




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 46-54.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0835
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lupeng SUN1( ), Yang YANG1, Weichao WANG1, Tingdong FU2, Guangsheng ZHOU2, Fenghua ZHANG1(
), Yang YANG1, Weichao WANG1, Tingdong FU2, Guangsheng ZHOU2, Fenghua ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2021-09-25
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Fenghua ZHANG
孙鲁鹏1( ), 杨洋1, 王卫超1, 傅廷栋2, 周广生2, 张凤华1(
), 杨洋1, 王卫超1, 傅廷栋2, 周广生2, 张凤华1( )
)
通讯作者:
张凤华
作者简介:孙鲁鹏 E-mail:190508751@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lupeng SUN, Yang YANG, Weichao WANG, Tingdong FU, Guangsheng ZHOU, Fenghua ZHANG. Ion Response Mechanism of Canola Seedlings to Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 46-54.
孙鲁鹏, 杨洋, 王卫超, 傅廷栋, 周广生, 张凤华. 油菜苗期对盐碱胁迫的离子响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 46-54.
电导率 Conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | pH | Na+含量 Na+ content/(mg·g-1) | Cl-含量 Cl- content/(mg·g-1) | SO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.70 | 7.41 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 3.80 |
Table 1 Main soil parameters
电导率 Conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | pH | Na+含量 Na+ content/(mg·g-1) | Cl-含量 Cl- content/(mg·g-1) | SO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.70 | 7.41 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 3.80 |
处理 Treatment | 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | |
| 轻度Low | 0.76 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 0.12 |
| 中度Moderate | 1.27 | 2.32 | 1.22 | 0.19 |
| 重度High | 2.55 | 4.63 | 2.44 | 0.38 |
Table 2 Salt types and content of combined saline-alkali salt
处理 Treatment | 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | |
| 轻度Low | 0.76 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 0.12 |
| 中度Moderate | 1.27 | 2.32 | 1.22 | 0.19 |
| 重度High | 2.55 | 4.63 | 2.44 | 0.38 |
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 干重Dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root/shoot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
茎叶 Stem and leaf | 根 Root | |||
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.34±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.23±0.06 b | 0.02±0.01 b | 0.07±0.02 a | |
| 重度High | 0.08±0.01 c | 0.01±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.83±0.01 a | 0.14±0.02 a | 0.17±0.02 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.58±0.00 b | 0.09±0.01 b | 0.15±0.01 a | |
| 重度High | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.02±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 b | |
Table 3 Biomass and root/shoot ratio of canola at different seedling stages under combined saline-alkali salt stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 干重Dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root/shoot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
茎叶 Stem and leaf | 根 Root | |||
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.34±0.05 a | 0.02±0.00 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.23±0.06 b | 0.02±0.01 b | 0.07±0.02 a | |
