nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its potential of substituting [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2018, 24(1):1-21. | |
| 12 | CHEN Y, TANG X, YANG S M, et al.. Contributions of different N sources to crop N nutrition in a Chinese rice field [J]. Pedosphere, 2010, 20(2):198-208. |
| 13 | THUY N H, SHAN Y, BIYAY S, et al.. Nitrogen supply in rice-based cropping systems as affect by crop residue management [J]. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2008, 72(2):514-523. |
| 14 | TODA M, UCHIDA Y. Long-term use of green manure legume and chemical fertilizer affect soil bacterial community structures but not the rate of soil nitrate decrease when excess carbon and nitrogen are applied [J]. Soil Res., 2017, 55(6):524-533. |
| 15 | ZHU B, YI L, HU Y, et al.. Nitrogen release from incorporated 15N-labelled Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) residue and its dynamics in a double rice cropping system [J]. Plant Soil, 2014, 374(1/2):331-344. |
| 16 | 刘春增,常单娜,李本银,等.种植翻压紫云英配施化肥对稻田土壤活性有机碳氮的影响[J].土壤学报,2017,54(3):656-668. |
| LIU C Z, CHANG D N, LI B Y, et al.. Effects of planting and incorporation of Chinese milk vetch coupled with application of chemical fertilizer on active organic carbon and nitrogen in paddy soil [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2017, 54(3):656-668. | |
| 17 | 唐海明,肖小平,汤文光,等.冬季覆盖作物秸秆还田对水稻植株养分积累与转运的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2018,20(8):63-73. |
| TANG H M, XIAO X P, TANG W G, et al.. Effects of covering paddy field by crop straw in winter on nutrition accumulation and translocation of rice plant [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2018, 20(8):63-73. | |
| 18 | 高嵩涓,曹卫东,白金顺,等.长期冬种绿肥改变红壤稻田土壤微生物生物量特性[J].土壤学报,2015,52(4):902-910. |
| GAO S J, CAO W D, BAI J S, et al.. Long-term application of winter green manures changed the soil microbial biomass properties in red paddy soil [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2015, 52(4):902-910. | |
| 19 | 程会丹,鲁艳红,聂军,等.减量化肥配施紫云英对稻田土壤碳、氮的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2020,39(6):1259-1270. |
| CHENG H D, LU Y H, NIE J, et al.. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with Chinese milk vetch on soil carbon and nitrogen in paddy fields [J]. J. Agron. Environ. Sci., 2020, 39(6):1259-1270. | |
| 20 | FONTAINE S, MARIOTTI A, ABBADIE L. The priming effect of organic matter: a question of microbial competition? [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2003, 35(6):837-843. |
| 21 | 朱强,张静,郭再华,等.稻草和紫云英联合还田下施氮水平对水稻产量及土壤氮素形态的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(12):2177-2183. |
| ZHU Q, ZHANG J, GUO Z H, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen inputs on rice yield and soil nitrogen forms under incorporation of rice straw and Chinese milk vetch [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(12):2177-2183. | |
| 22 | 才硕,时红,潘晓华,等.绿肥与稻草联合还田对机插稻光合特性、养分吸收和产量品质的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2020,42(2):229-240. |
| CAI S, SHI H, PAN X H, et al.. Influence of the combination of returning green manure cultivation and rice straw on photosynthetic characteristics and nutrient absorption and yield quality of machine-transplanted double-season rice [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2020, 42(2):229-240. | |
| 23 | 黄山,汤军,廖萍,等.冬种紫云英与稻草还田对双季水稻产量和土壤性状的互作效应[J].江西农业大学学报,2016,38(2):215-222. |
| HUANG S, TANG J, LIAO P, et al.. Interaction of winter legume manure covering (Astragalus sinicus L.) and straw retention on yield and soil properties in a double rice cropping system [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2016, 38(2):215-222. | |
