




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 174-183.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0837
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Yuxin CHEN1( ), Hongmei ZHAO2, Weijun YANG1(
), Hongmei ZHAO2, Weijun YANG1( ), Mei YANG1, Song GUO1, Shilong SONG1, Chao HUI1
), Mei YANG1, Song GUO1, Shilong SONG1, Chao HUI1
Received:2022-10-04
Accepted:2023-04-06
Online:2024-05-15
Published:2024-05-14
Contact:
Weijun YANG
陈雨欣1( ), 赵红梅2, 杨卫君1(
), 赵红梅2, 杨卫君1( ), 杨梅1, 郭颂1, 宋世龙1, 惠超1
), 杨梅1, 郭颂1, 宋世龙1, 惠超1
通讯作者:
杨卫君
作者简介:陈雨欣 E-mail:1498257246@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuxin CHEN, Hongmei ZHAO, Weijun YANG, Mei YANG, Song GUO, Shilong SONG, Chao HUI. Effects of Biochar on Soil Microbial Carbon Source Utilization and Spring Wheat Yield[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 174-183.
陈雨欣, 赵红梅, 杨卫君, 杨梅, 郭颂, 宋世龙, 惠超. 生物质炭对土壤微生物碳源利用及春小麦产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 174-183.
处理 Treatment | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Mcintosh指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0B0 | 0.61±0.01 i | 0.94±0.00 c | 2.95±0.01 e | 4.80±0.03 g |
| N0B1 | 0.69±0.02 h | 0.95±0.00 b | 3.02±0.03 cd | 5.03±0.18 f |
| N0B2 | 0.72±0.02 g | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.02±0.01 cd | 5.32±0.10 e |
| N0B3 | 0.78±0.01 de | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.07±0.02 b | 5.64±0.05 d |
| N1B0 | 0.72±0.02 g | 0.94±0.00 c | 2.96±0.02 e | 5.45±0.14 e |
| N1B1 | 0.85±0.01 c | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.13±0.01 a | 5.83±0.03 c |
| N1B2 | 0.93±0.01 a | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.11±0.00 a | 6.54±0.06 a |
| N1B3 | 0.88±0.01 b | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.13±0.00 a | 6.09±0.07 b |
| N2B0 | 0.77±0.01 ef | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.01±0.01 d | 5.86±0.08 c |
| N2B1 | 0.80±0.01 d | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.01±0.00 d | 6.08±0.04 b |
