




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 201-210.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0302
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
张余莽1,2( ), 陈贵娟3, 常洪艳1, 王永恒1, 刘淑霞1(
), 陈贵娟3, 常洪艳1, 王永恒1, 刘淑霞1( ), 应允秀2
), 应允秀2
收稿日期:2023-04-18
接受日期:2023-12-05
出版日期:2025-01-15
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
刘淑霞
作者简介:张余莽 E-mail: zhangym198410@ 163.com;
基金资助:
Yumang ZHANG1,2( ), Guijuan CHEN3, Hongyan CHANG1, Yongheng WANG1, Shuxia LIU1(
), Guijuan CHEN3, Hongyan CHANG1, Yongheng WANG1, Shuxia LIU1( ), Yunxiu YING2
), Yunxiu YING2
Received:2023-04-18
Accepted:2023-12-05
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Shuxia LIU
摘要:
保水剂在土壤中降解能力低,会对土壤环境产生危害,利用聚天冬氨酸和膨润土为原料,制备了新型的可降解土壤保水剂。设置水分胁迫处理和正常灌溉处理2组水分处理,在2组水分处理下分别施用市售腐殖酸保水剂(TA)和12.5(TB1)、17.5(TB2)、22.5(TB3)、27.5(TB4)和32.5 kg·hm-2(TB5)的新型土壤保水剂,以不施用保水剂为对照(CK),探讨其对玉米苗期生长发育的影响。结果表明,施用保水剂在玉米苗期可提高土壤含水量,当保水剂加入量为22.5 kg·hm-2效果最好,保水剂用量为32.5 kg·hm-2时对玉米出苗有显著抑制作用;在水分胁迫条件下,施用保水剂各处理的株高、茎粗、叶绿素含量和超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶活性均显著高于CK;同时施用保水剂能显著降低丙二醛和脯氨酸含量;其中,以保水剂用量为22.5 kg·hm-2(TB3)效果最佳。以上结果表明,新型土壤保水剂效果明显,对我国的农业节水有一定的推进作用。
中图分类号:
张余莽, 陈贵娟, 常洪艳, 王永恒, 刘淑霞, 应允秀. 水分胁迫下新型土壤保水剂对玉米苗期发育的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 201-210.
Yumang ZHANG, Guijuan CHEN, Hongyan CHANG, Yongheng WANG, Shuxia LIU, Yunxiu YING. Effect of New Degradable Soil Water-retaining Agent on Growth and Development of Maize Seedlings Under Water Stress at Seedling Stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 201-210.
水分条件 Water condition | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 茎粗 Stem diameter/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 65.50±1.76 αc | 1.20±0.03 αc | |
| TA | 68.37±0.90 αab | 1.28±0.07 αab | |
| TB1 | 66.23±1.12 αbc | 1.22±0.04 αbc | |
| +W | TB2 | 67.50±0.85 αabc | 1.23±0.04 αabc |
| TB3 | 69.10±2.04 αa | 1.30±0.02 αa | |
| TB4 | 66.73±0.76 αabc | 1.27±0.02 αabc | |
| TB5 | 66.80±0.70 αabc | 1.26±0.01 αabc | |
| CK | 51.60±1.18 βd | 0.78±0.04 βc | |
| TA | 56.30±0.66 βab | 1.13±0.07 βa | |
| TB1 | 55.53±0.86 βbc | 1.08±0.06 βab | |
| -W | TB2 | 57.13±0.70 βab | 1.11±0.02 βa |
| TB3 | 57.97±0.95 βa | 1.14±0.02 βa | |
| TB4 | 55.57±1.42b βc | 1.12±0.01 βa | |
| TB5 | 54.03±0.74 βc | 1.02±0.08 βb |
表1 不同水分条件下施用保水剂处理的玉米苗期株高和茎粗
Table 2 Maize seedling height and stem diameter with water retaining agent applied under different water conditions
水分条件 Water condition | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 茎粗 Stem diameter/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 65.50±1.76 αc | 1.20±0.03 αc | |
