




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 60-72.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0214
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yongxu GUAN( ), Zhicheng SUN, Yan WANG, Yuan LI, Xiaoli SUN, Bowei JIA(
), Zhicheng SUN, Yan WANG, Yuan LI, Xiaoli SUN, Bowei JIA( ), Mingzhe SUN(
), Mingzhe SUN( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Accepted:2024-12-03
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
Bowei JIA,Mingzhe SUN
关永旭( ), 孙志成, 王研, 李媛, 孙晓丽, 贾博为(
), 孙志成, 王研, 李媛, 孙晓丽, 贾博为( ), 孙明哲(
), 孙明哲( )
)
通讯作者:
贾博为,孙明哲
作者简介:关永旭 E-mail:1348815413@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yongxu GUAN, Zhicheng SUN, Yan WANG, Yuan LI, Xiaoli SUN, Bowei JIA, Mingzhe SUN. Functional Analysis of Arabidopsis thalianaAtCHX19 Gene in Response to Salt-alkali Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 60-72.
关永旭, 孙志成, 王研, 李媛, 孙晓丽, 贾博为, 孙明哲. 拟南芥AtCHX19基因在盐碱胁迫应答中的功能解析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 60-72.

Fig. 4 Sequence comparison of CHXproteins of Group Ⅳ in Arabidopsis thalianaNote:The red line identifies the Na+/H+ exchanger conserved domain position.
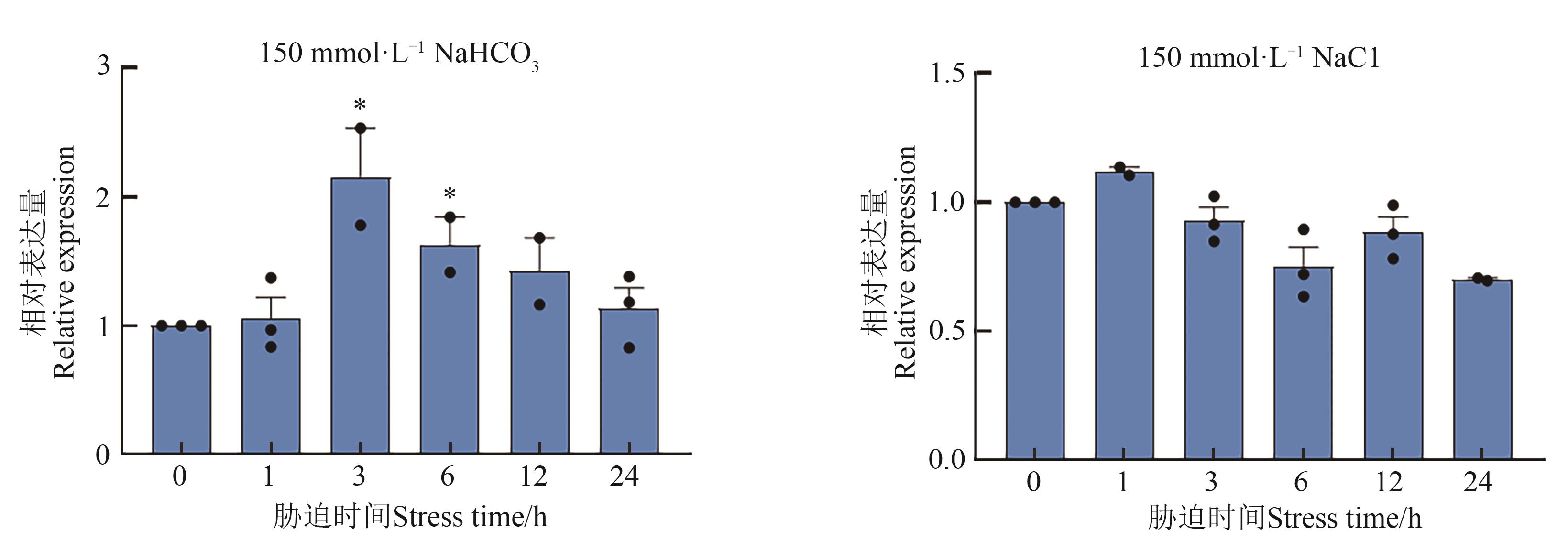
Fig. 7 Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of expression of AtCHX19 gene under different stress treatmetnsNote: * indicates significant difference compared with the expression of 0 h at P<0.05 level.