| N2B2 | 0.75±0.01 f | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.03±0.01 c | 5.41±0.04 e |
| N2B3 | 0.86±0.01 bc | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.07±0.04 b | 5.95±0.03 bc |
| B | ns | ns | * | ns |
| N | * | ns | ns | ns |
| B×N | ** | ** | ** | ** |
Table 1 Diversity index of soil microbial metabolic function in different wheat fields
处理 Treatment | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Mcintosh指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0B0 | 0.61±0.01 i | 0.94±0.00 c | 2.95±0.01 e | 4.80±0.03 g |
| N0B1 | 0.69±0.02 h | 0.95±0.00 b | 3.02±0.03 cd | 5.03±0.18 f |
| N0B2 | 0.72±0.02 g | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.02±0.01 cd | 5.32±0.10 e |
| N0B3 | 0.78±0.01 de | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.07±0.02 b | 5.64±0.05 d |
| N1B0 | 0.72±0.02 g | 0.94±0.00 c | 2.96±0.02 e | 5.45±0.14 e |
| N1B1 | 0.85±0.01 c | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.13±0.01 a | 5.83±0.03 c |
| N1B2 | 0.93±0.01 a | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.11±0.00 a | 6.54±0.06 a |
| N1B3 | 0.88±0.01 b | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.13±0.00 a | 6.09±0.07 b |
| N2B0 | 0.77±0.01 ef | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.01±0.01 d | 5.86±0.08 c |
| N2B1 | 0.80±0.01 d | 0.94±0.00 c | 3.01±0.00 d | 6.08±0.04 b |
| N2B2 | 0.75±0.01 f | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.03±0.01 c | 5.41±0.04 e |
| N2B3 | 0.86±0.01 bc | 0.95±0.00 a | 3.07±0.04 b | 5.95±0.03 bc |
| B | ns | ns | * | ns |
| N | * | ns | ns | ns |
| B×N | ** | ** | ** | ** |
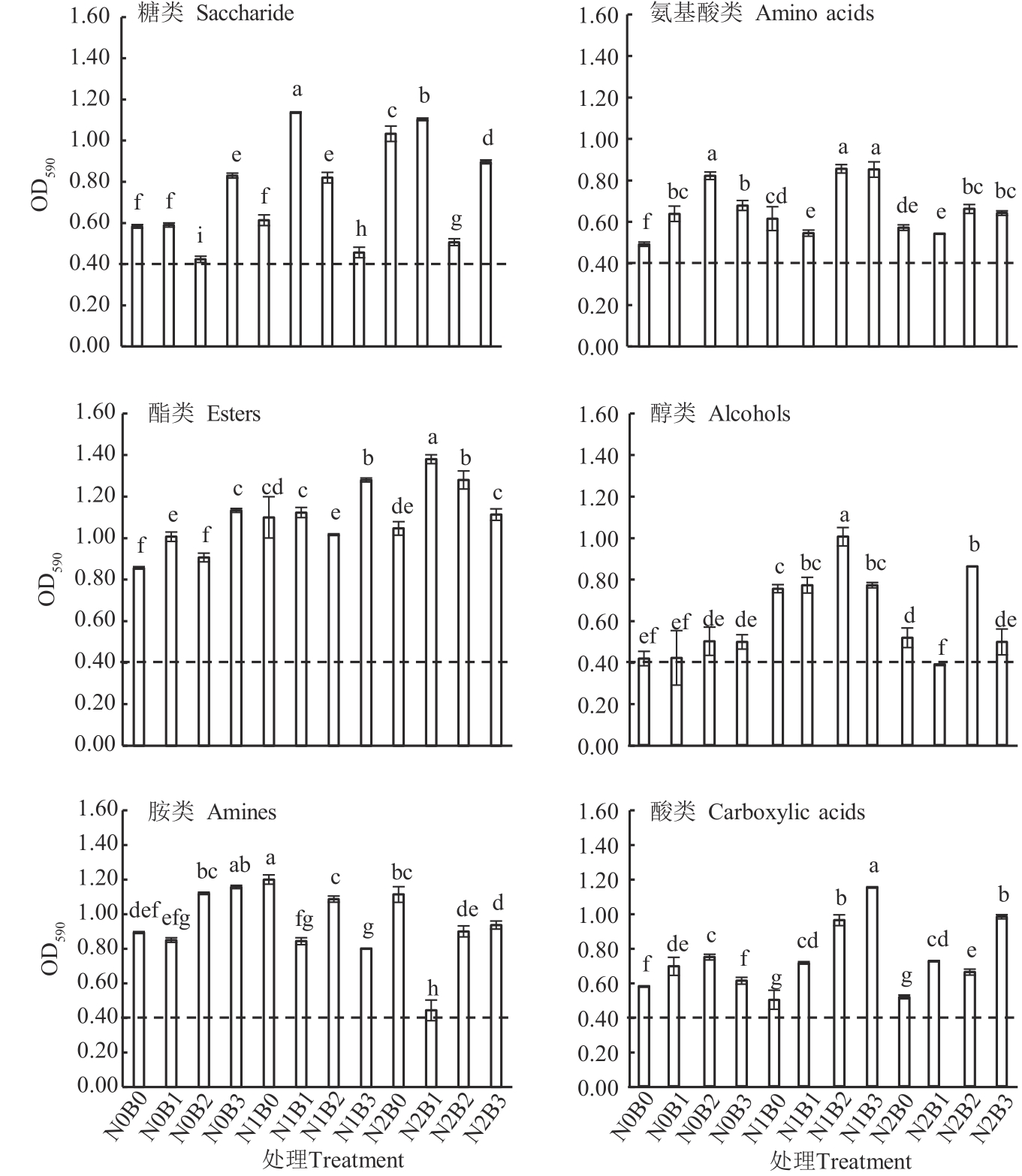
Fig. 2 Soil microbial utilization capacity of various carbon sources in wheat field under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level. * and ** indicate significant at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively,ns indicates not significant.
