




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 142-152.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0630
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-08-02
接受日期:2021-11-22
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2023-04-17
通讯作者:
张月辰
作者简介:董伟欣 E-mail:dongweixin.yuxin@163.com;
基金资助:
Weixin DONG1( ), Dongxiao LI2, Yuechen ZHANG2(
), Dongxiao LI2, Yuechen ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2021-08-02
Accepted:2021-11-22
Online:2023-01-15
Published:2023-04-17
Contact:
Yuechen ZHANG
摘要:
合理施用氮素可提高氮素利用效率,并最终影响玉米的产量和品质。为研究不同氮素水平对玉米生理参数及产量品质的影响,以‘先玉335’和‘京农科728’为试验材料,分别设N1(150 kg·hm-2)、N2(210 kg·hm-2)、N3(270 kg·hm-2)和N4(330 kg·hm-2)4种施氮水平,分析不同氮素水平对玉米生长、生理参数、产量和籽粒品质的影响。研究表明,2个玉米品种的株高、叶面积和地上部干重随着施氮量的增加而升高,而茎粗从N1至N3处理不断增大,到N4处理降低,另外叶面积指数和叶片夹角同样表现为随着施氮量的增加而升高,京农科728的叶面积指数高于先玉335,且各个处理之间的差异未达到显著水平;叶绿素含量均表现出从吐丝期至灌浆期升高,到成熟期又降低的趋势,施氮量从N1至N3处理逐渐升高,到N4处理又降低;可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖含量随着生育进程的推进而升高,且‘京农科728’略高于‘先玉335’,此外,可溶性蛋白在3个时期均随着施氮量的增加而不断升高,而可溶性糖含量从N1至N2处理升高,到N3和N4处理又降低;超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶活性随着施氮量的增加而呈现升高趋势,丙二醛含量呈现相反的变化趋势;2个品种均在N2处理下的产量最高,施氮量超过210 kg·hm-2产量却降低,因此,N2(210 kg·hm-2)处理为最佳的施氮量。由此可见,适量增加氮素可促进玉米干物质和碳水化合物的积累,并最终提高产量和品质,为河北省山前平原区减氮栽培提供了参考。
中图分类号:
董伟欣, 李东晓, 张月辰. 不同氮素水平对夏玉米生理参数及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 142-152.
Weixin DONG, Dongxiao LI, Yuechen ZHANG. Effects of Different Nitrogen Levels on Physiological Parameters, Yield and Quality of Maize[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 142-152.
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 250.60±5.73 b | 286.20±23.40 b | 290.10±21.29 a |
| N2 | 251.00±7.04 ab | 298.60±15.76 b | 299.60±7.09 a | ||
| N3 | 258.00±10.32 ab | 302.40±8.41 ab | 303.60±12.20 a | ||
| N4 | 266.60±8.47 a | 305.20±16.35 a | 311.50±5.32 a |
表1 不同处理下玉米株高、茎粗、叶面积和地上部干重
Table 1 Plant height, stem diameter, leaf area and shoot dry weight of maize under different treatments
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 250.60±5.73 b | 286.20±23.40 b | 290.10±21.29 a |
| N2 | 251.00±7.04 ab | 298.60±15.76 b | 299.60±7.09 a | ||
| N3 | 258.00±10.32 ab | 302.40±8.41 ab | 303.60±12.20 a | ||
| N4 | 266.60±8.47 a | 305.20±16.35 a | 311.50±5.32 a |
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 239.80±14.06 b | 254.70±13.94 a | 255.20±8.56 a |
| N2 | 250.80±3.70 a | 257.54±10.28 a | 259.80±8.58 a | ||
| N3 | 252.80±7.85 a | 260.00±8.00 a | 261.20±11.61 a | ||
| N4 | 254.20±3.77 a | 265.80±21.53 a | 265.90±6.58 a | ||
茎粗 Stem diameter/cm | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 6.02±0.23 b | 6.02±0.54 c | 7.85±0.68 a |
| N2 | 6.96±0.35 a | 7.09±0.25 ab | 8.09±0.55 a | ||
| N3 | 7.15±0.40 a | 7.42±0.67 a | 8.14±0.70 a | ||
| N4 | 6.82±0.46 a | 6.83±0.23 b | 8.03±0.15 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 4.36±2.28 a | 5.88±2.78 b | 6.75±3.88 a | |
| N2 | 4.47±2.20 a | 6.72±3.65 ab | 7.37±3.82 a | ||
