




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 155-164.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0544
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
任志超1( ), 穆耀辉2, 姚旭阳1, 李淑娥2, 张永峰2, 任天宝1, 刘国顺1, 殷全玉1(
), 穆耀辉2, 姚旭阳1, 李淑娥2, 张永峰2, 任天宝1, 刘国顺1, 殷全玉1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-15
接受日期:2023-11-07
出版日期:2025-01-15
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
殷全玉
作者简介:任志超 E-mail:1132007123@qq.com;
基金资助:
Zhichao REN1( ), Yaohui MU2, Xuyang YAO1, Shue LI2, Yongfeng ZHANG2, Tianbao REN1, Guoshun LIU1, Quanyu YIN1(
), Yaohui MU2, Xuyang YAO1, Shue LI2, Yongfeng ZHANG2, Tianbao REN1, Guoshun LIU1, Quanyu YIN1( )
)
Received:2023-07-15
Accepted:2023-11-07
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Quanyu YIN
摘要:
为探究疫霉侵染下烟草对哈茨木霉施用顺序的生理响应,采用盆栽试验方法,以接种清水为对照(CK),设置5个哈茨木霉处理,分别为接种疫霉孢子悬浮液(T1);接种哈茨木霉孢子悬浮液(T2);先接种疫霉孢子悬浮液,后接种哈茨木霉孢子悬浮液(T3);先接种哈茨木霉孢子悬浮液,后接种疫霉孢子悬浮液(T4);同时接种疫霉孢子悬浮液和哈茨木霉孢子悬浮液(T5),探究哈茨木霉接种顺序对疫霉侵染下烟草生物学性状、生理特性和诱导抗性的影响。结果表明,在烟株生长上,T4处理烟株的农艺性状较CK增幅最大,且地下部干、鲜重较CK分别增加103.73%、8.30%;在烟株生理特性上,哈茨木霉可缓解疫霉对烟株光合色素积累和根系活力的抑制作用,同时对二者有显著增益效果,还可增强烟株内碳氮代谢相关酶的活性。移栽后21 d,T4处理的硝酸还原酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性较CK分别提高13.14%和6.40%;在防治效果上,T4处理烟株黑胫病的发病率和病情指数最低,分别为39.39%和13.89%,且抗氧化酶活性最高。综上,烟株对哈茨木霉接种顺序的生理响应存在显著差异。在生产中,可提前接种哈茨木霉菌剂来促进烟草生长发育,抑制黑胫病的发病率。以上研究结果为调控烟草生长发育及黑胫病的综合防治奠定了理论基础。
中图分类号:
任志超, 穆耀辉, 姚旭阳, 李淑娥, 张永峰, 任天宝, 刘国顺, 殷全玉. 疫霉侵染下烟草对哈茨木霉接种顺序的生理响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 155-164.
Zhichao REN, Yaohui MU, Xuyang YAO, Shue LI, Yongfeng ZHANG, Tianbao REN, Guoshun LIU, Quanyu YIN. Physiological Response of Tobacco Infected by Phytophthora to Trichoderma harzianum Inoculation Sequence[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 155-164.