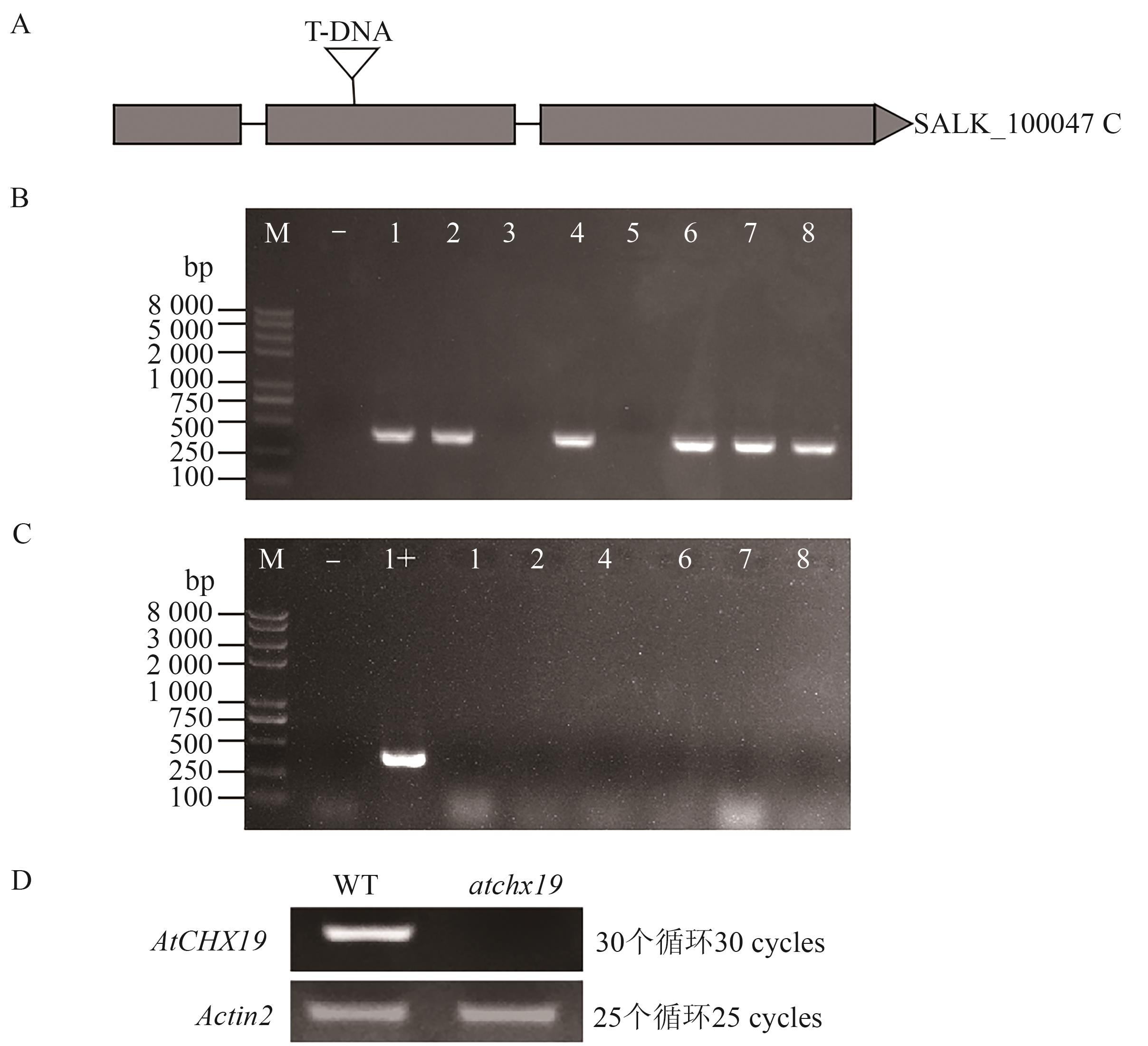
Fig. 8 Identification of T-DNA insertion mutants of AtCHX19 transgenic Arabidopsis thalianaA: T-DNA was inserted into the mutant SALK_100047C; B: PCR identification of AtCHX19 siliencing insertion; C: PCR identification of AtCHX19 siliencing homozygous; D: Identification of atchx19 mutants by RT-PCR. M—Trans2K Plus Ⅱ DNA Marker; - —Negative control; + —Positive control; 1~8—Arabidopsis mutants
序号 Number | 基因名称 Gene name | 登录号 Accession number | 编码蛋白类型 Encoding protein type | 非生物胁迫表达模式 Expression pattern under abiotic stress | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AtNHX1 | AT5G27150 | Na+/H+ 逆向转运蛋白 Na+/H+ antiporter protein | 受渗透和盐胁迫诱导 Induced by osmosis and salt stress | [ |
| 2 | AtNHX3 | AT5G55470 | Na+/H+ 逆向转运蛋白 Na+/H+ antiporter protein | 受渗透和盐胁迫诱导 Induced by osmosis and salt stress | [ |
Table 1 Functional annotation of AtCHX19 interacting proteins
序号 Number | 基因名称 Gene name | 登录号 Accession number | 编码蛋白类型 Encoding protein type | 非生物胁迫表达模式 Expression pattern under abiotic stress | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AtNHX1 | AT5G27150 | Na+/H+ 逆向转运蛋白 Na+/H+ antiporter protein | 受渗透和盐胁迫诱导 Induced by osmosis and salt stress | [ |
| 2 | AtNHX3 | AT5G55470 | Na+/H+ 逆向转运蛋白 Na+/H+ antiporter protein | 受渗透和盐胁迫诱导 Induced by osmosis and salt stress | [ |
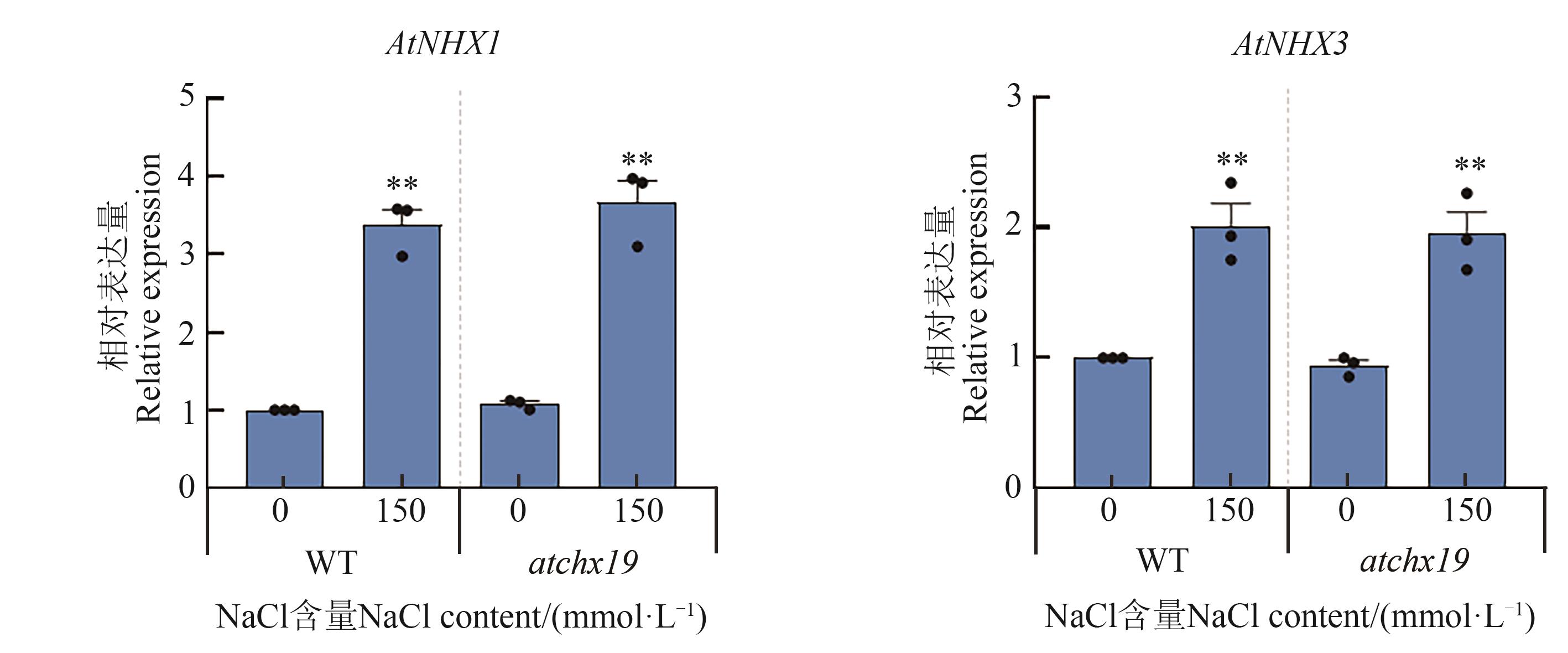
Fig. 9 Expression of AtNHX1 and AtNHX3 genes under 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatmentNote: ** indicates significant difference with 0 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatment at P<0.01 level.
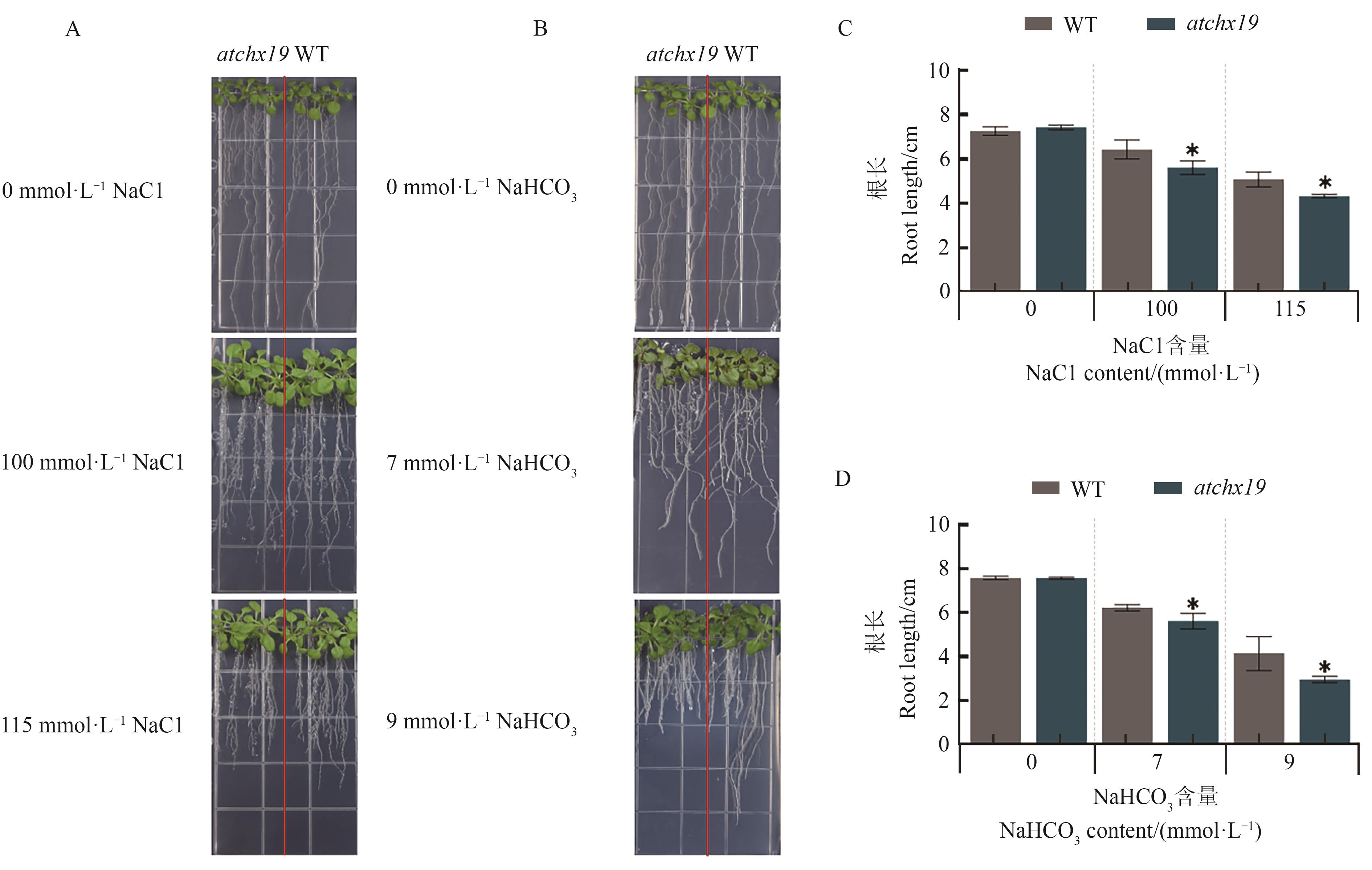
Fig. 10 Phenotypy of WT and mutant atchx19 atyoung seedlings stage under saline-alkali stressA: Phenotype of seedling under NaCl treatment; B: Phenotype of seedling under NaHCO3 treatment; C: Root length of seedling under NaCl treatment; D: Root length of seedling under NaHCO3 treatment. * indicates significant difference compared with WT at P<0.05 level

