




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 155-167.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0827
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Xiao WANG( ), Xiangfei XIN(
), Xiangfei XIN( ), Yan YAN, Jimin WANG
), Yan YAN, Jimin WANG
Received:2024-10-10
Accepted:2024-12-26
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
Xiangfei XIN
通讯作者:
辛翔飞
作者简介:王潇 E-mail:wx2023caas@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiao WANG, Xiangfei XIN, Yan YAN, Jimin WANG. Analysis of Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Carbon Emission from Animal Husbandry in Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 155-167.
王潇, 辛翔飞, 闫琰, 王济民. 山东省畜牧业碳排放演变特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 155-167.
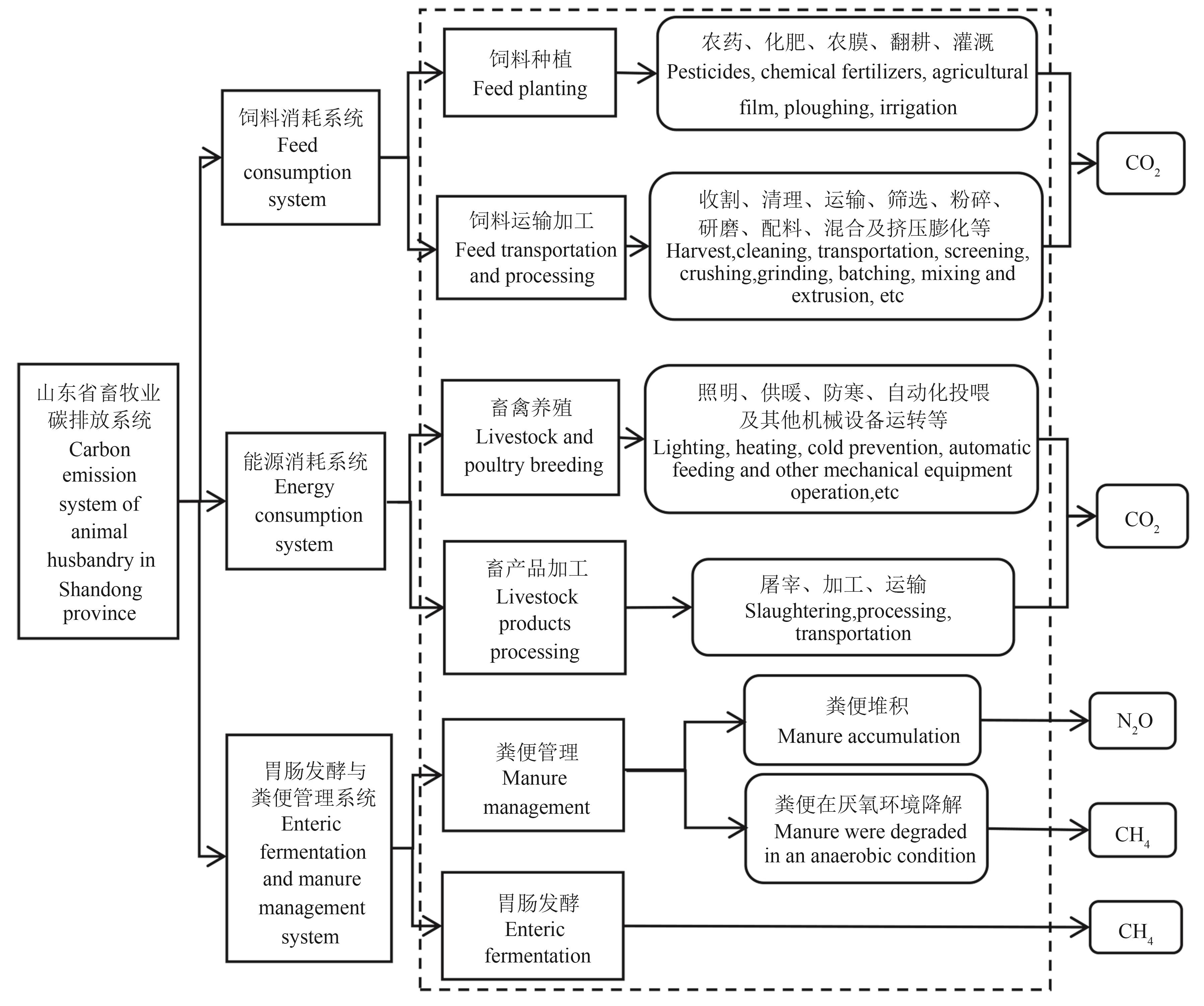
Fig. 1 Carbon emission system of animal husbandry in Shandong provinceNote: CO2 is also produced during manure accumulation and anaerobic degradation, but is not included in the methodology.
