




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 215-223.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0247
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Junyu ZHOU1( ), Yu GU1, Haiyong WU1, Mingde LI1, Qiongfeng LIU1, Xuan ZHOU1, Chunhua DONG1,2(
), Yu GU1, Haiyong WU1, Mingde LI1, Qiongfeng LIU1, Xuan ZHOU1, Chunhua DONG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Accepted:2024-07-29
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
Chunhua DONG
周峻宇1( ), 谷雨1, 吴海勇1, 李明德1, 刘琼峰1, 周旋1, 董春华1,2(
), 谷雨1, 吴海勇1, 李明德1, 刘琼峰1, 周旋1, 董春华1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
董春华
作者简介:周峻宇E-mail: zjy00001@126.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Junyu ZHOU, Yu GU, Haiyong WU, Mingde LI, Qiongfeng LIU, Xuan ZHOU, Chunhua DONG. Effects of Citric Acid on Enhance the Remediation of Cd-contaminated Soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 215-223.
周峻宇, 谷雨, 吴海勇, 李明德, 刘琼峰, 周旋, 董春华. 柠檬酸强化籽粒苋修复镉污染土壤效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 215-223.
污染程度 Pollution degree | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/(cmol·kg-1) | 全氮 Total | 速效氮 | 有效磷 | 总Cd Total | 有效态Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中度Moderate | 6.8 | 25.1 | 16.1 | 2.11 | 195 | 7.03 | 1.33 | 0.449 |
| 轻度Low | 6.2 | 28.3 | 10.7 | 2.09 | 204 | 16.44 | 0.54 | 0.173 |
Table 1 Initial physiochemical properties of 0 to 20 cm topsoil in the studied paddy field sites
污染程度 Pollution degree | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/(cmol·kg-1) | 全氮 Total | 速效氮 | 有效磷 | 总Cd Total | 有效态Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中度Moderate | 6.8 | 25.1 | 16.1 | 2.11 | 195 | 7.03 | 1.33 | 0.449 |
| 轻度Low | 6.2 | 28.3 | 10.7 | 2.09 | 204 | 16.44 | 0.54 | 0.173 |
