




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 180-188.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0781
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-09-06
接受日期:2021-11-22
出版日期:2022-05-15
发布日期:2022-06-06
通讯作者:
丁伟
作者简介:陈奎元 E-mail: 479115079@qq.com;
基金资助:
Kuiyuan CHEN( ), Hui LIU, Wei DING(
), Hui LIU, Wei DING( )
)
Received:2021-09-06
Accepted:2021-11-22
Online:2022-05-15
Published:2022-06-06
Contact:
Wei DING
摘要:
为探究草甘膦对大豆田土壤养分及其功能酶活性的影响,以转基因抗草甘膦大豆呼交06-698为材料,采用田间试验方法,研究了1.2、2.4、3.6 kg·hm-2草甘膦对大豆田土壤氮(N)、磷(P)、钾(K)及其功能酶活性的影响。2年试验结果均表明,在草甘膦2.4 kg·hm-2和3.6 kg·hm-2用量下,大豆田土壤碱解氮含量、速效磷含量、脲酶、纤维素酶、磷酸酶和根瘤固氮酶活性显著降低,降低峰值分别为10.57%、11.30%、67.66%、40.62%、45.88%和74.49%,过氧化氢酶活性显著升高,2年间的升高峰值为131.93%,速效钾含量不受草甘膦影响。这种影响随草甘膦施用后时间延长而逐步恢复正常,长时间不会对土壤养分及其功能酶活性带来不利影响。通过主成分与综合评价方法分析,草甘膦用量为2.4和3.6 kg·hm-2时,以土壤N、P、K养分及其功能酶活性为主成分的土壤质量均高于CK。研究结果可为农田生态系统可持续利用和转基因抗草甘膦大豆商业化种植提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
陈奎元, 刘卉, 丁伟. 草甘膦对大豆田土壤养分及其功能酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 180-188.
Kuiyuan CHEN, Hui LIU, Wei DING. Effect of Glyphosate on Soil Nutrient and the Functional Enzyme Activities in Soybean Fields[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 180-188.
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 碱解氮含量 Alkaline soluble nitrogen content/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | ||
| 2019 | CK | 156.25±4.44 c | 159.20±2.53 b | 170.15±1.93 a | 152.04±3.86 c |
| T1 | 172.68±1.93 a | 169.52±0.97 a | 160.04±1.93 b | 176.47±1.93 a | |
| T2 | 167.20±1.93 ab | 145.72±3.18 c | 153.73±4.44 bc | 167.20±3.18 b | |
| T3 | 162.57±2.63 b | 148.25±3.18 c | 150.36±5.51 c | 141.93±3.86 d | |
| 2020 | CK | 168.55±3.74 a | 157.31±7.20 a | 135.32±3.85 a | 129.26±10.32 a |
| T1 | 150.61±6.78 b | 115.74±9.89 c | 120.79±0.22 b | 117.51±6.47 ab | |
| T2 | 150.86±2.73 b | 137.34±9.99 b | 121.55±8.27 b | 111.57±3.06 b | |
| T3 | 133.17±2.73 c | 140.50±1.95 b | 134.56±8.10 a | 119.02±10.09 ab | |
表1 不同处理下土壤碱解氮含量
Table 1 Soil alkaline soluble nitrogen content under different treatments