病级 Disease level | 分级标准 Distinguishing criteria |
|---|---|
| 0 | 全株无病 No disease in the whole plant |
| 1 | 茎部病斑不超过茎围的1/3,或1/3以下叶片凋萎 Stem lesions do not exceed 1/3 of stem circumference, or less than 1/3 of leaf wilt |
| 3 | 茎部病斑环绕茎围1/3~1/2,或1/3~1/2叶片凋萎 Stem lesions around 1/3~1/2 stem circumference, or 1/3~1/2 of leaf wilt |
| 5 | 茎部病斑超过茎围的1/2,但未全部围绕茎围,或1/2~2/3叶片凋萎 Stem lesions exceed 1/2 of the stem circumference, but do not completely surround, or 1/2~2/3 of leaf wilt |
| 7 | 茎部病斑全部环绕茎围,或2/3以上叶片凋萎 Stem lesions are all around the stem circumference, or more than 2/3 of leaves wilt |
| 9 | 病株基本枯死 Infected plant basically died |
表1 烟草黑胫病分级标准
Table 1 Classification standard of tobacco black shank disease
病级 Disease level | 分级标准 Distinguishing criteria |
|---|---|
| 0 | 全株无病 No disease in the whole plant |
| 1 | 茎部病斑不超过茎围的1/3,或1/3以下叶片凋萎 Stem lesions do not exceed 1/3 of stem circumference, or less than 1/3 of leaf wilt |
| 3 | 茎部病斑环绕茎围1/3~1/2,或1/3~1/2叶片凋萎 Stem lesions around 1/3~1/2 stem circumference, or 1/3~1/2 of leaf wilt |
| 5 | 茎部病斑超过茎围的1/2,但未全部围绕茎围,或1/2~2/3叶片凋萎 Stem lesions exceed 1/2 of the stem circumference, but do not completely surround, or 1/2~2/3 of leaf wilt |
| 7 | 茎部病斑全部环绕茎围,或2/3以上叶片凋萎 Stem lesions are all around the stem circumference, or more than 2/3 of leaves wilt |
| 9 | 病株基本枯死 Infected plant basically died |
处理 Treatment | 株高 Height/cm | 茎围 Girth/cm | 节距 Pitch/cm | 最大叶面积 Maximum leaf area/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 33.20±0.30 b | 4.0±0.15 b | 4.13±0.21 b | 593.44±27.53 c |
| T1 | 24.00±0.62 d | 3.4±0.20 c | 3.57±0.12 c | 466.02±19.67 e |
| T2 | 36.60±0.56 a | 4.7±0.20 a | 4.70±0.20 a | 733.74±10.29 a |
| T3 | 25.03±0.72 d | 3.5±0.06 c | 3.70±0.10 c | 513.40±20.82 d |
| T4 | 35.53±1.77 a | 4.4±0.12 a | 4.43±0.21 a | 693.40±10.01 b |
| T5 | 31.53±0.57 c | 3.8±0.12 b | 3.90±0.10 b | 579.45±17.47 d |
表2 不同处理下烟株的生长发育
Table 2 Growth and development of tobacco plants under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 株高 Height/cm | 茎围 Girth/cm | 节距 Pitch/cm | 最大叶面积 Maximum leaf area/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 33.20±0.30 b | 4.0±0.15 b | 4.13±0.21 b | 593.44±27.53 c |
| T1 | 24.00±0.62 d | 3.4±0.20 c | 3.57±0.12 c | 466.02±19.67 e |
| T2 | 36.60±0.56 a | 4.7±0.20 a | 4.70±0.20 a | 733.74±10.29 a |
| T3 | 25.03±0.72 d | 3.5±0.06 c | 3.70±0.10 c | 513.40±20.82 d |
| T4 | 35.53±1.77 a | 4.4±0.12 a | 4.43±0.21 a | 693.40±10.01 b |
| T5 | 31.53±0.57 c | 3.8±0.12 b | 3.90±0.10 b | 579.45±17.47 d |
处理 Treatment | 地上部鲜质量 Aboveground fresh mass/g | 地下部鲜质量 Underground fresh mass/g | 地上部干质量 Aboveground dry mass/g | 地下部干质量 Underground dry mass/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80.67±1.96 c | 7.23±0.25 c | 13.40±0.46 c | 1.33±0.15 bc | 12.24±0.19 a |
