




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 20-32.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0679
李双1( ), 王爱英2, 焦浈2, 池青2, 孙昊2, 焦涛1(
), 王爱英2, 焦浈2, 池青2, 孙昊2, 焦涛1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-17
接受日期:2022-10-19
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-04
通讯作者:
焦涛
作者简介:李双 E-mail:lishuang970715@163.com;
基金资助:
Shuang LI1( ), Aiying WANG2, Zhen JIAO2, Qing CHI2, Hao SUN2, Tao JIAO1(
), Aiying WANG2, Zhen JIAO2, Qing CHI2, Hao SUN2, Tao JIAO1( )
)
Received:2022-08-17
Accepted:2022-10-19
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
Tao JIAO
摘要:
为探究不同抗盐性小麦对盐胁迫的响应差异,选用‘百农889’和‘中国春’小麦品种,利用200 mmol·L-1 NaCl溶液处理离体叶片和小麦幼苗,对盐胁迫后小麦幼苗叶片的生理、生化特征进行分析,并基于转录组数据分析差异基因表达及可变剪切事件。结果表明,盐胁迫下,‘百农889’离体叶片的失绿程度较‘中国春’轻微;伊文思蓝染色后,‘中国春’离体叶片的蓝色着色范围更大,且细胞相对活性显著降低;‘中国春’幼苗表现出明显的萎蔫、倒伏,‘百农889’幼苗的形态与对照组无明显差异;2个品种的相对电解质渗漏率都有所增加,但‘中国春’幼苗的相对电解质渗漏率增幅更大;‘中国春’的净光合速率(net photosynthetic rate,Pn)和气孔导度(stomatal conductance,Gs)受到显著抑制,‘百农889’的净光合速率和气孔导度与对照比无明显变化。转录组测序结果分析表明,与‘中国春’相比,‘百农889’中上调差异表达基因2 299个,下调差异表达基因2 527个;对差异表达基因的GO(gene ontology)富集分析发现,与叶绿体、光合作用和质膜相关的功能基因被显著富集;KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)富集分析发现,与植物激素信号转导和植物次生代谢物相关的通路被显著富集。盐胁迫下,‘中国春’表现出更多的可变剪切事件,且主要富集在RNA转运和内质网蛋白加工等通路中。因此,小麦可以通过调控与叶绿素、质膜、次生代谢物以及光合作用相关基因的表达来抵抗盐胁迫,可变剪切事件的发生也说明小麦可以通过调控基因互作网络来应对盐胁迫。
中图分类号:
李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32.
Shuang LI, Aiying WANG, Zhen JIAO, Qing CHI, Hao SUN, Tao JIAO. Physiological and Chemical Characteristics and Transcriptome Analysis of Different Type of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 20-32.
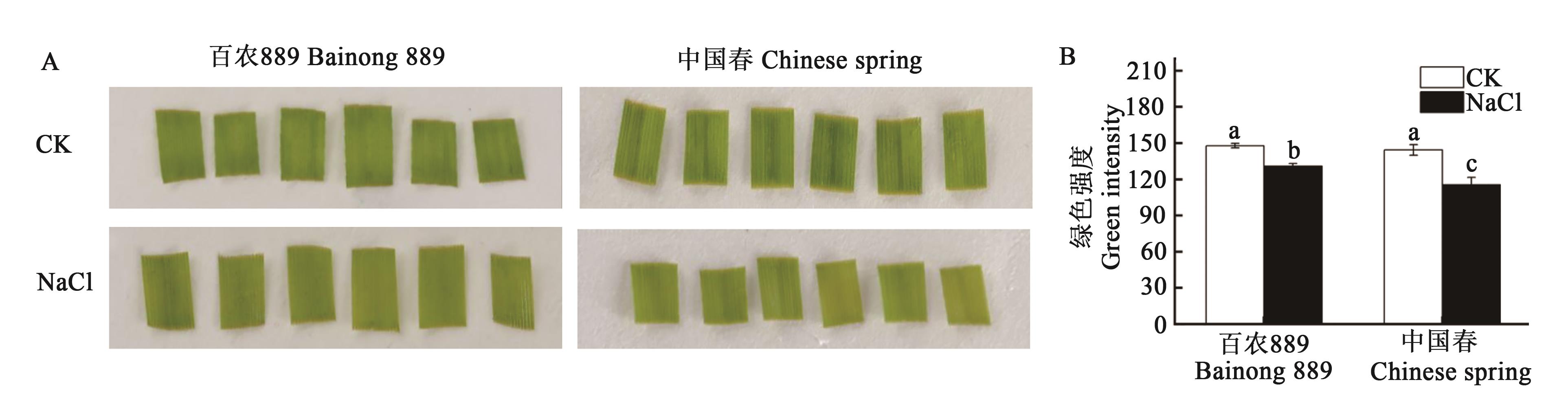
图1 盐胁迫下小麦离体叶片的形态和绿色强度A:叶片形态;B:叶片的绿色强度。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 1 Leaf morphology and geen intensity of isolated wheat leaf under salt stressA: Leaf morphology; B: Green intensity of leaf. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
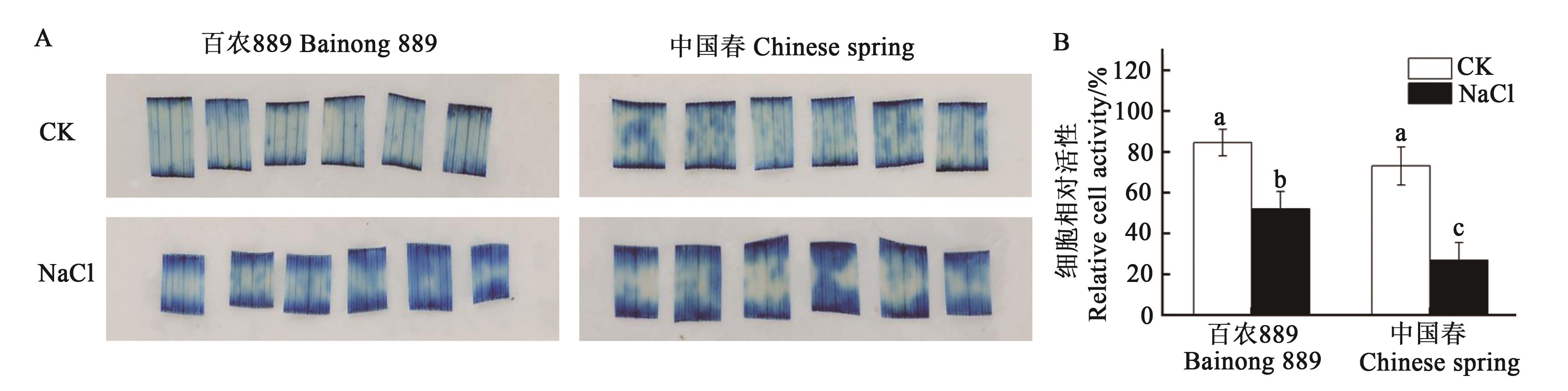
图2 盐胁迫下小麦离体叶片的伊文思蓝染色及细胞相对活性A:伊文思蓝染色;B:细胞相对活性。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 2 Evans blue staining and relative cell activity in isolated leaves of under salt stressA: Evans blue staining; B: Relative cell activity. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