年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 碱解氮含量 Alkaline soluble nitrogen content/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | ||
| 2019 | CK | 156.25±4.44 c | 159.20±2.53 b | 170.15±1.93 a | 152.04±3.86 c |
| T1 | 172.68±1.93 a | 169.52±0.97 a | 160.04±1.93 b | 176.47±1.93 a | |
| T2 | 167.20±1.93 ab | 145.72±3.18 c | 153.73±4.44 bc | 167.20±3.18 b | |
| T3 | 162.57±2.63 b | 148.25±3.18 c | 150.36±5.51 c | 141.93±3.86 d | |
| 2020 | CK | 168.55±3.74 a | 157.31±7.20 a | 135.32±3.85 a | 129.26±10.32 a |
| T1 | 150.61±6.78 b | 115.74±9.89 c | 120.79±0.22 b | 117.51±6.47 ab | |
| T2 | 150.86±2.73 b | 137.34±9.99 b | 121.55±8.27 b | 111.57±3.06 b | |
| T3 | 133.17±2.73 c | 140.50±1.95 b | 134.56±8.10 a | 119.02±10.09 ab | |
年份 Years | 处理 Treatment | 速效磷含量Available phosphorus content/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | ||
| 2019 | CK | 28.02±0.81 c | 38.25±0.96 a | 36.37±0.22 b | 35.46±1.08 a |
| T1 | 33.20±0.81 a | 35.08±1.59 b | 34.56±1.62 c | 33.07±0.49 b | |
| T2 | 31.84±1.76 ab | 33.46±0.41 b | 37.86±0.81 b | 34.43±0.79 ab | |
| T3 | 30.28±0.30 b | 34.75±0.68 b | 39.93±0.19 a | 33.65±0.74 b | |
| 2020 | CK | 29.25±1.66 b | 38.57±2.16 a | 33.85±1.51 a | 37.41±2.16 a |
| T1 | 34.75±1.70 a | 35.08±0.27 b | 33.33±1.85 a | 32.61±1.00 b | |
| T2 | 33.52±0.89 ab | 34.69±1.59 b | 34.56±1.29 a | 35.08±1.08 ab | |
| T3 | 29.89±1.65 ab | 33.91±1.97 b | 35.46±1.75 a | 36.18±0.79 a | |
表2 不同处理下土壤速效磷含量
Table 2 Soil available phosphorus content under different treatments
年份 Years | 处理 Treatment | 速效磷含量Available phosphorus content/(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | ||
| 2019 | CK | 28.02±0.81 c | 38.25±0.96 a | 36.37±0.22 b | 35.46±1.08 a |
| T1 | 33.20±0.81 a | 35.08±1.59 b | 34.56±1.62 c | 33.07±0.49 b | |
| T2 | 31.84±1.76 ab | 33.46±0.41 b | 37.86±0.81 b | 34.43±0.79 ab | |
| T3 | 30.28±0.30 b | 34.75±0.68 b | 39.93±0.19 a | 33.65±0.74 b | |
| 2020 | CK | 29.25±1.66 b | 38.57±2.16 a | 33.85±1.51 a | 37.41±2.16 a |
| T1 | 34.75±1.70 a | 35.08±0.27 b | 33.33±1.85 a | 32.61±1.00 b | |
| T2 | 33.52±0.89 ab | 34.69±1.59 b | 34.56±1.29 a | 35.08±1.08 ab | |
