




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 222-232.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0268
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
米春娇1( ), 孙洪仁1(
), 孙洪仁1( ), 张吉萍2, 吕玉才2, 张砚迪3
), 张吉萍2, 吕玉才2, 张砚迪3
收稿日期:2023-04-06
接受日期:2023-06-25
出版日期:2025-01-15
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
孙洪仁
作者简介:米春娇 E-mail:mcj@cau.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Chunjiao MI1( ), Hongren SUN1(
), Hongren SUN1( ), Jiping ZHANG2, Yucai LYU2, Yandi ZHANG3
), Jiping ZHANG2, Yucai LYU2, Yandi ZHANG3
Received:2023-04-06
Accepted:2023-06-25
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Hongren SUN
摘要:
为给我国番茄测土施磷提供有效参考,在数据库中检索我国开展的番茄施肥相关试验文献,并采用零散试验数据整合法和养分平衡-地力差减法新应用公式,对我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标与推荐施磷量进行研究。结果表明,我国番茄露地土壤有效磷第1~6级丰缺指标依次为:≥296.9、76.6~296.8、19.8~76.5、5.1~19.7、1.3~5.0和<1.2 mg·kg-1,设施土壤有效磷第1~6级丰缺指标依次为:≥298.4、79.0~298.3、20.9~78.9、5.5~20.8、1.5~5.4和<1.4 mg·kg-1,露地+设施土壤有效磷第1~6级丰缺指标依次为:≥313.0、81.0~312.9、20.9~80.9、5.4~20.8、1.4~5.3和<1.3 mg·kg-1。当磷肥当季利用率15%~35%、番茄目标产量45~195 t·hm-2时,土壤有效磷丰缺级别第1~6级的推荐施磷量依次为0、13~130、26~260、39~390、51~520和64~650 kg·hm-2。该研究建立了我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标推荐施磷系统,为我国番茄测土施磷提供了科学依据。
中图分类号:
米春娇, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 张砚迪. 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标和推荐施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 222-232.
Chunjiao MI, Hongren SUN, Jiping ZHANG, Yucai LYU, Yandi ZHANG. Abundance-deficiency Index of Soil Available Phosphorus and Recommended Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rates for Tomato in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 222-232.
种植条件 Planting contidion | 地区(试验数量) Region involved (number of experiments) | 品种 数量 Number of varieties | 土壤 类型 数量 Number of soil types | 土壤pH Soil pH | 土壤有效磷含量 Soil available P content/ (mg·kg-1) | 缺磷处理 产量 Yield of no P fertilization treatment/ (kg·hm-2) | 施磷处理 产量 Yield of P fertilization treatment/ (kg·hm-2) | 施磷量 P application rate (P2O5)/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
露地 Open field | 北京(40)、辽宁(18)、新疆(10)、浙江(6)、天津(3)、重庆(2)、贵州(2)、安徽(1)、福建(1)、甘肃(1)、内蒙古(1)、宁夏(1)、山东(1)、山西(1)、上海(1)、 Beijing(45), Liaoning(18),Xinjiang(10),Zhejiang(6),Tianjin(3),Chongqing(2),Guizhou(2),Anhui(1),Fujian(1),Gansu(1),Inner Mongolia(1),Ningxia(1),Shandong(1),Shanxi(1),Shanghai(1) | 23 | 16 | 5.6~8.9 | 3.4~368.7 | 5 877~161 037 | 6 357~180 510 | 22~675 |
设施 Facility | 辽宁(17)、山东(16)、河南(8)、河北(7)、北京(5)、甘肃(5)、陕西(3)、安徽(2)、山西(2)、黑龙江(1)、江苏(1)、内蒙古(1)、宁夏(1) Liaoning(17),Shandong(16),Henan(8),Hebei(7),Beijing(5), Gansu(5),Shaanxi(3),Anhui(2),Shanxi(2),Heilongjiang(1),Jiangsu(1),Inner Mongolia(1),Ningxia(1) | 35 | 19 | 5.3~8.4 | 6.9~582.0 | 31 260~220 464 | 42 400~230 432 | 29~891 |
表1 我国番茄施磷试验文献中与土壤有效磷丰缺指标研究相关信息
Table 1 Relevant information about soil available P abundance-deficiency index from P fertilization experimental literature for tomato in China
种植条件 Planting contidion | 地区(试验数量) Region involved (number of experiments) | 品种 数量 Number of varieties | 土壤 类型 数量 Number of soil types | 土壤pH Soil pH | 土壤有效磷含量 Soil available P content/ (mg·kg-1) | 缺磷处理 产量 Yield of no P fertilization treatment/ (kg·hm-2) | 施磷处理 产量 Yield of P fertilization treatment/ (kg·hm-2) | 施磷量 P application rate (P2O5)/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
露地 Open field | 北京(40)、辽宁(18)、新疆(10)、浙江(6)、天津(3)、重庆(2)、贵州(2)、安徽(1)、福建(1)、甘肃(1)、内蒙古(1)、宁夏(1)、山东(1)、山西(1)、上海(1)、 Beijing(45), Liaoning(18),Xinjiang(10),Zhejiang(6),Tianjin(3),Chongqing(2),Guizhou(2),Anhui(1),Fujian(1),Gansu(1),Inner Mongolia(1),Ningxia(1),Shandong(1),Shanxi(1),Shanghai(1) | 23 | 16 | 5.6~8.9 | 3.4~368.7 | 5 877~161 037 | 6 357~180 510 | 22~675 |
设施 Facility | 辽宁(17)、山东(16)、河南(8)、河北(7)、北京(5)、甘肃(5)、陕西(3)、安徽(2)、山西(2)、黑龙江(1)、江苏(1)、内蒙古(1)、宁夏(1) Liaoning(17),Shandong(16),Henan(8),Hebei(7),Beijing(5), Gansu(5),Shaanxi(3),Anhui(2),Shanxi(2),Heilongjiang(1),Jiangsu(1),Inner Mongolia(1),Ningxia(1) | 35 | 19 | 5.3~8.4 | 6.9~582.0 | 31 260~220 464 | 42 400~230 432 | 29~891 |
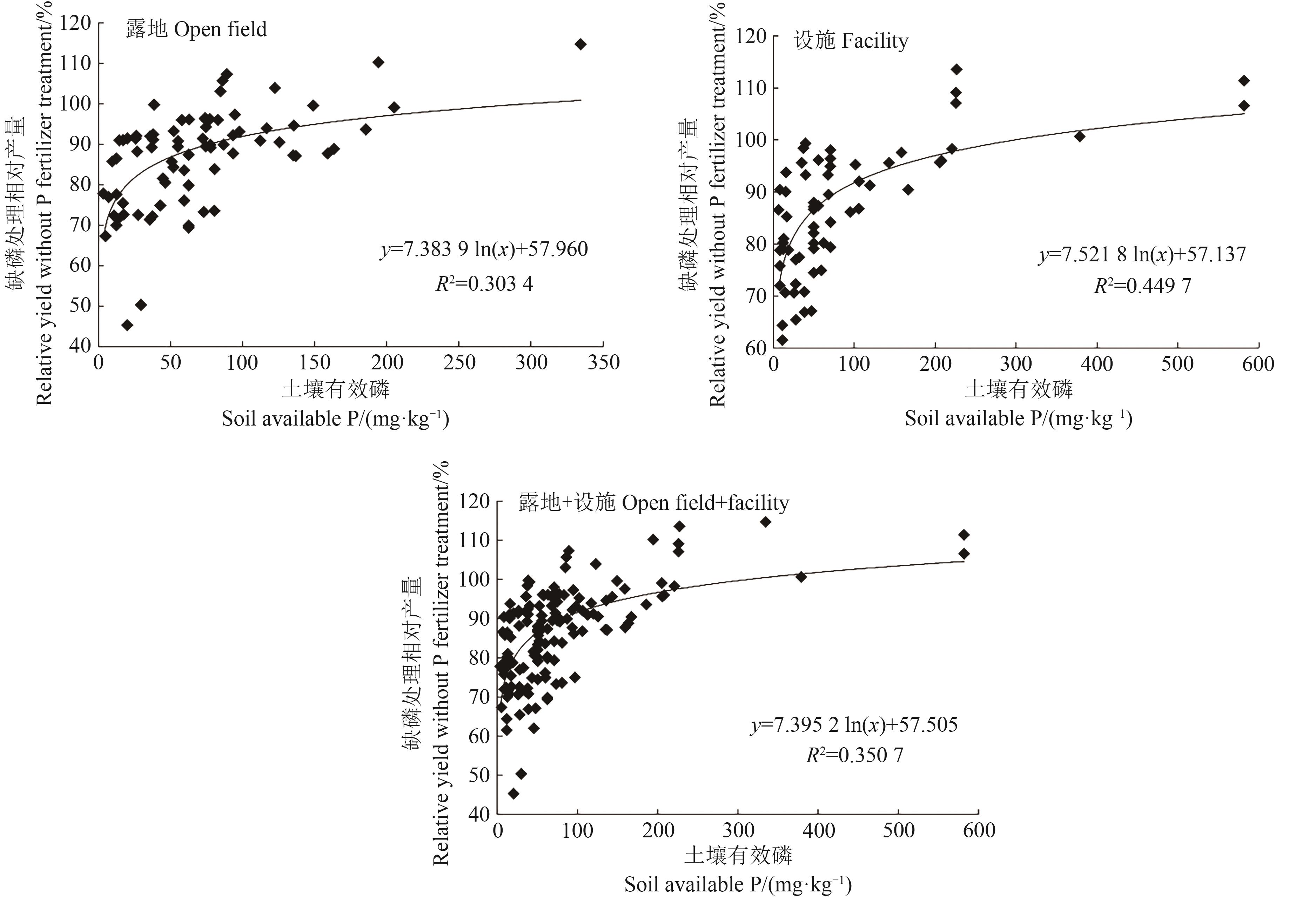
图1 我国土壤有效磷含量与番茄缺磷处理相对产量回归关系
Fig. 1 Regression relationship between soil available P content and relative yield without P fertilizer treatment for tomato in China
| 丰缺级别 Abundance-deficiency level | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
缺磷处理相对产量 Relative yield without P fertilizer treatment/% | <60 | 60~70 | 70~80 | 80~90 | 90~100(95) | ≥100(95) | |
土壤有效磷 Soil available P/ (mg·kg-1) | 露地 Open field | < | 5.1~19.7 | 19.8~76.5 | 76.6~296.8(150.8) | ≥296.9(150.9) | |
| 设施 Facility | < | 20.9~78.9 | 79.0~298.3(153.4) | ≥298.4(153.5) | |||
| 露地+设施 Open field+facility | < | 5.4~20.8 | 20.9~80.9 | 81.0~312.9(159.1) | ≥313.0(159.2) | ||
表2 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标
Table 2 Abundance-deficiency index of soil available P for tomato in China