Fig. 11 Phenotypic of WT and mutant atchx19 at seedling stage under saline-alkali stressA:Phenotype; B:Survival rate; * indicates significant difference between muntant and WT at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 12 Contents of Na+, K+ in WT and mutant atchx19 under different treatmentsA: K+ content under different treatments; B: Na+ content under different treatments; C: K+/Na+ under controltreatment; D: K+/Na+ under NaHCO3 treatment. * and ** indicate significant differences ampared with WT at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively
| [1] | MUKHOPADHYAY R, SARKAR B, JAT H S, et al.. Soil salinity under climate change:challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2021, 280:111736 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [2] | LIU L L, WANG B S. Protection of halophytes and their uses for cultivation of saline-alkali soil in China [J/OL]. Biology, 2021, 10(5): 353 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [3] | 葛瑶, 栾明鉴, 张雪楠,等.中国盐生植物分布与盐碱地类型的关系[J].齐鲁工业大学学报,2021,35(2):14-20. |
| GE Y, LUAN M J, ZHANG X N, et al.. The relationship between the distribution of halophytes in China and the types of saline-alkali land [J]. J.Qilu Univ. Technol., 2021,35(2):14-20. | |
| [4] | 刘丹, 王柯蔼, 倪蓬,等.大豆GolS基因家族鉴定及盐旱胁迫下的表达分析[J].生物工程学报, 2022, 38(10): 3757-3772. |
| LIU D, WANG K A, NI P, et al.. Identification of soybean GolS gene family and analysis of expression patterns under salt and drought stresses [J]. Chin. J. Biotechnol., 2022, 38(10): 3757-3772. | |
| [5] | CHEN J P, LI X X, YE X X, et al.. An S-ribonuclease binding protein EBS1 and brassinolide signaling are specifically required for Arabidopsis tolerance to bicarbonate [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2021, 72(4): 1449-1459. |
