




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 192-200.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0531
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Yan WU1( ), Leping ZOU2, Huijie SONG1, Dandan HU1, Kailou LIU1(
), Leping ZOU2, Huijie SONG1, Dandan HU1, Kailou LIU1( ), Wanli LIANG3
), Wanli LIANG3
Received:2023-07-10
Accepted:2024-03-04
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Kailou LIU
吴艳1( ), 邹乐萍2, 宋惠洁1, 胡丹丹1, 柳开楼1(
), 邹乐萍2, 宋惠洁1, 胡丹丹1, 柳开楼1( ), 梁万里3
), 梁万里3
通讯作者:
柳开楼
作者简介:吴艳 E-mail:wuyan070620@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yan WU, Leping ZOU, Huijie SONG, Dandan HU, Kailou LIU, Wanli LIANG. Effect of Controlled-release Nitrogen Fertilizer Combined Urea on Ammonium Nitrogen of Surface Water and Early Rice Yield[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 192-200.
吴艳, 邹乐萍, 宋惠洁, 胡丹丹, 柳开楼, 梁万里. 控释氮肥和尿素配施对田面水铵态氮和早稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 192-200.
处理 Treatment | 总氮用量 Amount of total nitrogen | 控释氮用量 Amount of controlled-release nitrogen | 磷 Phosphorus | 钾 Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | 0 | 0.0 | 75 | 135 |
| N69 | 69 | 41.4 | 75 | 135 |
| N104 | 104 | 62.4 | 75 | 135 |
| N138 | 138 | 82.8 | 75 | 135 |
| N173 | 173 | 103.8 | 75 | 135 |
| N207 | 207 | 124.2 | 75 | 135 |
Table 1 Rates of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers in different treatments
处理 Treatment | 总氮用量 Amount of total nitrogen | 控释氮用量 Amount of controlled-release nitrogen | 磷 Phosphorus | 钾 Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | 0 | 0.0 | 75 | 135 |
| N69 | 69 | 41.4 | 75 | 135 |
| N104 | 104 | 62.4 | 75 | 135 |
| N138 | 138 | 82.8 | 75 | 135 |
| N173 | 173 | 103.8 | 75 | 135 |
| N207 | 207 | 124.2 | 75 | 135 |
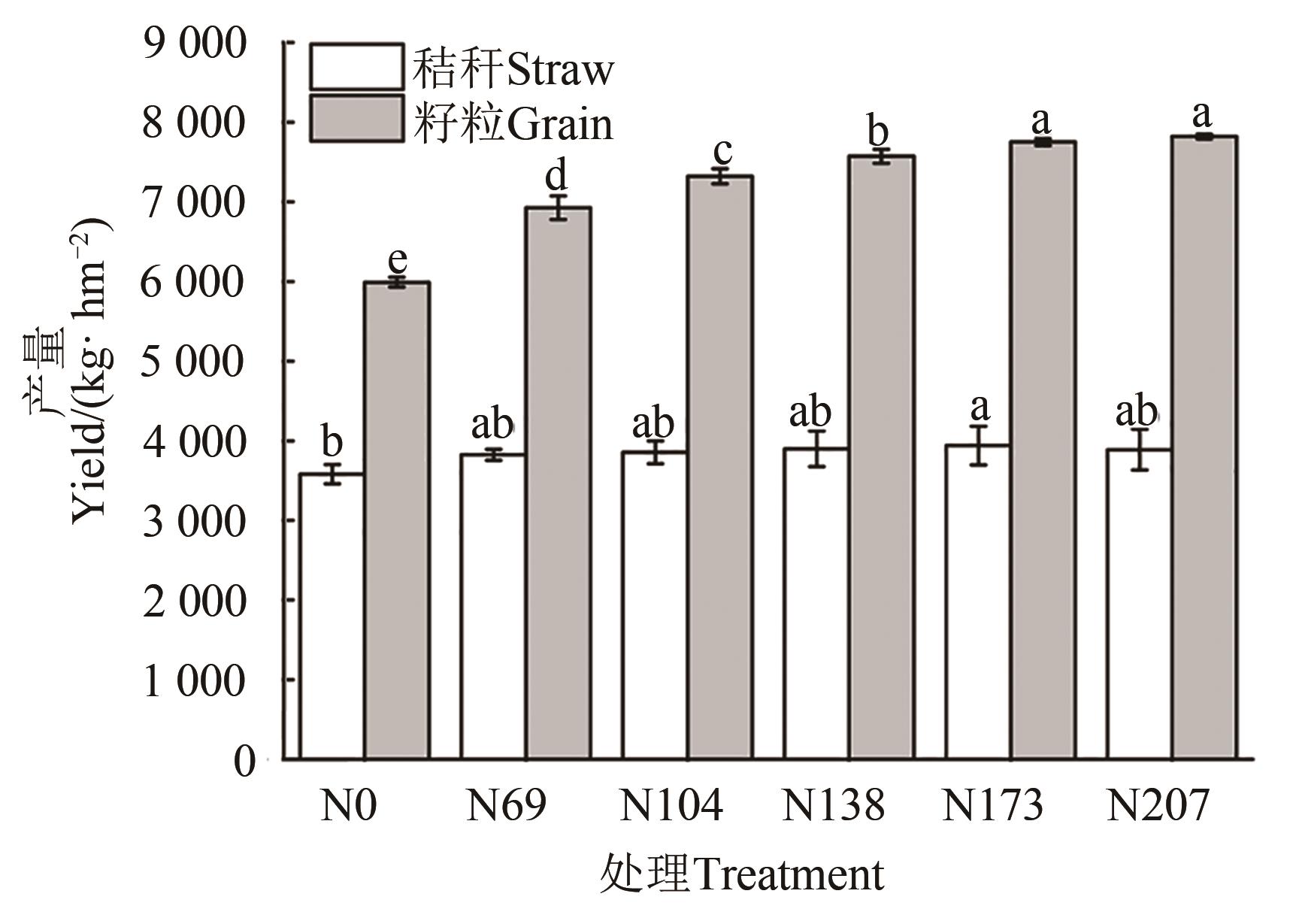
Fig. 1 Grain and straw yield of rice in different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
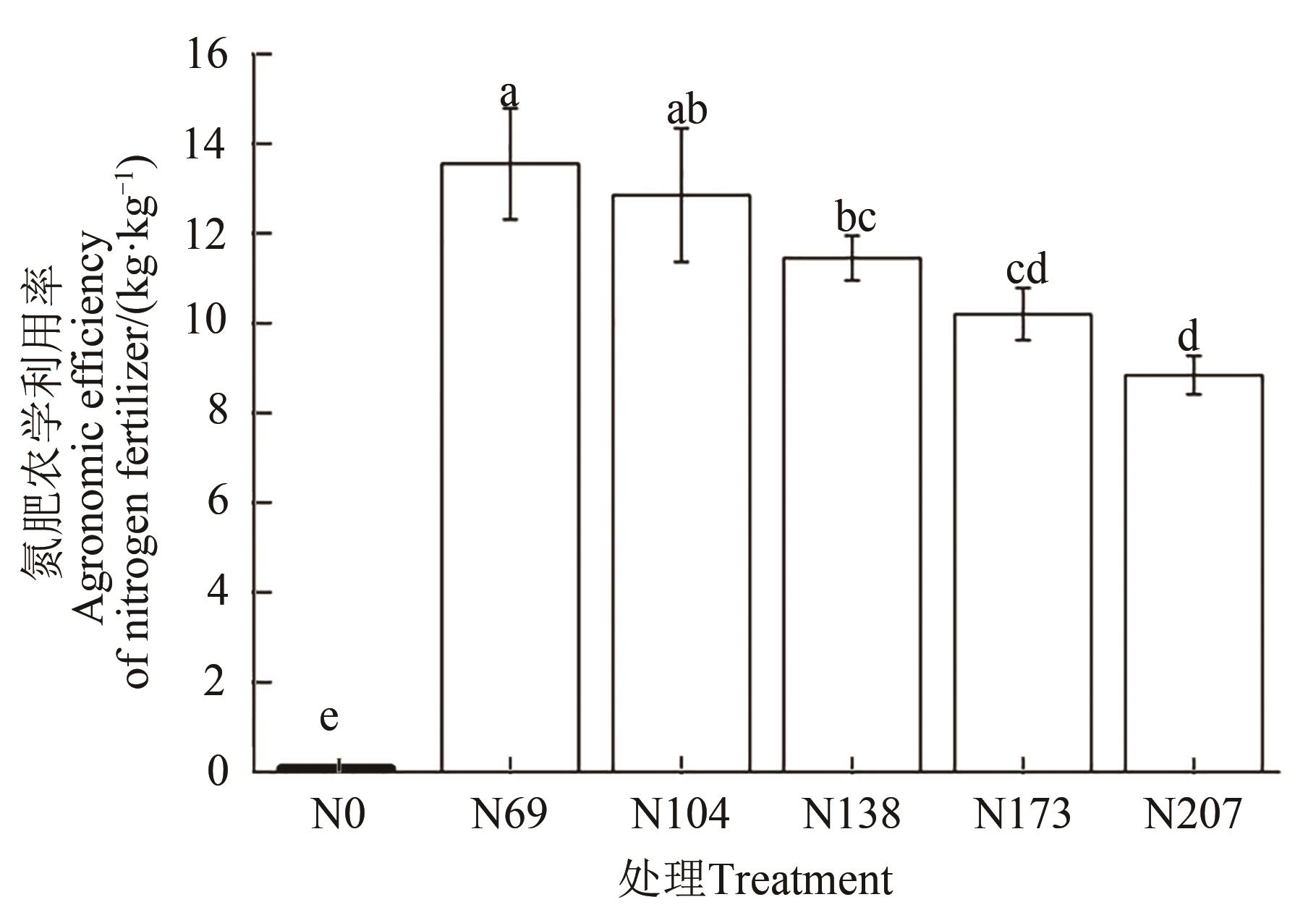
Fig. 2 Nitrogen agronomic efficiency of rice in different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| N0 | 1.71±0.12 e | 1.98±0.25 e | 1.52±0.09 d | 1.44±0.07 e | 1.15±0.06 e |
| N69 | 2.16±0.22 d | 6.32±0.17 d | 2.32±0.18 c | 2.20±0.10 d | 4.84±0.10 d |
| N104 | 3.05±0.16 c | 9.85±0.07 c | 9.32±0.14 b | 8.62±0.23 c | 6.98±0.15 c |
| N138 | 3.48±0.31 b | 10.82±0.25 b | 9.51±0.37 b | 9.02±0.35 c | 7.66±0.04 b |
| N173 | 3.84±0.07 a | 10.97±0.16 b | 9.86±0.12 a | 10.14±0.11 b | 7.84±0.08 ab |
| N207 | 4.11±0.09 a | 12.79±0.14 a | 10.14±0.04 a | 10.64±0.39 a | 7.81±0.10 a |
Table 2 Ammonium nitrogen content of surface water in different treatments
处理 Treatment | 施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| N0 | 1.71±0.12 e | 1.98±0.25 e | 1.52±0.09 d | 1.44±0.07 e | 1.15±0.06 e |
| N69 | 2.16±0.22 d | 6.32±0.17 d | 2.32±0.18 c | 2.20±0.10 d | 4.84±0.10 d |
| N104 | 3.05±0.16 c | 9.85±0.07 c | 9.32±0.14 b | 8.62±0.23 c | 6.98±0.15 c |
