




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 122-131.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.1092
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
尹兴盛1( ), 包玲凤2,3, 濮永瑜1, 孙加利1, 张庆3, 李海平1, 杨明英3, 林跃平1, 王怀鑫1, 何永宏2, 杨佩文3(
), 包玲凤2,3, 濮永瑜1, 孙加利1, 张庆3, 李海平1, 杨明英3, 林跃平1, 王怀鑫1, 何永宏2, 杨佩文3( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-24
接受日期:2022-04-12
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-08-25
通讯作者:
杨佩文
作者简介:尹兴盛 E-mail: 1791426254@qq.com;
基金资助:
Xingsheng YIN1( ), Lingfeng BAO2,3, Yongyu PU1, Jiali SUN1, Qing ZHANG3, Haiping LI1, Mingying YANG3, Yueping LIN1, Huaixin WANG1, Yonghong HE2, Peiwen YANG3(
), Lingfeng BAO2,3, Yongyu PU1, Jiali SUN1, Qing ZHANG3, Haiping LI1, Mingying YANG3, Yueping LIN1, Huaixin WANG1, Yonghong HE2, Peiwen YANG3( )
)
Received:2021-12-24
Accepted:2022-04-12
Online:2023-07-15
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Peiwen YANG
摘要:
为解析植烟土壤质量与烟草青枯病发生发展的关系以及减氮配施生物有机肥对烟草青枯病的防控效果,以常规施氮为对照,设置4个减氮水平(5%、10%、15%和20%)+生物有机肥处理的田间小区试验,研究了减氮配施生物有机肥模式对土壤主要理化性质、烟叶产量和质量的影响,并进一步考察了对烟草青枯病的田间防效,基于相关性分析解析土壤理化因子与病情指数间的关系。结果表明,减氮配施生物有机肥各处理的土壤容重、pH下降,土壤碳氮比、有机碳含量、碳储量、氮储量、土壤蔗糖酶活性、脲酶活性、微生物量碳、微生物量氮均不同程度增加,烟叶产量、上等烟比例、中上等烟比例均显著提升。烟草青枯病病情指数显著降低70.32%~75.31%,平均防治效果为69.64%~75.97%。其中,减氮15%配施生物有机肥处理为最佳模式。相关性分析结果表明,病情指数与土壤碳氮比、有机碳、碳储量、氮储量、蔗糖酶活性、脲酶活性、微生物量碳和生物量碳氮比呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与pH呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与微生物量氮呈负相关(P<0.05),与土壤容重、碱解氮、有效磷和速效钾呈正相关(P<0.05)。在试验条件下,适当减氮并配施生物有机肥能有效改善土壤质量,提高烟叶产量和质量,降低烟草青枯病的发生。
中图分类号:
尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131.
Xingsheng YIN, Lingfeng BAO, Yongyu PU, Jiali SUN, Qing ZHANG, Haiping LI, Mingying YANG, Yueping LIN, Huaixin WANG, Yonghong HE, Peiwen YANG. Effects of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Bio-organic