| 丰缺级别 Abundance-deficiency level | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
缺磷处理相对产量 Relative yield without P fertilizer treatment/% | <60 | 60~70 | 70~80 | 80~90 | 90~100(95) | ≥100(95) | |
土壤有效磷 Soil available P/ (mg·kg-1) | 露地 Open field | < | 5.1~19.7 | 19.8~76.5 | 76.6~296.8(150.8) | ≥296.9(150.9) | |
| 设施 Facility | < | 20.9~78.9 | 79.0~298.3(153.4) | ≥298.4(153.5) | |||
| 露地+设施 Open field+facility | < | 5.4~20.8 | 20.9~80.9 | 81.0~312.9(159.1) | ≥313.0(159.2) | ||
目标产量 Target yield/ (t·hm-2) | 磷肥当季利用率 P fertilizer efficiency in current season/% | 推荐施磷量 Recommended P fertilizer application amount /(kg·hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 45 | 35 | ≥64 | 51 | 39 | 26 | 13 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥75 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 15 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥90 | 72 | 54 | 36 | 18 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥113 | 90 | 68 | 45 | 23 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 60 | 35 | ≥86 | 69 | 51 | 34 | 17 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥100 | 80 | 60 | 40 | 20 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥120 | 96 | 72 | 48 | 24 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥200 | 160 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 0 | |
| 75 | 35 | ≥107 | 86 | 64 | 43 | 21 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥125 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥188 | 150 | 113 | 75 | 38 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥250 | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | |
| 90 | 35 | ≥129 | 103 | 77 | 51 | 26 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥180 | 144 | 108 | 72 | 36 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥225 | 180 | 135 | 90 | 45 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 105 | 35 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥175 | 140 | 105 | 70 | 35 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥210 | 168 | 126 | 84 | 42 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥263 | 210 | 158 | 105 | 53 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥350 | 280 | 210 | 140 | 70 | 0 | |
| 120 | 35 | ≥171 | 137 | 103 | 69 | 34 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥200 | 160 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥240 | 192 | 144 | 96 | 48 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥400 | 320 | 240 | 160 | 80 | 0 | |
| 135 | 35 | ≥193 | 154 | 116 | 77 | 39 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥225 | 180 | 135 | 90 | 45 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥270 | 216 | 162 | 108 | 54 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥338 | 270 | 203 | 135 | 68 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 150 | 35 | ≥214 | 171 | 129 | 86 | 43 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥250 | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥375 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 75 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥500 | 400 | 300 | 200 | 100 | 0 | |
| 165 | 35 | ≥236 | 189 | 141 | 94 | 47 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥275 | 220 | 165 | 110 | 55 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥330 | 264 | 198 | 132 | 66 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥413 | 330 | 248 | 165 | 83 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥550 | 440 | 330 | 220 | 110 | 0 | |
| 180 | 35 | ≥257 | 206 | 154 | 103 | 51 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥360 | 288 | 216 | 144 | 72 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥600 | 480 | 360 | 240 | 120 | 0 | |
| 195 | 35 | ≥279 | 223 | 167 | 111 | 56 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥325 | 260 | 195 | 130 | 65 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥390 | 312 | 234 | 156 | 78 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥488 | 390 | 293 | 195 | 98 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥650 | 520 | 390 | 260 | 130 | 0 | |
表3 我国番茄在不同目标产量和不同磷肥当季利用率下各个丰缺级别土壤的推荐施磷量
Table 3 Recommended P fertilizer application amount of soil in different abundance-deficiency levels under different target yields and utilization rate of P fertilizer in current season for tomato in China
目标产量 Target yield/ (t·hm-2) | 磷肥当季利用率 P fertilizer efficiency in current season/% | 推荐施磷量 Recommended P fertilizer application amount /(kg·hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 45 | 35 | ≥64 | 51 | 39 | 26 | 13 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥75 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 15 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥90 | 72 | 54 | 36 | 18 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥113 | 90 | 68 | 45 | 23 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 60 | 35 | ≥86 | 69 | 51 | 34 | 17 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥100 | 80 | 60 | 40 | 20 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥120 | 96 | 72 | 48 | 24 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥200 | 160 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 0 | |