| 24 | 周国朋,谢志坚,曹卫东,等.稻草高茬-紫云英联合还田改善土壤肥力提高作物产量[J].农业工程学报,2017, 33(23):157-163. |
| ZHOU G P, XIE Z J, CAO W D, et al.. Co-incorporation of high rice stubble and Chinese milk vetch improving soil fertility and yield of rice [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2017, 33(23):157-163. | |
| 25 | ZHOU G P, GAO S J, LU Y H, et al.. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China [J/OL]. Soil Till. Res., 2020, 197:104499 [2023-06-06]. . |
| 26 | 中华人民共和国农业部. 稻米直链淀粉的测定 分光光度法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 27 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会/国家视频药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 28 | 翟虎渠,曹树青,万建民,等.超高产杂交稻灌浆期光合功能与产量的关系[J].中国科学(生命科学),2002,32(3):211-217. |
| 29 | 姚允聪,王绍辉,孔云.弱光条件下桃叶片结构及光合特性与叶绿体超微结构变化[J].中国农业科学,2007,40(4):855-863. |
| YAO Y C, WANG S H, KONG Y. Characteristics of photosynthesis machinism in different peach species under low light intensity [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2007, 40(4):855-863. | |
| 30 | 郭智,刘红江,张岳芳,等.氮磷减施对水稻剑叶光合特性、产量及氮素利用率的影响[J].西南农业学报,2017,30(10):2263-2269. |
| GUO Z, LIU H J, ZHANG Y F, et al.. Effects of reducing nitrogen and phosphorus application on photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaves, grain yield, and nitrogen use efficiency of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar Nanjing 9108 [J]. J. Southwest. Agric. Sci., 2017, 30(10):2263-2269. | |
| 31 | CAI S, PITTELKOW C M, ZHAO X, et al.. Winter legume-rice rotations can reduce nitrogen pollution and carbon footprint while maintaining net ecosystem economic benefits [J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2018, 19(9):289-300. |
| 32 | 唐海明,肖小平,汤文光,等.冬季覆盖作物对双季稻光合特性的影响[J].杂交水稻,2011,26(2):64-68. |
| TANG H M, XIAO X P, TANG W G, et al.. Effects of different winter cover plants on photosynthetic characteristics of double-cropping rice [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2011, 26(2):64-68. | |
| 33 | 裴鹏刚,张均华,朱练峰,等.秸秆还田耦合施氮水平对水稻光合特性、氮素吸收及产量形成的影响[J].中国水稻科学,2015,29(3):282-290. |
| PEI P G, ZHANG J H, ZHU L F, et al.. Effects of straw returning coupled with N application on rice photosynthetic characteristics, nitrogen uptake and grain yield formation [J]. Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2015, 29(3):282-290. | |
| 34 | KUMAR K, GOH K M. Biological nitrogen fixation, accumulation of soil nitrogen and nitrogen balance for white clover (Trifolium repens L.) and field pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown for seed [J]. Field Crops Res., 2000, 68(1):49-59. |
| 35 | 才硕,时红,潘晓华,等.绿肥与稻草联合还田对机插双季稻生长和产量的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2019,41(4):631-640. |
| CAI S, SHI H, PAN X H, et al.. Influence of the combination of returning green manure cultivation and rice straw on the growth and yield formation of machine-transplanted early-late season double-cropping rice [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2019, 41(4):631-640. | |
| 36 | ZHOU G P, GAO S J, CHANG D N, et al.. Using milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) to promote rice straw decomposition by regulating enzyme activity and bacterial community [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2021, 319:124215 [2023-06-06]. . |
| 37 | 陈丽楠,彭显龙,刘元英,等.养分管理对寒地水稻干物质积累及运转的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2010,41(5):52-55. |
| CHEN L N, PENG X L, LIU Y Y, et al.. Effect of nutrient management on dry matter accumulation and translocation of rice in cold area [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2010, 41(5):52-55. | |
