




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 168-176.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0737
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
张月欣1, 麻云霞1, 马秀枝1( ), 张金旺2, 王月林3, 俞海生4
), 张金旺2, 王月林3, 俞海生4
收稿日期:2022-09-02
接受日期:2023-02-19
出版日期:2023-12-15
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
马秀枝
作者简介:张月欣 E-mail:1668681793@.qq.com;
基金资助:
Yuexin ZHANG1, Yunxia MA1, Xiuzhi MA1( ), Jinwang ZHANG2, Yuelin WANG3, Haisheng YU4
), Jinwang ZHANG2, Yuelin WANG3, Haisheng YU4
Received:2022-09-02
Accepted:2023-02-19
Online:2023-12-15
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Xiuzhi MA
摘要:
为揭示大青山自然保护区榆树林土壤酶活性与土壤养分随林龄增加的变化趋势及其规律,以大青山3种不同林龄(10、25、40 a)榆树林为研究对象,测定0—10、10—20、20—30、30—40 cm土层土壤pH、速效氮、速效磷、速效钾、有机质、蔗糖酶、过氧化氢酶、多酚氧化酶共8个指标,分析不同林龄榆树土壤酶活性与土壤养分含量变化特征及其相互关系。结果表明,随林龄增加榆树林土壤有机质和速效钾含量呈上升趋势;速效氮、速效磷先升高后降低,土壤pH逐渐降低。随着土壤深度的加深,土壤有机质、速效氮、速效磷、速效钾含量均呈现较明显的表聚现象。过氧化氢酶活性随林龄的增加逐渐降低;蔗糖酶、脲酶活性呈现先增加后降低的趋势,随着土层深度的加深酶活性逐渐降低。土壤养分与酶活性之间存在一定的相关性,速效氮和速效磷与蔗糖酶和脲酶存在显著正相关(P<0.05);速效钾和有机质与过氧化氢酶存在显著负相关(P<0.05);主成分分析结果表明,25 a林龄0—10 cm土层土壤肥力最高。研究结果为榆树林可持续经营和土壤肥力提升提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
张月欣, 麻云霞, 马秀枝, 张金旺, 王月林, 俞海生. 大青山不同林龄榆树林的土壤酶和养分特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 168-176.
Yuexin ZHANG, Yunxia MA, Xiuzhi MA, Jinwang ZHANG, Yuelin WANG, Haisheng YU. Soil Nutrient Characteristics of Ulmus pumila L. Forest at Different Ages in Daqingshan[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 168-176.
| 样地 Sample plot | 林龄 Forest age/a | 林分密度 Stand density/hm2 | 坡向 Exposure | 坡度 Slop/(°) | 海拔 Elevation/m | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 800 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 19 | 1 385 | 110°45′25′′E | 36°16′13′′N |
| 2 | 25 | 703 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 24 | 1 430 | 110°44′10′′E | 36°16′18′′N |
| 3 | 40 | 680 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 27 | 1 290 | 110°44′32′′E | 36°14′39′′N |
表1 样地基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of sample
| 样地 Sample plot | 林龄 Forest age/a | 林分密度 Stand density/hm2 | 坡向 Exposure | 坡度 Slop/(°) | 海拔 Elevation/m | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 800 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 19 | 1 385 | 110°45′25′′E | 36°16′13′′N |
| 2 | 25 | 703 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 24 | 1 430 | 110°44′10′′E | 36°16′18′′N |
| 3 | 40 | 680 | 阳坡 Sunny slope | 27 | 1 290 | 110°44′32′′E | 36°14′39′′N |
指标 Index | 林龄 Forest age | 土层 Layer | 林龄×土层 Forest age×layer |
|---|---|---|---|
速效氮 AN | 18.252** | 23.101* | 5.205* |
速效磷 AP | 42.781** | 17.695* | 3.112* |
| 速效钾AK | 8.571* | 4.735 | 0.280 |
有机质 SOM | 34.256* | 15.474* | 3.247* |
| pH | 32.147* | 3.134 | 0.035 |