| TA | 68.37±0.90 αab | 1.28±0.07 αab | |
| TB1 | 66.23±1.12 αbc | 1.22±0.04 αbc | |
| +W | TB2 | 67.50±0.85 αabc | 1.23±0.04 αabc |
| TB3 | 69.10±2.04 αa | 1.30±0.02 αa | |
| TB4 | 66.73±0.76 αabc | 1.27±0.02 αabc | |
| TB5 | 66.80±0.70 αabc | 1.26±0.01 αabc | |
| CK | 51.60±1.18 βd | 0.78±0.04 βc | |
| TA | 56.30±0.66 βab | 1.13±0.07 βa | |
| TB1 | 55.53±0.86 βbc | 1.08±0.06 βab | |
| -W | TB2 | 57.13±0.70 βab | 1.11±0.02 βa |
| TB3 | 57.97±0.95 βa | 1.14±0.02 βa | |
| TB4 | 55.57±1.42b βc | 1.12±0.01 βa | |
| TB5 | 54.03±0.74 βc | 1.02±0.08 βb |
水分条件 Water condition | 处理 Treatment | 干物质量 Dry matter weight/g | |
|---|---|---|---|
地上 Overground | 地下 Underground | ||
| CK | 1.87±0.02 αd | 0.75±0.04 αd | |
| TA | 2.31±0.09 αa | 0.83±0.02 αa | |
| TB1 | 2.07±0.05 αc | 0.77±0.04 αbc | |
| +W | TB2 | 2.14±0.04 αbc | 0.80±0.01 αab |
| TB3 | 2.31±0.06 αa | 0.84±0.02 αa | |
| TB4 | 2.18±0.01 αb | 0.78±0.03 αbc | |
| TB5 | 1.81±0.03 αd | 0.72±0.01 αd | |
| CK | 0.92±0.15 βd | 0.50±0.03 βd | |
| TA | 1.35±0.09 βa | 0.66±0.04 βa | |
| TB1 | 1.21±0.08 βbc | 0.56±0.03 βc | |
| -W | TB2 | 1.24±0.09 βb | 0.59±0.02 βbc |
| TB3 | 1.38±0.10 βa | 0.68±0.01 βa | |
| TB4 | 1.25±0.06 βb | 0.61±0.02 βb | |
| TB5 | 1.16±0.02 βc | 0.49±0.01 βd | |
表2 不同水分条件下施用保水剂处理的玉米苗期干物质量
Table 2 Dry matter quality of maize seedling under different water conditions with water retaining agent
水分条件 Water condition | 处理 Treatment | 干物质量 Dry matter weight/g | |
|---|---|---|---|
地上 Overground | 地下 Underground | ||
| CK | 1.87±0.02 αd | 0.75±0.04 αd | |
| TA | 2.31±0.09 αa | 0.83±0.02 αa | |
| TB1 | 2.07±0.05 αc | 0.77±0.04 αbc | |
| +W | TB2 | 2.14±0.04 αbc | 0.80±0.01 αab |
| TB3 | 2.31±0.06 αa | 0.84±0.02 αa | |
| TB4 | 2.18±0.01 αb | 0.78±0.03 αbc | |
| TB5 | 1.81±0.03 αd | 0.72±0.01 αd | |
| CK | 0.92±0.15 βd | 0.50±0.03 βd | |
| TA | 1.35±0.09 βa | 0.66±0.04 βa | |
| TB1 | 1.21±0.08 βbc | 0.56±0.03 βc | |
| -W | TB2 | 1.24±0.09 βb | 0.59±0.02 βbc |
| TB3 | 1.38±0.10 βa | 0.68±0.01 βa | |
| TB4 | 1.25±0.06 βb | 0.61±0.02 βb | |
| TB5 | 1.16±0.02 βc | 0.49±0.01 βd | |
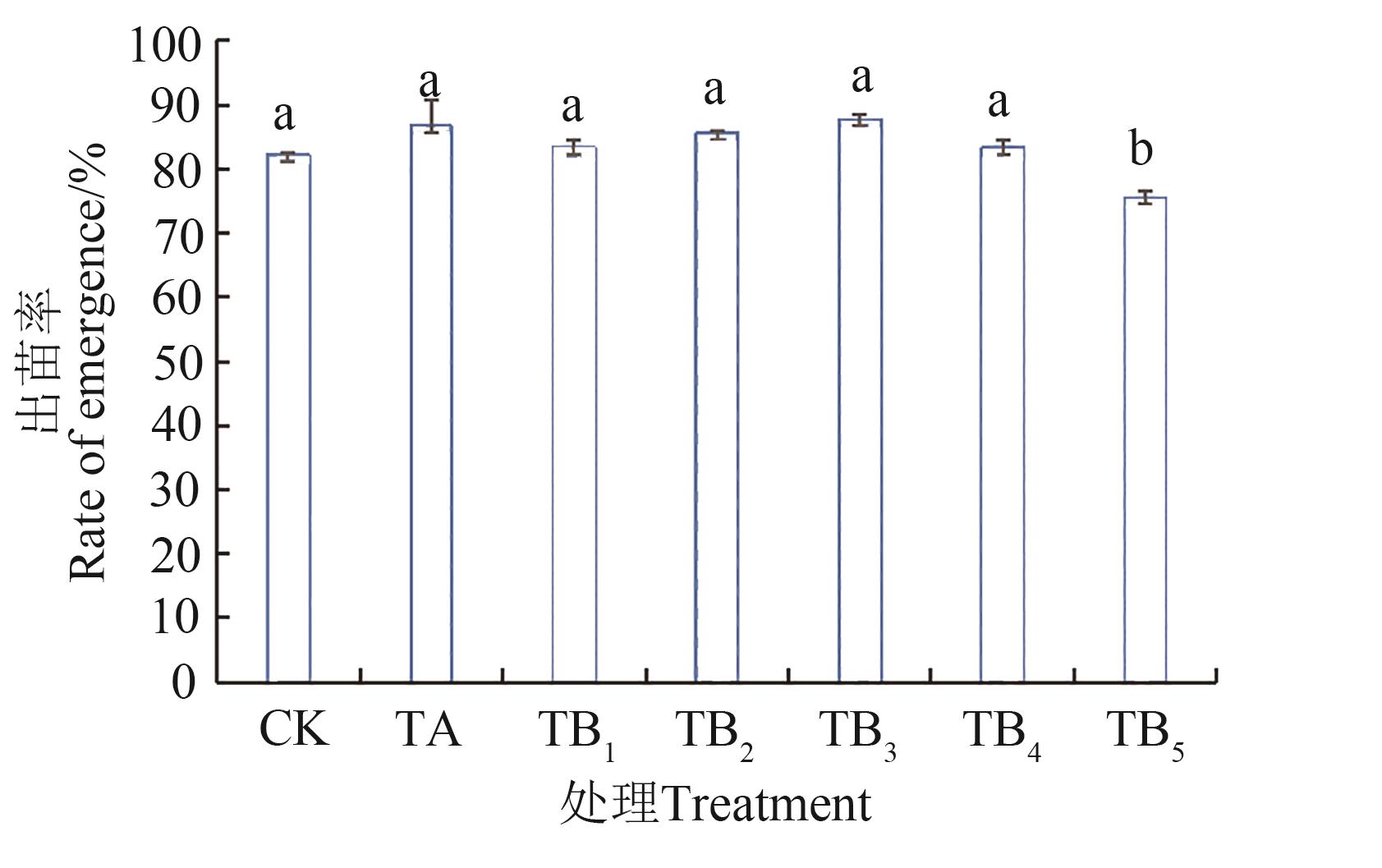
图2 正常水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米出苗率注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Emergence rate of maize with water retaining agent under normal water conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
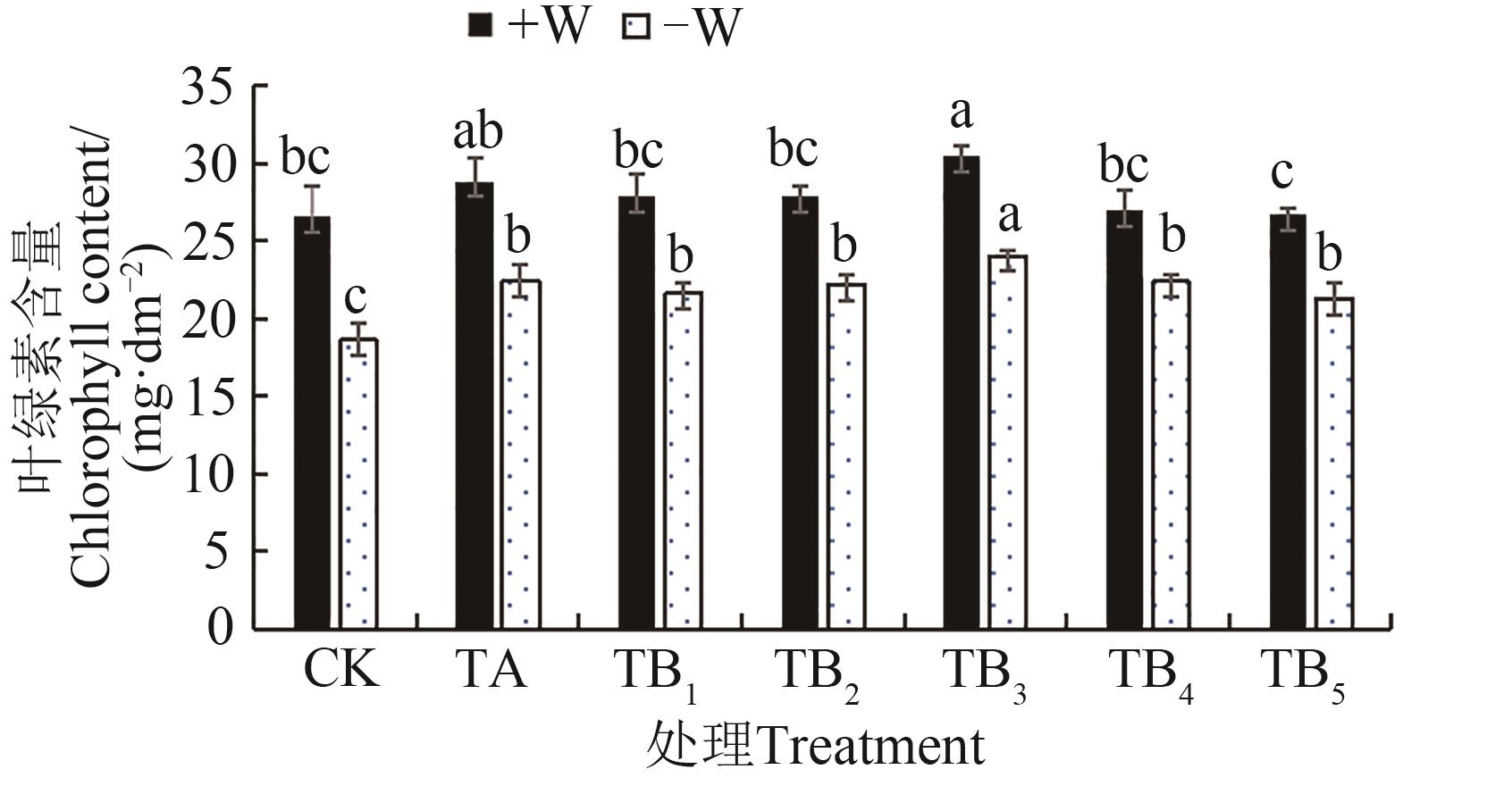
图3 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期叶绿素含量注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Chlorophyll content of maize seedling under different water conditions with water retaining agentNote:Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