| N3 | 4.83±2.32 a | 7.28±4.50 a | 7.41±3.43 a | ||
| N4 | 4.48±2.11 a | 7.13±2.25 a | 7.29±3.11 a | ||
叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 521.33±23.04 a | 531.72±34.23 b | 612.62±47.73 a |
| N2 | 537.33±25.38 a | 545.38±37.23 ab | 618.53±93.86 a | ||
| N3 | 556.14±33.54 a | 570.54±40.45 a | 625.14±13.86 a | ||
| N4 | 602.80±42.87 a | 616.03±64.76 a | 636.46±33.55 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 515.40±28.37 a | 519.72±29.36 b | 532.42±52.77 b | |
| N2 | 521.93±20.21 a | 547.77±43.41 ab | 569.40±30.49 a | ||
| N3 | 527.05±39.49 a | 573.83±17.83 a | 582.23±50.41 a | ||
| N4 | 539.63±51.22 a | 591.74±25.09 a | 615.38±58.37 a | ||
地上部干重 Dry weight above ground/g | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 140.00±17.32 a | 170.00±26.46 c | 366.67±57.74 b |
| N2 | 153.33±15.28 a | 216.67±55.08 bc | 440.00±26.46 b | ||
| N3 | 160.00±17.32 a | 263.33±15.28 ab | 450.00±88.88 b | ||
| N4 | 183.33±35.12 a | 303.33±32.15 a | 590.00±55.68 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 140.00±20.00 a | 213.33±20.82 a | 406.67±49.33 b | |
| N2 | 150.00±10.00 a | 236.67±25.17 a | 423.33±81.45 b | ||
| N3 | 153.33±5.77 a | 240.00±17.32 a | 446.67±41.63 b | ||
| N4 | 163.33±15.28 a | 243.33±47.26 a | 470.00±30.00 a |
表1 不同处理下玉米株高、茎粗、叶面积和地上部干重 (续表Continued)
Table 1 Plant height, stem diameter, leaf area and shoot dry weight of maize under different treatments
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 239.80±14.06 b | 254.70±13.94 a | 255.20±8.56 a |
| N2 | 250.80±3.70 a | 257.54±10.28 a | 259.80±8.58 a | ||
| N3 | 252.80±7.85 a | 260.00±8.00 a | 261.20±11.61 a | ||
| N4 | 254.20±3.77 a | 265.80±21.53 a | 265.90±6.58 a | ||
茎粗 Stem diameter/cm | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 6.02±0.23 b | 6.02±0.54 c | 7.85±0.68 a |
| N2 | 6.96±0.35 a | 7.09±0.25 ab | 8.09±0.55 a | ||
| N3 | 7.15±0.40 a | 7.42±0.67 a | 8.14±0.70 a | ||
| N4 | 6.82±0.46 a | 6.83±0.23 b | 8.03±0.15 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 4.36±2.28 a | 5.88±2.78 b | 6.75±3.88 a | |
| N2 | 4.47±2.20 a | 6.72±3.65 ab | 7.37±3.82 a | ||
| N3 | 4.83±2.32 a | 7.28±4.50 a | 7.41±3.43 a | ||
| N4 | 4.48±2.11 a | 7.13±2.25 a | 7.29±3.11 a | ||
叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 521.33±23.04 a | 531.72±34.23 b | 612.62±47.73 a |
| N2 | 537.33±25.38 a | 545.38±37.23 ab | 618.53±93.86 a | ||
| N3 | 556.14±33.54 a | 570.54±40.45 a | 625.14±13.86 a | ||
| N4 | 602.80±42.87 a | 616.03±64.76 a | 636.46±33.55 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 515.40±28.37 a | 519.72±29.36 b | 532.42±52.77 b | |
| N2 | 521.93±20.21 a | 547.77±43.41 ab | 569.40±30.49 a | ||
| N3 | 527.05±39.49 a | 573.83±17.83 a | 582.23±50.41 a | ||
| N4 | 539.63±51.22 a | 591.74±25.09 a | 615.38±58.37 a | ||
地上部干重 Dry weight above ground/g | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 140.00±17.32 a | 170.00±26.46 c | 366.67±57.74 b |
| N2 | 153.33±15.28 a | 216.67±55.08 bc | 440.00±26.46 b | ||