物种 Species | 肠道发酵 Enteric fermentation | 粪便管理 Manure management | 参考来源 Reference source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CH4 | N2O | ||
| 猪Swine | 1.000 | 3.50 | 0.53 | [ |
| 禽Poultry | 0.000 | 0.02 | 0.02 | [ |
| 牛Cattle | 55.000 | 2.00 | 1.34 | [ |
| 羊 | 5.000 | 0.16 | 0.33 | [ |
| 兔Rabbit | 0.254 | 0.08 | 0.02 | [ |
Table 1 Carbon emission coefficient of enteric fermentation and manure management of each animal species
物种 Species | 肠道发酵 Enteric fermentation | 粪便管理 Manure management | 参考来源 Reference source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CH4 | N2O | ||
| 猪Swine | 1.000 | 3.50 | 0.53 | [ |
| 禽Poultry | 0.000 | 0.02 | 0.02 | [ |
| 牛Cattle | 55.000 | 2.00 | 1.34 | [ |
| 羊 | 5.000 | 0.16 | 0.33 | [ |
| 兔Rabbit | 0.254 | 0.08 | 0.02 | [ |
系统边界 System boundary | 符号 Sign | 指标 Index | 值 Value | 参考来源 Reference source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
饲料粮种植消耗 Feed and grain planting consumption | ej1 | 小麦碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of wheat | 1.22 | [ |
玉米碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of corn | 1.5 | |||
饲料粮加工消耗 Feed and grain processing consumption | ej2 | 小麦碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of wheat | 0.031 9 | |
玉米碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of corn | 0.010 2 | |||
大豆碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of soybean | 0.101 3 | |||
畜禽饲养消耗 Livestock and poultry feeding consumption | pricee | 畜禽养殖用电单价/(元·kW-1·h-1)Unit price of livestock and poultry breeding electricity consumption/(yuan·kW-1·h-1) | 0.427 5 | [ |
| pricec | 畜禽养殖用煤单价/(元·t-1) Unit price of coal used for livestock and poultry breeding/(yuan·t-1) | 800 | ||
| ef | 电能消耗碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of electricity consumption/(t·MW-1·t-1) | 0.971 4 | [ | |
| ec | 煤炭消耗碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of coal consumption | 1.98 | [ | |
畜禽加工消耗 Consumption of livestock and poultry processing | MJ u | 牛肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of beef slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 4.37 | [ |
猪肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of pork slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 3.76 | |||
羊肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of mutton slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 10.4 | |||
禽肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of poultry slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 2.59 | |||
| 禽蛋屠宰加工耗能系数Energy consumption coefficient of poultry egg slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 8.16 |
Table 2 Carbon emission coefficient of each system by the life cycle assessment method
系统边界 System boundary | 符号 Sign | 指标 Index | 值 Value | 参考来源 Reference source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
饲料粮种植消耗 Feed and grain planting consumption | ej1 | 小麦碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of wheat | 1.22 | [ |
玉米碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of corn | 1.5 | |||