表2 林龄和土层处理对土壤养分双因素方差分析
Table 2 Effects of forest age and soil layer treatment on soil nutrients by two-way ANOVA
指标 Index | 林龄 Forest age | 土层 Layer | 林龄×土层 Forest age×layer |
|---|---|---|---|
速效氮 AN | 18.252** | 23.101* | 5.205* |
速效磷 AP | 42.781** | 17.695* | 3.112* |
| 速效钾AK | 8.571* | 4.735 | 0.280 |
有机质 SOM | 34.256* | 15.474* | 3.247* |
| pH | 32.147* | 3.134 | 0.035 |
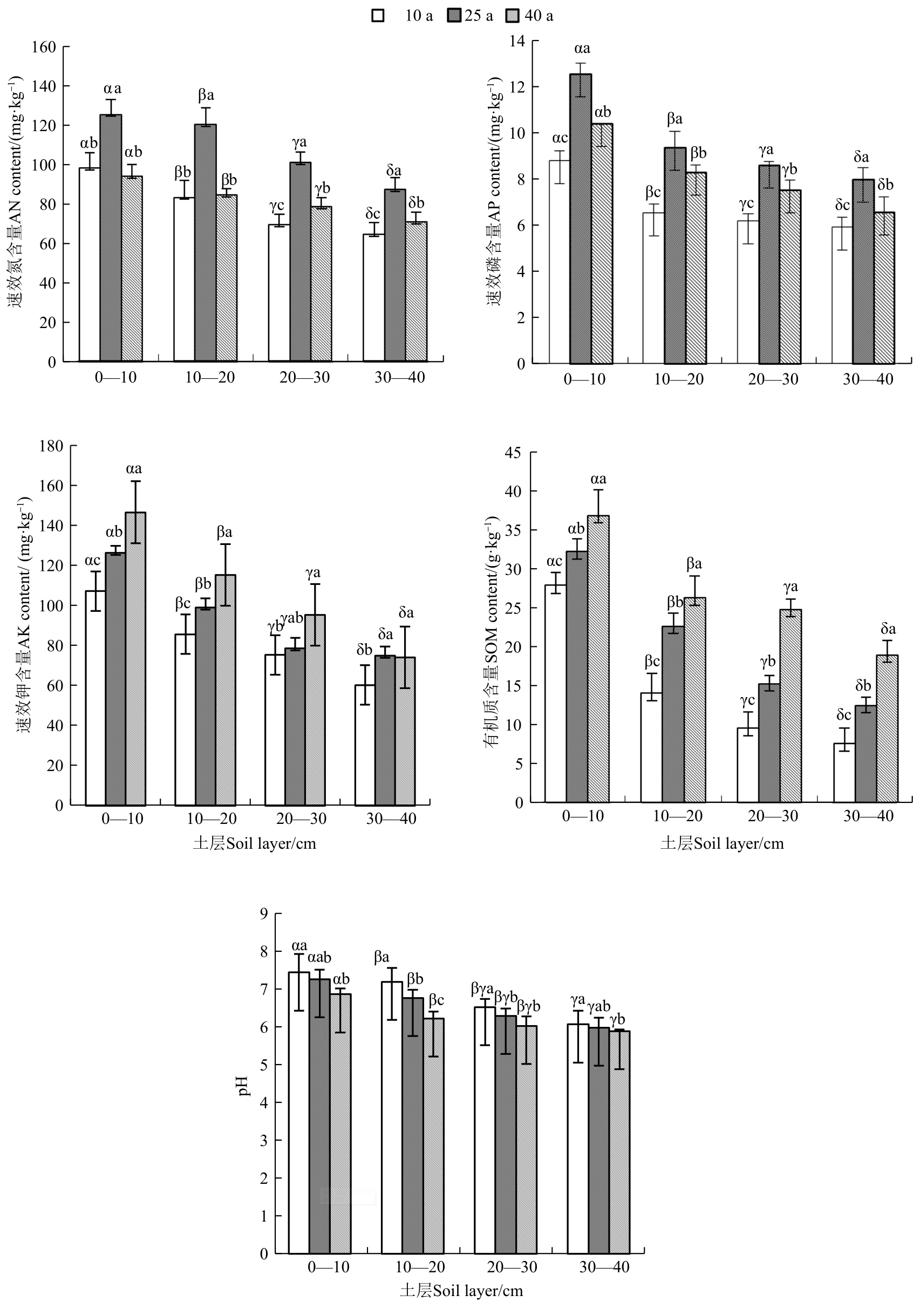
图1 4个土层土壤理化性质与林龄的关系注:不同英文字母表示同一土层不同林龄间差异在P<0.05水平显著;不同希腊字母代表同一林龄不同土层间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 1 Relationship between physical and chemical properties of the soil and the age of the four soil layersNote: Different English letters represent significant differences between different forest ages in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different Greek letters represent significant differences between different soil layers of the same forest age at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 林龄 Forest age | 土层 Soil layer | 林龄×土层 Forest age×soil layer |
|---|---|---|---|
蔗糖酶 Invertase | 12.519* | 3.354 | 0.652 |
过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 10.248* | 8.042* | 5.128* |
脲酶 Urease | 32.471* | 4.574* | 2.648* |
表3 林龄和土层处理对土壤酶活性双因素方差分析
Table 3 Result of two factor ANOVA of effects of forest age and soil layer treatment on soil enzyme activity
指标 Index | 林龄 Forest age | 土层 Soil layer | 林龄×土层 Forest age×soil layer |
|---|---|---|---|
蔗糖酶 Invertase | 12.519* | 3.354 | 0.652 |
过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 10.248* | 8.042* | 5.128* |
脲酶 Urease | 32.471* | 4.574* | 2.648* |
土层 Soil layer/cm | 林龄 Forest age/a | 蔗糖酶 Invertase/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) | 脲酶 Urease/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.03±0.01 αb | 4.87±0.14 αa | 0.47±0.13 αc | |
| 0—10 | 25 | 1.38±0.13 αa | 4.14±0.11 αb | 0.68±0.14 αa |
| 40 | 1.29±0.09 αa | 3.85±0.14 αc | 0.52±0.05 αb | |
| 10 | 0.61±0.01 βb | 4.53±0.09 αa | 0.30±0.12 αc | |
| 10—20 | 25 | 0.87±0.01 βa | 3.83±0.18 αb | 0.56±0.09 αa |
| 40 | 0.81±0.02 βa | 3.17±0.05 βc | 0.43±0.11 αb | |
| 10 | 0.53±0.03 γc | 3.94±0.13 βa | 0.26±0.01 βc | |
| 20—30 | 25 | 0.71±0.02 γa | 3.21±0.09 βb | 0.50±0.03 βa |
| 40 | 0.69±0.02 γb | 2.64±0.10 βγc | 0.36±0.02 βa | |
| 10 | 0.44±0.01 δc | 3.37±0.11 γa | 0.23±0.01 βc | |
| 30—40 | 25 | 0.57±0.01 δb | 2.68±0.12 γb | 0.41±0.01 βa |
| 40 | 0.52±0.01 δa | 2.31±0.08 γc | 0.33±0.01 βa |
表4 不同林龄榆树林土壤酶活性
Table 4 Soil enzyme activity in different forest age
土层 Soil layer/cm | 林龄 Forest age/a | 蔗糖酶 Invertase/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) | 脲酶 Urease/(μmol·d-1·mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.03±0.01 αb | 4.87±0.14 αa | 0.47±0.13 αc | |
| 0—10 | 25 | 1.38±0.13 αa | 4.14±0.11 αb | 0.68±0.14 αa |
