




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 173-181.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0936
收稿日期:2023-12-20
接受日期:2024-02-26
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
作者简介:蓝江林 E-mail:529770269@qq.com
基金资助:
Jianglin LAN( ), Rongfeng XIAO, Jieping WANG, Haifeng ZHANG, Bo LIU
), Rongfeng XIAO, Jieping WANG, Haifeng ZHANG, Bo LIU
Received:2023-12-20
Accepted:2024-02-26
Online:2025-05-15
Published:2025-05-20
摘要:
为研究整合微生物组菌剂(整合菌剂)对番茄植株生长的影响,采用大棚基质栽培法,设置种植过一茬番茄的旧基质(TA)、旧基质+10%整合微生物组菌剂(TB)和未种植过番茄的新基质(TC)共3个处理,测定不同处理下番茄植株的生长及根际细菌群落多样性。结果表明,与TA处理相比,TB处理能够显著促进番茄植株生长,但对旧基质的营养状况无显著改善,因此使用时应配合其他(生物)有机肥等,以改善基质微生物种群结构和营养水平。采用16S rRNA高通量测序技术分析番茄根部基质中细菌群落多样性,共检测到细菌40门、121纲、291目、438科和748属,丰度最高的菌门是变形菌门(35.24%~38.25%),其次为放线菌门(13.20%~20.60%);TB处理显著提高了放线菌门的丰度,降低了厚壁菌门的丰度,但对基质细菌群落的多样性和丰富度影响较小。放线菌门和变形菌门与基质全钾、全氮和有机质含量呈正相关,与总磷和pH呈负相关;厚壁菌门、绿弯菌门和酸杆菌门与总磷和pH呈正相关,与全钾、全氮和有机质含量呈负相关。基质理化因子中的pH、全氮、总磷和全钾含量对基质细菌群落结构影响显著,其中全氮是影响基质细菌门水平群落结构的最重要环境因子。因此,在番茄基质重复使用过程中,整合微生物组菌剂应配合施用适量的氮肥,有利于提高基质养分含量及改善基质微生物群落结构,进而保障番茄基质生态系统的良好发展。
中图分类号:
蓝江林, 肖荣凤, 王阶平, 张海峰, 刘波. 整合微生物组菌剂对番茄植株生长及根际细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 173-181.
Jianglin LAN, Rongfeng XIAO, Jieping WANG, Haifeng ZHANG, Bo LIU. Effects of Integrated Microbiome Agent on Tomato Plant Growth and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Diversity[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 173-181.
处理 Treatment | 定植后时间Time after planting/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | |
| TA | 31.23±1.87 c | 36.97±2.59 c | 44.43±2.95 c | 54.33±1.32 c |
| TB | 36.47±2.51 b | 44.07±1.56 b | 52.73±1.91 b | 71.77±1.51 b |
| TC | 46.43±1.65 a | 55.68±2.11 a | 71.76±1.98 a | 93.52±2.98 a |
表1 不同处理下番茄的株高 (cm)
Table 1 Plant height of tomato under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 定植后时间Time after planting/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | |
| TA | 31.23±1.87 c | 36.97±2.59 c | 44.43±2.95 c | 54.33±1.32 c |
| TB | 36.47±2.51 b | 44.07±1.56 b | 52.73±1.91 b | 71.77±1.51 b |
| TC | 46.43±1.65 a | 55.68±2.11 a | 71.76±1.98 a | 93.52±2.98 a |
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 全氮含量 TN content/% | 总磷含量 TP content/% | 全钾含量 TK content/% | 有机质含量 OM content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 7.10±0.06 a | 1.03±0.05 a | 0.63±0.02 a | 0.27±0.02 b | 41.76±1.01 b |
| TB | 7.00±0.03 a | 1.04±0.11 a | 0.61±0.03 a | 0.30±0.02 b | 42.83±1.53 b |
| TC | 6.60±0.06 b | 1.06±0.08 a | 0.46±0.09 b | 0.44±0.03 a | 50.43±2.12 a |
表2 不同处理番茄基质理化性质
Table 2 Physico-chemical properties of tomoto substrate
