




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 147-155.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0651
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Yongjun XIE( ), Xiaozhuo PAN, Fuhui CHEN, Kaibo YIN, Jiayue JIN, Yibing WANG(
), Xiaozhuo PAN, Fuhui CHEN, Kaibo YIN, Jiayue JIN, Yibing WANG( )
)
Received:2023-08-30
Accepted:2024-02-06
Online:2024-07-15
Published:2024-07-12
Contact:
Yibing WANG
谢勇俊( ), 潘小卓, 陈福慧, 尹凯波, 金嘉悦, 王一兵(
), 潘小卓, 陈福慧, 尹凯波, 金嘉悦, 王一兵( )
)
通讯作者:
王一兵
作者简介:谢勇俊 E-mail:jun146ban@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yongjun XIE, Xiaozhuo PAN, Fuhui CHEN, Kaibo YIN, Jiayue JIN, Yibing WANG. Screening, Identification and Biocontrol of Bacteria Degrading Ginseng Phenolic Acid Autotoxic Substances[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 147-155.
谢勇俊, 潘小卓, 陈福慧, 尹凯波, 金嘉悦, 王一兵. 人参酚酸类自毒物质降解菌的筛选鉴定及生防研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 147-155.
培养基 Culture medium | 组分 Component |
|---|---|
筛选培养基 Screening medium | 1 L培养基含(NH2)SO₄ 2 g、CaCl₂ 0.1 g、NaH2PO4 0.5 g、K2HPO4 0.5 g、MgSO4·7H2O 0.2 g、碳源(水杨酸、没食子酸、邻苯二甲酸、对羟基苯甲酸、丁香酸、香草酸、肉桂酸、魏酸)500 mg,1 000 mL蒸馏水,pH 7.2,固体培养基加入20 g琼脂粉 1 L medium contains 2 g (NH2)SO₄, 0.1 g CaCl₂, 0.5 g NaH2PO4, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.2 g MgSO4·7H2O, 500 mg carbon source (salicylic acid, gallic acid, phthalic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, butyric acid, vanillic acid, cinnamic acid and ferulic acid), 1 000 mL water,and pH 7.2, the solid medium contains 20 g agar powder |
Hugh-Leifson 培养基 Hugh-Leifson medium | 1 L培养基含葡萄糖10 g,蛋白胨2 g,磷酸氢二钾0.3 g,氯化钠5 g,琼脂3~5 g, 质量浓度为1% 溴麝香草酚蓝3 mL 1 L medium contains 10 g glucose, 2 g peptone, 0.3 g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 5 g sodium chloride, 3~5 g agar and 3 mL 1% bromomuscohol blue by mass |
明胶培养基 Gelatin medium | 1 L培养基含蛋白胨5 g,牛肉膏3 g,明胶120 g,pH 6.8~7.0 1 L medium contains 5 g peptone, 3 g beef paste, 120 g gelatin, pH 6.8~7.0 |
硝酸盐培养基 Nitrate medium | 1 L培养基含KNO3(不含NO2-)0.2 g,蛋白胨5 g,pH 7.4 1 L medium contains 0.2 g KNO3 (NO2- free), 5 g peptone, pH 7.4 |
尿素培养基 Urea medium | 1 L培养基含尿素20.0 g,Na2HPO4 9.5 g,酵母浸膏0.1 g,酚红0.01 g,KH2PO4 9.1 g, pH (6.8±0.2) 1 L medium contains 20.0 g urea, 9.5 g Na2HPO4, 0.1 g yeast extract, 0.01 g phenol red, 9.1 g KH2PO4, and pH (6.8±0.2) |
LB培养基 LB medium | 1 L培养基含胰蛋白胨10 g、酵母提取物5 g、氯化钠10 g 1 L medium contains 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 10 g sodium chloride |
Table 1 Test the required medium formulation
培养基 Culture medium | 组分 Component |
|---|---|