| N3 | 160.00±17.32 a | 263.33±15.28 ab | 450.00±88.88 b | ||
| N4 | 183.33±35.12 a | 303.33±32.15 a | 590.00±55.68 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 140.00±20.00 a | 213.33±20.82 a | 406.67±49.33 b | |
| N2 | 150.00±10.00 a | 236.67±25.17 a | 423.33±81.45 b | ||
| N3 | 153.33±5.77 a | 240.00±17.32 a | 446.67±41.63 b | ||
| N4 | 163.33±15.28 a | 243.33±47.26 a | 470.00±30.00 a |
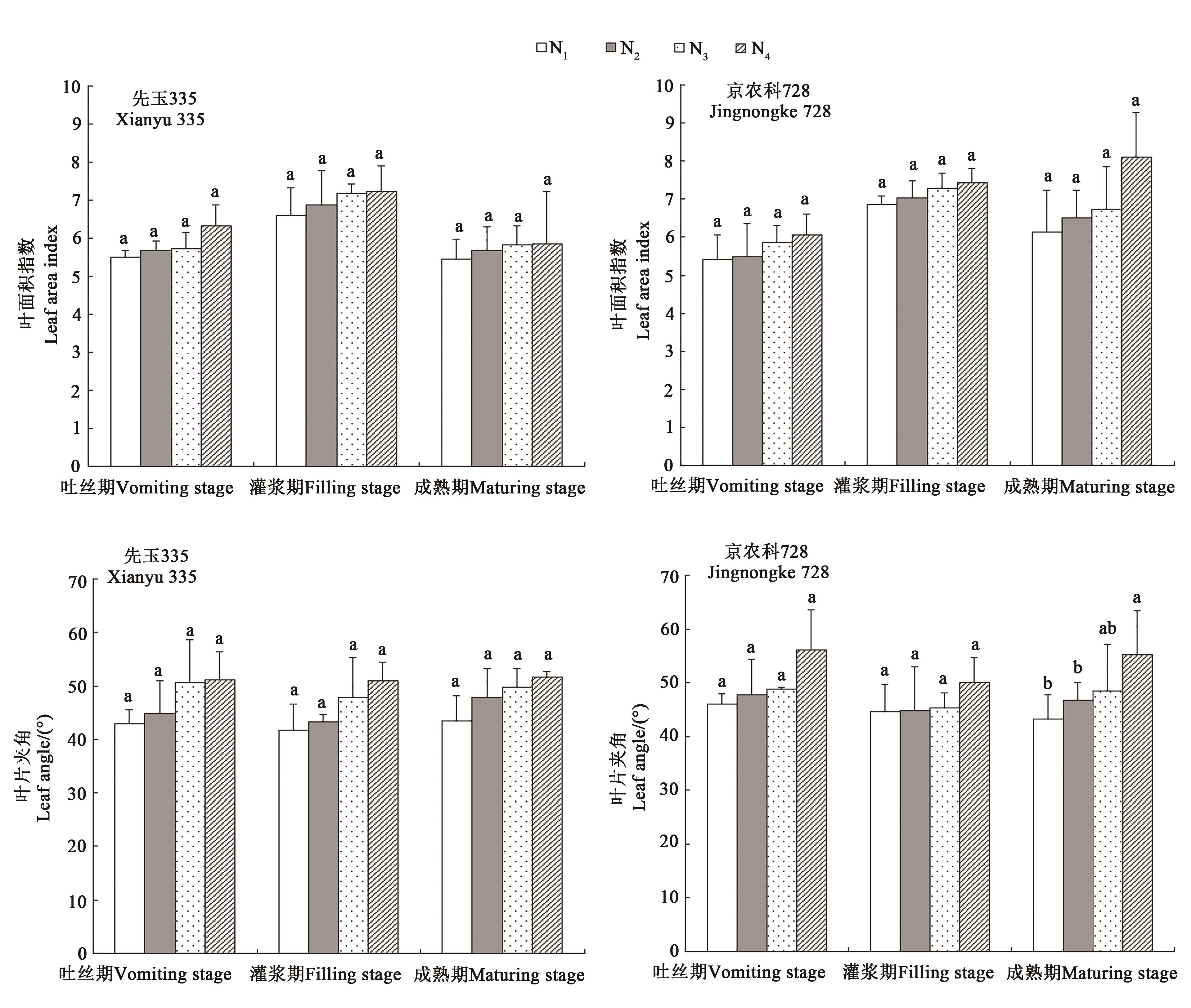
图1 不同处理下玉米叶面积指数和叶片夹角注:同一时期不同小写字母表示处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig.1 Leaf area index and leaf angle of maize under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters at the same time indicate the significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
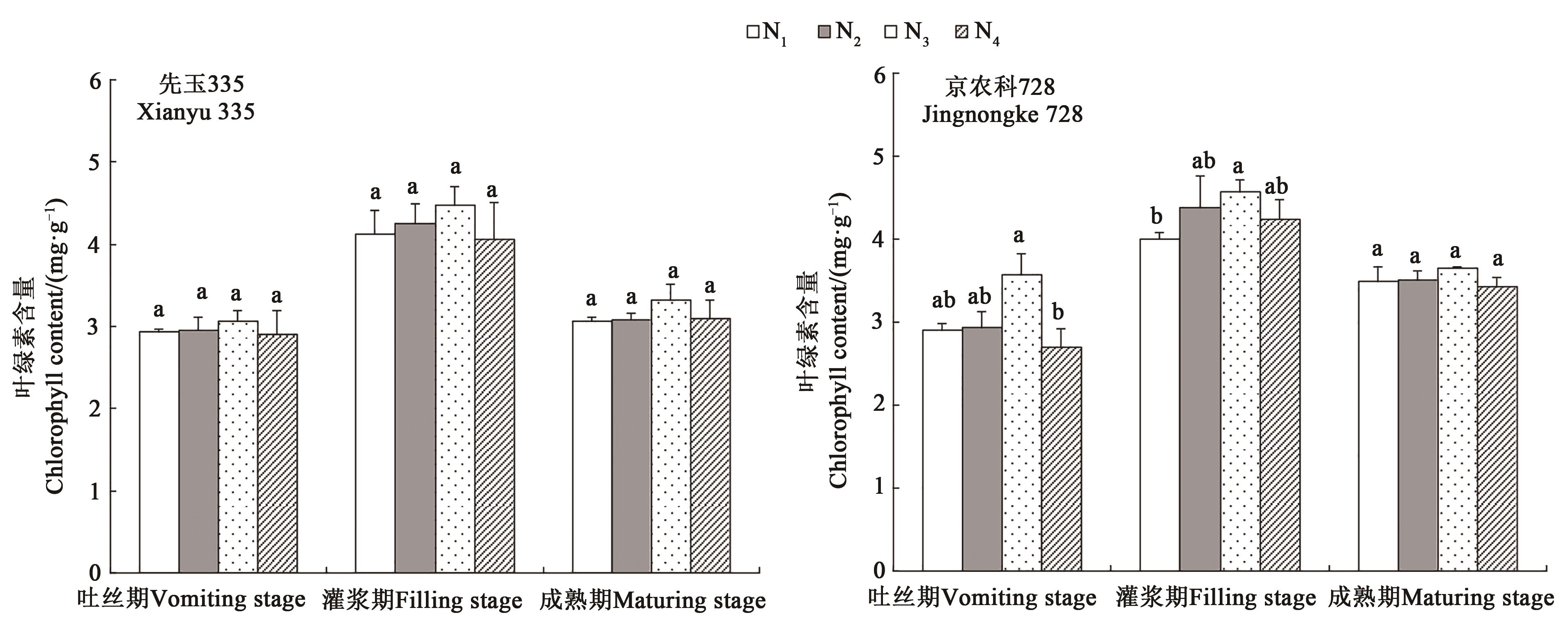
图2 不同处理下玉米穗位叶叶绿素含量注:同一时期不同小写字母表示处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig. 2 Chlorophyll content of maize ear leaves under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters at the same time indicate the significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
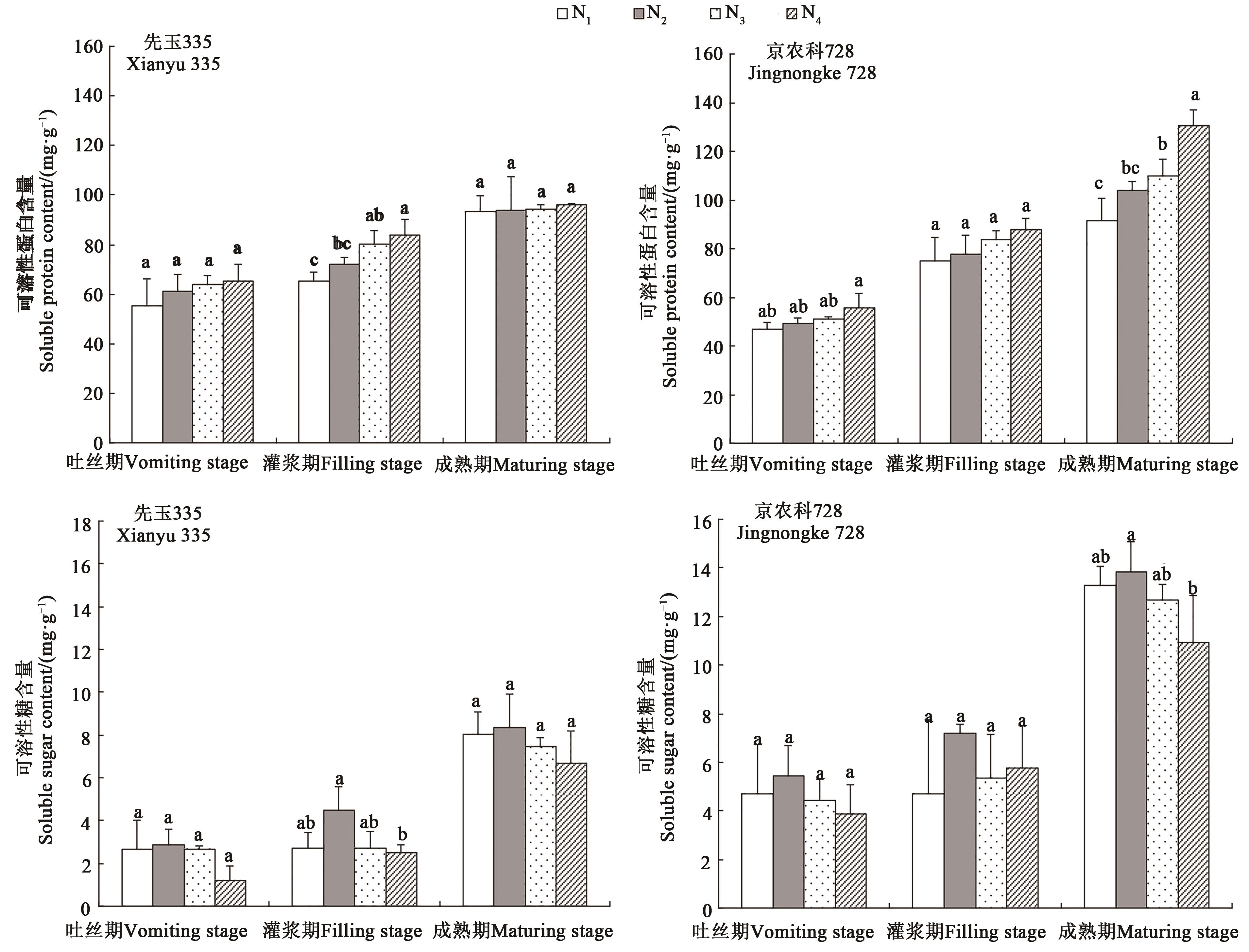
图3 不同处理下玉米可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖含量注:同一时期不同小写字母表示处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig. 3 Soluble protein and soluble sugar content of maize under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters at the same time indicate the significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SOD活性 SOD activity/(U·g-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 227.01±54.15 a | 231.23±32.15 b | 218.93±36.74 b |
| N2 | 252.66±21.57 a | 340.09±33.80 a | 258.84±19.41 ab | ||
| N3 | 267.39±26.49 a | 352.92±27.13 a | 285.92±19.14 a | ||
| N4 | 297.80±92.92 a | 365.75±10.69 a | 293.53±40.88 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 287.35±21.16 b | 399.49±17.41 b | 199.92±30.87 b | |
| N2 | 361.95±37.29 a | 443.68±38.75 ab | 261.22±20.21 ab | ||
| N3 | 374.78±26.91 a | 473.62±48.54 ab | 272.15±19.49 ab | ||
| N4 | 375.73±19.77 a | 489.29±31.75 a | 294.48±26.91 a | ||
POD活性 POD activity/ (△470·g-1·min-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 97.92±2.57 a | 111.75±5.22 b | 118.17±5.55 b |
| N2 | 98.33±8.75 a | 113.75±0.66 b | 127.75±5.20 a | ||
| N3 | 104.00±4.18 a | 117.42±1.01 ab | 129.50±6.97 a | ||
| N4 | 104.00±5.41 a | 121.42±3.76 a | 130.00±4.36 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 105.21±3.88 a | 106.58±2.63c | 115.58±7.97 a | |
| N2 | 107.45±4.33 a | 108.42±1.81 bc | 116.75±1.29 a | ||
| N3 | 110.58±4.51 a | 112.08±1.66 ab | 117.83±5.79 a | ||
| N4 | 111.67±3.76 a | 114.42±3.83 a | 119.67±9.17 a | ||
MDA含量 MDA Content/ (µmol·g-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 18.09±1.46 a | 19.27±4.28 a | 23.91±2.29 a |
| N2 | 16.86±2.45 a | 17.21±2.35 a | 23.55±2.41 a | ||
| N3 | 14.89±1.05 a | 16.51±1.39 a | 22.65±3.46 a | ||
| N4 | 13.98±1.83 a | 16.02±4.08 a | 22.57±3.97 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 16.14±2.50 a | 20.55±2.61 a | 21.42±1.56 a | |