| T3 | 29.89±1.65 ab | 33.91±1.97 b | 35.46±1.75 a | 36.18±0.79 a | |
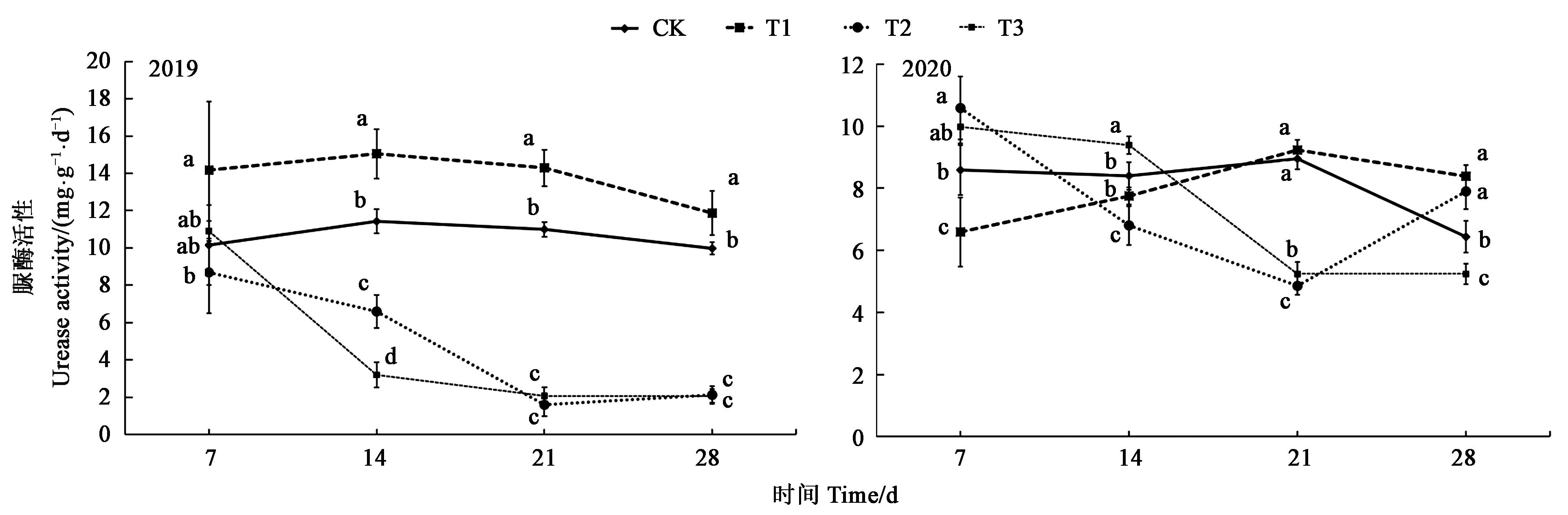
图2 不同处理下土壤脲酶活性注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig.2 Soil urease activity under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters in the figure indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
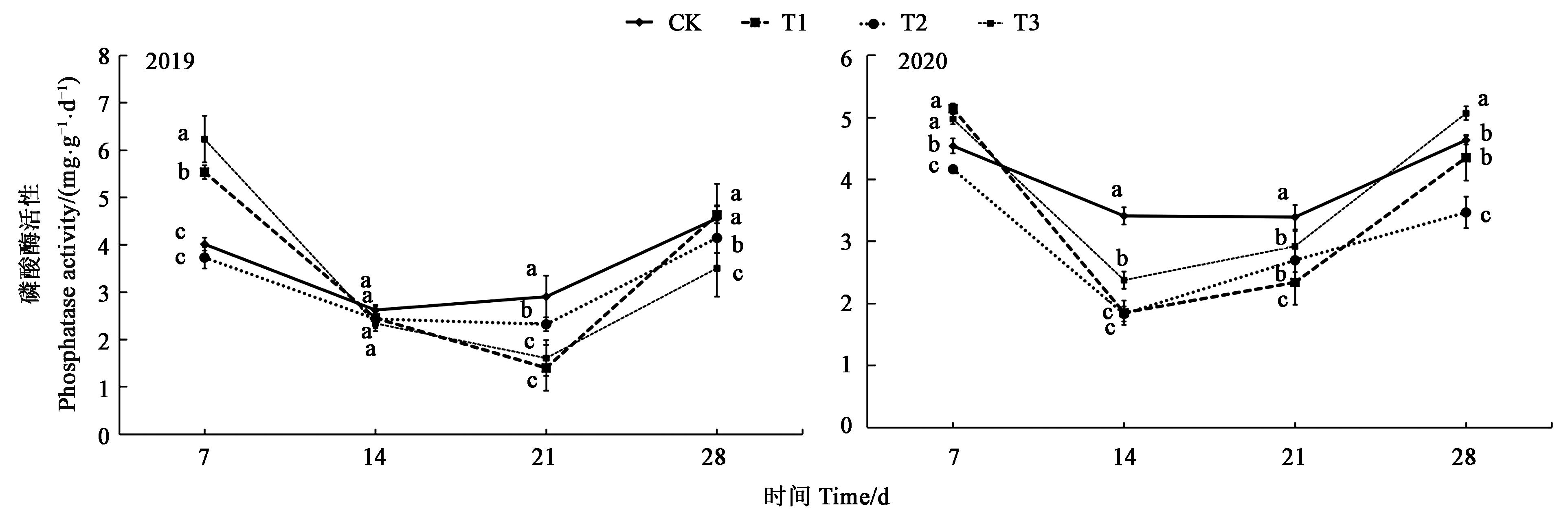
图3 不同处理下土壤磷酸酶活性注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig.3 Soil phosphatase activity under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters in the figure indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
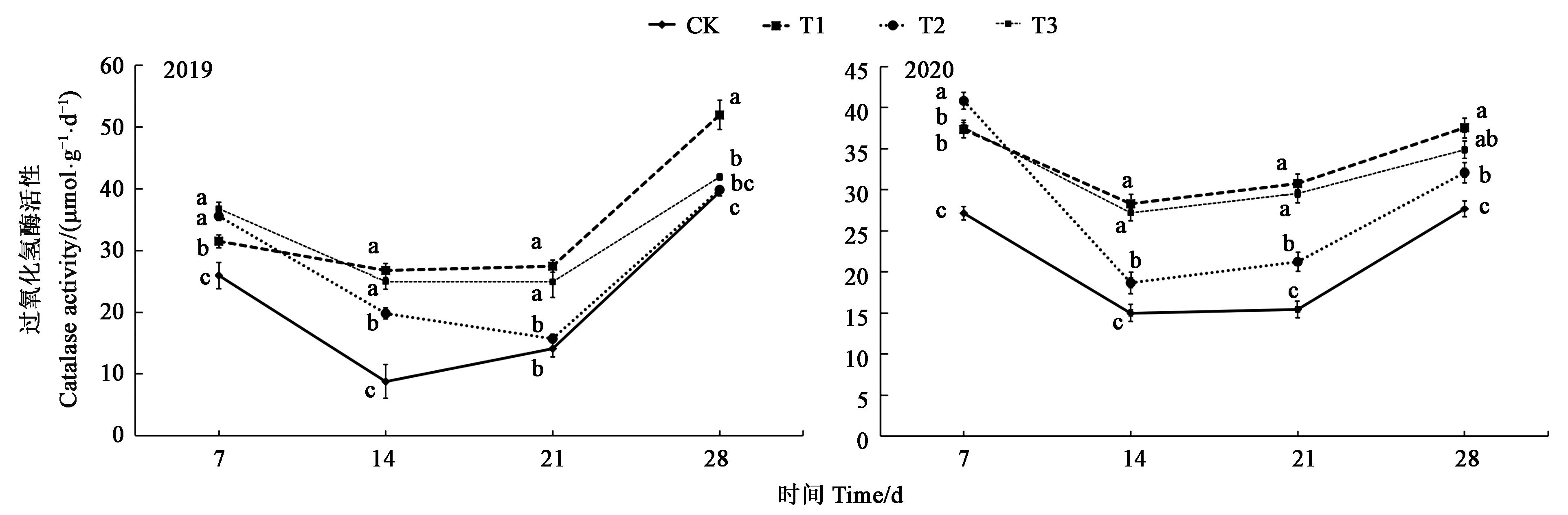
图4 不同处理下土壤过氧化氢酶活性注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig.4 Soil catalase activity under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters in the figure indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
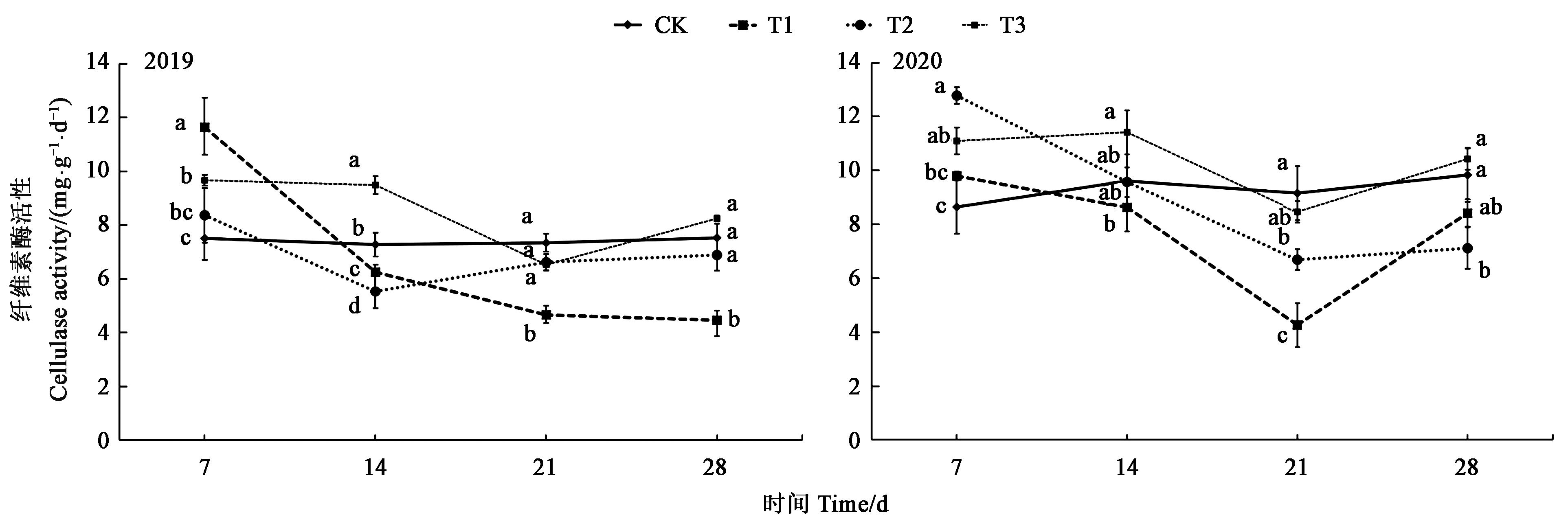
图5 不同处理下土壤纤维素酶活性注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig.5 Soil cellulase activity under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters in the figure indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
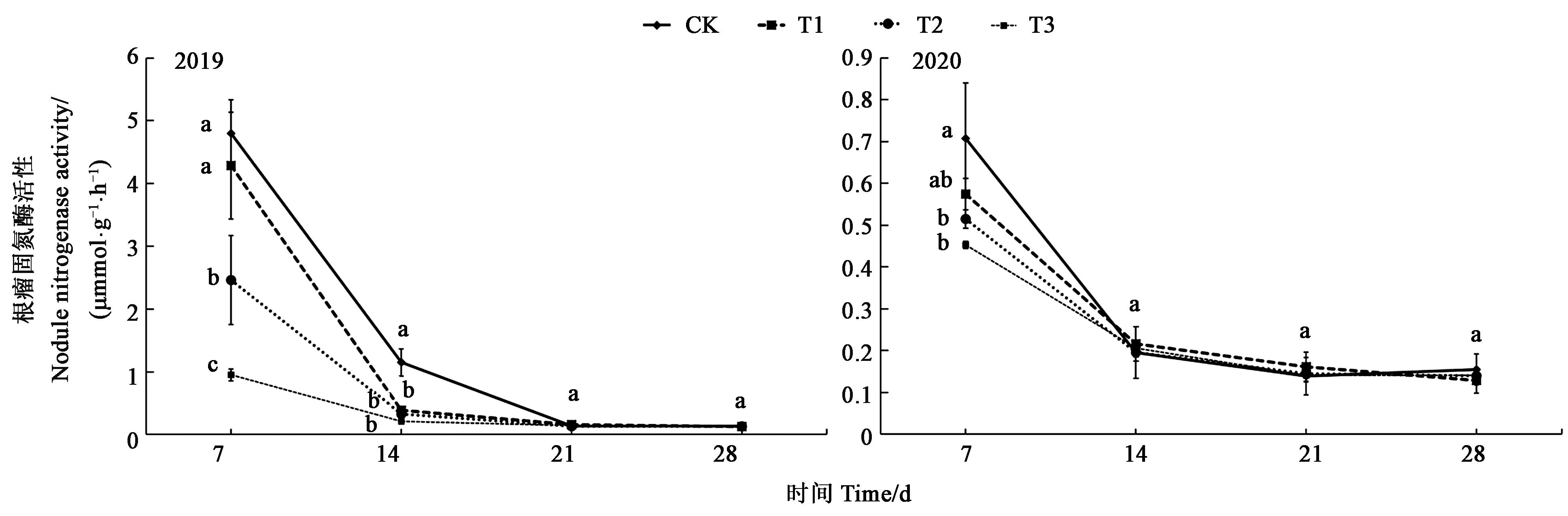
图6 不同处理下根瘤固氮酶活性注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig.6 Nodule nitrogenase activity under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters in the figure indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 脲酶 Urease | 磷酸酶 Phosphatase | 过氧化 氢酶 Catalase | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 根瘤固氮酶 Nodule nitrogenase | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
脲酶 Urease | 1. 00 | |||||||
磷酸酶 Phosphatase | 0.26 | 1. 00 | ||||||
过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.02 | 0.56** | 1. 00 | |||||
纤维素酶 Cellulase | 0.24 | 0.45** | 0.08 | 1. 00 | ||||
根瘤固氮酶 Nodule nitrogenase | 0.36* | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 1. 00 | |||
碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 0.22 | 0.12 | -0.01 | -0.17 | 0.34 | 1. 00 | ||
速效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.31 | -0.45** | -0.40* | -0.13 | -0.47** | -0.10 | 1. 00 | |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.12 | 0.48** | 0.18 | 0.68** | 0.33 | -0.40* | -0.44** | 1. 00 |
