




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 206-217.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0304
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Chenguang ZHAO1,2( ), Siyun NIU2, Xun CHEN3, Li FANG1, Haitao LI1, Peixing WANG4, Binbin SHEN4, Yuanzhi SHI1(
), Siyun NIU2, Xun CHEN3, Li FANG1, Haitao LI1, Peixing WANG4, Binbin SHEN4, Yuanzhi SHI1( )
)
Received:2021-04-12
Accepted:2021-07-26
Online:2022-06-15
Published:2022-06-21
Contact:
Yuanzhi SHI
赵晨光1,2( ), 牛司耘2, 陈勋3, 方丽1, 李海涛1, 王佩星4, 沈镔镔4, 石元值1(
), 牛司耘2, 陈勋3, 方丽1, 李海涛1, 王佩星4, 沈镔镔4, 石元值1( )
)
通讯作者:
石元值
作者简介:赵晨光 E-mail:297071141@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chenguang ZHAO, Siyun NIU, Xun CHEN, Li FANG, Haitao LI, Peixing WANG, Binbin SHEN, Yuanzhi SHI. Effects of Compound Fertilizer on Tea Yield, Quality and Fertility of Tea Garden Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 206-217.
赵晨光, 牛司耘, 陈勋, 方丽, 李海涛, 王佩星, 沈镔镔, 石元值. 复合肥料对茶叶产量、品质及茶园土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 206-217.
| 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | pH | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% | v a i l a b l e p h o s p h o r u s /(mg·kg-1) 有效磷 A | v a i l a b l e p o t a s s i u m / (mg·kg-1) 速效钾 A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 3.66 | 2.72 | 2.35 | 29.90 | 63.05 |
| 10—20 | 3.70 | 1.44 | 1.10 | 21.41 | 55.70 |
| 20—30 | 3.68 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 3.58 | 41.10 |
| 30—40 | 3.72 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 2.71 | 35.00 |
| 40—90 | 3.82 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.82 | 24.70 |
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of soil foundation
| 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | pH | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/% | v a i l a b l e p h o s p h o r u s /(mg·kg-1) 有效磷 A | v a i l a b l e p o t a s s i u m / (mg·kg-1) 速效钾 A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 3.66 | 2.72 | 2.35 | 29.90 | 63.05 |
| 10—20 | 3.70 | 1.44 | 1.10 | 21.41 | 55.70 |
| 20—30 | 3.68 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 3.58 | 41.10 |
| 30—40 | 3.72 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 2.71 | 35.00 |
| 40—90 | 3.82 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.82 | 24.70 |