Fertilization on Tobacco Soil Characteristics and Tobacco Bacterial Wilt Control[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 122-131.
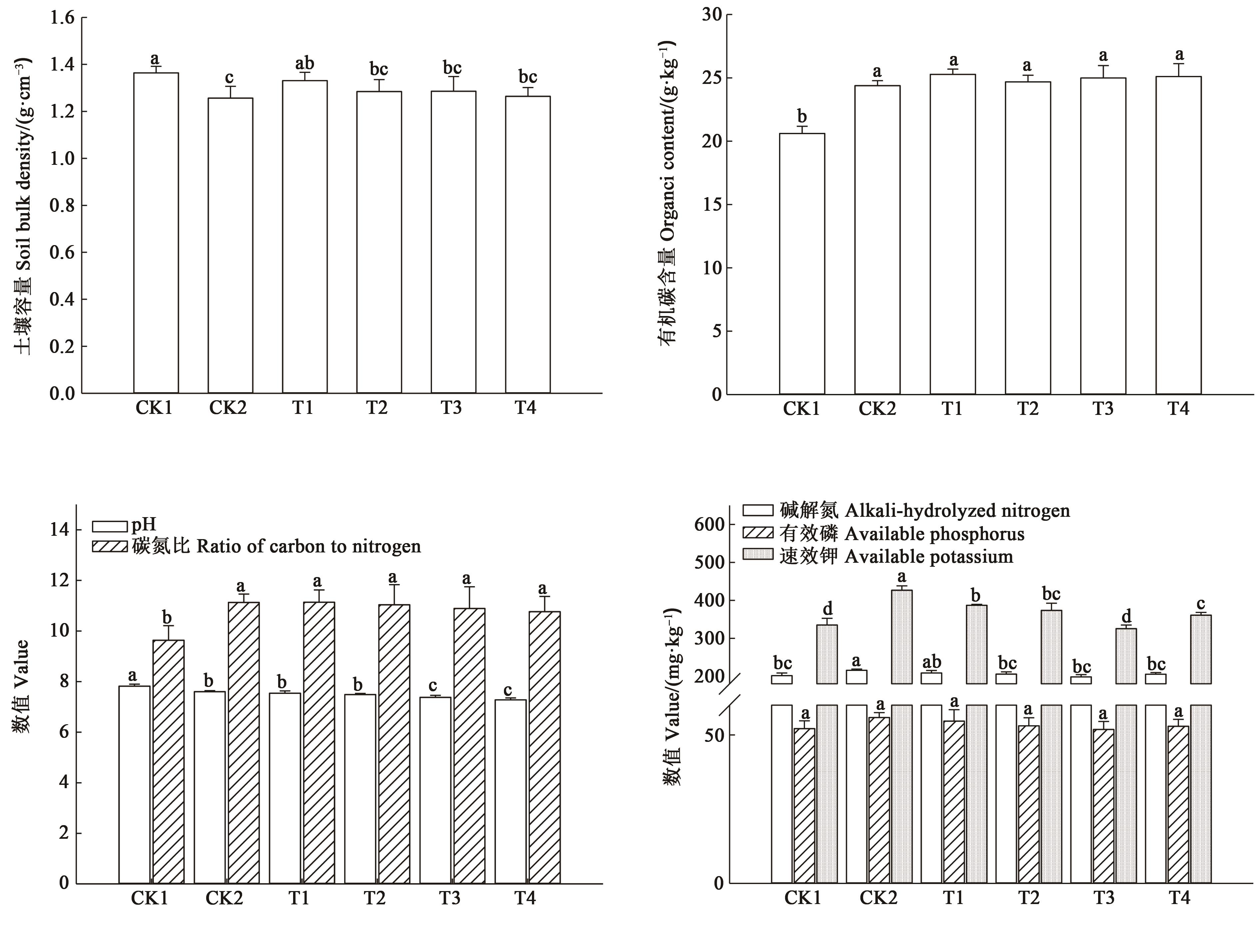
图1 不同施肥处理下的土壤主要理化性质注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Main physical and chemical properties of soil under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
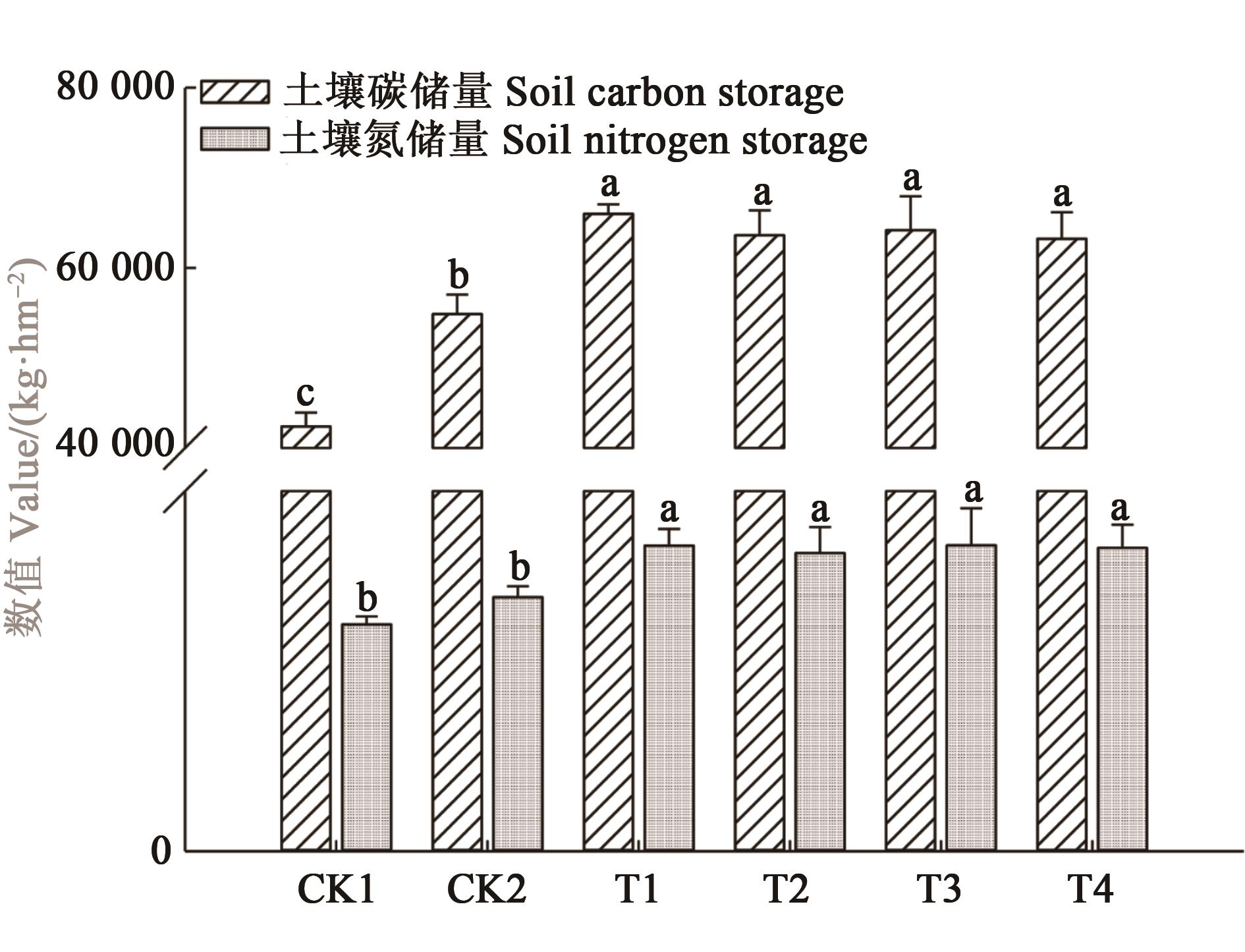
图2 不同施肥措施下的土壤碳储量和氮储量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Soil carbon storage and nitrogen storage of soil under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
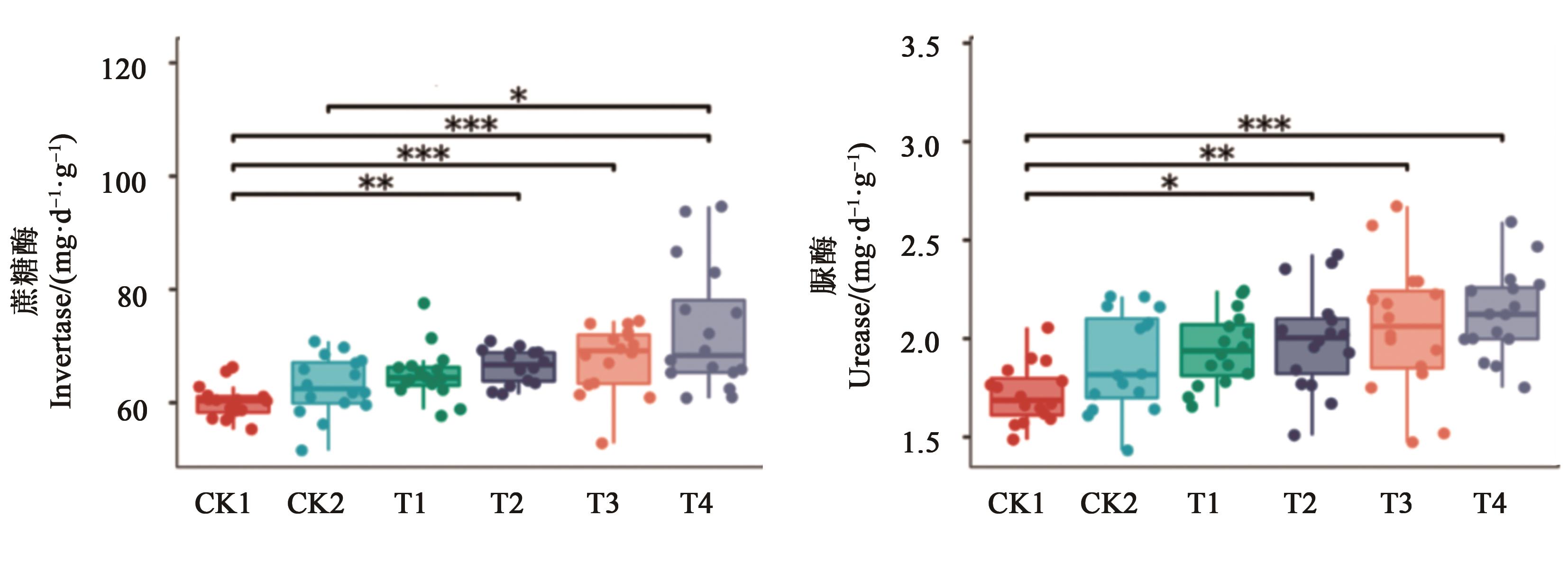
图3 不同施肥措施下的土壤蔗糖酶和脲酶活性注:*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Activity of soil invertase and urease under different fertilization treatmentsNote:*,** and *** mean significant differences at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.