| 75 | 35 | ≥107 | 86 | 64 | 43 | 21 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥125 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥188 | 150 | 113 | 75 | 38 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥250 | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | |
| 90 | 35 | ≥129 | 103 | 77 | 51 | 26 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥180 | 144 | 108 | 72 | 36 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥225 | 180 | 135 | 90 | 45 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 105 | 35 | ≥150 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 30 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥175 | 140 | 105 | 70 | 35 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥210 | 168 | 126 | 84 | 42 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥263 | 210 | 158 | 105 | 53 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥350 | 280 | 210 | 140 | 70 | 0 | |
| 120 | 35 | ≥171 | 137 | 103 | 69 | 34 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥200 | 160 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥240 | 192 | 144 | 96 | 48 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥400 | 320 | 240 | 160 | 80 | 0 | |
| 135 | 35 | ≥193 | 154 | 116 | 77 | 39 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥225 | 180 | 135 | 90 | 45 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥270 | 216 | 162 | 108 | 54 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥338 | 270 | 203 | 135 | 68 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 150 | 35 | ≥214 | 171 | 129 | 86 | 43 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥250 | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥375 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 75 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥500 | 400 | 300 | 200 | 100 | 0 | |
| 165 | 35 | ≥236 | 189 | 141 | 94 | 47 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥275 | 220 | 165 | 110 | 55 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥330 | 264 | 198 | 132 | 66 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥413 | 330 | 248 | 165 | 83 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥550 | 440 | 330 | 220 | 110 | 0 | |
| 180 | 35 | ≥257 | 206 | 154 | 103 | 51 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥300 | 240 | 180 | 120 | 60 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥360 | 288 | 216 | 144 | 72 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥600 | 480 | 360 | 240 | 120 | 0 | |
| 195 | 35 | ≥279 | 223 | 167 | 111 | 56 | 0 |
| 30 | ≥325 | 260 | 195 | 130 | 65 | 0 | |
| 25 | ≥390 | 312 | 234 | 156 | 78 | 0 | |
| 20 | ≥488 | 390 | 293 | 195 | 98 | 0 | |
| 15 | ≥650 | 520 | 390 | 260 | 130 | 0 | |
| 1 | 孙永珍, 贺靖, 魏芳, 等. “十三五”我国番茄产业发展及其国际竞争力评价[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2023, 36(1):112-116. |
| SUN Y Z, HE J, WEI F, et al.. Evaluation on the development and international competitiveness of China’s tomato industry during the 13th Five-Year Plan period [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2023, 36(1):112-116. | |
| 2 | 周鸣铮. 中国的测土施肥[J]. 土壤通报, 1987(1):7-13. |
| 3 | 黄德明. 我国农田土壤养分肥力状况及丰缺指标[J]. 华北农学报, 1988, 3(2):46-53. |
| HUANG D M. Soil fertility and fertility index for cropland soils in China [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 1988, 3(2):46-53. | |
| 4 | 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 冮丽华, 等. 我国水稻土壤有效磷和速效钾丰缺指标与适宜磷钾施用量研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(5):1-10. |
| SUN H R, ZHANG J P, GANG L H, et al.. Study on the abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and K and appropriate nutrient application rates of P and K for rice in China [J]. China Rice, 2018, 24(5):1-10. | |
| 5 | 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 冮丽华, 等. 中国小麦土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(21):30-37. |
| SUN H R, ZHANG J P, GANG L H, et al.. The abundance-deficiency indices of soil available P and appropriate phosphrous application rates for wheat in China [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2019, 35(21):30-37. | |
| 6 | 孙洪仁, 赵雅晴, 曾红, 等. 中国若干区域玉米土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(2):26-34. |
| SUN H R, ZHAO Y Q, ZENG H, et al.. The abundance-deficiency indices of soil available P and appropriate phosphorus application rates for corn in several regions of China [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2017(2):26-34. | |
| 7 | 孙洪仁, 冮丽华, 张吉萍, 等. 中国马铃薯土壤氮磷钾丰缺指标与适宜施肥量[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(5):78-85. |