| 40 | 1.29±0.09 αa | 3.85±0.14 αc | 0.52±0.05 αb | |
| 10 | 0.61±0.01 βb | 4.53±0.09 αa | 0.30±0.12 αc | |
| 10—20 | 25 | 0.87±0.01 βa | 3.83±0.18 αb | 0.56±0.09 αa |
| 40 | 0.81±0.02 βa | 3.17±0.05 βc | 0.43±0.11 αb | |
| 10 | 0.53±0.03 γc | 3.94±0.13 βa | 0.26±0.01 βc | |
| 20—30 | 25 | 0.71±0.02 γa | 3.21±0.09 βb | 0.50±0.03 βa |
| 40 | 0.69±0.02 γb | 2.64±0.10 βγc | 0.36±0.02 βa | |
| 10 | 0.44±0.01 δc | 3.37±0.11 γa | 0.23±0.01 βc | |
| 30—40 | 25 | 0.57±0.01 δb | 2.68±0.12 γb | 0.41±0.01 βa |
| 40 | 0.52±0.01 δa | 2.31±0.08 γc | 0.33±0.01 βa |
| 指标Index | pH | 速效氮AN | 速效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有机质SOM | 蔗糖酶Invertase | 脲酶Urease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 速效氮AN | 0.112 | ||||||
| 速效磷AP | -0.128 | 0.764* | |||||
| 速效钾AK | -0.521** | -0.037 | 0.263 | ||||
| 有机质SOM | -0.614** | 0.203 | 0.417 | 0.695** | |||
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | -0.517 | 0.633* | 0.154* | 0.528 | 0.263 | ||
| 脲酶Urease | -0.208 | 0.259* | 0.466* | 0.571 | 0.809 | 0.718* | |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.262* | -0.275 | -0.570 | -0.384* | -0.572* | 0.652* | 0.456 |
表5 土壤养分与酶活性的相关性
Table 5 Correlations between soil nutrients and enzyme activity
| 指标Index | pH | 速效氮AN | 速效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有机质SOM | 蔗糖酶Invertase | 脲酶Urease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 速效氮AN | 0.112 | ||||||
| 速效磷AP | -0.128 | 0.764* | |||||
| 速效钾AK | -0.521** | -0.037 | 0.263 | ||||
| 有机质SOM | -0.614** | 0.203 | 0.417 | 0.695** | |||
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | -0.517 | 0.633* | 0.154* | 0.528 | 0.263 | ||
| 脲酶Urease | -0.208 | 0.259* | 0.466* | 0.571 | 0.809 | 0.718* | |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.262* | -0.275 | -0.570 | -0.384* | -0.572* | 0.652* | 0.456 |
主成分 Principal ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
第1主成分 The first principal component | 7.14 | 59.42 | 61.24 |
第2主成分 The second principal component | 1.96 | 15.59 | 76.83 |
表6 土壤主成分分析
Table 6 Analysis of soil principal components
主成分 Principal ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
第1主成分 The first principal component | 7.14 | 59.42 | 61.24 |
第2主成分 The second principal component | 1.96 | 15.59 | 76.83 |
原始变量 Raw variable | 第1主成分 The first principal component | 第2主成分 The second principal component |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.928 | 0.293 |
| 速效氮AN | 0.141 | 0.697 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.392 | -0.844 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.658 | 0.483 |
| 有机质SOM | 0.703 | 0.473 |
| 脲酶Urease | -0.493 | 0.572 |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.782 | 0.273 |