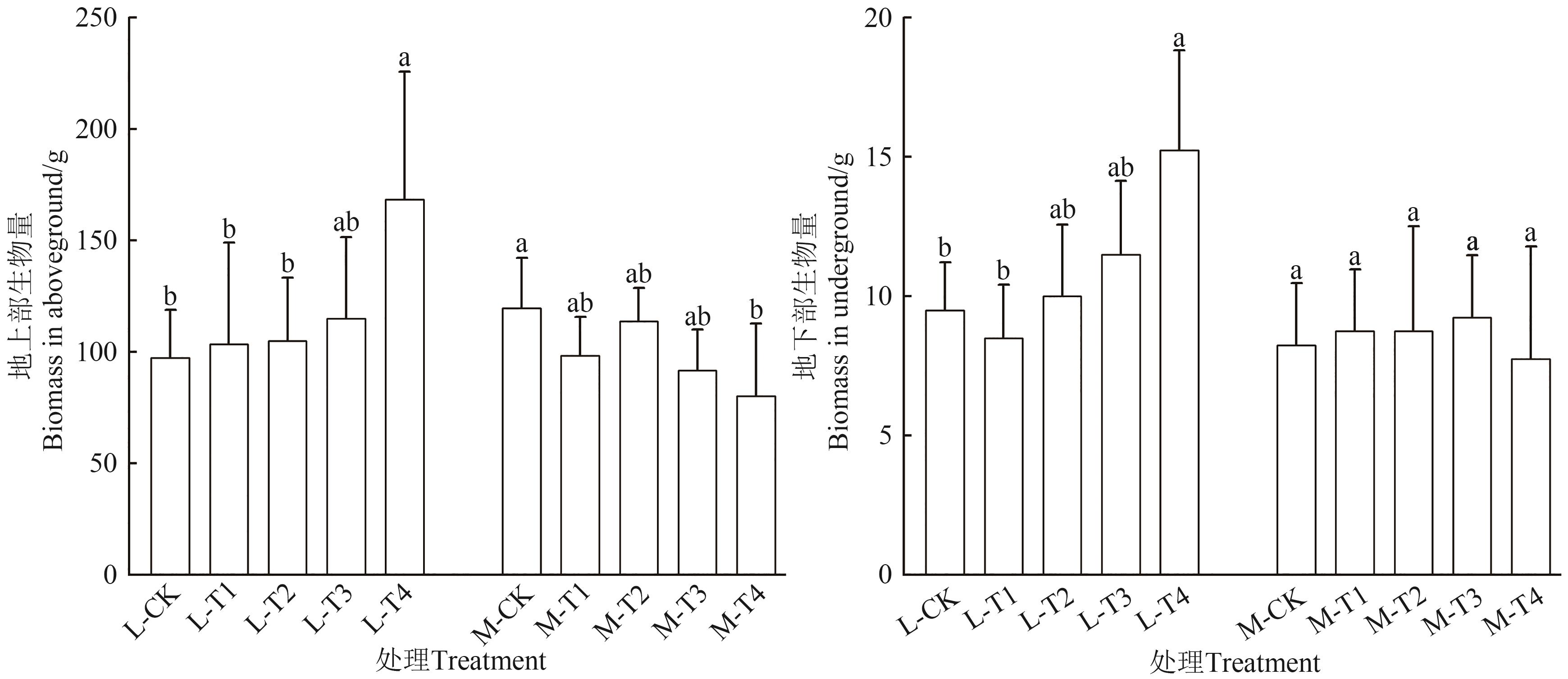
Fig. 1 Biomass of A. hypochondriacus L. with different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in soil with the same pollution level indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
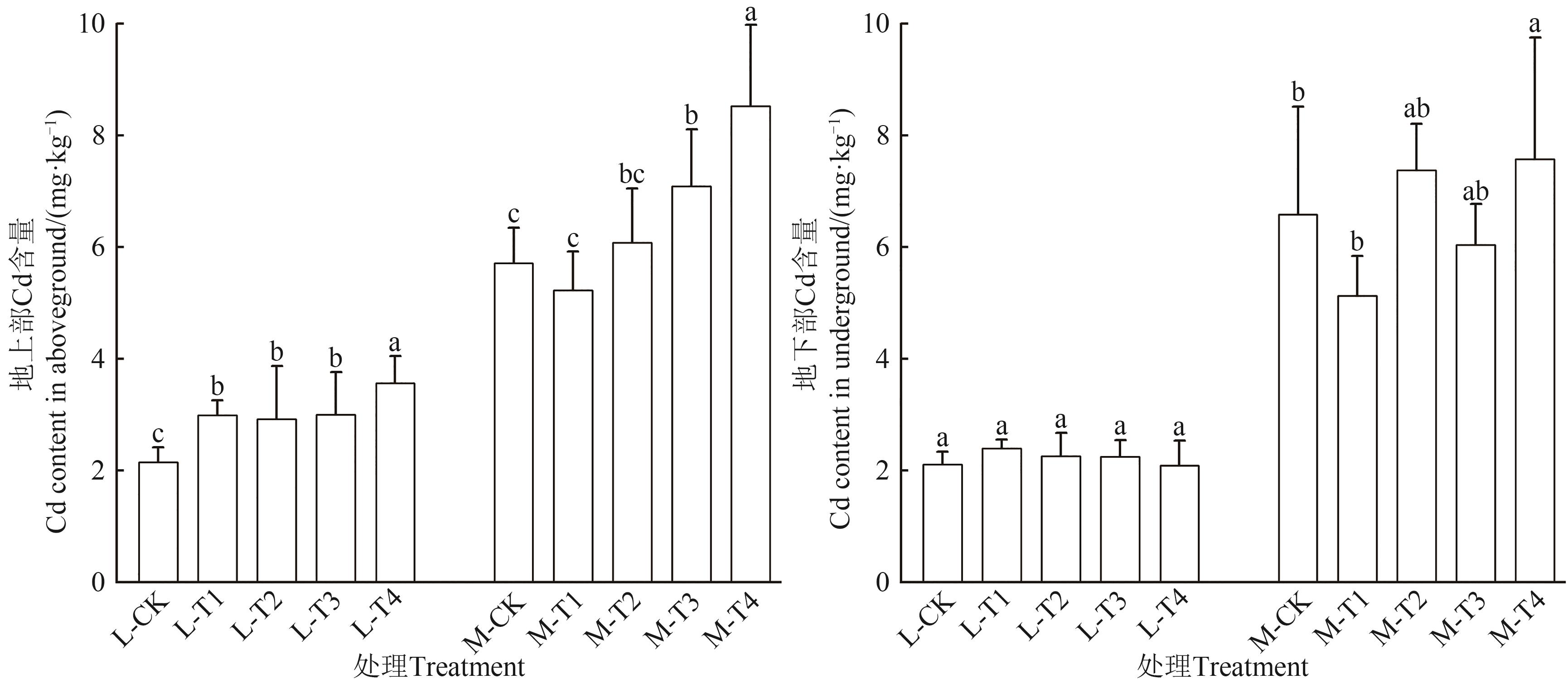
Fig. 2 Cd content in aboveground and underground of A. hypochondriacus L. with different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in soil with the same pollution level indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
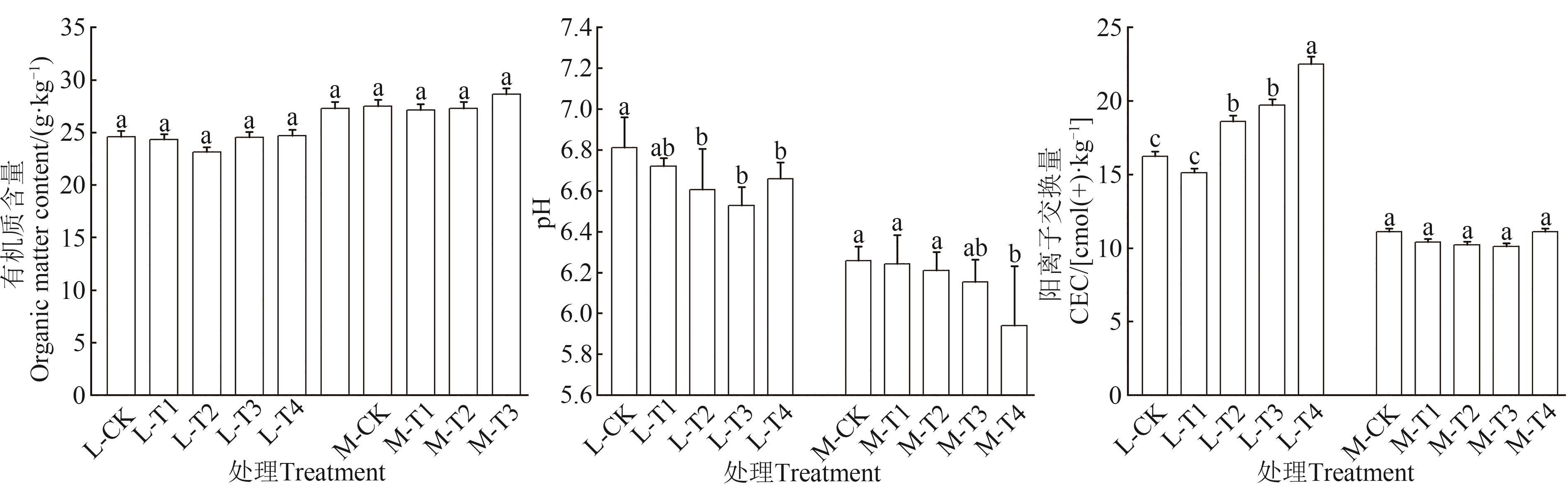
Fig. 3 Soil chemical properties with different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in soil with the same pollution level indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 土壤Cd组分 Soil Cd fraction | 总Cd Total Cd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
可交换态Cd CdEXC | 碳酸盐结合态Cd CdCB | 铁锰氧化物结合态Cd CdOX | 有机结合态Cd CdOM | 残渣态Cd CdRES | ||
| L-CK | 0.163±0.019 b (37.57%) | 0.065±0.006 a (15.04%) | 0.115±0.017 a (26.59%) | 0.033±0.013 a (7.51%) | 0.058±0.005 ab (13.29%) | 0.433±0.010 a |
| L-T1 | 0.158±0.005 b (39.13%) | 0.053±0.005 b (13.04%) | 0.110±0.001 a (27.33%) | 0.023±0.005 b (4.97%) | 0.063±0.010 a (15.53%) | 0.403±0.010 b |
| L-T2 | 0.165±0.008 b (42.38%) | 0.053±0.003 b (13.24%) | 0.098±0.006 b (25.17%) | 0.020±0.001 b (5.30%) | 0.058±0.005 b (13.91%) | 0.391±0.017 b |
| L-T3 | 0.180±0.008 a (45.00%) | 0.055±0.006 b (13.75%) | 0.095±0.006 b (23.75%) | 0.020±0.001 b (5.00%) | 0.050±0.001 b (12.50%) | 0.400±0.008 b |
| L-T4 | 0.181±0.010 a (46.30%) | 0.050±0.006 b (13.57%) | 0.090±0.008 b (22.22%) | 0.018±0.005 b (5.56%) | 0.050±0.002 b (12.35%) | 0.388±0.006 b |