| SUN H R, GANG L H, ZHANG J P, et al.. The abundance-deficiency indexes of soil NPK and appropriate fertilization rates for potato in China [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2020, 36(5):78-85. | |
| 8 | 武书敏, 黄德明, 徐建铭, 等. 露地西红柿土壤养分丰缺指标研究[J]. 蔬菜, 1986(3):5-8. |
| 9 | 吴建繁. 北京市无公害蔬菜诊断施肥与环境效应研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2001. |
| WU J F. Study on diagnostic fertilization and environmental effect for non-pollution vegetables in Beijing [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2001. | |
| 10 | 张连云. 基于“3414”试验的土壤氮磷钾丰缺指标制定与应用研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学, 2008. |
| ZHANG L Y. Studies on abundance and deficiency index of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for the soil based on the experiment of “3414” [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2008. | |
| 11 | 康翠娥, 蔡利, 蔡锐. 保护地番茄施肥指标体系的初步建立[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2013(2):70-72. |
| 12 | 刘顺国, 韩晓日, 刘小虎. 辽宁省保护地主要蔬菜土壤养分丰缺指标建立初探[J]. 农业科技与装备, 2015(9):7-10. |
| LIU S G, HAN X R, LIU X H. Primary discussion on soil nutrition plentiful-lack index setting of main vegetables in protection area in Liaoning province [J]. Agric. Sci. Technol. Equip., 2015(9):7-10. | |
| 13 | 孙洪仁, 曾红, 刘江扬, 等. 中国农牧交错带燕麦土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(10):101-105. |
| SUN H R, ZENG H, LIU J Y, et al.. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and appropriate phosphorus application rate for oats in the farming-grazing transitional zone of China [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2018, 34(10):101-105. | |
| 14 | 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 等. 中国北方甜菜土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国糖料, 2019, 41(1):23-27. |
| SUN H R, ZHANG J P, LYU Y C, et al.. Abundance-deficiency index of soil available phosphorus and appropriate phosphorus application rates for sugar beet in the north of China [J]. Sugar Crops China, 2019, 41(1):23-27. | |
| 15 | 钟培阁, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 中国南方甘蔗土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国糖料, 2021, 43(1):51-56. |
| ZHONG P G, SUN H R, ZHANG J P, et al.. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available phosphorus and appropriate fertilizer application rates for surgarcane in the south of China [J]. Sugar Crops China, 2021, 43(1):51-56. | |
| 16 | 王彦, 朱凯迪, 孙洪仁, 等. 中国苹果土壤养分丰缺指标与适宜施肥量初步研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5):69-78. |
| WANG Y, ZHU K D, SUN H R, et al.. Abundance-deficiency index of soil nutrients and appropriate fertilizer application rates for apple planting in China: a preliminary study [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2022, 38(5):69-78. | |
| 17 | 吕志伟, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 中国棉花土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(2):197-206. |
| LYU Z W, SUN H R, ZHANG J P, et al.. Abundance-deficiency index of soil available phosphorus and the appropriate amount of phosphorus fertilizer application for cotton in China [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2022(2):197-206. | |
| 18 | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 等. 我国紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与推荐施磷量[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2022, 27(5):199-215. |
| SUN H R, WANG X G, BU Y J, et al.. Abundance and deficiency index of soil available P and the recommended P application rates for alfalfa in China [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2022, 27(5):199-215. | |
| 19 | 朱凯迪, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 我国籽实和饲草谷子土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8):2207-2216. |
| ZHU K D, SUN H R, ZHANG J P, et al.. The abundance-deficiency index of soil N and recommended nitrogen fertilizer application rates for grain and forage millets in China [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2022, 30(8):2207-2216. | |
| 20 | 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥土壤有效养分丰缺分级改良方案[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(19):1-5. |
| SUN H R, CAO Y, LIU L, et al.. An improved scheme for the grading of abundance and deficiency of soil available nutrients in soil testing and fertilizer recommendation [J]. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Veterinary Med., 2014(19):1-5. | |
| 21 | 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. “养分平衡-地力差减法”确定适宜施肥量的新应用公式[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(7):1-4. |
| SUN H R, CAO Y, LIU L, et al.. A new application formula for determining the appropriate amount of fertilizer application with the methods of nutrient balance and dissimilar subtraction of soil fertility [J]. Heilongjiang An. Sci. Veterinary Med., 2014(7):1-4. | |
| 22 | 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥不同丰缺级别土壤的适宜施肥量[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(23):7-11. |
