




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (10): 71-82.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0112
冀薇1( ), 樊莹2, 黄家兴1, 杨慧鹏1, 徐进1, 李小英1, 郭岳琴1, 吴跃国3, 李继莲1, 姚军1(
), 樊莹2, 黄家兴1, 杨慧鹏1, 徐进1, 李小英1, 郭岳琴1, 吴跃国3, 李继莲1, 姚军1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-18
接受日期:2024-04-21
出版日期:2024-10-15
发布日期:2024-10-18
通讯作者:
姚军
作者简介:冀薇 E-mail:jw15532321501@163.com;
基金资助:
Wei JI1( ), Ying FAN2, Jiaxing HUANG1, Huipeng YANG1, Jin XU1, Xiaoying LI1, Yueqin GUO1, Yueguo WU3, Jilian LI1, Jun YAO1(
), Ying FAN2, Jiaxing HUANG1, Huipeng YANG1, Jin XU1, Xiaoying LI1, Yueqin GUO1, Yueguo WU3, Jilian LI1, Jun YAO1( )
)
Received:2024-02-18
Accepted:2024-04-21
Online:2024-10-15
Published:2024-10-18
Contact:
Jun YAO
摘要:
授粉对蓝莓生产至关重要,为探究不同授粉强度下柱头的响应机制及其特性,以‘蓝源(M7)’为研究对象,比较不同花龄下柱头可授性,并对花粉活力进行测定,然后对3种授粉强度处理下的蓝莓柱头进行转录组测序和分析。结果表明,随花龄的不断延长,‘蓝源(M7)’柱头可授性表现为先升高后逐渐降低的趋势,在开花第2天可授性最强。3种授粉强度的花粉表现出不同的活力,随着授粉强度的增加,柱头内参与花粉管生长调节的钙依赖蛋白激酶17(Cpk17)和涉及肌醇含量的肌醇加氧酶(MIOX1)等基因的表达量显著提高。对差异表达基因的GO(gene ontology)富集分析发现,与碳水化合物代谢、肌醇加氧酶活性和细胞壁组织相关的功能基因被显著富集;KEGG(kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)富集分析发现,与植物-病原体互作和肌醇膦酸代谢相关的通路被显著富集。由此推测,授粉强度的增加可能对柱头和花粉的识别过程产生影响,通过参与柱头和花粉间的信号转导、激素合成过程对花粉管的生长起促进作用,进而影响受精过程。以上结果为理解蓝莓柱头对不同授粉强度的响应机制提供了理论参考,为蓝莓的精确授粉提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