| [6] | LI J F, SHEN L K, HAN X L, et al.. Phosphatidic acid-regulated SOS2 controls sodium and potassium homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress [J/OL]. Embo J., 2023, 42(8):e112401 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [7] | 柳参奎,张欣欣,程玉祥.“植物细胞内pH调控系统”是适应环境逆境的一个耐性机制[J].分子植物育种, 2004(2):179-186. |
| LIU S K, ZHANG X X, CHENG Y X. Is the “plant intracellular pH regulation system” a tolerance mechanism adapting to environmental stress [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2004(2): 179-186. | |
| [8] | 李静, 刘明, 孙晶, 等.Na+(K+)/H+转运蛋白NHX基因的研究进展[J].大豆科学,2011,30(6):1035-1039. |
| LI J, LIU M, SUN J, et al.. Progress of research on Na+(K+)/H+ antiporter NHX gene [J]. Soybean Sci., 2011, 30(6): 1035-1039. | |
| [9] | ZHENG S, PAN T, FAN L G, et al.. A novel AtKEA gene family,homolog of bacterial K+/H+ antiporters,plays potential roles in K+ homeostasis and osmotic adjustment in Arabidopsis [J/OL].PLoS One, 2013,8(11):e81463 [2024-01-20].. |
| [10] | 卜华虎.玉米Na+/H+质子泵ZmNHX1功能的初步研究[D].北京:中央民族大学,2011. |
| BU H H. Preliminary study on function of maize Na+/H+ proton pump ZmNHX1 [D]. Beijing: Minzu University of China, 2011. | |
| [11] | 张东亮,吴筱林,田晓芹,等.藜麦CqKEA基因家族的鉴定及表达 [J].烟台大学学报(自然科学与工程版),2021,34(4):400-405. |
| ZHANG D L, WU X L, TIAN X Q,et al.. Identification and expression of CqKEA gene family in Chenopodium quinoa [J]. J. Yantai Univ. (Nat. Sci. Eng.),2021, 34(4): 400-405. | |
| [12] | 才晓溪,沈阳,周伍红,等.大豆CHX基因家族全基因组鉴定与生物信息学分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2018,37(12):5360-5369. |
| CAI X X, SHEN Y, ZHOU W H, et al.. Genome-wide identification and bioinformatics analysis of soybean CHX gene family [J]. Genom. Appl. Biol., 2018, 37(12): 5360-5369. | |
| [13] | 贾博为,金军,庄齐,等.玉米CHX基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J].黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2022,34(4):23-30, 64. |
| JIA B W, JIN J, ZHUANG Q, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of maize CHX family [J]. J.Heilongjiang Bayi Agric. Univ., 2022, 34(4):23-30, 64. | |