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | 0.839 | -0.162 |
表7 旋转后主成分因子载荷
Table 7 Rotates the main component factor load
原始变量 Raw variable | 第1主成分 The first principal component | 第2主成分 The second principal component |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.928 | 0.293 |
| 速效氮AN | 0.141 | 0.697 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.392 | -0.844 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.658 | 0.483 |
| 有机质SOM | 0.703 | 0.473 |
| 脲酶Urease | -0.493 | 0.572 |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.782 | 0.273 |
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | 0.839 | -0.162 |
林龄 Forest age/a | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 第1主成分 The first principal component | 第2主成分 The second principal component | 综合得分 Overall score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0—10 | -0.08 | 0.58 | 0.23 | 4 |
| 10—20 | 0.69 | 0.15 | -0.14 | 7 | |
| 20—30 | 0.14 | 0.29 | -0.36 | 10 | |
| 30—40 | -0.12 | 0.33 | -0.43 | 12 | |
| 25 | 0—10 | -0.34 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 1 |
| 10—20 | 0.65 | -1.01 | 0.47 | 2 | |
| 20—30 | 0.25 | -0.11 | 0.06 | 6 | |
| 30—40 | -0.17 | 0.09 | -0.27 | 9 | |
| 40 | 0—10 | -1.03 | 0.14 | 0.38 | 3 |
| 10—20 | 0.33 | -0.24 | 0.12 | 5 | |
| 20—30 | 0.15 | -0.37 | -0.19 | 8 | |
| 30—40 | 0.14 | -0.32 | -0.41 | 11 |
表8 不同树龄榆树土壤肥力综合评价
Table 8 Comprehensive evaluation table for soil nutrient of different tree age elm tree
林龄 Forest age/a | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 第1主成分 The first principal component | 第2主成分 The second principal component | 综合得分 Overall score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0—10 | -0.08 | 0.58 | 0.23 | 4 |
| 10—20 | 0.69 | 0.15 | -0.14 | 7 | |
| 20—30 | 0.14 | 0.29 | -0.36 | 10 | |
| 30—40 | -0.12 | 0.33 | -0.43 | 12 | |
| 25 | 0—10 | -0.34 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 1 |
| 10—20 | 0.65 | -1.01 | 0.47 | 2 | |
| 20—30 | 0.25 | -0.11 | 0.06 | 6 | |
| 30—40 | -0.17 | 0.09 | -0.27 | 9 | |
| 40 | 0—10 | -1.03 | 0.14 | 0.38 | 3 |
| 10—20 | 0.33 | -0.24 | 0.12 | 5 | |
| 20—30 | 0.15 | -0.37 | -0.19 | 8 | |
| 30—40 | 0.14 | -0.32 | -0.41 | 11 |
| 1 | 杨潇.内蒙古大青山主要森林植被生产力与碳储量研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2013. |
| YANG X. Productivity and carbon reserves study on of main forest vegetation in Daqingshan mountain Inner Mongolia [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,2013. | |
| 2 | 凯歌,唐国力,姬茹,等.内蒙古大青山自然保护区生态服务价值评估与建设[J].前沿,2021(2):75-82. |
| KAI G, TANG G L, JI R, et al.. Evaluation and construction of ecological service value in Daqingshan Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia [J]. Forward Position, 2021(2):75-82. | |
| 3 | 葛晓改,肖文发,曾立雄,等. 三峡库区不同林龄马尾松土壤养分与酶活性的关系[J].应用生态学报,2012, 23(2):445-451. |