表3 土壤酶活性及土壤养分含量的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between soil enzyme activity and soil nutrients
相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 脲酶 Urease | 磷酸酶 Phosphatase | 过氧化 氢酶 Catalase | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 根瘤固氮酶 Nodule nitrogenase | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
脲酶 Urease | 1. 00 | |||||||
磷酸酶 Phosphatase | 0.26 | 1. 00 | ||||||
过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.02 | 0.56** | 1. 00 | |||||
纤维素酶 Cellulase | 0.24 | 0.45** | 0.08 | 1. 00 | ||||
根瘤固氮酶 Nodule nitrogenase | 0.36* | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 1. 00 | |||
碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 0.22 | 0.12 | -0.01 | -0.17 | 0.34 | 1. 00 | ||
速效磷 Available phosphorus | -0.31 | -0.45** | -0.40* | -0.13 | -0.47** | -0.10 | 1. 00 | |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.12 | 0.48** | 0.18 | 0.68** | 0.33 | -0.40* | -0.44** | 1. 00 |
主成分 Principal components | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution value/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution value/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.938 | 36.730 | 36.730 |
| 2 | 1.645 | 20.566 | 57.296 |
| 3 | 1.201 | 15.012 | 72.308 |
表4 主成分的特征值、方差贡献率和累计方差贡献率
Table 4 Eigenvalue,variance contribution rate and cumulative variance contribution rate of principal components
主成分 Principal components | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution value/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution value/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.938 | 36.730 | 36.730 |
| 2 | 1.645 | 20.566 | 57.296 |
| 3 | 1.201 | 15.012 | 72.308 |
处理名称 Treatments | F1 | 排名 Rank | F2 | 排名 Rank | F3 | 排名 Rank | S | 综合排名 Comprehensive rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80.247 318 | 2 | 36.672 495 | 2 | 6.842 781 2 | 3 | 35.166 675 | 3 |
| T1 | 79.883 578 | 4 | 37.453 245 | 1 | 6.355 119 2 | 4 | 34.729 540 | 4 |