| 重度High | 0.08±0.01 c | 0.01±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.83±0.01 a | 0.14±0.02 a | 0.17±0.02 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.58±0.00 b | 0.09±0.01 b | 0.15±0.01 a | |
| 重度High | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.02±0.00 c | 0.09±0.02 b | |
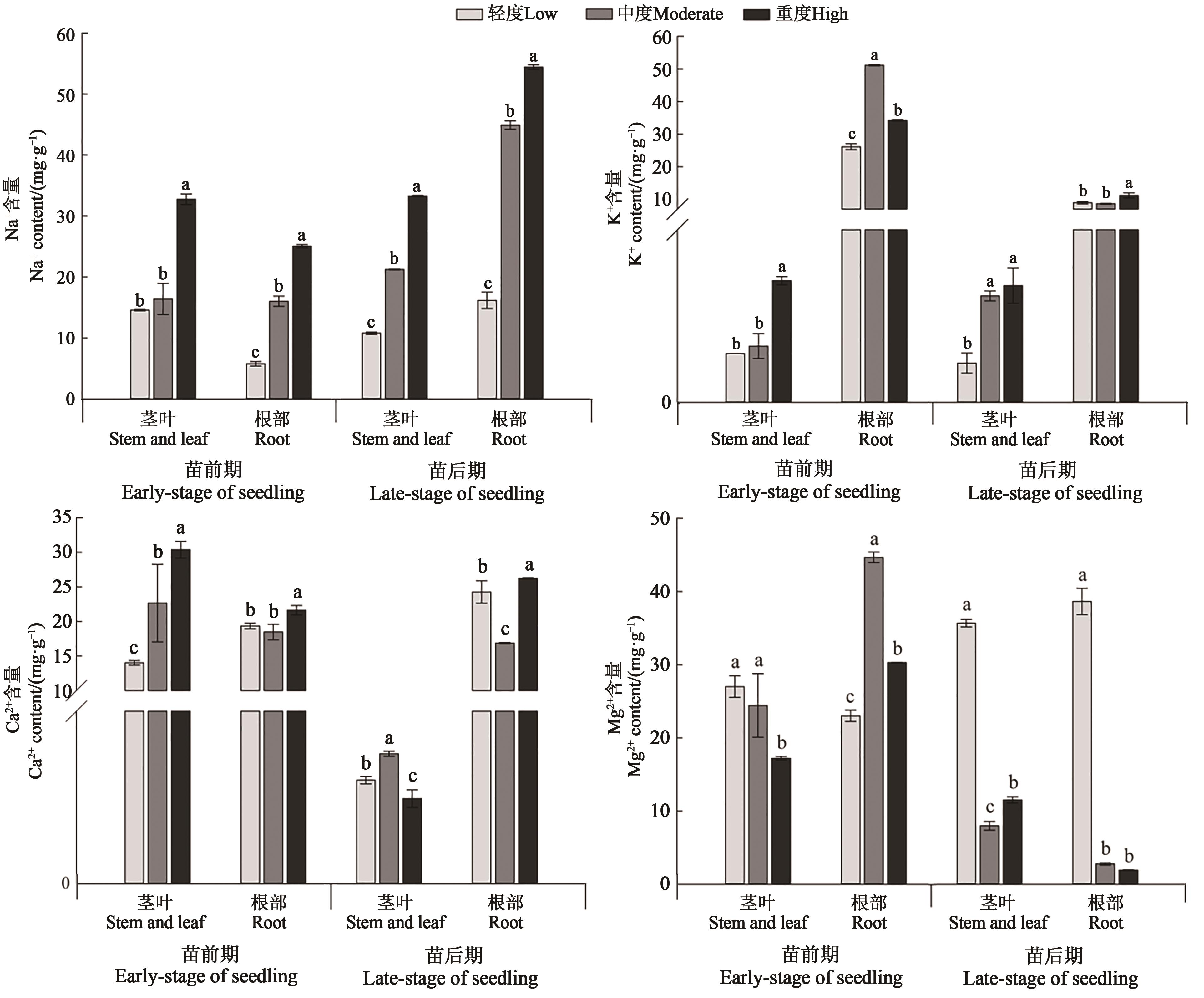
Fig. 1 Na+,K+,Ca2+,Mg2+ contents of canola seedling in different growth stages under combined saline-alkali stressNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
生长阶段 Growth stage | 器官 Organ | 处理 Treatment | Na+/K+ | Na+/Ca2+ | Na+/Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 25.70±0.18 aα | 1.04±0.03 aβ | 0.54±0.03 bα |
| 中度Moderate | 25.39±1.79 aα | 0.73±0.08 bβ | 0.70±0.25 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 23.24±0.50 bα | 1.08±0.07 aβ | 1.90±0.03 aβ | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 0.22±0.02 cβ | 0.30±0.02 cβ | 0.25±0.03 cβ | |
| 中度Moderate | 0.31±0.02 bβ | 0.87±0.01 bβ | 0.36±0.02 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 0.73±0.01 aβ | 1.16±0.03 aβ | 0.83±0.01 aβ | ||
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 24.83±6.48 aα | 9.00±0.44 cα | 0.30±0.00 bβ |
| 中度Moderate | 17.25±0.87 aβ | 14.11±0.29 bα | 2.67±0.20 aα | ||
| 重度High | 25.00±3.94 aα | 33.98±3.56 aα | 2.89±0.11 aα | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 1.80±0.08 bα | 0.67±0.05 cα | 0.42±0.03 cα | |
| 中度Moderate | 5.19±0.15 aα | 2.66±0.03 aα | 16.19±1.08 bα | ||
| 重度High | 4.87±0.36 aα | 2.07±0.02 bα | 28.22±0.61 aα |
Table 4 Ion ratio in canola seedlings at different growth stages under combined saline-alkali stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 器官 Organ | 处理 Treatment | Na+/K+ | Na+/Ca2+ | Na+/Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 25.70±0.18 aα | 1.04±0.03 aβ | 0.54±0.03 bα |
| 中度Moderate | 25.39±1.79 aα | 0.73±0.08 bβ | 0.70±0.25 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 23.24±0.50 bα | 1.08±0.07 aβ | 1.90±0.03 aβ | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 0.22±0.02 cβ | 0.30±0.02 cβ | 0.25±0.03 cβ | |
| 中度Moderate | 0.31±0.02 bβ | 0.87±0.01 bβ | 0.36±0.02 bβ | ||
| 重度High | 0.73±0.01 aβ | 1.16±0.03 aβ | 0.83±0.01 aβ | ||
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 轻度Low | 24.83±6.48 aα | 9.00±0.44 cα | 0.30±0.00 bβ |
| 中度Moderate | 17.25±0.87 aβ | 14.11±0.29 bα | 2.67±0.20 aα | ||
| 重度High | 25.00±3.94 aα | 33.98±3.56 aα | 2.89±0.11 aα | ||
根 Root | 轻度Low | 1.80±0.08 bα | 0.67±0.05 cα | 0.42±0.03 cα | |
| 中度Moderate | 5.19±0.15 aα | 2.66±0.03 aα | 16.19±1.08 bα | ||
| 重度High | 4.87±0.36 aα | 2.07±0.02 bα | 28.22±0.61 aα |
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.009±0.001 c | 0.288±0.020 b | 0.467±0.026 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.012±0.002 b | 1.190±0.117 a | 0.547±0.150 a | |
| 重度High | 0.031±0.001 a | 1.076±0.052 a | 0.435±0.009 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.076±0.021 c | 0.074±0.006 b | 1.386±0.101 c |
| 中度Moderate | 0.302±0.022 a | 0.189±0.005 a | 6.080±0.565 b | |
| 重度High | 0.198±0.039 b | 0.062±0.007 c | 9.762±0.225 a |
Table 5 Ion selective transport coefficient of canola seedling at different growth stages combined saline-alkali stress