| SUN H R, CAO Y, LIU L, et al.. The appropriate amount of fertilizer application for the soils with different levels of nutrient abundance and deficiency using soil testing and fertilizer recommendation [J]. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Veterinary Med., 2014(23):7-11. | |
| 23 | 蔡绍珍, 陈建美. 地膜覆盖栽培番茄干物质积累与养分吸收分配规律的初步研究[J]. 中国蔬菜, 1983(2):1-6. |
| 24 | 张福锁, 陈新平, 陈清. 中国主要作物施肥指南[M]. 北京:中国农业大学出版社, 2009:126-127. |
| 25 | 李建勇, 高俊杰, 徐守国, 等. 化肥施用量对有机基质栽培番茄养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(3):602-606. |
| LI J Y, GAO J J, XU S G, et al.. Effect of chemical fertilizer dose on nutrient absorption and utilization of tomato cultured in organic substrate [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2011, 19(3):602-606. | |
| 26 | 周丽群. 果类蔬菜大量元素水溶肥配方选择与应用效果研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2013. |
| ZHOU L Q. Formula selection and application effects of macronutrient type water-soluble fertilizer for fruity vegetables [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| 27 | 管西林, 吴长春, 刘彬, 等. 设施基质条件下不同茬口樱桃番茄的养分吸收及分配规律研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 49(6):1415-1422. |
| GUAN X L, WU C C, LIU B, et al.. Nutrients uptake and distribution in different cropping seasons of cherry tomato in substrate culture [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 49(6):1415-1422. | |
| 28 | 魏建林, 谭德水, 宋效宗, 等. 鲁中典型种植区设施番茄养分供需特征研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2020, 52(11):15-19, 45. |
| WEI J L, TAN D S, SONG X Z, et al.. Nutrient supply and demand characteristics of greenhouse tomato in typical planting area of central Shandong province [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2020, 52(11):15-19, 45. | |
| 29 | 何世朋, 梁斌, 武德军, 等. 设施菜地番茄的养分需求规律[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35():282-288. |
| HE S P, LIANG B, WU D J, et al.. Nutrient demand of tomato in the facility vegetable field [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2020, 35(S1):282-288. | |
| 30 | 李书田, 艾超, 何萍, 等. 我国主要蔬菜的养分吸收和需求特征[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2022(1):41-48. |
| LI S T, AI C, HE P, et al.. Characteristics of major Chinese vegetables in nutrient uptake and requirement [J]. China Veget., 2022(1):41-48. | |
| 31 | 史坚. 氮磷钾镁配比施用对春番茄产量和质量的影响[J]. 上海蔬菜, 1989(1):35, 3. |
| 32 | 肖纪珍, 任凤兰, 热沙来提. 番茄对氮磷钾的吸收规律及肥料施用效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 1990(3):114-116. |
| 33 | 朱本岳, 马秋兰, 孙韧, 等. 氮磷钾肥不同用量和配比对番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 1992(3):131-133. |
| 34 | 刘子江, 李荣华, 左敬兰, 等. 保护地番茄产量与施用化肥效应的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 1994, 25(5):222-223. |
| 35 | 周艺敏, 景海春, 兰耀龙, 等. 钾及其他元素配合施用对几种作物产量和品质的影响[J]. 土壤肥料, 1995(1):18-21, 25. |
| 36 | 董翔云, 王德清, 郭鹏程. 磷石膏在几种蔬菜作物上的应用试验[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 1996, 27(1):65-70. |
| DONG X Y, WANG D Q, GUO P C. Application of phosphorus gypsum on some vegetable crops [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 1996,27(1):65-70. | |
| 37 | 李远新, 李进辉, 何莉莉, 等. 氮磷钾配施对保护地番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国蔬菜, 1997(4):12-15. |
| LI Y X, LI J H, HE L L, et al.. The effect of N P K mixed application on yields and quality of tomato in solar greenhouse [J]. China Veget., 1997(4):12-15. | |
| 38 | 刘枫, 叶舒娅, 王文军, 等. 茄果类蔬菜营养特性及施肥效应研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 1997,25(4):56-58, 61. |
| LIU F, YE S Y, WANG W J, et al.. Nutrition characters of solanceae vegetables and fertilization effect [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 1997,25(4):56-58, 61. | |
| 39 | 朱亚萍, 石孝均, 赵治书. 番茄配方施肥研究[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 1999, 21(2):3-5. |
| ZHU Y P, SHI X J, ZHAO Z S. A study on specifically prescribed fertilization in tomato cultivation [J]. J. Southwest Agric. Univ., 1999, 21(2):3-5. | |
| 40 | 范富, 张继星, 张卫国, 等. 大棚秋番茄直播高产施肥措施数学模型的研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2002, 17(3):104-108. |
| FAN F, ZHANG J X, ZHANG W G, et al.. Models for application of fertilizer to autumnal tomatoes of growing directly for high yield in green house [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2002,17(3):104-108. | |
| 41 | 王晓燕, 郭小军, 付峰, 等. 氮、磷、钾对番茄产量的影响[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2004(5):29-30. |
| 42 | 陈明昌, 许仙菊, 张强, 等. 磷、钾与钙配合对保护地番茄钙吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(2):236-242. |
| CHEN M C, XU X J, ZHANG Q, et al.. Effects of the phosphorus, potassium cooperated with calcium on Ca absorption of tomato in greenhouse [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2005,11(2):236-242. | |
| 43 | 黄珍发. 番茄氮磷钾平衡施肥试验初报[J]. 福建热作科技, 2005(4):6-7. |
| 44 | 熊汉琴, 王朝辉. 温室番茄水肥耦合数学模型研究[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2006(5):44-46. |
| 45 | 杨建国, 马晓红, 李淑玲, 等. 滴灌条件下日光温室番茄平衡施肥研究[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2006(1):13-14. |