编号 Code | 处理 Treatment | 生产厂家 Manufacturer | 肥料养分比例(N∶P2O5∶K20) Fertilizer nutrient ratio (N∶P2O5∶K20) | 施氮量 N application rate /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 不施肥(CK) No fertilization(CK) | — | — | — |
| T2 | 控释复合肥 Controlled-release fertilizer | 山东多益成肥料科技有限公司 Shandong Doing-well Fertilizer Technology Co. Ltd. | 30∶5∶6 | 450 |
| T3 | 碳基复合肥 Carbon-based compound fertilizer | 山东戴威肥业有限公司 Shandong Daiwei Fertilizer Industry Co. Ltd. | 13.5∶13.5∶13.5 | 450 |
| T4 | 脲甲醛复合肥 Urea and formaldehyde compound fertilizer | 武汉绿茵化工有限公司 Wuhan Lvyin Chemical Co. Ltd. | 30∶5∶6 | 450 |
| T5 | 茶树专用肥 Specialty fertilizer of tea tree | 浙江巨隆化肥有限公司 Zhejiang Julong Fertilizer Co. Ltd. | 22.0∶8.0∶12.2 | 450 |
| T6 | 习惯施肥处理 Custom fertilizer | 山东三方化工集团有限公司 Shandong Sanfang Chemical Group Co. Ltd. | 17∶17∶17 | 700 |
Table 2 Nutrient formula of test fertilizer
编号 Code | 处理 Treatment | 生产厂家 Manufacturer | 肥料养分比例(N∶P2O5∶K20) Fertilizer nutrient ratio (N∶P2O5∶K20) | 施氮量 N application rate /(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 不施肥(CK) No fertilization(CK) | — | — | — |
| T2 | 控释复合肥 Controlled-release fertilizer | 山东多益成肥料科技有限公司 Shandong Doing-well Fertilizer Technology Co. Ltd. | 30∶5∶6 | 450 |
| T3 | 碳基复合肥 Carbon-based compound fertilizer | 山东戴威肥业有限公司 Shandong Daiwei Fertilizer Industry Co. Ltd. | 13.5∶13.5∶13.5 | 450 |
| T4 | 脲甲醛复合肥 Urea and formaldehyde compound fertilizer | 武汉绿茵化工有限公司 Wuhan Lvyin Chemical Co. Ltd. | 30∶5∶6 | 450 |
| T5 | 茶树专用肥 Specialty fertilizer of tea tree | 浙江巨隆化肥有限公司 Zhejiang Julong Fertilizer Co. Ltd. | 22.0∶8.0∶12.2 | 450 |
| T6 | 习惯施肥处理 Custom fertilizer | 山东三方化工集团有限公司 Shandong Sanfang Chemical Group Co. Ltd. | 17∶17∶17 | 700 |
| 处理 Treatment | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氨基酸含量 Amino acid content/% | 茶多酚含量 Polyphenols content/% | 酚氨比 Phenol ammonia ratio | 氨基酸含量 Amino acid content/% | 茶多酚含量Polyphenols content/% | 酚氨比 Phenol ammonia ratio | |
| T1 | 3.55±0.63 a | 21.26±4.14 ab | 5.99 a | 3.24±0.24 c | 20.97±1.49 ab | 6.46 a |
| T2 | 3.90±0.49 a | 19.16±1.98 b | 4.91 b | 4.01±0.49 b | 21.65±1.19 a | 5.41 b |
| T3 | 3.81±0.59 a | 19.01±2.35 b | 4.99 b | 4.59±0.38 ab | 20.14±1.26 ab | 4.38 c |
| T4 | 3.57±0.26 a | 17.63±1.81 bc | 4.94 b | 3.98±0.21 b | 21.19±2.03 ab | 5.31 b |
| T5 | 3.54±0.38 a | 16.83±3.07 c | 4.75 c | 4.25±0.27 b | 19.76±0.91 b | 4.65 c |
| T6 | 3.57±0.34 a | 21.88±2.44 a | 6.13 a | 5.01±0.52 a | 23.25±0.70 a | 4.64 c |