| N2 | 15.62±2.01 a | 19.72±5.68 a | 20.65±3.31 a | ||
| N3 | 15.50±0.42 a | 17.44±1.03 a | 19.24±1.43 a | ||
| N4 | 10.82±3.31 b | 17.05±1.68 a | 19.08±1.38 a |
表2 不同处理下玉米SOD、POD活性和MDA含量
Table 2 SOD, POD activity and MDA content of maize under different treatments
指标 Index | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期 Vomiting stage | 灌浆期 Filling stage | 成熟期 Maturing stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SOD活性 SOD activity/(U·g-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 227.01±54.15 a | 231.23±32.15 b | 218.93±36.74 b |
| N2 | 252.66±21.57 a | 340.09±33.80 a | 258.84±19.41 ab | ||
| N3 | 267.39±26.49 a | 352.92±27.13 a | 285.92±19.14 a | ||
| N4 | 297.80±92.92 a | 365.75±10.69 a | 293.53±40.88 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 287.35±21.16 b | 399.49±17.41 b | 199.92±30.87 b | |
| N2 | 361.95±37.29 a | 443.68±38.75 ab | 261.22±20.21 ab | ||
| N3 | 374.78±26.91 a | 473.62±48.54 ab | 272.15±19.49 ab | ||
| N4 | 375.73±19.77 a | 489.29±31.75 a | 294.48±26.91 a | ||
POD活性 POD activity/ (△470·g-1·min-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 97.92±2.57 a | 111.75±5.22 b | 118.17±5.55 b |
| N2 | 98.33±8.75 a | 113.75±0.66 b | 127.75±5.20 a | ||
| N3 | 104.00±4.18 a | 117.42±1.01 ab | 129.50±6.97 a | ||
| N4 | 104.00±5.41 a | 121.42±3.76 a | 130.00±4.36 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 105.21±3.88 a | 106.58±2.63c | 115.58±7.97 a | |
| N2 | 107.45±4.33 a | 108.42±1.81 bc | 116.75±1.29 a | ||
| N3 | 110.58±4.51 a | 112.08±1.66 ab | 117.83±5.79 a | ||
| N4 | 111.67±3.76 a | 114.42±3.83 a | 119.67±9.17 a | ||
MDA含量 MDA Content/ (µmol·g-1 FW) | 先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 18.09±1.46 a | 19.27±4.28 a | 23.91±2.29 a |
| N2 | 16.86±2.45 a | 17.21±2.35 a | 23.55±2.41 a | ||
| N3 | 14.89±1.05 a | 16.51±1.39 a | 22.65±3.46 a | ||
| N4 | 13.98±1.83 a | 16.02±4.08 a | 22.57±3.97 a | ||
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 16.14±2.50 a | 20.55±2.61 a | 21.42±1.56 a | |
| N2 | 15.62±2.01 a | 19.72±5.68 a | 20.65±3.31 a | ||
| N3 | 15.50±0.42 a | 17.44±1.03 a | 19.24±1.43 a | ||
| N4 | 10.82±3.31 b | 17.05±1.68 a | 19.08±1.38 a |
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 穗数 Ears number/ (104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains number per spike | 单穗重 Single panicle weight/g | 穗粒重 Panicle grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 11.22±0.10 b | 567.80±78.38 b | 184.58±23.66 b | 156.88±22.64 c | 8 411.36±358.56 b |
| N2 | 12.06±0.51 a | 632.40±53.19 a | 217.16±20.29 a | 185.18±16.22 a | 10 243.08±339.19 a | |
| N3 | 11.28±0.35 b | 600.20±36.65 ab | 208.39±15.91 a | 177.83±13.47 ab | 9 978.33±298.99 ab | |
| N4 | 10.72±0.42 b | 601.40±47.37 ab | 199.30±16.07 ab | 169.79±13.51 bc | 8 698.27±376.53 b | |
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 13.44±0.48 a | 479.50±51.85 a | 198.68±21.75 a | 168.80±18.23 a | 10 842.92±367.98 a |