碳源种类 Type of carbon source | 主成分1 PC1 | 主成分2 PC2 |
|---|---|---|
氨基酸 Amino acids | 0.93 | 0.08 |
糖类 Saccharide | -0.61 | 0.34 |
醇类 Alcohols | 0.66 | 0.18 |
酯类 Esters | -0.06 | 0.85 |
胺类 Amines | 0.39 | -0.78 |
酸类 Carboxylic acids | 0.63 | 0.60 |
Table 2 Principal component load matrix
碳源种类 Type of carbon source | 主成分1 PC1 | 主成分2 PC2 |
|---|---|---|
氨基酸 Amino acids | 0.93 | 0.08 |
糖类 Saccharide | -0.61 | 0.34 |
醇类 Alcohols | 0.66 | 0.18 |
酯类 Esters | -0.06 | 0.85 |
胺类 Amines | 0.39 | -0.78 |
酸类 Carboxylic acids | 0.63 | 0.60 |
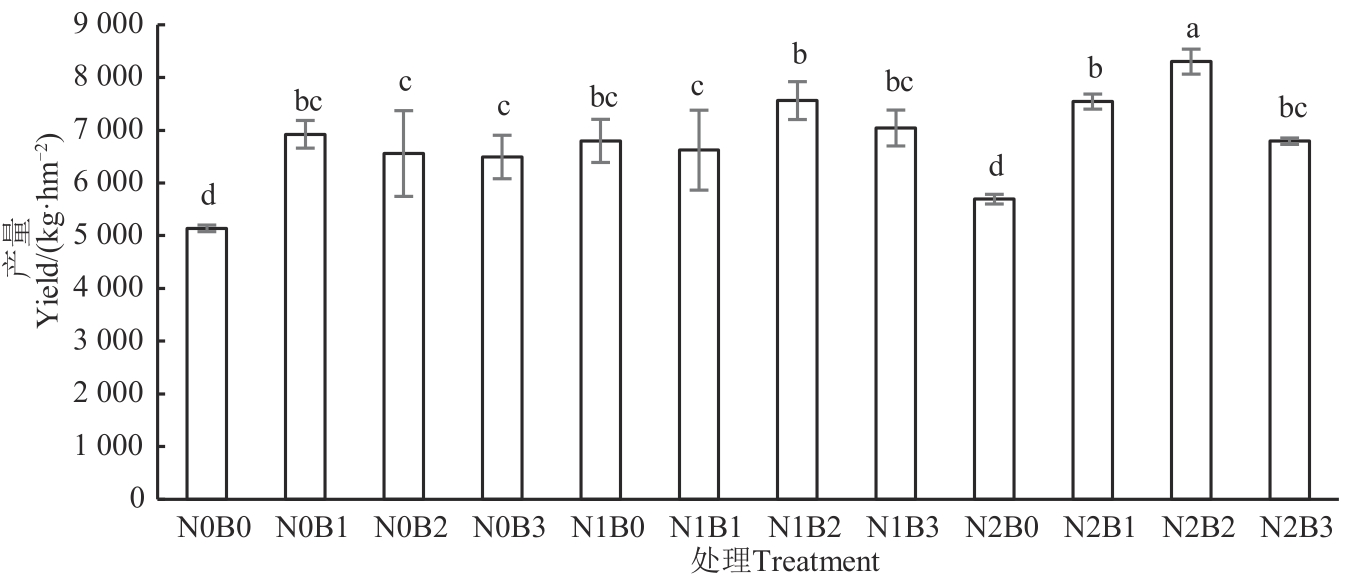
Fig. 4 Spring wheat yield under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | McIntosh指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.59** | |||
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.83** | 0.81** | ||
| McIntosh指数 McIntosh index | 0.94** | 0.34* | 0.64** | |
| 产量 Yield | 0.42** | 0.40* | 0.30 | 0.38* |
Table 3 Correlation between soil microbial functional diversity and spring wheat yield
指标 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | McIntosh指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.59** | |||
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.83** | 0.81** | ||
| McIntosh指数 McIntosh index | 0.94** | 0.34* | 0.64** | |
| 产量 Yield | 0.42** | 0.40* | 0.30 | 0.38* |
| 1 | 孔丝纺, 姚兴成, 张江勇, 等. 生物质炭的特性及其应用的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(4): 716-723. |
| KONG S F, YAO X C, ZHANG J Y, et al.. Review of characteristics of biochar and research progress of its applications [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2015, 24(4): 716-723. | |
| 2 | LIU Y X, LU H H, YANG S M, et al.. Impacts of biochar addition on rice yield and soil properties in a cold waterlogged paddy for two crop seasons [J]. Field Crops Res., 2016, 191: 161-167. |
| 3 | 邢东建, 杨卫君, 贺佳琪, 等. 减磷加炭对北疆灌区土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(11): 39-44. |
| XING D J, YANG W J, HE J Q, et al.. Effects of phosphorus reduction and biochar addition on soil physical and chemical properties in north Xinjiang irrigated area [J]. China Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(11): 39-44. | |
| 4 | 贺佳琪, 杨卫君, 贾永红, 等. 减磷加炭对北疆春小麦磷素利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(3): 13-19. |
| HE J Q, YANG W J, JIA Y H, et al.. Effect of reducing phosphate fertilizer and applying biochar on phosphorus utilization and yield of spring wheat in northern Xinjiang [J]. China Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(3): 13-19. | |
| 5 | 刘晓霞, 吴东涛, 朱伟锋, 等. 外源添加生物炭对水稻产量和土壤性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2016, 57(11): 1776-1779. |
| 6 | 韦思业. 不同生物质原料和制备温度对生物炭物理化学特征的影响[D].广州:中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2017. |
| WEI S Y. Influence of biomass feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures on physical and chemical properties of biochar [D]. Guangzhou : University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017. | |
| 7 | 谢迎新, 刘宇娟, 张伟纳, 等. 潮土长期施用生物炭提高小麦产量及氮素利用率[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(14): 115-123. |
| XIE Y X, LIU Y J, ZHANG W N, et al.. Long-term application of biochar in fluvio-aquatic soil improving wheat yield and nitrogen utilization [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2018, 34(14): 115-123. | |
| 8 | 高文翠, 杨卫君, 贺佳琪, 等. 生物炭添加对麦田土壤微生物群落代谢的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(12): 3998-4004. |
