




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 166-177.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0148
邵社刚1( ), 李婷2(
), 李婷2( ), 柳勇2, 林兰稳2, 张东1, 倪栋1, 李俊杰2, 朱立安2(
), 柳勇2, 林兰稳2, 张东1, 倪栋1, 李俊杰2, 朱立安2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-01
接受日期:2022-04-17
出版日期:2023-09-15
发布日期:2023-09-28
通讯作者:
朱立安
作者简介:邵社刚 E-mail: sg.shao@rioh.cn基金资助:
Shegang SHAO1( ), Ting LI2(
), Ting LI2( ), Yong LIU2, Lanwen LIN2, Dong ZHANG1, Dong NI1, Junjie LI2, Li’an ZHU2(
), Yong LIU2, Lanwen LIN2, Dong ZHANG1, Dong NI1, Junjie LI2, Li’an ZHU2( )
)
Received:2022-03-01
Accepted:2022-04-17
Online:2023-09-15
Published:2023-09-28
Contact:
Li’an ZHU
摘要:
为探究促腐菌剂对秸秆腐解理化性质及微生物群落结构变化的影响,以水稻秸秆为原料,设置添加促腐菌剂处理(JF)和未添加对照(CK),测定分析其理化指标和微生物群落结构变化特征。结果表明,添加促腐菌剂对堆体腐解率、pH、有机碳、全氮和碳氮比(C/N)无显著影响,但堆体全磷含量较CK显著增加8.4%,碳磷比(C/P)显著降低9.1%。门水平上,优势细菌群落为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和放线菌门(Actinobacteria),优势真菌群落为担子菌门(Basidiomycota)、子囊菌门(Ascomycota)和未确认真菌门(Unclassified fungi)。JF处理的细菌Proteobacteria、Actinobacteria丰度分别在第0~8、8~28天大于CK,真菌Basidiomycota、Ascomycota、Unclassified fungi分别在堆体升温期、冷却期和成熟期依次演替,丰度均大于CK。属水平上,优势细菌群落为芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、假黄单胞菌属(Pseudoxanthomonas)、大肠杆菌-志贺氏菌属(Escherichia-Shigella)、克罗诺杆菌属(Cronobacter)、纤维弧菌属(Cellvibrio)、类芽孢杆菌属(Paenibacillus);优势真菌群落为拟鬼伞属(Coprinopsis)、曲霉属(Aspergillus)、节担菌属(Wallemia)、黑果菌属(Melanocarpus)、嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)。JF处理的细菌Escherichia-Shigella和Cronobacter丰度在升温期分别较CK高0.3%~4.5%和1.3%~3.1%;真菌Wallemia丰度较CK高3.9%~4.5%,且Melanocarpus、Thermomyces丰度在第8天分别较CK高39.2%、39.1%。典型对应分析表明,全氮、有效磷分别是影响细菌、真菌群落最重要的环境指标。综上所述,外源促腐菌剂通过提高水稻秸秆部分成熟度指标、增加部分功能微生物群落丰度而影响其腐解,为提高水稻秸秆还田利用率提供理论和科学依据。
中图分类号:
邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177.
Shegang SHAO, Ting LI, Yong LIU, Lanwen LIN, Dong ZHANG, Dong NI, Junjie LI, Li’an ZHU. Effects of Exogenous Promoting Bacteria Agent on Decomposition Characteristics and Microbial Community Structure of Rice Straw[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 166-177.
