




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 195-204.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0007
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
庆福1,2( ), 梁洪月1,2,3, 孙静4, 鲁新蕊2, 梁运江1(
), 梁洪月1,2,3, 孙静4, 鲁新蕊2, 梁运江1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-04
接受日期:2024-09-30
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-06-23
通讯作者:
梁运江
作者简介:庆福 E-mail:z18147046454@163.com;
基金资助:
Fu QING1,2( ), Hongyue LIANG1,2,3, Jing SUN4, Xinrui LU2, Yunjiang LIANG1(
), Hongyue LIANG1,2,3, Jing SUN4, Xinrui LU2, Yunjiang LIANG1( )
)
Received:2024-01-04
Accepted:2024-09-30
Online:2025-06-15
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Yunjiang LIANG
摘要:
为改善黑土区土壤结构、提高土壤肥力,以黑土区长期定位试验为研究平台,以不施生物炭和氮肥为对照(CK),设置10(C1)、20(C2)和50 g·kg-1(C3)3个生物炭水平和0(N0)、300(N1)和600 kg·hm-2(N2)3个氮肥水平,研究生物炭-氮肥配施对土壤团聚体和有机碳含量的影响,并探讨其最大影响因子。结果表明,与CK相比,生物炭-氮肥配施使土壤容重降低2.73%~8.20%,土壤含水量增加1.04%~31.24%,各处理间差异不显著。生物炭-氮肥配施促进了<0.053 mm团聚体向≥2 mm团聚体的转化;团聚体稳定性显著提高,≥0.25 mm土壤团聚体质量比(R0.25)、平均重量直径(mean weigh diameter,MWD)和几何平均直径(geometric mean diameter,GMD)的增幅分别为25.06%、21.71%和12.50%;各粒级团聚体的有机碳含量均增加,其中≥2 mm团聚体和<0.053 mm团聚体的有机碳含量显著增加,增幅分别为13.19%~54.42%和13.78%~41.34%。主成分分析表明,R0.25是影响土壤有机碳含量的关键因子,C2N1处理是改良黑土结构的最佳配施处理。以上研究结果为遏制东北地区黑土退化、提升地力提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
庆福, 梁洪月, 孙静, 鲁新蕊, 梁运江. 生物炭-氮肥配施对东北黑土团聚体及有机碳含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 195-204.
Fu QING, Hongyue LIANG, Jing SUN, Xinrui LU, Yunjiang LIANG. Effects of Combined Application of Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Aggregate and Organic Carbon Content of Black Soil in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 195-204.
处理 Treatment | 施用量Application amount | |
|---|---|---|
| C/(g·kg-1) | N/(kg·hm-2) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 |
| C1N0 | 10 | 0 |