| [14] | SZE H, PADMANABAN S, CELLIER F, et al.. Expression patterns of a novel AtCHX gene family highlight potential roles in osmotic adjustment and K+ homeostasis in pollen development [J]. Plant Physiol., 2004, 136(1):2532-2547. |
| [15] | PADMANABAN S, CHANROJ S, KWAK J M, et al.. Participation of endomembrane cation/H+ exchanger AtCHX20 in osmoregulation of guard cells [J]. Plant Physiol., 2007, 144(1): 82-93. |
| [16] | LU Y X, CHANROJ S, ZULKIFLI L, et al.. Pollen tubes lacking a pair of K+ transporters fail to target ovules in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2011, 23(1): 81-93. |
| [17] | SONG C P, GUO Y, QIU Q S, et al..A probable Na+(K+)/H+ exchanger on the chloroplast envelope functions in pH homeostasis and chloroplast development in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(27):10211-10216. |
| [18] | CHANROJ S, LU Y X, PADMANABAN S, et al.. Plant-specific cation/H+ exchanger 17 and its homologs are endomembrane K+ transporters with roles in protein sorting [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2011,286(39):33931-33941. |
| [19] | PADMANABAN S, CZERNY D D, LEVIN K A, et al.. Transporters involved in pH and K+ homeostasis affect pollen wall formation,male fertility,and embryo development [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2017, 68(12): 3165-3178. |
| [20] | JIA B W, SUN M Z, DUANMU H Z, et al.. GsCHX19.3,a member of cation/H(+) exchanger superfamily from wild soybean contributes to high salinity and carbonate alkaline tolerance [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1): 9423 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [21] | 杨浩. GsCHX19基因对肇东紫花苜蓿的遗传转化及新株系的培育[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2017. |
| YANG H. Transformation of GsCHX19 gene into Medicago sativa L. and cultivation new strains [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [22] | GOODSTEIN D M, SHU S Q, HOWSON R, et al.. Phytozome:a comparative platform for green plant genomics [J].Nucl. Acids Res., 2012, 40(D1):D1178-D1186. |