饲料粮加工消耗 Feed and grain processing consumption | ej2 | 小麦碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of wheat | 0.031 9 | |
玉米碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of corn | 0.010 2 | |||
大豆碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of soybean | 0.101 3 | |||
畜禽饲养消耗 Livestock and poultry feeding consumption | pricee | 畜禽养殖用电单价/(元·kW-1·h-1)Unit price of livestock and poultry breeding electricity consumption/(yuan·kW-1·h-1) | 0.427 5 | [ |
| pricec | 畜禽养殖用煤单价/(元·t-1) Unit price of coal used for livestock and poultry breeding/(yuan·t-1) | 800 | ||
| ef | 电能消耗碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of electricity consumption/(t·MW-1·t-1) | 0.971 4 | [ | |
| ec | 煤炭消耗碳排放系数 Carbon emission coefficient of coal consumption | 1.98 | [ | |
畜禽加工消耗 Consumption of livestock and poultry processing | MJ u | 牛肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of beef slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 4.37 | [ |
猪肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of pork slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 3.76 | |||
羊肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of mutton slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 10.4 | |||
禽肉屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of poultry slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 2.59 | |||
| 禽蛋屠宰加工耗能系数Energy consumption coefficient of poultry egg slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 8.16 |
系统边界 System boundary | 符号 Sign | 指标 Index | 值 Value | 参考来源 Reference source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
畜禽加工消耗 Consumption of livestock and poultry processing | MJ u | 牛奶屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of milk slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 1.12 | [ |
| v | Unit electric heat value | 3.6 | ||
CH4全球升温潜能值 CH4 global warming potential value | 21 | [ | ||
N2O全球升温潜能值 N2O global warming potential value | 310 |
Table 2 Carbon emission coefficient of each system by the life cycle assessment method
系统边界 System boundary | 符号 Sign | 指标 Index | 值 Value | 参考来源 Reference source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
畜禽加工消耗 Consumption of livestock and poultry processing | MJ u | 牛奶屠宰加工耗能系数 Energy consumption coefficient of milk slaughtering and processing/(MJ·kg-1) | 1.12 | [ |
| v | Unit electric heat value | 3.6 | ||
CH4全球升温潜能值 CH4 global warming potential value | 21 | [ | ||
N2O全球升温潜能值 N2O global warming potential value | 310 |
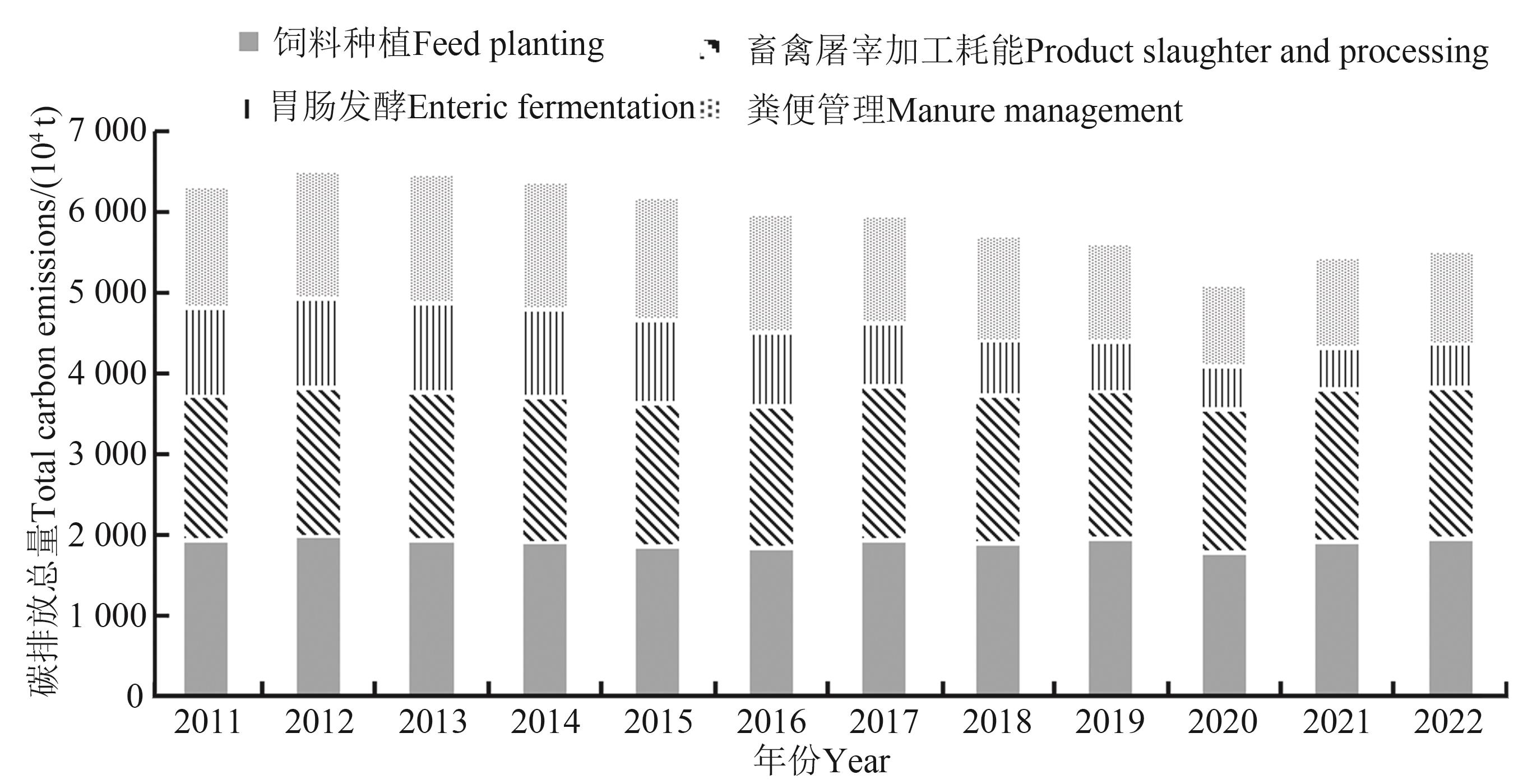
Fig. 2 Total carbon emission of Shandong province from 2011 to 2022Note: Because the carbon emissions of feed processing and livestock and poultry breeding are relatively small and negligible from other carbon emission sources, they are not listed in the figure.
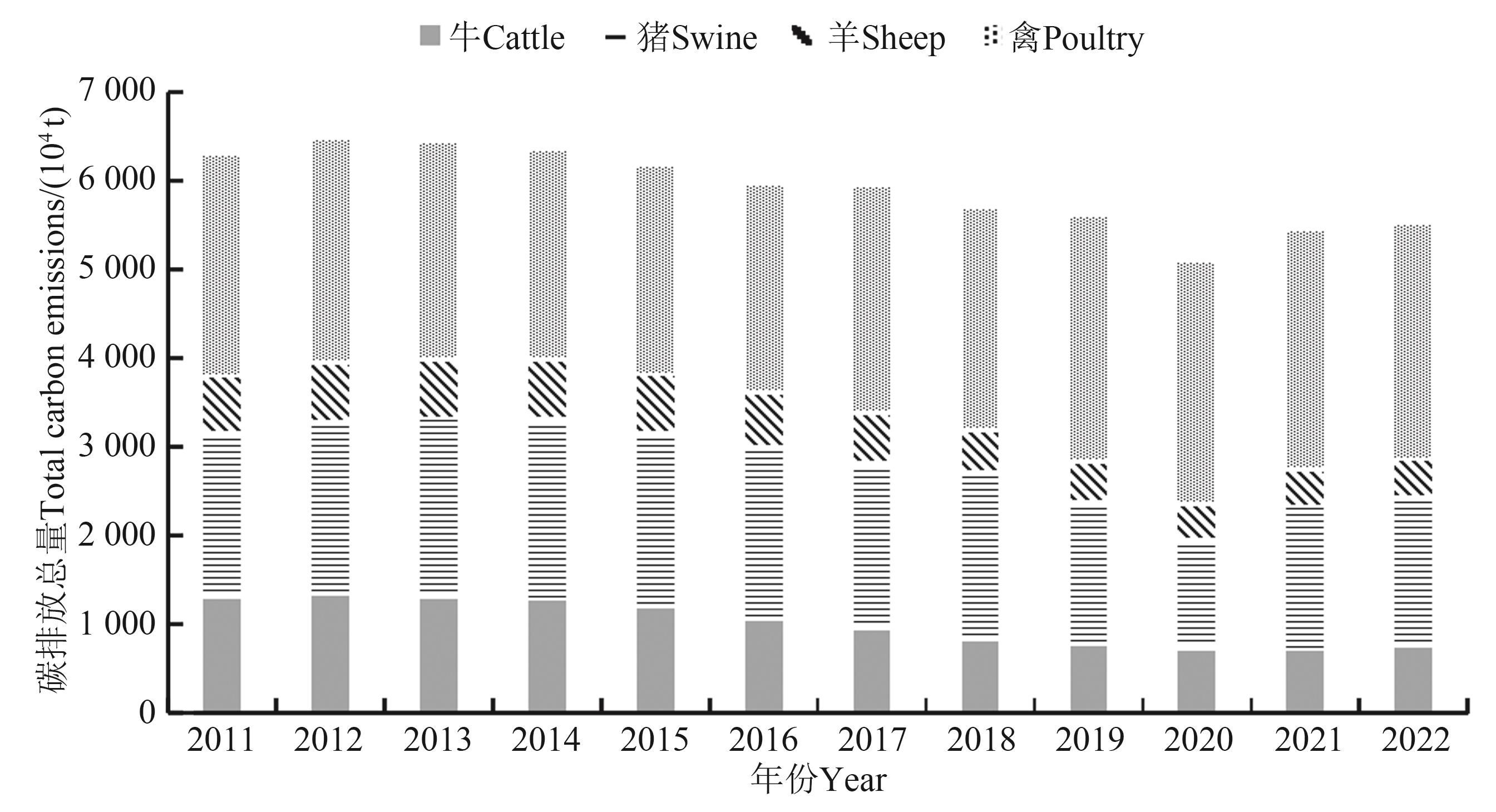
Fig. 3 Total carbon emission of all livestock breeds in Shandong province from 2011 to 2022Note: Because rabbits have carbon emissions of rabit is relatively low, and is it negligible to other livestock species, it is not listed in the figure.
