




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 153-161.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0729
• 食品质量 加工储运 • 上一篇
周晓凤1,2( ), 李湘钰1,3, 冯岚3, 吴翠云1,3(
), 李湘钰1,3, 冯岚3, 吴翠云1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-05
接受日期:2024-04-09
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-03-14
通讯作者:
吴翠云
作者简介:周晓凤 E-mail:853843047@qq.com;
基金资助:
Xiaofeng ZHOU1,2( ), Xiangyu LI1,3, Lan FENG3, Cuiyun WU1,3(
), Xiangyu LI1,3, Lan FENG3, Cuiyun WU1,3( )
)
Received:2023-10-05
Accepted:2024-04-09
Online:2025-03-15
Published:2025-03-14
Contact:
Cuiyun WU
摘要:
为进一步明确梨果实中酚类物质含量的空间分布特征,选取晚秀和85-8-13为试材,采用紫外分光光度法及高效液相色谱法,开展梨果实不同部位总黄酮、总酚及酚类物质组成含量的分布差异研究。结果表明,晚秀和85-8-13果实不同部位的总酚、总黄酮含量均表现为果皮>果核>果肉(上、中、下、内、外),且85-18-13果实各部位的总酚、总黄酮含量均显著高于晚秀。梨果实中检测出熊果苷、儿茶素、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、槲皮葡萄糖苷、槲皮素鼠李糖苷、山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷、山柰酚-3-O-葡萄糖苷、山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-芸香糖苷、莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷共13种酚类物质,其中晚秀果实中的酚类物质的种类更多,而85-18-13酚类物质的含量更高。梨果实中各酚类物质含量均表现为果皮>果核>果肉,且近果梗处果肉的熊果苷含量均高于其他部位;其次为近萼洼处果肉的绿原酸、表儿茶素含量较高。主成分综合评价表明,果皮得分远高于果核及果肉,晚秀在近果心和萼洼处果肉的酚类物质含量较高,而85-8-13在近果梗和萼洼处果肉的酚类物质含量略高于其余部位。以上研究结果为梨品质调控与遗传改良提供了补充和参考。
中图分类号:
周晓凤, 李湘钰, 冯岚, 吴翠云. 梨果实酚类物质组成及含量差异研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 153-161.
Xiaofeng ZHOU, Xiangyu LI, Lan FENG, Cuiyun WU. Study on Differences in Phenolic Composition and Content of Pear Fruit[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 153-161.
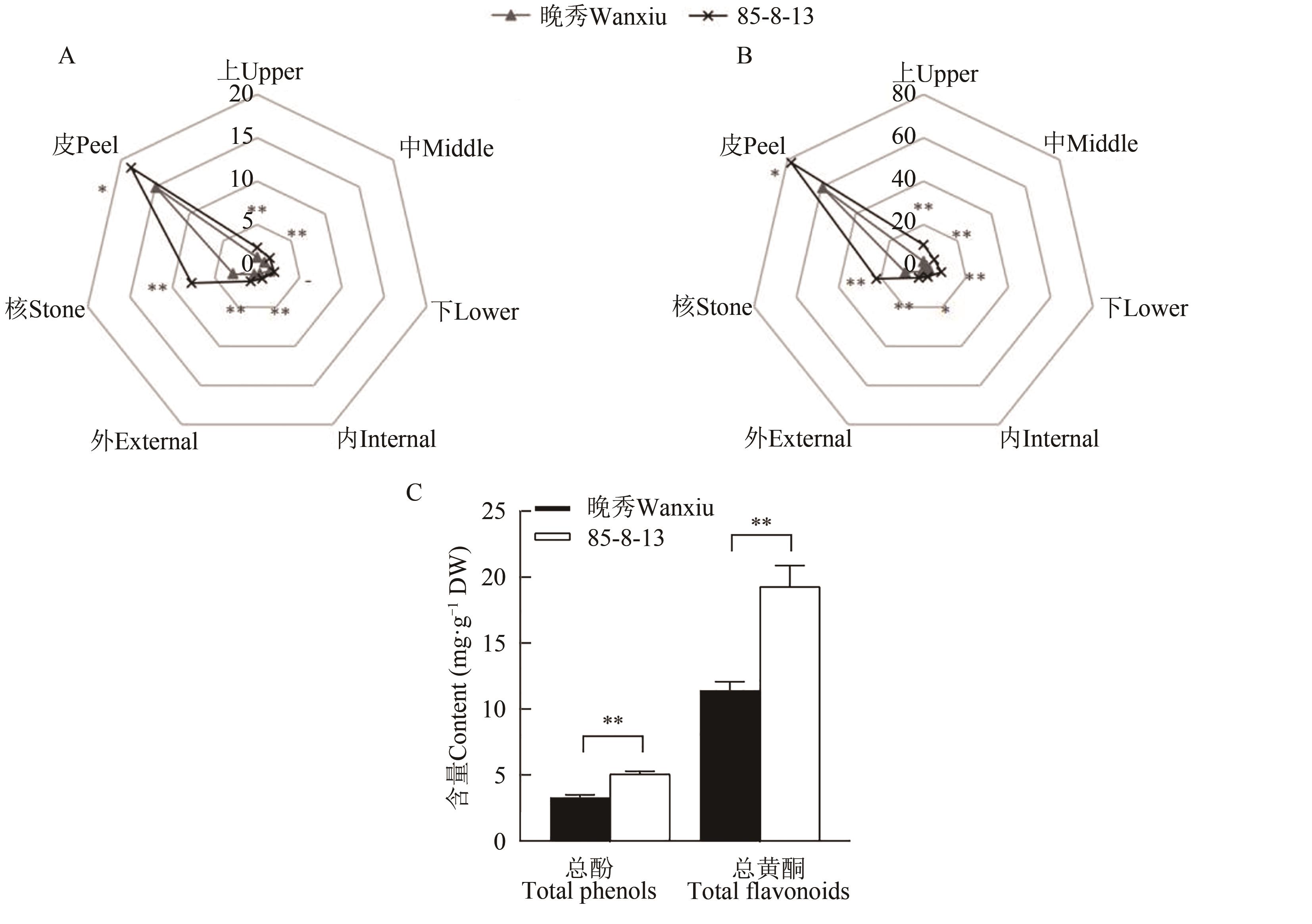
图1 梨果实不同部位的总酚、总黄酮含量A:总酚;B:总黄酮;C:不同梨品种间总酚、总黄酮含量。*和**分别表示不同品种间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Contents of total phenols and total flavonoids in different parts of pear fruitA: Total phenols; B: Total flavonoids; C: Total phenols and flavonoids content among different varieties. * and ** indicate significant differences between different varieties at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 组分 Component | 晚秀 Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | 显著性Significant |
|---|---|---|---|
| 熊果苷Arbutin | 989.22 | 1 255.70 | ** |
| 儿茶素 Catechin | 85.71 | 73.40 | ** |
| 绿原酸 Chlorogenic acid | 175.47 | 483.53 | ** |
| 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 182.92 | 369.17 | ** |
| 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 66.31 | 0.18 | ** |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 18.35 | 118.44 | ** |
| 莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 2.92 | 9.05 | ** |
| 槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 120.76 | — | — |
| 槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 20.87 | 18.22 | ns |
| 异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 71.36 | — | — |
| 山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 51.63 | 311.40 | ** |