| C2N0 | 20 | 0 |
| C3N0 | 50 | 0 |
| C1N1 | 10 | 300 |
| C2N1 | 20 | 300 |
| C3N1 | 50 | 300 |
| C1N2 | 10 | 600 |
| C2N2 | 20 | 600 |
| C3N2 | 50 | 600 |
表 1 不同处理的生物炭和氮肥施用量
Table 1 Application amounts of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 施用量Application amount | |
|---|---|---|
| C/(g·kg-1) | N/(kg·hm-2) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 |
| C1N0 | 10 | 0 |
| C2N0 | 20 | 0 |
| C3N0 | 50 | 0 |
| C1N1 | 10 | 300 |
| C2N1 | 20 | 300 |
| C3N1 | 50 | 300 |
| C1N2 | 10 | 600 |
| C2N2 | 20 | 600 |
| C3N2 | 50 | 600 |
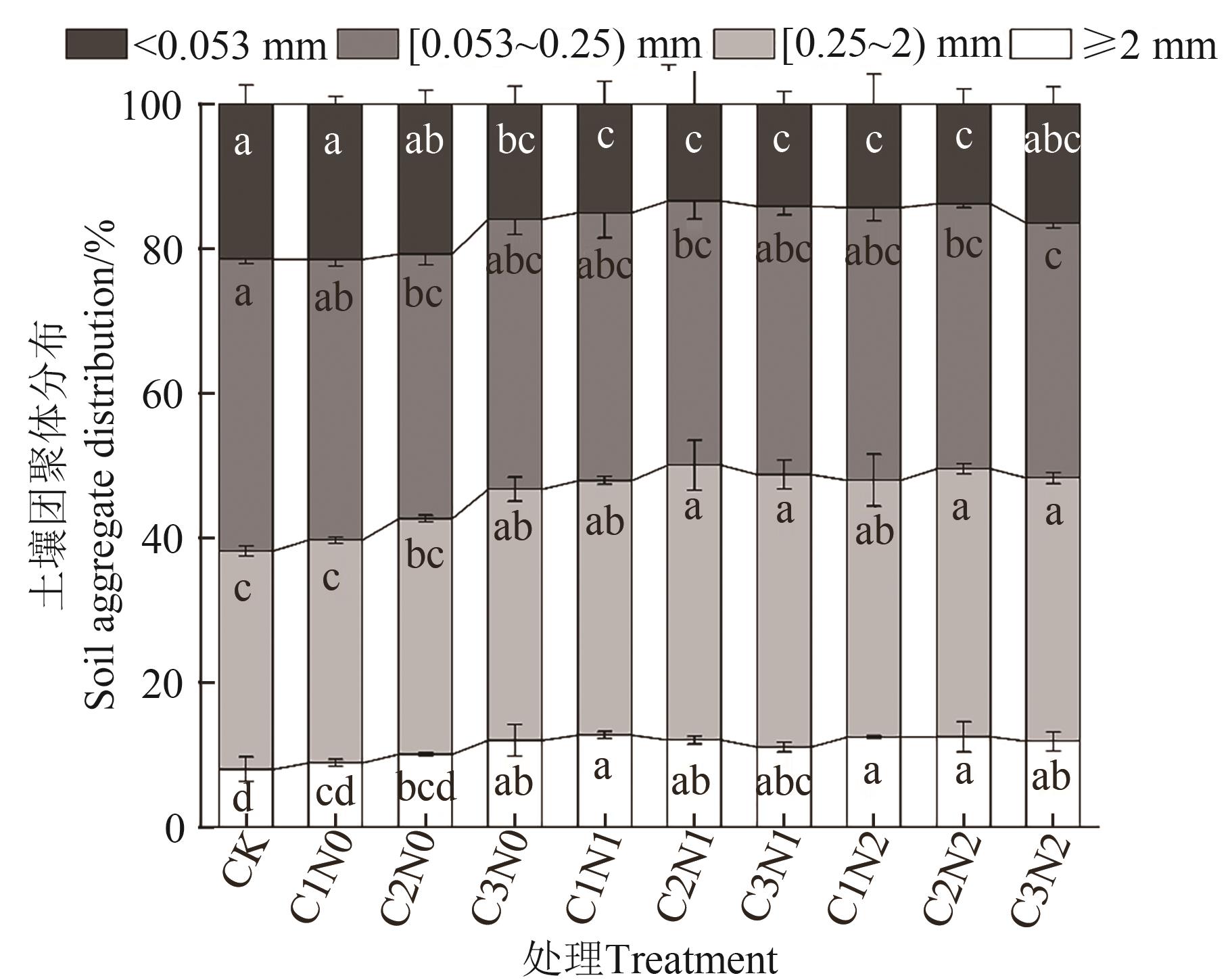
图2 不同处理下土壤各级团聚体的分布注:不同小写字母表示同一粒级团聚体不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Distribution of soil aggregate under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments of same type of aggregate at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | R0.25/% | 平均重量直径MWD/mm | 几何平均直径GWD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 38.16±2.10 c | 0.38±0.03 c | 0.49±0.02 b |
| C1N0 | 39.68±0.41 bc | 0.39±0.01 bc | 0.49±0.00 b |
| C2 N0 | 42.64±0.55 b | 0.42±0.01 b | 0.51±0.01 b |
| C3 N0 | 46.72±2.28 a | 0.46±0.03 a | 0.55±0.02 a |
| C1N1 | 47.91±0.49 a | 0.47±0.01 a | 0.55±0.01 a |
| C2N1 | 50.02±4.00 a | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.57±0.04 a |
| C3N1 | 48.72±1.87 a | 0.46±0.01 a | 0.56±0.01 a |
| C1N2 | 47.97±3.65 a | 0.47±0.02 a | 0.56±0.03 a |
| C2N2 | 49.53±1.90 a | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.56±0.02 a |
| C3N2 | 48.27±1.84 a | 0.46±0.02 a | 0.55±0.02 a |
表2 不同处理下土壤团聚体稳定性
Table 2 Stability of soil aggregates under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | R0.25/% | 平均重量直径MWD/mm | 几何平均直径GWD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 38.16±2.10 c | 0.38±0.03 c | 0.49±0.02 b |
| C1N0 | 39.68±0.41 bc | 0.39±0.01 bc | 0.49±0.00 b |