| N2 | 13.56±0.63 a | 489.36±43.51 a | 199.78±31.07 a | 170.77±27.27 a | 11 060.38±288.78 a | |
| N3 | 13.89±0.39 a | 461.10±39.05 a | 190.07±23.01 a | 163.12±19.58 a | 10 824.18±358.92 a | |
| N4 | 13.56±0.48 a | 488.60±61.73 a | 192.35±27.74 a | 163.86±22.86 a | 10 612.52±318.47 b |
表3 不同处理下玉米产量构成因素及产量
Table 3 Yield components and yield of maize under different treatments
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 穗数 Ears number/ (104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains number per spike | 单穗重 Single panicle weight/g | 穗粒重 Panicle grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 11.22±0.10 b | 567.80±78.38 b | 184.58±23.66 b | 156.88±22.64 c | 8 411.36±358.56 b |
| N2 | 12.06±0.51 a | 632.40±53.19 a | 217.16±20.29 a | 185.18±16.22 a | 10 243.08±339.19 a | |
| N3 | 11.28±0.35 b | 600.20±36.65 ab | 208.39±15.91 a | 177.83±13.47 ab | 9 978.33±298.99 ab | |
| N4 | 10.72±0.42 b | 601.40±47.37 ab | 199.30±16.07 ab | 169.79±13.51 bc | 8 698.27±376.53 b | |
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 13.44±0.48 a | 479.50±51.85 a | 198.68±21.75 a | 168.80±18.23 a | 10 842.92±367.98 a |
| N2 | 13.56±0.63 a | 489.36±43.51 a | 199.78±31.07 a | 170.77±27.27 a | 11 060.38±288.78 a | |
| N3 | 13.89±0.39 a | 461.10±39.05 a | 190.07±23.01 a | 163.12±19.58 a | 10 824.18±358.92 a | |
| N4 | 13.56±0.48 a | 488.60±61.73 a | 192.35±27.74 a | 163.86±22.86 a | 10 612.52±318.47 b |
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/ (mg·g-1FW) | 淀粉含量 Starch content/% | 脂肪含量 Crude fat content/% | 氨基酸含量 Lysine content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 49.20±0.43 d | 30.96±0.09 c | 3.73±0.04 b | 13.59±0.12 b |
| N2 | 60.73±0.39 c | 32.88±0.14 b | 4.31±0.05 a | 16.59±1.01 a | |
| N3 | 62.51±0.29 a | 33.56±0.19 a | 3.95±0.04 b | 13.86±0.07 b | |
| N4 | 61.68±0.45 b | 32.74±0.25 b | 3.92±0.06 b | 12.89±0.21 b | |
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 50.55±0.16 c | 31.55±0.11 b | 4.08±0.04 b | 12.75±0.23 b |
| N2 | 57.18±0.49 b | 32.39±0.11 b | 5.08±0.09 a | 15.57±0.03 a | |
| N3 | 62.41±0.28 a | 34.62±1.21 a | 4.32±0.03 b | 12.34±0.22 b | |
| N4 | 56.31±1.79 b | 31.53±0.89 b | 4.03±0.32 b | 11.57±1.14 b |
表4 不同处理下玉米籽粒品质
Table 4 Grain quality of maize under different treatments
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/ (mg·g-1FW) | 淀粉含量 Starch content/% | 脂肪含量 Crude fat content/% | 氨基酸含量 Lysine content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
先玉335 Xianyu 335 | N1 | 49.20±0.43 d | 30.96±0.09 c | 3.73±0.04 b | 13.59±0.12 b |
| N2 | 60.73±0.39 c | 32.88±0.14 b | 4.31±0.05 a | 16.59±1.01 a | |
| N3 | 62.51±0.29 a | 33.56±0.19 a | 3.95±0.04 b | 13.86±0.07 b | |
| N4 | 61.68±0.45 b | 32.74±0.25 b | 3.92±0.06 b | 12.89±0.21 b | |
京农科728 Jingnongke 728 | N1 | 50.55±0.16 c | 31.55±0.11 b | 4.08±0.04 b | 12.75±0.23 b |
| N2 | 57.18±0.49 b | 32.39±0.11 b | 5.08±0.09 a | 15.57±0.03 a | |