筛选培养基 Screening medium | 1 L培养基含(NH2)SO₄ 2 g、CaCl₂ 0.1 g、NaH2PO4 0.5 g、K2HPO4 0.5 g、MgSO4·7H2O 0.2 g、碳源(水杨酸、没食子酸、邻苯二甲酸、对羟基苯甲酸、丁香酸、香草酸、肉桂酸、魏酸)500 mg,1 000 mL蒸馏水,pH 7.2,固体培养基加入20 g琼脂粉 1 L medium contains 2 g (NH2)SO₄, 0.1 g CaCl₂, 0.5 g NaH2PO4, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.2 g MgSO4·7H2O, 500 mg carbon source (salicylic acid, gallic acid, phthalic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, butyric acid, vanillic acid, cinnamic acid and ferulic acid), 1 000 mL water,and pH 7.2, the solid medium contains 20 g agar powder |
Hugh-Leifson 培养基 Hugh-Leifson medium | 1 L培养基含葡萄糖10 g,蛋白胨2 g,磷酸氢二钾0.3 g,氯化钠5 g,琼脂3~5 g, 质量浓度为1% 溴麝香草酚蓝3 mL 1 L medium contains 10 g glucose, 2 g peptone, 0.3 g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 5 g sodium chloride, 3~5 g agar and 3 mL 1% bromomuscohol blue by mass |
明胶培养基 Gelatin medium | 1 L培养基含蛋白胨5 g,牛肉膏3 g,明胶120 g,pH 6.8~7.0 1 L medium contains 5 g peptone, 3 g beef paste, 120 g gelatin, pH 6.8~7.0 |
硝酸盐培养基 Nitrate medium | 1 L培养基含KNO3(不含NO2-)0.2 g,蛋白胨5 g,pH 7.4 1 L medium contains 0.2 g KNO3 (NO2- free), 5 g peptone, pH 7.4 |
尿素培养基 Urea medium | 1 L培养基含尿素20.0 g,Na2HPO4 9.5 g,酵母浸膏0.1 g,酚红0.01 g,KH2PO4 9.1 g, pH (6.8±0.2) 1 L medium contains 20.0 g urea, 9.5 g Na2HPO4, 0.1 g yeast extract, 0.01 g phenol red, 9.1 g KH2PO4, and pH (6.8±0.2) |
LB培养基 LB medium | 1 L培养基含胰蛋白胨10 g、酵母提取物5 g、氯化钠10 g 1 L medium contains 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 10 g sodium chloride |
| 编号Number | 比对结果Alignment result | 相似度Similarity/% |
|---|---|---|
| 14XC | 铜绿假单胞菌Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 99.52 |
| 19AW | Pseudomonas furukawaii | 99.67 |
| BH1AW | Pandoraea morbifera | 99.87 |
| BH2XC | 木糖氧化无色杆菌Achromobacter xylosoxidans | 99.55 |
| D2 | Pseudomonas qingdaonensis | 99.86 |
| DXH1 | 德莱无色杆菌Achromobacter deleyi | 99.22 |
| L1 | Methylorubrum populi | 99.85 |
| MSZ | 涅斯特连科氏菌Nesterenkonia | 99.72 |
| S1 | 伯克霍尔德菌Burkholderia FNTGs | 100.00 |
| RG1 | 副伯克霍尔德氏菌Paraburkholderia phytofirmans | 99.86 |
Table 2 Sequence alignment based on 16S rRNA gene
| 编号Number | 比对结果Alignment result | 相似度Similarity/% |
|---|---|---|
| 14XC | 铜绿假单胞菌Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 99.52 |
| 19AW | Pseudomonas furukawaii | 99.67 |
| BH1AW | Pandoraea morbifera | 99.87 |
| BH2XC | 木糖氧化无色杆菌Achromobacter xylosoxidans | 99.55 |
| D2 | Pseudomonas qingdaonensis | 99.86 |
| DXH1 | 德莱无色杆菌Achromobacter deleyi | 99.22 |
| L1 | Methylorubrum populi | 99.85 |
| MSZ | 涅斯特连科氏菌Nesterenkonia | 99.72 |
| S1 | 伯克霍尔德菌Burkholderia FNTGs | 100.00 |