Table 3 Quality of tea bud shoot under different fertilization treatments in 2019 and 2020
| 处理 Treatment | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氨基酸含量 Amino acid content/% | 茶多酚含量 Polyphenols content/% | 酚氨比 Phenol ammonia ratio | 氨基酸含量 Amino acid content/% | 茶多酚含量Polyphenols content/% | 酚氨比 Phenol ammonia ratio | |
| T1 | 3.55±0.63 a | 21.26±4.14 ab | 5.99 a | 3.24±0.24 c | 20.97±1.49 ab | 6.46 a |
| T2 | 3.90±0.49 a | 19.16±1.98 b | 4.91 b | 4.01±0.49 b | 21.65±1.19 a | 5.41 b |
| T3 | 3.81±0.59 a | 19.01±2.35 b | 4.99 b | 4.59±0.38 ab | 20.14±1.26 ab | 4.38 c |
| T4 | 3.57±0.26 a | 17.63±1.81 bc | 4.94 b | 3.98±0.21 b | 21.19±2.03 ab | 5.31 b |
| T5 | 3.54±0.38 a | 16.83±3.07 c | 4.75 c | 4.25±0.27 b | 19.76±0.91 b | 4.65 c |
| T6 | 3.57±0.34 a | 21.88±2.44 a | 6.13 a | 5.01±0.52 a | 23.25±0.70 a | 4.64 c |
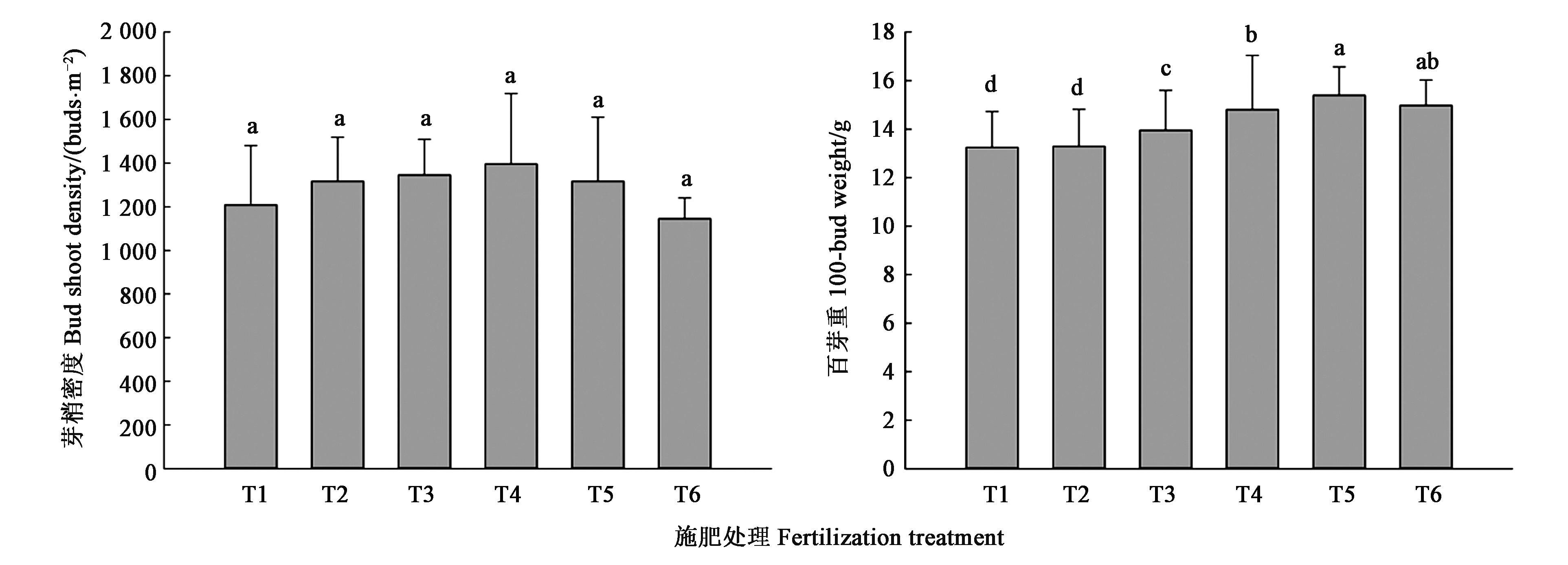
Fig.3 Bud shoot density and 100 bud weight under different fertilization treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level.
| 年份Year | 处理Ttreatment | N/% | C/% | P/(g·kg-1) | K/(g·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | ||
| 2019 | T1 | 4.87±0.14 b | 2.91±0.07 b | 45.45±0.34 a | 46.59±0.26 a | 4.72±0.13 a | 2.91±0.33 b | 18.36±0.49 a | 18.77±3.21 b |
| T2 | 5.14±0.08 a | 2.96±0.09 ab | 45.27±0.18 a | 46.64±0.11 a | 4.68±0.09 a | 2.91±0.39 b | 17.48±0.45 a | 18.41±2.54 b | |
| T3 | 5.19±0.11 a | 3.13±0.08 a | 44.88±0.21 a | 46.63±0.15 a | 4.78±0.05 a | 2.94±0.25 b | 19.95±0.45 a | 18.90±1.73 b | |
| T4 | 4.95±0.07 ab | 3.07±0.09 ab | 45.30±0.25 a | 46.58±0.23 a | 4.73±0.10 a | 3.18±0.30 ab | 18.27±0.47 a | 19.65±1.28 b | |
| T5 | 5.05±0.13 ab | 3.20±0.17 a | 45.28±0.26 a | 46.48±0.07 a | 4.68±0.12 a | 3.32±0.22 a | 18.34±0.39 a | 18.35±0.92 b | |
| T6 | 5.25±0.10 a | 3.19±0.11 a | 44.71±0.28 a | 46.55±0.17 a | 4.68±0.07 a | 3.33±0.48 a | 19.14±0.25 a | 20.59±1.24 a | |
| 2020 | T1 | 4.16±0.80 a | 2.62±0.22 a | 55.61±6.61 a | 46.61±0.10 a | 5.96±0.37 b | 2.88±0.10 b | 20.34±0.98 a | 15.32±0.76 a |
| T2 | 4.18±0.31 a | 2.93±0.05 a | 54.73±5.22 a | 46.87±0.27 a | 6.27±0.34 ab | 2.96±0.18 b | 20.54±0.38 a | 15.96±1.40 a | |
| T3 | 4.82±0.45 a | 3.01±0.09 a | 55.57±5.15 a | 46.78±0.26 a | 6.28±0.82 ab | 2.96±0.10 b | 21.37±1.68 a | 16.40±0.80 a | |
| T4 | 4.17±0.59 a | 2.95±0.18 a | 53.42±7.27 a | 46.85±0.11 a | 6.02±0.77 ab | 2.93±0.13 b | 20.29±1.52 a | 14.73±1.70 a | |