| M-CK | 0.655±0.010 b (51.57%) | 0.195±0.010 a (15.35%) | 0.283±0.033 a (22.64%) | 0.050±0.008 a (3.94%) | 0.083±0.005 a (6.50%) | 1.290±0.034 a |
| M-T1 | 0.735±0.017 a (58.80%) | 0.153±0.010 b (12.20%) | 0.238±0.084 a (19.00%) | 0.045±0.006 a (3.60%) | 0.080±0.008 a (6.40%) | 1.230±0.042 a |
| M-T2 | 0.695±0.022 a (55.27%) | 0.163±0.026 b (12.92%) | 0.268±0.021 a (21.27%) | 0.050±0.001 a (3.98%) | 0.083±0.005 a (6.56%) | 1.233±0.048 a |
| M-T3 | 0.705±0.027 a (55.08%) | 0.170±0.012 b (13.28%) | 0.275±0.026 a (21.48%) | 0.050±0.002 a (3.91%) | 0.080±0.002 a (6.25%) | 1.280±0.037 a |
| M-T4 | 0.723±0.010 a (57.68%) | 0.160±0.002 b (12.78%) | 0.243±0.026 a (19.36%) | 0.048±0.005 a (3.79%) | 0.080±0.003 a (6.39%) | 1.253±0.019 a |
Table 2 Content and proportion of soil Cd fraction with different treatments
处理 Treatment | 土壤Cd组分 Soil Cd fraction | 总Cd Total Cd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
可交换态Cd CdEXC | 碳酸盐结合态Cd CdCB | 铁锰氧化物结合态Cd CdOX | 有机结合态Cd CdOM | 残渣态Cd CdRES | ||
| L-CK | 0.163±0.019 b (37.57%) | 0.065±0.006 a (15.04%) | 0.115±0.017 a (26.59%) | 0.033±0.013 a (7.51%) | 0.058±0.005 ab (13.29%) | 0.433±0.010 a |
| L-T1 | 0.158±0.005 b (39.13%) | 0.053±0.005 b (13.04%) | 0.110±0.001 a (27.33%) | 0.023±0.005 b (4.97%) | 0.063±0.010 a (15.53%) | 0.403±0.010 b |
| L-T2 | 0.165±0.008 b (42.38%) | 0.053±0.003 b (13.24%) | 0.098±0.006 b (25.17%) | 0.020±0.001 b (5.30%) | 0.058±0.005 b (13.91%) | 0.391±0.017 b |
| L-T3 | 0.180±0.008 a (45.00%) | 0.055±0.006 b (13.75%) | 0.095±0.006 b (23.75%) | 0.020±0.001 b (5.00%) | 0.050±0.001 b (12.50%) | 0.400±0.008 b |
| L-T4 | 0.181±0.010 a (46.30%) | 0.050±0.006 b (13.57%) | 0.090±0.008 b (22.22%) | 0.018±0.005 b (5.56%) | 0.050±0.002 b (12.35%) | 0.388±0.006 b |
| M-CK | 0.655±0.010 b (51.57%) | 0.195±0.010 a (15.35%) | 0.283±0.033 a (22.64%) | 0.050±0.008 a (3.94%) | 0.083±0.005 a (6.50%) | 1.290±0.034 a |