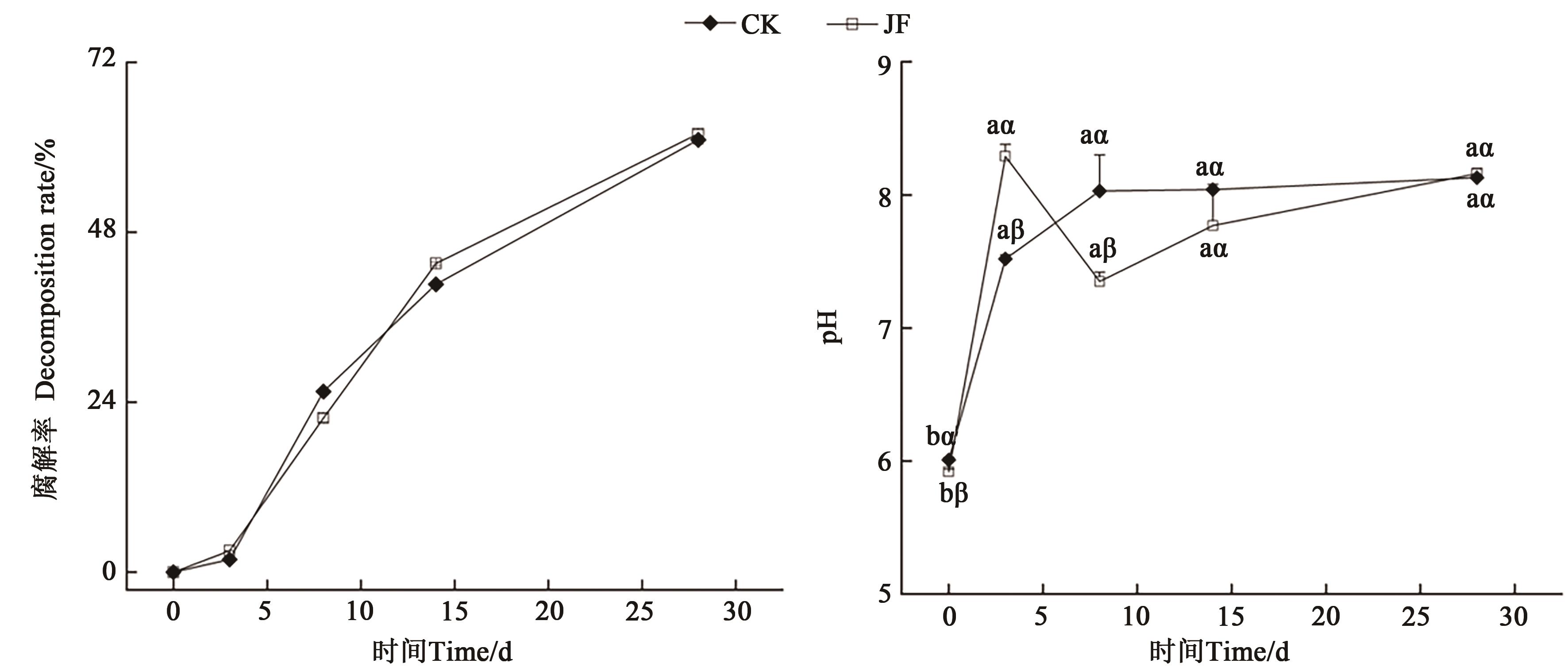
图2 腐解过程中腐解率和pH变化注:不同英文字母表示相同处理不同腐解时间内差异在P<0.05水平显著,不同希腊字母表示相同腐解时间不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Changes of decomposition rate and pH during the decomposing processNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level among different decomposing times under same treatment, different Greek letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level among different treatments under same decomposing time.
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | 有机碳 Total organic C /% | 全氮 Total N /% | 全磷 Total P/% | 碳氮比 C/N | 碳磷比 C/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 39.8±0.2 aα | 1.55±0.04 cα | 0.33±0.00 cα | 25.6±0.0 aα | 120.5±0.5 aα |
| JF | 41.1±0.5 aα | 1.64±0.01 bcα | 0.34±0.01 dα | 25.0±0.2 aα | 120.4±1.1 aα | |
| 3 | CK | 40.1±0.6 aα | 1.63±0.02 cα | 0.34±0.01 cβ | 24.7±0.6 aα | 118.4±4.3 abα |
| JF | 39.1±0.3 bα | 1.55±0.05 cα | 0.39±0.01 cα | 25.2±1.0 aα | 100.5±2.6 bβ | |
| 8 | CK | 39.6±0.3 aα | 2.19±0.01 bα | 0.44±0.00 bα | 18.1±0.2 bα | 89.1±0.6 bβ |
| JF | 38.4±0.2 bcβ | 2.15±0.07 abα | 0.41±0.00 cβ | 18.0±0.7 bα | 94.1±1.3 bα | |
| 14 | CK | 36.5±0.3 bα | 2.29±0.03 bα | 0.46±0.02 bβ | 16.0±0.3 cα | 79.7±0.8 cα |
| JF | 37.2±0.1 cα | 2.30±0.01 aα | 0.59±0.01 bα | 16.2±0.1 bα | 62.9±1.1 cβ | |
| 28 | CK | 34.4±0.2 cα | 2.42±0.02 aα | 0.59±0.01 aβ | 14.2±0.1 cα | 58.2±0.9 dα |
| JF | 33.9±0.2 dα | 2.44±0.02 aα | 0.64±0.01 aα | 13.9±0.1 cα | 52.9±1.3 dβ |
表1 腐解过程中有机碳、全氮、全磷、碳氮比和碳磷比的变化
Table 1 Changes of total organic C, total N, total P, C/N and C/P during the decomposing process
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | 有机碳 Total organic C /% | 全氮 Total N /% | 全磷 Total P/% | 碳氮比 C/N | 碳磷比 C/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 39.8±0.2 aα | 1.55±0.04 cα | 0.33±0.00 cα | 25.6±0.0 aα | 120.5±0.5 aα |