| RG1 | 副伯克霍尔德氏菌Paraburkholderia phytofirmans | 99.86 |
| 项目Item | 结果Result | 项目Item | 结果Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏染色Gram stainning method | - | 硝酸盐还原试验Nitratereduction test | - |
| 吲哚试验Indole test | - | 明胶液化试验Gelatinliquefaction test | - |
| 甲基红试验Methylred test | + | 尿素酶试验Urease test | + |
| V⁃P试验 V⁃P test | + | 氧化-发酵试验Oxidation⁃fermentation test | + |
Table 3 Physiological and biochemical test results of strain S1
| 项目Item | 结果Result | 项目Item | 结果Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏染色Gram stainning method | - | 硝酸盐还原试验Nitratereduction test | - |
| 吲哚试验Indole test | - | 明胶液化试验Gelatinliquefaction test | - |
| 甲基红试验Methylred test | + | 尿素酶试验Urease test | + |
| V⁃P试验 V⁃P test | + | 氧化-发酵试验Oxidation⁃fermentation test | + |
酚酸种类 Type of phenolic acid | 标准曲线 Standard curve | 检测波长 Wave length/nm | 菌株 Strain | 降解率 Degradation rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水杨酸Salicylic acid | y=0.005 74x-0.011 91,R2=0.995 0 | 300 | S1 | 65.32 |
| 香草酸Vanillic acid | y=0.006 57x+0.041 87,R2=0.996 2 | 260 | 14XC | 55.00 |
| 丁香酸Syringic acid | y=0.004 47x+0.035,R2=0.990 8 | 280 | DXH1 | 48.00 |
对羟基苯甲酸 Para-hydroxybenzoic acid | y=0.107 90x-0.019 97,R2=0.999 7 | 225 | D2 | 43.00 |
| 邻苯二甲酸Phthalic acid | y=0.004 19x+0.001 86,R2=0.998 9 | 216 | L1 | 41.37 |
| 肉桂酸Cinnamic acid | y=0.016 66x-0.039 72,R2=0.990 8 | 278 | RG1 | 34.00 |
Table 4 Degradation effects of six strains of ginseng autotoxic substances degrading bacteria
酚酸种类 Type of phenolic acid | 标准曲线 Standard curve | 检测波长 Wave length/nm | 菌株 Strain | 降解率 Degradation rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水杨酸Salicylic acid | y=0.005 74x-0.011 91,R2=0.995 0 | 300 | S1 | 65.32 |
| 香草酸Vanillic acid | y=0.006 57x+0.041 87,R2=0.996 2 | 260 | 14XC | 55.00 |
| 丁香酸Syringic acid | y=0.004 47x+0.035,R2=0.990 8 | 280 | DXH1 | 48.00 |
对羟基苯甲酸 Para-hydroxybenzoic acid | y=0.107 90x-0.019 97,R2=0.999 7 | 225 | D2 | 43.00 |
| 邻苯二甲酸Phthalic acid | y=0.004 19x+0.001 86,R2=0.998 9 | 216 | L1 | 41.37 |
| 肉桂酸Cinnamic acid | y=0.016 66x-0.039 72,R2=0.990 8 | 278 | RG1 | 34.00 |
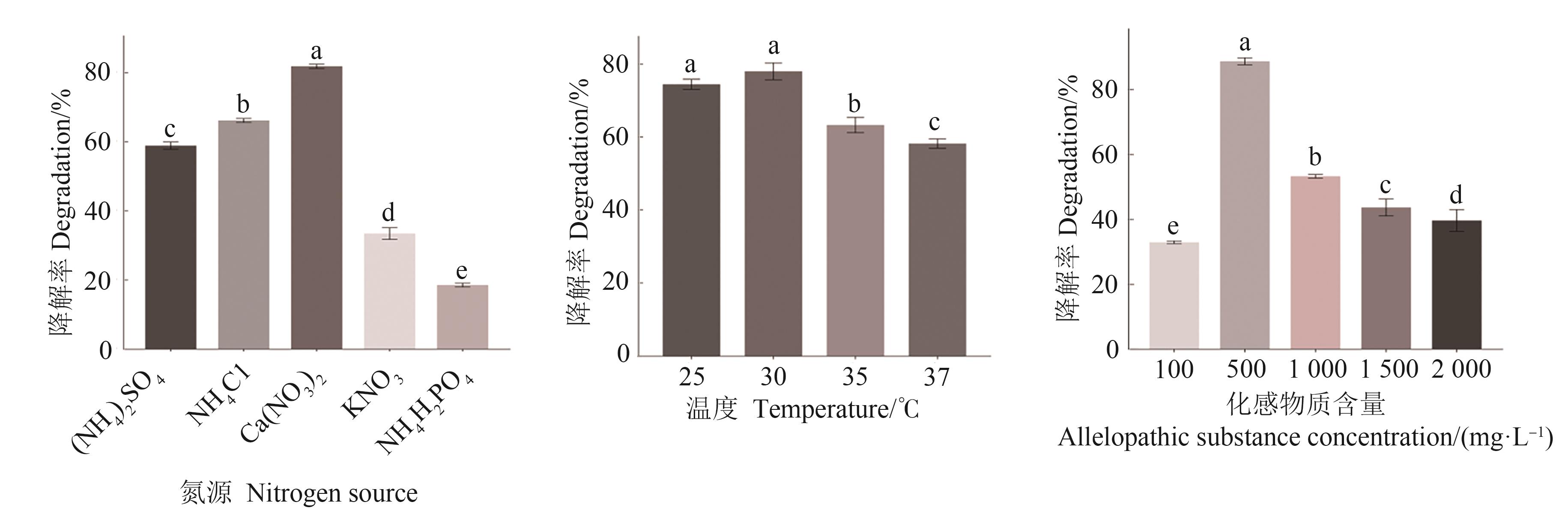
Fig. 3 Degradation rate of strain S1on salicylic acid under different cultured conditionsNote:Different lowercase letter indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 胚根长 Radicle length /mm | 胚轴长/mm Hypocotyl length /mm | RI胚根长 RI of radicle length | RI胚轴长 RI of hypocotyl length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 53.42±5.70 a | 27.95±8.76 a | — | — |
| SA0.025 | 46.87±12.04 ab | 13.57±4.16 bc | -0.128±0.18 b | -0.514±0.03 b |