图4 不同施肥处理下的土壤微生物量注:*表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Soil microbial biomass analysis of soil under different fertilization treatmentsNote:* means significant differences at P<0.05 level.
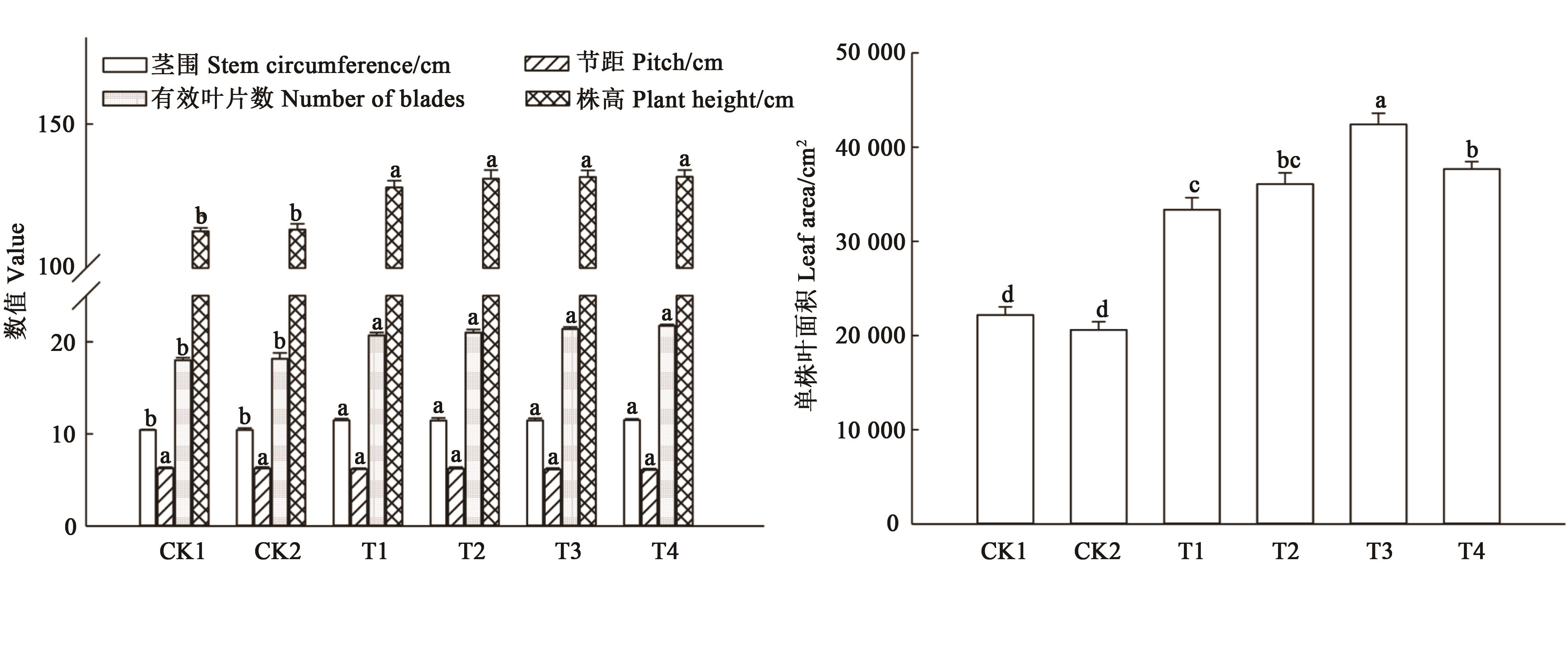
图5 不同施肥处理下的烤烟农艺性状注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.5 Agronomic characters of flue-cured tobacco under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
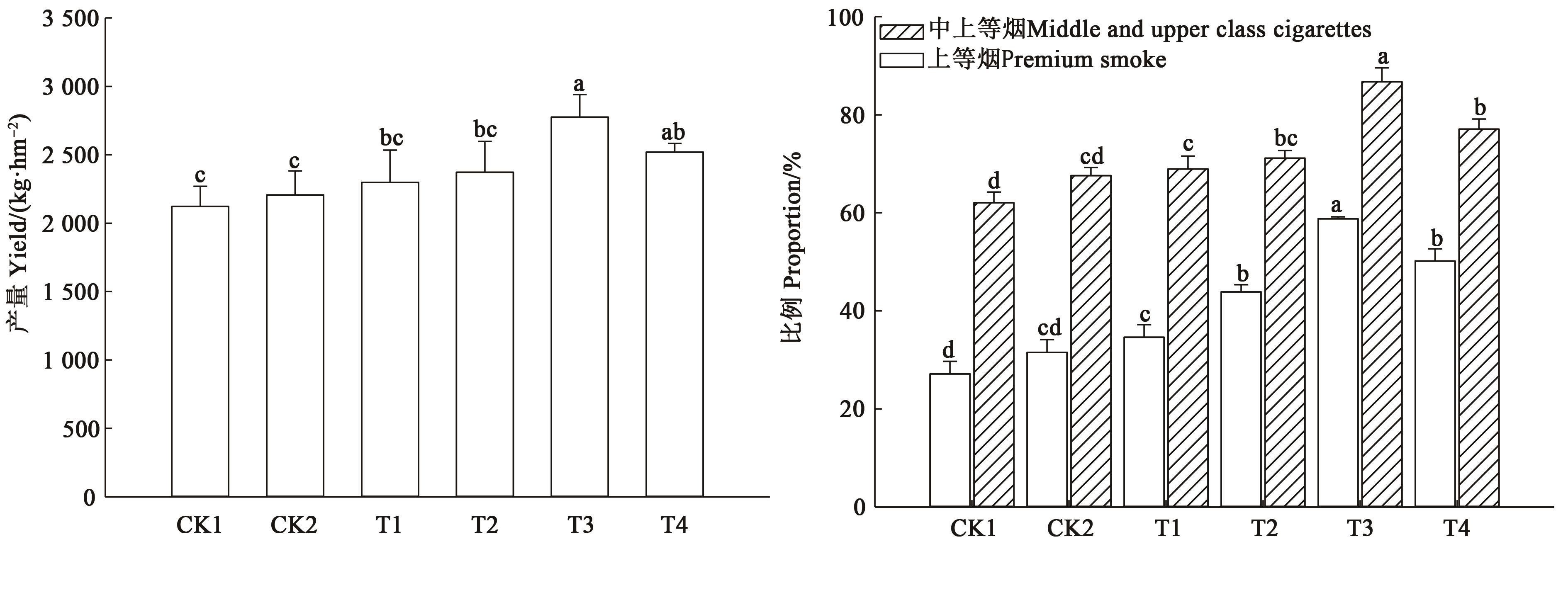
图6 不同施肥处理下的烤烟产量和质量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.6 Yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco of soil under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in the same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | CK2 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | |
| 病情指数 Disease index | 8.02±0.80 a | 5.00±0.52 b | 2.38±0.09 c | 2.22±0.18 c | 1.98±0.08 c | 1.90±0.13 c |
| 防治效果 Control effect/% | — | 37.64±1.12 b | 69.64±2.32 a | 71.77±2.57 a | 74.54±2.50 a | 75.97±0.98 a |
表1 烟草青枯病的发生情况
Table 1 Controlling effect of different treatments on Ralstoniasolanacearum
指标 Index | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | CK2 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | |
| 病情指数 Disease index | 8.02±0.80 a | 5.00±0.52 b | 2.38±0.09 c | 2.22±0.18 c | 1.98±0.08 c | 1.90±0.13 c |
| 防治效果 Control effect/% | — | 37.64±1.12 b | 69.64±2.32 a | 71.77±2.57 a | 74.54±2.50 a | 75.97±0.98 a |
指标 Index | BD | C/N | SOC | pH | AN | AP | AK | SCS | SNS | INV | URE | SMBC | SMBN | SMBC/SMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
病情指数 Disease index | 0.357 | -0.560** | -0.699** | 0.812** | 0.141 | 0.059 | 0.005 | -0.901** | -0.736** | -0.480* | -0.534** | -0.793** | -0.233 | -0.666** |
表2 病情指数与土壤理化性质、碳氮储量、酶活、微生物量的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between disease index and soil physical and chemical properties, carbon and nitrogen storage, enzyme activity, and microbial biomass
指标 Index | BD | C/N | SOC | pH | AN | AP | AK | SCS | SNS | INV | URE | SMBC | SMBN | SMBC/SMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
病情指数 Disease index | 0.357 | -0.560** | -0.699** | 0.812** | 0.141 | 0.059 | 0.005 | -0.901** | -0.736** | -0.480* | -0.534** | -0.793** | -0.233 | -0.666** |
| 1 | 杨天杰,王玉鑫,王佳宁,等.不同基质生物有机肥防控番茄土传青枯病及促生效果研究[J].土壤,2021,53(5):961-968. |
| YANG T J, WANG Y X, WANG J N, et al.. Effects of different bioorganic fertilizer on tomato bacterial wilt and plant growth promotion [J]. Soils, 2021,53(5):961-968. | |
| 2 | 吴晓宗,王岩.生物有机肥防治烟草青枯病及对土壤微生物多样性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(4):193-199. |
| WU X Z, WANG Y. Research of bio-organic fertilizer on prevention of tobacco bacterial wilt and its effects on soil microbial diversity [J]. China Soils Fert.,2019(4):193-199. | |
| 3 | 戚瑞敏,赵秉强,李娟,等.添加牛粪对长期不同施肥潮土有机碳矿化的影响及激发效应[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(S2):118-127. |
