













中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 216-224.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0317
• 方法与技术创新 • 上一篇
曹子健1,2( ), 邱艳红3, 王爽4, 赵娟1, 郑素月2, 乔广行1, 秦文韬1(
), 邱艳红3, 王爽4, 赵娟1, 郑素月2, 乔广行1, 秦文韬1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-17
接受日期:2022-05-18
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-07
通讯作者:
秦文韬
作者简介:曹子健 E-mail:18821710624@163.com;
基金资助:
Zijian CAO1,2( ), Yanhong QIU3, Shuang WANG4, Juan ZHAO1, Suyue ZHENG2, Guanghang QIAO1, Wentao QIN1(
), Yanhong QIU3, Shuang WANG4, Juan ZHAO1, Suyue ZHENG2, Guanghang QIAO1, Wentao QIN1( )
)
Received:2022-04-17
Accepted:2022-05-18
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-07
Contact:
Wentao QIN
摘要:
植物病原物种类繁多,且气候变化及全球化发展加剧了病原的扩散。快速可靠的植物病原诊断技术对病害的流行预警和防控管理具有重要作用。随着技术发展,多重PCR技术因具有精准、高效的特点而被广泛应用到生命科学的多个领域。对多重PCR技术的原理及其在植物病原真菌、细菌、病毒、线虫检测中的应用进行了系统综述,分析了该技术目前存在的问题及解决方式,并展望了该技术未来的发展前景。
中图分类号:
曹子健, 邱艳红, 王爽, 赵娟, 郑素月, 乔广行, 秦文韬. 多重PCR技术在植物病原物检测中的应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 216-224.
Zijian CAO, Yanhong QIU, Shuang WANG, Juan ZHAO, Suyue ZHENG, Guanghang QIAO, Wentao QIN. Application of Multiplex PCR on Detection of Plant Pathogens[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 216-224.
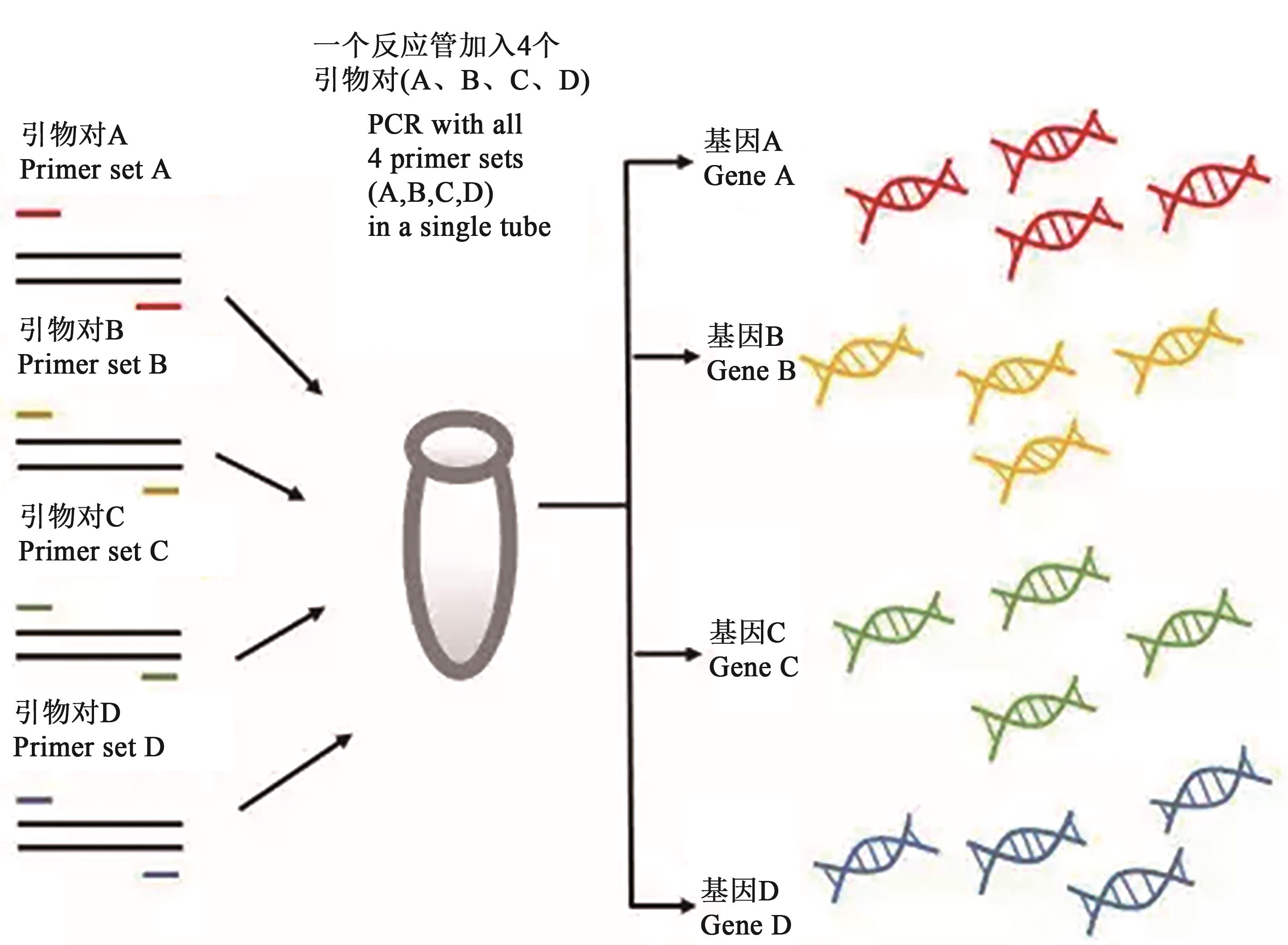
图1 多重PCR原理注:图片引自http://www.bioon.com.cn/doc/showarticle.asp?newsid=84624。
Fig. 1 Principle of multiplex PCRNote:Figure is cited from http://www.bioon.com.cn/doc/showarticle.asp?newsid=84624.
特点 Character | 扩增 Amplification | 检测 Detection |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 Advantage | 通量高,效率高,可同时实现多靶标扩增。 High flux, high efficiency, multile targets can be amplified at the same time. | 凝胶电泳检测便捷、成本低,且检测速度快。 Gel electrophoresis detection is characterized by convenient, low cost and fast. |
| 缺点Disadvantage | 易出现非特异性扩增,进而影响靶标扩增效率和体系稳定性。 Nonspecific amplification is easy to occur, which will affect the target amplification efficiency and system stability. | 凝胶电泳检测通量受凝胶分辨率的限制,且容易因光学误差而降低检测灵敏度;不能确定所检测到的病原是否具有活性和侵染性,无法推断出有关微生物细胞完整性的信息。 The flux of gel electrophoresis is limited by gel resolution, and the sensitivity is easily reduced due to optical error; whether the detected pathogens are active and infectious, and information about microbial cell integrity are impossible to determine or infer. |
可结合的技术 Combinable technology | 荧光探针、微流控芯片、液相芯片、膜层析等。 Fluorescent probe, microfluidic chip, liquid chip, membrane chromatography, etc. | 毛细管电泳、荧光探针熔解曲线等。 Capillary electrophoresis, fluorescence probe melting curve, etc. |
表 1 多重PCR的优缺点及可结合的技术
Table 1 Advantages, disadvantages and the combinable technologies of multiplex PCR
特点 Character | 扩增 Amplification | 检测 Detection |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 Advantage | 通量高,效率高,可同时实现多靶标扩增。 High flux, high efficiency, multile targets can be amplified at the same time. | 凝胶电泳检测便捷、成本低,且检测速度快。 Gel electrophoresis detection is characterized by convenient, low cost and fast. |
| 缺点Disadvantage | 易出现非特异性扩增,进而影响靶标扩增效率和体系稳定性。 Nonspecific amplification is easy to occur, which will affect the target amplification efficiency and system stability. | 凝胶电泳检测通量受凝胶分辨率的限制,且容易因光学误差而降低检测灵敏度;不能确定所检测到的病原是否具有活性和侵染性,无法推断出有关微生物细胞完整性的信息。 The flux of gel electrophoresis is limited by gel resolution, and the sensitivity is easily reduced due to optical error; whether the detected pathogens are active and infectious, and information about microbial cell integrity are impossible to determine or infer. |