| N3 | 62.41±0.28 a | 34.62±1.21 a | 4.32±0.03 b | 12.34±0.22 b | |
| N4 | 56.31±1.79 b | 31.53±0.89 b | 4.03±0.32 b | 11.57±1.14 b |
| 1 | 徐建文,梅旭荣,居辉,等. 黄淮海地区冬小麦关键生育期不同灌溉水平对产量影响的模拟[J]. 作物学报,2014,40(8):1485-1492. |
| XU J W, MEI X R, JU H,et al.. Simulation of winter wheat yield in response to irrigation level at critical growing stages in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014, 40(8):1485-1492. | |
| 2 | 白由路. 植物营养与肥料研究的回顾与展望[J]. 中国农业科学,2015,48(17):3477-3492. |
| BAI Y L. Review on research in plant nutrition and fertilizers [J]. China Agric. Sci., 2015, 48(17):3477-3492. | |
| 3 | 侯云鹏,陆小平,赵世英,等. 平衡施肥对春玉米产量及养分吸收的影响[J]. 玉米科学,2014,22(4):126-131. |
| HOU Y P, LU X P, ZHAO S Y,et al.. Effect of balanced fertilization on spring maize yield and nutrient absorption [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2014, 22(4):126-131. | |
| 4 | 王晨光,赵美娟,裴文东,等. 施氮量对粮饲兼用玉米子粒产量和饲用品质的影响[J]. 玉米科学,2020,28(6):148-153. |
| WANG C G, ZHAO M J, PEI W D,et al.. Effects of nitrogen rates on grain yield and forage quality of dual-purpose maize [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2020, 28(6):148-153. | |
| 5 | 李丽丽,李锐娟,苗振振. 施氮量对玉米杂交种邯丰79产量和主要农艺性状的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(12):152-154. |
| LI L L, LI R J, MIAO Z Z. Effect of nitrogen application on yield and main agronomic characters of hanfeng 79 [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(12):152-154. | |
| 6 | OLIWA-STASIAK K, MOLNAR C I, ARSHAK K,et al.. Development of a PCR assay for identification of the Bacillus cereus group species [J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2010,108(1):266-273. |
| 7 | 周青云,李梦初,漆栋良,等. 拔节期淹水条件下施氮量对春玉米生理特性的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2020,39(2):40-44. |
| ZHOU Q Y, LI M C, QI D L,et al.. Effects of nitrogen rate on physiological characteristics of spring maize under water logging at jointing stage [J]. J. Irrig. Drain., 2020, 39(2):40-44. | |
| 8 | ERISMAN J W, SUTTON M A, GALLOWAY J,et al.. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world? [J]. Nat. Geosci., 2008, 1(10):636-639. |
| 9 | 李小坤. 水稻营养特性及科学施肥[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2016:35-37. |
| 10 | 于宁宁,任佰朝,赵斌,等. 施氮量对夏玉米籽粒灌浆特性和营养品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2019,30(11):3771-3776. |
| YU N N, REN B C, ZHAO B,et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on grain filling characteristics and nutritional quality of summer maize [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(11):3771-3776. | |
| 11 | 苌建峰,董朋飞,王秀玲,等. 氮肥运筹对不同夏玉米品种碳氮代谢协调性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2017,50(12):2282-2293. |
| CHANG J F, DONG P F, WANG X L,et al.. Effect of nitrogen application on carbon and nitrogen metabolism of different summer maize varieties [J]. China Agric. Sci., 2017,50(12):2282-2293. | |
| 12 | 孟瑶,刘赵月,李晶,等. 施氮量对高密春玉米籽粒关键酶及产量品质的影响[J]. 西南农业学报,2020,33(6):1146-1152. |