| T5 | 4.18±1.38 a | 3.18±0.14 a | 54.74±5.22 a | 47.00±0.26 a | 6.27±0.34 ab | 2.82±0.30 b | 20.54±0.38 a | 15.77±1.47 a | |
| T6 | 4.36±0.57 a | 3.07±0.09 a | 55.93±8.30 a | 46.84±0.61 a | 6.68±0.63 a | 3.20±0.23 a | 21.51±1.57 a | 15.90±1.20 a | |
Table 4 Nutrient elements content in tea shoot of different fertilization treatments
| 年份Year | 处理Ttreatment | N/% | C/% | P/(g·kg-1) | K/(g·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | 春茶 Spring tea | 夏秋茶Summer and autumn tea | ||
| 2019 | T1 | 4.87±0.14 b | 2.91±0.07 b | 45.45±0.34 a | 46.59±0.26 a | 4.72±0.13 a | 2.91±0.33 b | 18.36±0.49 a | 18.77±3.21 b |
| T2 | 5.14±0.08 a | 2.96±0.09 ab | 45.27±0.18 a | 46.64±0.11 a | 4.68±0.09 a | 2.91±0.39 b | 17.48±0.45 a | 18.41±2.54 b | |
| T3 | 5.19±0.11 a | 3.13±0.08 a | 44.88±0.21 a | 46.63±0.15 a | 4.78±0.05 a | 2.94±0.25 b | 19.95±0.45 a | 18.90±1.73 b | |
| T4 | 4.95±0.07 ab | 3.07±0.09 ab | 45.30±0.25 a | 46.58±0.23 a | 4.73±0.10 a | 3.18±0.30 ab | 18.27±0.47 a | 19.65±1.28 b | |
| T5 | 5.05±0.13 ab | 3.20±0.17 a | 45.28±0.26 a | 46.48±0.07 a | 4.68±0.12 a | 3.32±0.22 a | 18.34±0.39 a | 18.35±0.92 b | |
| T6 | 5.25±0.10 a | 3.19±0.11 a | 44.71±0.28 a | 46.55±0.17 a | 4.68±0.07 a | 3.33±0.48 a | 19.14±0.25 a | 20.59±1.24 a | |
| 2020 | T1 | 4.16±0.80 a | 2.62±0.22 a | 55.61±6.61 a | 46.61±0.10 a | 5.96±0.37 b | 2.88±0.10 b | 20.34±0.98 a | 15.32±0.76 a |
| T2 | 4.18±0.31 a | 2.93±0.05 a | 54.73±5.22 a | 46.87±0.27 a | 6.27±0.34 ab | 2.96±0.18 b | 20.54±0.38 a | 15.96±1.40 a | |
| T3 | 4.82±0.45 a | 3.01±0.09 a | 55.57±5.15 a | 46.78±0.26 a | 6.28±0.82 ab | 2.96±0.10 b | 21.37±1.68 a | 16.40±0.80 a | |
| T4 | 4.17±0.59 a | 2.95±0.18 a | 53.42±7.27 a | 46.85±0.11 a | 6.02±0.77 ab | 2.93±0.13 b | 20.29±1.52 a | 14.73±1.70 a | |
| T5 | 4.18±1.38 a | 3.18±0.14 a | 54.74±5.22 a | 47.00±0.26 a | 6.27±0.34 ab | 2.82±0.30 b | 20.54±0.38 a | 15.77±1.47 a | |
| T6 | 4.36±0.57 a | 3.07±0.09 a | 55.93±8.30 a | 46.84±0.61 a | 6.68±0.63 a | 3.20±0.23 a | 21.51±1.57 a | 15.90±1.20 a | |

Fig.4 The content of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in different soil layers under different fertilization treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level.

Fig.5 Soil available phosphorus content in topsoil layers under different fertilization treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level.