可结合的技术 Combinable technology | 荧光探针、微流控芯片、液相芯片、膜层析等。 Fluorescent probe, microfluidic chip, liquid chip, membrane chromatography, etc. | 毛细管电泳、荧光探针熔解曲线等。 Capillary electrophoresis, fluorescence probe melting curve, etc. |
| 1 | RISTAINO J B, ANDERSON P K, BEBBER D P, et al.. The persistent threat of emerging plant disease pandemics to global food security [J/OL]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 2021, 118(23):e2022239118 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 2 | 罗雪爱.论我国植保工作新常态及应对策略[J].现代农业研究,2020,26(3):141-142. |
| LUO X A. On the new normal of plant protection in China and its countermeasures [J]. Mod. Agric. Res., 2020, 26(3):141-142. | |
| 3 | IGWE D O, ANYANWU C B, AFIUKWA C A, et al.. Phenotypic and molecular screenings for determination of cassava mosaic disease (CMD) status in farmer’s fields in Ebonyi State, Nigeria [J]. Mol. Biol. Repo., 2021, 48(1):227-240. |
| 4 | NAGRALE D T, SHARMA L, KUMAR S, et al.. Current trends in plant disease diagnostics and management practices || paradigm shift in plant disease diagnostics: a journey from conventional diagnostics to nano-diagnostics [M/OL]. Springer Cham: Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2016 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 5 | CHAMBERLAIN J S, GIBBS R A, RANIER J E, et al.. Deletion screening of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 1988, 16(23): 11141-11156. |
| 6 | SINT D, RASO L, TRAUGOTT M. Advances in multiplex PCR: balancing primer efficiencies and improving detection success [J]. Meth. Ecol. Evol., 2012, 3(5):898-905. |
| 7 | SÁNCHEZ-NAVARRO J A, APARICIO F, HERRANZ M C, et al.. Simultaneous detection and identification of eight stone fruit viruses by one-step RT-PCR [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2005, 111(1):77-84. |
| 8 | 张平平,王浩然,郭兆彪,等.多重生物检测技术研究进展[J].军事医学,2012,36(9):713-717. |
| ZHANG P P, WANG H R, GUO Z B, et al.. Advances in research on multiple biological detecting technologies [J]. Mil. Med. Sci., 2012, 36(9):713-717. | |
| 9 | 钟泽澄,王进,张师音.多重PCR技术研究进展[J].生物工程学报,2020,36(2):171-179. |
| ZHONG Z C, WANG J, ZHANG S Y. Advances in multiple PCR technology studies [J]. Chin. J. Biotech., 2020, 36(2):171-179. | |
| 10 | ZHAO X, LIN C, WANG J, et al.. Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens [J]. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, 24(03):297-312. |
| 11 | 秦文韬,王忠跃,张昊.环介导恒温扩增技术在植物病原物检测中的应用[J].中国农业科技导报,2013,15(3):169-174. |
| QIN W T, WANG Z Y, ZHANG H. Application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification in detecting plant pathogens [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2013, 15(3):169-174. | |
| 12 | MATTHEWS M C, MOSTERT D, NDAYIHANZAMASO P, et al. Quantitative detection of economically important Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense strains in Africa in plants, soil and water [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(7):e0236110 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 13 | 韩长志.炭疽菌属真菌分类研究现状及发展趋势[J].中国植保导刊,2015,35(6):24-30. |