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 全氮含量 TN content/% | 总磷含量 TP content/% | 全钾含量 TK content/% | 有机质含量 OM content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 7.10±0.06 a | 1.03±0.05 a | 0.63±0.02 a | 0.27±0.02 b | 41.76±1.01 b |
| TB | 7.00±0.03 a | 1.04±0.11 a | 0.61±0.03 a | 0.30±0.02 b | 42.83±1.53 b |
| TC | 6.60±0.06 b | 1.06±0.08 a | 0.46±0.09 b | 0.44±0.03 a | 50.43±2.12 a |
| 处理Treatment | 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 37 | 105 | 255 | 384 | 646 |
| TB | 39 | 113 | 265 | 395 | 670 |
| TC | 37 | 115 | 265 | 385 | 636 |
表3 不同处理下细菌的生物学分类
Table 3 Biological classification of bacteria under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 37 | 105 | 255 | 384 | 646 |
| TB | 39 | 113 | 265 | 395 | 670 |
| TC | 37 | 115 | 265 | 385 | 636 |
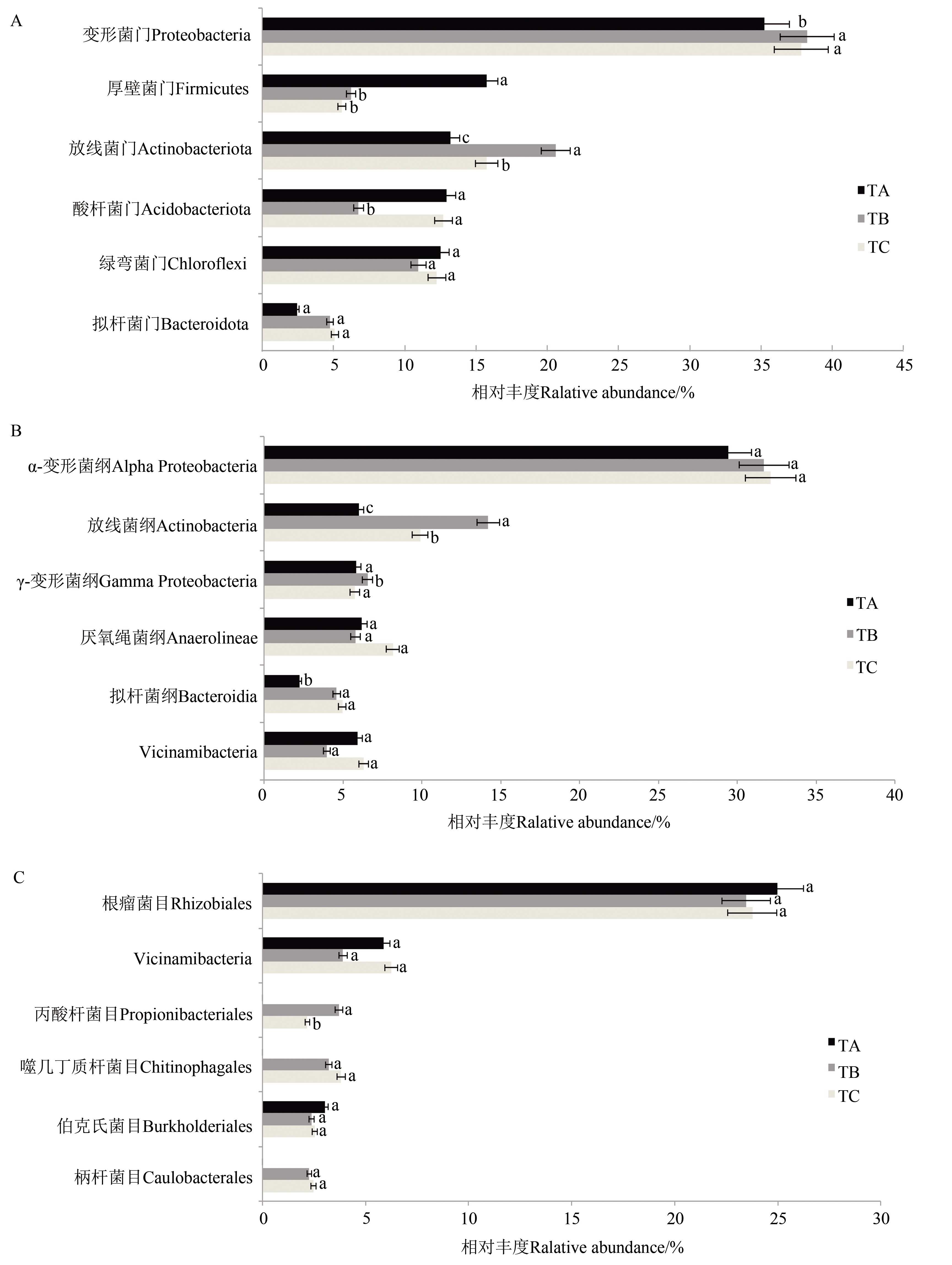
图2 番茄根际基质细菌不同分类阶元细菌物种丰度A:门水平;B:纲水平;C:目水平。不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 2 Community composition of bacterial in substrate at different taxonomic orderA: Phyla level; B: Class level; C: Order level. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
| 处理Treatment | Simpson指数Simpson index | Shannon指数Shannon index | Chao指数Chao index |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 0.22±0.04 a | 1.86±0.11 a | 37.52±4.76 a |
| TB | 0.22±0.02 a | 1.95±0.07 a | 33.87±1.55 a |
| TC | 0.21±0.02 a | 1.96±0.07 a | 35.33±1.25 a |
表4 不同处理下基质细菌群落的多样性指数
Table 4 Diversity index of bacteria community under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | Simpson指数Simpson index | Shannon指数Shannon index | Chao指数Chao index |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 0.22±0.04 a | 1.86±0.11 a | 37.52±4.76 a |
| TB | 0.22±0.02 a | 1.95±0.07 a | 33.87±1.55 a |
| TC | 0.21±0.02 a | 1.96±0.07 a | 35.33±1.25 a |

图4 基质细菌在门水平的群落结构与基质理化性质的相关性
Fig. 4 Relationship analysis between bacterial community structure at phylum level and substrate physic-chemical properties
| 1 | BARDGETT R D, VAN DER PUTTEN W H.Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning [J].Nature, 2014,515:505-511. |
| 2 | YANG Y D, REN Y F, WANG X Q,et al..Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria responding differently to fertilizer type and irrigation frequency as revealed by Illumina Miseq sequencing [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2018,18(3):1029-1040. |
| 3 | BEI S K, ZHANG Y L, LI T T,et al..Response of the soil microbial community to different fertilizer inputs in a wheat-maize rotation on a calcareous soil [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ.,2018,260:58-69. |