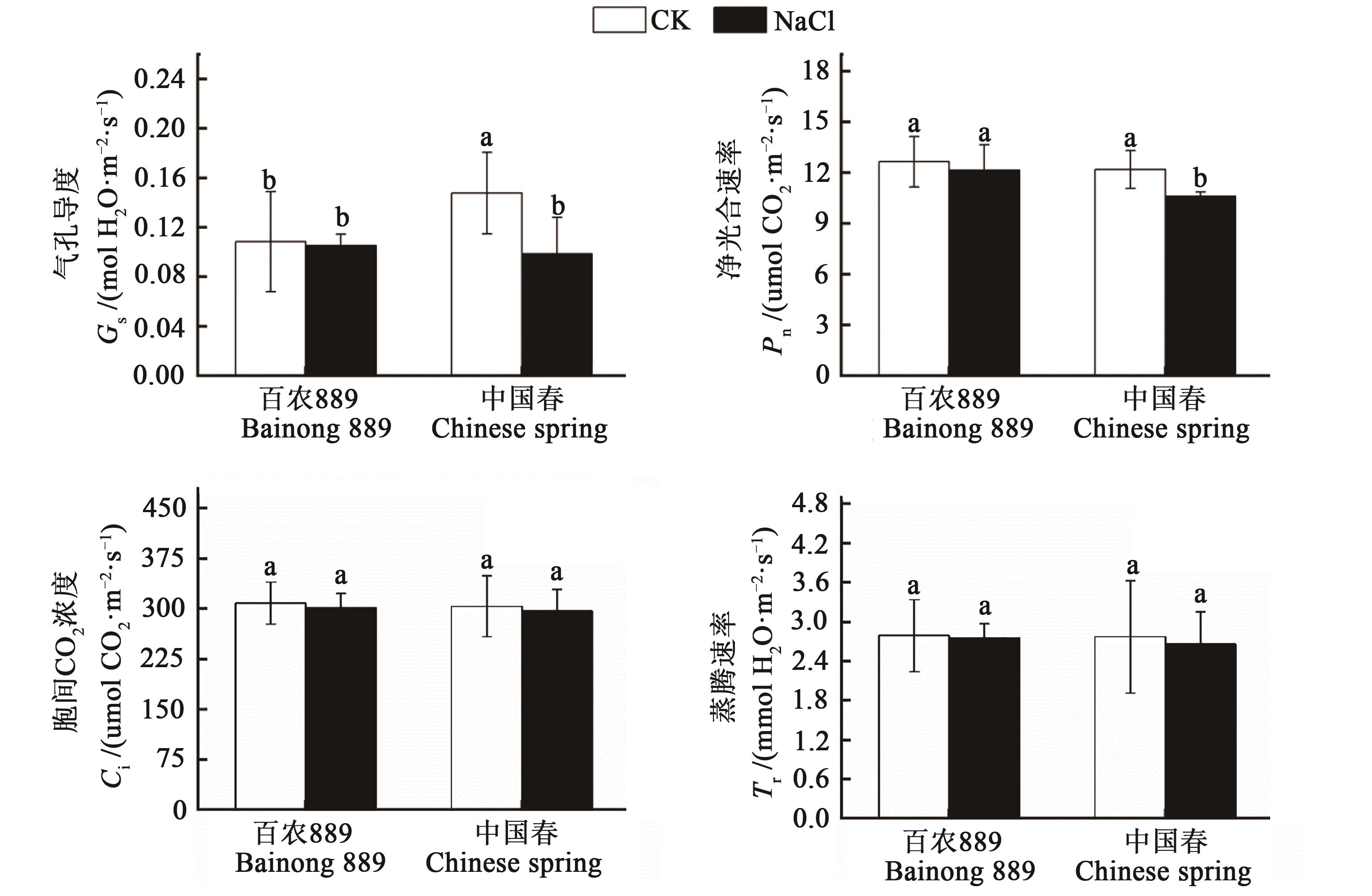
图4 盐胁迫下‘百农889’‘中国春’叶片的光合特性注:不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Photosynthetic characteristics of leaf of ‘Bainong 889’ and ‘Chinese spring’ under salt stressNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
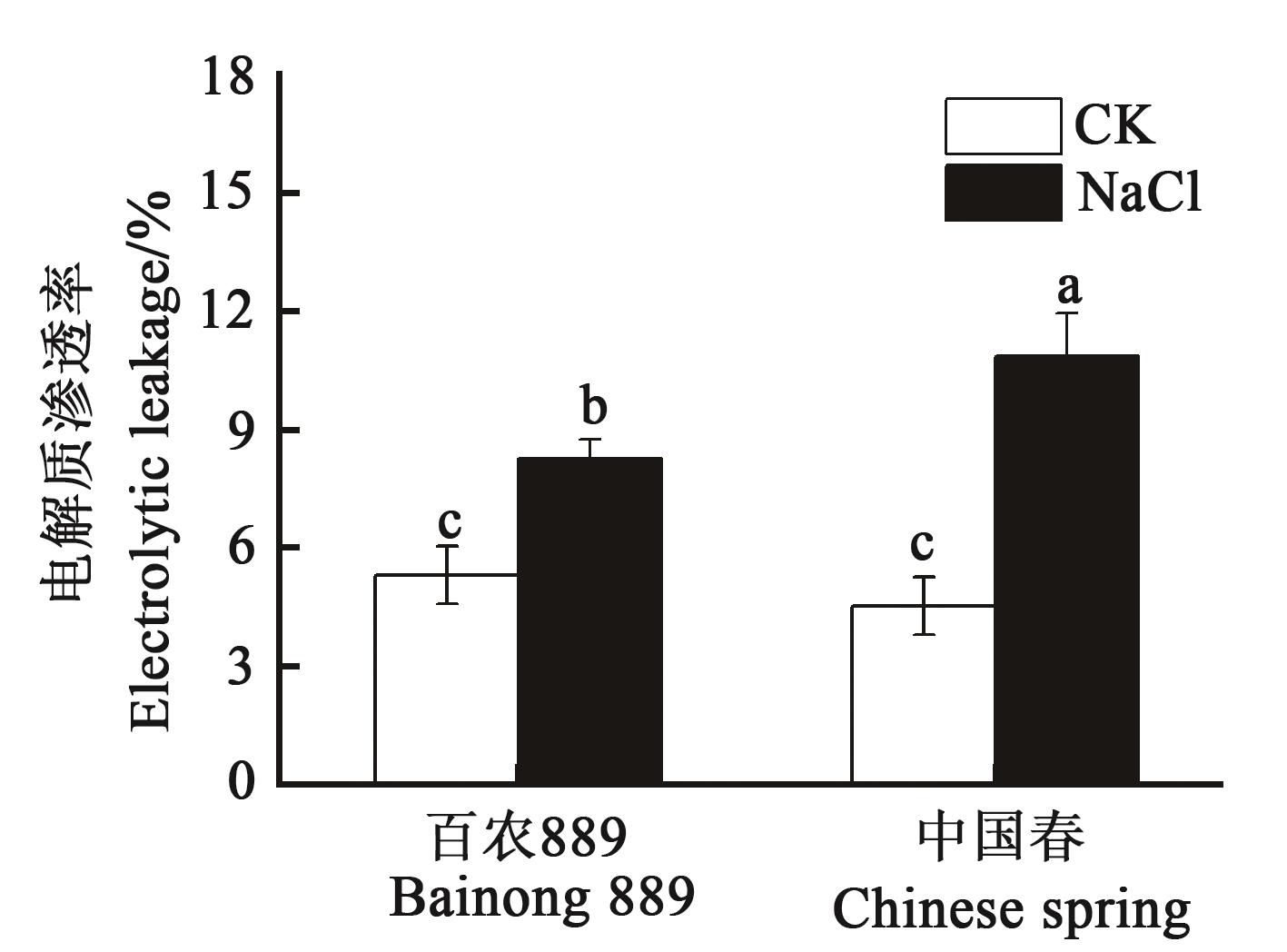
图5 盐胁迫下‘百农889’‘中国春’叶片相对电解质渗透率Fig. 5 Relative electrolyte leakage rate of leaves in ‘Bainong 889’ and ‘Chinese spring’ under salt stress注:不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。Note:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
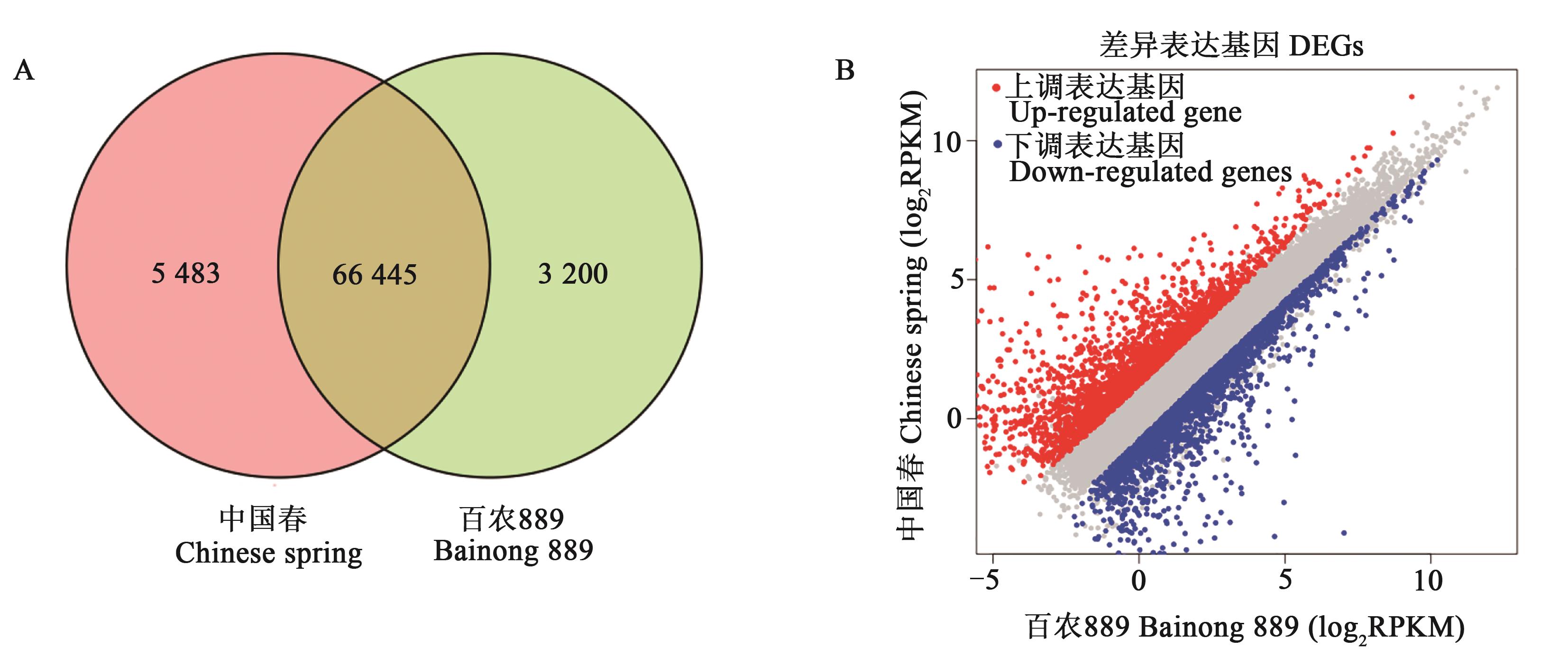
图6 盐胁迫下小麦叶片中基因的分布和差异表达A:基因分布情况的维恩图;B:盐胁迫下两个品种小麦差异表达基因表达量的散点图
Fig. 6 Gene distribution and differential expression in wheat leaves under salt stressA: Venn diagram of gene distribution; B: Scatter plot of differentially expressed genes in two wheat cultivars under salt stress

图7 盐胁迫下小麦叶片差异表达基因的GO富集(前10条)A:上调基因;B:下调基因
Fig. 7 GO enrichment map of DEGs in wheat leaves under salt stress (top 10)A: Up-regulated gene; B: Down-regulated gene
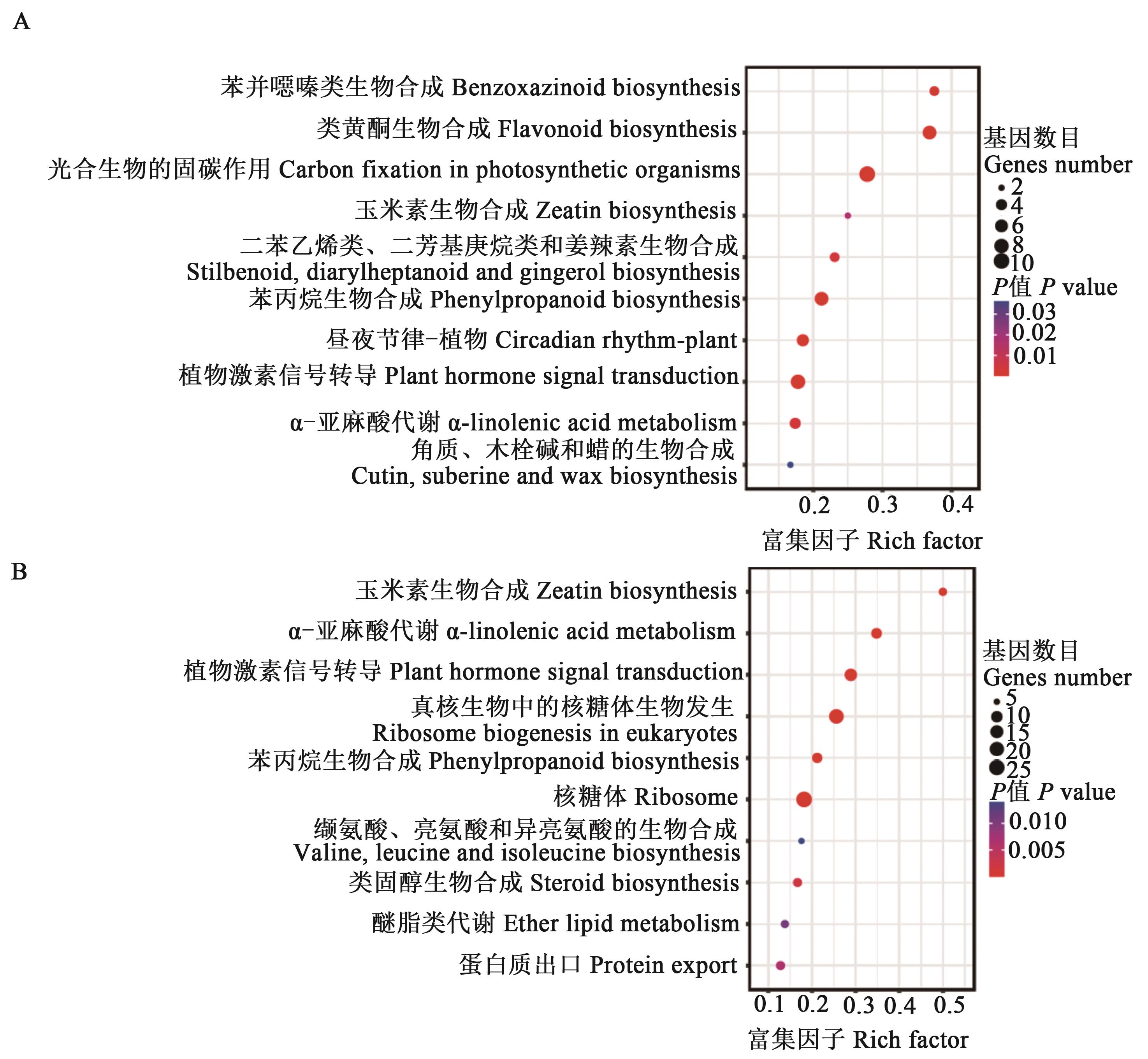
图8 盐胁迫下小麦叶片差异表达基因的KEGG通路富集(前10条)A:上调基因;B:下调基因
Fig. 8 KEGG pathway enrichment of differentially expressed genes in wheat leaves under salt stress (top 10)A: Up-regulated gene; B: Down-regulated gene
| 可变剪切事件AS event | 基因数/可变剪切数 Genes number/ASs number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
中国春 Chinese spring | 百农889 Bainong 889 | ||
| 总计Total | 8 966/14 307 | 8 880/14 173 | |
| SE | 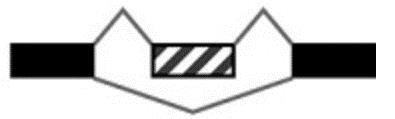 | 5 685/7 954 | 5 668/7 931 |
| A5SS | 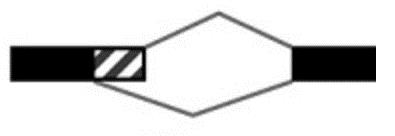 | 1 312/1 476 | 1 286/1 445 |
| A3SS |  | 3 113/3 785 | 3 066/3 716 |
| MXE |  | 329/142 | 333/421 |
| RI |  | 603/680 | 583/660 |
表1 转录组中可变剪切基因数/事件数统计
Table 1 Variable splicing gene number/event number statistics in transcriptome
| 可变剪切事件AS event | 基因数/可变剪切数 Genes number/ASs number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
中国春 Chinese spring | 百农889 Bainong 889 | ||
| 总计Total | 8 966/14 307 | 8 880/14 173 | |
| SE |  | 5 685/7 954 | 5 668/7 931 |
| A5SS |  | 1 312/1 476 | 1 286/1 445 |
| A3SS |  | 3 113/3 785 | 3 066/3 716 |