| QI R M, ZHAO B Q, LI J, et al.. Effects of cattle manure addition on soil organic carbon mineralization and priming effects under long-term fertilization regimes [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016,32(S2):118-127. | |
| 4 | MOSADDEGHI M R, MAHBOUBI A A, SAFADOUS A. Short-term effects of tillage and manure on some soil physical properties and maize root growth in a sandy loam soil in western Iran [J]. Soil Tillage Res.,2008,104(1):173-179. |
| 5 | 王磊,高方胜,曹逼力,等.有机肥和化肥配施对不同熟期大白菜土壤生物特性及产量品质的影响[J].生态学杂志,2022,41(1):66-72. |
| WANG L, GAO F S, CAO B L, et al.. Effects of combined organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer application on soil biological characteristics,yield,and quality of Chinese cabbage with different maturity periods [J].Chin. J. Ecol.,2022,41(1):66-72. | |
| 6 | 王静,王磊,刘耀斌,等.长期施氮肥对黄棕壤微生物生物性状的影响及其调控因素[J].中国生态农业学报,2021,29(5):833-843. |
| WANG J, WANG L, LIU Y B, et al.. Effects and associated regulatory factors of the microbial characteristics of yellow-brown soils following long-term nitrogen fertilization [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2021,29(5):833-843. | |
| 7 | 唐海明,李超,肖小平,等.有机肥氮投入比例对双季稻田根际土壤微生物生物量碳、氮和微生物熵的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(4):1335-1343. |
| TANG H M, LI C, XIAO X P, et al.. Effects of different manure nitrogen input ratio on rhizosphere soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and microbial quotient in double-cropping rice field [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019,30(4):1335-1343. | |
| 8 | BANDICK A K, DICK R P. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem.,1999,31(11): 1471-1479 . |
| 9 | TRASAR C C, LEIROS M C, GIL SOTRES F. Hydrolytic enzyme activities in agricultural and forest soils. Some implications for their use as indicators of soil quality [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2008, 40( 9):2146-2155. |
| 10 | KIBOI M N, NGETICH K F, MUGENDI D N, et al.. Microbial biomass and acid phosphomonoesterase activity in soils of the central highlands of Kenya [J/OL]. Geod. Reg.,2018,15:e00193[2022-04-11]. . |
| 11 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:14-109. |
| 12 | 李倩,李晓秀,吴会军,等.不同气候和施肥条件下保护性耕作对农田土壤碳氮储量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(6):1539-1549. |
| LI Q, LI X X, WU H J, et al.. Effects of conservation tillage practices on soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in farmland under different climatic types and fertilization conditions [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2018,24(6):1539-1549. | |
| 13 | 吴金水,林启美,黄巧云,等.土壤微生物量测定方法及其应用[M].北京:气象出版社,2006:3-13. |
| 14 | 申国明,陈爱国,王程栋,等. 烟草农艺性状调查测量方法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2010. |
| 15 | 国家技术监督局. 烤烟: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,1992. |
| 16 | 任广伟,孔凡玉,王凤龙,等. 烟草病虫害分级及调查方法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2008. |