| 4 | JIANG Y, LUAN L, HU K,et al..Trophic interactions as determinants of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community with cascading plant-promoting consequences [J/OL].Microbiome,2020,8(1):142 [2023-11-20]. . |
| 5 | YANG Y, WANG P, ZENG Z. Dynamics of bacterial communities in a 30-year fertilized paddy field under different organic-inorganic fertilization strategies [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2019,9(1):14 [2023-11-20]. . |
| 6 | 刘波,陈倩倩,王阶平,等.整合微生物组菌剂的提出、研发与应用[J]. 中国农业科学,2019, 52(14):2450-2467. |
| LIU B, CHEN Q Q, WANG J P, et al.. Proposition, development and application of the integrated microbiome agent (IMA) [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(14):2450-2467. | |
| 7 | 郑雪芳,刘波,朱育菁,等.整合微生物组菌剂对番茄种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响及其对青枯病的防治效果[J].中国生物防治学报,2019,35(6):908-914. |
| ZHENG X F, LIU B, ZHU Y J, et al.. Effects of an integrated microbiome agent on tomato seed germination and plant growth,and its control efficiency against bacterial wilt [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Contr., 2019,35(6):908-914. | |
| 8 | 蓝江林,陈燕萍,肖荣凤,等.整合微生物组菌剂对西瓜种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响及其对枯萎病的防治效果[J].福建农业科技,2023,54(6):28-33. |
| LAN J L, CHEN Y P, XIAO R F, et al.. Effects of the integrated microbiome agent on the seed germination and seedling growth of watermelon and its control effect against Fusarium wilt [J].Fujian Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023,54(6):28-33. | |
| 9 | 辛景树,郑磊,马常宝,等. 土壤 检测第24部分:土壤全氮的测定 自动定氮仪法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2012. |
| 10 | 环境保护部. 土壤总磷的测定 碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2011. |
| 11 | 张万儒,黄钺,杨光滢,等. 土壤 全钾测定法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,1999. |
| 12 | 环境保护部. 土壤 有机碳测定:重铬酸钾氧化-分光光度法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2011. |
| 13 | 田有国,辛景树,任意,等. 土壤检测第2部分:土壤PH的测定:):[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2006. |
| 14 | 陈梅春,朱育菁,刘波,等.基于宏基因组茉莉花植株土壤细菌多样性研究[J].农业生物技术学报,2018,26(9):1480-1493. |
| CHEN M C, ZHU Y J, LIU B,et al..Diversity research of the soil bacteria of Jasminum sambac ait based on metagenome [J]. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2018,26(9):1480-1493. | |
| 15 | WANG X X, ZHAO F, ZHANG G,et al.. Vermicompost improves tomato yield and quality and the biochemical properties of soils with different tomato planting history in a greenhouse study [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017,8:1978 [2023-11-20]. . |