| MENG Y, LIU Z Y, LI J,et al.. Effects of nitrogen rate on grain yield and quality and key enzyme metabolism of spring maize under high density [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 33(6):1146-1152. | |
| 13 | XIN Z, SUI S J, LIU H Y,et al.. Effect of different application rate of nitrogen fertilizer under straw return on maize yield and in organic nitrogen accumulation [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2014, 31(3):279-284. |
| 14 | CHEN Y, XIAO C, WU D,et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on grain yield and grain nitrogen concentration in two maize hybrids with nitrogen remobilization efficiency [J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2015, 62(62):79-89. |
| 15 | 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2000:56. |
| 16 | 曲春香,沈颂东,王雪峰,等. 用考马斯亮蓝测定植物粗提液中可溶性蛋白质含量方法的研究[J]. 苏州大学学报(自然科学版),2006,22(2):82-85. |
| QU C X, SHEN S D, WANG X F,et al.. Study on determination of soluble protein content in plant crude extract by coomassie brilliant blue [J]. J. Suzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2006, 22(2):82-85. | |
| 17 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2000:123-128. |
| 18 | 王云奇,陶洪斌,黄收兵,等. 施氮模式对夏玉米氮肥利用和产量效益的影响[J]. 核农学报,2013,27(2):219-224. |
| WANG Y Q, TAO H B, HUANG S B,et al.. Effects of nitreogen patterns on nitrogen use and yield benefit of summer maize [J]. Atca Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2013, 27(2): 219-224. | |
| 19 | 张光宇. 不同施氮水平对糯玉米农艺性状和品质性状的影响[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学,2016. |
| ZHANG G Y. Study of influence of the shape of waxy maize agronomic and quality traits with different nitrogen levels [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 20 | 姚丹丹. 施氮量对春玉米农艺性状、产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[D]. 秦皇岛:河北科技师范学院,2020. |
| YAO D D. Effects of nitrogen application on agronomic characters, yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization of spring maize [D]. Qinhuangdao:Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology, 2020. | |
| 21 | 张盼盼,张桂堂,黄璐,等. 氮肥减施下不同基因型玉米氮效率差异及生理特性研究[J]. 河南农业科学,2021,50(5):13-23. |
| ZHANG P P, ZHANG G T, HUANG L,et al.. Nitrogen efficiency and physiological characters of different maize genotypes under nitrogen fertilization reduction [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2021, 50(5):13-23. | |
| 22 | 崔文芳,高聚林,屈佳伟,等. 氮高效玉米杂交种穗三叶氮积累及生理特性对氮效率的贡献[J]. 玉米科学,2015,23(5):75-82. |
| CUI W F, GAO J L, QU J W,et al.. Contribution of nitrogen efficient maize hybrid spike three leaf nitrogen accumulation and physiological characteristics to the nitrogen efficiency [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2015, 23(5):75-82. | |
| 23 | KORKOVELOS A E, GOULAS C K. Divergent masss election for leaf chlorophyll content measured using chlorophyll meter readings in a maize composite population [J]. Crop Sci., 2011,51(4):1437-1443. |
| 24 | 刘瑀. 不同基因型春玉米氮效率差异比较研究[D]. 大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学,2015. |