| 异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 0.89 | 3.05 | ** |
| 山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 30.58 | 31.37 | ns |
表1 2个梨品种(系)果实酚类物质组分及含量 (μg·g-1DW)
Table 1 Phenolic components and contents in fruits of 2 pear varieties (lines)
| 组分 Component | 晚秀 Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | 显著性Significant |
|---|---|---|---|
| 熊果苷Arbutin | 989.22 | 1 255.70 | ** |
| 儿茶素 Catechin | 85.71 | 73.40 | ** |
| 绿原酸 Chlorogenic acid | 175.47 | 483.53 | ** |
| 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 182.92 | 369.17 | ** |
| 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 66.31 | 0.18 | ** |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 18.35 | 118.44 | ** |
| 莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 2.92 | 9.05 | ** |
| 槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 120.76 | — | — |
| 槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 20.87 | 18.22 | ns |
| 异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 71.36 | — | — |
| 山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 51.63 | 311.40 | ** |
| 异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 0.89 | 3.05 | ** |
| 山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 30.58 | 31.37 | ns |
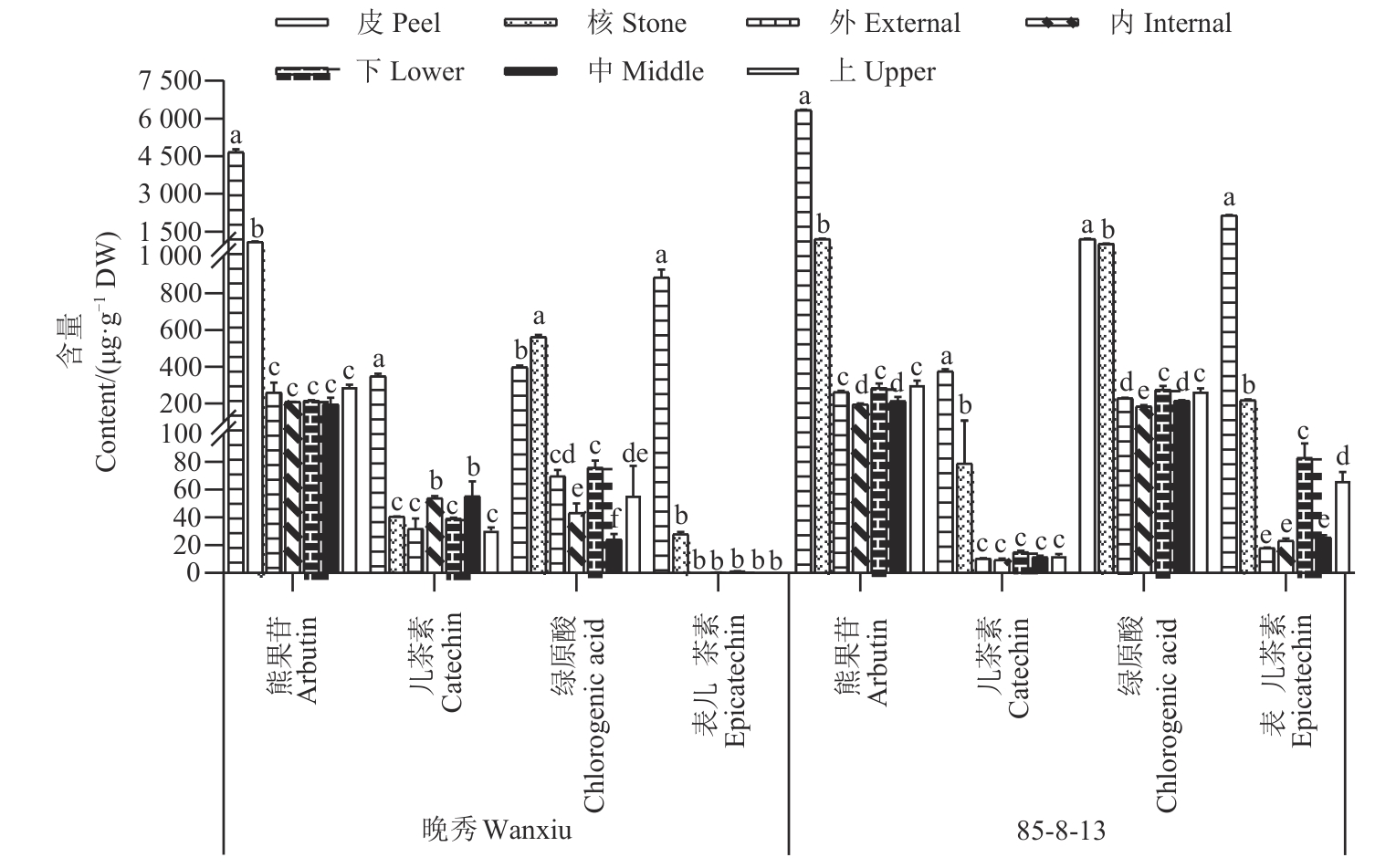
图2 梨果实不同部位4种主要酚类物质的含量注:不同小写字母表示不同部位间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Contents of 4 major phenolic substances in different parts of pear fruitNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different parts at P<0.05 level.
品种(系) Variety (line) | 组分 Componen | 果皮 Peel | 果核 Stone | 果肉Pulp | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
上部 Upper | 中部 Middle | 下部 Lower | 内部 Internal | 外部External | ||||
晚秀 Wanxiu | 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 66.31 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 18.35 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 2.92 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 120.76 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 20.87 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 71.36 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 51.63 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 1.37 | 0.41 | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 30.58 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 85-8-13 | 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 0.18 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 236.27 | — | — | — | 0.62 | — | — | |
莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 16.82 | — | — | — | 1.28 | — | — | |
槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 18.22 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 620.85 | — | — | — | 1.94 | — | — | |