| M-T1 | 0.735±0.017 a (58.80%) | 0.153±0.010 b (12.20%) | 0.238±0.084 a (19.00%) | 0.045±0.006 a (3.60%) | 0.080±0.008 a (6.40%) | 1.230±0.042 a |
| M-T2 | 0.695±0.022 a (55.27%) | 0.163±0.026 b (12.92%) | 0.268±0.021 a (21.27%) | 0.050±0.001 a (3.98%) | 0.083±0.005 a (6.56%) | 1.233±0.048 a |
| M-T3 | 0.705±0.027 a (55.08%) | 0.170±0.012 b (13.28%) | 0.275±0.026 a (21.48%) | 0.050±0.002 a (3.91%) | 0.080±0.002 a (6.25%) | 1.280±0.037 a |
| M-T4 | 0.723±0.010 a (57.68%) | 0.160±0.002 b (12.78%) | 0.243±0.026 a (19.36%) | 0.048±0.005 a (3.79%) | 0.080±0.003 a (6.39%) | 1.253±0.019 a |
处理 Treatment | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 移除率 Removal rate/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Aboveground | 地下部Underground | 总 Total | 地上部 Aboveground | 总 Total | |||
| L-CK | 1.04±0.25 b | 4.97±0.53 c | 4.89±0.61 a | 4.97±0.43 c | 6.06±1.60 c | 6.64±1.60 c | |
| L-T1 | 1.25±0.12 b | 7.35±0.63 b | 5.89±0.22 a | 7.24±0.61 b | 9.77±2.20 b | 10.39±2.27 b | |
| L-T2 | 1.26±0.22 b | 7.49±1.19 ab | 5.75±1.55 a | 7.32±1.76 ab | 9.61±2.65 b | 10.33±2.97 b | |
| L-T3 | 1.32±0.17 b | 7.38±1.21 ab | 5.56±0.58 a | 7.20±1.59 ab | 10.17±2.28 b | 10.96±2.42 b | |
| L-T4 | 1.75±0.29 a | 8.75±1.26 a | 5.14±0.93 a | 8.47±1.12 a | 18.98±4.86 a | 20.04±4.48 a | |
| M-CK | 0.91±0.21 a | 4.46±0.65 b | 5.13±1.51 a | 4.51±0.69 b | 6.67±1.41 a | 7.22±1.60 a | |
| M-T1 | 1.03±0.11 a | 4.22±0.55 b | 4.15±0.65 a | 4.22±0.55 b | 5.03±1.18 a | 5.50±0.93 a | |
| M-T2 | 0.83±0.15 a | 4.96±0.84 b | 6.06±1.01 a | 5.04±0.82 ab | 7.11±1.84 a | 7.79±2.08 a | |
| M-T3 | 1.17±0.36 a | 5.56±1.03 ab | 4.73±0.71 a | 5.49±1.90 ab | 6.24±2.21 a | 6.78±2.18 a | |