| GAO W C, YANG W J, HE J Q, et al.. Effects of biochar on soil microbial community metabolism in wheat field [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2020, 39(12): 3998-4004. | |
| 9 | 赵辉, 周运超, 任启飞. 不同林龄马尾松人工林土壤微生物群落结构和功能多样性演变[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1): 227-238. |
| ZHAO H, ZHOU Y C, REN Q F. Evolution of soil microbial community structure and functional diversity in pinus massoniana plantations with age of stand [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2020, 57(1): 227-238. | |
| 10 | XU N, TAN G C, WANG H Y, et al.. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure [J/OL]. Eur. J. Soil Biol., 2016, 74: 004 [2022-09-03]. . |
| 11 | 聂新星, 李志国, 张润花, 等. 生物炭及其与化肥配施对灰潮土土壤理化性质、微生物数量和冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(9): 27-32. |
| NIE X X, LI Z G, ZHANG R H, et al.. Effects of biochar and its combined application with chemical fertilizers on physical and chemical properties and microbial quantity of fluvo-aquic soil and winter wheat yield [J]. China Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 32(9): 27-32. | |
| 12 | 顾美英,唐光木,葛春辉,等.不同秸秆还田方式对和田风沙土土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(4): 489-498. |
| GU M Y, TANG G M, GE C H, et al.. Effects of straw incorporation modes on microbial activity and functional diversity in sandy soil [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2016,24(4):489-498. | |
| 13 | 王光飞,马艳,郭德杰,等. 不同用量秸秆生物炭对辣椒疫病防控效果及土壤性状的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(1): 204-215. |
| WANG G F, MA Y, GUO D J, et al.. Application-rate-dependent effects of straw biochar on control of phytophthora blight of chilli pepper and soil properties [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2017, 54(1) : 204-215. | |
| 14 | 李晓韦, 韩上, 雷之萌, 等. 氮素形态对油菜秸秆腐解及养分释放规律的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(5): 717-725. |
| LI X W, HAN S, LEI Z M, et al.. Effects of nitrogen forms on decomposition and nutrient release of rapeseed straw [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2019, 27(5): 717-725. | |
| 15 | 惠超, 杨卫君, 宋世龙, 等. 生物炭施用对麦田土壤团聚体机械稳定性及春小麦产量的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(2): 349-355. |
| HUI C, YANG W J, SONG S L, et al.. Effects of biochar application on mechanical stability of soil aggregates and yield of spring wheat [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2022, 53(2): 349-355. | |
| 16 | KOLTON M, HAREL Y M, PASTERNAK Z, et al.. Impact of biochar application to soil on the root-associated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, 77(14): 4924-4930. |
| 17 | 房彦飞,徐文修,符小文,等.冬小麦施氮对复播大豆土壤微生物区系及产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(8): 1826-1833. |
| FANG Y F, XU W X, FU X W, et al.. Effect of nitrogen applied in winter wheat on soil microflora and yield of summer-sowing soybean [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2020, 34(8): 1826-1833. | |
| 18 | 王顶,伊文博,李欢,等. 玉米间作和施氮对土壤微生物代谢功能多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(3): 793-800. |
| WANG D, YI W B, LI H, et al.. Effects of intercropping and nitrogen application on soil microbial metabolic functional diversity inmaize cropping soil [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2022, 33(3): 793-800. | |
| 19 | 韩晓日,葛银凤,李娜,等.连续施用生物炭对土壤理化性质及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2017, 48(4): 392-398. |