异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 3.05 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 31.37 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
表2 梨果实不同部位的9种酚类物质含量 (μg·g-1DW)
Table 2 Contents of 9 phenolic substances in different parts of pear fruit
品种(系) Variety (line) | 组分 Componen | 果皮 Peel | 果核 Stone | 果肉Pulp | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
上部 Upper | 中部 Middle | 下部 Lower | 内部 Internal | 外部External | ||||
晚秀 Wanxiu | 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 66.31 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 18.35 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 2.92 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 120.76 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 20.87 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 71.36 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 51.63 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 1.37 | 0.41 | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 30.58 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 85-8-13 | 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 0.18 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 236.27 | — | — | — | 0.62 | — | — | |
莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 16.82 | — | — | — | 1.28 | — | — | |
槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 18.22 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 620.85 | — | — | — | 1.94 | — | — | |
异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 3.05 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 31.37 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
指标 Index | 主成分Principal component | |
|---|---|---|
| 晚秀Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | |
| 熊果苷Arbutin | 0.993 | 0.998 |
| 儿茶素 Catechin | 0.993 | 0.995 |
| 绿原酸 Chlorogenic acid | 0.528 | 0.798 |
| 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 0.999 | 1.000 |
| 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 0.997 | 0.993 |
| 槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 0.997 | — |
| 槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 0.997 | — |
| 山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 0.975 | 0.996 |
| 山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 12.148 | 10.559 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 93.448 | 95.993 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 93.448 | 95.993 |
表3 梨果实不同部位酚类物质主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis of phenolic components from different parts of pear fruit
指标 Index | 主成分Principal component | |
|---|---|---|
| 晚秀Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | |
| 熊果苷Arbutin | 0.993 | 0.998 |
| 儿茶素 Catechin | 0.993 | 0.995 |
| 绿原酸 Chlorogenic acid | 0.528 | 0.798 |
| 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 0.999 | 1.000 |