| GE X G, XIAO W F, ZENG L X, et al.. Relationships between soil nutrient contents and soil enzyme activities in Pinus massoniana stands with different ages in Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2012, 23(2):445-451. | |
| 4 | 刘善江,夏雪,陈桂梅,等. 土壤酶的研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2011,27(21):1-7. |
| LIU S J, XIA X, CHEN G M, et al.. Study progress on function and affecting factors of soil enzymes [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2011, 27(21):1-7. | |
| 5 | 金志凤,黄敬峰,李波,等. 基于GIS及气候-土壤-地形因子的浙江省茶树栽培适宜性评价[J].农业工程学报,2011,27(3):231-236. |
| JIN Z F, HUANG J F, LI B, et al.. Suitability evaluation of tea trees cultivation based on GIS in Zhejiang province [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2011, 27(3):231-236. | |
| 6 | 涂程伟,彭彩云,柳苹玉,等. 华西雨屏区不同林龄杉木人工林土壤酶活性的动态变化[J].东北林业大学学报,2021, 49(7):91-95. |
| TU C W, PENG C Y, LIU P Y, et al.. Seasonal dynamics of soil enzyme activities in Cunninghamia lanceolata forest of different ages in Rainy Area of Western China [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2021, 49(7):91-95. | |
| 7 | 罗亚进.不同林龄桉树人工林土壤微生物及土壤酶活性的研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2014. |
| LUO Y J. Study on soil microorganism and soil enzyme activity along a chronosequence of Eucalyptus plantation [D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2014. | |
| 8 | 严绍裕.不同林龄湿地松林土壤酶活性与土壤养分特征[J].森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(1):24-29. |
| YAN S Y. Characteristics of soil nutrient and enzyme activity in Pinus elliottii forest at different ages [J]. J. For. Environ.,2020, 40(1):24-29. | |
| 9 | 赵思思,梁海永,王晓叶,等.榆树种质资源的研究进展[J].河北林果研究, 2017,32():232-237. |
| ZHAO S S, LIANG H Y, WANG X Y,et al.. A study on the research progress of elm germplasm resources [J]. Hebei For. Fruit Res., 2017,32 (S1):232-237. | |
| 10 | MA X, HEAL K V, LIU A,et al.. Nutrient cycling and distribution in different-aged plantations of Chinese fir in southern China [J]. For. Ecol. Manage., 2007, 243(1):61-69. |
| 11 | 张志永,朱媛,时忠杰,等. 浑善达克沙地榆树疏林植被和土壤的空间分异特征[J].生态环境学报,2019, 28(10):1936-1944. |
| ZHANG Z Y, ZHU Y, SHI Z J,et al.. Spatial distribution of vegetation and soil in Ulmus pumila-dominated savanna in the Otindag sandy land [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci.,2019,28(10): 1936-1944. | |
| 12 | 赵娜,胡春元,李钢铁,等.浑善达克沙地中部地区榆树分布密度与土壤养分状况关系的研究[J].现代农业,2009(7):61-64. |
| 13 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006: 1-495. |
| 14 | 关荫松.土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京:农业出版社,1986: 1-376. |
| 15 | 孙鹏跃,徐福利,王渭玲,等. 华北落叶松人工林地土壤养分与土壤酶的季节变化及关系 [J].浙江农林大学学报,2016, 33(6):944-952. |