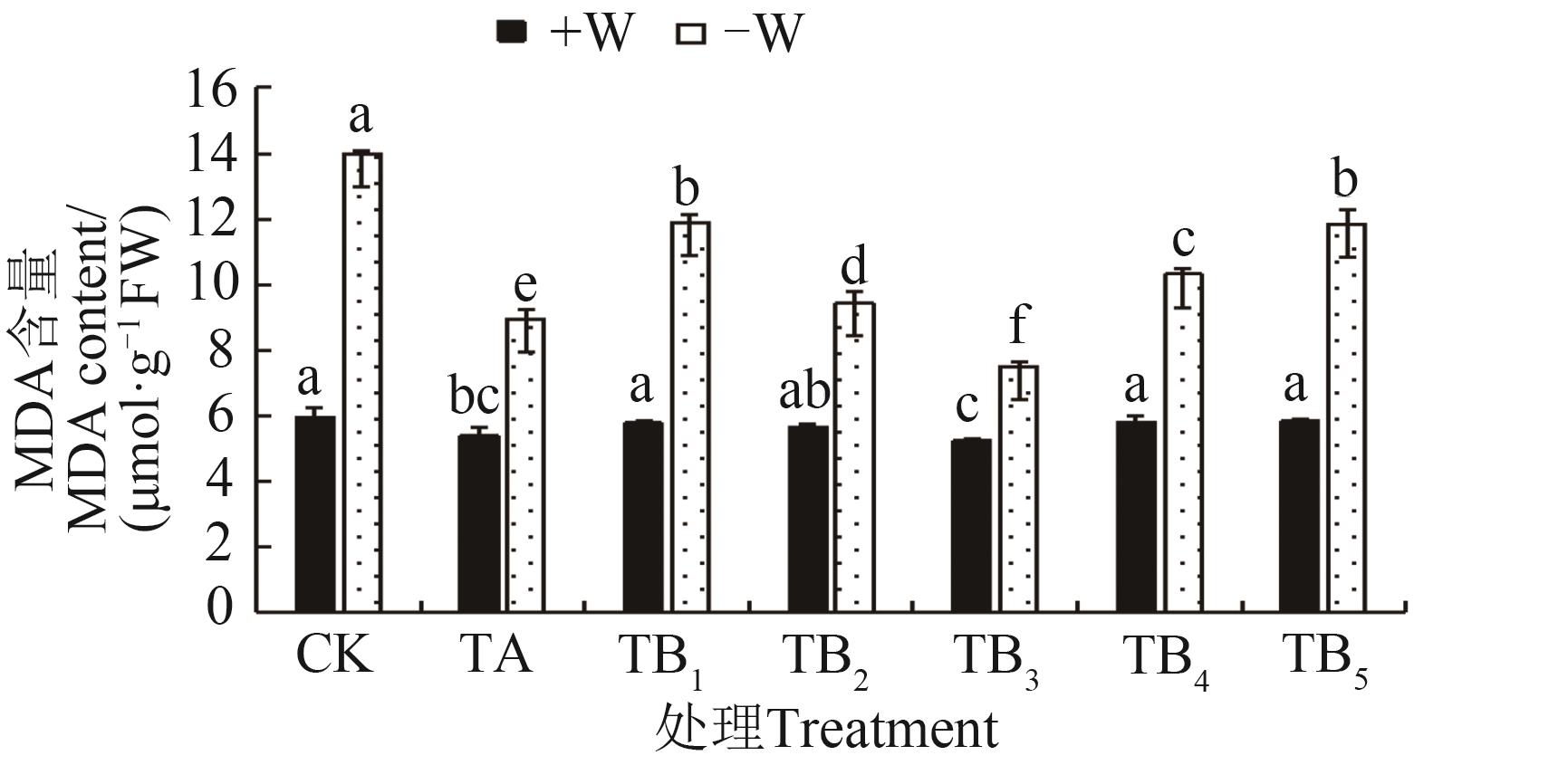
图4 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期MDA含量注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 MDA content of maize seedling under different water conditions with water retaining agentNote: Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
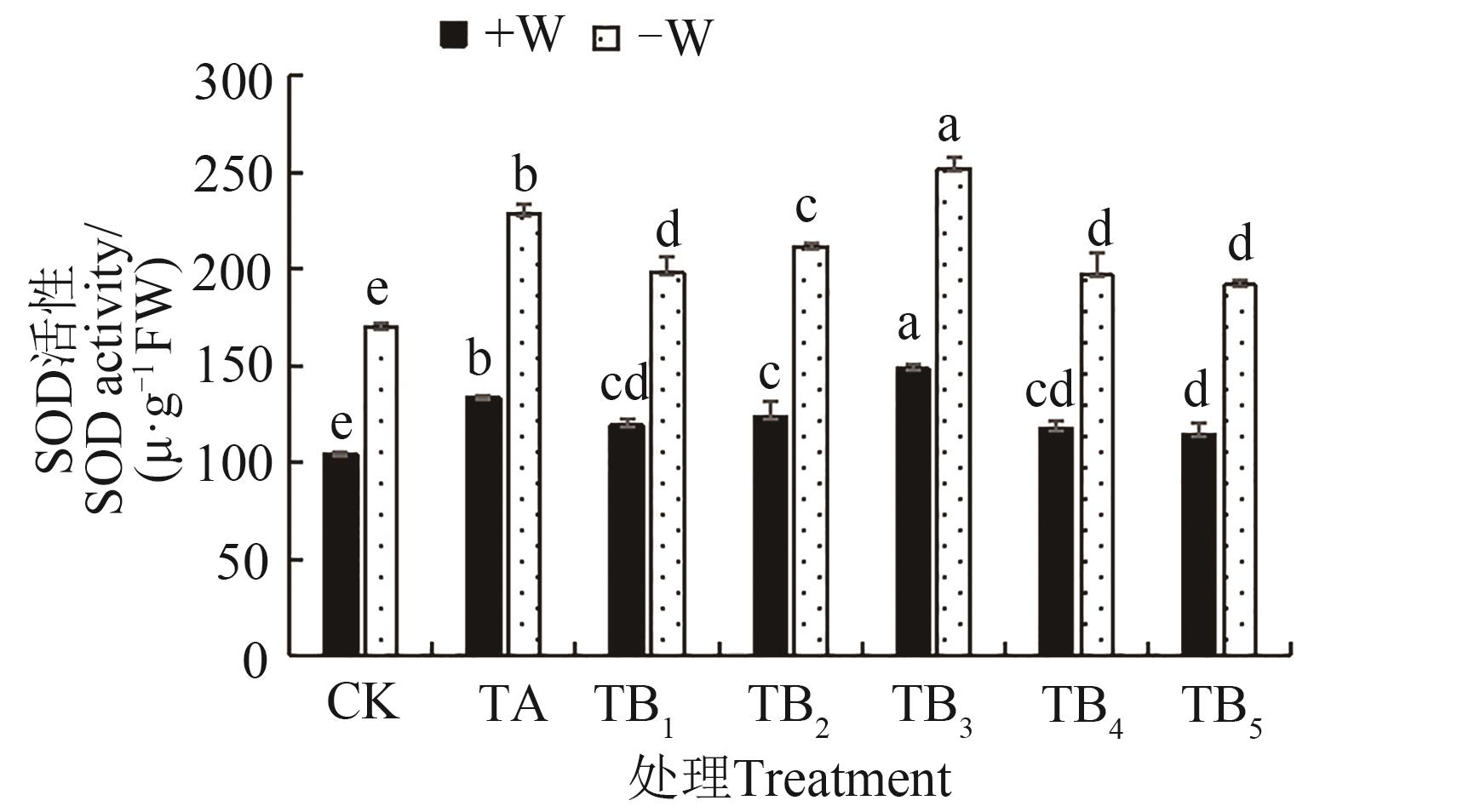
图5 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期SOD活性注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 SOD activity of maize seedling under different water conditions with water retaining agentNote:Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
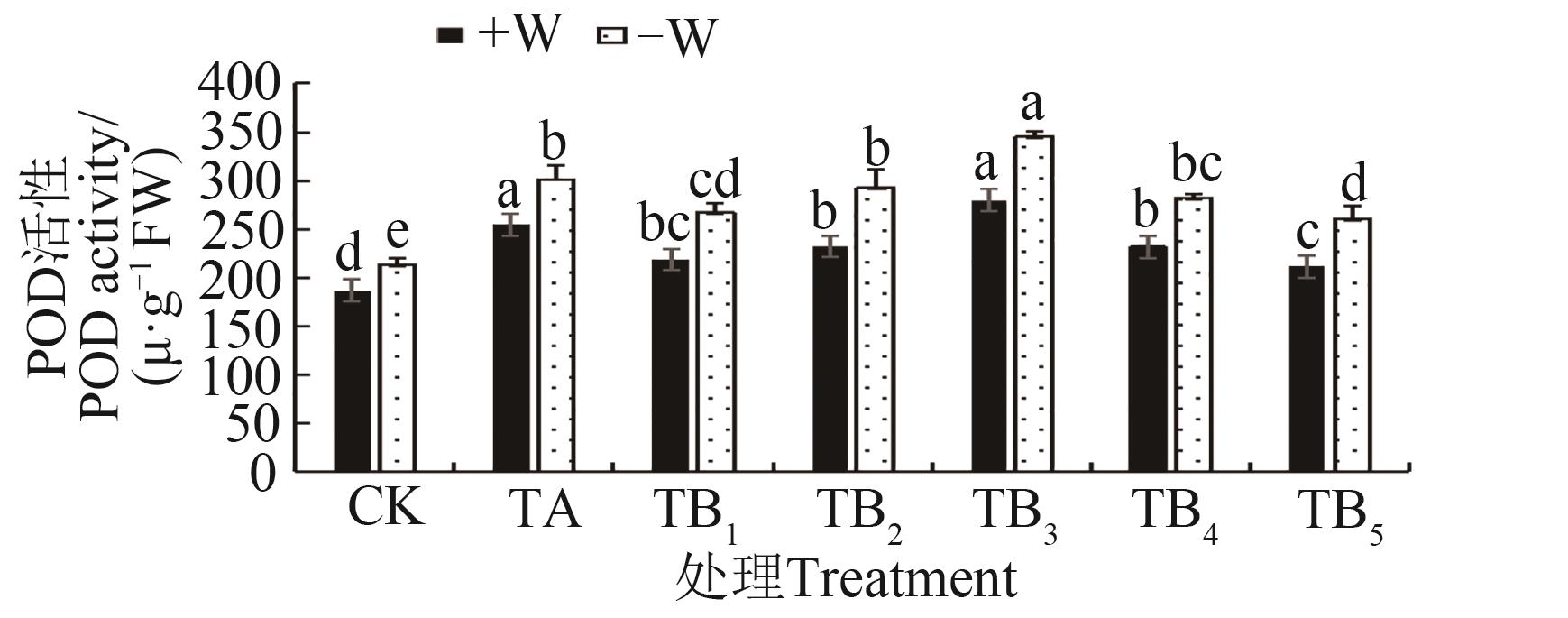
图6 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期POD活性注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 POD activity of maize seedling with water retaining agent under different water conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.

图7 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期CAT活性注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 CAT activity of maize seedling with water retaining agent under different water conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
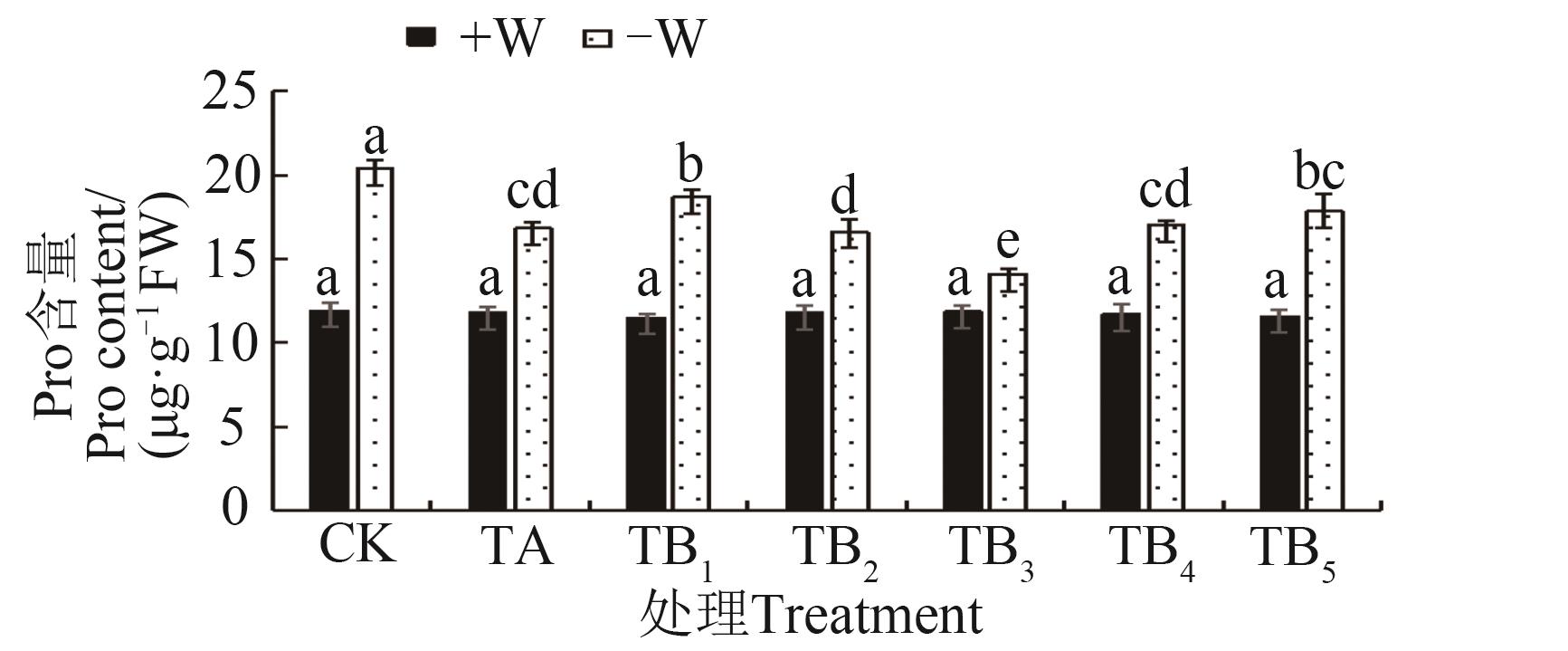
图8 不同水分条件下施用保水剂的玉米苗期脯氨酸含量注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 8 Proline content in maize seedling with water-retaining agent under different water conditionsNote: Different lowercase letters of same index indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 鲁晨曦, 张军泽, 赵廷阳, 等. 我国人工林生态系统的水成本核算[J]. 自然资源学报, 2016, 31(5):743-754. |
| LU C X, ZHANG J Z, ZHAO T Y, et al.. Water costs of afforestation and natural-restoration in China [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2016, 31(5):743-754. | |
| 2 | 步青云, 曹娜, 曹晓红, 等. 我国水资源开发利用中的环境管理问题及对策探讨[J]. 环境保护, 2019(9):61-63. |
| BU Q Y, CAO N, CAO X H, et al.. Environmental management of water resources exploitation and utilization in China: problems and strategies [J]. Environ. Prot., 2019(9):61-63. | |
| 3 | 陈晓艺, 曹雯, 王晓东, 等. 淮河流域南部作物生长季农业气候资源特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018,27(6):1005-1015. |
| CEHN X Y, CAO W, WANG X D, et al.. Analysis of agroclimatic resource characteristics of main crops growing season in the south of Huaihe River Basin [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2018,27(6):1005-1015. | |
| 4 | 胡聪敏, 王欣. 节水灌溉对农业可持续发展的影响[J]. 吉林农业:下半月, 2013(4):4. |
| 5 | 熊仕发,吴立文,陈益存,等. 不同种源白栎幼苗叶片对干旱胁迫的响应及抗旱性评价[J]. 生态学杂志,2020,39(12):3924-3933. |