| JF | 41.1±0.5 aα | 1.64±0.01 bcα | 0.34±0.01 dα | 25.0±0.2 aα | 120.4±1.1 aα | |
| 3 | CK | 40.1±0.6 aα | 1.63±0.02 cα | 0.34±0.01 cβ | 24.7±0.6 aα | 118.4±4.3 abα |
| JF | 39.1±0.3 bα | 1.55±0.05 cα | 0.39±0.01 cα | 25.2±1.0 aα | 100.5±2.6 bβ | |
| 8 | CK | 39.6±0.3 aα | 2.19±0.01 bα | 0.44±0.00 bα | 18.1±0.2 bα | 89.1±0.6 bβ |
| JF | 38.4±0.2 bcβ | 2.15±0.07 abα | 0.41±0.00 cβ | 18.0±0.7 bα | 94.1±1.3 bα | |
| 14 | CK | 36.5±0.3 bα | 2.29±0.03 bα | 0.46±0.02 bβ | 16.0±0.3 cα | 79.7±0.8 cα |
| JF | 37.2±0.1 cα | 2.30±0.01 aα | 0.59±0.01 bα | 16.2±0.1 bα | 62.9±1.1 cβ | |
| 28 | CK | 34.4±0.2 cα | 2.42±0.02 aα | 0.59±0.01 aβ | 14.2±0.1 cα | 58.2±0.9 dα |
| JF | 33.9±0.2 dα | 2.44±0.02 aα | 0.64±0.01 aα | 13.9±0.1 cα | 52.9±1.3 dβ |
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | 硝态氮 NO | 铵态氮 NH | 有效磷 Olsen-P/(mg·kg-1) | 特征紫外吸光度 SUVA254 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 19.9±1.8 bα | 164.0±3.6 cα | 150.8±1.9 aα | 2.87±0.06 bβ |
| JF | 16.0±0.5 cβ | 94.8±4.1 cβ | 148.5±1.1 aα | 3.15±0.05 bα | |
| 3 | CK | 19.9±1.8 bα | 4 669.4±70.0 aα | 120.7±1.9 bα | 1.87±0.04 dβ |
| JF | 17.9±0.9 cα | 4 708.4±213.0 aα | 113.3±2.2 bα | 2.20±0.05 dα | |
| 8 | CK | 32.3±4.9 aα | 795.2±40.8 bβ | 85.0±2.2 cα | 2.61±0.04 cα |
| JF | 24.8±1.6 aα | 975.2±19.8 bα | 86.4±1.3 cα | 2.20±0.00 dβ | |
| 14 | CK | 19.3±4.1 bα | 39.5±6.2 dβ | 31.7±0.6 dβ | 2.65±0.02 cα |
| JF | 18.7±0.8 bcα | 98.1±3.2 cα | 34.5±0.3 dα | 2.72±0.06 cα | |
| 28 | CK | 31.9±4.1 aα | 43.6±1.5 dβ | 25.8±0.9 dα | 3.36±0.08 aα |
| JF | 22.1±2.6 abβ | 87.3±8.8 cα | 26.2±0.2 dα | 3.45±0.00 aα |
表2 腐解过程中硝态氮、铵态氮、有效磷和特征紫外吸光度的变化
Table 2 Changes of NO3--N, NH4+-N, Olsen-Pand SUVA254 during the decomposing process
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | 硝态氮 NO | 铵态氮 NH | 有效磷 Olsen-P/(mg·kg-1) | 特征紫外吸光度 SUVA254 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CK | 19.9±1.8 bα | 164.0±3.6 cα | 150.8±1.9 aα | 2.87±0.06 bβ |