| SA2.5 | 46.61±3.58 ab | 12.30±1.01 bc | -0.124±0.06 b | -0.539±0.10 b |
| SA250 | 35.77±4.55 b | 7.10±1.60 c | -0.330±0.05 b | -0.731±0.10 c |
| SA250+S1 | 60.13±8.71 a | 18.31±2.89 b | 0.154±0.13 a | -0.145±0.02 a |
Table 5 Radicle and hypocotyl lengths of ginseng seed under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 胚根长 Radicle length /mm | 胚轴长/mm Hypocotyl length /mm | RI胚根长 RI of radicle length | RI胚轴长 RI of hypocotyl length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 53.42±5.70 a | 27.95±8.76 a | — | — |
| SA0.025 | 46.87±12.04 ab | 13.57±4.16 bc | -0.128±0.18 b | -0.514±0.03 b |
| SA2.5 | 46.61±3.58 ab | 12.30±1.01 bc | -0.124±0.06 b | -0.539±0.10 b |
| SA250 | 35.77±4.55 b | 7.10±1.60 c | -0.330±0.05 b | -0.731±0.10 c |
| SA250+S1 | 60.13±8.71 a | 18.31±2.89 b | 0.154±0.13 a | -0.145±0.02 a |
| 1 | 张益恺,初赛君,董亚南,等.简述长白山人参在大健康产业中的应用[J].人参研究,2023,35(1):34-37. |
| 2 | 孙仁爽,赵敏婧,隋艳艳,等.人参药材抗氧化活性的研究[J].人参研究,2023,35(3):28-31. |
| 3 | BLOK W J, BOLLEN G J. The role of autotoxins from root residues of the previous crop in the replant disease of Asparagus [J]. Netherlands J. Plant Pathol., 1993, 99(3):29-40. |
| 4 | BENNETT J A, KLIRONOMOS J. Mechanisms of plant-soil feedback: interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers [J]. New Phytol., 2018, 222(1):91-96. |
| 5 | 周亭亭,战宇,李琼,等.人参属药用植物化感物质种类及其作用机制研究进展[J/OL].特产研究,2023:1-6 [2023-07-20].. |
| ZHOU T T, ZHAN Y, LI Q, et al.. Research progress on the types and mechanism of allelochemicals in ginseng medicinal plant [J/OL]. Spec. Res., 2023: 1-6 [2023-07-20]. . | |
| 6 | 李自博.人参根系自毒物质在连作障碍中的化感作用及其缓解途径研究[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2018. |
| LI Z B. Allelopathy of autotoxic compounds and mitigation method for ginseng continuous cropping obstacle [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 7 | HE C N, GAO W W, YANG J X, et al.. Identification of autotoxic compounds from fibrous roots of Panax quinquefolium L. [J]. Plant Soil, 2009, 318(1/2):63-72. |
| 8 | 陈福慧,谢勇俊,贾清文,等.林下连作种植参根际土壤可培养微生物区系及细菌群落对酚酸类化感物质的响应[J].广西科学,2023,30(3):468-477. |
| CHEN F H, XIE Y J, JIA Q W, et al.. Response of culturable microflora and bacterial community to phenolic allelochemica in rhizosphere soil of continuous cropping Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer under forest [J]. Guangxi Sci., 2023, 30(3):468-477. | |
| 9 | 刘莹,孙文松,李玲,等.人参连作障碍及防治措施研究进展[J].园艺与种苗,2020,40(7):26-29. |
| LIU Y, SUN W S, LI L, et al.. Research progress on consecutive monoculture problems and control measures of Panax ginseng [J]. Hortic. Seed, 2020, 40(7):26-29. | |