| HAN C Z. Research review on taxonomy of genus Colletotrichum and its development trend [J]. Chin. Plant Prot., 2015, 35(6):24-30. | |
| 14 | 杨怡华,王明郧,曹瑱艳,等.麦冬主要病害病原菌巢式多重PCR检测方法的建立[J].植物保护学报,2021,48(4):742-747. |
| YANG Y H, WANG M Y, CAO Z Y, et al.. Nested multiplex PCR to detect two major fungal pathogens of mondo grass Ophiopogon japonicus [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2021, 48(4):742-747. | |
| 15 | WANG N Y, CAMA A B, MARIN V M, et al. Development of a multiplex high-throughput diagnostic assay for the detection of strawberry crown rot diseases using high-resolution melting analysis [J]. Phytopathology, 2021, 111(8):1470-1483. |
| 16 | WALLON T, SAUVAGEAU A, VAN DER HEYDEN H. Detection and quantification of Rhizoctonia solani and Rhizoctonia solani ag1-ib causing the bottom rot of lettuce in tissues and soils by multiplex qPCR [J/OL]. Plants-Basel, 2021, 10(1):57 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 17 | MORCIA C, TUMINO G, GASPARO G, et al.. Moving from qPCR to chip digital PCR assays for tracking of some Fusarium species causing fusarium head blight in cereals [J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(9):1307-1307. |
| 18 | 刘芮池,程有普,柴阿丽,等.蔬菜土传病原菌三重PCR检测体系的建立与应用[J].中国农业科学, 2019, 52(12):2069-2078. |
| LIU R C, CHENG Y P, CHAI A L, et al.. Establishment and application of a triplex PCR detection system for vegetable soil-borne pathogens [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(12):2069-2078. | |
| 19 | VILLARINO M, DE CAL A, MELGAREJO P, et al.. Development of a multiplex PCR for the identification of Fusarium solani and F. oxysporum in a single step [J]. J. Plant Dis. Prot., 2021, 128(5):1275-1290. |
| 20 | 蒋继志,郭俊亭,李丽艳.致病疫霉拮抗真菌研究进展[J].河北大学学报(自然科学版),2012,32(1):105-112. |
| JIANG J Z, GUO J T, LI L Y. Advances of antagonistic fungi against Phytophthora infestans [J]. J. Hebei Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2012, 32(1):105-112. | |
| 21 | LIAO F, HUANG G M, ZHU L H, et al.. Quadruplex PCR detection of three quarantine Phytophthora pathogens of berries [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2019, 154:1041-1049. |
| 22 | CHOI H J, HONG S W, KIM H J, et al.. Development of a multiplex PCR method to detect fungal pathogens for quarantine on exported cacti [J]. Plant Pathol. J., 2016, 32(1):53-57. |
| 23 | WEILAND J E, SCAGEL C F, GRUNWALD N J, et al.. Soilborne Phytophthora and Pythium diversity from rhododendron in propagation, container, and field production systems of the pacific northwest [J]. Plant Dis., 2020, 104(6):1841-1850. |
| 24 | ARORA H, SHARMA A, SHARMA S, et al.. Pythium damping-off and root rot of capsicum annuum l.: impacts, diagnosis, and management [J/OL]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(4):823 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 25 | REDEKAR N R, EBERHART J L, PARKE J L. Diversity of Phytophthora, Pythium, and Phytopythium species in recycled irrigation water in a container nursery [J]. Phyt. J., 2019, 3(1):31-45. |
| 26 | ISHIGURO Y, ASANO T, OTSUBO K, et al.. Simultaneous detection by multiplex PCR of the high-temperature-growing Pythium species: P. aphanidermatum, P. helicoides and P. myriotylum [J]. J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2013, 79(5):350-358. |