| 17 | 张广雨,胡志明,褚德朋,等.生物炭对根际土壤微生态的调控及对烟草青枯病的防控作用[J].中国烟草学报,2020,26(6):81-88. |
| ZHANG G Y, HU Z M, CHU D P, et al.. Regulation of biochar on rhizosphere soil microecology and its control effect on tobacco bacterial wilt [J]. Acta Tob. Sin., 2020,26(6):81-88. | |
| 18 | MA D K, YIN L N, JU W L, et al.. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China [J/OL]. Field Crops Res.,2021, 266(25):108146 [2022-04-11]. . |
| 19 | 唐琨,朱伟文,周文新,等.土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展[J].作物研究,2013,27(2):207-212. |
| TANG K, ZHU W W, ZHOU W X, et al.. Research progress on effects of soil pH on plant growth and development [J]. Crop Res., 2013,27(2):207-212. | |
| 20 | MASELESELE, OGOLA J B, MUROVHI R N. Macadamia husk compost improved physical and chemical properties of a sandy loam soil [J/OL]. Sustainability,2021,13(13):6997 [2022-04-11]. . |
| 21 | 胡玮,李桂花,任意,等.不同碳氮比有机肥组合对低肥力土壤小麦生物量和部分土壤肥力因素的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2011(2):22-27. |
| HU W, LI G H, REN Y, et al.. The effects of combined organic manure in different carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on wheat biomass and soil fertility in low fertility soil [J]. China Soils Fert., 2011(2):22-27. | |
| 22 | 张永亮,于铁峰,郝凤.施肥和混播对人工草地土壤速效养分含量的影响[J].中国草地学报,2021,43(9):88-96. |
| ZHANG Y L, YU T F, HAO F. Responses of soil available nutrients content in legume-grass mixture grassland to fertilization and mixed sowing ratio [J]. Chin. J. Grassl.,2021,43(9):88-96. | |
| 23 | 孙轲,黎建强,杨关吕,等.滇中高原云南松林枯落物输入对土壤碳氮储量及其分布格局的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(8):3100-3110. |
| SUN K, LI J Q, YANG G L, et al.. Effect of alterations in forest litter inputs on soil C and N storage distribution in Pinus yunnanensis forest in central Yunnan Plateau [J]. Acta Eco. Sin., 2021,41(8):3100-3110. | |
| 24 | 王永鹏,张广宇,陈兵,等.外源性养分对土壤碳氮储量及阳春砂养分吸收效率的影响[J].广东农业科学,2021,48(6):54-63. |
| WANG Y P, ZHANG G Y, CHEN B, et al.. Effects of exogenous nutrients on soil carbon and nitrogen storage and nutrient absorption efficiency of amomum villosum [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2021,48(6):54-63. | |
| 25 | 朱利霞.不同调控措施对旱作农田土壤碳氮及微生物学特性的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2018. |
| ZHU L X. Effects of different management practices on soil carbon and nitrogen and related microbial processes in rain-fed farmlands [J]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2018. | |
| 26 | 杨宁,邹冬生,杨满元,等.衡阳紫色土丘陵坡地不同植被恢复阶段土壤酶活性特征研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(6):1516-1524. |
| YANG N, ZOU D S, YANG M Y, et al.. Soil enzyme activities in different re-vegetation stages on sloping-land with purple soils in Hengyang of Hunan province,China [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci.,2013,19(6):1516-1524. | |
| 27 | 李想,刘艳霞,陈风雷,等.长期不同施肥处理对贵州植烟土壤酶活及微生物群落的影响[J].中国烟草学报,2019,25(6):50-59. |