冀薇, 樊莹, 黄家兴, 杨慧鹏, 徐进, 李小英, 郭岳琴, 吴跃国, 李继莲, 姚军. 不同授粉强度对蓝莓柱头响应机制的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 71-82.
Wei JI, Ying FAN, Jiaxing HUANG, Huipeng YANG, Jin XU, Xiaoying LI, Yueqin GUO, Yueguo WU, Jilian LI, Jun YAO. Transcriptome Analysis of Stigma Response Mechanism of Blueberry with Different Pollination Intensity[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 71-82.
开花时间 Flowering time/d | 柱头可授性 Stigma receptivity |
|---|---|
| 0 | + |
| 1 | ++ |
| 2 | +++ |
| 3 | + |
| 4 | +/– |
| 5 | – |
| 6 | – |
表 1 不同花龄的柱头可授性
Table 1 Stigma receptivity of different flower ages
开花时间 Flowering time/d | 柱头可授性 Stigma receptivity |
|---|---|
| 0 | + |
| 1 | ++ |
| 2 | +++ |
| 3 | + |
| 4 | +/– |
| 5 | – |
| 6 | – |
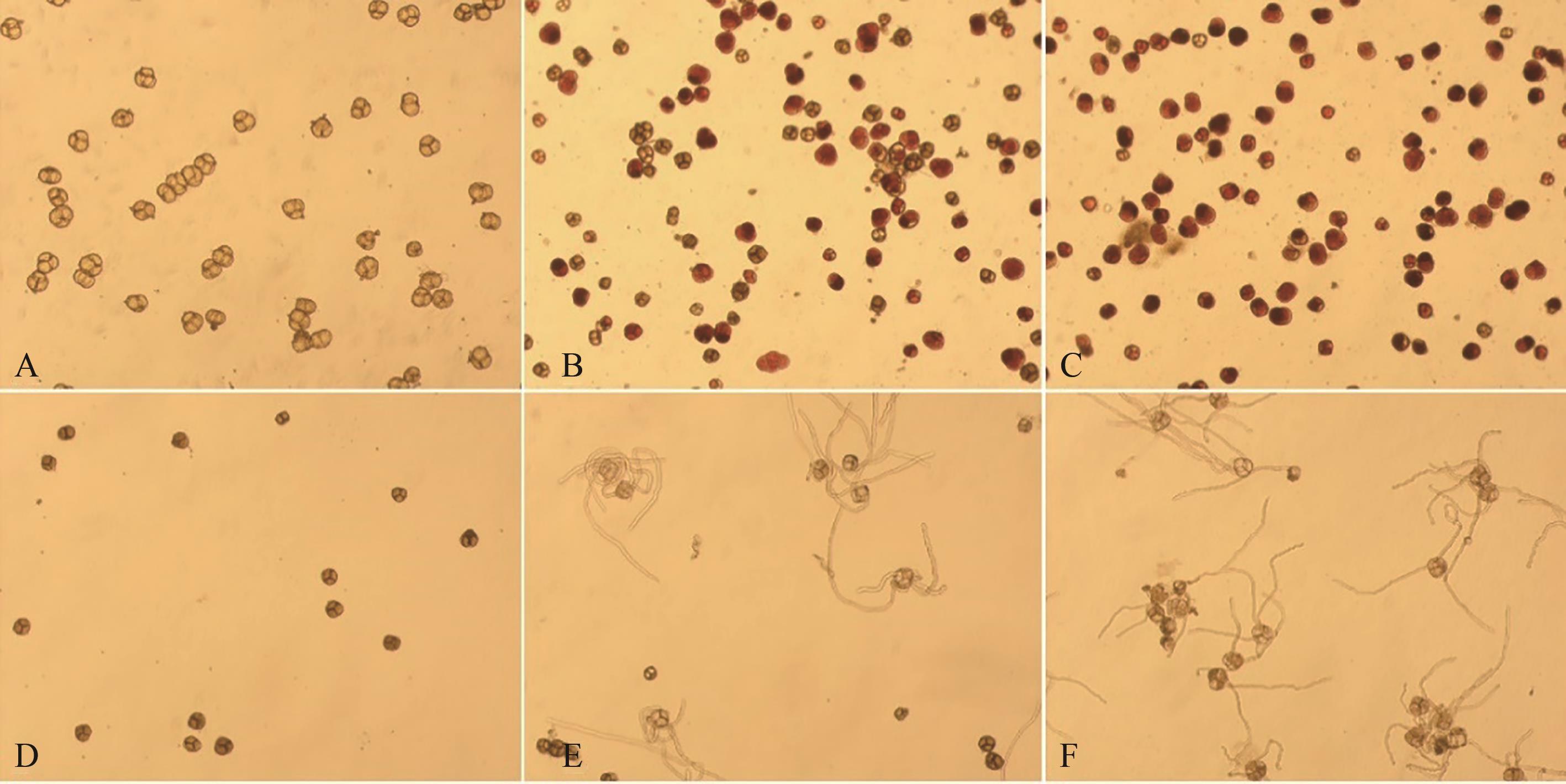
图1 不同处理花粉的TTC染色和体外培养A:F0处理TTC染色;B:F50处理TTC染色;C:F100处理TTC染色;D:F0处理体外培养;E:F50处理体外培养;F:F100处理体外培养
Fig. 1 TTC staining and culture in vitro of pollen under different treatmentsA: TTC staining of F0 treatment; B: TTC staining of F50 treatment; C: TTC staining of F100 treatment; D: Culture medium method of F0 treatment; E: Culture medium method of F50 treatment; F: Culture medium method of F100 treatment

图3 F0与F50处理差异表达基因的GO富集分析注:*代表在P<0.05水平显著富集。
Fig. 3 Go enriched analysis of differentially expressed gene between F0 and F50 treatmentsNote: * indicates significant enrichment at P<0.05 level.