| 27 | 代玉立,甘林,滕振勇,等.玉米大斑病菌和小斑病菌交配型多重PCR检测方法的建立与应用[J].中国农业科学,2020,53(3):527-538. |
| DAI Y L, GAN L, TENG Z Y, et al.. Establishment and application of a multiple PCR method to detect mating types of Exserohilum turcicum and Bipolaris maydis [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2020, 53(3):527-538. | |
| 28 | CATARA V, CUBERO J, POTHIER J F, et al.. Trends in molecular diagnosis and diversity studies for phytosanitary regulated Xanthomonas [J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(4):862-862. |
| 29 | STRAYER A L, JEYAPRAKASH A, MINSAVAGE G V, et al.. A multiplex real-time PCR assay differentiates four Xanthomonas species associated with bacterial spot of tomato [J]. Plant Dis., 2016, 100(8):1660-1668. |
| 30 | DELCOURT S, VERNIèRE C, BOYER C, et al.. Revisiting the specificity of PCR primers for diagnostics of Xanthomonas citri pv. citri by experimental and in silico analyses [J]. Brit. J. Anaesth., 2013, 97(3):373-378. |
| 31 | ROBÈNE I, MAILLOT-LEBON V, CHABIRAND A, et al.. Development and comparative validation of genomic-driven PCR-based assays to detect Xanthomonas citri pv. citri in citrus plants [J/OL]. BMC Microbiol., 2020, 20(1):296 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 32 | JOUEN E, CHIROLEU F, MAILLOT-LEBON V, et al.. A duplex quantitative real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. dieffenbachiae from diseased and latently infected anthurium tissue [J]. J. Microbiol. Meth., 2019, 161:74-83. |
| 33 | WEBBER J B, PUTNAM M, SERDANI M, et al.. Characterization of isolates of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. corylina, the causal agent of bacterial blight, from Oregon hazelnut orchards [J]. J. Plant Pathol., 2020, 102(3):799-812. |
| 34 | THAPA S P, OLEARY M, JACQUES M A, et al.. Comparative genomics to develop a specific multiplex PCR assay for detection of Clavibacter michiganensis [J]. Phytopathology, 2020, 110(3):556-566. |
| 35 | HE Y L, CHEN Y Y, ZHANG Y W, et al.. Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex strains obtained from Guangxi, China and their pathogenicity on plants in the Cucurbitaceae family and other botanical families [J]. Plant Pathol., 2021, 70(6):1445-1454. |
| 36 | SHARMA K, KREUZE J, ABDURAHMAN A, et al.. Molecular diversity and pathogenicity of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex associated with bacterial wilt of potato in rwanda [J]. Plant Dis., 2021, 105(4):770-779. |
| 37 | JIANG G F, WEI Z, XU J, et al.. Bacterial wilt in China: history, current status, and future perspectives [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8:1549 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 38 | 李得铭,翟子翔,邓涛,等.番茄青枯菌分离与三重PCR体系建立[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(11):3655-3661. |
| LI D M, ZHAI Z X, DENG T, et al.. Isolation of tomato R.solanacearum and establishment of triple PCR system [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(11):3655-3661. | |
| 39 | KANG I J, KANG M H, NOH T H, et al. Simultaneous detection of three bacterial seed-borne diseases in rice using multiplex polymerase chain reaction [J]. Plant Pathol. J., 2016, 32(6): 575-579. |