| MXE |  | 329/142 | 333/421 |
| RI |  | 603/680 | 583/660 |

图9 盐胁迫下‘中国春’和‘百农889’中特异和差异可变剪切A:盐胁迫下2个小麦品种中发生可变剪切基因的比较;B:百农889的差异可变剪切事件数量
Fig. 9 Specific and differential variable shear of ‘Chinese spring’ and ‘Bainong 889’ under salt stressA: Comparison of variable splicing genes in 2 wheat varieties under salt stress; B: Number of differential variable shearing events

图10 盐胁迫下中国春和百农889中差异可变剪切的富集分析A:GO富集分析;B:KEGG富集分析
Fig. 10 Enrichment analysis of differential variable shear in Chinese spring and Bainong 889 under salt stressA: GO enrichment analysis; B: KEGG enrichment analysis
| 1 | JAMES R A, BLAKE C, BYRT C S, et al.. Major genes for Na+ exclusion, Nax1 and Nax2 (wheat HKT1;4 and HKT1;5 ), decrease Na+ accumulation in bread wheat leaves under saline and waterlogged conditions [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2011, 62(8):2939-2947. |
| 2 | 朱建峰,杨秀艳,武海雯,等.植物种子萌发期耐盐碱性提高技术研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2020,36(2):158-168. |
| ZHU J F, YANG X Y, WU H W, et al.. Research advances in salt and alkali tolerance improvement technology at the seed germination stage [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2020, 36(2):158-168. | |
| 3 | YU Z P, DUAN X B, LUO L, et al.. How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2020, 25(11):1117-1130. |
| 4 | SONG J, WANG B S. Using euhalophytes to understand salt tolerance and to develop saline agriculture: Suaeda salsa as a promising model [J]. Ann. Bot., 2015, 115(3):541-553. |
| 5 | 朱建峰,崔振荣,吴春红,等.我国盐碱地绿化研究进展与展望[J].世界林业研究,2018,31(4):70-75. |
| ZHU J F, CUI Z R, WU C H, et al.. Research advances and prospect of saline and alkali land greening in China [J]. World For. Res., 2018, 31(4):70-75. | |
| 6 | 白龙强,李衍素,于贤昌,等.土壤含盐量对有机基质栽培番茄生长、光合特性及产量的影响[J].中国蔬菜,2013(2):41-45. |
| BAI L Q, LI Y S, YU X C, et al.. Effects of soil Salinity on growth, photosynthetic characters and yield of tomato cultivated in organic substrate [J]. China Veget., 2013(2):41-45. | |
| 7 | 齐月.CaCl2对盐胁迫下百合植株生理生化的影响[D].大连:大连理工大学,2019. |
| QI Y. Physiological and biochemical effect of CaCl2 on lily under salt stress [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 8 | 包灵.盐胁迫对盐角草幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2017. |