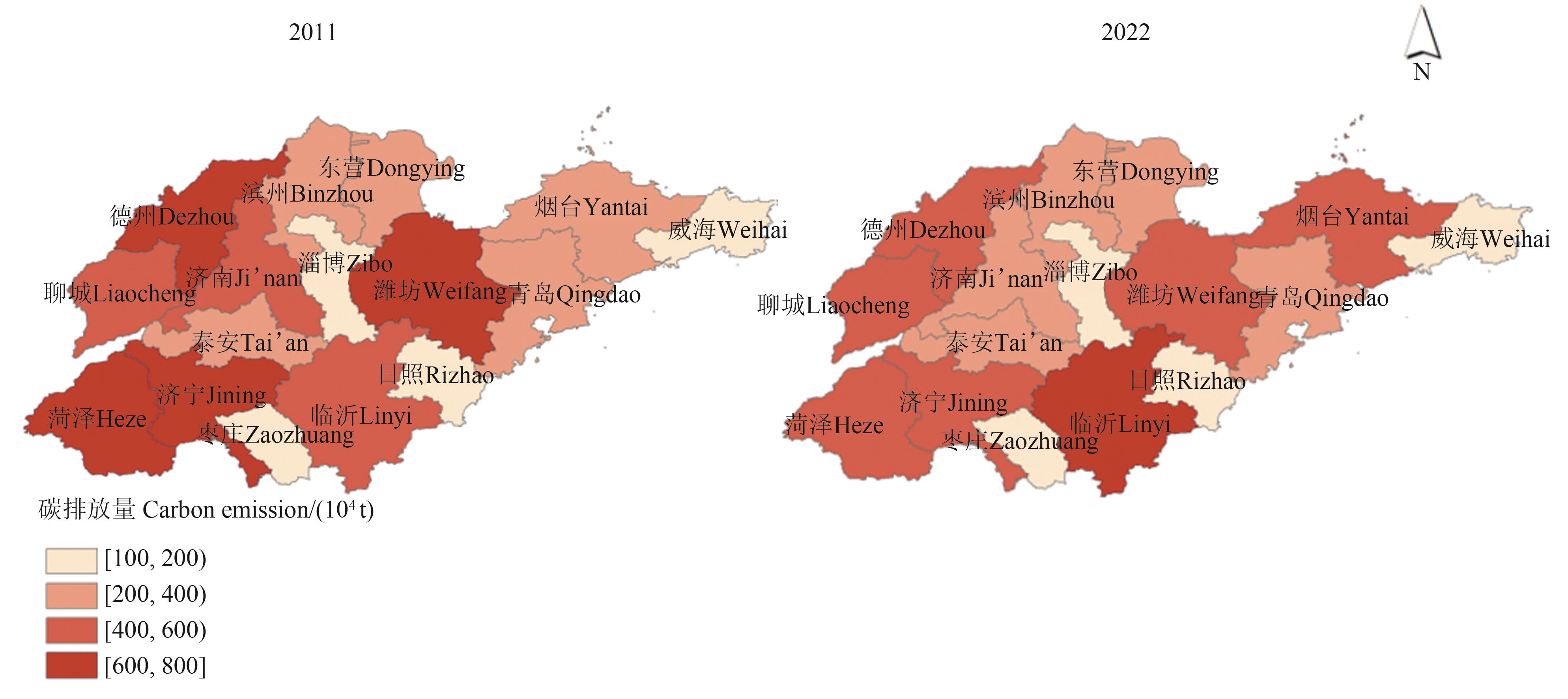
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution diagram of carbon emission from animal husbandry in Shandong provinceNote:Based on the standard map GS(2024)1158 of the National Resources Ministry’s standard map service website, the base map has not been modified.