| 40 | JONES R A C. Plant virus emergence and evolution: origins, new encounter scenarios, factors driving emergence, effects of changing world conditions, and prospects for control [J]. Virus Res., 2009, 141(2):113-130. |
| 41 | SINGHAL P, NABI S U, YADAV M K, et al.. Mixed infection of plant viruses: diagnostics, interactions and impact on host [J]. J. Plant Dis. Prot., 2021, 128(2):353-368. |
| 42 | 秦文韬,王忠跃,张昊.环介导恒温扩增技术(LAMP)及其在植物病毒检测中的研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2013,29(21):170-174. |
| QIN W T, WANG Z Y, ZHANG H. The progress of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (lamp) and its application in detection of plant virus [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2013, 29(21):170-174. | |
| 43 | XUE B, SHANG J, YANG J, et al.. Development of a multiplex RT-PCR assay for the detection of soybean mosaic virus, bean common mosaic virus and cucumber mosaic virus in field samples of soybean [J/OL]. J. Virol. Meth., 2021, 298:114278 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 44 | 袁俊杰,袁淑珍,卢乃会,等.花生矮化病毒和番茄环斑病毒的双重DPO-RT-PCR检测[J].植物保护学报,2021,48(4):931-932. |
| YUAN J J, YUAN S Z, LU N H, et al.. Duplex DPO-RT-PCR detection of peanut stunt virus and tomato ringspot virus [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2021, 48(4):931-932. | |
| 45 | MAINA S, ZHENG L D, RODONI B C. Targeted genome sequencing (TG-Seq) approaches to detect plant viruses [J/OL]. Viruses-Basel, 2021, 13(4):583 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 46 | 李明骏,廖萌,蒋开蓉,等.五种玉米病毒多重PCR检测体系的建立[J].植物保护学报,2021,48(2):465-466. |
| LI M J, LIAO M, JIANG K R, et al.. Establishment of a multiplex PCR assay for detection of five maize-infecting viruses [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2021,48(2):465-466. | |
| 47 | LI X Q, LI Y, HU W L, et al.. Simultaneous multiplex RT-PCR detection of four viruses associated with maize lethal necrosis disease [J/OL]. J. Vir. Meth., 2021, 298:114286 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 48 | 黄爱军,王莹,丁敏,等.柑橘4种病毒多重PCR检测技术的建立及应用[J].园艺学报,2019,46(8):1616-1622. |
| HUANG A J, WANG Y, DING M, et al.. Establishment and application of multiplex PCR rapid detection of four citrus viruses[J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2019, 46(8):1616-1622. | |
| 49 | PENG Q D, QIU L, YANG T, et al.. A multiple reverse transcription PCR assay for simultaneous detection of four main viruses in kiwifruit [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2020, 156(4):1207-1212. |
| 50 | ZHAO X T, LIU X L, GE B B, et al.. A multiplex RT-PCR for simultaneous detection and identification of five viruses and two viroids infecting chrysanthemum [J]. Arch. Virol., 2015, 160(5):1145-1152. |
| 51 | MULLER E, ULLAH I, DUNWELL J M, et al.. Identification and distribution of novel badnaviral sequences integrated in the genome of cacao (Theobroma cacao) [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1): 8270 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 52 | BRAUN-KIEWNICK A, KIEWNICK S. Real-time PCR, a great tool for fast identification, sensitive detection and quantification of important plant-parasitic nematodes [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2018, 152(2):271-283. |