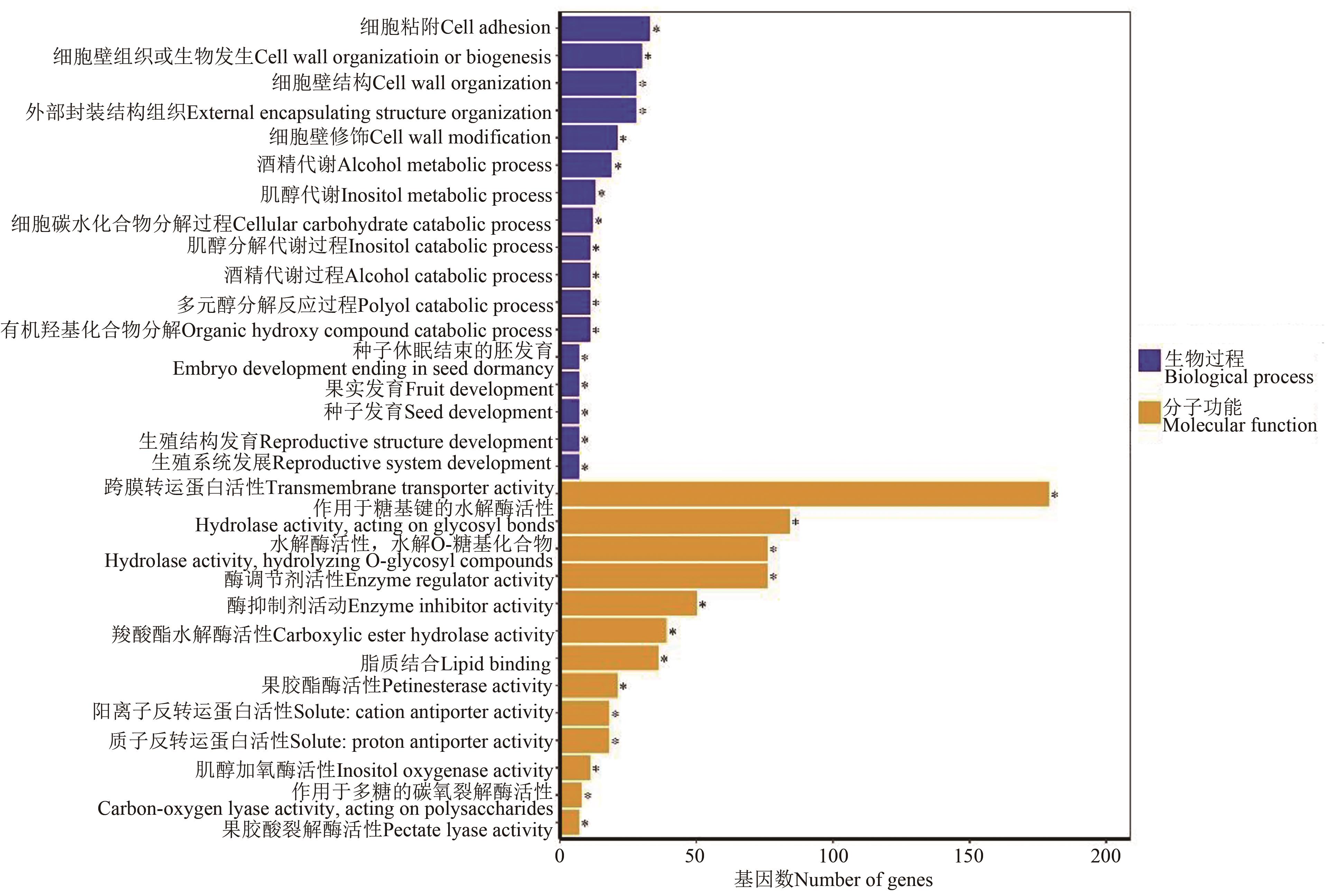
图4 F0与F100处理差异表达基因的GO富集分析注:*代表在P<0.05水平显著富集。
Fig. 4 Go enriched analysis of differentially expressed gene between F0 and F100 treatmentsNote: * indicates significant enrichment at P<0.05 level.
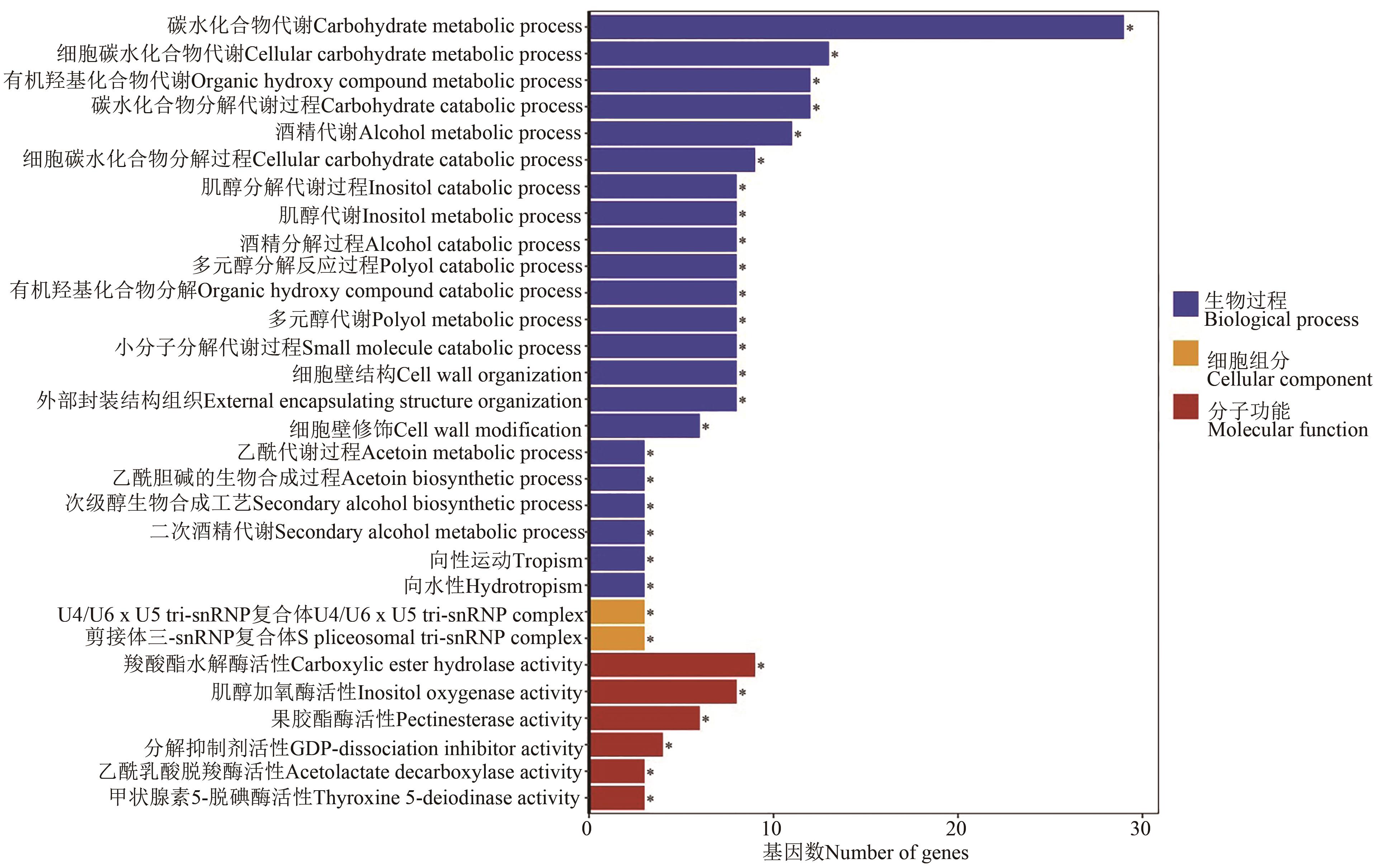
图5 F50与F100处理差异表达基因的GO富集分析注:*代表在P<0.05水平显著富集。
Fig. 5 Go enriched analysis of differentially expressed gene between F50 and F100 treatmentsNote: * indicates significant enrichment at P<0.05 level.
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00040 | 戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸相互转化 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 3.79×10-5 | 0.002 | 10(2.18) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 5.17×10-3 | 0.081 | 5(1.09) |
| ath00062 | 脂肪酸延伸 Fatty acid elongation | 6.61×10-3 | 0.081 | 4(0.87) |
| ath04145 | 吞噬体 Phagosome | 7.12×10-3 | 0.081 | 6(1.31) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 7.27×10-3 | 0.081 | 60(13.10) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 8.05×10-3 | 0.081 | 9(1.97) |
| ath00196 | 光合作用-天线蛋白 Photosynthesisantenna proteins | 0.012 | 0.103 | 3(0.66) |
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 0.022 | 0.167 | 5(1.09) |
| ath00592 | α-亚麻酸代谢 Alpha-linolenic acid metabolism | 0.062 | 0.415 | 3(0.66) |
| ath00966 | 芥子油苷生物合成 Glucosinolate biosynthesis | 0.084 | 0.502 | 2(0.44) |
表2 F0与F50间DEGs的KEGG富集分析
Table 2 KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs between F0 and F50 treatments
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00040 | 戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸相互转化 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 3.79×10-5 | 0.002 | 10(2.18) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 5.17×10-3 | 0.081 | 5(1.09) |
| ath00062 | 脂肪酸延伸 Fatty acid elongation | 6.61×10-3 | 0.081 | 4(0.87) |
| ath04145 | 吞噬体 Phagosome | 7.12×10-3 | 0.081 | 6(1.31) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 7.27×10-3 | 0.081 | 60(13.10) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 8.05×10-3 | 0.081 | 9(1.97) |
| ath00196 | 光合作用-天线蛋白 Photosynthesisantenna proteins | 0.012 | 0.103 | 3(0.66) |
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 0.022 | 0.167 | 5(1.09) |
| ath00592 | α-亚麻酸代谢 Alpha-linolenic acid metabolism | 0.062 | 0.415 | 3(0.66) |
| ath00966 | 芥子油苷生物合成 Glucosinolate biosynthesis | 0.084 | 0.502 | 2(0.44) |
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00040 | 戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸相互转化 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 9.26×10-15 | 1.06×10-12 | 61(1.44) |
| ath04145 | 吞噬体 Phagosome | 1.49×10-10 | 8.56×10-9 | 47(1.11) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 2.70×10-6 | 1.04×10-4 | 454(10.72) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 1.92×10-5 | 5.53×10-4 | 55(1.30) |
| ath00564 | 甘油磷脂代谢 Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 5.56×10-5 | 1.28×10-3 | 36(0.85) |
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 2.77×10-4 | 5.30×10-3 | 29(0.68) |
| ath00565 | 醚脂质代谢 Ether lipid metabolism | 3.59×10-4 | 5.90×10-3 | 15(0.35) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 4.50×10-4 | 6.46×10-3 | 22(0.52) |