| C2 N0 | 42.64±0.55 b | 0.42±0.01 b | 0.51±0.01 b |
| C3 N0 | 46.72±2.28 a | 0.46±0.03 a | 0.55±0.02 a |
| C1N1 | 47.91±0.49 a | 0.47±0.01 a | 0.55±0.01 a |
| C2N1 | 50.02±4.00 a | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.57±0.04 a |
| C3N1 | 48.72±1.87 a | 0.46±0.01 a | 0.56±0.01 a |
| C1N2 | 47.97±3.65 a | 0.47±0.02 a | 0.56±0.03 a |
| C2N2 | 49.53±1.90 a | 0.48±0.03 a | 0.56±0.02 a |
| C3N2 | 48.27±1.84 a | 0.46±0.02 a | 0.55±0.02 a |
指标 Index | ≥2 mm | [0.25,2) mm | [0.053,0.25) mm | <0.053 mm | 平均重量直径 MWD | 平均几何直径 GMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0.25,2] mm | 0.614** | |||||
| (0.053,0.25] mm | -0.464** | -0.385* | ||||
| <0.053 mm | -0.714** | -0.869** | 0.016 | |||
| 平均重量直径MWD | 0.935** | 0.851** | -0.431* | -0.883** | ||
| 平均几何直径GMD | 0.827** | 0.914** | -0.253 | -0.970** | 0.966** | |
| R0.25 | 0.841** | 0.943** | -0.459* | -0.896** | 0.976** | 0.974** |
表 3 团聚体组成与稳定性的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between aggregate composition and stability
指标 Index | ≥2 mm | [0.25,2) mm | [0.053,0.25) mm | <0.053 mm | 平均重量直径 MWD | 平均几何直径 GMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0.25,2] mm | 0.614** | |||||
| (0.053,0.25] mm | -0.464** | -0.385* | ||||
| <0.053 mm | -0.714** | -0.869** | 0.016 | |||
| 平均重量直径MWD | 0.935** | 0.851** | -0.431* | -0.883** | ||
| 平均几何直径GMD | 0.827** | 0.914** | -0.253 | -0.970** | 0.966** | |
| R0.25 | 0.841** | 0.943** | -0.459* | -0.896** | 0.976** | 0.974** |
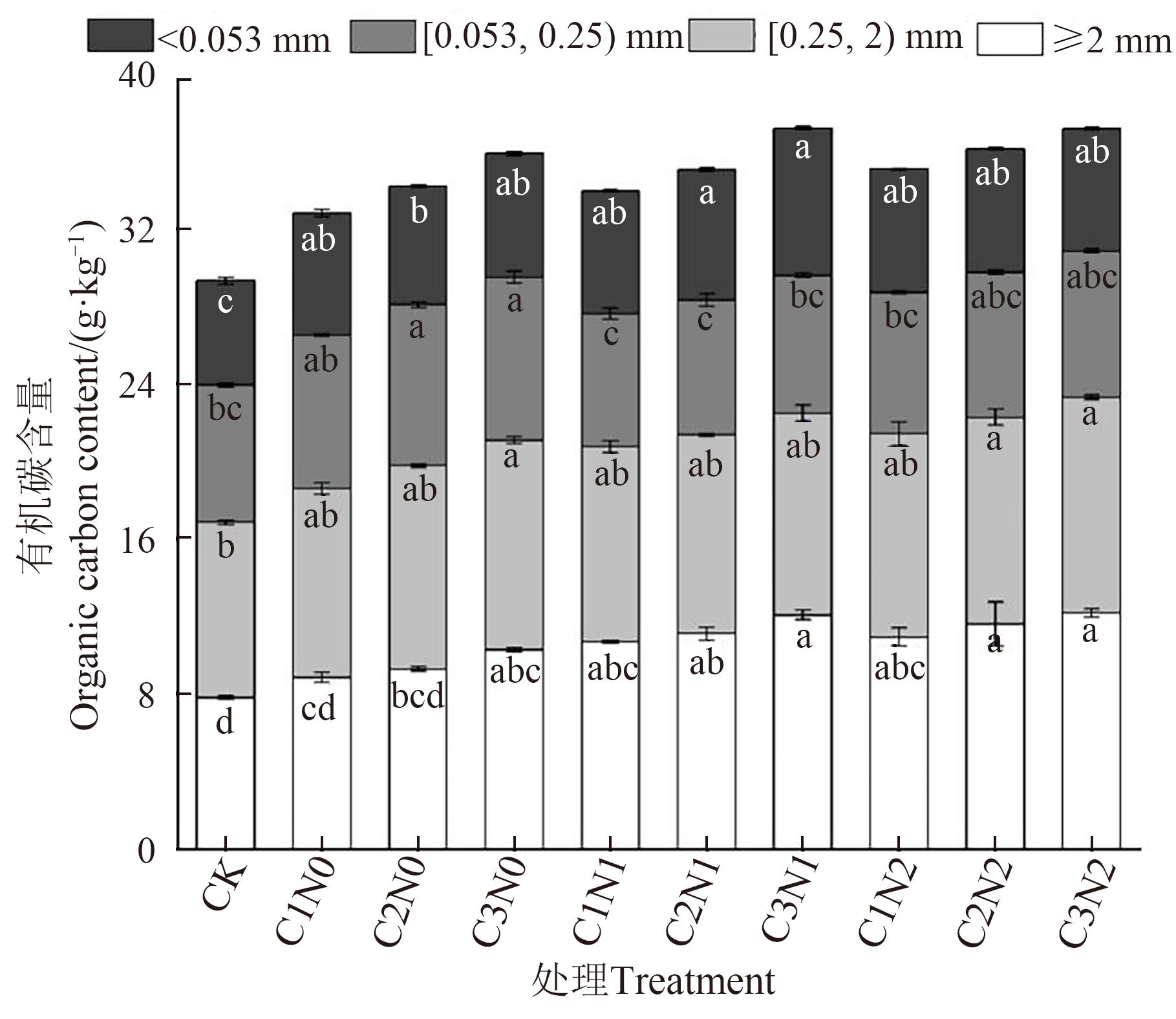
图 3 不同处理下团聚体的有机碳含量注:不同小写字母表示同一粒级团聚体不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Organic carbon content in aggregates under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significantly differences between different treatments of the same type of aggregate at P<0.05 level.