| HAN X R, GE Y F, LI N, et al.. Effects of continuous application of biochar on soil physic-chemical properties and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2017, 48(4): 392-398. | |
| 20 | 霍丽丽, 姚宗路, 赵立欣, 等. 典型农业生物炭理化特性及产品质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(16): 249-257. |
| HUO L L, YAO Z L, ZHAO L X, et al.. Physical and chemical properties and product quality evaluation of biochar from typical agricultural residues [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019, 35(16): 249-257. | |
| 21 | 陈心想, 耿增超, 王森, 等. 施用生物炭后塿土土壤微生物及酶活性变化特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(4): 751-758. |
| CHEN X X, GENG Z C, WANG S, et al.. Effects of biochar amendment on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in loess soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2014, 33(4): 751-758. | |
| 22 | 王博, 刘扣珠, 任天宝,等. 减氮条件下生物炭对烤烟根系发育及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(3):45-50. |
| WANG B, LIU K Z, REN T B, et al.. Effect of biochar on the roots and soil microorganisms of flue-cured tobacco under the condition of nitrogen reduction [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(3): 45-50. | |
| 23 | 阚正荣, 濮超, 祁剑英, 等. 施用生物炭对华北平原冬小麦土壤水分和籽粒产量的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(4): 1-10. |
| KAN Z R, PU C, QI J Y, et al.. Effects of biochar on soil water and grain yield of winter wheat in the North China Plain [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2019, 24(4): 1-10. | |
| 24 | 邓万刚, 吴鹏豹, 赵庆辉, 等. 低量生物质炭对2种热带牧草产量和品质的影响研究初报[J]. 草地学报, 2010,18(6):844-847, 853. |
| DENG W G, WU P B, ZHAO Q H, et al.. The effect of biochar on grass yield and quality [J]. Acta Agrestla Sin., 2010,18(6):844-847, 853. | |
| 25 | 刘敏, 纪立东, 王锐, 等. 施用生物质炭条件下减施氮肥对玉米生长和土壤的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(19): 216-222. |
| 26 | 宋大利, 习向银, 黄绍敏, 等. 秸秆生物炭配施氮肥对潮土土壤碳氮含量及作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 369-379. |
| SONG D L, XI X Y, HUANG S M, et al.. Effects of combined application of straw biochar and nitrogen on soil carbon and nitrogen contents and crop yields in a fluvo-aquic soil [J]. J. Plant Nut. Fert., 2017, 23(2): 369-379. | |
| 27 | 马艳, 王光飞. 生物炭防控植物土传病害研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2014(6):14-20. |
| MA Y, WANG G F. Review of biochar utilization on soil-borne disease control [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2014(6):14-20. | |
| 28 | 周志红, 李心清, 邢英, 等. 生物炭对土壤氮素淋失的抑制作用[J]. 地球与环境, 2011,39(2): 278-284. |
| ZHOU Z H, LI X Q, XING Y, et al.. Effect of biochar amendment on nitrogen leaching in soil [J]. Earth Environ., 2011, 39(2): :278-284. | |
| 29 | 陈庆华, 许卓, 汤计超, 等.生物炭对土壤氮磷流失和油菜产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(11): 130-137. |
| CHEN Q H, XU Z, TANG J C, et al.. Influences of adding biochar on loss of nitrogen and phosphorus and yield of rape in soil [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(11): 130-137. |
| [1] | Limin GAO, Zechen GU, Xuefei GONG, Lianming CUI, Dongsen GUO, Ying ZHOU, Lin WANG, Qishun WEI. Effects of Grass Growing on the Productivity of Orchard-Soil System in China: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 184-194. |