| T1 | 54.87±1.22 f | 6.90±0.40 c | 9.17±0.25 f | 1.03±0.15 c | 8.95±0.09 c |
| T2 | 111.77±3.74 a | 14.73±1.36 a | 18.33±0.15 a | 2.67±0.42 a | 13.18±1.05 a |
| T3 | 63.20±2.86 e | 7.13±0.25 b | 10.77±0.76 e | 1.27±0.06 bc | 8.98±0.53 c |
| T4 | 87.57±2.55 b | 7.83±0.21 b | 14.73±0.78 b | 1.57±0.21 b | 12.57±0.58 a |
| T5 | 72.90±2.65 d | 7.43±0.12 c | 12.10±0.50 d | 1.33±0.06 c | 10.20±0.27 b |
表3 不同处理下烟株的生物积累量
Table 3 Biomass accumulation of tobacco plants under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 地上部鲜质量 Aboveground fresh mass/g | 地下部鲜质量 Underground fresh mass/g | 地上部干质量 Aboveground dry mass/g | 地下部干质量 Underground dry mass/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80.67±1.96 c | 7.23±0.25 c | 13.40±0.46 c | 1.33±0.15 bc | 12.24±0.19 a |
| T1 | 54.87±1.22 f | 6.90±0.40 c | 9.17±0.25 f | 1.03±0.15 c | 8.95±0.09 c |
| T2 | 111.77±3.74 a | 14.73±1.36 a | 18.33±0.15 a | 2.67±0.42 a | 13.18±1.05 a |
| T3 | 63.20±2.86 e | 7.13±0.25 b | 10.77±0.76 e | 1.27±0.06 bc | 8.98±0.53 c |
| T4 | 87.57±2.55 b | 7.83±0.21 b | 14.73±0.78 b | 1.57±0.21 b | 12.57±0.58 a |
| T5 | 72.90±2.65 d | 7.43±0.12 c | 12.10±0.50 d | 1.33±0.06 c | 10.20±0.27 b |
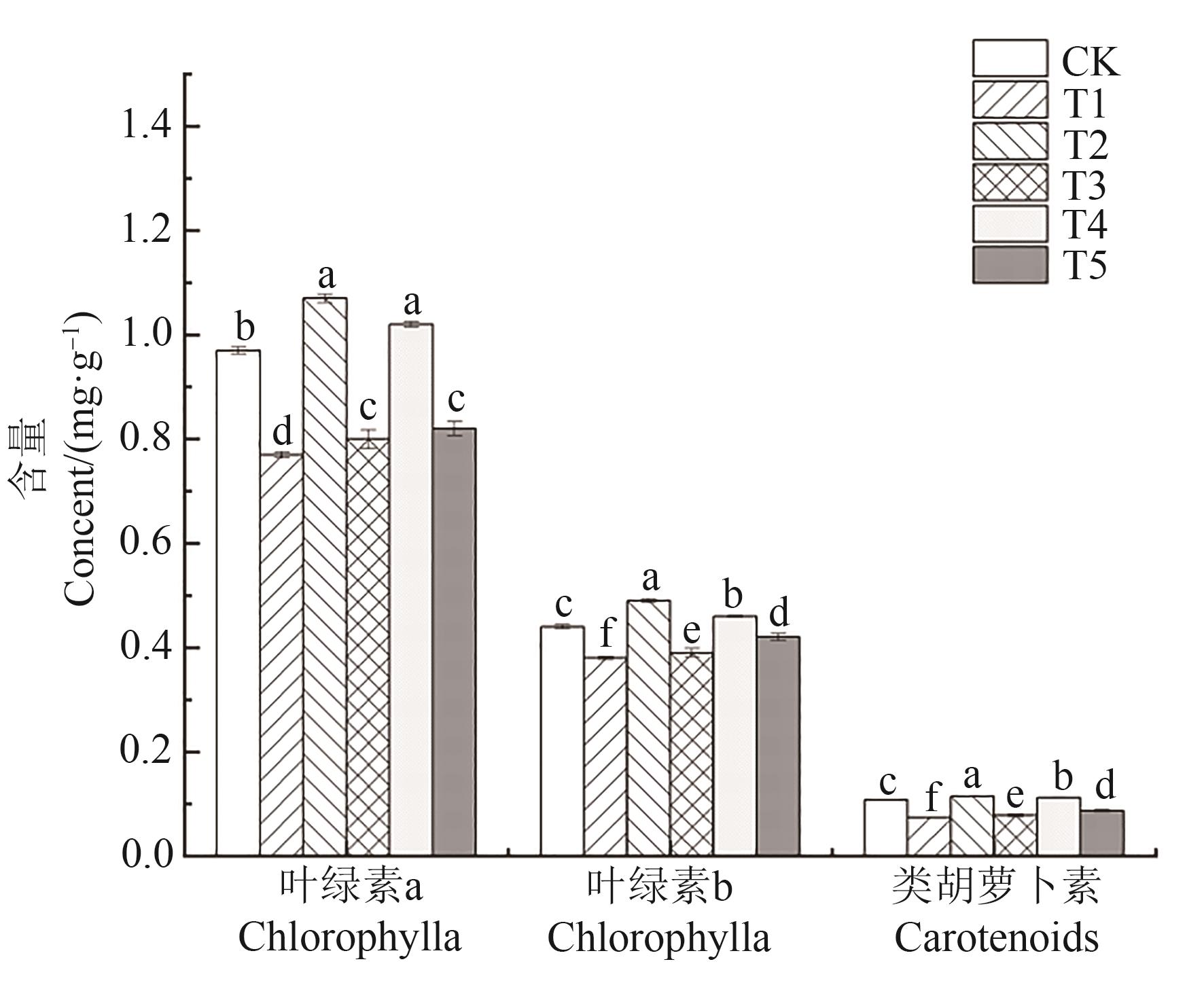
图2 不同处理下烟株的光合色素含量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Photosynthetic pigment content of tobacco plants under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 发病率 Morbidity/% | 病情指数 Disease index/% | 防治效果 Effect of prevention/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00±0.00 e | — | — |
| T1 | 100.00 a | 57.74±2.03 a | — |
| T2 | 0.00±0.00 e | — | — |
| T3 | 84.85±2.35 b | 46.33±2.58 b | 15.15±2.06 c |
| T4 | 39.39±1.69 d | 13.89±1.88 d | 60.61±1.34 a |
| T5 | 57.58±1.24 c | 25.12±1.12 c | 42.42±2.02 b |
表4 不同处理对黑胫病的防治效果
Table 4 Control of different treatments on black shank
处理 Treatment | 发病率 Morbidity/% | 病情指数 Disease index/% | 防治效果 Effect of prevention/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00±0.00 e | — | — |
| T1 | 100.00 a | 57.74±2.03 a | — |
| T2 | 0.00±0.00 e | — | — |
| T3 | 84.85±2.35 b | 46.33±2.58 b | 15.15±2.06 c |
| T4 | 39.39±1.69 d | 13.89±1.88 d | 60.61±1.34 a |
| T5 | 57.58±1.24 c | 25.12±1.12 c | 42.42±2.02 b |
处理 Treatment | 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g-1 FW) | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/ (U·g-1 FW) | 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g-1 FW) | 过氧化氢酶 CAT/(nmol·min-1·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.35±0.23 e | 104.71±1.90 e | 278.20±14.80 c | 129.98±4.16 d |
| T1 | 7.73±0.25 a | 85.16±2.59 d | 263.20±4.40 d | 118.47±3.86 e |
| T2 | 5.59±0.03 d | 133.42±5.67 c | 363.00±9.70 b | 155.60±3.60 c |