| N138 | 3.48±0.31 b | 10.82±0.25 b | 9.51±0.37 b | 9.02±0.35 c | 7.66±0.04 b |
| N173 | 3.84±0.07 a | 10.97±0.16 b | 9.86±0.12 a | 10.14±0.11 b | 7.84±0.08 ab |
| N207 | 4.11±0.09 a | 12.79±0.14 a | 10.14±0.04 a | 10.64±0.39 a | 7.81±0.10 a |
处理 Treatment | 施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| N0 | 8.57±0.34 e | 40.15±0.21 e | 22.32±1.17 f | 10.66±0.08 e | 5.54±0.13 d |
| N69 | 11.28±0.35 d | 130.86±1.33 d | 47.12±1.38 e | 34.26±0.17 d | 24.48±0.65 c |
| N104 | 15.27±0.47 c | 198.13±2.21 c | 95.57±0.51 d | 85.25±1.84 c | 34.72±1.36 b |
| N138 | 18.42±1.32 b | 217.74±3.13 b | 111.55±0.49 c | 109.12±2.21 b | 38.44±1.84 a |
| N173 | 19.02±0.66 b | 219.34±5.48 b | 119.18±1.20 b | 111.78±0.95 b | 39.38±1.58 a |
| N207 | 20.86±0.92 a | 254.30±4.99 a | 162.59±2.41 a | 116.48±2.61 a | 49.14±0.20 a |
Table 3 Ammonium nitrogen total amount of surface water in different treatments
处理 Treatment | 施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| N0 | 8.57±0.34 e | 40.15±0.21 e | 22.32±1.17 f | 10.66±0.08 e | 5.54±0.13 d |
| N69 | 11.28±0.35 d | 130.86±1.33 d | 47.12±1.38 e | 34.26±0.17 d | 24.48±0.65 c |
| N104 | 15.27±0.47 c | 198.13±2.21 c | 95.57±0.51 d | 85.25±1.84 c | 34.72±1.36 b |
| N138 | 18.42±1.32 b | 217.74±3.13 b | 111.55±0.49 c | 109.12±2.21 b | 38.44±1.84 a |
| N173 | 19.02±0.66 b | 219.34±5.48 b | 119.18±1.20 b | 111.78±0.95 b | 39.38±1.58 a |
| N207 | 20.86±0.92 a | 254.30±4.99 a | 162.59±2.41 a | 116.48±2.61 a | 49.14±0.20 a |
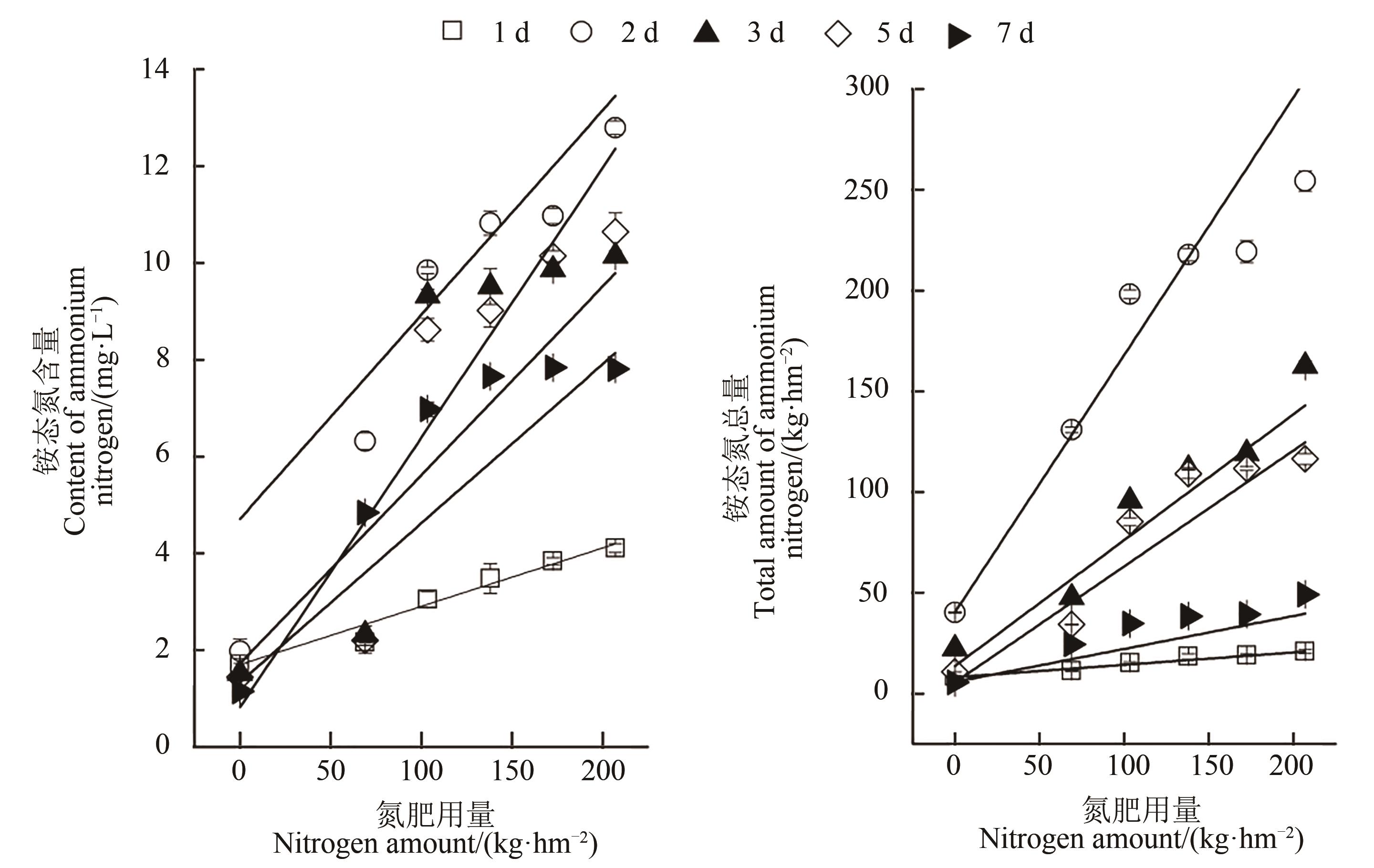
Fig. 3 Relatioships between nitrogen amount with content and total amount of ammonium nitrogen in surface water under different time after fertilization
施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | 铵态氮含量 Content of ammonium nitrogen | 铵态氮总量 Total amount of ammonium nitrogen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | P值 P value | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | P值 P value | |
| 1 | y=0.01x+1.70 | 0.981 2 | 0.001 | y=0.06x+8.14 | 0.946 8 | 0.001 |
| 2 | y=0.04x+4.70 | 0.763 8 | 0.014 | y=1.28x+40.30 | 0.975 7 | 0.001 |
| 3 | y=0.03x+1.30 | 0.710 4 | 0.022 | y=0.62x+13.67 | 0.962 3 | 0.001 |
| 5 | y=0.06x+0.80 | 0.847 7 | 0.006 | y=0.58x+5.55 | 0.992 7 | 0.001 |
| 7 | y=0.04x+1.70 | 0.889 5 | 0.003 | y=0.16x+5.81 | 0.984 3 | 0.001 |
Table 4 Fitting equations between nitrogen rates with content and total amount of ammonium nitrogen in surface water under different time after fertilization
施肥后天数 Days after fertilization/d | 铵态氮含量 Content of ammonium nitrogen | 铵态氮总量 Total amount of ammonium nitrogen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | P值 P value | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | P值 P value | |
| 1 | y=0.01x+1.70 | 0.981 2 | 0.001 | y=0.06x+8.14 | 0.946 8 | 0.001 |
| 2 | y=0.04x+4.70 | 0.763 8 | 0.014 | y=1.28x+40.30 | 0.975 7 | 0.001 |
| 3 | y=0.03x+1.30 | 0.710 4 | 0.022 | y=0.62x+13.67 | 0.962 3 | 0.001 |