| ath04130 | 囊泡运输中的SNARE相互作用 SNARE interactions in vesicular transport | 7.39×10-4 | 9.39×10-3 | 19(0.45) |
| ath00561 | 甘油脂代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 8.17×10-4 | 9.39×10-3 | 23(0.54) |
表3 F0与F100间DEGs的KEGG富集分析
Table 3 KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs between F0 and F100 treatments
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00040 | 戊糖和葡萄糖醛酸相互转化 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 9.26×10-15 | 1.06×10-12 | 61(1.44) |
| ath04145 | 吞噬体 Phagosome | 1.49×10-10 | 8.56×10-9 | 47(1.11) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 2.70×10-6 | 1.04×10-4 | 454(10.72) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 1.92×10-5 | 5.53×10-4 | 55(1.30) |
| ath00564 | 甘油磷脂代谢 Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 5.56×10-5 | 1.28×10-3 | 36(0.85) |
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 2.77×10-4 | 5.30×10-3 | 29(0.68) |
| ath00565 | 醚脂质代谢 Ether lipid metabolism | 3.59×10-4 | 5.90×10-3 | 15(0.35) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 4.50×10-4 | 6.46×10-3 | 22(0.52) |
| ath04130 | 囊泡运输中的SNARE相互作用 SNARE interactions in vesicular transport | 7.39×10-4 | 9.39×10-3 | 19(0.45) |
| ath00561 | 甘油脂代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 8.17×10-4 | 9.39×10-3 | 23(0.54) |
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 1.09×10-8 | 5.97×10-7 | 14(1.48) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 1.16×10-7 | 3.20×10-6 | 11(1.17) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 1.29×10-5 | 2.09×10-4 | 15(1.59) |
| ath04130 | 囊泡运输中的SNARE相互作用 SNARE interactions in vesicular transport | 1.52×10-5 | 2.09×10-4 | 8(0.85) |
| ath00564 | 甘油磷脂代谢 Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 2.09×10-3 | 2.03×10-2 | 8(0.85) |
| ath04070 | 磷脂酰肌醇信号系统 Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 2.21×10-3 | 2.03×10-2 | 7(0.74) |
| ath00380 | 色氨酸代谢 Tryptophan metabolism | 3.11×10-3 | 2.45×10-2 | 6(0.64) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 4.43×10-3 | 3.05×10-2 | 68(7.21) |
| ath00561 | 甘油脂代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 1.36×10-2 | 8.33×10-2 | 5(0.53) |
| ath00941 | 类黄酮生物合成 Flavonoid biosynthesis | 1.66×10-2 | 9.14×10-2 | 3(0.32) |
表4 F50与F100间DEGs的KEGG富集分析
Table 4 KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs between F50 and F100 treatments
通路ID Pathway ID | 通路名称 Pathway name | P值 P value | Padj值 Padj value | DEGs数量(比例) Number of DEGs (percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ath00562 | 肌醇膦酸代谢 Inositol phosphate metabolism | 1.09×10-8 | 5.97×10-7 | 14(1.48) |
| ath00053 | 抗坏血酸和醛酸盐代谢 Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 1.16×10-7 | 3.20×10-6 | 11(1.17) |
| ath04626 | 植物-病原体互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 1.29×10-5 | 2.09×10-4 | 15(1.59) |
| ath04130 | 囊泡运输中的SNARE相互作用 SNARE interactions in vesicular transport | 1.52×10-5 | 2.09×10-4 | 8(0.85) |
| ath00564 | 甘油磷脂代谢 Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 2.09×10-3 | 2.03×10-2 | 8(0.85) |