| M-T4 | 1.17±0.26 a | 6.96±1.40 a | 6.20±1.97 a | 6.89±1.44 a | 7.12±2.57 a | 7.73±2.81 a | |
Table 3 Enrichment,transport and removal characteristics of Cd from A. hypochondriacus L. under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 移除率 Removal rate/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Aboveground | 地下部Underground | 总 Total | 地上部 Aboveground | 总 Total | |||
| L-CK | 1.04±0.25 b | 4.97±0.53 c | 4.89±0.61 a | 4.97±0.43 c | 6.06±1.60 c | 6.64±1.60 c | |
| L-T1 | 1.25±0.12 b | 7.35±0.63 b | 5.89±0.22 a | 7.24±0.61 b | 9.77±2.20 b | 10.39±2.27 b | |
| L-T2 | 1.26±0.22 b | 7.49±1.19 ab | 5.75±1.55 a | 7.32±1.76 ab | 9.61±2.65 b | 10.33±2.97 b | |
| L-T3 | 1.32±0.17 b | 7.38±1.21 ab | 5.56±0.58 a | 7.20±1.59 ab | 10.17±2.28 b | 10.96±2.42 b | |
| L-T4 | 1.75±0.29 a | 8.75±1.26 a | 5.14±0.93 a | 8.47±1.12 a | 18.98±4.86 a | 20.04±4.48 a | |
| M-CK | 0.91±0.21 a | 4.46±0.65 b | 5.13±1.51 a | 4.51±0.69 b | 6.67±1.41 a | 7.22±1.60 a | |
| M-T1 | 1.03±0.11 a | 4.22±0.55 b | 4.15±0.65 a | 4.22±0.55 b | 5.03±1.18 a | 5.50±0.93 a | |
| M-T2 | 0.83±0.15 a | 4.96±0.84 b | 6.06±1.01 a | 5.04±0.82 ab | 7.11±1.84 a | 7.79±2.08 a | |
| M-T3 | 1.17±0.36 a | 5.56±1.03 ab | 4.73±0.71 a | 5.49±1.90 ab | 6.24±2.21 a | 6.78±2.18 a | |
| M-T4 | 1.17±0.26 a | 6.96±1.40 a | 6.20±1.97 a | 6.89±1.44 a | 7.12±2.57 a | 7.73±2.81 a | |

Fig. 4 Correlation analysis of influencing factors of remediation characteristics of A. hypochondriacus L. under different Cd pollution levelsNote: Different colors indicate the strength of the correlation between variables, blue indicates positive correlation, red indicates negative correlation; *,** and *** indicate significant corrections at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels,respectively.