| BAN L. Effect of stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Salicornia europaea seedings [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 9 | 贾旭梅,朱燕芳,王海,等.垂丝海棠应对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应[J].生态学报,2019,39(17):6349-6361. |
| JIA X M, ZHU Y F, WANG H, al.el. Study on physiological response of Malus halliana to saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(17):6349-6361. | |
| 10 | ZHANG J L, SHI H Z. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of plant salt tolerance [J]. Photosynt. Res., 2013, 115(1):1-22. |
| 11 | 陈小梅,任崴,马林.13个小麦品种(系)的耐盐性研究[J].新疆农业科学,2011,48(12):2211-2216. |
| CHEN X M, REN W, MA L. The study on salt-tolerance of thirteen wheat varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2011, 48(12):2211-2216. | |
| 12 | 冯巩俐,徐玉玲,蒋晓煜,等.两种春小麦幼苗光合特性对盐胁迫的响应比较[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2020,55(1):45-55. |
| FENG G L, XU Y L, JIANG X Y, et al.. Comparsion of photosynthetic characteristics of two spring wheat seedlings to salt stress [J] J. Gansu Agric.Univ., 2020, 55(1):45-55. | |
| 13 | 钮力亚,王伟,王伟伟,等.盐胁迫下小麦品种生理指标的变化规律[J].中国农学通报,2019,35(2):1-4. |
| NIU L Y, WANG W, WANG W W, et al.. Physiological indexes of wheat varieties under salt stress: the change law [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2019, 35(2):1-4. | |
| 14 | 余世洲.普通小麦种质资源耐盐性鉴定及相关基因挖掘[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2020. |
| YU S Z. Identification of salinity tolerance and mining the related functional genes in common wheat (Triticum aestuvum L.) [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2020. | |
| 15 | 韩化南.小麦渐渗系盐碱胁迫应答与发育调控相关性研究[D].济南:山东大学,2018. |
| HAN H N. Correlation between salt/alkali stress response and developmentai regulation in wheat introgression lines [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018. | |
| 16 | 王爱英,李双,焦浈,等.PEG-6000模拟干旱对不同抗性小麦品种光合和叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2022,57(4):47-59. |
| WANG A Y, LI S, JIAO Z, et al.. Effects of PEG-6000 simulated drought stress on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of different drought resistant wheat varieties [J]. J. Gansu Agric. Univ., 2022, 57(4):47-59. | |