| LI X, LIU Y X, CHEN F L, et al.. Effects of long-term different fertilization treatments on soil enzyme activity and microbial community in tobacco-growing soil of Guizhou province [J]. Acta Tob. Sin., 2019,25(6):50-59. | |
| 28 | 武杞蔓,田诗涵,李昀烨,等.微生物菌肥对设施黄瓜生长、产量及品质的影响[J].生物技术通报,2022, 38(1): 125-131. |
| WU Q M, TIAN S H, LI Y Y, et al.. Effect of microbial fertilizer on Cucumis sativus L. growth, yield and quality [J].Biotechnol. Bull.,2022,38(1): 125-131. | |
| 29 | 杨滨娟,黄国勤,钱海燕.秸秆还田配施化肥对土壤温度、根际微生物及酶活性的影响[J].土壤学报,2014,51(1):150-157. |
| YANG B J, HUANG G Q, QIAN H Y. Effects of straw incorporation plus chemical fertilizer on soil temperature,root micro-organisms and enzyme activities [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin.,2014,51(1):150-157. | |
| 30 | 郭策,赵兴敏,王楠,等.秸秆还田配施氮肥对黑钙土有机碳及微生物量碳氮的影响[J].河南农业大学学报,2022,56(1):21-30. |
| GUO C, ZHAO X M, WANG N, et al.. Effect of straw returning with nitrogen on organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in chernozem [J]. J. Henan Agric.Univ.,2022,56(1):21-30. | |
| 31 | 周慧,史海滨,张文聪,等.有机无机肥配施对盐渍化土壤微生物量和呼吸的影响[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(15):86-95. |
| ZHOU H, SHI H B, ZHANG W C, et al.. Effects of the combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial biomass and soil respiration in saline soil [J]. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2021,37(15):86-95. | |
| 32 | 王宇峰,孟会生,李廷亮,等.培肥措施对复垦土壤微生物碳氮代谢功能多样性的影响[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(24):81-90. |
| WANG Y F, MENG H S, LI T L, et al.. Effects of fertilization regime on the functional diversity of microbial carbon and nitrogen metabolism in reclaimed soil [J]. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020,36(24):81-90. | |
| 33 | DE VRIES F T, HOFFLAND E, EEKEREN NVAN, et al.. Fungal/bacterial ratios in grasslands with contrasting nitrogen management [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2006,38(8): 2092-2103. |
| 34 | 宋以玲,于建,陈士更,等.化肥减量配施生物有机肥对油菜生长及土壤微生物和酶活性影响[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(1):352-360. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G, et al.. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with application of bio-organic fertilizer on rape growth,microorganism and enzymes activities in soil [J]. Soil Water Conserv.,2018,32(1):352-360. | |
| 35 | 钱海燕,杨滨娟,黄国勤,等.秸秆还田配施化肥及微生物菌剂对水田土壤酶活性和微生物数量的影响[J].生态环境学报,2012,21(3):440-445. |
| QIAN H Y, YANG B J, HUANG G Q, et al.. Effects of returning rice straw to fields with fertilizers and microorganism liquids on soil enzyme activities and microorganisms in paddy fields [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci.,2012,21(3):440-445. | |
| 36 | 岳明灿,王志国,陈秋实,等.减施化肥配施微生物菌剂对番茄产质量和土壤肥力的影响[J].土壤,2020,52(1):68-73. |
| YUE M C, WANG Z G, CHEN Q S, et al.. Effects of reduction of chemical fertilizer combined with application of microbial agents on growth and soil fertility of cherry tomato [J]. Soils,2020,52(1):68-73. | |