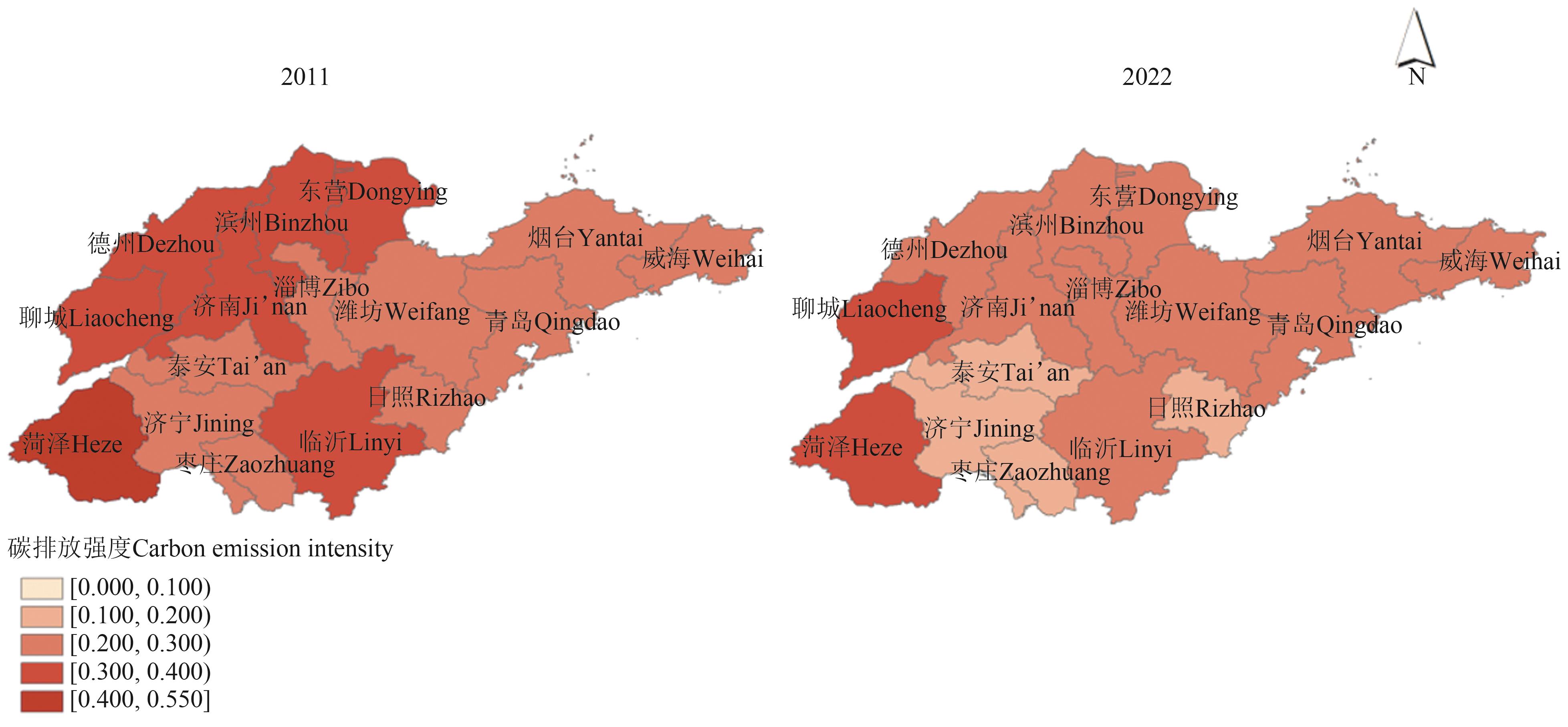
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution diagram of carbon emission intensity in animal husbandry in Shandong provinceNote:Based on the standard map GS(2024)1158 of the National Resources Ministry’s standard map service website, the base map has not been modified.
年份 Year | 经济发展水平 Level of economic development | 经济产出碳强度 Carbon intensity of economic output | 机械总动力水平 Total prime mover power capacity | 机械总动力消耗碳强度 Carbon intensity per unit of prime Mover power consumption | 人口规模 Population size | 人均碳排放量 Per capita carbon intensity | 人均产值 Per capita output | 机械总动力消耗强度 Prime mover power consumption intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 0.009 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.033 5 | -0.022 7 | 0.001 5 | 0.008 3 | -0.000 2 | -0.001 0 |
| 2013 | 0.011 7 | -0.013 9 | 0.041 6 | -0.041 3 | 0.001 3 | -0.003 3 | -0.000 3 | -0.001 5 |
| 2014 | 0.003 2 | -0.007 8 | 0.004 5 | -0.009 1 | 0.002 1 | -0.006 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 |
| 2015 | 0.007 4 | -0.017 1 | 0.004 4 | -0.014 3 | 0.001 9 | -0.011 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 |
| 2016 | 0.014 1 | -0.025 0 | 0.006 0 | -0.017 4 | 0.003 5 | -0.015 0 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 1 |
| 2017 | -0.010 0 | 0.008 8 | 0.006 8 | -0.008 2 | 0.002 0 | -0.003 5 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 4 |
| 2018 | -0.016 7 | 0.003 6 | 0.008 0 | -0.021 1 | 0.001 4 | -0.014 9 | -0.000 4 | -0.000 9 |
| 2019 | -0.012 8 | 0.008 4 | 0.020 6 | -0.024 5 | 0.001 0 | -0.006 0 | -0.000 1 | -0.001 7 |
| 2020 | 0.011 7 | -0.042 0 | 0.0158 | -0.045 9 | 0.001 8 | -0.032 7 | -0.000 2 | 0.000 0 |
| 2021 | 0.038 3 | -0.015 1 | 0.055 6 | -0.031 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.023 2 | -0.002 6 | -0.000 7 |
| 2022 | 0.005 6 | -0.000 1 | 0.013 0 | -0.007 2 | -0.000 2 | 0.005 8 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 1 |