| 10 | 向维,韦小兰,曹科鑫,等.三七皂苷类自毒物质降解细菌分离及其降解特性[J].广西植物,2023,43(7):1173-1181. |
| XIANG W, WEI X L, CAO K X, et al.. Isolation and characterization of autotoxic saponins-degrading bacterial strains from Panax notoginseng [J]. Guihaia, 2023, 43(7):1173-1181. | |
| 11 | 王罗涛,杨冬英,邓琳梅,等.三七根际土壤中皂苷类自毒物质降解拮抗细菌的分离筛选[J].南方农业学报,2020,51(2):305-312. |
| WANG L T, YANG D Y, DENG L M, et al.. Isolation and screening of antagonistic autotoxin-degrading bacteria in Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen rhizosphere soil [J]. J. South Agric., 2020, 51(2):305-312. | |
| 12 | 赵亚慧,华雪洁,杜海岩,等.花生化感物质降解菌和抗连作拮抗菌复合菌剂应用效果的研究[J].土壤通报,2016,47(3):599-604. |
| ZHAO Y H, HUA X J, DU H Y, et al.. Research on the application effect of compound bacterium agent for allelochemicals degradation bacteria and antagonistic bacteria resistance to continuous cropping [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2016, 47(3):599-604. | |
| 13 | 张娜.微生物菌剂对设施番茄连作障碍的防治效果[J].蔬菜,2022(11):29-31. |
| ZHANG N. Effects of microbial inoculants on control of continuous cropping obstacles of facilities tomato [J]. Vegetables, 2022(11):29-31. | |
| 14 | 毛宁,薛泉宏,唐明,等.放线菌对对羟基苯甲酸的降解作用及草莓生长的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2010,12(5):103-108. |
| MAO N, XUE Q H, TANG M, et al.. Degradation of para-hydroxybenzoic acid by actinom yces and its effects on strawberry growth [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2010, 12(5):103-108. | |
| 15 | 肖蓉,邓舒,赵菁,等.自毒物质对羟基苯甲酸降解细菌ZH2的分离与应用[J].农学学报,2021,11(7):84-91. |
| XIAO R, DENG S, ZHAO J, et al.. An autotoxicity p-hydroxybenzoic acid-degrading strain ZH2: isolation and application [J]. J. Agron., 2021, 11(7):84-91. | |
| 16 | 东秀珠,蔡妙英.常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M].北京:科学出版社,2001:66-127. |
| 17 | GIBBONS N E, BUCHANAN R E. 伯杰细菌鉴定手册[M].北京:科学出版社,1984:446-450. |
| 18 | BRUCE-WILLIAMSON G, RICHARDSON D R. Bioassays for allelopathy: measuring treatment responses with independent controls [J]. J. Chem. Ecol., 1988, 14 (1):181-187. |
| 19 | 崔丙健,崔二苹,刘春成,等.土壤改良剂对再生水滴灌根际土壤菌群多样性及病原菌和抗生素抗性基因丰度的影响[J].环境科学,2022,43(10):4765-4778. |
| CUI B J, CUI E P, LIU C C, et al.. Effects of soil amendments on the bacterial diversity and abundances of pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes in rhizosphere soil under drip irrigation with reclaimed water [J]. Environ. Sci., 2022, 43(10):4765-4778. | |
| 20 | WANG X Q, CHEN D X, WANG J, et al.. Cloning and analysis of genes controlling antibacterial activities of Burkholderia pyrrocinia strain Lyc2 [J]. Curr. Microbiol., 2019, 76:1003-1009. |