| 17 | 刘楠,林植芳.用伊文思蓝染色法检测植物整体叶片的细胞活性[J].植物生理学报,2011,47(6):570-574. |
| LIU N, LIN Z F. Use of evans blue for testing cell viability of intact leaves of plant [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2011, 47(6):570-574. | |
| 18 | DIONISIO-SESE M L, TOBITA S. Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress [J]. Plant Sci., 1998, 135(1):1-9. |
| 19 | 江梦圆.干旱胁迫对冬小麦生长的影响机理及模拟研究[D].南京:南京信息工程大学,2020. |
| JIANG M Y. The study of influencing mechanism of drought stress on winter wheat growth and its model simulation [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2020. | |
| 20 | International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium. Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome [J]. Science, 2018, 361(6403):661-678. |
| 21 | MORTAZAVI A, WILLIAMS B A, MCCUE K, et al.. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq [J]. Nat. Methods, 5(7):621-628. |
| 22 | ROBINSON M D, MCCARTHY D J, SMYTH G K. EdgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(1):139-140. |
| 23 | WRIGHT G M, SIMON R M. A random variance model for detection of differential gene expression in small microarray experiments [J]. Bioinformatics, 2003, 19(18):2448-2455. |
| 24 | SHEN S H, PARK J W, LU Z X, et al.. rMATS: robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2014, 111(51):5593-5601. |
| 25 | 蔡晓锋,胡体旭,叶杰,等.植物盐胁迫抗性的分子机制研究进展[J].华中农业大学学报,2015,34(3):134-141. |
| CAI X F, HU T X, YE J, et al.. Molecular mechanisms of salinity tolerance in plants [J]. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ., 2015, 34(3):134-141. | |
| 26 | 齐琪,马书荣,徐维东.盐胁迫对植物生长的影响及耐盐生理机制研究进展[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(8):2741-2746. |
| QI Q, MA S R, XU W D. Advances in the effects of salt stress on plant growth and physiological mechanisms of salt tolerance [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(8):2741-2746. | |
| 27 | GONG X L, CHAO L, ZHOU M, et al.. Oxidative damages of maize seedlings caused by exposure to a combination of potassium deficiency and salt stress [J]. Plant Soil, 2011, 340(1-2):443-452. |
| 28 | 刘国华,周兴元,杨士虎.盐胁迫对3种四照花属植物生理特性的影响[J].西部林业科学,2018,47(2):59-64. |