| T3 | 7.15±0.26 b | 138.31±2.43 c | 368.50±3.70 b | 162.35±3.07 b |
| T4 | 5.78±0.14 d | 168.21±5.59 a | 421.73±8.61 a | 174.85±3.47 a |
| T5 | 6.40±0.28 c | 158.08±2.51 b | 370.00±6.52 b | 167.10±2.91 b |
表5 不同处理下烟株的MDA含量和抗氧化酶活性
Table 5 MDA content and antioxidant enzyme activity of tobacco plants under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g-1 FW) | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/ (U·g-1 FW) | 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g-1 FW) | 过氧化氢酶 CAT/(nmol·min-1·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.35±0.23 e | 104.71±1.90 e | 278.20±14.80 c | 129.98±4.16 d |
| T1 | 7.73±0.25 a | 85.16±2.59 d | 263.20±4.40 d | 118.47±3.86 e |
| T2 | 5.59±0.03 d | 133.42±5.67 c | 363.00±9.70 b | 155.60±3.60 c |
| T3 | 7.15±0.26 b | 138.31±2.43 c | 368.50±3.70 b | 162.35±3.07 b |
| T4 | 5.78±0.14 d | 168.21±5.59 a | 421.73±8.61 a | 174.85±3.47 a |
| T5 | 6.40±0.28 c | 158.08±2.51 b | 370.00±6.52 b | 167.10±2.91 b |
| 1 | 申贵,王源超,郑小波.不同寄主来源寄生疫霉菌株的遗传变异分析[J].生物多样性,2003,11(6):486-490. |
| SHEN G, WANG Y C, ZHENG X B. Genetic variation among Phytophthora parasitica strains isolated from different host plants [J]. Biodiversity Sci., 2003,11(6):486-490. | |
| 2 | REN X L, ZHANG N, CAO M H, et al.. Biological control of tobacco black shank and colonization of tobacco roots by a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain C5 [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2012, 48(6):613-620. |
| 3 | BAO Y G, DING N, QIN Q L, et al.. Genetic mapping of the Ph gene conferring disease resistance to black shank in tobacco [J/OL]. Mol. Breed., 2019, 39:1036x [2023-06-15]. . |
| 4 | HAN T, YOU C, ZHANG L, et al.. Biocontrol potential of antagonist Bacillus subtilis Tpb55 against tobacco black shank [J]. Biol. Control, 2016, 61(2):195-205. |
| 5 | 贾孟媛,王越洋,唐培培,等.烟草黑胫病生防菌的筛选鉴定及其防效[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,49(3):329-334. |
| JIA M Y, WANG Y Y, TANG P P,et al... Screening and identification of biocontrol bacteria for tobacco black shank disease and evaluation of the control effect [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ., 2023, 49(3):329-334. | |
| 6 | 向立刚,汪汉成,罗飞,等.感染青枯病与黑胫病烟株的根际土壤、根及茎秆微生物代谢特征分析[J].烟草科技,2023, 56(3):17-24. |
| XIANG L G, WANG H C, LUO F, et al.. Metabolic characteristics of microorganisms in rhizosphere soil, roots, andstalks of tobacco plants infected with bacterial wilt and black shank [J]. Tob. Sci. Tech., 2023, 56 (3):17-24. | |
| 7 | GAI X T, LU C H, XIA Z Y, et al.. Crop rotation suppresses tobacco black shank disease incited by Phytophthora nicotianae and influenced the structure of rhizosphere bacterial communities [J]. J. Plant Pathol., 2023, 16(2):1-10. |
| 8 | 任锡跃,刘涛,朱发亮,等.β-氨基丁酸对烟草黑胫病的抗性诱导[J].烟草科技,2023,56(1):47-51, 65. |