生长阶段 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
苗前期 Early-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.009±0.001 c | 0.288±0.020 b | 0.467±0.026 a |
| 中度Moderate | 0.012±0.002 b | 1.190±0.117 a | 0.547±0.150 a | |
| 重度High | 0.031±0.001 a | 1.076±0.052 a | 0.435±0.009 a | |
苗后期 Late-stage of seedling | 轻度Low | 0.076±0.021 c | 0.074±0.006 b | 1.386±0.101 c |
| 中度Moderate | 0.302±0.022 a | 0.189±0.005 a | 6.080±0.565 b | |
| 重度High | 0.198±0.039 b | 0.062±0.007 c | 9.762±0.225 a |
| 1 | YANG J Y, ZHENG W, TIAN Y, et al.. Effects of various mixed salt-alkaline stresses on growth, photosynthesis, and photosynthetic pigment concentrations of Medicago rutheniumca seedlings [J]. Photosynthetic, 2011, 49:275-284. |
| 2 | PAZ R C, REINOSO H, ESPASABDIN F D, et al.. Akaline saline and mixed saline alkaline induce physiologicaland morphoanatomical changes in Lotus tenuis shoots [J]. Plant Biol., 2014, 16(6):1042-1049. |
| 3 | 乌凤章,王贺新.盐胁迫对高丛越橘幼苗生长及离子平衡的影响[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(11):3335-3341. |
| WU F Z, WANG H X. Effects of salt stress on growth and ion homeostasis of highbush blueberry seedlings [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2019, 38(11):3335-3341. | |
| 4 | ZHU X J, YANG J S, LIANG Y C, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium on photosynthesis and its related physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under salt stress [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2004, 37(10):1497-1503. |
| 5 | LOUPASSAKI M H, CHARTZOULAKIS K S, DIGALAKI N B, et al.. Effects of salt stress on concentration of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium in leaves, shoots, and roots of six olive cultivars [J]. J. Plant Nutr., 2002, 25(11):2457-2482. |
| 6 | ZHANG J L, FLOWERS T J, WANG S M. Mechanisme of sodium up take by roots of higher plants [J]. Plant Soil, 2010, 326:45-60. |
| 7 | 韩志平,郭世荣,郑瑞娜,等.盐胁迫对小型西瓜幼苗体内离子分布的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(4):908-917. |
| HAN Z P, GUO S R, ZHENG R N, et al.. Effect of salinity on distribution of ions in mini-watermelon seedlings [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2013, 19(4):908-917. | |
| 8 | 熊韬,胡国智,吴海波,等.盐碱胁迫对甜瓜幼苗离子吸收和分配的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2019,56(7):1258-1266. |
| XIONG T, HU G Z, WU H B, et al.. Effects of saline-alkali stress on ion absorption and distribution in melon seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2019, 56(7):1258-1266. | |
| 9 | PAN J W, LI Z, DAI S J, et al.. Integrative analyses of transcriptomics and metabolomics upon seed germination of foxtail millet in response to salinity [J]. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1):12700-12712. |
| 10 | 黎咏蜀.饲用油菜栽培技术及营养价值研究[D].重庆:西南大学, 2014. |
| LI Y S. Research on cultivation techniques and nutritional value of forage oilseed [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2014. | |
| 11 | 张哲,殷艳,刘芳,等.我国油菜多功能开发利用现状及发展对策[J].中国油料作物学报,2018,40(5):618-623. |
| ZHANG Z, YIN Y, LIU F, et al.. Current situation and development countermeasures of Chinese rapeseed multifunctional development and utilization [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2018, 40(5):618-623. | |