| XIONG S F, WU L W, CHEN Y C,et al.. Response of leaf of Quercus fabri seedlings from different provenances to drought stress and drought resistance evaluation [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2020,39(12): 3924-3933. | |
| 6 | 徐露,张丹,向宇国,等.生物炭和保水剂施用对凉山州紫色土理化性质及水分特征的影响[J]. 西南农业学报,2021,34(4): 777-783. |
| XU L, ZHANG D, XIANG Y G, et al..Effects of biochar and polyacrylamide on water and fertilizer retention capacity of purple soil [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2021,34(4): 777-783. | |
| 7 | 于玲玲,赵贵元,崔婧婧,等.施用生物炭对玉米田土壤呼吸及水分利用效率的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50( 3) : 209-213. |
| 8 | 常潇月,常庆瑞,王晓凡,等.基于无人机高光谱影像玉米叶绿素含量估算[J].干旱地区农业研究,2019,37(1) :66-73. |
| CHANG X Y, CHANG Q R, WANG X F, et al..Estimation of maize leaf chlorophyll contents based on UAV hyperspectral drone image [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2019,37(1):66-73. | |
| 9 | YANG L X, YANG Y, ZHANG C, et al..Influence of super absorbent pol-ymer on soil water retention,seed germination and plant survivals for rocky slopes eco-engineering [J]. Ecol. Eng., 2014,62: 27-32. |
| 10 | 刘辰宇,马蕊,罗文静,等.保水剂用量对胡杨幼苗生长、光合特性和抗逆生理的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2022,44(3):36-44. |
| LIU C Y, MA R, LUO W J, et al.. Effects of super absorbent polymer dosage on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and stress-resistance physiology of Populus euphratica seedlings [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2022,44(3):36-44. | |
| 11 | KHALED H, FAWY H A.Effect of different levels of humic acids on the nutrient content,plant growth,and soil properties under conditions of salinity [J].Soil Water Res.,2011,6(1): 21-29. |
| 12 | 陈瑞环,王萍,刘云,等. 耐盐保水剂的合成及其性能[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(6):1750-1754, 1798. |
| CHEN R H, WANG P, LIU Y, et al.. Synthesis and performance of anti-salt water retention agent [J].Chem. Ind. Eng. Progress, 2015, 34(6):1750-1754, 1798. | |
| 13 | 李玉和, 胡伟, 秦端端, 等. 利用保水剂调节污泥发酵起始水分的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12):2527-2534. |
| LI Y H, HU W, QIN D D, et al.. Study on regulation of sewage sludge water content by water retaining agent at the initial stage of composting [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(12):2527-2534. | |
| 14 | 李荣,勉有明,侯贤清,等.秸秆还田下保水剂用量对砂性土性状与玉米产量的影响[J].农业机械学报,2021,52(9):260-271. |
| LI R, MIAN Y M, HOU X Q, et al.. Effect of super absorbent polymer rate on sandy soil property and maize yield under straw returning [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach.,2021,52(9):260-271. | |