Table 3 Contribution rate of carbon emission drivers of animal husbandry in Shandong Province from 2012 to 2022
年份 Year | 经济发展水平 Level of economic development | 经济产出碳强度 Carbon intensity of economic output | 机械总动力水平 Total prime mover power capacity | 机械总动力消耗碳强度 Carbon intensity per unit of prime Mover power consumption | 人口规模 Population size | 人均碳排放量 Per capita carbon intensity | 人均产值 Per capita output | 机械总动力消耗强度 Prime mover power consumption intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 0.009 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.033 5 | -0.022 7 | 0.001 5 | 0.008 3 | -0.000 2 | -0.001 0 |
| 2013 | 0.011 7 | -0.013 9 | 0.041 6 | -0.041 3 | 0.001 3 | -0.003 3 | -0.000 3 | -0.001 5 |
| 2014 | 0.003 2 | -0.007 8 | 0.004 5 | -0.009 1 | 0.002 1 | -0.006 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 |
| 2015 | 0.007 4 | -0.017 1 | 0.004 4 | -0.014 3 | 0.001 9 | -0.011 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 |
| 2016 | 0.014 1 | -0.025 0 | 0.006 0 | -0.017 4 | 0.003 5 | -0.015 0 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 1 |
| 2017 | -0.010 0 | 0.008 8 | 0.006 8 | -0.008 2 | 0.002 0 | -0.003 5 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 4 |
| 2018 | -0.016 7 | 0.003 6 | 0.008 0 | -0.021 1 | 0.001 4 | -0.014 9 | -0.000 4 | -0.000 9 |
| 2019 | -0.012 8 | 0.008 4 | 0.020 6 | -0.024 5 | 0.001 0 | -0.006 0 | -0.000 1 | -0.001 7 |
| 2020 | 0.011 7 | -0.042 0 | 0.0158 | -0.045 9 | 0.001 8 | -0.032 7 | -0.000 2 | 0.000 0 |
| 2021 | 0.038 3 | -0.015 1 | 0.055 6 | -0.031 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.023 2 | -0.002 6 | -0.000 7 |
| 2022 | 0.005 6 | -0.000 1 | 0.013 0 | -0.007 2 | -0.000 2 | 0.005 8 | -0.000 1 | -0.000 1 |
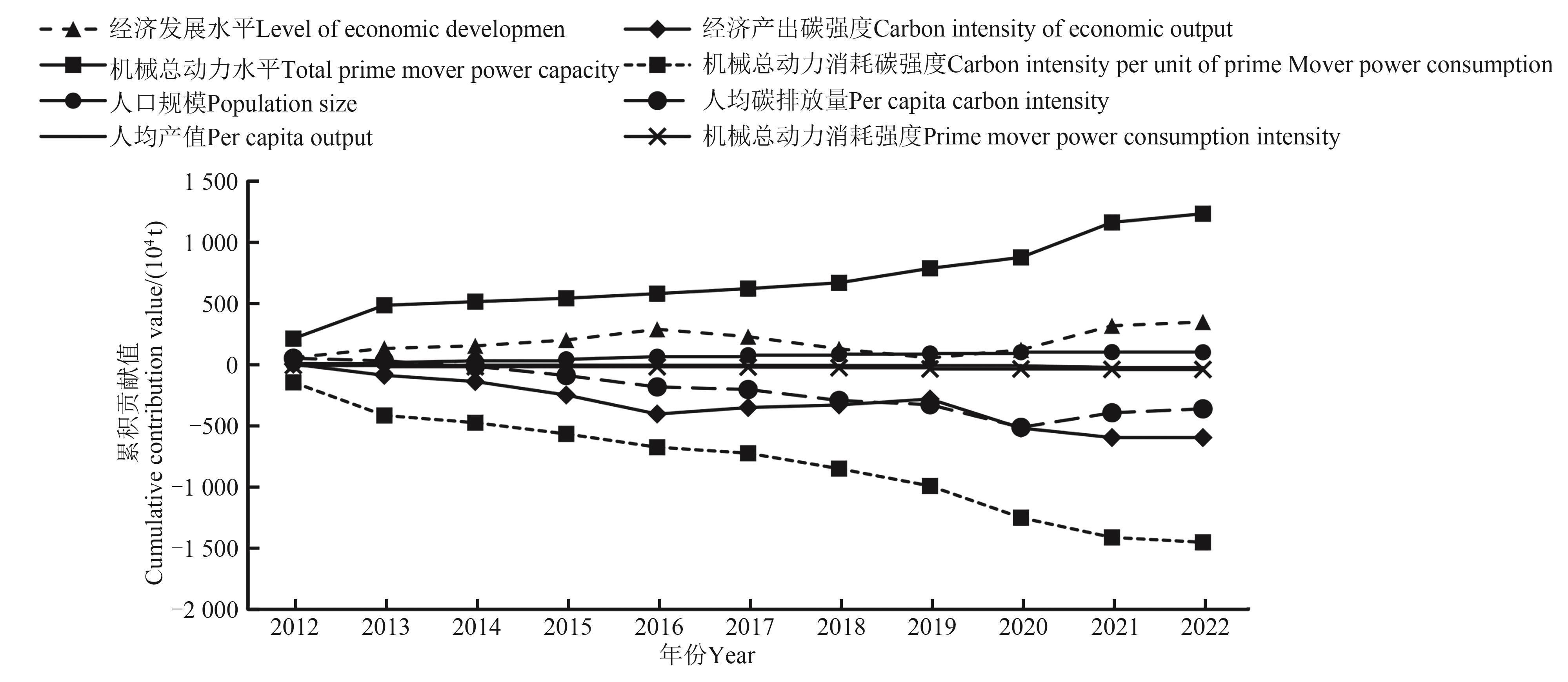
Fig. 6 Cumulative contribution values of the factors affecting carbon emissions in Shandong Province from 2012 to 2022Note: The cumulative contribution value is based on 2011, and the contribution value of each factor to the carbon emission of animal husbandry in Shandong province is added up year by year.