| JF | 16.0±0.5 cβ | 94.8±4.1 cβ | 148.5±1.1 aα | 3.15±0.05 bα | |
| 3 | CK | 19.9±1.8 bα | 4 669.4±70.0 aα | 120.7±1.9 bα | 1.87±0.04 dβ |
| JF | 17.9±0.9 cα | 4 708.4±213.0 aα | 113.3±2.2 bα | 2.20±0.05 dα | |
| 8 | CK | 32.3±4.9 aα | 795.2±40.8 bβ | 85.0±2.2 cα | 2.61±0.04 cα |
| JF | 24.8±1.6 aα | 975.2±19.8 bα | 86.4±1.3 cα | 2.20±0.00 dβ | |
| 14 | CK | 19.3±4.1 bα | 39.5±6.2 dβ | 31.7±0.6 dβ | 2.65±0.02 cα |
| JF | 18.7±0.8 bcα | 98.1±3.2 cα | 34.5±0.3 dα | 2.72±0.06 cα | |
| 28 | CK | 31.9±4.1 aα | 43.6±1.5 dβ | 25.8±0.9 dα | 3.36±0.08 aα |
| JF | 22.1±2.6 abβ | 87.3±8.8 cα | 26.2±0.2 dα | 3.45±0.00 aα |
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | Chao1指数Chao1 index | Shannon指数Shannon index | 覆盖率Coverage/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | ||
| 0 | CK | 752.7±3.9 cα | 149.0±3.3 bβ | 5.63±0.10 bcα | 2.65±0.29 abα | 99.7±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 774.9±18.2 cα | 189.1±13.1 abα | 5.50±0.06 cα | 3.00±0.06 abα | 99.7±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
| 3 | CK | 1 585.6±42.0 aα | 192.7±15.6 aα | 6.89±0.13 aα | 4.15±0.18 aα | 99.2±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 676.9±28.4 aα | 236.7±18.8 aα | 6.79±0.05 aα | 4.15±0.15 aα | 99.1±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
| 8 | CK | 1 632.9±52.7 aα | 195.2±5.4 aα | 5.51±0.05 cα | 3.62±0.55 abα | 99.1±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 218.6±28.1 bβ | 112.0±27.5 bcα | 5.36±0.10 cα | 1.96±0.78 bα | 99.4±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 | |
| 14 | CK | 1 103.6±13.5 bα | 49.6±5.1 dα | 6.06±0.14 bα | 0.06±0.01 cα | 99.5±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 |
| JF | 1 111.5±53.0 bα | 44.9±9.7 cα | 5.98±0.03 bα | 0.21±0.18 cα | 99.4±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 | |