| 46 | 何帅, 周建伟, 赵献军. 膜下滴灌加工番茄的施肥效应分析[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2007(2):63-64, 60. |
| 47 | 李熹. 日光温室番茄磷肥需求阈值研究[D]. 石家庄:河北师范大学, 2007. |
| LI X. The research on threshold value of phosphate fertilizer in helio-greenhouse [D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2007. | |
| 48 | 马生发, 王正旭. 大棚番茄控释氮素与磷、钾肥最佳配合施用量研究[J]. 西北农业学报, 2007,16(6):267-272. |
| MA S F, WANG Z X. Optimization on application amount of controlled release N with P2O5 and K2O in tomato of greenhouse [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2007,16(6):267-272. | |
| 49 | 彭志良, 赵泽英, 胡明文, 等. 氮磷钾不同配比对早熟番茄产量的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2007(3):17-18. |
| 50 | 赵泽英, 彭志良, 王海, 等. 贵州省低热地区早春番茄平衡施肥数学模型研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007,35(23):7140-7141. |
| ZHAO Z Y, PENG Z L, WANG H, et al.. Study on mathematical model of balanced fertilization for earlier tomato in lower altitude areas in Guizhou [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2007,35(23):7140-7141. | |
| 51 | 高兵, 陈永智, 李俊良, 等. 保护地番茄氮磷钾肥效应研究[J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008,25(2):135-139. |
| GAO B, CHEN Y Z, LI J L, et al.. Study on the effect of N, P and K fertilizer on greenhouse tomato [J]. J. Qingdao Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2008,25(2):135-139. | |
| 52 | 刘新社, 黄绍敏. 豫东潮土长期定位施肥对设施番茄肥料利用率的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2008(12):97-102. |
| LIU X S, HUANG S M. Long-term effect of location fertilization on fertilizer utilization efficiency of protected tomato in fluvor aquic soil in the east of Henan province [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2008(12):97-102. | |
| 53 | 张乐森. 滨州保护地番茄氮磷钾肥料效应研究[J]. 蔬菜, 2008(10):27-31. |
| 54 | 张涛, 闵炬, 施卫明, 等. 不同磷钾肥配比对大棚蔬菜养分吸收、产量及品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2008,24(5):668-673. |
| ZHANG T, MIN J, SHI W M, et al.. Effects of chemical potash and phosphorus fertilizer input on yield, nutrient uptake and fruit quality of vegetables cultivated in plastic greenhouse [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2008,24(5):668-673. | |
| 55 | 张彦才, 李若楠, 王丽英, 等. 磷肥对日光温室番茄磷营养和产量及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008,14 (6):1193-1199. |
| ZHANG Y C, LI R N, WANG L Y, et al.. Effect of phosphorus fertilization on tomato phosphorous nutrition, yield and soil enzyme activities [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2008,14(6):1193-1199. | |
| 56 | 何明才, 陈宏宇, 吴赵平, 等. 氮磷不同配比施肥对加工番茄生长及产量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2009(2):73-74. |
| HE M C, CHEN H Y, WU Z P, et al.. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on the growth and yield of process tomato [J]. Northern Hortic., 2009(2):73-74. | |
| 57 | 汤明尧, 张炎, 胡伟, 等. 施肥对加工番茄生长发育和养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(3):26-30. |
| TANG M Y, ZHANG Y, HU W, et al.. Effects of fertilization on growth and nutrient absorption of processing tomato [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2009(3):26-30. | |
| 58 | 王恒, 金圣爱, 李俊良, 等. 山东寿光日光温室番茄磷钾肥效研究[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2009(8):48-53. |
| WANG H, JIN S A, LI J L, et al.. Studies on P and K fertilizer effects in tomato greenhouse in Shouguang city of Shandong province [J]. China Veget., 2009(8):48-53. | |
| 59 | 姚晓明, 罗明. 番茄3414试验研究[J]. 北京农业, 2009(18):36-39. |
| YAO X M, LUO M. Studies on 3414 experimental of tomato [J]. Beijing Agric., 2009(18):36-39. | |
| 60 | 龚江, 王海江, 谢海霞, 等. 膜下滴灌氮、磷、钾耦合效应对加工番茄生长和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47(5):854-858. |
| GONG J, WANG H J, XIE H X, et al.. Effect of N, P and K coupling action on growth and yield of processing tomato under film drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2010, 47(5):854-858. | |
| 61 | 沙海宁, 孙权, 李建设, 等. 不同施磷量对设施番茄生长、产量的影响及最佳施用量研究[J]. 长江蔬菜, 2010(20):59-62. |
| SHA H N, SUN Q, LI J S, et al.. Effect of phosphate on growth and yield of tomato and optimum application rate in greenhouse [J]. J. Changjiang Veget., 2010(20):59-62. | |
| 62 | 袁亭亭. 嫁接栽培与施肥水平对番茄生长发育及养分吸收利用特性的影响[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2010. |
| YUAN T T. Effect of fertilization and grafting on the growth, development and nutrient absorption and using characteristics of tomato [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2010. | |
| 63 | 张德军. 氮磷钾配施对温室秋冬茬番茄产量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2010(4):61-63. |
| ZHANG D J. Effect of different N, P, K ratios on yield of autumn-winter tomato in greenhouse [J]. Northern Hortic., 2010(4):61-63. | |
| 64 | 姜雪峰. 中产田番茄“3414”施肥试验总结[J]. 现代农业, 2011(6):22-24. |
| 65 | 刘克桐, 蔡新. 焉耆盆地加工番茄测土配方施肥试验报告[J]. 新疆农业科技, 2011(3):52-53. |
| 66 | 秦嘉海, 陈修斌, 肖占文, 等. 河西走廊日光温室主要土类供磷能力及蔬菜磷素最佳施用量的研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2011, 29(3):169-173. |