| 21 | 许玉. Tsukamurella tyrosinosolvens P9、Burkholderia pyrrocinia P10与花生互作机制的比较研究[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2022. |
| XU Y. Comparative study on the interaction mechanism between Tsukamurella tyrosinosolvens P9, Burkholderia pyrrocinia P10 and peanut [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022. | |
| 22 | HAN L, ZHANG H, XU Y, et al.. Biological characteristics and salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting effects of an ACC deaminase-producing Burkholderia pyrrocinia strain isolated from the tea rhizosphere [J]. Arch. Microbiol., 2021, 203:2279-2290. |
| 23 | 王鹏飞.丹参自毒物质的鉴定及其在腐解液和根际土中的含量分析[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2021. |
| WANG P F. Identification of autotoxic substances from Salvia miltiorrhiza and analysis of their contents in decomposed solution and rhizosphere soil [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 24 | 张博洋,陈彦宏,栗锦鹏,等.自毒物质降解菌缓解药用植物连作障碍的作用及机制研究进展[J].中国野生植物资源,2023,42(11):7-14. |
| ZHANG B Y, CHEN Y H, LI J P, et al.. Research progress on the role and mechanisms of autotoxicity-degrading bacteria in alleviating continuous cropping obstacles of medicinal plants [J]. Chin. Wild Plant Res., 2023, 42(11):7-14. | |
| 25 | 李敏,张丽叶,张艳江,等.酚酸类自毒物质微生物降解转化研究进展[J].生态毒理学报,2019,14(3):72-78. |
| LI M, ZHANG L Y, ZHANG Y J, et al.. Review on the microbial biodegradation and metabolism of autotoxic phenolic acids [J]. Asian J. Ecotoxicol., 2019, 14(3):72-78. | |
| 26 | PEETERS C, ZLOSNIK J E A, SPILKER T, et al.. Burkholderia pseudomultivorans sp. nov., a novel Burkholderia cepacia complex species from human respiratory samples and the rhizosphere [J]. Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 2013, 36(7):483-489. |
| 27 | WILHELM R C, DERITO C M, SHAPLEIGH J P, et al.. Phenolic acid-degrading Paraburkholderia prime decomposition in forest soil [J/OL]. Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 2020, 9: 317347 [2023-07-20]. . |
| [1] | Linbo SHI, Qing PENG, Xiaoqing XU, Yuwei ZHANG, Shuo YANG, Dandan TIAN, Mengxin HE, Bo SHI, Yu QIAO. Effects of Co-culture of Lactobacillus casei NA-2 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGG on Antibacterial Activity [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 63-71. |