| LIU G H, ZHOU X Y, YANG S H. The effects of salt stress on physiology characteristics of Dendrobenthamia [J]. J. West China For. Sci., 2018, 47(2):59-64. | |
| 29 | 贾旭梅,朱燕芳,王海,等.垂丝海棠应对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应[J].生态学报,2019,39(17):6349-6361. |
| JIA X M, ZHU Y F, WANG H, et al.. Study on physiological response of Malus halliana to saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(17):6349-6361. | |
| 30 | 石玉.外源硅对番茄幼苗水分胁迫伤害的缓解效应及机理研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2014. |
| SHI Y. Study on alleviative effects of exogenous silicon on water stress-induced injury and the underl ying mechanisms in tomato seedlings [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014. | |
| 31 | LIN Z F, LIU N, LIN G Z, et al.. Factors altering the membrane fluidity of spinach thylakoid as determined by fluorescence polarization [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2011, 33(3):1019-1024. |
| 32 | 徐宇,肖化云,郑能建,等.植物组织中游离氨基酸在盐胁迫下响应的研究进.环境科学与技术[J].2016,39(7):40-47. |
| XU Y, XIAO H Y, ZHENG N J, et al.. Progress on responding of free amino acid in plants to salt stress [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2016, 39(7):40-47. | |
| 33 | 梁勇.外源硒对硬粒小麦营养积累及盐胁迫缓解效应研究[D].成都:成都大学,2020. |
| LIANG Y. Alleviating effects of exogenous selenium on nutrient accumulation and salt stress in durum wheat [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University, 2020. | |
| 34 | 余燕.多胺对小麦耐铝性的调控作用及其机理[D].杭州:浙江大学,2016. |
| YU Y. The role of polyamines in adaptive response to aluminum toxicity in two wheat genotypes differing in aluminum tolerance [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016. | |
| 35 | THALHAMMER A, HINCHA D K, ZUTHER E. Measuring freezing tolerance: electrolyte leakage and chlorophyll fluorescence assays [J]. Methods Mol. Biol., 2014, 1166(3):15-24. |
| 36 | MANE A V, KARADGE B A, SAMANT J S. Salinity induced changes in photosynthetic pigments and polyphenols of Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle [J]. Pharm. Chem. J., 2010, 2(3):338-347. |
| 37 | 何奇江.盐胁迫下雷竹的离子响应及生理生态变化[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2011. |