| 12 | 郭丛阳,王天河,杨文元,等.河西地区麦后复种饲用(绿肥)油菜栽培技术及效益分析[J].草业科学,2008,25(3):90-92. |
| GUO C Y, WANG T H, YANG W Y, et al.. Growing technology and profit analyzation of grazing (or green manure) Brassica napus grown after harvesting wheat in Hexi Corridor [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2008, 25(3):90-92. | |
| 13 | 油菜品种华油杂62[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2010, 49(11):2770. |
| 14 | 李惠英,陈良.盐胁迫对草坪草萌发生长及代谢的影响[J].草业科学,2018,35(11):2584-2592. |
| LI H Y, CHEN L. Effect of salt stress on turfgrass growth and metabolism [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2018, 35(11):2584-2592. | |
| 15 | 史晓艳,李维弟,余露,等.玛纳斯河流域农灌区土壤盐渍化遥感定量评价[J].灌溉排水学报,2018,37(11):69-75, 83. |
| SHI X Y, LI W D, YU L, et al.. Using remote sensing to evaluate soil salinization distribution over the irrigation areas in the Manas river basin [J]. J. Irrigat. Drain., 2018,37(11):69-75, 83. | |
| 16 | 罗家雄.新疆垦区盐碱地改良[M].北京:水利电力出版社,1985:1-128. |
| 17 | 郁万文,曹福亮,蔡金峰,等.盐碱胁迫对喜树幼苗生长及体内离子选择性运输的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2015,43(11):1-5. |
| YU W W, CAO F L, CAI J F, et al.. Effects of saline and alkali stresses in growth and mineral nutrition selective transportation of Camptotheca acuminate Decne [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2015, 43(11):1-5. | |
| 18 | 周琦,祝遵凌. NaCl胁迫对2种鹅耳枥幼苗生长及离子吸收、分配与运输的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2015,37(12):7-16. |
| ZHOU Q, ZHU Z L. Effects of NaCl stress on seedling growth and mineral ions uptake, distribution and transportation of two varieties of Carpinus L. [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2015, 37(12):7-16. | |
| 19 | WANG S F, HU Y X, LI Z L, et al.. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and mineral ion uptake, transportation and distribution of Quercus virginiana [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010, 30(17):4609-4616. |
| 20 | 李先婷,曹靖,魏晓娟,等.NaCl渐进胁迫对啤酒大麦幼苗生长、离子分配和光合特性的影响[J].草业学报,2013,22(6):108-116. |
| LI X T, CAO J, WEI X J, et al.. Effect of extended exposure to NaCl stress on the growth, ion distribution and photosynthetic characteristics of malting barley (Hordeum vulgare) [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2013, 22(6):108-116. | |
| 21 | 朱义,谭贵娥,何池全,等.盐胁迫对高羊茅(Festuca arundinacea)幼苗生长和离子分布的影响[J].生态学报,2007, 27(12):5447-5454. |
| ZHU Y, TAN G E, HE C Q, et al.. Effect of salinization on growth and ion homeostasis in seedlings of Festuca arundinacea [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2007, 27(12):5447-5454. | |
| 22 | 王薇薇,祖艳侠,吴永成,等.盐胁迫对豇豆幼苗离子分布的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2019,47(12):161-164. |
| 23 | 张继伟,赵昕,石勇,等.盐胁迫下沙米(Agriophyllum squarrosum)矿质离子吸收与分配特征[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):702-707. |
| ZHANG J W, ZHAO X, SHI Y, et al.. Ion absorption and distribution of Agriophyllum squarrosum seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. J. Desert Res., 2016, 36(3):702-707. | |
| 24 | 李玉梅,郭修武,姜云天.牛叠肚幼苗对盐胁迫的离子响应[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(2):353-361. |