| QIN J H, CHEN X B, XIAO Z W, et al.. Phosphorus supply ability of soils and optimum phosphorus application rate for vegetables in the greenhouses in Hexi Corridor [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2011, 29(3):169-173. | |
| 67 | 袁亭亭, 宋小艺, 王忠宾, 等. 嫁接与施肥对番茄产量及氮、磷、钾吸收利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1):131-136. |
| YUAN T T, SONG X Y, WANG Z B, et al.. Effect of grafting cultivation and fertilization on the yield, NPK uptake and utilization of tomatoes [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2011, 17(1):131-136. | |
| 68 | 康喜存. 低产田设施番茄测土配方施肥校验报告[J]. 吉林蔬菜, 2012(5):62-63. |
| 69 | 孔庆玲. 磷钾肥配方增施对番茄产量影响的研究[J]. 吉林农业, 2013(5):22,24. |
| 70 | 朱静华, 李玉华, 李明悦, 等. 氮、磷、钾对设施蔬菜产量及养分循环的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(7):148-154. |
| ZHU J H, LI Y H, LI M Y, et al.. Effects of N, P, K on output and nutrient cycling under greenhouse condition [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2013, 29(7):148-154. | |
| 71 | 李凌欣. 南票区测土配方施肥参数试验总结[J]. 中国农业信息, 2014(9):106. |
| 72 | 苗锋, 刘全凤, 阚晓君, 等. 无公害番茄硝酸盐含量控制技术研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2014, 18(3):20-23. |
| MIAO F, LIU Q F, KAN X J, et al.. Study on control technology of nitrate content of pollution-free tomato [J]. J. Hebei Agric. Sci., 2014, 18(3):20-23. | |
| 73 | 王明斌. 凤城市宝山镇西红柿“2+1”肥效田间试验报告[J]. 农民致富之友, 2014(14):133. |
| 74 | 于海涛. 低产田设施番茄测土配方施肥校验报告[J]. 北京农业, 2014(36):29. |
| 75 | 张晓宏, 王著龙, 梁霞. 缓释配方肥对加工番茄产量和品质及效益的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2014(7):172-175. |
| ZHANG X H, WANG Z L, LIANG X. Influence on slow-release formula fertilizer on yield, quality and efficiency of processing tomato [J]. Northern Hortic., 2014(7):172-175. | |
| 76 | 陈惠玲, 褚超, 胡现荣, 等. 氮肥不同用量及氮磷钾配施对设施番茄产量与品质的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(5):106-107. |
| 77 | 金小溪. 桓仁县设施番茄栽培2+X肥料效应试验研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(16):78,80. |
| 78 | 李红波, 徐海霞, 张春奇. ‘洛番12号’最佳氮、磷、钾需肥配比试验[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2015, 28(2):31-33. |
| LI H B, XU H X, ZHANG C Q. Best ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for ‘Luofan 12’ tomato [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2015, 28(2):31-33. | |
| 79 | 张恩平, 谭福雷, 王月, 等. 氮磷钾与有机肥配施对番茄产量品质及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(10):2059-2067. |
| ZHANG E P, TAN F L, WANG Y, et al.. Effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manure on nutritional quality, yield of tomato and soil enzyme activities [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2015, 42(10):2059-2067. | |
| 80 | 赵方华, 姜波. 加工番茄的施肥模型[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(6):147-149. |
| 81 | 何金明, 高峻岭, 宋克光, 等. 磷肥用量对番茄产量、磷素利用及土壤有效磷的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(31):40-45. |
| HE J M, GAO J L, SONG K G, et al.. Effect of phosphorus application rate on tomato yield and phosphorus utilization and soil available phosphorus [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 32(31):40-45. | |
| 82 | 蒲明, 张鹏, 宋学栋, 等. 日光温室番茄氮磷钾优化施肥研究[J]. 甘肃农业, 2016(11):24-25. |
| 83 | 史建硕, 张彦才, 王丽英, 等. 聚磷酸铵水溶肥对设施番茄产量品质以及磷素吸收的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2016, 31():36-40. |
| SHI J S, ZHANG Y C, WANG L Y, et al.. Effects of soluble ammonium polyphosphate fertilizer on yield,quality and phosphorous uptake of tomato in a plastic greenhouse [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2016, 31(S1):36-40. | |
| 84 | 唐晓东, 张树全, 陈燕霞, 等. 紫色土上番茄的田间肥效试验[J]. 中国农技推广, 2016, 32(8):57-60. |
| 85 | 王文娟. 日光温室番茄灌溉制度及水肥耦合效应研究[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2016. |
| WANG W J. Study on the irrigation regime and water-fertilizer coupling of tomato in solar greenhouse [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 86 | 吴传洲, 朱克保, 奚波, 等. 不同氮、磷、钾肥施用量对大棚番茄产量、经济效益和品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(11):156-158. |
| WU C Z, ZHU K B, XI B, et al.. Effects of different fertilization dosages of N, P and K on the yield, economic benefit and quality of greenhouse tomato [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2016, 44(11):156-158. | |
| 87 | 张守才, 赵征宇, 孙永红, 等. 设施栽培番茄的氮磷钾肥料效应研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(2):65-71. |
| ZHANG S C, ZHAO Z Y, SUN Y H, et al.. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on tomato cultivation in greenhouse [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2016(2):65-71. | |
| 88 | 李青军, 张炎, 胡伟, 等. 施肥方式对滴灌加工番茄干物质积累、养分吸收和产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(4):93-98. |
| LI Q J, ZHANG Y, HU W, et al.. Effects of fertilization on dry matter accumulation, nutrient uptake and yield of processing tomato under drip irrigation [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2017(4):93-98. | |
| 89 | 李若楠, 武雪萍, 张彦才, 等. 减量施磷对温室菜地土壤磷素积累、迁移与利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(20):3944-3952. |