| T2 | 80.127 036 | 3 | 36.396 559 | 3 | 8.087 030 2 | 2 | 38.417 347 | 1 |
| T3 | 80.298 817 | 1 | 34.518 943 | 4 | 9.287 650 8 | 1 | 36.006 689 | 2 |
表5 土壤质量主成分得分及排名
Table 5 Soil nutrient principal components scores and rankings
处理名称 Treatments | F1 | 排名 Rank | F2 | 排名 Rank | F3 | 排名 Rank | S | 综合排名 Comprehensive rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80.247 318 | 2 | 36.672 495 | 2 | 6.842 781 2 | 3 | 35.166 675 | 3 |
| T1 | 79.883 578 | 4 | 37.453 245 | 1 | 6.355 119 2 | 4 | 34.729 540 | 4 |
| T2 | 80.127 036 | 3 | 36.396 559 | 3 | 8.087 030 2 | 2 | 38.417 347 | 1 |
| T3 | 80.298 817 | 1 | 34.518 943 | 4 | 9.287 650 8 | 1 | 36.006 689 | 2 |
| 1 | PRIMOST J E, MARINO D J G, APARICIO V C, et al.. Glyphosate and AMPA, “pseudo-persistent” pollutants under real-world agricultural management practices in the Mesopotamic Pampas agroecosystem, Argentina [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2017, 229:771-779. |
| 2 | JEYASEKHAR M P. A study to investigate the organic carbon status of glyphosate soils [J]. Int. J. Environ. Res., 2021, 3(1):23-27. |
| 3 | LANE M, LORENZ N, SAXENA J, et al.. Microbial activity, community structure and potassium dynamics in rhizosphere soil of soybean plants treated with glyphosate [J]. Pedobiologia, 2012, 55(3):153-159. |
| 4 | 姚玉波.大豆根瘤固氮特性与影响因素的研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2012. |
| YAO Y B. Study on characteristics of nodule nitrogen fixation and influencing factors of soybean [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 5 | 周垂帆,林静雯,李莹,等.草甘膦对土壤磷形态及有效性的影响[J].西北林学院学报, 2016, 31(6): 71-77. |
| ZHOU C F, LIN J W, LI Y, et al.. Effects of glyphosate on inorganic phosphorus transformation in soil [J]. J. Northwest Forest.Univ., 2016,31(6):71-77. | |
| 6 | 呼蕾,和文祥,王旭东,等.草甘膦的土壤酶效应研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(4): 680-685. |
| HU L, HE W X, WANG X D, et al.. Effect of glyphosate on soil enzyme [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2009, 28(4): 680-685. | |