| LI Y M, GUO X W, JIANG Y T. Response of ions in Rubus crataegifolius seedlings to salt stress [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2016, 33(2):353-361. | |
| 25 | YANG Y, ZHENG Q S, LIU M, et al.. Difference in sodium spatial distribution in the shoot of two canola cultivars under saline stress [J]. Narnia, 2012, 53(6):1083-1092. |
| 26 | 徐靖宇.盐胁迫下野大豆(Glycine soja)光合特性、离子动态平衡及其相关关系研究[D].长春:东北师范大学, 2016. |
| XU J Y. The photosynthetic characteristics, ion homeostasis and the correlation between them in Glycine soja under salt stress [D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2016. | |
| 27 | MOLLER I S, GILLIHAM M, JHA D, et al.. Shoot Na+ exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na+ transport in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(7):2163-2178. |
| 28 | WU H, SHABALA L, LIU X, et al.. Linking salinity stress tolerance with tissue specific Na+ sequestration in wheat roots [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 6:71 [2021-09-05]. . |
| 29 | 车永梅,唐静,陈康,等.一氧化氮对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗叶绿素荧光参数和光合特性的影响[J].玉米科学,2009,17(3):91-94. |
| CHE Y M, TANG J, CHEN K, et al.. Effects of nitric oxide on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and photosynthetic characteristics of maize seedling under salt stress [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2009, 17(3):91-94. | |
| 30 | 马琛,乙引,张习敏,等.钙离子在植物生理调节中的作用[J].贵州农业科学,2010,38(2):36-41. |
| MA C, YI Y, ZHANG X M, et al.. Effect of the regulation of plant physiology on calcium ion [J]. Guizhou Agric. Sci., 2010, 38(2):36-41. | |
| 31 | 周艳.GSH缓解番茄幼苗盐胁迫的耐盐机制研究[D].石河子:石河子大学,2019. |
| ZHOU Y. Salt-tolerant mechanism of GSH alleciates salt-induced stress in tomato seedlings [D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019. | |
| 32 | 张科,张道远,王雷,等.自然生境下盐角草的离子吸收、运输特征[J].干旱区研究,2007,24(4):480-486. |
| ZHANG K, ZHANG D Y, WANG L, et al.. Study on the ionic absorption and transport in Salicornia europaea L. growing in natural habitas in Xinjiang [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2007, 24 (4):480-486. | |
| 33 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N, et al.. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(16):5565-5577. | |
| 34 | 刘正祥,张华新,杨秀艳,等.NaCl胁迫下沙枣幼苗生长和阳离子吸收、运输与分配特性[J].生态学报,2014,34(2):326-336. |
| LIU Z X, ZHANG H X, YANG X Y, et al.. Growth, and cationic absorption, transportation and allocation of Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2014, 34(2):326-336. | |
| 35 | 王龙强,米永伟,蔺海明.盐胁迫对枸杞属两种植物幼苗离子吸收和分配的影响[J].草业学报,2011,20(4):129-136. |
| WANG L Q, MI Y W, LIN H M. Effect of salt stress on ion absorption and distribution of two Lycium seedlings [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2011, 20(4):129-136. | |
| 36 | 萨如拉,刘景辉,刘伟,等.燕麦对碱胁迫的阳离子响应机制[J].作物学报,2014,40 (2):362-368. |
| SA R L, LIU J H, LIU W, et al.. Cation-responsive mechanisms of oats to alkali stress [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014, 40 (2):362-368. | |
| 37 | TEAKLE N L, FLOWERS T J, REAL D, et al.. Lotus tenuis tolerates the interactive effects of salinity and waterlogging by 'excluding' Na+ and Cl- from the xylem [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2007, 58(8):2169-2180. |