| 5 | y=0.06x+0.80 | 0.847 7 | 0.006 | y=0.58x+5.55 | 0.992 7 | 0.001 |
| 7 | y=0.04x+1.70 | 0.889 5 | 0.003 | y=0.16x+5.81 | 0.984 3 | 0.001 |
| 1 | 孔祥智,何欣玮.粮食安全背景下早稻生产的战略价值与发展路径[J].农村经济,2022(10):37-46. |
| 2 | 吴云天,杨远柱,杨冬奇,等.长江流域杂交早稻发展面临的问题及对策[J].杂交水稻,2005,20(4):1-3. |
| WU Y T, YANG Y Z, YANG D Q,et al..Problems and countermeasures in development of early hybrid rice in Yangtze River valley [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2005,20(4):1-3. | |
| 3 | 魏颖娟,夏冰,赵杨,等. 15N示踪不同施氮量对超级稻产量形成及氮素吸收的影响[J].核农学报, 2016,30(4):783-791. |
| WEI Y J, XIA B, ZHAO Y, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application on yield formation and the nitrogen absorption and utilization of super rice based on 15N-tracing [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2016,30(4):783-791. | |
| 4 | 彭少兵,黄见良,钟旭华,等.提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略[J].中国农业科学,2002,35(9):1095-1103. |
| PENG S B, HUANG J L, ZHONG X H, et al.. Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2002,35(9):1095-1103. | |
| 5 | 金树权,陈若霞,汪峰,等.不同氮肥运筹模式对稻田田面水氮浓度和水稻产量的影响[J].水土保持学报,2020,34(1):242-248. |
| JIN S Q, CHEN R X, WANG F,et al..Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer application modes on the variation of nitrogen concentration in paddy field surface water and the yield of rice [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2020,34(1):242-248. | |
| 6 | 彭玉,孙永健,蒋明金,等.不同水分条件下缓/控释氮肥对水稻干物质量和氮素吸收、运转及分配的影响[J].作物学报,2014,40(5):859-870. |
| PENG Y, SUN Y J, JIANG M J,et al..Effects of water management and slow/controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on biomass and nitrogen accumulation,translocation,and distribution in rice [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014,40(5):859-870. | |
| 7 | 周旋, 康兴蓉, 彭建伟, 等. 聚氨酯包膜氮肥减施对双季早稻生长、产量及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 153-161. |
| ZHOU X, KANG X R, PENG J W, et al.. Effects of reduction application of polyurethane coated urea on growth, yield and economic benefit of double-cropping early rice [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021,23(7):153-161. | |
| 8 | YE Y S, LIANG X Q, CHEN Y X, et al.. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice.Effects on dry matter accumulation,yield,water and nitrogen use [J]. Field Crops Res., 2013,144:212-224. |
| 9 | 侯红乾,冀建华,刘益仁,等.缓/控释肥对双季稻产量、氮素吸收和平衡的影响[J].土壤,2018,50(1):43-50. |
| HOU H Q, JI J H, LIU Y R, et al.. Effects of slow/controlled-release fertilizer on grain yield,N uptake and soil N balance in double cropping rice [J]. Soils, 2018,50(1):43-50. | |
| 10 | 王宝档,王朝贤,董作为,等.缓控释氮肥与尿素配施对水稻产量及氮肥效率的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2022,63(1):32-34. |
| 11 | 付月君,王昌全,李冰,等.控释氮肥与尿素配施对单季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].土壤,2016,48(4):648-652. |
| FU Y J, WANG C Q, LI B, et al.. Effects of combined application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea on rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Soils, 2016,48(4):648-652. | |