| LI R N, WU X P, ZHANG Y C, et al.. Effects of reduced phosphorus fertilization on soil phosphorus accumulation, leaching and utilization in greenhouse vegetable production [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2017, 50(20):3944-3952. | |
| 90 | 于新峰, 张春奇, 李红波. 氮磷钾不同配比对早春大棚番茄产量的影响[J]. 蔬菜, 2017(4):36-38. |
| 91 | 洪霞. 温室番茄产量-品质-环境效应组合评价模型构建及其水肥响应[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2018. |
| HONG X. Combination evaluation model of tomato yield quality environment effect and its response to water and fertilizer in greenhouse [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2018. | |
| 92 | 任如冰. 不同施肥方式对土壤钾素有效性及番茄产量品质的影响[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2018. |
| REN R B. Effect of different fertilization methods on soil potassium availability and yield and quality of tomato [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 93 | 孙骏鹏, 李进. 低肥力土壤番茄“3414”不完全方案肥料效应试验[J]. 中国园艺文摘, 2018, 34(2):39-41, 66. |
| 94 | 田悦悦. 长期缺钾对设施番茄根系分泌物及根际微生态的影响[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2018. |
| TIAN Y Y. Effects of long-term potassium deficiency on tomato root exudates and rhizosphere microecology [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 95 | 燕宏玲. 设施番茄栽培2+1肥料效应试验[J]. 农业科技通讯, 2018(9):137-139. |
| 96 | 杨雪梅, 姚永定. 山西夏县番茄肥料利用率试验初探[J]. 现代农业, 2019(5):14-16. |
| 97 | 赵伟, 杨圆圆, 蒋丽媛, 等. 减施磷肥提高设施番茄氮磷钾生理效率并减少土壤速效磷累积[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(10):1710-1718. |
| ZHAO W, YANG Y Y, JIANG L Y, et al.. Reducing conventional phosphorus input increase physiological efficiencies of absorbed nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in greenhouse tomato and decrease soil available phosphorus accumulation [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019, 25(10):1710-1718. | |
| 98 | 郑新娟, 徐柏林. 氮磷钾肥对设施番茄产量与含糖量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(21):151-152, 169. |
| ZHENG X J, XU B L. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on tomato yield and sugar content in facilities [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2019, 47(21):151-152, 169. | |
| 99 | 王婷婷, 杨恒哲, 李元峰, 等. 聚磷酸铵复合肥对设施番茄的肥效研究[J]. 农学学报, 2020, 10(9):33-37. |
| WANG T T, YANG H Z, LI Y F, et al.. The fertilizer efficiency of ammonium polyphosphate compound fertilizer on tomato in greenhouse [J]. J. Agric., 2020, 10(9):33-37. | |
| 100 | 徐海霞, 李红波, 张春奇. ‘洛番15号’最优氮磷钾配比施肥区间的确定[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2020, 33(7):51-55. |
| XU H X, LI H B, ZHANG C Q. Determination of the optimum fertilization interval of ‘Luofan 15’ tomato [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2020, 33(7):51-55. | |
| 101 | 陈小慧, 高飞, 韩宝, 等. 不同肥料配施对番茄品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国果菜, 2022, 42(6):67-73. |
| CHEN X H, GAO F, HAN B, et al.. Effects of different fertilizers application on tomato quality and soil nutrient [J]. China Fruit Veget., 2022, 42(6):67-73. | |
| 102 | 山楠, 串丽敏, 李明悦, 等. 养分专家系统推荐施肥在番茄上的应用效果[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2022, 35(4):45-50. |
| SHAN N, CHUAN L M, LI M Y, et al.. Application effects of nutrient expert fertilizer recommendation on tomato production [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2022, 35(4):45-50. | |
| 103 | 向茂红, 郭鹏, 濮小英, 等. 河西走廊加工番茄基于“3414”肥效影响[J]. 基层农技推广, 2022, 10(4):35-39. |
| [1] | 张俊蕾, 盖晓彤, 赵正婷, 刘弟, 王金凤, 姜宁, 刘雅婷. 烟草番茄斑萎病毒RT-LAMP检测体系的建立及优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [2] | 张福林, 奚瑞, 刘宇翔, 陈兆龙, 余庆辉, 李宁. 番茄BURP结构域基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [3] | 王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [4] | 李名博, 刘玉乐, 穆志民, 郭俊旺, 卫勇, 任东悦, 贾济深, 卫泽中, 栗宇红. 基于YOLOX-L-TN模型的番茄果实识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 97-105. |
| [5] | 黄大野, 余志斌, 万中义, 杨丹, 李金萍, 曹春霞. 产褐黄色链霉菌HEBRC45958菌株防控番茄棒孢叶斑病研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 136-142. |
| [6] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [7] | 杜彩艳, 鲁海燕, 熊艳竹, 孙曦, 孙秀梅, 普继雄, 张乃明. 连续两年沼液与化肥配施对桃生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [8] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [9] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 王艳君, 王娜娜. 改性纤维素对旱稻萌发和旱地土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 168-175. |
| [10] | 陈春林, 王琳洋, 单梦伟, 裴甜甜, 王吉庆, 肖怀娟, 李娟起, 李猛, 杜清洁. 发酵花生壳和牛粪替代草炭基质的番茄育苗效果分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 205-214. |
| [11] | 姚佳, 刘加欣, 苏焱, 苏小娟. 烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [12] | 聂婷婷, 董乙强, 杨合龙, 阿斯太肯·居力海提, 周时杰, 安沙舟. 围栏封育对蒿类荒漠植物-土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 178-187. |
| [13] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [14] | 张月欣, 麻云霞, 马秀枝, 张金旺, 王月林, 俞海生. 大青山不同林龄榆树林的土壤酶和养分特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 168-176. |
| [15] | 张璐, 郑磊, 刘思汝, 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 张强, 徐明岗. 土壤初始有效磷和交换性镁含量改变了小麦生长对pH的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 173-181. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号