| 因子 Factor | 主成分1 PC1 | 主成分2 PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| X1:容重 Bulk density | -0.871 | -0.007 |
| X2:含水量 Water content | 0.520 | 0.818 |
| X3:R0.25 | 0.996 | -0.005 |
| X4:平均重量直径MWD | 0.991 | 0.008 |
| X5:平均几何直径GMD | 0.992 | -0.010 |
| X6:<0.053 mm | -0.967 | 0.017 |
| X7:有机碳SOC | 0.754 | -0.540 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 78.454 | 13.738 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 78.454 | 92.193 |
表 4 团聚体有机碳含量影响因子主成分分析
Table 4 Principal component analysis of aggregate organic carbon content influencing factors
| 因子 Factor | 主成分1 PC1 | 主成分2 PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| X1:容重 Bulk density | -0.871 | -0.007 |
| X2:含水量 Water content | 0.520 | 0.818 |
| X3:R0.25 | 0.996 | -0.005 |
| X4:平均重量直径MWD | 0.991 | 0.008 |
| X5:平均几何直径GMD | 0.992 | -0.010 |
| X6:<0.053 mm | -0.967 | 0.017 |
| X7:有机碳SOC | 0.754 | -0.540 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 78.454 | 13.738 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 78.454 | 92.193 |
处理 Treatment | F1值 F1 value | F2值 F2 value | F值 F value | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | -4.16 | 0.04 | -3.26 | 10 |
| C1N0 | -3.48 | -0.31 | -2.77 | 9 |
| C2 N0 | -2.08 | -0.20 | -1.66 | 8 |
| C3 N0 | 0.59 | 2.24 | 0.77 | 6 |
| C1N1 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 7 |
| C2N1 | 2.29 | 0.77 | 1.90 | 1 |
| C3N1 | 1.21 | -0.32 | 0.91 | 5 |
| C1N2 | 1.39 | -1.17 | 0.93 | 4 |
| C2N2 | 2.05 | -1.17 | 1.45 | 2 |
| C3N2 | 1.36 | -0.04 | 1.06 | 3 |
表5 主成分评价值和综合评价值
Table 5 Principal component Tevaluation value and comprehensive evaluation value
处理 Treatment | F1值 F1 value | F2值 F2 value | F值 F value | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | -4.16 | 0.04 | -3.26 | 10 |
| C1N0 | -3.48 | -0.31 | -2.77 | 9 |
| C2 N0 | -2.08 | -0.20 | -1.66 | 8 |
| C3 N0 | 0.59 | 2.24 | 0.77 | 6 |
| C1N1 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 7 |
| C2N1 | 2.29 | 0.77 | 1.90 | 1 |
| C3N1 | 1.21 | -0.32 | 0.91 | 5 |
| C1N2 | 1.39 | -1.17 | 0.93 | 4 |
| C2N2 | 2.05 | -1.17 | 1.45 | 2 |
| C3N2 | 1.36 | -0.04 | 1.06 | 3 |
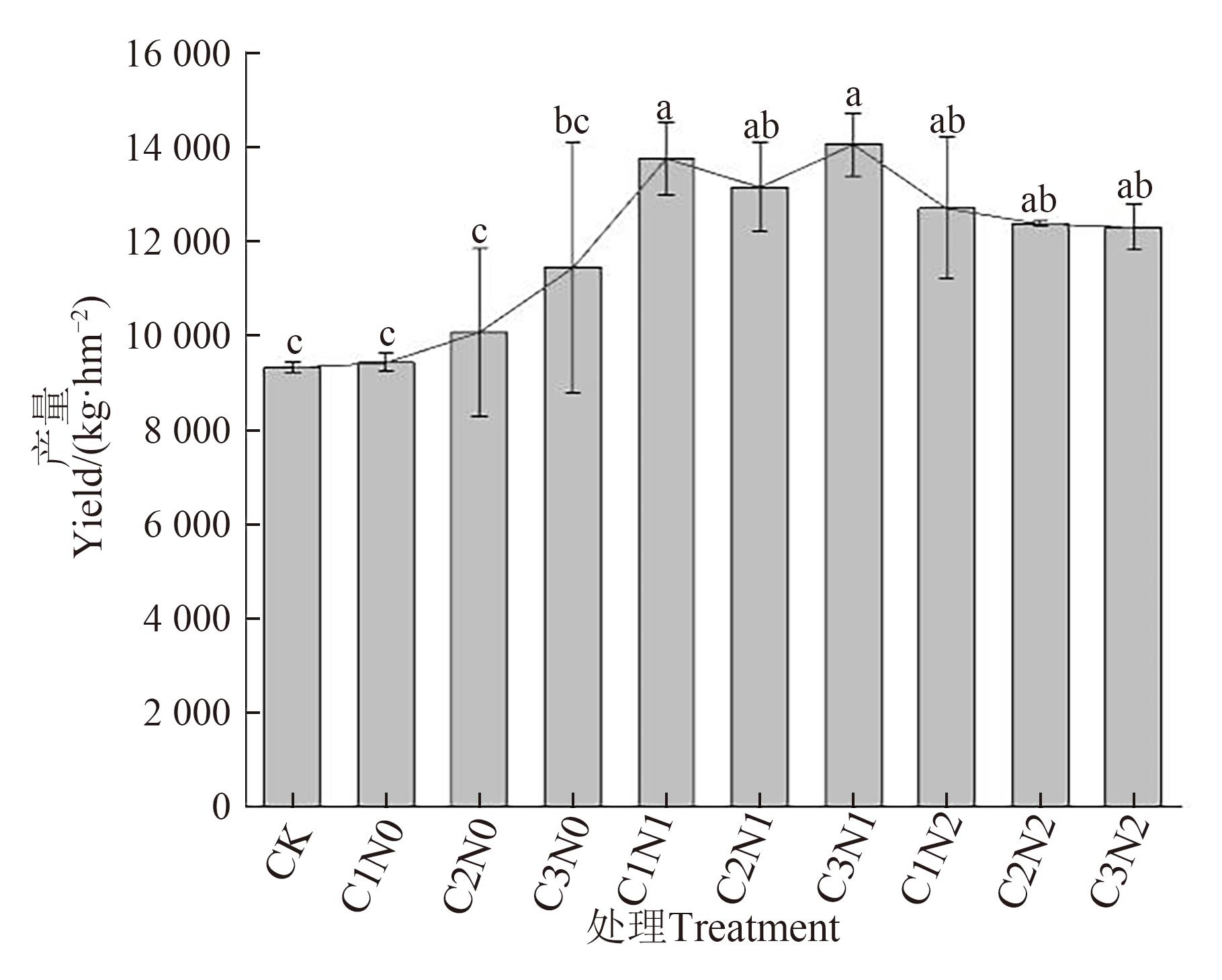
图 4 不同处理下玉米产量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Maize yield under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 穗重 Panicle weight/g | 穗粒数 Kernels per spike | 千粒重 Thousand grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 17.17±1.43 c | 179.25±2.72 d | 448.33±70.27 d | 367.33±16.04 bc |
| C1N0 | 16.73±2.74 c | 227.12±90.19 cd | 476.67±95.45 cd | 361.00±75.45 c |
| C2N0 | 18.53±1.00 bc | 345.63±72.48 a | 489.67±83.56 bcd | 410.33±74.78 abc |
| C3N0 | 17.61±2.80 bc | 239.92±63.48 bcd | 545.67±134.78 abcd | 388.67±43.82 bc |
| C1N1 | 20.50±1.19 ab | 333.55±12.65 a | 620.00±18.33 a | 441.00±15.39 ab |
| C2N1 | 19.40±0.96 abc | 307.33±14.47 abc | 635.00±31.58 a | 442.67±12.22 ab |
| C3N1 | 22.35±2.51 a | 316.60±45.46 ab | 650.33±50.74 a | 415.00±14.42 abc |
| C1N2 | 18.82±1.05 bc | 235.53±8.81 bcd | 582.33±15.14 abc | 478.33±47.61 a |
| C2N2 | 19.87±0.04 abc | 325.20±8.19 a | 590.33±2.31 abc | 478.33±3.51 a |
| C3N2 | 18.93±0.86 bc | 303.46±7.87 abc | 610.67±46.61 ab | 437.00±4.00 abc |
表6 不同处理下玉米产量相关性状
Table 6 Traits on yield of maize under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 穗重 Panicle weight/g | 穗粒数 Kernels per spike | 千粒重 Thousand grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 17.17±1.43 c | 179.25±2.72 d | 448.33±70.27 d | 367.33±16.04 bc |
| C1N0 | 16.73±2.74 c | 227.12±90.19 cd | 476.67±95.45 cd | 361.00±75.45 c |
| C2N0 | 18.53±1.00 bc | 345.63±72.48 a | 489.67±83.56 bcd | 410.33±74.78 abc |
| C3N0 | 17.61±2.80 bc | 239.92±63.48 bcd | 545.67±134.78 abcd | 388.67±43.82 bc |