| 16 | FU H D, ZHANG G X, ZHANG F, et al.. Effects of continuous tomato monoculture on soil microbial properties and enzyme activities in a solar greenhouse [J/OL]. Sustainability, 2017,9:317 [2023-11-20]. . |
| 17 | 李沁爽,郭天文,谭雪莲,等.微生物菌剂对马铃薯植株干物质累积、土壤酶活性及产量的影响[J].国土与自然资源研究,2022,197(2):91-94. |
| LI Q S, GUO T W, TAN X L, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on soil enzyme activities and yield of potato dry matter accumulation [J]. Territory Nat. Resour. Study, 2022,197(2):91-94. | |
| 18 | 常娜,张雪娇,马璐璐,等.微生物菌剂对小麦生长及土传病害预防效果的影响[J].作物杂志,2017(1):155-160. |
| CHANG N, ZHANG X J, MA L L, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on growth and prevention of soil borne diseases of wheat [J].Crops, 2017(1):155-160. | |
| 19 | 宋以玲,于建,陈士更,等.复合微生物菌剂对棉花生理特性及根际土壤微生物和化学性质的影响[J].土壤,2019,51(3):477-487. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G, et al.. Effects of complex microbial agent on cotton physiological characteristics,microorganism and physicochemical properties in rhizosphere soil [J]. Soils,2019,51(3):477-487. | |
| 20 | 郑雪芳,刘波,朱育菁,等.设施番茄连作障碍土壤修复及其对青枯病害的防治效果[J].中国生物防治学报,2018,34(1):117-123. |
| ZHENG X F, LIU B, ZHU Y J,et al..Soil restoration for continuous cropping obstacles in tomato greenhouse field and the control effect against bacterial wilt disease [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Control, 2018,34(1):117-123. | |
| 21 | 张慧,余端,杭晓宁,等.稻菜轮作下不同施氮处理对土壤微生物多样性的影响[J].西南农业学报,2023,36(3):550-556. |
| ZHANG H, YU D, HANG X N, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen treatments on soil microbial diversity under rice-vegetable rotation [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2023,36(3):550-556. | |
| 22 | 李春顺,李伟鹏,付金存,等.磷肥减量施用对土壤磷含量、微生物群落及烟株磷吸收的影响[J].作物研究, 2023,37(1):28-34. |
| LI C S, LI W P, FU J C, et al.. Effects of reduced application of phosphate fertilizer on soil phosphorus content,microbial community and phosphorus uptake in tobacco plants [J]. Crop Res., 2023,37(1):28-34. | |
| 23 | 郑威,彭玉华,申文辉,等.不同林龄杉木人工林细菌群落多样性及其影响因素[J].生态科学,2023,42(3):37-45. |
| ZHENG W, PENG Y H, SHEN W H,et al..Soil bacterial diversity and its control factors of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation of different ages [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2023,42(3):37-45. | |
| 24 | 罗飞,李文红,刘亭亭,等.高通量测序解析烟草苗床期基质细菌和真菌群落结构与多样性变化[J].中国烟草学报,2023,29(2):79-88. |
| LUO F, LI W H, LIU T T,et al..Community structure and diversity of bacteria and fungi in substrate of tobacco seedling based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Acta Tab. Sin., 2023,29(2):79-88. | |
| 25 | 李凤,周方园,张广志,等.促生菌对基质栽培番茄根系细菌群落的影响[J].微生物学通报,2022,49(2):583-597. |