| HE Q J. The ionic response and physiological ecological changes of Ph . praecox under salt stress [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2011. | |
| 38 | 赵秀婷,王延双,段劼,等.盐胁迫对红花玉兰嫁接苗生长和光合特性的影响[J].林业科学,2021,57(4):43-53. |
| ZHAO X T, WANG Y S, DUAN J, et al.. Effects of salt stress on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Magnolia wufengensis grafted seedlings [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2021, 57(4):43-53. | |
| 39 | 董明,再吐尼古丽·库尔班,吕芃,等.高粱苗期耐盐性转录组分析和基因挖掘[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(22):3987-4001. |
| DONG M, KUERBAN Z, LV F, et al.. Transcriptome analysis and gene mining of salt tolerance in sorghum seedlings (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(22):3987-4001. | |
| 40 | 卢锐,李培英.偃麦草盐胁迫下转录组分析[J].草地学报,2020,28(1):31-44. |
| LU R, LI P Y. Transcriptome analysis of elytrigia under salt stress [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2020, 28(1):31-44. | |
| 41 | 康益晨.马铃薯响应碱性盐胁迫的生理及分子机制研究[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2021. |
| KANG Y C. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of Solanum tuberosum L. in response to alkaline salt stress [D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 42 | 黄婷.紫花苜蓿响应盐胁迫的比较转录组学分析和植物耐盐机制研究[D].银川:宁夏大学,2020. |
| HUANG T. Comparative transcriptome analysis of alfalfa responses to salt stress and the investigation of mechanism of plant salt tolerance [D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2020. | |
| 43 | 冯雅岚,熊瑛,张均,等.可变剪切在植物发育和非生物胁迫响应中的作用[J].核农学报,2020,34(1):62-70. |
| FENG Y L, XIONG Y, ZHANG J, et al.. Role of alternative splicing in plant development and abiotic stress responses [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2020, 34(1):62-70. | |
| 44 | 解元坤.栽培稻和野生稻间可变剪切的全基因组差异研究[D].沈阳:沈阳师范大学,2020. |
| JIE Y K. Genome-wide differences in alternative splicing between subspecies Oryza sativa and Oryza rufipogon Griff [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2020. | |
| 45 | 张贝贝.甜瓜对盐碱胁迫的形态学与生理生化响应和转录组分析[D].福州:福建农林大学,2019. |
| ZHANG B B. Response of melon to saline-alkali stress at morphological, physiological, biochemical and transcriptome levels [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. | |