| SNU P Y, XU F L, WANG W L, et al.. Season dynamics of soil nutrients and soil enzyme activities in Larix principis rupprechtii plantations [J]. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ., 2016, 33(6):944-952. | |
| 16 | 张可可,蒋德明,余海滨,等.接种菌根菌剂对科尔沁沙地4种造林幼苗生长特性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2017, 36(7):1791-1800. |
| ZHANG K K, JIANG D M, YU H B,et al.. Impacts of mycorrhizal fungi inoculum on growth characteristics of four kinds of afforestation seedings in Horqin sandy land,China [J]. Chin. J. Ecol.,2017,36(7):1791-1800. | |
| 17 | 王真辉,林希昊,陈秋波,等.不同树龄橡胶林土壤养分变化特征及对细根的影响[J].热带作物学报,2009,30(8):1094-1098. |
| WANG Z H, LIN X H, CHEN Q B,et al..Variation characteristics of soil environment and ist effect on hairy roots of Hevea brasiliensis at different ages [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops,2009, 30(8):1094-1098. | |
| 18 | 张社奇,王国栋,张蕾.黄土高原刺槐林对土壤养分时空分布的影响[J].水土保持学报,2008, 22(5):91-95. |
| ZHANG S Q, WANG G D, ZHANG L. Time-space distributive feature of soil nutrient and chemical characteristics of Robinia Pseudoacia L. plantation forestland in Losee Plateau [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv.,2008, 22 (5):91-95. | |
| 19 | 张振国,李祥友,于弘,等. 道地药材滁菊产地土壤有效养分特征分析[J].安徽农学通报,2021,27(12):102-104, 107. |
| 20 | 蔡葵,蒋菊生,彭宗波,等.不同树龄胶园土壤养分分布规律研究[J].林业资源管理,2015(4):92-97, 103. |
| CAI K, JIANG J S, PENG Z B, et al.. Study on distribution of nutrients in rubber plantations of different ages [J]. For. Resour. Manage., 2015(4):92-97, 103. | |
| 21 | 崔莉娜,郭弘婷,李维扬,等.不同林龄杉木人工林菌根侵染特征研究[J].生态学报,2019,39(6):1926-1934. |
| CUI L N, GUO H T, LI W Y, et al.. Study on the characteristics of mycorrhizal colonization in Chinese fir plantations at different ages [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin.,2019,39(6):1926-1934. | |
| 22 | 任启文,王鑫,李联地,等.小五台山不同海拔土壤理化性质垂直变化规律[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(1):241-247. |
| REN Q W, WANG X, LI L D,et al..Vertical variation of soil physical and chemical properties at different altitudes in Xiaowutai Mountain [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv.,2019,33(1):241-247. | |
| 23 | 王伟东,王渭玲,徐福利,等.秦岭西部中幼龄华北落叶松林地土壤养分与酶活性特征研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(4):1032-1039. |
| WANG W D, WANG W L, XU F L, et al.. Characteristics of soil nutrients and enzyme activites in young and middle aged Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in western Qinling Mountains [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert.,2015,21(4):1032-1039. | |
| 24 | 焦如珍,杨承栋,屠星南,等.杉木人工林不同发育阶段林下植被、土壤微生物、酶活性及养分的变化[J].林业科学研究,1997,10(4):337-383. |
| JIAO R Z, YANG C D, TU X N,et al..The change of undergrowth,soil microorganism,enzyme activity and nutrient in different develpoing stage of the Chinese fir plantation [J]. For. Res.,1997,10(4):337-383. | |