| 38 | 董春华,高菊生,曾希柏,等.长期有机无机肥配施下红壤性稻田水稻产量及土壤有机碳变化特征[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2014,20(2):336-345. |
| DONG C H, GAO J S, ZENG X B, et al.. Effects of long-term organic manure and inorganic fertilizer combined application on rice yield and soil organic carbon content in reddish paddy fields [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2014, 20(2):336-345. | |
| 39 | 沈亚强,程旺大,张红梅.绿肥及秸秆还田对水稻生长和产量的影响[J].中国稻米,2011,17(4):27-29. |
| 40 | 刘颖颖,卜容燕,唐杉,等.连续秸秆–紫云英协同还田对双季稻产量、养分积累及土壤肥力的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(6):1008-1016. |
| LIU Y Y, BU R Y, TANG S, et al.. Effect of continuous straw-Chinese milk vetch synergistic return to the field on yield, nutrient accumulation and soil fertility of double cropping rice [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(6):1008-1016. | |
| 41 | 聂鑫,鲁艳红,廖育林,等.化肥减施下紫云英不同翻压量对水稳性团聚体及双季稻产量的影响[J].华北农学报,2020,35(6):155-164. |
| NIE X, LU Y H, LIAO Y L, et al.. Effects of the incorporation of various amounts of Chinese milk vetch and reducing chemical fertilizer on water-stable aggregates and yield in double cropping rice System [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2020, 35(6):155-164. | |
| 42 | 高嵩涓,周国朋,曹卫东.南方稻田紫云英作冬绿肥的增产节肥效应与机制[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(12):2115-2126. |
| GAO S J, ZHOU G P, CAO W D. Effects of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) as winter green manure on rice yield and rate of fertilizer application in rice paddies in south China [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(12):2115-2126. | |
| 43 | 王吕,崔月贞,吴玉红,等.绿肥稻秆协同还田下氮肥减量的增产和培肥短期效应[J].作物学报,2022,48(4):952-961. |
| WANG L, CUI Y Z, WU Y H, et al.. Effects of rice stalks mulching combined with green manure (Astragalus smicus L.) incorporated into soil and reducing nitrogen fertilizer rate on rice yield and soil fertility [J]. Acta Agro. Sin., 2022, 48(4):952-961. | |
| 44 | CHENG W D, ZHANG G P, ZHAO G P, et al. Variation in rice quality of different cultivars and grain positions as affected by water management [J]. Field Crops Res., 2003, 80(3):245-252. |
| 45 | 唐健,唐闯,郭保卫,等.氮肥施用量对机插优质晚稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J].作物学报,2020,46(1):117-130. |
| TANG J, TANG C, GUO B W, et al.. Effect of nitrogen application on yield and rice quality of mechanical transplanting high quality late rice [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2020, 46(1):117-130. | |
| 46 | 王国骄,宋鹏,杨振中,等.秸秆还田对水稻光合物质生产特征、稻米品质和土壤养分的影响[J].作物杂志,2021(4):67-72. |
| WANG G J, SONG P, YANG Z Z, et al.. Effects of straw returning on photosynthetic matter production Characteristics, quality of rice and soil nutrients [J]. Crops, 2021(4):67-72. | |
| 47 | 陈梦云,李晓峰,程金秋,等.秸秆全量还田与氮肥运筹对机插优质食味水稻产量及品质的影响[J].作物学报,2017,43(12):1802-1816. |
| CHEN M Y, LI X F, CHENG J Q, et al.. Effects of total straw returning and nitrogen application regime on grain yield and quality in mechanical transplanting japonica rice with good taste quality [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2017, 43(12):1802-1816. | |
| 48 | 何虎,黄山,才硕,等.稻草全量还田下氮肥运筹对双季晚稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2015,37(3):385-391. |
| HE H, HUANG S, CAI S, et al.. Effects of nitrogen management on grain yield and quality of late rice under full amount of straw return [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2015, 37(3):385-391. | |
| 49 | 赵全志,高桐梅,李梦琴,等.糯米群体光合速率的比较及其与品质的关系[J].华北农学报,2005,20(6):1-3. |
| ZHAO Q Z, GAO T M, LI M Q, et al.. Comparison and relationship between canopy apparent photosynthetic rate and grain quality of glutinous rice [J].Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2005, 20(6):1-3. | |