| 12 | 宋惠洁,吴艳,余红英,等.控释氮肥配比对红壤区双季直播稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J].土壤与作物,2023,12(1):53-60. |
| SONG H J, WU Y, YU H Y, et al.. Ratios of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer effects on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-cropping direct seeding rice in red soil area [J].Soils Crops, 2023,12(1):53-60. | |
| 13 | 程爽,车阳,田晋钰,等.水稻缓控释氮肥应用研究现状与展望[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2020,41(2):1-8. |
| CHENG S, CHE Y, TIAN J Y,et al..Research advances and prospects of slow-controlled release nitrogen fertilizer in rice [J]. J. Yangzhou Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2020,41(2):1-8. | |
| 14 | 刘宝林,邹小云,宋来强,等.控释氮肥用量对早熟油菜产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J].中国油料作物学报,2018,40(4):558-565. |
| LIU B L, ZOU X Y, SONG L Q,et al..Effects of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer application on yield and nitrogen absorption and utilization of early mature rapeseed [J]. Chin. J.Oil Crop Sci., 2018,40(4):558-565. | |
| 15 | 党翼,张建军,赵刚,等.控释尿素和普通尿素配施对旱地玉米产量和水氮利用效率的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(6):156-165. |
| DANG Y, ZHANG J J, ZHAO G, et al.. Effects of mixed applying of controlled-release urea and conventional urea on yield,water and nitrogen utilization of maize in dryland [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol.,2022,24(6):156-165. | |
| 16 | 姬景红,李玉影,刘双全,等.控释尿素对黑龙江地区水稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].土壤通报,2018,49(4):876-881. |
| JI J H, LI Y Y, LIU S Q, et al.. Effects of controlled-release urea on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of rice in different regions of Heilongjiang [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2018,49(4):876-881. | |
| 17 | 吕思琪,张迪,徐文越,等.不同控释氮肥运筹对粳稻养分吸收与氮素利用的影响[J].中国稻米,2020,26(1):67-71, 74. |
| LYU S Q, ZHANG D, XU W Y, et al.. Effects of different controlled release nitrogen fertilizers on nutrient uptake and nitrogen utilization of japonica rice [J]. China Rice, 2020,26(1):67-71, 74. | |
| 18 | 鲁艳红,聂军,廖育林,等.不同控释氮肥减量施用对双季水稻产量和氮素利用的影响[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(2):155-161, 174. |
| LU Y H, NIE J, LIAO Y L, et al.. Effects of application reduction of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on yield of double cropping rice and nitrogen nutrient uptake [J].J.Soil Water Conserv., 2016,30(2):155-161, 174. | |
| 19 | 柳云龙, 卢小遮, 龚峰景, 等. 稻田施肥后田面水氮素动态变化特征[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017,45(21):268-271. |
| 20 | ZHAO Z, SHA Z M, LIU Y B, et al.. Modeling the impacts of alternative fertilization methods on nitrogen loading in rice production in Shanghai [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2016,566:1595-1603. |