| ath04070 | 磷脂酰肌醇信号系统 Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 2.21×10-3 | 2.03×10-2 | 7(0.74) |
| ath00380 | 色氨酸代谢 Tryptophan metabolism | 3.11×10-3 | 2.45×10-2 | 6(0.64) |
| ath01100 | 代谢途径 Metabolic pathways | 4.43×10-3 | 3.05×10-2 | 68(7.21) |
| ath00561 | 甘油脂代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 1.36×10-2 | 8.33×10-2 | 5(0.53) |
| ath00941 | 类黄酮生物合成 Flavonoid biosynthesis | 1.66×10-2 | 9.14×10-2 | 3(0.32) |
| 1 | TAKIKAWA M, INOUE S, HORIO F, et al.. Dietary anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice [J]. J. Nutr., 2010, 140(3):527-533. |
| 2 | BABA A B, NIVETHA R, CHATTOPADHYAY I, et al.. Blueberry and malvidin inhibit cell cycle progression and induce mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis by abrogating the JAK/STAT-3 signalling pathway [J]. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2017, 109(Pt 1):534-543. |
| 3 | 马艳萍.蓝莓的生物学特性、栽培技术与营养保健功能[J].中国水土保持,2006(2):47-49. |
| 4 | FALQUE M, VINCENT A, VAISSIERE B E, et al.. Effect of pollination intensity on fruit and seed set in cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) [J]. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 1995, 8(6):354-360. |
| 5 | 高尚,曹小勇,胡选萍,等.不同授粉量对天麻果实发育及结实的影响[J].生物学杂志,2022, 39(2):80-83. |
| GAO S, CAO X Y, HU X P, et al.. Study on the effects of different pollen load on fruit development and seed setting of Gastrodia elata [J]. J. Biol., 2022, 39(2):80-83. | |
| 6 | 申晋山,武文卿,马卫华,等.蜜蜂数量对红富士苹果授粉效果的影响[J].山西农业科学,2022, 50(9):1303-1308. |
| SHEN J S, WU W Q, MA W H, et al.. Effects of bee number on pollination of Fuji apple [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2022, 50(9):1303-1308. | |
| 7 | BASKIN J M, BASKIN C C. Pollen limitation and its effect on seed germination [J]. Seed Sci. Res., 2018, 28(4):253-260. |
| 8 | DOGTEROM M H, WINSTON M L, MUKAI A. Effect of pollen load size and source (self, outcross) on seed and fruit production in highbush blueberry cv. ‘Bluecrop’ (Vaccinium corymbosum; Ericaceae) [J]. Am. J. Bot., 2000, 87(11):1584-1591. |
| 9 | COSTA V, ANGELINI C, DE FEIS I, et al.. Uncovering the complexity of transcriptomes with RNA-Seq [J/OL]. J. Biomed. Biotechnol., 2010, 2010:853916 [2024-01-05].. |
| 10 | FENG C, CHEN M, XU C J, et al.. Transcriptomic analysis of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit development and ripening using RNA-Seq [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2012, 13:19 [2024-01-05]. . |
| 11 | DENG S, CHENG C, LIU Z, et al.. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals a role for anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in the formation of purple peel in Minhou wild banana (Musa itinerans Cheesman) [J]. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol., 2019, 94(2):184-200. |
| 12 | LIU X R, LIU C, LIU X C, et al.. Comprehensive transcriptome analyses of carbohydrate metabolism and flavonoid biosynthesis in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) during fruit maturation [J]. Int. J. Agric. Biol., 2020, 1(24):101-111. |