| 38 | 乌凤章,朱心慰,胡锐锋,等.NaCl胁迫对2个蓝莓品种幼苗生长及离子吸收、运输和分配的影响[J].林业科学,2017,53(10):40-49. |
| WU F Z, ZHU X W, HU R F, et al.. Effects of NaCl stress on growth ion uptake, transportation and distribution of two blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) cultivars seedlings [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2017, 53(10):40-49. |
| [1] | Heping WAN, Hao ZHANG, Yi YU, Jingdong CHEN, Changli ZENG, Lun ZHAO, Jing WEN, Jinxiong SHEN, Tingdong FU. Study and Application of Salt and Alkali Tolerance in Rapeseed [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(12): 59-67. |
| [2] | Quanquan WEI, Ying GAO, Jiulan GOU, Meng ZHANG, Yong RAO, Bin YANG, Di FAN, Wenhao FENG, Huagui XIAO. Effects of Different Sowing Rates and Sowing Methods on the Nutrient Absorption, Utilization and Yield of Winter Rapeseed in Yellow Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 182-191. |
| [3] | Fan ZHANG, Yue GU, Chen CAO, Baohua LIU. Effect of Rape Straw Fiber on Pore Characteristics of Cement Mortar [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 189-195. |
| [4] | YIN Yan, YIN Liang, ZHANG Xuekun, GUO Jingli, WANG Jijun. Status and Countermeasure of The High-quality Development of Rapeseed Industry in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 1-7. |
| [5] | LUO Lisha, LIAO Guiping, LIU Fan, GUAN Chunyun. Rape Variety Identification Based on Canopy Spectral Parameters [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 93-106. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wen\|yu, ZHANG Wei\|xin, GE Dao\|kuo, CAO Hong\|xin*, LIU Yan, FENG Chun\|. Research Trends Analysis of Oilseed Rape During Recent 10 Years Based on Web of Science [J]. , 2014, 16(6): 164-172. |
| [7] |
XIONG Qiu-fang, WEN Jing, LI Xing-hua, SHEN Jin-xiong*.
Technological Innovation and Industrial Development of Rapeseed in China [J]. , 2014, 16(3): 14-22. |
| [8] | ZHANG Wei\|xin1,2, CAO Hong\|xin2*, ZHU Yan1*, LIU Yan2, . Research Progress on Rapeseed Crop Model [J]. , 2014, 16(1): 82-90. |
| [9] | YIN Yan, WANG Han-zhong. Achievement, Problem and Scientific Policy of Rapeseed Industry Development in China [J]. , 2012, 14(4): 1-7. |
| [10] | LI Xiang1, ZHU Qing-hua1, GAO Qin1, LV Rong1, PAN Liang-wen1, LI Jun-yi2, ZHANG . Inter-laboratory Validation of A Plasmid Reference Molecule Suitable For Genetically Modified Canola RT73 Event-Specific Detection [J]. , 2011, 13(6): 33-40. |
| [11] | ZHANG Fang1,2, CHENG Yong1, GU Tei-cheng2, YIN Yan1. Present Status and Countermeasure Suggestions for Rapeseed Seed Industry Development of China [J]. , 2011, 13(4): 15-22. |
| [12] | YIN Yan1, CHEN Zhao-bo2, YU Jian2, WANG Han-zhong1, FENG Zhong-chao3. Analysis of Potential for Rapeseed Production in China [J]. , 2010, 12(3): 16-21. |
| [13] | HU Xiao-mei, ZHU Xin, WANG Jian-mei, YANG Yi, LI Xu-feng. Analysis on Differences of ABCD Gene Expression in Bud and Flower Development of Rape (Brassica napus) [J]. , 2007, 9(5): 80-86. |
| [14] | . [J]. , 2004, 6(4): 62-66. |
| [15] | . [J]. , 2004, 6(1): 18-21. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号