| REN X Y, LIU T, ZHU F L, et al.. Resistance induction by β-aminobutyric acid against tobacco black shank disease [J]. Tob. Sci. Tech., 2023, 56(1):47-51, 65. | |
| 9 | SONG R F, TAN Y J, AHMED W, et al.. Unraveling the expression of differentially expressed proteins and enzymatic activity in response to Phytophthora nicotianae across different flue-cured tobacco cultivars [J]. BMC Microbiol., 2022, 22(1):1-13. |
| 10 | TIAN S F, CHEN Y P, ZI S H, et al.. Thiamine induces resistance in tobacco against black shank [J]. Aust. Plant Path., 2022, 51(2):231-243. |
| 11 | 匡志豪,王典,云菲,等.哈茨木霉施用方式对烟草生长、黑胫病防治及诱导抗性的影响[J].山东农业科学,2023, 55(2):119-126. |
| KUANG Z H, WANG D, YUN F, et al.. Effects of Trichoderma harzianum application methods on tobacco growth, black shank control and induced resistance [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2023, 55(2):119-126. | |
| 12 | 王全贞,夏贤仁,邓涛,等.3种生物制剂在宣威南部烟区的防病提质效果研究[J].湖南农业科学,2023,449(2):57-62. |
| WANG Q Z, XIA X R, DENG T, et al.. Effect of three biological agents on disease control and quality improvement in the southern Xuanwei area [J]. Hunan Agric. Sci., 2023,449 (2):57-62. | |
| 13 | 王典,匡志豪,孙晓伟,等.哈茨木霉对烟草生长/产质量及黑胫病防效的影响[J].贵州农业科学,2023,51(3):27-35. |
| WANG D, KUANG Z H, SUN X W, et al.. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum on growth, yield and quality of tobacco and control effect of black shank disease [J]. Guizhou Agric. Sci., 2023, 51(3):27-35. | |
| 14 | 李玥,罗丽芬,王烜东,等.三七根际耐皂苷木霉菌的分离鉴定及其拮抗促生活性评价[J].中国农业大学学报,2023,28(8):133-143. |
| LI Y, LUO L F, WANG X D, et al.. Isolation and identification of ginsenosides-tolerant Trichoderma strains from rhizosphere of Panax notoginseng and evaluation of their effect on antagonistic and growth promotion activity [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2023, 28(8):133-143. | |
| 15 | GHISALBERTI E L.Anti-infective agents produced by the hyphomycetes genera Trichoderma and Gliocladium [J]. Curr. Med. Chem. Ant. Infective Agents, 2002, 1(4):343-374. |
| 16 | ILLESCAS M, PEDRERO-MÉNDEZ A, PITORINI-BOVOLINI M, et al.. Phytohormone production profiles in Trichoderma species and their relationship to wheat plant responses to water stress [J/OL]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(8):991 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 17 | 付香,王贺新,王碟,等.棘孢木霉的分离鉴定及其对蓝莓生长发育的影响[J].中国果树,2023(6):46-53. |
| FU X, WANG H X, WANG D, et al.. Isolation and identification of Trichoderma spinosum and its effect on the growth and development of blueberries [J]. Chin. Fruit. Tree, 2023(6):46-53. | |
| 18 | ANHAR A, PUTRI D H, ADVINDA L, et al.. Molecular characterization of Trichoderma strains from west sumatera, indonesia and their beneficial effects on rice seedling growth [J]. J. Crop Sci. Biol., 2021, 24:441-448. |