| [1] | SUBSCRIBE H, CONTACT A, FOCUS T, et al.. Growing greenhouse gas emissions due to meat production [J]. Environ. Dev., 2013, 5: 156-163. |
| [2] | GERBER P J, STEINFELD H, HENDERSON B, et al.. Tackling Climate Change Through Livestock——A Global Assessment of Emissions and Mitigation Opportunities [M]. Rome: FAO, 2013:1-256. |
| [3] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局.中国统计年鉴2022 [M].北京:中国统计出版社, 2022: 1-936. |
| [4] | LIU G, MÜLLER D B. Addressing sustainability in the aluminum industry: a critical review of life cycle assessments [J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2012, 35: 108-117. |
| [5] | 马于清,曹丁戈,罗文海,等.基于生命周期的我国畜禽养殖业碳排放核算[J].中国环境科学, 2024, 44(5): 2799-2810. |
| MA Y Q, CAO D G, LUO W H, et al.. The evaluation of the livestock and poultry production of carbon emissions in China based on life cycle assessment [J]. China Environ. Sci., 2024, 44(5): 2799-2810. | |
| [6] | AKIFUMI O, KAZATO O, AKIRA S, et al.. Life cycle assessment of sustainable broiler production systems: effects of low-protein diet and litter incineration [J/OL]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(10): 921 [2024-09-20]. . |
| [7] | ROSEN R A. Is the ipcc’s 5THASSESSMENT a denier of possible macroeconomic benefits from mitigating climate change? [J/OL]. Clim. Change Econ., 2016, 7(1): 1640003 [2024-09-20]. . |
| [8] | 梁耀文,王明利.中国生猪产业碳排放经验解构与动态达峰路径选择[J].农业经济问题, 2023, 44(10): 101-115. |
| LIANG Y W, WANG M L. Deconstructing the experience of China’s pig industry carbon emissions and choosing a dynamic path to peak [J]. Issu. Agric. Econ., 2023, 44(10): 101-115. | |
| [9] | LESSCHEN J P, VAN DEN BERG M, WESTHOEK H J, et al.. Greenhouse gas emission profiles of European livestock sectors [J]. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol., 2011, 166: 16-28. |
| [10] | HENDERSON B, GODDE C, MEDINA-HIDALGO D, et al.. Closing system-wide yield gaps to increase food production and mitigate GHGs among mixed crop-livestock smallholders in Sub-Saharan Africa [J]. Agric. Syst., 2016, 143: 106-113. |
| [11] | 熊学振,韩振,孙雨萌,等.中国畜产品进口格局及其资源环境效应研究[J].自然资源学报, 2023, 38(5): 1378-1392. |
| XIONG X Z, HAN Z, SUN Y M, et al.. Study of China's animal products import pattern and its resource and environmental effects [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2023, 38(5): 1378-1392 | |
| [12] | LI S, QIN Y, SUBBIAH J, et al.. Life cycle assessment of the U.S. beef processing through integrated hybrid approach [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod., 2020, 265: 121813 [2024-09-20]. . |
| [13] | 胡向东,王济民.中国畜禽温室气体排放量估算[J].农业工程学报, 2010, 26(10): 247-252. |
| HU X D, WANG J M. Estimation of livestock greenhouse gases discharge in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2010, 26(10): 247-252. | |
| [14] | 吴强,张园园,张明月.中国畜牧业碳排放的量化评估、时空特征及动态演化:2001—2020[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(6): 65-71. |
| WU Q, ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG M Y. Quantitative assessment, temporal and spatial characteristics and dynamic evolution of China’s animal husbandry carbon emissions [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2022, 36(6): 65-71. | |
| [15] | 孟祥海,程国强,张俊飚,等.中国畜牧业全生命周期温室气体排放时空特征分析[J].中国环境科学, 2014,3 4(8): 2167-2176. |
| MENG X H, CHENG G Q, ZHANG J B, et al.. Analyze on the spatialtemporal characteristics of GHG estimation of livestock's by life cycle assessment in China [J]. China Environ. Sci., 2014, 34(8): 2167-2176. | |
| [16] | 姚成胜,钱双双,李政通,等.中国省际畜牧业碳排放测度及时空演化机制[J].资源科学, 2017, 39(4): 698-712. |
| YAO C S, QIAN S S, LI Z T, et al.. Provincial animal husbandry carbon emissions in China and temporal-spatial evolution mechanism [J]. Resour. Sci., 2017, 39(4): 698-712. | |
| [17] | 戴小文,李金花,何艳秋,等.2000—2020年中国畜牧业区域碳排放公平性与排放效率[J].资源科学, 2023, 45(1): 62-76. |
| DAI X W, LI J H, HE Y Q, et al.. Regional equity and efficiency of carbon emissions of China's livestock industry in 2000—2020 [J]. Resour. Sci., 2023, 45 (1): 62-76. | |
| [18] | 何小田.山东省农业碳排放时空特征及趋势预测[J].黑龙江粮食, 2023(8): 124-126. |
| [19] | 曹海琳.山东省畜牧业碳排放测算及影响因素研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2023. |
| [20] | 陈苏,胡浩.中国畜禽温室气体排放时空变化及影响因素研究[J].中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26(7): 93-100. |
| CHEN S, HU H. Study on the spatial-temporal changes and influence factors of greenhouse gases emission from livestock and poultry in China [J]. China Popul. Resour. Environ., 2016, 26(7): 93-100. | |
| [21] | 尚莉媛,崔姹,赵慧峰.京津冀畜牧业碳排放效率时空演变特征及影响因素分析[J].中国农业资源与区划, 2023, 44(12): 190-199. |
| SHANG L Y, CUI C, ZHAO H F. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency of animal husbandry in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Res. Region. Plan., 2023, 44(12):190-199. | |
| [22] | 白雪冰,胡浩,周应恒,等.中国畜牧业碳排放的时空演进及其影响因素分析[J].中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(9): 260-274. |
| BAI X B, HU H, ZHOU Y H, et al.. Study on space-time evolution and influence factors of carbon emissions in China's animal husbandry [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2023, 28(9):260-274. | |
| [23] | HE D, DENG X, WANG X, et al.. Livestock greenhouse gas emission and mitigation potential in China [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2023, 348: 119494 [2024-09-20]. . |
| [24] | 闫庆友,尹洁婷.基于广义迪氏指数分解法的京津冀地区碳排放因素分解[J].科技管理研究, 2017, 37(19): 239-245. |