| 46 | 冯雅岚,熊瑛,张均,等.可变剪切在植物发育和非生物胁迫响应中的作用[J].核农学报,2020,34(1):62-70. |
| FENG Y L, XIONG I, ZHANG J, et al.. Role of alternative splicing in plant development and abiotic stress responses [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2020, 34(1):62-70. | |
| 47 | 李娇,郭予琦,崔伟玲,等.玉米苗期SR蛋白基因家族的干旱胁迫应答[J].遗传,2014,36(7):697-706. |
| LI J, GUO Y Q, CUI W L, et al.. Response of maize serine/arginine-rich protein gene family in seedlings to drought stress [J]. Hereditas, 2014, 36(7):697-706. |
| [1] | 张宏, 李卫国, 张晓东, 卢必慧, 张琤琤, 李伟, 马廷淮. 基于HJ-1星和GF-1号影像融合特征提取冬小麦种植面积[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 109-119. |
| [2] | 张景云, 关峰, 石博, 万新建. 小麦根系分泌物对苦瓜幼苗生长及土壤生物学环境的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 181-190. |
| [3] | 王韵弘, 苗琪, 李俊超, 王红叶, 张济世, 崔振岭. 田间管理措施对滨海盐渍地区中低产田生产力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 163-172. |
| [4] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [5] | 杨圣艳, 曹漫, 郭宝石, 杨超, 侯智霞. 不同铁环境对蓝莓生长及叶片叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 52-62. |
| [6] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [7] | 姜雪敏, 陈向前, 李红燕, 姜奇彦. 小麦盐胁迫响应的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [8] | 田蕊, 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆抗旱遗传位点及候选基因发掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 69-82. |
| [9] | 赵明宇, 贾浩, 石晓宇, 潘义, 黄妤韵, 王凯澄, 褚庆全. 近30年黄淮海农作区冬小麦水足迹分布变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 138-147. |
| [10] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [11] | 吴雨露, 扈嘉鑫, 陈宇熙, 郑炳松, 闫道良. 外施α-酮戊二酸对盐胁迫下海滨锦葵生长、碳氮磷养分积累及其计量关系的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [12] | 朱莹雪, 王琪, 马献发, 焦玉生, 高金旭, 毛卫佳, 付佳, 孙雪岽, 元野. 烤烟生长期叶片颜色特征值及其氮素诊断模型[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 54-62. |
| [13] | 麻仲花, 陈娟, 吴娜, 满本菊, 王晓港, 者永清, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期光合特性与总生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [14] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [15] | 王小婷, 张芃芃. 集胞藻6803中丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶系统发育和功能概述[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 66-76. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号