| 21 | HUA L L, ZHAI L M, LIU J, et al.. Characteristics of nitrogen losses from a paddy irrigation-drainage unitsystem [J/OL]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2019, 285: 106629 [2023-06-10]. . |
| 22 | YANG Y, LI N, NI X Y, et al.. Combining deep flooding and slow-release urea to reduce ammonia emission from rice fields [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod., 2020, 244: 118745 [2023-06-10]. . |
| 23 | LÜ H D, WANG X Y, PAN Z L, et al.. Assessment of the crucial factors influencing the responses of ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions to controlled release nitrogen fertilizer:a meta-analysis [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2023,22(11):3549-3559. |
| 24 | 张福锁,王激清,张卫峰,等.中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径[J].土壤学报,2008,45(5):915-924. |
| ZHANG F S, WANG J Q, ZHANG W F,et al..Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2008,45(5):915-924. | |
| 25 | 国家环境保护总局,水和废水监测分析方法编委会.水和废水监测分析方法[M].4版.北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002: 279-280. |
| 26 | 董燕,王正银.缓/控释复合肥料对土壤氮素库的调控作用[J].生态学报,2010,30(24):6707-6714. |
| DONG Y, WANG Z Y.Effects of slow/controlled release compound fertilizers on the forms of soil nitrogen [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010,30(24):6707-6714. | |
| 27 | 袁嫚嫚,叶舒娅,刘枫,等.不同控释氮肥对水稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J].广东农业科学,2011,38(9):56-57. |
| YUAN M M, YE S Y, LIU F, et al.. Different controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on yield and nitrogen utilization rate of rice [J].Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2011,38(9):56-57. | |
| 28 | 宋付朋,张民,史衍玺,等.控释氮肥的氮素释放特征及其对水稻的增产效应[J].土壤学报,2005,42(4):619-627. |
| SONG F P, ZHANG M, SHI Y X, et al.. Releasing characteristics of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer and its effects on rice yield [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2005,42(4):619-627. | |
| 29 | ZHANG Y J, REN W C, ZHU K Y, et al.. Substituting readily available nitrogen fertilizer with controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer improves crop yield and nitrogen uptake while mitigating environmental risks:a global meta-analysis [J/OL]. Field Crops Res., 2024,306:109221[2023-06-10].. |
| 30 | 聂军,郑圣先.控释肥料不同用量水平对水稻氮素利用和产量的影响[J].湖南农业科学,2001(6):37-39. |
| NIE J, ZHENG S X. Effect of different amount of controlled fertilizer release on Nitrogen utilization and rice yield [J].Hunan Agric. Sci., 2001(6):37-39. | |
| 31 | 郑圣先,聂军,熊金英,等.控释肥料提高氮素利用率的作用及对水稻效应的研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2001,7(1):11-16. |
| ZHENG S X, NIE J, XIONG J Y,et al..Study on role of controlled release fertilizer in increasing the efficiency of nitrogen utilization and rice yield [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2001,7(1):11-16. | |
| 32 | 周亮,荣湘民,谢桂先,等.不同氮肥施用对双季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].土壤,2014,46(6):971-975. |