| 7 | YU Y, ZHANG H, ZHOU Q. Using soil available P and activities of soil dehydrogenase and phosphatase as indicators for biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticide methamidophos and glyphosate [J]. Soil Sediment Contam., 2011, 20(6):688-701. |
| 8 | LANE M, LORENZ N, SAXENA J, et al.. The effect of glyphosate on soil microbial activity, microbial community structure, and soil potassium [J]. Pedobiologia, 2012, 55(6):688-701. |
| 9 | FAN L, FENG Y, WEAVER D B, et al.. Glyphosate effects on symbiotic nitrogen fixation in glyphosate-resistant soybean [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2017, 121:11-19. |
| 10 | 严君,韩晓增.盆栽条件下土壤无机氮浓度对大豆结瘤、固氮和产量的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2014, 47(10): 1929-1938. |
| YAN J, HAN X Z. Effect of soil inorganic N concentrations on the nodulation, N2 fixation and yield in soybean in a pot experiment [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2014, 47(10): 1929-1938. | |
| 11 | 姜伟丽,马小艳,彭军,等.除草剂草甘膦对棉田土壤酶活性的影响[J].棉花学报, 2014, 26(5): 431-437. |
| JIANG W L, MA X Y, PENG J, et al.. Effects of glyphosate on soil enzyme activities in cotton fields [J]. Cotton. Sci., 2014, 26(5): 431-437. | |
| 12 | 侯文军,邹明,李宝福,等.草甘膦对桉树人工林土壤酶活性的影响[J].东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(11): 76-79. |
| HOU W J, ZOU M, LI B F, et al.. Effect of glyphosate on soil enzyme activities in eucalyptus plantations [J]. J. Northeast Forest.Univ., 2020, 48(11): 76-79. | |
| 13 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M]. 3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000: 22-23. |
| 14 | 丁伟, 杨隆华, 程茁,等.氟磺胺草醚对大豆根瘤固氮酶活性及光合速率的影响 [J].作物杂志, 2010(4): 81-84. |
| DING W, YANG L H, CHENG Z, et al.. Effect of fomesafen on nitrogenase activity and net photosynthesis rate in soybean [J]. Crops, 2010(4): 81-84. | |
| 15 | 张立峰, 丁伟. 复合微生物菌肥对水稻苗床土壤养分及pH值的影响[J].江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(11): 67-69. |
| 16 | JENKINS M E, KRAUSZ R F, MATTHEWS J L, et al.. Control of volunteer horseradish and Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) with dicamba and glyphosate [J]. Weed Technol., 2017, 31(6): 852-862. |
| 17 | 陶波,蒋凌雪,沈晓峰,等.草甘膦对土壤微生物的影响[J].中国油料作物学报, 2011, 33(2): 162-168, 179. |