| 13 | BOAVIDA L C, BORGES F, BECKER J D, et al.. Whole genome analysis of gene expression reveals coordinated activation of signaling and metabolic pathways during pollen-pistil interactions in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2011, 155(4):2066-2080. |
| 14 | 徐晓辉.玉米柱头全基因组表达谱分析及花粉-柱头互作相关基因的鉴定[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2012. |
| XU X H. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in maize silk and the ldentification of genes involved in pollen-silk interaction [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 15 | 杨芩,任永权,廖优江,等.五个兔眼蓝莓品种有效可授期研究[J].北方园艺,2013(14):5-7. |
| YANG Q, REN Y Q, LIAO Y J, et al.. Study on effective pollination period of five cultivars of rabbiteye blueberry [J]. Northern Hortic., 2013,(14):5-7. | |
| 16 | YANG Q, LIU E, FU Y, et al.. High temperatures during flowering reduce fruit set in rabbiteye blueberry [J]. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 2019, 144(5):339-351 |
| 17 | WALTERS J, ISAACS R. Pollen germination and tube growth in northern highbush blueberry are inhibited by extreme heat [J]. Hortscience, 2023, 58(6):635-645 |
| 18 | JIA W, WANG Y, MI Z, et al.. Optimization of culture medium for in vitro germination and storage conditions of Exochorda racemosa pollen [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13:994214 [2024-01-05]. . |
| 19 | 杜学林,刘悦明,黄子锋,等.三角梅属5个品种的花粉活力及柱头可授性比较分析[J].热带作物学报,2022, 43(7):1459-1466. |
| DU X L, LIU Y M, HUANG Z F, et al.. Comparative analysis of pollen viability and stigma receptivity of five Bougainvillea cultivars [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2022, 43(7):1459-1466. | |
| 20 | 宇航.树莓杂交育种技术研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2023. |
| YU H. Study on raspberry cross breeding technology [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| 21 | VAN DOORN W G, WOLTERING E J. Physiology and molecular biology of petal senescence [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2008, 59(3):453-480. |
| 22 | KAO T H, MCCUBBIN A G. How flowering plants discriminate between self and non-self pollen to prevent inbreeding [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93(22):12059-12065. |
| 23 | 王海静,李明媛,武军凯,等.‘鸭梨’及其自交亲和性芽变‘金坠梨’花粉蛋白质组病原防御相关蛋白表达分析[J].河北科技师范学院学报,2018,32(1):1-8. |
| WANG H J, LI M Y, WU J K, et al.. Proteomic analysis of pathogen defense related proteins from self-incompatible ‘Yali’ and its spontaneous self-compatible mutant ‘Jinzhuili’ [J]. J. Hebei Norm. Univ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 32(1):1-8. | |
| 24 | 张小飞.拟南芥配子体发育的基因表达谱特征研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2021. |
| ZHANG X F. Gene expression profile characteristics analysis of gametophyte development in Arabidopsis thaliana [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2021. | |
| 25 | LIU B, MORSE D, CAPPADOCIA M. Compatible pollinations in Solanum chacoense decrease both S-RNase and S-RNase mRNA [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(6):e5774 [2024-01-05]. . |
| 26 | ZHAO P, ZHANG L, ZHAO L. Dissection of the style's response to pollination using transcriptome profiling in self-compatible (Solanum pimpinellifolium) and self-incompatible (Solanum chilense) tomato species [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2015, 15:119 [2024-01-05]. . |