| 25 | 杨承栋,焦如珍.杉木人工林根际土壤性质变化的研究[J].林业科学,1999,35(6):2-9. |
| YANG C D, JIAO R Z. Research on change of rhizosphere soil properties of chinese fir plantation [J]. For. Res.,1999,35(6):2-9. | |
| 26 | 刘顺,刘喜帅,朱新传,等.陈山红心杉土壤养分、酶活性的根际效应及肥力评价[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(2):492-501. |
| LIU S, LIU X S, ZHU X C, et al.. Rhizosphere effects of nutrients and enzyme activities of Cunninghania lanceolata and soil fertility assessment [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2017, 23(2):492-501. | |
| 27 | 宫欢欢,尤一泓,林勇明,等.不同林龄木麻黄纯林土壤酶活性与土壤养分研究[J].江西农业大学学报,2017,39(3):516-524. |
| GONG H H, YOU Y H, LIN Y M, et al.. Soil enzyme activities and soil nutrients under Casuarina equisetifolia pure forest at different stand ages [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2017, 39(3):516-524. | |
| 28 | 丁波,丁贵杰,赵熙州,等.间伐对杉木人工林土壤酶活性及微生物的影响[J].林业科学研究,2017,30(6):1059-1065. |
| DING B, DING G J, ZHAO X Z, et al.. Impacts of thinning on soil enzymes activity and microoganisms in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation [J]. For. Res., 2017, 30(6):1059-1065. | |
| 29 | 刘顺,吴珍花,郭晓敏,等.不同林龄陈山红心杉土壤微生物群落结构特征[J].应用与环境生态学报, 2016,22(3):510-517. |
| LIU S, WU Z H, GUO X M, et al.. Soil microbial community structure characteristics of Chenshan Red-heart Chinese fir of different stand ages [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2016, 22(3):510-517. |
| [1] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [2] | 杜彩艳, 鲁海燕, 熊艳竹, 孙曦, 孙秀梅, 普继雄, 张乃明. 连续两年沼液与化肥配施对桃生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [3] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [4] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [5] | 任棚, 吕晓桂, 石磊. 大气压冷等离子体持续和间隔处理对燕麦种子萌发的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 215-221. |
| [6] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [7] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [8] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 王艳君, 王娜娜. 改性纤维素对旱稻萌发和旱地土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 168-175. |
| [9] | 金鑫, 张璐, 吴鹏, 李萍, 谭伟, 桂明英. 遮光处理对盆景灵芝生长发育和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 147-156. |
| [10] | 郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188. |
| [11] | 姚佳, 刘加欣, 苏焱, 苏小娟. 烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [12] | 聂婷婷, 董乙强, 杨合龙, 阿斯太肯·居力海提, 周时杰, 安沙舟. 围栏封育对蒿类荒漠植物-土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 178-187. |
| [13] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [14] | 郭巨先, 欧阳碧珊, 李桂花, 符梅, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 陆美莲. 微生物有机肥对连作菜薹生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [15] | 郭胜微, 边思文, 丁建文, 张晓辰, 杨兴, 杜锦, 向春阳. 糯玉米萌发期耐低温品种资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号