| 15 | GE H C, PANG W, LUO D K. Graft copolymerization of chitosan with acrylic acid under microwave irradiation and its water absorbency [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 66(3):372-378. |
| 16 | 乔宁,李美芹,吕金浮,等.番茄黄化曲叶病毒双抗体夹心ELISA检测方法的初步建立[J].核农学报 2013,27(4): 473-478. |
| QIAO N, LI M Q, LYU J F, et al..Establishment of double antibody sandwich ELISA for tomato yellow leaf curl virus [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2013,27(4): 473-478. | |
| 17 | ZHAO Y, FANG L, TAN T. Optimization of the preparation of a poly (aspartic acid) superabsorbent resin with response surface methodology [J]. J. Appl. Polymer Sci., 2006, 102(3):2616-2622. |
| 18 | 侯贤清, 李荣, 何文寿,等. 保水剂施用量对土壤水分利用及马铃薯生长的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2015, 41(5):558-566. |
| HOU X Q, LI R, HE W S, et al..Effect of super absorbent dosage on water use of soil and growth of potato [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2015, 41(5):558-566. | |
| 19 | GAO T M, WU Y, LI F, et al.. Effects of water stress on physiological characteristics and growth under water stress in seedling of sesame [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2017,31(11):2229-2235. |
| 20 | 岑宇, 刘美珍. 凝结水对干旱胁迫下羊草和冰草生理生态特征及叶片形态的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(11):1119-1207. |
| CEN Y, LIU M Z. Effects of dew on eco-physiological traits and leaf structures of Leymus chinensis and Agropy roncristatum grown under drought stress [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2017, 41(11):1119-1207. | |
| 21 | 赵国庆.冬小麦产量与水分利用效率对活化水灌溉的响应研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2021. |
| ZHAO G Q. Study on the response of winter wheat yield and water-use efficiency to activated water irrigation [D]. Yangling: Northwest A& F University, 2021. | |
| 22 | 叶满辉, 王丽. 聚天冬氨酸/木质纤维素水凝胶的制备及吸附性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016,33(9): 2094-2103. |
| YE M H, WANG L. Preparation and absorption properties of polyaspartic acid/lignocellulose hydrogels [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sin., 2016,33(9): 2094-2103. | |
| 23 | LIU X H, WANG W J, DING Y F, et al.. Study on the synthesis conditions of scale inhibitor,polyaspartic acid derivative [J]. Ind. Water Treat., 2014, 34(1):61-64. |
| 24 | 田茜, 王栋, 张文兰, 等. 老化处理对大豆种子活力及线粒体抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(4):168-175. |
| TIAN X, WANG D, ZHANG W L, et al.. Effect of artificial aging on soybean seed vigor and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in mitochondria [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2016,52(4):168-175. | |