| 37 | 石磊,王军,陈云,等.化肥减量配施生物菌肥对色素辣椒生长的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2021,58(5):854-865. |
| SHI L, WANG J, CHEN Y, et al.. Effects of combined application of bio-bacterial manure with reduced chemical fertilizer on pigment pepper growth [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci.,2021,58(5):854-865. | |
| 38 | 周进.生物菌肥施用对温室辣椒光合特性、产量和品质的影响[J].北方园艺,2021(1):42-47. |
| ZHOU J. Effects of microbial fertilizer application on photosynthetic charateristics,yield and quality of greenhouse pepper [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021(1):42-47. | |
| 39 | 杨志刚,叶英杰,常海文,等.生物有机肥及土壤修复剂对干制辣椒生长、品质及产量的影响[J].北方园艺,2020(19):1-7. |
| YANG Z G, YE Y J, CHANG H W, et al.. Effects of microbial fertilizer and soil amendment on the growth,quality and yield of dry prpper [J]. Northern Hortic.,2020(19):1-7. | |
| 40 | HOLZAPFEL C, SHAHROKH P, KAFKEWITZ D. Polyphenol oxidase activity in the roots of seedlings of Bromus (Poaceae) and other grass genera [J]. Am. J. Bot.,2010,97(7): 1195-1199. |
| 41 | 陈巧玲,胡江,汪汉成,等.生物有机肥对盆栽烟草根际青枯病原菌和短短芽孢杆菌数量的影响[J].南京农业大学学报,2012,35(1):75-79. |
| CHEN Q L, HU J, WANG H C, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer application on population of ralstoniasolanacearum and brevibacillusbrevis in tobacco rhizosphere [J]. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ.,2012,35(1):75-79. |
| [1] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [2] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [3] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [4] | 郭巨先, 欧阳碧珊, 李桂花, 符梅, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 陆美莲. 微生物有机肥对连作菜薹生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [5] | 闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [6] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [7] | 苏煜, 黄劭理. 增施生物有机肥对烤烟光合特性及根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 164-171. |
| [8] | 李敏, 李钢铁, 张宏武, 陈家欢. 平茬对3种苗木来源蛋白桑林地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 172-182. |
| [9] | 范娜,彭之东,白文斌*,赵建武. 微生物菌剂对土壤酶活性及高粱生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 185-192. |
| [10] | 王思霁, 国艳春, 曾路生, 孙显旻, 初庆刚, 王胜. 碱蓬播种量对滨海盐碱地土壤酶活性和团聚性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 179-185. |
| [11] | 黄艳飞, 陈君梅, 辛亚宁, 吴庆丽. 石膏对苏打盐碱土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 139-146. |
| [12] | 高日平, §, 刘小月, §, 杜二小, 韩云飞, 任永峰, 高宇, 赵沛义, 李焕春, 张鹏, . 垄膜沟播与秸秆还田对内蒙古黄土高原玉米农田土壤水分、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 181-190. |
| [13] | 杨晶晶,张青青*,吐尔逊娜依·热依木,阿马努拉·依明尼亚孜,雪热提江·麦提努日. 游牧和定居对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤真菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| [14] | 刘松涛1,田春丽1,曹雯梅1,郑贝贝1,李鹏程2,董合林2. 基于不同土壤质地棉花根际微生物和酶活性特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 73-79. |
| [15] | 张杰1,2,马亚君1,贺志斌1,高芳芳1,张少骅1,王超然1,赵丹晨1. 微生物肥料替代化肥在苹果种植中的应用效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(7): 128-135. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号