| 19 | 廉华,马光恕,李梅,等.棘孢木霉菌剂对黄瓜生理特性及产质量的影响[J].中国农业大学学报,2021,26(6):42-52. |
| LIAN H, MA G S, LI M, et al.. Effects of Trichoderma asperellum agents on physiological characteristics, yield and quality of cucumber [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2021,26(6):42-52. | |
| 20 | 沈海斌,王前程,陈捷,等.三株木霉对番茄枯萎病的防治效果和机理研究[J].植物生理学报,2023,59(5):965-976. |
| SHEN H B, WANG Q C, CHEN J, et al.. Efficacy and mechanism of three Trichoderma strains for control of tomato Fusarium wilt [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2023, 59(5):965-976. | |
| 21 | CELAR F A, KOS K. Compatibility of the commercial biological control agents Trichoderma asperellum (ICC 012) and Trichoderma gamsii (ICC 080) with selected herbicides [J]. J. Plant Dis. Prot., 2022, 129(1):85-92. |
| 22 | GADERER R, LAMDAN N L, FRISCHMANN A, et al.. Sm2, a paralog of the Trichoderma cerato-platanin elicitor Sm1, is also highly important for plant protection conferred by the fungal-root interaction of Trichoderma with maize [J/OL]. BMC Microbiol., 2015, 15(1):2 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 23 | UMADEVI P, ANANDARAJ M. Proteomic analysis of the tripartite interaction between black pepper, Trichoderma harzianum and Phytophthora capsici provides insights into induced systemic resistance mediated by Trichoderma spp [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2019, 154: 607-620. |
| 24 | 申国明,陈爱国,王程栋,等. 烟草农艺性状调查测量方法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2010. |
| 25 | 许大全.叶绿素含量的测定及其应用中的几个问题[J].植物生理学通讯,2009,45(9):896-898. |
| XU D Q. Several problems in measurement and application of chlorophyll content [J]. Plant Physiol. Commun., 2009, 45(9):896-898. | |
| 26 | 高俊凤.植物生理学实验技术[M].西安:世界图书出版公司,2000:1-287. |
| 27 | LI S H, YANG D Q, TIAN J, et al.. Physiological and transcriptional response of carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism in tomato plant leaves to nickel ion and nitrogen levels [J/OL]. Sci. Hortic., 2022, 292:110620 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 28 | ARFAN M, ZHANG D W, ZOU L J, et al.. Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide crosstalk mediates brassinosteroids induced cold stress tolerance in Medicago truncatula [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20(1):144 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 29 | 任广伟,孔凡玉,王凤龙,等. 烟草病虫害分级及调查方法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2008. |
| 30 | SHI R, HUBERT H, DEXTER-BOONE A, et al.. Identification and validation of SNP markers associated with Wz-mediated Phytophthora nicotianae resistance in Nicotiana tabacum L [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding., 2019, 39(7):2 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 31 | 尤佳琪,吴明德,李国庆,等.木霉在植物病害生物防治中的应用及作用机制[J].中国生物防治学报,2019,35(6):966-976. |