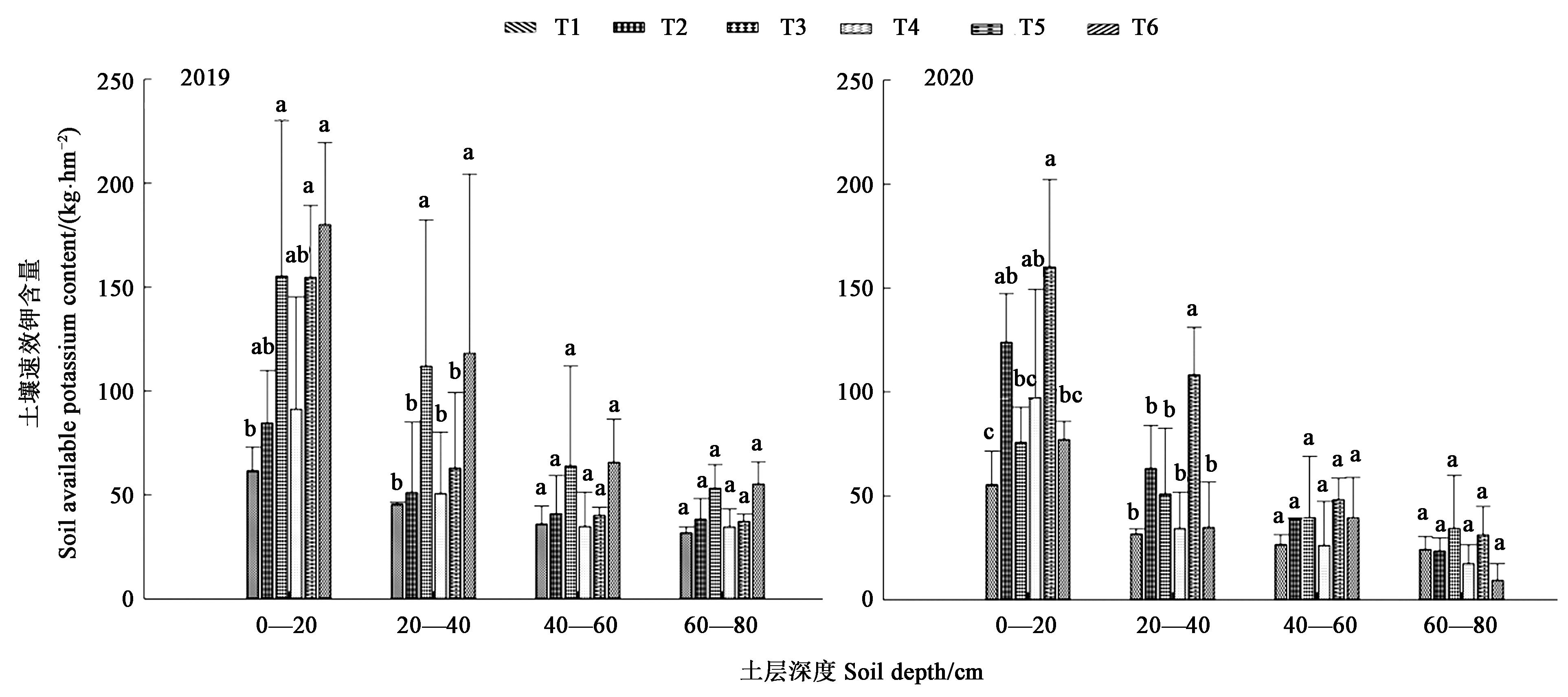
Fig.6 The content of available potassium in different soil layers under different fertilization treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treat- ment | 手采春茶 产量 Yield of hand picked spring tea/(kg·hm-2) | 机采春茶 产量 Yield of mechanical picked spring tea/ (kg·hm-2) | 机采夏秋茶 产量 Yield of mechanical picked summer and autumn tea/(kg·hm-2) | 茶园年收入 Annual income of tea plantation/ (104 yuan·hm-2) | 肥料用量 fertilizer amount/ (kg·hm-2) | 肥料单价 Fertilizer price/ (yuan·kg-1) | 肥料成本 The cost of fertilizer/(104 yuan·hm-2) | 人工费用 Labor cost/(104yuan·hm-2) | 利润 Profit/(104yuan·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 2 189.58 | 6 184.30 | 8 030.17 | 17.22 | — | — | — | 9.56 | 7.66 |
| T2 | 3 200.42 | 6 785.43 | 9 951.15 | 23.91 | 1 500.00 | 4.00 | 0.60 | 14.20 | 9.11 |
| T3 | 3 501.67 | 6 739.73 | 9 783.76 | 25.66 | 3 333.30 | 5.00 | 1.67 | 16.47 | 7.53 |
| T4 | 3 560.83 | 7 199.47 | 9 792.20 | 26.20 | 1 500.00 | 4.00 | 0.60 | 15.64 | 9.96 |
| T5 | 3 572.92 | 7 625.95 | 10 231.51 | 26.53 | 2 045.50 | 3.50 | 0.72 | 15.81 | 10.01 |
| T6 | 3 456.25 | 7 409.49 | 9 445.10 | 25.59 | 2 647.10 | 0.93 | 9.27 | 15.55 | 9.76 |
Table 5 Tea garden annual economic benefits
处理 Treat- ment | 手采春茶 产量 Yield of hand picked spring tea/(kg·hm-2) | 机采春茶 产量 Yield of mechanical picked spring tea/ (kg·hm-2) | 机采夏秋茶 产量 Yield of mechanical picked summer and autumn tea/(kg·hm-2) | 茶园年收入 Annual income of tea plantation/ (104 yuan·hm-2) | 肥料用量 fertilizer amount/ (kg·hm-2) | 肥料单价 Fertilizer price/ (yuan·kg-1) | 肥料成本 The cost of fertilizer/(104 yuan·hm-2) | 人工费用 Labor cost/(104yuan·hm-2) | 利润 Profit/(104yuan·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 2 189.58 | 6 184.30 | 8 030.17 | 17.22 | — | — | — | 9.56 | 7.66 |
| T2 | 3 200.42 | 6 785.43 | 9 951.15 | 23.91 | 1 500.00 | 4.00 | 0.60 | 14.20 | 9.11 |
| T3 | 3 501.67 | 6 739.73 | 9 783.76 | 25.66 | 3 333.30 | 5.00 | 1.67 | 16.47 | 7.53 |
| T4 | 3 560.83 | 7 199.47 | 9 792.20 | 26.20 | 1 500.00 | 4.00 | 0.60 | 15.64 | 9.96 |
| T5 | 3 572.92 | 7 625.95 | 10 231.51 | 26.53 | 2 045.50 | 3.50 | 0.72 | 15.81 | 10.01 |
| T6 | 3 456.25 | 7 409.49 | 9 445.10 | 25.59 | 2 647.10 | 0.93 | 9.27 | 15.55 | 9.76 |
| 1 | 苏祝成.茶产业组织结构与绩效研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2001. |
| SU Z C. Studies on organizational structure and economic performance of tea industry [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2001. | |
| 2 | JAROSIEWICZ A, TOMASZEWSKA OMASZEWSKA M. Controlled-release NPK fertilizer encapsulated by polymeric membranes [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2003, 51(2): 413-417. |
| 3 | 张民,史衍玺,杨守祥,等.控释和缓释肥的研究现状与进展[J].化肥工业,2001,28(5):27-30, 63. |
| ZHANG M, SHI Y X, YANG S X, et al.. Status quo of study of controlled-release and slow-release fertilizers and progress made in this respect [J]. J.Chem.Fert.Ind., 2001, 28(5): 27-30, 63. | |
| 4 | 曾婕,张德全,闻禄,等.长期不同施肥模式对茶叶产量与土壤肥力的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2020,48(3):161-166. |