| 28 | CK | 1 266.7±38.2 bα | 100.7±3.4 cα | 6.61±0.03 aα | 2.26±0.32 bα | 99.4±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 183.3±12.7 bα | 103.4±4.1 cα | 6.17±0.11 bβ | 2.42±0.04 bα | 99.5±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
表3 腐解过程中细菌、真菌群落丰富度与多样性的变化
Table 3 Changes of bacterial and fungal community diversity and richness indices during the decomposing process
时间 Time/d | 处理 Treatment | Chao1指数Chao1 index | Shannon指数Shannon index | 覆盖率Coverage/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | 细菌Bacterium | 真菌Fungus | ||
| 0 | CK | 752.7±3.9 cα | 149.0±3.3 bβ | 5.63±0.10 bcα | 2.65±0.29 abα | 99.7±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 774.9±18.2 cα | 189.1±13.1 abα | 5.50±0.06 cα | 3.00±0.06 abα | 99.7±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
| 3 | CK | 1 585.6±42.0 aα | 192.7±15.6 aα | 6.89±0.13 aα | 4.15±0.18 aα | 99.2±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 676.9±28.4 aα | 236.7±18.8 aα | 6.79±0.05 aα | 4.15±0.15 aα | 99.1±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
| 8 | CK | 1 632.9±52.7 aα | 195.2±5.4 aα | 5.51±0.05 cα | 3.62±0.55 abα | 99.1±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 218.6±28.1 bβ | 112.0±27.5 bcα | 5.36±0.10 cα | 1.96±0.78 bα | 99.4±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 | |
| 14 | CK | 1 103.6±13.5 bα | 49.6±5.1 dα | 6.06±0.14 bα | 0.06±0.01 cα | 99.5±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 |
| JF | 1 111.5±53.0 bα | 44.9±9.7 cα | 5.98±0.03 bα | 0.21±0.18 cα | 99.4±0.0 | 100.0±0.0 | |
| 28 | CK | 1 266.7±38.2 bα | 100.7±3.4 cα | 6.61±0.03 aα | 2.26±0.32 bα | 99.4±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 |
| JF | 1 183.3±12.7 bα | 103.4±4.1 cα | 6.17±0.11 bβ | 2.42±0.04 bα | 99.5±0.0 | 99.9±0.0 | |
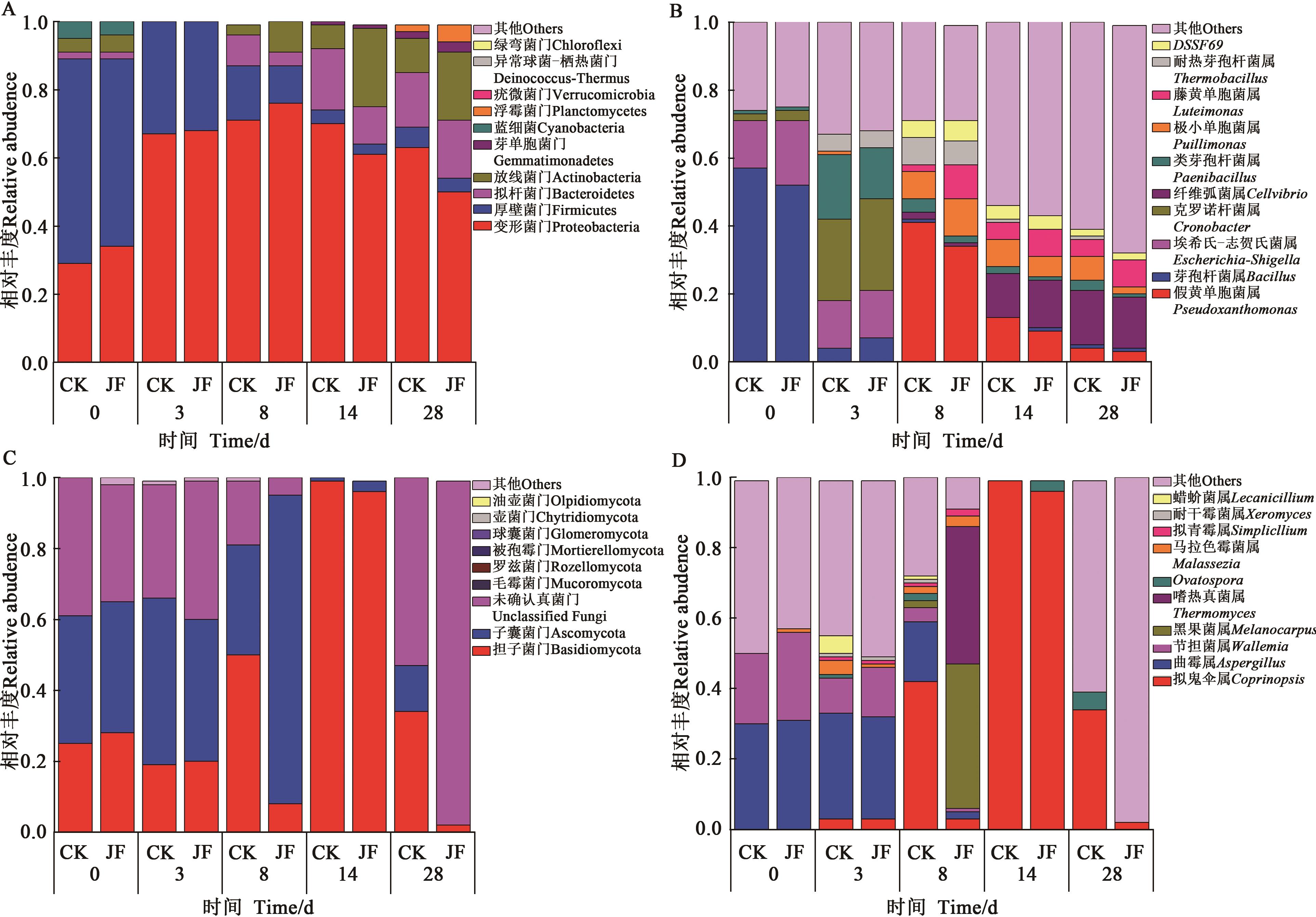
图3 细菌、真菌群落在门和属分类水平的分布特征变化A:门分类水平上细菌群落变化特征;B:属分类水平上细菌群落变化特征;C:门分类水平上真菌群落变化特征;D:属分类水平上真菌群落变化特征