| C1N1 | 20.50±1.19 ab | 333.55±12.65 a | 620.00±18.33 a | 441.00±15.39 ab |
| C2N1 | 19.40±0.96 abc | 307.33±14.47 abc | 635.00±31.58 a | 442.67±12.22 ab |
| C3N1 | 22.35±2.51 a | 316.60±45.46 ab | 650.33±50.74 a | 415.00±14.42 abc |
| C1N2 | 18.82±1.05 bc | 235.53±8.81 bcd | 582.33±15.14 abc | 478.33±47.61 a |
| C2N2 | 19.87±0.04 abc | 325.20±8.19 a | 590.33±2.31 abc | 478.33±3.51 a |
| C3N2 | 18.93±0.86 bc | 303.46±7.87 abc | 610.67±46.61 ab | 437.00±4.00 abc |
| 1 | 韩晓增,李娜.中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J].地理科学,2018,38(7):1032-1041. |
| HAN X Z, LI N. Research progress of black soil in Northeast China [J]. Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2018, 38(7):1032-1041. | |
| 2 | 李保国,刘忠,黄峰,等.巩固黑土地粮仓保障国家粮食安全[J].中国科学院院刊,2021,36(10):1184-1193. |
| LI B G, LIU Z, HUANG F, et al.. Ensuring national food security by strengthening high-productivity black soil granary in northeast China [J]. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci., 2021, 36(10):1184-1193. | |
| 3 | 贺旭杨,肖洋.东北典型黑土区土壤养分现状[J].水利科技与经济, 2022,28(8):90-93. |
| HE X Y, XIAO Y. Current status of soil nutrients in the typical black soil in northeast China [J]. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ., 2022, 28(8):90-93. | |
| 4 | LI L J, BURGER M, DU S L, et al.. Change in soil organic carbon between 1981 and 2011 in croplands of Heilongjiang province, Northeast China [J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2016,96(4):1275-1283. |
| 5 | HE M J, XIONG X N, WANG L, et al.. A critical review on performance indicators for evaluating soil biota and soil health of biochar-amended soils [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2021,414:125378 [2023-12-05]. . |
| 6 | LUO G W, LI L, FRIMAN V P, et al.. Organic amendments increase crop yields by improving microbe-mediated soil functioning of agroecosystems:a meta-analysis [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2018, 124:105-115. |
| 7 | 吴昱,赵雨森,刘慧,等.秸秆生物炭对黑土区坡耕地生产能力影响分析与评价[J].农业机械学报,2017,48(7):247-256. |
| WU Y, ZHAO Y S, LIU H, et al.. Analysis and evaluation of influence of straw biochar on soil productivity of sloping land in black soil region [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2017,48(7):247-256. | |
| 8 | GITHINJI L. Effect of biochar application rate on soil physical and hydraulic properties of a sandy loam [J]. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci., 2014, 60(4):457-470. |
| 9 | LEHMANN J. Bio-energy in the black [J]. Front. Ecol. Environ., 2007, 5(7):381-387. |
| 10 | 王怀鹏,姜辉,孙继英,等.生物炭对东北农田黑土理化性质及微生物特性应用进展分析[J].耕作与栽培,2023,43(5):67-69. |
| WANG H P, JIANG H, SUN J Y, et al.. Progress in the application of biochar to the physicochemical properties and microbial characteristics of black soil in northeastern farmland [J]. Till. Cultiv., 2023, 43(5):67-69. | |
| 11 | 陈温福,张伟明,孟军.农用生物炭研究进展与前景[J].中国农业科学,2013,46(16):3324-3333. |
| CHEN W F, ZHANG W M, MENG J. Advances and prospects in research of biochar utilization in agriculture [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2013, 46(16): 3324-3333. | |
| 12 | 潘根兴,张阿凤,邹建文,等.农业废弃物生物黑炭转化还田作为低碳农业途径的探讨[J].生态与农村环境学报,2010,26(4):394-400. |
| PAN G X, ZHANG A F, ZOU J W, et al.. Biochar from agro-byproducts used as amendment to croplands:an option for low carbon agriculture [J]. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ., 2010, 26(4):394-400. | |
| 13 | 刘晓雨,卞荣军,陆海飞,等.生物质炭与土壤可持续管理:从土壤问题到生物质产业[J].中国科学院院刊,2018,33(2):184-190. |
| LIU X Y, BIAN R J, LU H F, et al.. Biochar for sustainable soil management:biomass technology and industry from soil perspectives [J]. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci., 2018, 33(2):184-190. | |