| [1] | SHAH V, DAVEREY A. Phytoremediation:a multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil [J/OL].Environ. Technol. Innov.,2020,18:100774 [2024-02-06]. . |
| [2] | LI Y, LIU K H, WANG Y,et al.. Improvement of cadmium phytoremediation by Centella asiatica L.after soil inoculation with cadmium-resistant Enterobacter sp. FM-1 [J]. Chemosphere,2018,202:280-288. |
| [3] | ZHU H H, CHEN L, XING W, et al.. Phytohormones-induced senescence efficiently promotes the transport of cadmium from roots into shoots of plants:a novel strategy for strengthening of phytoremediation [J/OL]. J.Hazard.Mater.,2020,388:122080 [2024-02-06]. . |
| [4] | BAKER A J, BROOKS R. Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements. a review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry [J]. Biorecovery, 1989, 1(2):81-126. |
| [5] | SALT D E, PRINCE R C, PICKERING I J, et al.. Mechanisms of cadmium mobility and accumulation in Indian mustard [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 1995, 109(4):1427-1433. |
| [6] | LIU W, SHU W S, LAN C Y. Viola baoshanensis, a plant that hyperaccumulates cadmium [J]. Chin.Sci.Bull.,2004,49(1):29-32. |
| [7] | RAN J K, ZHENG W, WANG H B, et al.. Indole-3-acetic acid promotes cadmium (Cd) accumulation in a Cd hyperaccumulator and a non-hyperaccumulator by different physiological responses [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf.,2020,191:110213[2024-02-26]. . |
| [8] | 谷雨,黄铁平,唐珍琦,等.籽粒苋修复土壤重金属污染研究进展[J].农学学报,2020,10(10):41-45. |
| GU Y, HUANG T P, TANG Z Q, et al.. Remediation of heavy metal pollution contaminated soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus: research progress [J]. J. Agric., 2020, 10(10):41-45. | |
| [9] | XU W, SHAFI M, PENTTINEN P, et al.. Bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soil as affected by different mass ratios of biochars [J]. Environ. Technol., 2020,41(25):3329-3337. |
| [10] | 许伟伟, 滕玉婷, 任静华,等. 不同活化剂对镉、铅单一及复合污染土壤的修复效果影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(8):882-886, 890. |
| XU W W, TENG Y T, REN J H, et al.. Effect of different activators on the remediation of Cd and Pb single and compound contaminated soils [J]. Environ. Pollut. Control, 2019, 41(8): 882-886, 890. | |
| [11] | SINHAL V K, SRIVASTAVA A, SINGH V P. EDTA and citric acid mediated phytoextraction of Zn,Cu,Pb and Cd through marigold (Tagetes erecta) [J]. J.Environ.Biol.,2010,31(3):255-259. |
| [12] | SHAKOOR M B, ALI S, FARID M, et al.. Heavy metal pollution, a global problem and its remediation by chemically enhanced phytoremediation: a review [J]. J. Biod. Environ. Sci., 2013, 3:12-20. |
| [13] | BAREEN F E. Chelate assisted phytoextraction using oilseed brassicas [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2012, 21:289-311. |
| [14] | ANWER S, ASHRAF M Y, HUSSAIN M, et al.. Citric acid mediated phytoextraction of cadmium by maize (Zea mays L.) [J]. Pakistan. J. Bot.,2012, 44(6):1831-1836. |
| [15] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中镉的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2023. |
| [16] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2013:1-495. |
| [17] | 国家环境保护局国家技术监督局. 土壤质量铅、镉的测定 石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,1997. |
| [18] | 刘凤枝,刘铭,蔡彦明,等. 土壤质量有效态铅和镉的测定 原子吸收法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2009. |
| [19] | TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M.Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Anal. Chem., 1979,51(7):844-851. |
| [20] | 刘萍,翟崇治,余家燕,等. Cd、Pb复合污染下柠檬酸对龙葵修复效率及抗氧化酶的影响[J].环境工程学报,2012,6(4):1387-1392. |