| 27 | SHI D, TANG C, WANG R, et al.. Transcriptome and phytohormone analysis reveals a comprehensive phytohormone and pathogen defence response in pear self-/cross-pollination [J]. Plant Cell Rep., 2017, 36(11):1785-1799. |
| 28 | 齐秀娟.‘天源红’猕猴桃授粉受精生理特性及其相关差异蛋白质组学研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2013. |
| QI X J. Study on physiological characteristics and differential proteomics of pollination and fertilization In ‘Tianyuanhong’ kiwifruit [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| 29 | MALHO R, TREWAVAS A J. Localized apical increases of cytosolic free calcium control pollen tube orientation [J]. Plant Cell, 1996, 8(11):1935-1949. |
| 30 | STEER M W, STEER J M. Pollen tube tip growth [J]. New Phytol., 1989, 111(3):323-358. |
| 31 | MESSERLI M, ROBINSON K R. Tip localized Ca2+ pulses are coincident with peak pulsatile growth rates in pollen tubes of Lilium longiflorum [J]. J. Cell Sci., 1997, 110(Pt 11):1269-1278. |
| 32 | PARYS J B, DE SMEDT H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and its receptors [J]. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 2012, 740:255-279. |
| 33 | BERRIDGE M J, IRVINE R F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction [J]. Nature, 1984, 312(5992):315-321. |
| 34 | MONTEIRO D, LIU Q, LISBOA S, et al.. Phosphoinositides and phosphatidic acid regulate pollen tube growth and reorientation through modulation of [Ca2+]c and membrane secretion [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2005, 56:1665-1674. |
| 35 | KRICHEVSKY A, KOZLOVSKY S V, TIAN G W, et al.. How pollen tubes grow [J]. Dev. Biol., 2007, 303(2):405-420. |
| 36 | YONG J L, SZUMLANSKI A, YANG N Z, et al.. Rho-GTPase-dependent filamentous actin dynamics coordinate vesicle targeting and exocytosis during tip growth [J]. J. Cell Biol., 2008, 181(7):1155-1168. |
| 37 | MALHO R, LIU Q, MONTEIRO D, et al.. Signalling pathways in pollen germination and tube growth [J]. Protoplasma, 2006, 228(1/3):21-30. |
| 38 | ALFORD S R, RANGARAJAN P, WILLIAMS P, et al.. Myo-Inositol oxygenase is required for responses to low energy conditions in Arabidopsis thaliana [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2012, 3:69 [2024-01-05]. . |
| 39 | KANTER U, USADEL B, GUERINEAU F, et al.. The inositol oxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis is involved in the biosynthesis of nucleotide sugar precursors for cell-wall matrix polysaccharides [J]. Planta, 2005, 221(2):243-254. |
| 40 | RUI Y, DINNENY J R. A wall with integrity:surveillance and maintenance of the plant cell wall under stress [J]. New Phytol., 2020, 225(4):1428-1439. |
| 41 | DE WIN A H, PIERSON E S, DERKSEN J. Rational analyses of organelle trajectories in tobacco pollen tubes reveal characteristics of the actomyosin cytoskeleton [J]. Biophys. J., 1999, 76(3):1648-1658. |
| 42 | STAIGER C J, POULTER N S, HENTY J L, et al.. Regulation of actin dynamics by actin-binding proteins in pollen [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2010, 61(7):1969-1986. |