| 14 | HANSEN V, MÜLLER-STÖVER D, AHRENFELDT J, et al.. Gasification biochar as a valuable by-product for carbon sequestration and soil amendment [J]. Biomass Bioenergy, 2015, 72:300-308. |
| 15 | 张影,刘星,任秀娟,等.秸秆及其生物炭对土壤碳库管理指数及有机碳矿化的影响[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(3):153-159, 165. |
| ZHANG Y, LIU X, REN X J, et al.. Effects of straw and biochar on soil carbon pool management index and organic carbon mineralization [J].J.Soil Water Conserv., 2019,33(3):153-159, 165. | |
| 16 | 陈新邦,唐光木,张云舒,等.不同类型外源碳添加对灰漠土土壤碳储量的影响[J].水土保持学报,2023,37(3):330-335. |
| CHEN X B, TANG G M, ZHANG Y S, et al.. Effects of different types of exogenous carbon addition on soil carbon storage in grey desert soil [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2023, 37(3):330-335. | |
| 17 | SONG D L, CHEN L, ZHANG S, et al.. Combined biochar and nitrogen fertilizer change soil enzyme and microbial activities in a 2-year field trial [J/OL]. Eur. J. Soil Bio., 2020, 99:103212 [2023-12-05]. . |
| 18 | CRISCUOLI I, VENTURA M, WIEDNER K, et al.. Stability of woodchips biochar and impact on soil carbon stocks: Results from a two-year field experiment [J/OL]. Forests, 2021, 12(10):1350 [2023-12-05]. . |
| 19 | 姚佳,刘加欣,苏焱,等.烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2023,25(3):140-151. |
| YAO J, LIU J X, SU Y, et al.. Effects of combined application of tobacco stem biochar and nitrogen fertilizers on corn growth and soil properties in seeding stage [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(3):140-151. | |
| 20 | ZHANG H Q, QIN Y, LI Z Z, et al.. Mixed application of biochar, maize straw, and nitrogen can improve organic carbon fractions and available nutrients of a sandy soil [J]. Arid Land Res. Manage., 2023, 37(1):115-133. |
| 21 | 李晨,陈明婉,金鑫,等.施入生物炭对热带农田土壤团聚体组成及碳氮含量的影响[J].土壤通报,2023, 54(5):1071-1079. |
| LI C, CHEN M W, JIN X, et al.. Effects of biochar application on soil aggregate composition and carbon and nitrogen contents in tropical farmland [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2023, 54(5):1071-1079. | |
| 22 | 钱莲文,余甜甜,梁旭军,等.茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5a后的稳定性研究[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(7):1442-1447. |
| QIAN L W, YU T T, LIANG X J, et al.. Stability of biochar after application for 5 years in the amendment of acidified tea garden soil [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2022, 31(7):1442-1447. | |
| 23 | HILLEL D. Fundamentals of Soil Physics [M]. New York: Academic press, 2013:1-268. |
| 24 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| 25 | 魏永霞,肖敬萍,王鹤,等.施加生物炭对黑土区坡耕地改土培肥效应的持续影响[J].农业机械学报,2021,52(3):305-314. |
| WEI Y X, XIAO J P, WANG H, et al.. Continual influences of applying biochar on soil improvements in sloping farmland of black soil region in northeast China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2021, 52(3):305-314. | |
| 26 | 赵蕊蕊,刘勇,王凯.生物炭和有机肥对毛白杨人工林地木质分解及土壤养分循环相关酶活性的影响[J].林业科学,2023,59(11):1-11. |
| ZHAO R R, LIU Y, WANG K. Effects of biochar and manure on wood decomposition and soil enzyme activities related soil nutrient cycling in a triploid Populus tomentosa plantation [J].Sci. Silvae Sin., 2023, 59(11):1-11. | |
| 27 | BLANCO-CANQUI H.Does biochar application alleviate soil compaction? review and data synthesis [J/OL]. Geoderma, 2021,404:115317 [2023-12-05]. . |
| 28 | LUO C Y, YANG J J, CHEN W, et al.. Effect of biochar on soil properties on the Loess Plateau:results from field experiments [J/OL]. Geoderma, 2020,369:114323 [2023-12-05].. |
| 29 | HORÁK J, ŠIMANSKÝ V, IGAZ D. Biochar and biochar with N fertilizer impact on soil physical properties in a silty loam Haplic Luvisol [J]. J. Ecol. Eng., 2019, 20(7):31-38. |
| 30 | 解倩,王丽梅,齐瑞鹏,等.生物炭对黄绵土水分入渗和持水性能的影响[J].地球环境学报,2016,7(1):65-76, 86. |