| TAO B, JIANG L X, SHEN X F, et al.. Effects of glyphosate on soil microorganisms [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2011, 33(2): 162-168, 179. | |
| 18 | 冷建田.草甘膦除草剂对高寒地区转基因大豆田间杂草群落的影响[D].北京:中国农业科学院, 2012. |
| LENG J T. Effect of glyphosate on weed communities of transgenic soybean field in the high latitude and cold region [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012. | |
| 19 | OBOUR A K, STAHLMAN P W, HOLMAN J D. Soil chemical properties as influenced by long-term glyphosate-resistant corn and soybean production in the central Great Plains, USA [J]. Geoderma, 2016, 277: 1-9. |
| 20 | VEREECKEN H. Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: a review [J]. Pest Manag. Sci., 2005, 61(12): 1139-1151. |
| 21 | 章秋艳,李刚,杨志国,等.转基因大豆种植对根际土壤酶活性和养分的影响[J].中国油料作物学报, 2014, 36(3): 409-413. |
| ZHANG Q Y, LI G, YANG Z G, et al.. Effects of transgenic soybean on enzyme activities and nutrients in rhizosphere soil [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2014, 36(3): 409-413. | |
| 22 | ZHENG L, LI Y, SHANG W, et al.. The inhibitory effect of cadmium and/or mercury on soil enzyme activity, basal respiration, and microbial community structure in coal mine-affected agricultural soil [J]. Ann. Microbiol., 2019, 69(8): 849-859. |
| 23 | SPRANKLE P, MEGGITT W F, Adsorption PENNER D., mobility, and microbial degradation of glyphosate in the soil [J]. Weed Sci., 1975, 23(3): 229-234. |
| 24 | KULIKOVA N A, ZHELEZOVA A D, VOROPANOV M G, et al.. Monoammonium phosphate effects on glyphosate in soils: mobilization, phytotoxicity, and alteration of the microbial community [J]. Eurasian Soil Sci., 2020, 53(6): 787-797. |
| 25 | 刘攀.草甘膦对土壤微生态的影响及其抗性和降解真菌的研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2009. |
| LIU P. Effects of glyphosate on the soil microecosystem and research of glyphosate-degradation and glyphosate-resistance fungi [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2009. | |
| 26 | JORGE B, MELLADO R P. Relative effect of glyphosate on glyphosate-tolerant maize rhizobacterial communities is not altered by soil properties [J]. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, 22(2): 159-165. |