| [2] | Yahong ZHAO, Qianyu HU, Rong XIA, Zhijiang WANG, Yonghui XIE, Xianwen YE, Lei YU, Ying QI, Shaowu YANG, Zhiqin XUE, Zhixing WU, Feiyan HUANG, Tianhua HAN. Effects of Biochar Fertilizer on Rhizosphere Flora and Physicochemical Properties of Flue-cured Tobacco Susceptible to Root Knot Nematode [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 206-214. |
| [3] | Rigui ASHEN, Rongping ZHANG, Ningning ZHOU, Tingyu FENG, Lin ZHOU, Peng MA, Lise AER, Xuehuan LIAO, Keyuan ZHANG. Effects of Silicon, Calcium, Potassium and Magnesium Fertilizer and Density on Rice Yield Formation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 155-163. |
| [4] | Gang ZHAO, Shuying WANG, Shangzhong LI, Jianjun ZHANG, Yi DANG, Lei WANG, Xingmao LI, Wanli CHENG, Gang ZHOU, Shengli NI, Tinglu FAN. Effects of Precipitation on Yield and Water Consumption of Winter Wheat in Loess Plateau in Recent 40 Years [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 164-173. |
| [5] | Zhongyi LI, Hongqin TANG, Wenbin DONG, Caihui WEI, Tieguang HE. Effects of Co-incorporation of Rice Straw and Chinese Milk Vetch on Photosynthetic Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 171-180. |
| [6] | Jiayu HU, Yang YANG, Hongyan ZHANG, Bingyang GAO, Linglu WANG, Junying YAN, Xiaomei SUN, Yanan ZHAO, Youliang YE. Effect of Topdressing Different Types of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Growth and Yield of Intercropped Peanut with Wheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 191-197. |
| [7] | Hui WANG, Hongyu FU, Yunkai YUE, Guoxian CUI, Wei SHE. Ramie Yield SSA-BP Prediction Model Based on Climate Variables [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 110-118. |
| [8] | Yanfei FANG, Xiaoying LUO, Jianghua TANG, Tingting SUN, Luzhen WANG, Tian TANG, Wenxiu XU. Effects of Sowing Methods on Yield, Dry Matter and Water Use Efficiency of Spring Wheat in Dryland [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [9] | Jing GAO, Minggang XU, Ran LI, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Lei ZHENG. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 186-196. |
| [10] | Yuanyuan DUAN, Xiaohong LIU, Tao TANG, Fanfan WANG, Jingmao YOU, Xiaoliang GUO, Jie GUO. Effects of Planting Density on Growth and Quality of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [11] | Ying ZHOU, Jingyong LI, Linxiu DAI, Dicai AO, Ziyi LI, Fan YANG, Junwei GU, Qiang XU, Zhi DOU, Hui GAO. Effect of Melatonin Spraying on Rice Yield Formation and Lodging Resistance Under Rice-Crayfish Coculture Mode [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 34-42. |
| [12] | Wei WANG, Qiang ZHAO, Abuduaini Munire·, Alimu·Amuli, Xinxin LI, Yangqing TIAN. Effects of Different Exogenous Substances on Chemical Capping and Yield and Quality of Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [13] | Chenyang ZHANG, Minggang XU, Fei WANG, Ran LI, Nan SUN. Effects of Manure Application on Soybean Yield and Soil Nutrients in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [14] | Zhigang ZHENG, Li XIANG, Gongyi LIU, Cai XU, Bin QIN, Weiqin WANG, Huabin ZHENG, Qiyuan TANG. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Density on Growth and Yield of Orderly Machine-thrown Early Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [15] | Yaxuan MENG, Wei MA, Xuhang YAO, Yingqi SUN, Xin ZHONG, Shan HUANG, Qiaoyun WENG, Yinghui LIU, Jincheng YUAN. Study on the Response Factors of Maize Yield to Nitrogen Fertilizer [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号