| 25 | 何海军, 寇思荣, 王晓娟. 干旱胁迫对不同株型玉米光合特性及产量性状的影响 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2011, 29(3):63-66, 74. |
| HE H J, KOU S R, WANG X J. Effects of drought stress onphotosynthetic characteristics and yield components of different plant types of corn [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2011, 29(3):63-66, 74. | |
| 26 | 赵玉坤, 武继承. 不同用量保水剂对玉米苗期生理生态特性的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2010(6):33-36. |
| ZHAO Y K, WU J C. Effects of different quantity water-retaining agent on ecophysiological characteristics of maize in seedling stage [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2010(6):33-36. | |
| 27 | 张丽光, 李丹, 刘磊, 等. 不同施肥种植模式对玉米光合特性、养分效率及产量性状的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(2):115-119. |
| ZHANG L G, LI D, LIU L, et al.. Effects of different fertilization and planting patter on photosynthetic charaters, nutrients efficiency and yield traits of maize [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2013, 27(2):115-119. | |
| 28 | 李长志, 李欢, 刘庆, 等. 不同生长时期干旱胁迫甘薯根系生长及荧光生理的特性比较[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(2):511-517. |
| LI C Z, LI H, LIU Q, et al.. Comparison of root development and fluorescent physiological characteristics of sweet potato exposure to drought stress in different growth stages [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2016, 22(2):511-517. | |
| 29 | WANG Y F, ZHANG Z Q, LIU H M, et al.. Overexpression of an alfalfa (Medicago sativa) gene, MsDUF, negatively impacted seed germination and response to osmotic stress in transgenic tobacco [J]. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Culture, 2018, 132(3):525-534. |
| 30 | 忽雪琦, 李东阳, 严加坤, 等. 干旱胁迫下外源茉莉酸甲酯对玉米幼苗根系吸水的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018,54(6): 991-998. |
| HU X Q, LI D Y, YAN J K, et al.. Effects of exogenous methyl jasmonate on water absorption capacity of maize (Zea mays L.) seedling root under drought stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2018,54(6):991-998. | |
| 31 | 陈浩维, 邓明华, 黄尧瑶, 等. 干旱胁迫对玫瑰花瓣膜脂过氧化及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(5):885-893. |
| CHEN H W, DENG M H, HUANG Y Y, et al..Membrane lipid peroxidation andantioxygen enzyme activities of rose patals under drought stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2018,38(5):885-893. | |
| 32 | 杜彩艳, 金桂梅, 段宗颜, 等. 干旱胁迫对玉米苗期植株生长和保护酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(3):124-129. |