| 53 | PHILBRICK A N, ADHIKARI T B, LOUWS F J, et al.. Meloidogyne enterolobii, a major threat to tomato production: current status and future prospects for its management [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11:606395 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 54 | NIKITIN M M, STATSYUK N V, FRANTSUZOV P A, et al.. Rapid and simple detection of two potato cyst nematode species by real-time multiplex PCR using preserved microarray-based test systems [J]. Russ. J. Nematol., 2017, 25(1):51-60. |
| 55 | DJEBROUNE A, CHAKALI G, DE ANDRADE E, et al.. Integrative morphometric and molecular approach to update the impact and distribution of potato cyst nematodes Globodera rostochiensis and Globodera pallida (Tylenchida: Heteroderidae) in Algeria [J/OL]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(2):216 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 56 | GAMEL S, LETORT A, FOUVILLE D, et al.. Development and validation of real-time PCR assays based on novel molecular markers for the simultaneous detection and identification of Globodera pallida, G. rostochiensis and Heterodera schachtii [J]. Nematology, 2017, 19(7):789-804. |
| 57 | CAMACHO M J, NOBREGA F, LIMA A, et al.. Morphological and molecular identification of the potato cyst nematodes Globodera rostochiensis and G. pallida in Portuguese potato fields [J]. Nematology, 2017, 19(8):883-889. |
| 58 | PHAN K L, LE T M L, NGUYEN H T, et al.. First report and new molecular and morphological characterizations of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica, infecting ginger and long coriander in Vietnam [J]. J. Nematol., 2021, 53:1-8. |
| 59 | HU M X, ZHUO K, LIAO J L. Multiplex PCR for the simultaneous identification and detection of Meloidogyne incognita, M. enterolobii, and M. javanica using DNA extracted directly from individual galls [J]. Phytopathology, 2011, 101(11):1270-1277. |
| 60 | DEVRAN Z, POLAT I, MISTANOGLU I, et al.. A novel multiplex PCR tool for simultaneous detection of three root-knot nematodes [J]. Aust. Plant Pathol., 2018, 47(4):389-392. |
| 61 | JESZKE A, DOBOSZ R, OBREPALSKA-STEPLOWSKA A. A fast and sensitive method for the simultaneous identification of three important nematode species of the genus Ditylenchus [J]. Pest Manag. Sci., 2015, 71(2):243-249. |
| 62 | FILIPIAK A, WIECZOREK P, TOMALAK M. A fast and sensitive multiplex real-time PCR assay for simultaneous identification of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, B. mucronatus and B. fraudulentus -three closely related species from the xylophilus group [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2019, 155(1):239-251. |
| 63 | HUANG D Q, YAN G P, GUDMESTAD N, et al.. Developing a one-step multiplex PCR assay for rapid detection of four stubby-root nematode species, Paratrichodorus allius, P. minor, P. porosus, and Trichodorus obtusus [J]. Plant Dis., 2019, 103(3):404-410. |
| 64 | NAMBA S. Molecular and biological properties of phytoplasmas [J]. Proc. Jpn. Acad. B-Phys. Biol. Sci., 2019, 95(7):401-418. |