| LI F, ZHOU F Y, ZHANG G Z,et al..Impacts of growth-promoting bacteria on root bacterial community of tomato in substrate culture [J]. Microbiol. China, 2022,49(2):583-597. | |
| 26 | 赵淑文,李明,胡云.生物炭对设施无土基质栽培黄瓜根际土壤细菌群落的影响[J].北方园艺,2018(9):127-132. |
| ZHAO S W, LI M, HU Y. Effects of biochar on facilities soilless culture cucumber rhizosphere soil bacterial community [J].Northern Hortic., 2018(9):127-132. | |
| 27 | 郑雪芳,陈燕萍,肖荣凤,等.水肥菌一体化番茄基质栽培系统青枯病病株和健株根际微生物群落结构的差异[J].微生物学报,2022,62(4):1524-1535. |
| ZHENG X F, CHEN Y P, XIAO R F,et al..Difference of rhizobacterial community structure between bacterial wilt infected and healthy tomato plants in a substrate culture system [J]. Acta Microbiol. Sin., 2022,62(4):1524-1535. | |
| 28 | SADET-BOURGETEAU S, HOUOT S, DEQUIEDT S, et al..Lasting effect of repeated application of organic waste products on microbial communities in arable soils [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2018, 125:278-287. |
| 29 | 刘晓梅,苏文英, 纪伟, 等. 施肥方式对设施番茄产量及土壤细菌多样性、群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2023,64(1):148-152. |
| LIU X M, SU W Y, JI W, et al.. Effects of fertilization methods on yield,soil bacterial diversity and community structure in facility tomato [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2023,64(1):148-152. | |
| 30 | 濮永瑜,包玲凤,杨佩文,等.生物有机肥调控的碱性植烟土壤微生物群落多样性特征[J].西南农业学报,2022,35(4):780-789. |
| PU Y Y, BAO L F, YANG P W, et al.. Diversity characteristics of microbial communities in alkaline tobacco-growing soils regulated by bio-organic fertilizers [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2022,35(4):780-789. | |
| 31 | LIN Y T, LIN Y F, TSAI I J, et al.. Structure and diversity of soil bacterial communities in offshore islands [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019,9:4689 [2023-11-20]. . |
| 32 | 许小虎,车宗贤,赵旭,等.长期施用绿肥对小麦玉米间作土壤微生物的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(1):33-44. |
| XU X H, CHE Z X, ZHAO X,et al..Effects of long-term application of green manure on soil microorganisms in wheat maize intercropping [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2023,41(1):33-44. | |
| 33 | 刘晓飞,侯艳,马京求,等.放线菌的筛选及应用研究进展[J].饲料研究,2020,43(3):140-143. |
| LIU X F, HOU Y, MA J Q, et al.. Research progress in screening and application of actinomycetes [J]. Feed. Res., 2020,43(3):140-143. | |
| 34 | PAN T, HE H R, LI C, et al.. Streptomyces daqingensis sp. nov., isolated from saline-alkaline soil [J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2016, 66(3):1358-1363. |
| 35 | SHAH A M,SHAKEEL-U-REHMAN, HUSSAIN A,et al..Antimicrobial investigation of selected soil actinomycetes isolated from unexplored regions of Kashmir Himalayas,India [J]. Microb. Pathog., 2017,110:93-99. |