| ZHOU L, RONG X M, XIE G X,et al..Effects of different nitrogen fertilizers on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Soils,2014,46(6):971-975. | |
| 33 | 刘汝亮,王芳,王开军,等.控释氮肥侧条施用对东北地区水稻产量和氮肥损失的影响[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(2):252-256. |
| LIU R L, WANG F, WANG K J,et al..Effects of side strip application of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on rice yield and nitrogen loss in Northeast China [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2018,32(2):252-256. | |
| 34 | 黄巧义, 吴永沛, 黄旭, 等. 控释尿素与尿素配施对甜玉米产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 163-173. |
| HUANG Q Y, WU Y P, HUANG X, et al.. Impact of controlled-release urea combined with conventional urea on yield and nitrogen utilization efficiency of spring sweet corn under one-off application [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(2): 163-173. | |
| 35 | SU N, RONG X M, XIE G X, et al.. Effectiveness of a 10-year continuous reduction of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on production,nitrogen loss and utilization of double-cropping rice [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2024,912:168857 [2023-06-10].. |
| 36 | LI W W, AHMAD S, LIU D,et al..Subsurface banding of blended controlled-release urea can optimize rice yields while minimizing yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions [J].Crop J., 2023,11(3):914-921. |
| 37 | 田玉华,贺发云,尹斌,等.不同氮磷配合下稻田田面水的氮磷动态变化研究[J].土壤,2006,38(6):727-733. |
| TIAN Y H, HE F Y, YIN B, et al.. Dynamic changes of nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in surface water of paddy field [J]. Soils, 2006,38(6):727-733. | |
| 38 | 赵冬,颜廷梅,乔俊,等.稻季田面水不同形态氮素变化及氮肥减量研究[J].生态环境学报,2011,20(4):743-749. |
| ZHAO D, YAN T M, QIAO J, et al.. Change of different nitrogen forms in surface water of rice field and reduction of nitrogen fertilizer application in rice season [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2011,20(4):743-749. | |
| 39 | 叶玉适,梁新强,金熠,等.节水灌溉与控释肥施用对稻田田面水氮素变化及径流流失的影响[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(5):105-112, 118. |
| YE Y S, LIANG X Q, JIN Y, et al.. Dynamic variation and runoff loss of nitrogen in surface water of paddy field as affected by water-saving irrigation and controlled-release fertilizer application [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2014,28(5):105-112, 118. | |
| 40 | 侯朋福, 薛利祥, 周玉玲, 等. 掺混控释肥侧深施对稻田田面水氮素浓度的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019 (1): 16-21. |
| HOU P F, XUE L X, ZHOU Y L, et al.. The effect of side deep fertilization for resin blending controlled-release fertilizer on nitrogen concentration in surface water of paddy field [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2019 (1): 16-21. | |
| 41 | 施瑾,马彩婉.缓控释氮肥一次性施用对水稻甬优12产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2020,61(11):2219-2220, 2225. |
| 42 | 朱坚,石丽红,田发祥,等.湖南典型双季稻田氨挥发对施氮量的响应研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(5):1129-1138. |