| YAN Q Y, YIN J T. Factor decomposition of carbon emissions in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei: a study based on generalized divisia index method [J]. Sci. Technol. Manage. Res., 2017, 37(19): 239-245. | |
| [25] | VANINSKY A. Factorial decomposition of CO2 emissions: a generalized divisia index approach [J]. Energy Econ., 2014, 45: 389-400. |
| [26] | 邵帅, 张曦, 赵兴荣.中国制造业碳排放的经验分解与达峰路径:广义迪氏指数分解和动态情景分析[J].中国工业经济,2017(3): 44-63. |
| SHAO S, ZHANG X, ZHAO X R. Empirical decomposition and peaking pathway of carbon dioxide emissions of China's manufacturing sector: generalized divisia index method and dynamic scenario analysis [J]. China Ind. Econ., 2017(3): 44-63. | |
| [27] | 谢鸿宇,陈贤生,杨木壮,等.中国单位畜牧产品生态足迹分析[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(6): 3264-3270. |
| XIE H Y, CHEN X S, YANG M Z, et al.. The ecological footprint analysis of 1kg livestock product of China [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2009, 29(6): 3264-3270. | |
| [28] | 陈胜涛,张开华,张岳武.农业碳排放绩效的测量与脱钩效应[J].统计与决策, 2021, 37(22): 85-88. |
| [29] | 全国温室气体自愿减排注册登记系统及信息平台.2021年度减排项目中国区域电网基准线排放因子[EB/OL].(2023-11-17)[2024-09-20].. |
| [30] | GARNIER J, LE NOË J, MARESCAUX A, et al.. Long-term changes in greenhouse gas emissions from French agriculture and livestock (1852—2014): from traditional agriculture to conventional intensive systems [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 660: 1486-1501. |
| [31] | 胡川,韦院英,胡威.农业政策、技术创新与农业碳排放的关系研究[J].农业经济问题, 2018, 39(9): 66-75. |
| HU C, WEI Y Y, HU W. Research on the relationship between agricultural policy, technological innovation and agricultural carbon emissions [J]. Issues Agric. Econ., 2018, 39(9): 66-75. | |
| [32] | 汪开英,李鑫,陆建定,等.碳中和目标下畜牧业低碳发展路径[J].农业工程学报, 2022, 38(1): 230-238. |
| WANG K Y, LI X, LU J D, et al.. Low-carbon development strategies of livestock industry to achieve goal of carbon neutrality in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2022, 38(1): 230-238. | |
| [33] | 励汀郁,王明利.畜牧业助力"双碳"目标实现路径研究:基于不同国家的经验比较与启示[J].世界农业, 2023(1): 5-16. |
| LI T Y, WANG M L. Research on the realization path of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals assisted by animal husbandry: based on the experience comparison and enlightenment of different countries [J]. World Agric., 2023(1): 5-16. | |
| [34] | 辛翔飞,王潇,王济民.肉鸡产业高质量发展:问题挑战、趋势研判及政策建议[J].中国家禽, 2024, 46(1): 1-10. |
| XIN X F, WANG X, WANG J M. High-quality development of broiler industry: challenges, trend and policy [J]. China Poult., 2024, 46(1): 1-10. | |
| [35] | 农业农村部,财政部. 2024—2026 年农机购置与应用补贴实施意见[EB/OL]. (2024-04-22)[2024-09-20].. |
| [1] | Weiming WANG, Xin PAN, Deping KONG, Yu AN, Shuang GUO, Zhimei SUN, Cheng XUE, Rongjun SUN, Wenqi MA, Huasen XU. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Influencing Factors of Crop Diversification in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 16-27. |
| [2] | Fan YANG, Qingning LIN, Qi WANG, Shiping MAO. Exploration on Intelligent Path of Animal Husbandry from Perspective of Metauniverse [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 1-8. |
| [3] | Hongjun GUAN, Yuhuan CHEN, Aiwu ZHAO. Assessment of Carbon Neutrality Capacity of China’s Marine Fisheries [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 215-224. |
| [4] | Zhaohui ZHANG, Yifan JI, Zejun HE. Evolution in the Spatio-temporal Pattern on Animal Husbandry Green Development Competitiveness in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 12-23. |
| [5] | Xuezhen XIONG, Chun YANG, Xiaoping MA. Situation of China's Animal Husbandry Development and High-quality Development Strategy Selection [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 1-10. |
| [6] | Xue LI, Zifei LIU, Mingjun ZHAO, Lejun XU, Huiwu SUN. Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutralization Goals and Realization Paths of the Aquaculture and Fishing Industry in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 13-26. |
| [7] | TANG Xiaopeng, CHEN Lei, XIONG Kangning*. Application Prospect of EM Bacteria in Agricultural Production of Guizhou Karst Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(4): 129-138. |
| [8] | YUE Dong-dong1, WANG Lu-min1*, FANG Hai1, GENG Rui2, ZHAO Peng-fei2, . Development Strategy of Marine Fisheries in China Based on the Carbon Balance [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(4): 1-8. |
| [9] | WANG Xing, XUE Jian-fu, WANG Yu-qiao, LI Ke-jia, ZHAO Xin, ZHANG Hai-lin*. Evaluation on Carbon Balance of Crop Production in Western China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(3): 104-111. |
| [10] | CHEN Hui-ping, ZHANG Yan-rong*, HUANG Bing-kai. An Empirical Study on Factors Affecting Herbivorous Animal Husbandry Competitiveness based on Co-integration Analysis ——Taking Gansu Province as a Case [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(2): 192-199. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yingjun1, REN Jizhou2, WANG Mingli3, YANG Gaowen1. Discussion on the Position and Development Distribution of Forage Industry in Chinas Agricultural Industry Structure [J]. , 2013, 15(4): 61-71. |
| [12] | Alamus, WU Hong-xin, XIA Ming. Brief Discussion on Grass Products Safety and its Influence Factors [J]. , 2009, 11(S1): 82-86. |
| [13] | GU Xian-hong . Welfare Raising is Basic Requirement for Organic Animal Husbandry [J]. , 2007, 9(5): 63-67. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号