| LIU P, ZHAI C Z, YU J Y, et al.. Effect of citric acid on remediation efficiency and antioxidant enzyme of Solanum nigrum L.under Cd and Pb combined pollution [J]. Chin.J.Environ. Eng., 2012,6(4):1387-1392. | |
| [21] | 邓林,张娟娟,谢探春,等.柠檬酸对土壤-柳树系统中镉-芘污染生物有效性影响[J].南京大学学报(自然科学),2021,57(3):375-384. |
| DENG L, ZHANG J J, XIE T C, et al.. Effects of citric acid on the bioavailability of Cd-pyrene contamination in soil-willow system [J]. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 57(3):375-384. | |
| [22] | SHEN X, DAI M, YANG J W,et al..A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment:performance and challenges [J/OL]. Chemosphere,2022,291:132979 [2024-02-26]. . |
| [23] | GUO X F, ZHAO G H, ZHANG G X,et al..Effect of mixed chelators of EDTA,GLDA,and citric acid on bioavailability of residual heavy metals in soils and soil properties [J]. Chemosphere, 2018,209: 776-782. |
| [24] | OLADELE S O, OLADELE B B, AJALA R,et al..Emerging contaminants:evaluation of degradable chelators towards enhancing cadmium phytoextraction efficiency of bioenergy crop grown on polluted soil [J]. Emerg. Contam.,2021,7:139-148. |
| [25] | CHEN Y H, LIU M J, DENG Y W,et al..Comparison of ammonium fertilizers, EDTA, and NTA on enhancing the uptake of cadmium by an energy plant,Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach) [J]. J. Soils Sediments,2017,17(12):2786-2796. |
| [26] | BAO T, SUN T, SUN L. Low molecular weight organic acids in root exudates and cadmium accumulation in cadmium hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and nonhyperaccumulator Solanum lycopersicum L. [J]. African J. Biotechnol., 2011, 10:17180-17185. |
| [27] | JAVED M T, STOLTZ E, LINDBERG S,et al..Changes in pH and organic acids in mucilage of Eriophorum angustifolium roots after exposure to elevated concentrations of toxic elements [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2013,20(3):1876-1880. |
| [28] | 宋波,张云霞,田美玲,等.应用籽粒苋修复镉污染农田土壤的潜力[J].环境工程学报,2019,13(7):1711-1719. |
| SONG B, ZHANG Y X, TIAN M L, et al.. Potential for cadmium contaminated farmland remediation with Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2019,13(7):1711-1719. | |
| [29] | CHEN Z Q, LIU Q Z, CHEN S N, et al.. Roles of exogenous plant growth regulators on phytoextraction of Cd/Pb/Zn by Sedum alfredii Hance in contaminated soils [J/OL]. Environ.Pollut., 2022,293:118510 [2024-02-26]. . |
| [30] | 张小茜,张富贵,董祥林,等. Zn和Cd胁迫作用对长梗白菜形态和生理性能的生态毒理影响[J].环境化学,2022,41(1):22-30. |
| ZHANG X X, ZHANG F G, DONG X L, et al.. Ecotoxicological effects of Zn and Cd stress on the morphology and physiological properties of long-stalk cabbage [J]. Environ.Chem., 2022,41(1):22-30. | |
| [31] | 李凝玉,卢焕萍,李志安,等.籽粒苋对土壤中镉的耐性和积累特征[J].应用与环境生物学报,2010,16(1):28-32. |
| LI N Y, LU H P, LI Z A, et al.. Tolerance and accumulation of cadmium in soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2010,16(1):28-32. | |
| [32] | HSEU Z Y, JIEN S H, WANG S H, et al.. Using EDDS and NTA for enhanced phytoextraction of Cd by water spinach [J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2013,117:58-64. |
| [1] | Xiang WU, Juan LI, Yan CAO, Yanrong CHENG, Xuyu YAN, Ling LI. Research Advances on Plant Root Exudates in Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 12-20. |
| [2] | Junyu ZHOU, Yu GU, Zhenqi TANG, Haiyong WU, Qiongfeng LIU, Mingde LI. Effect of Compound Chelating Agent on Remediation of Cadmium Contaminated Farmland by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 186-194. |
| [3] | JIN Yong1,2, FU Qing-ling1, ZHENG Jin2, KANG Wei3, LIU Yong-hong1, HU Hong-qing1. Research Status on Phytoremediation of Copper Contaminated Soil with Hyperaccumulator [J]. , 2012, 14(4): 93-100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号