| [23] | BAILEY T L, BODEN M, BUSKE F A, et al.. MEME SUITE:tools for motif discovery and searching [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2009, 37: 202-208. |
| [24] | WAESE J, FAN J, PASHA A, et al.. ePlant:visualizing and exploring multiple levels of data for hypothesis generation in plant biology [J]. Plant Cell, 2017, 29(8): 1806-1821. |
| [25] | LETUNIC I, BORK P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2018, 46(D1):D493-D496. |
| [26] | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25 (4): 402-408.. |
| [27] | CHANROJ S, WANG G Y, VENEMA K, et al.. Conserved and diversified gene families of monovalent cation/H(+) antiporters from algae to flowering plants [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2012, 3:25 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [28] | PARDO J M, CUBERO B, LEIDI E O, et al.. Alkali cation exchangers:roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2006, 57(5):1181-1199. |
| [29] | PABUAYON I C M, JIANG J F, QIAN H J, et al.. Gain-of-function mutations of AtNHX1 suppress sos1 salt sensitivity and improve salt tolerance in Arabidopsis [J/OL]. Stress Biol.,2021, 1(1):14 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [30] | LIU H, WANG Q Q, YU M M, et al.. Transgenic salt-tolerant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) constitutively expressing an Arabidopsis thaliana vacuolar Na/H antiporter gene,AtNHX3,accumulates more soluble sugar but less salt in storage roots [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2008, 31(9):1325-1334. |
| [31] | CHANROJ S, PADMANABAN S, CZERNY D D, et al.. K+ transporter AtCHX17 with its hydrophilic C tail localizes to membranes of the secretory/endocytic system:role in reproduction and seed set [J]. Mol. Plant, 2013, 6(4):1226-1246. |
| [32] | LI Y, YE H, VUONG T D, et al.. A novel natural variation in the promoter of GmCHX1 regulates conditional gene expression to improve salt tolerance in soybean [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2024,75(3):1051-1062. |