| ZENG J, ZHANG D Q, WEN Let al.. Effects of different long-term fertilization patterns on yield of tea and soil fertility [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(3): 161-166. | |
| 5 | 张群峰,倪康,伊晓云,等.中国茶树镁营养研究进展与展望[J].茶叶科学,2021,41(1):19-27. |
| Zhang Q F, Ni K, Yi X Y, et al.. Advances of magnesium nutrition in tea plant [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2021, 41(1): 19-27. | |
| 6 | RUAN L, WANG L, WEI K, et al.. Comparative analysis of nitrogen spatial heterogeneity responses in low nitrogen susceptible and tolerant tea plants (Camellia sinensis) [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2019, 246: 182-189. |
| 7 | 李倩,王玉,侯君合,等.崂山绿茶品质及其与土壤肥力关系的研究[J].土壤通报,2010,41(5):1101-1104. |
| LI Q, WANG Y, HOU J H, et al.. Quality of Laoshan green tea and its relationship with soil fertility factor [J]. J. Soil Sci., 2010, 41(5): 1101-1104. | |
| 8 | 田润泉,吕闰强.配方施肥对茶园土壤养分状况及茶鲜叶产量品质的影响[J].茶叶学报,2016,57(3):149-152. |
| TIAN R Q, LYU R Q. Effect of formulated fertilization on nutrient in soil, quality and yield of tea shoots [J]. Acta Tea Sin., 2016, 57(3): 149-152. | |
| 9 | 马立锋,苏孔武,黎金兰,等.控释氮肥对茶叶产量、品质和氮素利用效率及经济效益的影响[J].茶叶科学,2015,35(4):354-362. |
| MA L F, SU K W, LI J L, et al.. Effects of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on tea yield, quality, nitrogen use efficiency and economic benefit [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2015, 35(4): 354-362. | |
| 10 | 陈琳,乔志刚,李恋卿,等.施用生物质炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J].生态与农村环境学报,2013,5(5):671-675. |
| CHEN L, QIAO Z G, LI L Q, et al.. Effects of biocher-based fertilizers on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2013, 5(5): 671-675. | |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 茶磨碎试样的制备及其干物质含量测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2014. |
| 12 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 茶游离氨基酸总量的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2014. |
| 13 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2018. |
| 14 | 王继琛. 长期施肥对稻麦轮作系统土壤细菌及氮转化微生物群落影响的研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2018. |
| WANG J C. Effects of long-trem different fertilization regimes on soil bacterial and nitrogen-cycling related communities in a rice-wheat rotation system [D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 15 | 尤雪琴,杨亚军,阮建云.田间条件下不同园龄茶树氮、磷、钾养分需求规律的研究[J].茶叶科学,2008,28(3):207-213. |
| YOU X Q, YANG Y J, RUAN J Y. Requirement on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by tea plants with different ages under field conditions[J]. J. Tea Sci., 2008, 28(3): 207-213. | |
| 16 | 李德超. 蒙顶山茶叶品牌现状调查及推广对策分析[D].成都:四川农业大学,2016. |
| Li D C.Mengding tea brands status investigate and extension countermeasures analysis [D].Chengdu:Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 17 | 倪康,廖万有,伊晓云 等.我国茶园施肥现状与减施潜力分析[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2019,25(3):421-432. |
| NI K, LIAO W Y, YIN X Y, et al.. Fertilization status and reduction potential in tea gardens of China [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019, 25(3): 421-432. | |
| 18 | 马立锋,陈红金,单英杰,等.浙江省绿茶主产区茶园施肥现状及建议[J].茶叶科学,2013,33(1):74-84. |