| 36 | 李巍,刘洋,罗钦,等.武夷山常绿阔叶林土壤微生物多样性的季节动态[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2017,25(2):115-126. |
| LI W, LIU Y, LUO Q,et al..Seasonal dynamics in soil microorganisms diversity of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyi mountains,southeastern China [J]. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot., 2017,25(2):115-126. | |
| 37 | 陈丽燕,戴华鑫,陈江华,等.豫中烟区土壤微生物特性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J].烟草科技,2017,50(5):1-9. |
| CHEN L Y, DAI H X, CHEN J H, et al.. Microbial characteristics and their relationships with physicochemical properties of soils in central Henan tobacco growing areas [J]. Tob. Sci. Technol., 2017,50(5):1-9. |
| [1] | 罗金城, 朱晓林, 魏小红, 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬. 番茄黄化曲叶病毒胁迫下外源NO对番茄抗氧化物酶基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 125-135. |
| [2] | 米春娇, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 张砚迪. 我国番茄土壤有效磷丰缺指标和推荐施磷量初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [3] | 李贤国, 戴麒, 王泽鹏, 陈兆龙, 闫会转, 李宁. 番茄CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [4] | 张俊蕾, 盖晓彤, 赵正婷, 刘弟, 王金凤, 姜宁, 刘雅婷. 烟草番茄斑萎病毒RT-LAMP检测体系的建立及优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [5] | 张福林, 奚瑞, 刘宇翔, 陈兆龙, 余庆辉, 李宁. 番茄BURP结构域基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [6] | 王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [7] | 李名博, 刘玉乐, 穆志民, 郭俊旺, 卫勇, 任东悦, 贾济深, 卫泽中, 栗宇红. 基于YOLOX-L-TN模型的番茄果实识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 97-105. |
| [8] | 黄大野, 余志斌, 万中义, 杨丹, 李金萍, 曹春霞. 产褐黄色链霉菌HEBRC45958菌株防控番茄棒孢叶斑病研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 136-142. |
| [9] | 陈春林, 王琳洋, 单梦伟, 裴甜甜, 王吉庆, 肖怀娟, 李娟起, 李猛, 杜清洁. 发酵花生壳和牛粪替代草炭基质的番茄育苗效果分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 205-214. |
| [10] | 李世民, 董琼, 金友帆, 李树萍, 李猛, 刘廷彪, 赵兴杰, 陈静, 叶平, 吕梦. 树番茄幼苗叶片性状和生理参数对遮阴的响应及评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 72-82. |
| [11] | 夏秀波, 李涛, 曹守军, 姚建刚, 王虹云, 张丽莉. 液态有机肥部分替代化肥对设施番茄根区细菌群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 187-196. |
| [12] | 刘迁杰,程云霞,贾凯,时振宇,张婧,魏少伟,吴慧*. 施氮量对复合沙培番茄氮代谢酶活性及品质和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 183-191. |
| [13] | 顾惠敏1,陈波浪1*,孙锦2. 菌根化育苗对盐胁迫下加工番茄生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| [14] | 陈潇洁, 吕德生, 王振华, 李文昊, 宗睿, 温越, 邹杰. 加气灌溉及水氮耦合滴灌对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 191-200. |
| [15] | 李艳梅1,周亚文2,张琳1,廖上强1*,孙焱鑫1*. 抗逆与渗透物质耦合对番茄产量及水分利用的调控及机制探讨[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 43-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号