Fig. 3 Analysis of distribution characteristics of bacterial and fungal communities at phylum and genus levelA: Distribution characteristics of bacterial communities at phylum level; B: Distribution characteristics of bacterial communities at genus level; C: Distribution characteristics of fungal communities at phylum level; D: Distribution characteristics of fungal communities at genus level
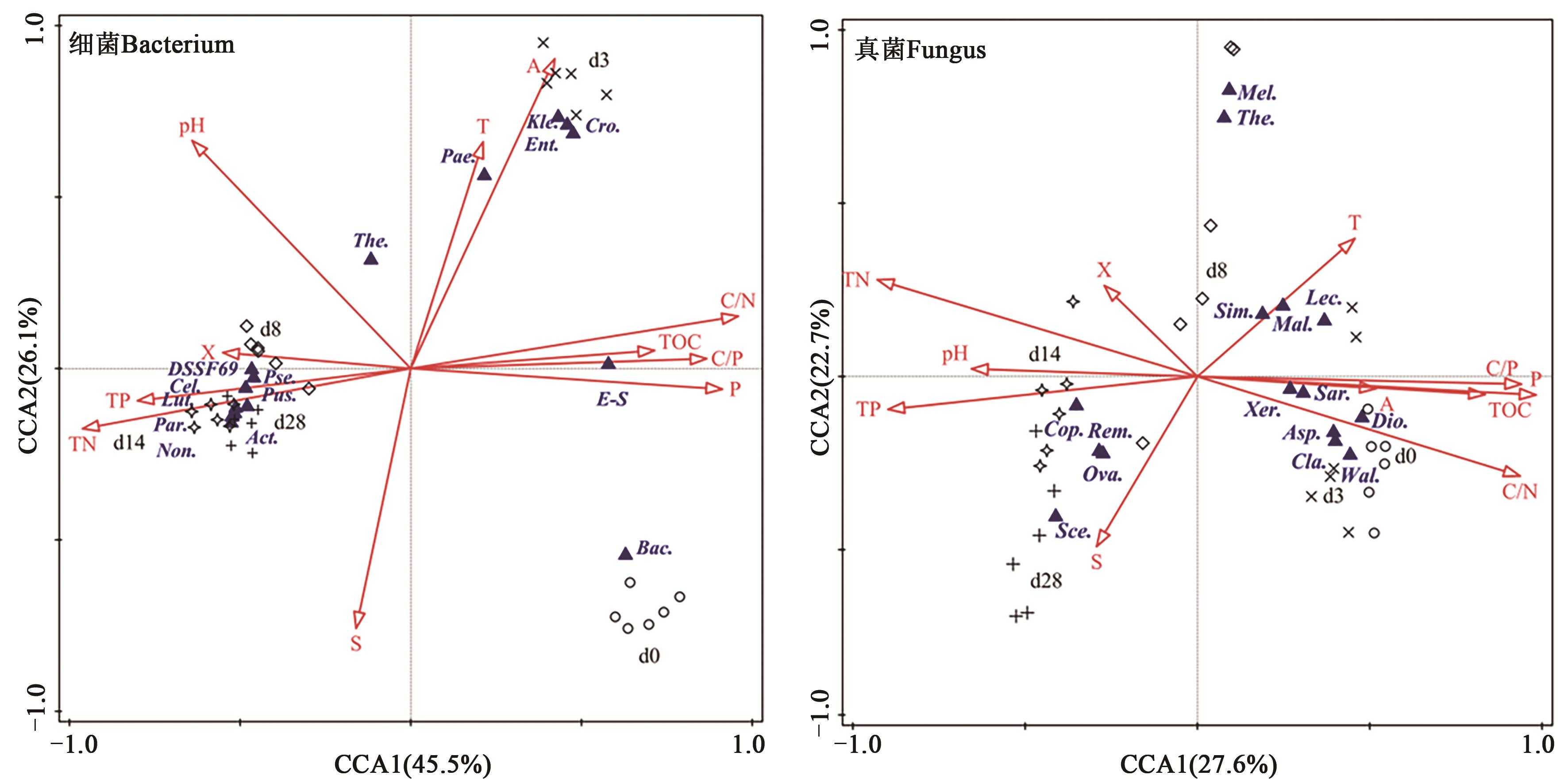
图4 属水平上微生物群落结构与理化性质的CCA分析注:d0、d3、d8、d14、d28分别表示腐解的第0、3、8、14、28天。 A—铵态氮; TP—总磷; TN—总氮; P—有效磷; S—SUVA254; T—温度; TOC—有机碳; C/N—C/N比; C/P—C/P比; X—硝态氮。Non.—野野村菌属; Act.—马杜拉放线菌属; Par.—副杆菌属; Bac.—芽孢杆菌属; Pae.—类芽孢杆菌属; The.—耐热芽孢杆菌属; Pus.—极小单胞菌属; Cel.—纤维弧菌属; Cro.—克罗诺杆菌属; Ent.—肠杆菌属; E-S—埃希氏-志贺氏菌属; Kle.—克雷伯氏菌属; Lut.—藤黄单胞菌属; Pse.—假黄单胞菌属; DSSF69—DSSF69。Cla.—分子孢子菌属; Asp.—曲霉属; Xer.—耐干霉菌属; The.—嗜热真菌属; Lec.—蜡蚧菌属; Sim.—Simplicillium; Sar.—帚枝霉属; Sce.—丝孢菌属; Mel.—黑果菌属; Ova.—Ovatospora; Rem.—Remersonia; Cop.—拟鬼伞属; Mal.—马拉色霉菌属; Dio.—Dioszegia; Wal.—节担菌属。
Fig. 4 Analysis of RDA of microbial community structure and physical and chemical properties at genus levelNote: d0, d3, d8, d14, d28 indicate the 0, 8th, 14th, 20th and 28th day of the composting process. A—NH4+-N; TP—Total phosphorus; TN—Total nitrogen; P—Olsen-P; S—SUVA254; T—Temperature; TOC—Total organic C; C/N—C/N ratio; C/P—C/P ratio; X—NH3--N. Non.—Nonomuraea; Act.—Actinomadura; Par.—Parapedobacter; Bac.—Bacillus; Pae.—Paenibacillus; The.—Thermobacillus; Pus.—Pusillimonas; Cel.—Cellvibrio; Cro.—Cronobacter; Ent.—Enterobacter; E-S—Escherichia-Shigella; Kle.—Klebsiella; Lut.—Luteimonas; Pse.—Pseudoxanthomonas. Cla.—Cladosporium; Asp.—Aspergillus; Xer.—Xeromyces; The.—Thermomyces; Lec.—Lecanicillium; Sim.—Simplicillium; Sar.—Sarocladium; Sce.—Scedosporium; Mel.—Melanocarpus; Ova.—Ovatospora; Rem.—Remersonia; Cop.—Coprinopsis; Mal.—Malassezia; Dio.—Dioszegia; Wal.—Wallemia.