| 65 | GHOLAMI J, BAHAR M, TALEBI M. Simultaneous detection and direct identification of Phytoplasmas in the aster yellows (16SrⅠ), clover proliferation (16SrⅥ) and stolbur (16SrⅫ) groups using a multiplex nested PCR assay in potato plants [J]. Potato Res., 2020, 63(3):403-415. |
| 66 | GALVAO S R, SABATO E O, BEDENDO I P. Occurrence and distribution of single or mixed infection of Phytoplasma and Spiroplasma causing corn stunting in Brazil [J]. Trop. Plant Pathol., 2021, 46(2):152-155. |
| 67 | PALLAS V, SANCHEZ-NAVARRO J A, JAMES D. Recent advances on the multiplex molecular detection of plant viruses and viroids [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9:2087 [2022-04-06]. . |
| 68 | CIAMPI-GUILLARDI M, MUÑOZ V N V, SILVA-JUNIOR G J, et al.. Molecular detection and quantification of Colletotrichum abscissum in sweet orange propagative material [J]. Plant Pathol., 2021, 00:1-10. |
| 69 | SHENG J, TAO T T, ZHU X Y, et al.. A multiplex PCR detection method for milk based on novel primers specific for Listeria monocytogenes 1/2a serotype [J]. Food Control, 2017, 86:183-190. |
| 70 | LI F, YE Q H, CHEN M T, et al.. Multiplex PCR for the identification of pathogenic Listeria in Flammulina velutipes plant based on novel specific targets revealed by pan-genome analysis [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2021, 11: 634255 [2022-04-06]. . |
| [1] | 李星, 赵宁, 江勇, 王志秀, 陈国宏, 白皓, 常国斌. 传感器技术在现代家禽生产中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 1-11. |
| [2] | 苗丽青, 马旭辉, 李素贞, 陈茹梅, 柳小庆. 虾青素的生物合成与产业化应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 21-29. |
| [3] | 胡秀文, 邓波, 王金斌, 刘华, 唐雪明, 王宇, 曾海娟, 蒋玮, 李红. 基于RPA技术对转CP4-EPSPS基因产品的快速检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 227-233. |
| [4] | 赵越, 卫勇, 单慧勇, 穆志民, 张健欣, 吴海云, 赵辉, 胡建龙. 基于深度学习的高分辨率麦穗图像检测方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 96-105. |
| [5] | 高姻燕, 孙义, 李葆春. 基于无人机RGB影像估测田间小麦穗数[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 103-110. |
| [6] | 胡冰, 时浩楠, 胡本伦, 赵思明, 刘茹, 贾才华. 食品中黄曲霉毒素检测方法研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 106-118. |
| [7] | 张微, 李志新, 赵雪, 张金鹏, 付春江, 刘卫平, 于倩倩. 同时快速检测马铃薯X病毒、Y病毒和S病毒试纸条的研制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 211-217. |
| [8] | 王禹, 王玲, 宗建华, 吕东晓, 王书茂. 拖拉机动态载荷加载平台设计与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 91-97. |
| [9] | 肖菲菲, 蒋蘋, 胡文武, 廖荣华, 张丹慧, 金生. 基于偏移补偿模型的极值点聚类苗带识别算法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 86-97. |
| [10] | 张庆1,2,赵晓美2,王娉2,刘冰1*,陈颖2*. 食品中产毒真菌核酸检测方法的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 91-98. |
| [11] | 董美,胡晓颖,孟丽霞,宛煜嵩,刘卫晓,金芜军,李亮*. cry1A基因通用检测方法的建立[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 174-180. |
| [12] | 王凯,林亚军,王舒丰,李淑娴,向志宇,夏利宁*. 新疆焉耆县不同动物源耐药沙门氏菌的MLST分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 111-122. |
| [13] | 刘英玉§,朱明月§,苏晓月*,胥兰,刘俊飞,郑晓风,张妍,郑晓琴. 新疆库尔勒地区羊源产志贺毒素大肠杆菌及其耐药性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 122-128. |
| [14] | 林卉,姜忠群,冒建华*. 人工湿地在农村生活污水处理中的应用及研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 129-136. |
| [15] | 陈天金1,任育锋2,柯小华1*. 中国与欧美农业科技创新体系对比研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(11): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 91
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 359
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号