| ZHU J, SHI L H, TIAN F X,et al..Responses of ammonia volatilization to nitrogen application amount in typical double cropping paddy fields in Hunan province [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2013,19(5):1129-1138. | |
| 43 | 黄思怡,田昌,谢桂先,等.控释尿素减少双季稻田氨挥发的主要机理和适宜用量[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2019,25(12):2102-2112. |
| HUANG S Y, TIAN C, XIE G X, et al.. Mechanism and suitable application dosage of controlled-release urea effectively reducing ammonia volatilization in double-cropping paddy fields [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019,25(12):2102-2112. | |
| 44 | 夏小江,胡清宇,朱利群,等.太湖地区稻田田面水氮磷动态特征及径流流失研究[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(4):21-25. |
| XIA X J, HU Q Y, ZHU L Q, et al.. Study on dynamic changes of nitrogen and phosphorus in surface water of paddy field and runoff loss in Taihu Region [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2011,25(4):21-25. | |
| 45 | LIU J, OUYANG X Q, SHEN J L, et al.. Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses were influenced by chemical fertilization but not by pesticide application in a double rice-cropping system in the subtropical hilly region of China [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ.,2020,715:136852 [2023-06-10].. |
| 46 | 刘红江,郭智,郑建初,等.前氮后移对水稻产量形成和农田氮素流失的影响[J].中国农学通报,2018,34(5):82-87. |
| LIU H J, GUO Z, ZHENG J C, et al.. Effect of postponing N application on rice yield formation and nitrogen runoff losses from the field [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2018,34(5):82-87. | |
| 47 | FU J, JIAN Y W, WU Y L,et al..Nationwide estimates of nitrogen and phosphorus losses via runoff from rice paddies using data-constrained model simulations [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod., 2021,279:123642 [2023-06-10]. . |
| [1] | Darong LI, Xiaoling LI, Wuxian ZHOU, Meide ZHANG, Xiaogang JIANG, Jinwen YOU, Hua WANG. Effects of Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Growth and Soil Properties of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 216-226. |
| [2] | Junya DUAN, Yuanyuan ZHAO, Tingting WANG, Jianyu WEI, Zheng WANG, Dexun WANG, Juan LI, Hongzhi SHI. Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Combined with Polyaspartic Acid on Nitrogen Utilization, Yield and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 227-238. |
| [3] | Qiang WU, Conglian WU, Xiaoyun WU, Jian WU, Xuanmei XU, Junsheng LAI, Weiyun HU, Bangchu GONG, Xibing JIANG. Effect of Different Fertilization Treatments on Yield and Fruit Quality of Castanea henryi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 228-237. |
| [4] | Tingting LIU, Xiyu HAO, Hui WANG, Jingwen LENG, Shihang GONG, Wei LIU. Correlation Analysis Between Yield and Agronomical Traits of Different Foxtail Millet Varieties in Semi-arid Area of Western Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 50-60. |