| 1 | 李廷亮, 王宇峰, 王嘉豪, 等. 我国主要粮食作物秸秆还田养分资源量及其对小麦化肥减施的启示[J]. 中国农业科学,2020, 53(23): 4835-4854. |
| LI T L, WANG Y F, WANG J H, et al.. Nutrient resource quantity from main grain crop straw incorporation and its enlightenment on chemical fertilizer reduction in wheat production in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2020, 53(23): 4835-4854. | |
| 2 | 霍丽丽, 赵立欣, 孟海波, 等. 中国农作物秸秆综合利用潜力研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(13): 218-224. |
| HUO L L, ZHAO L X, MENG H B, et al.. Study on straw multi-use potential in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019, 35(13): 218-224. | |
| 3 | IBRAHIM M, MAHMOUD E, IBRAHIM D. Assessing the impact of water treatment residuals and rice straw compost on soil physical properties and wheat yield in saline sodic soil [J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 2020, 51(18): 2388-2397. |
| 4 | WANG J, SUN N, XU M G, et al.. The influence of long-term animal manure and crop residue application on abiotic and biotic N immobilization in an acidified agricultural soil [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 337: 710-717. |
| 5 | CHEN Z M, WANG H Y, LIU X W, et al.. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice-wheat cropping system [J]. Soil Tillage Res., 2017, 165: 121-127. |
| 6 | YIN H J, ZHAO W Q, LI T, et al.. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: role of straw nutrient resources [J]. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2018, 81: 2695-2702. |
| 7 | CHAKMA S, RANJAN A, CHOUDHURY H A, et al.. Bioenergy from rice crop residues: role in developing economies [J]. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2016, 18(2): 373-394. |
| 8 | 朱雅琪, 王珊, 柳勇, 等. 腐秆剂用量、含水量及初始碳氮比对水稻秸秆腐解性能的影响初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(3): 601-611. |
| ZHU Y Q, WANG S, LIU Y, et al.. Effect of decomposition agent dosage, moisture content, and initial C/N ratio on decomposition of rice straw [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2019, 28(3): 601-611. | |
| 9 | ZHAO S C, QIU S J, XU X P, et al.. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2019, 138: 123-133. |
| 10 | 劳德坤, 张陇利, 李永斌, 等. 不同接种量的微生物秸秆腐熟剂对蔬菜副产物堆肥效果的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(6): 2979-2985. |
| LAO D K, ZHANG L L, LI Y B, et al.. Effect of different inoculation amounts of microbial straw decomposition agents on vegetable byproducts composting [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2015, 9(6): 2979-2985. | |
| 11 | YEE V F, JIŘĺ J K, CHEW T L, et al.. Efficiency of microbial inoculation for a cleaner composting technology [J]. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2018, 20: 517-527. |
| 12 | 陈帅, 刘峙嵘, 曾凯. 腐秆剂对水稻秸秆腐解性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(2): 839-844. |
| CHEN S, LIU Z R, ZENG K. Effect of straw-decomposing inoculant on decomposition of rice straw [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2016, 10(2): 839-844. | |
| 13 | FAN Y V, LEE C T, HO C S, et al.. Evaluation of microbial inoculation technology for composting [J]. Chem. Eng. Trans., 2017, 56: 433-438. |
| 14 | 宋志伟, 陈露露, 潘宇, 等. 3种菌剂对水稻秸秆降解性能的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(11): 2134-2141. |
| SONG Z W, CHEN L L, PAN Y, et al.. Influence of three microbial agents on the degradation performance of rice straw [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2018, 27(11): 2134-2141. | |
| 15 | WU D, WEI Z M, GAO X Z, et al.. Reconstruction of core microbes based on producing lignocellulolytic enzymes causing by bacterial inoculation during rice straw composting [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 315:123849 [2022-02-08]. . |
| 16 | 姚云柯, 周卫, 孙建光, 等. 田间条件下不同促腐菌对水稻秸秆腐解及胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(11): 2070-2080. |
| YAO Y K, ZHOU W, SUN J G, et al.. Effects of different straw-decomposition inoculants on increasing the activities of extracellular enzymes and decomposition of rice straw buried into soil [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2020, 26(11): 2070-2080. | |
| 17 | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999: 1-638. |
| 18 | 国家林业局. 森林土壤全氮的测定: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1999. |
| The State Forestry Administration of the People's Republic of China. Determination of total nitrogen in forest soil: [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 1999. | |
| 19 | GUO R, LI G, JIANG T, et al.. Effect of aeration rate, C/N ratio and moisture content on the stability and maturity of compost [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2012, 112: 171-178. |
| 20 | ABDEL-RAHMAN M A, EL-DIN M N, REFAAT B M, et al.. Biotechnological application of thermotolerant cellulose-decomposing bacteria in composting of rice straw [J]. Ann. Agric. Sci., 2016, 61(1) : 135-143. |
| 21 | 李荣华, 涂志能, Ali Amjad, 等. 生物炭复合菌剂促进堆肥腐熟及氮磷保留[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(8): 3449-3457. |
| LI R H, TU Z N, AMJAD A, et al.. Biochar carried microbial solution promotes compost maturity and nitrogen, phosphorus conservation [J]. China Environ. Sci., 2020, 40(8): 3449-3457. | |
| 22 | WEI Y Q, ZHAO Y, FAN Y Y, et al.. Impact of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation methods on phosphorus transformation and long-term utilization in composting [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2017, 241: 134-141. |
| 23 | WANG M H, LIU Y, WANG S Q, et al.. Development of a compound microbial agent beneficial to the composting of Chinese medicinal herbal residues [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2021, 330:124948 [2022-02-08]. . |
| 24 | CHIN Y P, AIKEN G R, O'LOUGHLIN E. Molecular weight, polydispersity and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28: 1853-1858. |