| YOU J Q, WU M D, LI G Q, et al.. Application and mechanism of Trichoderma in biological control of plant disease [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Control, 2019, 35(6):966-976. | |
| 32 | MARTÍNEZ-MEDINA A, DEL MAR ALGUACIL M, PASCUAL J A, et al.. Phytohormone profiles induced by Trichoderma isolates correspond with their biocontrol and plant growth-promoting activity on melon plants [J]. J. Chem. Ecol., 2014, 40:804-815. |
| 33 | SOFO A, TATARANNI G, XILOYANNIS C, et al.. Direct effects of Trichoderma harzianum strain T-22 on micropropagated shoots of GiSeLa6® (Prunus cerasus×Prunus canescens) rootstock [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2012, 76:33-38. |
| 34 | 殷全玉,匡志豪,王景,等.黑胫病不同抗性烤烟品种对哈茨木霉的生理响应[J].河南农业科学,2022,51(9):88-98. |
| YIN Q Y, KUANG Z H, WANG J, et al. Physiological responses of different black shank-resistance flue-cured tobacco varieties to Trichoderma harzianum [J]. Henan Agric. Sci., 2022, 51(9):88-98. | |
| 35 | GUZMÁN-GUZMÁN P, PORRAS-TRONCOSO M D, OLMEDO-MONFIL V, et al.. Trichoderma species: versatile plant symbionts [J]. Phytopathology, 2019, 109(1):6-16. |
| 36 | 董环宇,杨超群,郭笑维,等.不同抗性烟草品种(系)苗期接种PVY后生理生化指标变化[J].延边大学农学学报,2022,44(3):29-37. |
| DONG H Y, YANG C Q, GUO X W, et al.. Changes of physiological and biochemical indexes of different resistant tobacco varieties (lines) after PVY inoculation at seedling stage [J]. J. Agron. Yanbian Univ., 2022, 44(3):29-37. | |
| 37 | JIANG Y, SUN Y F, ZHENG D F, et al.. Physiological and transcriptome analyses for assessing the effects of exogenous uniconazole on drought tolerance in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11:14476 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 38 | 王诗雅,郑殿峰,项洪涛,等. 初花期淹水胁迫对大豆叶片AsA-GSH循环的损伤及烯效唑的缓解效应[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(2):271-285. |
| WANG S Y, ZHENG D F, XIANG H T, et al.. Damage of AsA-GSH cycle of soybean leaves under waterlogging stress at initial flowing stage and the mitigation effect of uniconazole [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2021, 54(2):71-285. | |
| 39 | ZARGAR S M, GUPTA N, NAZIR M, et al.. Impact of drought on photosynthesis: molecular perspective [J]. Plant Gene, 2017, 11:154-159. |
| 40 | 丁凯鑫,王立春,田国奎,等.干旱胁迫下不同品种马铃薯块茎膨大期叶片对烯效唑的生理响应[J].中国生态农业学报,2023,31(7):1067-1080. |
| DING K X, WANG L C, TIAN G K, et al.. Physiological responses of leaves of different potato varieties to uniconazole during tuber expansion stage under drought stress [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2023, 31(7):1067-1080. | |