| [5] | Wenxuan SHI, Jinfang TAN, Qian ZHANG, Lantao LI, Yilun WANG. Effect of One-off Fertilization on Yield and Nitrogen Fertilizer Efficiency of Summer Maize in Different Ecological Regions [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 193-202. |
| [6] | Mei WU, Jinzhu ZHANG, Zhenhua WANG, Jian LIU, Yue WEN, Xuanzhi LI. Effects of Water and Air Interaction on Physiological Growth and Yield of Maize Under Mulched Drip Irrigation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 189-200. |
| [7] | Liang SUN, Yi XU, Qin CAI, Jinghao GUO, Can ZHAO, Baowei GUO, Zhipeng XING, Zhongyang HUO, Hongcheng ZHANG, Yajie HU. Research Progress on Effects of Medium and Trace Elements on Yield and Quality of Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 9-19. |
| [8] | Xianyin SUN, Qiuhuan MU, Yong MI, Guangde LYU, Xiaolei QI, Yingying SUN, Xundong YIN, Ruixia WANG, Ke WU, Zhaoguo QIAN, Yan ZHAO, Minggang GAO. Classification and Evaluation of New Wheat Lines Based on GT Biplot [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 14-24. |
| [9] | Yukun QIN, Junying CHEN, Lijuan ZHANG. Response of Dry Matter Accumulation Characteristics and Yield of Cotton in North Jiangxi Cotton Region to Nitrogen Reduction Measures [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 191-199. |
| [10] | Shouhua PENG, Mingming XU, Jiqiang WEI, Lijun LIANG, Quan YE, Xiaoyuan CHI, Shaofeng ZHANG, Xiangli DONG. Effects of Increase Applying of Biofertilizer Strain FBR1 on Growth Development and Yield of Peanut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 200-205. |
| [11] | Yuxin CHEN, Hongmei ZHAO, Weijun YANG, Mei YANG, Song GUO, Shilong SONG, Chao HUI. Effects of Biochar on Soil Microbial Carbon Source Utilization and Spring Wheat Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 174-183. |
| [12] | Limin GAO, Zechen GU, Xuefei GONG, Lianming CUI, Dongsen GUO, Ying ZHOU, Lin WANG, Qishun WEI. Effects of Grass Growing on the Productivity of Orchard-Soil System in China: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 184-194. |
| [13] | Rigui ASHEN, Rongping ZHANG, Ningning ZHOU, Tingyu FENG, Lin ZHOU, Peng MA, Lise AER, Xuehuan LIAO, Keyuan ZHANG. Effects of Silicon, Calcium, Potassium and Magnesium Fertilizer and Density on Rice Yield Formation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 155-163. |
| [14] | Gang ZHAO, Shuying WANG, Shangzhong LI, Jianjun ZHANG, Yi DANG, Lei WANG, Xingmao LI, Wanli CHENG, Gang ZHOU, Shengli NI, Tinglu FAN. Effects of Precipitation on Yield and Water Consumption of Winter Wheat in Loess Plateau in Recent 40 Years [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 164-173. |
| [15] | Zhongyi LI, Hongqin TANG, Wenbin DONG, Caihui WEI, Tieguang HE. Effects of Co-incorporation of Rice Straw and Chinese Milk Vetch on Photosynthetic Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 171-180. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号