| XIE Q, WANG L M, QI R P, et al.. Effects of biochar on water infi ltration and water holding capacity of loessial soil [J]. J. Earth Environ., 2016, 7(1):65-76, 86. | |
| 31 | 代镇,李伟,韩娟,等.生物炭对土持水能力的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2019,37(6):265-273. |
| DAI Z, LI W, HAN J, et al.. Influences of biochar on soil water retention capacity in the Lou soil [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2019, 37(6):265-273. | |
| 32 | LEHMANN J, PEREIRA DA SILVA J, STEINER C, et al..Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological anthrosol and a ferralsol of the central Amazon Basin:fertilizer,manure and charcoal amendments [J]. Plant Soil, 2003, 249(2):343-357. |
| 33 | SUN J, LU X R, CHEN G S, et al.. Biochar promotes soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration, and regulates microbial community structures in mollisols from northeast China [J]. EGUsphere. 2022, 22:21-39. |
| 34 | BRODOWSKI S, JOHN B, FLESSA H, et al.. Aggregate-occluded black carbon in soil [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57(4):539-546. |
| 35 | 孙强,杨旭,孟军,等.生物炭对棕壤团聚体空间分布及有机碳的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2022,41(11):2515-2524. |
| SUN Q, YANG X, MENG J, et al.. Effects of biochar on soil aggregate spatial distribution and soil organic carbon in brown earth soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(11):2515-2524. | |
| 36 | CANTRELL K B, HUNT P G, UCHIMIYA M, et al.. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2012,107:419-428. |
| 37 | WANG D Y, FONTE S J, PARIKH S J, et al.. Biochar additions can enhance soil structure and the physical stabilization of C in aggregates [J]. Geoderma, 2017,303:110-117. |
| 38 | 邹瑞晗,王振华,朱艳,等.非灌溉季节生物炭施用对滴灌棉田土壤团聚体及其碳含量的影响[J].土壤通报,2023,54(3):626-635. |
| 39 | 朱玲,周蓉,沈玉叶,等.稻壳及稻壳生物炭对土壤团聚体稳定性及有机碳分布的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2023,29(2):242-252. |
| ZHU L, ZHOU R, SHEN Y Y, et al.. Effects of rice husk and its derived biochar on soil properties and stability of aggregates [J].J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2023, 29(2):242-252. | |
| 40 | 赵雅琦,栾好安,黄绍文.不同种植年限对核桃园土壤团聚体稳定性及其有机碳组分的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2024(1):8-18. |
| ZHAO Y Q, LUAN H A, HUANG S W, et al.. Effects of different plantation ages on soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated organic carbon fractions in walnut orchards [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2024(1):8-18. | |
| 41 | 尚应妮,胡斐南,赵世伟,等.不同胶结物质对黄绵土团聚体形成的影响[J].水土保持学报,2017,31(2):204-208, 239. |
| SHANG Y N, HU F N, ZHAO S W, et al.. Effects of cementing materials on the formation of loessial soil aggregates [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 31(2):204-208, 239. | |
| 42 | XIU L Q, ZHANG W M, SUN Y Y, et al.. Effects of biochar and straw returning on the key cultivation limitations of Albic soil and soybean growth over 2 years [J]. CATENA, 2019, 173: 481-493. |
| 43 | 姚俊红,武俊男,王呈玉,等.长期不同施氮量下黑土团聚体稳定性及有机碳含量的变化[J].农业环境科学学报,2024,43(1):102-110. |
| YAO J H, WU J N, WANG C Y, et al.. Changes in aggregates stability and organic carbon content of black soil following the use of different long-term nitrogen application rates [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2024, 43(1):102-110. | |
| 44 | 刘昊贶,徐聪,孙丽,等.生物炭和聚丙烯酰胺施用对土壤有机碳含量的影响及生态经济效益分析[J].江苏农业科学,2023,51(12):215-222. |
| 45 | LEHMANN J, JOSEPH S. Biochar for environmental management: an introduction [J]. Biochar Environ. Manage. Sci. Technol., 2009, 25(1):15801-15811. |
| 46 | OLADELE S O, ADEYEMO A J, AWODUN M A. Influence of rice husk biochar and inorganic fertilizer on soil nutrients availability and rain-fed rice yield in two contrasting soils [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 336:1-11. |