| MA L F, CHEN H J, SHAN Y J, et al.. Status and suggestions of tea garden fertilization on main green tea-producing counties in Zhejiang province [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2013, 33(1): 74-84. | |
| 19 | 舒启华.汉中市无性系良种茶园现状及品种选择建议[J].基层农技推广,2016,4(3):82-84. |
| Shu Q H.Current situation and variety selection suggestions of clonal improved tea gardens in Hanzhong City [J] Prim. Agric. Tech. Ext., 2016,4(3):82-84. | |
| 20 | RUAN J Y, Gerendás J, Härdter R, et al. Effect of nitrogen form and root-zone pH on growth and nitrogen uptake of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants [J]. Ann. Bot., 2007, 99(2): 301-310. |
| 21 | 吴晓荣,张蓓蓓,余云飞,等.硝化抑制剂对典型茶园土壤尿素硝化过程的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2017,36(10):2063-2070. |
| WU X R, ZHANG B B, YU Y F, et al. Effects of nitrification inhibitors on nitrification rate of urea in four typical tea soils [J]. J. Agro. Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(10): 2063-2070. | |
| 22 | 刘岑薇,叶菁,李艳春 等.生物炭对茶园酸性红壤氮素养分淋溶的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(5):181-186. |
| LIU C W, YE Q, LI Y C, et al.. Effects of Biochar on soil nitrogen leaching in acid red loam of tea garden[J]. J. Agric. Sci. Tech., 2020, 22(5): 181-186. | |
| 23 | RICHARDSON A E, HOCKING P J, SIMPSON R J, et al.. Plant mechanisms to optimize access to soil phosphorus [J]. Crop Pasture Sci., 2009, 60: 124-143. |
| 24 | 韩文炎,石元值,马立峰.茶园钾素研究进展与施钾技术[J].中国茶叶,2004(1):22-24. |
| HAN W Y, SHI Y Z, MA L F. Research progress of potassium in tea garden and potassium application technology [J]. China Tea, 2004(1): 22-24. | |
| 25 | RUAN J Y, MA L F, SHI Y Z. Potassium management in tea plantations: its uptake by field plants, status in soils, and efficacy on yields and quality of teas in China [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 2013, 176(3): 450-459. |
| 26 | TAN H W, DU C L, ZHOU L Q. Effect of magnesium fertilizer on sustaining upland agricultural development in Guangxi province [J]. Better Crops Int., 2000, 14(2): 13-15. |
| 27 | 牛新湘,马兴旺.农田土壤养分淋溶的研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2011,27(3):451-156. |
| NIU X X, MA X W. Research advances on leaching of fertilizer nutrients from agricultural soils [J]. China Agron. Bull., 2011, 27(3): 451-156. | |
| 28 | 段玉环,郑西来,辛佳,等.土壤中新型肥料氮素淋失特征研究[J].安徽农学通报,2016,22(8):16-20. |
| DUAN Y H, ZHENG X L, XIN J, et al.. Nitrogen leaching characteristics of new emerging fertilizers in soil [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 22(8): 16-20. | |
| 29 | 武志杰,石元亮,李东坡,等.稳定性肥料发展与展望[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(6):1614-1621. |
| WU Z J, SHI Y L, LI D P, et al.. The development and outlook of stabilized fertilizers [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci., 2017, 23(6): 1614-1621. | |
| 30 | 赵蒙,曾科,姚元林,等.聚脲甲醛缓释肥对太湖稻麦轮作体系氨挥发及产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2019,25(1)55-63. |
| ZHAO M, ZENG K, YAO Y L, et al.. Effects of polyuria-formaldehyde on ammonia volatilization and yield under rice-wheat rotation system in Taihu Region [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci., 2019, 25(1): 55-63. | |