| 27 | 吴玉红,田霄鸿,同延安,等.基于主成分分析的土壤肥力综合指数评价 [J].生态学杂志, 2010, 29(1): 173-180. |
| WU Y H, TIAN X H, TONG Y A, et al.. Assessment of integrated soil fertility index based on principal components analysis [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2010, 29(1): 173-180. |
| [1] | 何振嘉, 范王涛, 杜宜春, 王启龙. 基于土体有机重构的水肥耦合对土壤理化性质和水稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [2] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [3] | 范娜,彭之东,白文斌*,赵建武. 微生物菌剂对土壤酶活性及高粱生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 185-192. |
| [4] | 王思霁, 国艳春, 曾路生, 孙显旻, 初庆刚, 王胜. 碱蓬播种量对滨海盐碱地土壤酶活性和团聚性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 179-185. |
| [5] | 高日平, §, 刘小月, §, 杜二小, 韩云飞, 任永峰, 高宇, 赵沛义, 李焕春, 张鹏, . 垄膜沟播与秸秆还田对内蒙古黄土高原玉米农田土壤水分、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 181-190. |
| [6] | 刘倩1,2,李纪潮1,左应梅1,杨天梅1,杨美权1,张金渝*. 有机覆盖三七对土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [7] | 蒲全明1,杨鹏1*,邓榆川2,向承勇1,林邦民1,刘莉莎1,施松梅3,何泽民1,雍磊1. 不同施肥方式对冬春茬甘蓝根际土壤酶活性、土壤养分及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 130-139. |
| [8] | 秦富仓,牛晓乐,杨振奇,马鑫,任小同. 冒山小流域不同地形和土地利用下的土壤养分空间变异特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 138-148. |
| [9] | 刘岑薇,叶菁,李艳春,林怡,王义祥*. 生物炭对茶园酸性红壤氮素养分淋溶的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 181-186. |
| [10] | 刘松涛1,田春丽1,曹雯梅1,郑贝贝1,李鹏程2,董合林2. 基于不同土壤质地棉花根际微生物和酶活性特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 73-79. |
| [11] | 王梦园1,杜延全2,朱建强1*. 复合促生菌对小麦苗期生长和土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 98-106. |
| [12] | 李奉国1,马龙传2,孔勇3,孔磊4,李冠喜3*,周晶3*. 连作对大蒜土壤养分、微生物结构和酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(1): 141-147. |
| [13] | 尚天翠,刘影,赵玉. 新疆野生樱桃李林自然保护区不同海拔梯度土壤养分特征及相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(8): 119-127. |
| [14] | 杨小艳1,刘亚娟2,吴 红1,王忠伟1,雷开荣1,谢树章1*. 草甘膦抗性菌株的分离鉴定及其抗性基因的克隆[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(6): 47-54. |
| [15] | 珊丹,荣浩*,刘艳萍,邢恩德. 草原露天矿排土场微生物菌肥施用效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(6): 129-135. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号