| DU C Y, JIN G M, DUAN Z Y, et al.. Effect of drought stress on growth and activities of antioxidant enzymes of maize seedling [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2015, 33(3):124-129. | |
| 33 | GAO J, ZHANG R H, WANG W B, et al.. Effects of drought stress on performance of photosystem II in maize seedling stage [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015, 26(5):1391-1396. |
| 34 | ZHANG X H, GAO J, DU W L, et al.. Effects of drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics of maize hybrids at seedling stage [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2015, 41(1):154-159. |
| 35 | CUI L M, WANG X X, XUAN H D, et al.. Changes in several physiological and biochemical indices of maize seedling roots caused by drought stress [J]. Plant Dis. Pests, 2015(Z1),35-37, 43. |
| 36 | 柳燕兰, 郭贤仕, 马明生. 苗期干旱胁迫及复水对春玉米叶片光能利用特性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1):339-343. |
| LIU Y L, GUO X S, MA M S. Effects of drought stress and rehydration at seedling stage on light energy utilization and antioxidant enzyme activities of spring maize leaves [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2018, 32(1):339-343. | |
| 37 | YANG Y H, WU J C, ZHAO S W, et al..Effects of long-term super absorbent polymer and organic manure on soil structure and organic catbon distribution in different soil layers [J/OL]. Soil Tillage Res., 2021,206(7):104781[2023-03-16]. . |
| 38 | 张仁和, 薛吉全, 浦军. 干旱胁迫对玉米苗期植株生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(3):521-528. |
| ZHANG R H, XUE J Q, PU J. Effects of drought stress on plant growth and photosynthetic traits in maize seedlings [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2011, 37(3):521-528. | |
| 39 | 王军辉,查学强,姜绍通. 保水剂对玉米幼苗生长的影响[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2008,31(10):1644-1647. |
| WANG J H, ZHA X Q, JIANG S T. Study onwaterretaining agents influencing the growth of maize seedlings (Zea may) [J]. J. Hefei Univ. Technol., 2008,31(10):1644-1647. | |
| 40 | 杨杰. 保水剂对高羊茅种子萌发及幼苗生理的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(1):351-356. |
| YANG J. Effect of super ansorbent polymer on germination and physiological characteristics of festuca arundinacea [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 24(1):351-356. | |
| 41 | 温晓晴, 杨善, 周鸿凯, 等. 2种水分条件下钾肥对甘蔗叶片脯氨酸合成积累的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(7):109-114. |
| WEN X Q, YANG S, ZHOU H K, et al.. Effects of potassium fertilizer on biosynthesis and accumulation of proline in sugarcane leaves under two moisture conditions [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 44(7):109-114. | |