| [33] | ZHAO J, CHENG N H, MOTES C M, et al.. AtCHX13 is a plasma membrane K+ transporter [J].Plant Physiol.,2008,148(2):796-807. |
| [34] | ZHAO J, LI P H, MOTES C M, et al.. CHX14 is a plasma membrane K-efflux transporter that regulates K(+) redistribution in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2015, 38(11):2223-2238. |
| [35] | CELLIER F, CONÉJÉRO G, RICAUD L, et al.. Characterization of AtCHX17,a member of the cation/H+ exchangers,CHX family,from Arabidopsis thaliana suggests a role in K+ homeostasis [J]. Plant J.,2004, 39(6): 834-846. |
| [36] | EVANS A R, HALL D, PRITCHARD J, et al.. The roles of the cation transporters CHX21 and CHX23 in the development of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2012, 63(1):59-67. |
| [1] | Lei LING, Huixin JIANG, Mingjing LI, Yajie YIN, Naiyu CHEN, Xiaoju ZHAO. Proteinome and Metabolome Combined to Analyze the Response Mechanism of Oat to Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 61-71. |
| [2] | Min YAN, Yan WANG, Chengcheng WANG, Songchao GUO, Dengyang LU, Cuiyun WU. Effect of Mixed Saline-alkali Stress on Leaf Structure and Photosynthetic Fluorescence Properties of Jujube [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 57-65. |
| [3] | Lupeng SUN, Yang YANG, Weichao WANG, Tingdong FU, Guangsheng ZHOU, Fenghua ZHANG. Ion Response Mechanism of Canola Seedlings to Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 46-54. |
| [4] | Peixin LIANG, Rong TANG, Jianguo LIU. Effects of Mixed Saline-alkali Stress on Photosynthetic Physiology and Yield in Cyperus esculentus L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 195-204. |
| [5] | Guangke LUO, Rongbo MU, Bing XUE, Hua ZHANG, Yanping REN, Hao MA. Function and Characteristic Analysis of Haloxylon ammodendron NAC Transcription Factor HaNAC38 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 65-73. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号