| LIU Y. Comparative study on nitrogen use efficiency of spring maize with different genotypes [D]. Daqing:Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,2015. | |
| 25 | 张吉旺,胡昌浩,王空军,等. 种植密度对全株玉米饲用营养价值的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2005,38(6):1129-1131. |
| ZHANG J W, HU C H, WANG K J,et al.. Effects of plant density on forage nutritive value of whole plant corn [J]. China Agric. Sci., 2005, 38(6):1129-1131. | |
| 26 | 刘瑀,李佐同,杨克军,等. 施氮量对春玉米花粒期干物质积累与氮素运转特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志,2015(4):142-145. |
| LIU Y, LI Z T, YANG K J,et al.. Dry matter accumulation and nitrogen migration of spring maize for nitrogen application in the flowering and milking stages [J]. Crops, 2015(4):142-145. | |
| 27 | 姜涛. 氮肥运筹对夏玉米产量、品质及植株养分含量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(3):559-565. |
| JIANG T. Effects of nitrogen application regime on yield, quality and plant nutrient contents of summer maize [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2013, 19(3):559-565. |
| [1] | 杨茜, 吴娜, 赵匆, 韩羽, 麻仲花, 杨永森, 刘吉利. 施锌对盐碱地玉米生理特性及籽粒锌含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 166-176. |
| [2] | 杨文竹, 陈茹梅. 花青素玉米的育种进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 18-24. |
| [3] | 刘晓玉, 盛锡兴, 廖宗文, 林黎珍, 黎坤婷, 蔡燕飞, 陈火君. 生物-化学联用对钾长石的活化效果及其肥效[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 132-140. |
| [4] | 王帅, 宋伟, 王荣焕, 赵久然. 我国玉米生物学研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 23-31. |
| [5] | 李飞翔, 王鹏, 王云飞, 葛越锋, 唐凯怿, 李得志. 基于堆积试验的玉米包衣种子离散元参数标定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 97-107. |
| [6] | 程名, 朱莹, 王晓楠, 罗平, 陈勇, 郝转芳, 席章营. 玉米ZmSNAC13等位变异对抗旱性的调控研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 24-31. |
| [7] | 成广雷, 邱军, 王晓光, 徐田军, 陈传永, 张春原, 夏千千, 吴元奇, 赵久然, 王荣焕. 我国青贮玉米组合(品种)的农艺性状、生物产量和品质变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. |
| [8] | 孙华, 郭宁, 郑晓娟, 石洁, 张立荣, 闫红飞. 玉米穗腐病病原菌新知镰孢的鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [9] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 罗彦忠, 刘源, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因抗虫、耐除草剂及品质改良复合性状玉米BBHTL8-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 77-85. |
| [10] | 魏俞涌, 张庆法, 盛奎川. 生物炭对玉米醇溶蛋白/聚丙烯复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 161-168. |
| [11] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因复合抗虫耐除草剂玉米BFL4-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 31-37. |
| [12] | 樊鸿叶, , 李姚姚, 卢宪菊, 顾生浩, 郭新宇, 刘玉华. 基于无人机多光谱遥感的春玉米叶面积指数和地上部生物量估算模型比较研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 112-120. |
| [13] | 李双, 张伟, 王丽, 李孝军, 崔俊涛. 秸秆还田对不同地力黑土培肥与茎腐病害发生的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 80-90. |
| [14] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| [15] | 刘忠祥, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 周文期, 何海军, 周玉乾, 寇思荣. 快中子诱变突变体的表型鉴定及配合力效应分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 184-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号