| 41 | 马光恕,张渟,李润哲,等.拟康氏木霉菌剂对黄瓜幼苗生长、抗氧化系统及枯萎病防效的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2022,40(6):72-81, 107. |
| MA G S, ZHANG Z, LI R Z, et al.. Effects of Trichoderma pseudokoningiü agents on growth, antioxidant system and control effect against Fusarium wilt of cucumber seedlings [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2022, 40(6):72-81, 107. | |
| 42 | ELKELISH A A, ALHAITHLOUL H A S, QARI S H, et al.. Pretreatment with Trichoderma harzianum alleviates waterlogging-induced growth alterations in tomato seedlings by modulating physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2020, 171:103946 [2023-06-15]. . |
| 43 | 廉华,马光恕,靳亚忠,等.木霉分生孢子和厚垣孢子对黄瓜叶片抗氧化系统及枯萎病防效的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2021,39(4):71-79. |
| LIAN H, MA G S, JIN Y Z, et al.. Effects of Trichoderma conidia and chlamydospore on cucumber leaf antioxidant system and control efficacy of Fusarium wilt in cucumber [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2021, 39(4):71-79. |
| [1] | 赵鸿硕, 曹红雨, 高广磊, 孙哲, 张英, 丁国栋. 微生物诱导碳酸钙沉淀固沙对典型沙生植物叶片性状和生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 170-182. |
| [2] | 莫雯婧, 陈洪森, 桂芳泽, 洪慈清, 蔡鑫铠, 关雄, 潘晓鸿. 菌糠水提液对马铃薯致病疫霉的抑制机理[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 129-137. |
| [3] | 常峻嘉, 盖佳鑫, 陶刚, 莫转龙海. 哈茨木霉菌对烟草的促生及其黑胫病的诱导抗性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 168-176. |
| [4] | 李生梅, 庞博, 耿世伟, 宋武, 李红梅, 马茂森, 张茹, 王新燕, 高文伟. 棉花海陆回交群体盛铃期的光合特性及其生理基础[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 40-51. |
| [5] | 段媛媛, 刘晓洪, 唐涛, 王帆帆, 游景茂, 郭晓亮, 郭杰. 种植密度对湖北贝母生长及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [6] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [7] | 刘咏艳, 宋正熊, 金佳威, 王静, 徐敏, 周俊学, 李占民, 赵世民, 符云鹏, 代晓燕. 钼锌营养对烤烟生理特性及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 216-224. |
| [8] | 施玉萍, 刘一贤, 李国伟, 唐轶, 戴利铭, 李岚岚, 蔡志英. 橡胶树季风性落叶病病原菌的分离鉴定及其防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 114-122. |
| [9] | 杨茜, 吴娜, 赵匆, 韩羽, 麻仲花, 杨永森, 刘吉利. 施锌对盐碱地玉米生理特性及籽粒锌含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 166-176. |
| [10] | 王志丹, 刘吉利, 吴娜. 粉垄耕作对甜高粱光合生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 148-156. |
| [11] | 刘利佳, 徐志强, 何佳, 丁永乐, 孙聚涛. 哈茨木霉菌诱导烟草抗黑胫病代谢差异的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 91-105. |
| [12] | 张胜珍, 马艳芝. 氯化钙对盐胁迫下荆芥种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 65-71. |
| [13] | 石丽红, 唐海明, 肖小平, 李超, 刘曲, 程爱武, 程凯凯, 李微艳, 文丽. 双季稻区长期秸秆还田配施化肥对大麦生理特性与产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 143-152. |
| [14] | 王志恒,杨秀柳,邹芳,黄思麒,周吴艳,徐中伟,魏玉清*. 旱盐交叉胁迫对甜高粱种子萌发和生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 37-49. |
| [15] | 李艳梅1,周亚文2,张琳1,廖上强1*,孙焱鑫1*. 抗逆与渗透物质耦合对番茄产量及水分利用的调控及机制探讨[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 43-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号