| [2] | Tongyu ZHANG, Ying GOU, Qi LI, Li YANG. Effects of Ginseng Rust Rot on Ginseng Quality and Soil Related Factors [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [3] | Yancheng WANG, Jiyue ZHANG, Shuaiqi FENG, Xue LIANG, Zhen ZHANG, Weiwei DONG, Wenxiu JI. Effects of Exogenous PGPR Combined with Organic Fertilizers on Soil Properties and Stress Resistance of Ginseng Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [4] | Ning YAN, Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI. Effects of Reductive Soil Disinfestation on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Enzyme Activity in Continuous Cropping of Ginseng [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [5] | LIU Qian1,2, LI Jichao1, ZUO Yingmei1, YANG Tianmei1, YANG Meiquan1, ZHANG Jinyu1*. Influences of Organic Mulching on Soil Nutrient and Microbial Diversity of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [6] | LI Haocheng1,2, ZUO Yingmei2, YANG Shaobing2, YANG Tianmei2, LI Jichao2, YANG Weize2, ZHANG Jinyu2*. Ecological Effect of Root Exudates of Panax notoginseng on Continuous Cropping Obstacles and its Alleviating Methods [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(8): 159-167. |
| [7] |
.
Effects of LED Red and Blue Light on Growth, Yield and Saponin Content of American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius)
[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(4): 171-176.
|
| [8] | BAO Yuanyuan1, ZHANG Xinyong2, YANG Ming1, ZHANG Yuejiang1, MAO Zhongshun3, YANG Li3, FENG Guangquan3*. Residue Dynamics of Myclobutanil in Panax notoginseng and Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(8): 107-114. |
| [9] | CHEN Jine, LIU Hui, ZHAO Zhigang, ZHANG Hairong*. Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted Extraction of Panax notoginseng Root Polysaccharides Using Response Surface Methology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(4): 138-146. |
| [10] | YIN Ben-lin1,2, MI Yan-hua1*, HE Li-zhong1,2, CHEN Lu1, LU Cheng-yun3, WANG Lin-meng4. Effects of Planting Management Mode on Arsenic Residue in the Soil and Panax notoginseng [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(5): 148-156. |
| [11] | ZHANG Qing\|fang, YU Zong\|lian . A Strain of Lignin\|degrading Bacterias Screening and Optimization of Enzyme\|producing Condition [J]. , 2014, 16(2): 143-148. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zi-long, WANG Wen-quan. Formation Mechanism and Control Measures of Continuous Cropping Obstacles in Medicinal Plants [J]. , 2009, 11(6): 19-23. |
| [13] | ZHENG Huai-zhong, CHEN Fa-he, LI Shu-yan, SUN Jun-she, LIU Ping. Screening of High Nitrite Reductase Producing Strains and the Optimization of Fermentation [J]. , 2009, 11(3): 81-87. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号