| 50 | 张晓丽,王强,陈雷,等.东南亚特种水稻种质资源光合特性研究[J].植物遗传资源学报,2016,17(6):1008-1013. |
| ZHANG X L, WANG Q, CHEN L, et al.. Photosynthetic characters of special rice germplasm resources from southeast Asia [J]. J. Plant Genetic Resour., 2016, 17(6):1008-1013. | |
| 51 | HOU W F, KHAN M R, ZHANG J L, et al.. Nitrogen rate and plant density interaction enhances radiation interception, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of mechanically transplanted rice [J]. Argic. Ecosyst. Environ., 2019, 269:183-192. |
| 52 | 魏永霞,曹晓强,冀俊超,等.不同灌溉方式下旱直播水稻光合特性与干物质积累动态[J].农业机械学报,2021,52(10):358-368. |
| WEI Y X, CAO X Q, JI J C, et al.. Effects of different irrigation methods on photosynthetic characteristics and dry matter accumulation dynamics of dry direct seeding rice [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2021, 52(10):358-368. | |
| 53 | 郭相平,王甫,王振昌,等.不同灌溉模式对水稻抽穗后叶绿素荧光特征及产量的影响[J].灌溉排水学报,2017, 36(3):1-6. |
| GUO X P, WANG F, WANG Z C, et al.. Effects of irrigation modes on yield and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics after heading stage of rice [J]. J. Irrig. Drain., 2017, 36(3):1-6. | |
| 54 | 韩勇,李建国,姜秀英,等. 辽宁省水稻灌浆期光合特性及其与产量品质的相关性分析[J].吉林农业科学,2012,37(1):4-8. |
| HAN Y, LI J G, JIANG X Y, et al.. Correlation of photosynthetic characteristics at filling stage with yield and quality of rice in Liaoning province [J]. Jilin Agric. Sci., 2012, 37(1):4-8. | |
| 55 | 罗密,尹旺,邓仁菊,等. 不同甘薯品种(系)的光合特性研究[J].西南农业学报,2022,35(5):1039-1047. |
| LUO M, YIN W, DENG R J, et al.. Study on photosynthetic characteristics of different sweet potato varieties (lines) [J]. J. Southwest Agric. Sci., 2022, 35(5):1039-1047. | |
| 56 | 王会提,曾凡江,张波,等.不同种植方式下柽柳光合生理参数光响应特性研究[J].干旱区地理,2015,38(4):753-762. |
| WANG H T, ZENG F J, ZHANG B, et al.. Light response of Tamarix ramasissima ledeb. physiological parameters under different cropping patterns [J]. Arid Land Geogr., 2015, 38(4):753-762. | |
| 57 | 郭晓红,兰宇辰,胡月,等. 栽培方式对寒地水稻产量及光合特性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2020(6):220-227. |
| GUO X H, LAN Y C, HU Y, et al.. Effects of cultivation methods on yield and photosynthetic characteristics of rice in cold region [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2020(6):220-227. |
| [1] | 王辉, 付虹雨, 岳云开, 崔国贤, 佘玮. 基于气候变量的苎麻产量SSA-BP预测模型[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 110-118. |
| [2] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [3] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [4] | 段媛媛, 刘晓洪, 唐涛, 王帆帆, 游景茂, 郭晓亮, 郭杰. 种植密度对湖北贝母生长及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [5] | 周影, 李京咏, 戴林秀, 敖弟彩, 李梓逸, 杨帆, 顾军伟, 徐强, 窦志, 高辉. 稻虾共作模式下喷施褪黑素对水稻产量形成和抗倒伏特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 34-42. |
| [6] | 王为, 赵强, 穆妮热·阿卜杜艾尼, 阿里木·阿木力null, 李欣欣, 田阳青. 烯效唑复配不同外源物质对棉花化学封顶及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [7] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [8] | 郑志刚, 向丽, 刘功义, 徐彩, 覃斌, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 唐启源. 施氮量和密度对有序机抛早稻生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [9] | 孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [10] | 周文, 郭笑恒, 徐锐, 王晓丽, 牛慧伟, 韩丹, 邵惠芳. 烤烟间作半夏对烤烟生长及产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 161-169. |
| [11] | 陈登龙, 张雨翔, 宋佳佳, 陈鹏宇, 温祥珍, 李亚灵. 火山石沉积对鱼菜共生系统运行的探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 207-214. |
| [12] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [13] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [14] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [15] | 麻仲花, 陈娟, 吴娜, 满本菊, 王晓港, 者永清, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期光合特性与总生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号