| 47 | 周明星,樊军,王茜,等.免耕覆盖与生物炭对黑垆土团聚体稳定性和腐殖质性质的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2023,29(5): 848-859. |
| ZHOU M X, FAN J, WANG Q, et al.. Effects of no-tillage mulching and biochar application on the stability and humus properties of black loam soil aggregate [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2023, 29(5):848-859. | |
| 48 | 张鹏,贾志宽,王维,等.秸秆还田对宁南半干旱地区土壤团聚体特征的影响[J].中国农业科学,2012, 45(8):1513-1520. |
| ZHANG P, JIA Z K, WANG W, et al.. Effects of straw returning on characteristics of soil aggregates in semi-arid areas in southern Ningxia of China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2012, 45(8):1513-1520. | |
| 49 | 孟维山,朱芳妮,张博文,等.玉米秸秆及其生物炭还田对黑土理化性质及玉米产量的影响[J].吉林农业大学学报,2024, 46(5):721-730. |
| MENG W S, ZHU F N, ZHANG B W, et al.. Effects of straw and biochar application on the soil physicochemical properties and corn yield in a black soil [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2024, 46(5):721-730. | |
| 50 | 史多鹏,叶子壮,李杰,等.氮肥配施生物炭和脲酶抑制剂对夏玉米-冬小麦产量及氮素利用的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(4):51-60. |
| SHI D P, YE Z Z, LI J, et al.. Effects of nitrogen combined with biochar and urease inhibitor on yield and nitrogen utilization of summer maize-winter wheat system [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2023, 41(4):51-60. | |
| 51 | 谢丽华,李玲玲,谢军红,等.有机肥替代化肥对陇中旱区玉米生长及农田碳排放的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(6):1029-1038. |
| XIE L H, LI L L, XIE J H, et al.. Effects of substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer on maize growth and field carbon emission in dry farming area of Longzhong,Gansu province [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2022, 28(6):1029-1038. |
| [1] | 田甜, 杨振奇, 郭建英, 要振宇, 赵天启, 刘心宇, 王子薇. 放牧强度对荒漠草原土壤团聚体稳定性及可蚀性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 156-163. |
| [2] | 侯赛赛, 仝姗姗, 王鹏企, 谢冰雪, 张瑞芳, 王鑫鑫. 生物炭和秸秆对不同作物生长性状和养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 179-191. |
| [3] | 吴艳, 邹乐萍, 宋惠洁, 胡丹丹, 柳开楼, 梁万里. 控释氮肥和尿素配施对田面水铵态氮和早稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 192-200. |
| [4] | 段俊雅, 赵园园, 王婷婷, 韦建玉, 王政, 王德勋, 李娟, 史宏志. 减氮配施聚天冬氨酸对烤烟氮素利用及产质量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 227-238. |
| [5] | 张如艳, 李绅昊, 朱奇鹏, 冯太纲, 李红波, 邢泽炳, 羡瑜. 生物炭含量对园林绿化废弃物/聚乳酸复合材料物理力学性能影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 192-200. |
| [6] | 吕志伟, 李冬梅, 金梅娟, 张燕辉, 陶玥玥, 周新伟, 王海候. 热解温度及时间对生物炭理化性质及吸附性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 211-217. |
| [7] | 赵炳地, 张久明, 朱莹雪, 匡恩俊, 袁佳慧, 迟凤琴, 孙磊, 李宁. 不同秸秆还田量对土壤团聚体及有机碳含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 193-200. |
| [8] | 史丹一, 邱禹, 黄成真, 王娟. 酸改性生物炭对滨海盐渍土壤水分入渗特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 183-192. |
| [9] | 石纹碹, 谭金芳, 张倩, 李岚涛, 王宜伦. 一次性施肥对不同生态区夏玉米产量和氮肥效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 193-202. |
| [10] | 蒲子天, 王红, 赵斌, 王鑫鑫. 不同土壤改良物料对连作黄芩生长及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 189-198. |
| [11] | 付彦博, 冷冰冰, 扁青永, 董志多, 刘国宏, 李海峰, 温云梦, 郭文博, 张万旭. 生物炭和油菜幼苗对土壤重金属镉污染的钝化效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 183-190. |
| [12] | 陈雨欣, 赵红梅, 杨卫君, 杨梅, 郭颂, 宋世龙, 惠超. 生物质炭对土壤微生物碳源利用及春小麦产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 174-183. |
| [13] | 林玲, 朱玉洁, 冯雷, 唐光木, 张云舒, 徐万里. 老化棉秆炭对土壤性质和小麦氮肥利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 184-191. |
| [14] | 赵娅红, 胡骞予, 夏融, 王志江, 谢永辉, 叶贤文, 余磊, 齐颖, 羊绍武, 薛至勤, 吴治兴, 黄飞燕, 韩天华. 生物炭肥对易感根结线虫病烤烟根际菌群和理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 206-214. |
| [15] | 胡家钰, 杨阳, 张红燕, 高兵阳, 王灵璐, 闫军营, 孙笑梅, 赵亚南, 叶优良. 施用不同品种氮肥对麦套花生生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 191-197. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号