| 43 | 崔红慧.拟南芥基因AtAOG1和MBD3在配子体发育过程中的功能分析[D].北京:中国农业大学,2015. |
| CUI H H. Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis AtAOG1 and MBD3 genes in gametophyte development [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 44 | ZHENG Y, YAN J, WANG S, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the pectate lyase-like (PLL) gene family and functional analysis of two PLL genes in rice [J]. Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2018, 293(6):1317-1331. |
| 45 | KULIKAUSKAS R, MCCORMICK S. Identification of the tobacco and Arabidopsis homologues of the pollen-expressed LAT59 gene of tomato [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 1997, 34(5):809-814. |
| 46 | STEPANOVA A N, ROBERTSON-HOYT J, YUN J, et al.. TAA1-mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for hormone crosstalk and plant development [J]. Cell, 2008, 133(1):177-191. |
| 47 | MA W, LI J, QU B, et al.. Auxin biosynthetic gene TAR2 is involved in low nitrogen-mediated reprogramming of root architecture in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant J., 2014, 78(1):70-79. |
| 48 | ZHAO Y, HULL A K, GUPTA N R, et al.. Trp-dependent auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis: involvement of cytochrome P450s CYP79B2 and CYP79B3 [J]. Genes. Dev., 2002, 16(23):3100-3112. |
| 49 | CECCHETTI V, ALTAMURA M M, FALASCA G, et al.. Auxin regulates Arabidopsis anther dehiscence, pollen maturation, and filament elongation [J]. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(7):1760-1774. |
| 50 | WU J Z, LIN Y, ZHANG X L, et al.. IAA stimulates pollen tube growth and mediates the modification of its wall composition and structure in Torenia fournieri [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2008, 59(9):2529-2543. |
| [1] | 万云星, 闫自杨, 姚军, 郭立明, 朱金忠, 唐建宁, 乔彩云, 匡海鸥, 龚雪阳, 岳丹, 赵文正. 枸杞开花生物学及传粉特征研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 34-43. |
| [2] | 鲁一薇, 夏雪岩, 赵宇, 崔纪菡, 刘猛, 黄玫红, 褚程, 刘建军, 李顺国. 缺钾胁迫下谷子转录组分析及相关基因挖掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 30-44. |
| [3] | 赫淑华, 侯智霞, 王亚晶, 秦偲, 江颖, 张晓涵, 李洋. 秋季剪梢对温室蓝莓芽分化及内源激素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 55-62. |
| [4] | 李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [5] | 岳洁茹, 秦志列, 侯起岭, 苑少华, 郝小聪, 杨吉芳, 白秀成, 赵昌平, 张风廷, 孙辉. BS型小麦光温敏雄性不育系柱头外露规律研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 22-29. |
| [6] | 杨圣艳, 曹漫, 郭宝石, 杨超, 侯智霞. 不同铁环境对蓝莓生长及叶片叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 52-62. |
| [7] | 李相吴, 刘自扬, 徐玉俊, 祝建波, 吴燕民. 真菌诱导子调控紫草素合成的分子机制探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 78-88. |
| [8] | 郭瑞锋, 任月梅, 杨忠, 刘贵山, 任广兵, 张绶, 朱文娟. 草甘膦铵盐诱导谷子雄性不育的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 35-43. |
| [9] | 马淏,张开,金鑫*,姬江涛,朱旭. 基于高光谱成像技术的蓝莓果实成熟度识别研究(英文)[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 80-90. |
| [10] | 李彬彬,侯智霞*,杨俊枫,陈露,万如萌. ‘北陆’蓝莓叶片变色过程中类黄酮和糖的变化特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(3): 20-29. |
| [11] | 黎瑞源1,潘凡2,陈庆富2,石桃雄2*. 苦荞转录组EST-SSR发掘及多态性分析[J]. , 2015, 17(4): 42-52. |
| [12] | 张磊|戴瓯和|李杰坤|黄志平. 大豆雄性不育系柱头活力研究[J]. , 1999, 1(2): 63-65. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号