| 31 | 宋涛,尹俊慧,胡兆平 等.脲酶/硝化抑制剂减少农田土壤氮素损失的作用特征[J].农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(4):585-597. |
| SONG T, YIN J H, HU Z P, et al.. Characteristics of urease/nitrification inhibitors in reducing nitrogen losses in farmland soils[J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2021, 38(4): 585-597. | |
| 32 | 金晶,刁学刚,冯海强.2019年浙江茶产业现状及发展趋势预测[J].中国茶叶,2020,42(3)53-57. |
| JIN J, DIAO X G, FENG H Q. The current situation and development trend forecast of Zhejiang tea industry in 2019 [J]. Chin. Tea, 2020, 42(3): 53-57. |
| [1] | Yunping DONG, Yuzhou LONG, Xingjun LIN, Lizhen MO, Huakang ZHU, Qingyun ZHAO, Yan SUN. Effect of Different Fertilizer Applications on Yield, Quality and Economic Benefit of CoffeaArabica L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 197-203. |
| [2] | Xuan ZHOU, Pinling YANG, Jianwei PENG, Huiqing CHAI, Xuemei ZHONG, Xingrong KANG, Junyou LONG, Huiru ZHANG. Effects of Function Microbial Compound Fertilizer on Yield, Quality and Economic Benefit of Head Cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 184-192. |
| [3] | Wancang SUN, Xinwu PEI, Li MA, Xuefang WANG, Junyan WU, Xuecai LI, Yuanyuan PU, Lijun LIU, Peng CHAI, Xiaoze LI, Yujuan JIA, Jijun WANG, Fang LIU, Qixian CHEN, Jinxiong SHEN. Advances and Outlook of Winter Cover Crop Development Research in Northern China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 128-136. |
| [4] | ZHOU Xuan, KANG Xingrong, PENG Jianwei, YANG Xiangdong, ZHONG Xuemei, HU Wenfeng, LONG Junyou. Effects of Reduction Application of Polyurethane Coated Urea on Growth, Yield and Economic Benefit of Double-cropping Early Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 153-161. |
| [5] | ZHAO Jingwen, ZHANG Qingwei, LI Zheng, ZHANG Wentai*. Effects of Drip Irrigation Under Plastic Film and Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Salinity and Cotton Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(3): 102-108. |
| [6] | ZHAO Jianshe1,2, YANG Qiaoyun1,2, XIE Kaiquan1,2, WU Chao1,2, JIANG Gaoming3,4, LI Xiaofang1,2, HU Bo5, GUO Liyue3,4*. Analysis of Ecological Benefit of “Rice-duck Farming” Model and Its Economic Benefit in Ecological Farm [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(11): 149-156. |
| [7] | YAN Jinyao1, LU Junming2, HOU Wenfeng1, LI Xiaokun1*. Influence of Phosphorus Application Dosage on the Yield and Phosphorus Recovery Efficiency of Different Rice Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(8): 74-81. |
| [8] | LI Kaixu1, LU Jianwei1, LU Mingxing2, XU Weiming3, WANG Zhen4, PENG Wenyong5, LI Xiaokun1*. Effects of Different Special Formula Fertilizer on Rice Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Economic Benefit [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(1): 100-107. |
| [9] | HU He-nian, DOU Xue-cheng*. Studies on Economic Benefits Evaluation of Seed Industry based on DEA Model ——A Case Study of Zhangye Corn Seed Industry [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(6): 150-157. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号