| 25 | 唐朱睿, 席北斗, 何小松, 等. 猪粪堆肥过程中水溶性有机物结构演变特征[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(5): 1526-1532. |
| TANG Z R, XI B D, HE X S, et al.. Structural characteristics of dissolved organic compounds during swine manure composting [J]. Spectros. Spectr. Anal., 2018, 38(5): 1526-1532. | |
| 26 | NISHIJIMAN W, GERALD E, SPEITLE J. Fate of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon produced by ozonation on biological activated carbon [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 56(2): 113-119. |
| 27 | FENG J, WANG B, ZHANG D, et al.. Streptomyces griseorubens JSD-1 promotes rice straw composting efficiency in industrial-scale fermenter: evaluation of change in physicochemical properties and microbial community [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2021, 321: 124465-124475. |
| 28 | 夏金利, 王岩, 董春玲, 等. 不同促腐菌剂对园林废弃物堆肥理化性质和优势微生物群落的影响[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2021, 55(3): 551-560. |
| XIA J L, WANG Y, DONG C L, et al.. Effects of different microbial inoculants on the physical and chemical properties and dominant microbial communities in the composting process of garden waste [J]. J. Henan Agric. Univ., 2021, 55(3): 551-560. | |
| 29 | LIU N, HOU T, YIN H J, et al.. Effects of amoxicillin on nitrogen transformation and bacterial community succession during aerobic composting [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2019, 362: 258-265. |
| 30 | CHI P C, CHU S H, WANG B, et al.. Dynamic bacterial assembly driven by Streptomyces griseorubens JSD-1 inoculants correspond to composting performance in swine manure and rice straw co-composting [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 313:123692 [2022-02-08]. . |
| 31 | ZHANG M Y, LIANG W, TU Z N, et al.. Succession of bacterial community during composting: dissimilarity between compost mixture and biochar additive [J]. Biochar, 2021, 3(2): 229-237. |
| 32 | ZHANG L L, ZHANG H Q, WANG Z H, et al.. Dynamic changes of the dominant functioning microbial community in the compost of a 90-m3 aerobic solid state fermentor revealed by integrated meta-omics [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2016, 203: 1-10. |
| 33 | WANG X Q, KONG Z J, WANG Y H, et al.. Insights into the functionality of fungal community during the large scale aerobic co-composting process of swine manure and rice straw [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2020, 270: 110958 [2022-02-08].. |
| 34 | TIAN X P, YANG T, HE J Z, et al.. Fungal community and cellulose-degrading genes in the composting process of Chinese medicinal herbal residues [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2017, 241: 374-383. |
| 35 | MENG Q X, YANG W, MEN M Q, et al.. Microbial community succession and response to environmental variables during cow manure and corn straw composting [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10:529 [2022-02-08]. . |
| 36 | LU X L, WU H, SONG S L, et al.. Effects of multi-phase inoculation on the fungal community related with the improvement of medicinal herbal residues composting [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2021, 28: 27998-28013. |
| 37 | YUN C X, YAN C R, XUE Y H, et al.. Effects of exogenous microbial agents on soil nutrient and microbial community composition in greenhouse-derived vegetable straw composts [J/OL]. Sustainability, 2021, 13: 2925 [2022-02-08]. . |
| 38 | 蔡涵冰, 冯雯雯, 董永华, 等. 畜禽粪便和桃树枝工业化堆肥过程中微生物群演替及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(2): 997-1004. |
| CAI H B, FENG W W, DONG Y H, et al.. Microbial community succession in industrial composting with livestock manure and peach branches and relations with environmental factors [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(2): 997-1004. | |
| 39 | WEI H W, WANG L H, HASSAN M, et al.. Succession of the functional microbial communities and the metabolic functions in maize straw composting process [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2018, 256: 333-341. |
| 40 | JIANG X, DENG L T, MENG Q X, et al.. Fungal community succession under influence of biochar in cow manure composting [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2020, 27(19): 9658-9668. |
| [1] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [2] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [3] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [4] | 贾晶莹, 李雅辉, 伏兵哲, 马云, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿miRs表达谱分析及跨界潜力miRs初步筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 43-53. |
| [5] | 王旭东, 任雪冰, 汤舒, 郭琴, 薛梦瑶, 金鹏, 张云华. 污泥生物炭在土壤改良中的应用研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 165-173. |
| [6] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [7] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [8] | 靳建刚, 田再芳, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠. 不同施肥措施对饲用燕麦土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 152-160. |
| [9] | 赵柏霞, 闫建芳. 高通量技术分析‘砂蜜豆’甜樱桃不同组织内生细菌多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 66-77. |
| [10] | 闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [11] | 李洁, 林莹, 徐美玉, 王飞, 徐凌川. 泰山白首乌根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 70-81. |
| [12] | 赵宏岩, 谭君伟, 张杰, 陈浩楠, 王春旭, 赵地, 李海鹏, 朱李霞, 韩毅强. 小豆和绿豆茎基感病部位真菌群落结构研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 129-136. |
| [13] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [14] | 范鹤龄, 朱清, 孙雪冰, 张丽, 李长江, 陈萍, 黄小龙, 张荣萍. 不同农用酵素的微生物多样性和群落结构[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 179-189. |
| [15] | 李敏, 李钢铁, 张宏武, 陈家欢. 平茬对3种苗木来源蛋白桑林地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 172-182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号