| 42 | 王慧春. 干旱胁迫条件下光对脯氨酸合成的影响及其与ABA的关系[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2013. |
| WANG H C. Effects of light on proline synthesis under drought stress and its relationship with ABA [D].Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2013. | |
| 43 | LI L J, GU W R, MENG Y, et al.. Physiological and biochemical mechanism of spermidine improving drought resistance in maize seedlings under drought stress [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2018, 29(2):554-564. |
| 44 | 王利彬, 祖伟, 董守坤, 等. 干旱程度及时期对复水后大豆生长和代谢补偿效应的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(11):150-156. |
| WANG L B, ZU W, DONG S K, et al.. Effects of drought stresses and times on compensation effect after re-watering in soybean [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2015, 31(11):150-156. |
| [1] | 李江博, 高文举, 运晓东, 赵杰银, 耿世伟, 韩春斌, 陈全家, 陈琴. 不同水分胁迫处理对陆地棉核心种质资源的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 26-39. |
| [2] | 黄丽芳, 龙宇宙, 李金芹, 董云萍, 王晓阳, 陈鹏, 王宪文, 闫林. 低温胁迫对小粒种咖啡幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 60-67. |
| [3] | 陈炟, 巨吉生, 马麒, 徐守振, 刘娟娟, 袁文敏, 李吉莲, 王彩香, 宿俊吉. FeNPs对苗期棉花根系生长及其对干旱响应的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 49-57. |
| [4] | 郝艳玲, 闫伟. 混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| [5] | 崔宏亮, 宋晓晓, 姚庆, 安万刚, 邢宝, 秦培友. 伊犁河谷不同藜麦品种对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 32-45. |
| [6] | 彭田伟, 谢会雅, 李思军, 刘怡轩, 帅开峰, 彭媛媛, 王青, 李迪秦. 复硝酚钠和枯草芽孢杆菌复配对烟苗生长和生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 154-161. |
| [7] | 郭瑞锋, 任月梅, 杨忠, 刘贵山, 任广兵, 张绶, 朱文娟. 草甘膦铵盐诱导谷子雄性不育的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 35-43. |
| [8] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| [9] | 杨瑞萍1,刘瑞香1,马迎梅1*,郭占斌2,张宏武2,白宇1,赵新宇1. 不同藜麦资源的抗旱性评价及渗透调节剂对其抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| [10] | 张嘉雯,卢绍浩,赵喆,赵铭钦*. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下烟草幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 78-86. |
| [11] | 张琛,韩婷,马洁,杨涓,刘根红,郑国琦* . 起垄高度对黑果枸杞生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 153-161. |
| [12] | 胡博,闫伟*,刘宇,郝艳玲. 三种桑生理特性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(4): 61-67. |
| [13] | 田梅§,曹慧雅§,张明烁§,张子璇,杨冬月,李浩然,马春英*. 红花在萌发期和幼苗期对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(5): 49-54. |
| [14] | 秦岭,陈二影,杨延兵,张艳亭,孔清华,张华文,王海莲,王润丰,管延安*. 干旱和复水对不同耐旱型谷子品种苗期生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 146-151. |
| [15] | 王梦园1,杜延全2,朱建强1*. 复合促生菌对小麦苗期生长和土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 98-106. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号