| 山柰酚-双脱氧己糖苷 Kaempferol hexoside-dideoxyhexoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 芦丁 Rutin | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 莰菲醇-3-O-芸香糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 0.997 | 0.993 |
| 槲皮素葡萄糖苷 Quercetin glucoside | 0.997 | — |
| 槲皮素鼠李糖苷 Quercetin rhamnoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 异鼠李素3-O-芸香糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | 0.997 | — |
| 山柰酚3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 异鼠李素-3-O-葡糖苷 Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | 0.975 | 0.996 |
| 山柰酚-3-O-6-乙酰葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-6-acetylglucoside hexoside | 0.997 | 0.996 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 12.148 | 10.559 |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 93.448 | 95.993 |
| 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 93.448 | 95.993 |
部位 Part | 晚秀 Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | Y | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | |
| 上部果肉 Upper pulp | -1.46 | -1.36 | 6 | -1.33 | -1.28 | 4 |
| 中部果肉 Middle pulp | -1.43 | -1.34 | 4 | -1.39 | -1.33 | 6 |
| 下部果肉 Lower pulp | -1.43 | -1.34 | 4 | -1.25 | -1.20 | 3 |
| 内部果肉 Internal pulp | -1.42 | -1.33 | 3 | -1.41 | -1.36 | 7 |
| 外部果肉 External pulp | -1.45 | -1.35 | 5 | -1.38 | -1.32 | 5 |
| 果核 Stone | -0.69 | -0.64 | 2 | -0.58 | -0.55 | 2 |
| 果皮 Peel | 7.88 | 7.36 | 1 | 7.34 | 7.05 | 1 |
表4 梨果实不同部位酚类物质综合得分
Table 4 Comprehensive score of phenolic substances in different parts of pear fruit
部位 Part | 晚秀 Wanxiu | 85-8-13 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | Y | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 排序 Ranking | |
| 上部果肉 Upper pulp | -1.46 | -1.36 | 6 | -1.33 | -1.28 | 4 |
| 中部果肉 Middle pulp | -1.43 | -1.34 | 4 | -1.39 | -1.33 | 6 |
| 下部果肉 Lower pulp | -1.43 | -1.34 | 4 | -1.25 | -1.20 | 3 |
| 内部果肉 Internal pulp | -1.42 | -1.33 | 3 | -1.41 | -1.36 | 7 |
| 外部果肉 External pulp | -1.45 | -1.35 | 5 | -1.38 | -1.32 | 5 |
| 果核 Stone | -0.69 | -0.64 | 2 | -0.58 | -0.55 | 2 |
| 果皮 Peel | 7.88 | 7.36 | 1 | 7.34 | 7.05 | 1 |
| 1 | 张绍铃,谢智华.我国梨产业发展现状、趋势、存在问题与对策建议[J].果树学报,2019,36(8):1067-1072. |
| ZHANG S L, XIE Z H. Current status, trends, main problems and the suggestions on development of pear industry in China [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2019, 36(8):1067-1072. | |
| 2 | 张俊英,高文远,李霞.雪花梨提取物的抗炎及体外抗氧化活性的研究[J].食品工业,2012,33(12):94-96. |
| ZHANG J Y, GAO W Y, LI X. Anti-inflammatory effect of different extracts from snow pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) [J]. Food Ind., 2012, 33(12):94-96. | |
| 3 | 冯丽,宋曙辉.植物多酚种类及其生理功能的研究进展[J].江西农业学报,2007,19(10):105-107. |
| FENG L, SONG S H. Progress in plant polyphenols and their physiological functions [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2007, 19(10):105-107. | |
| 4 | 朱洁,王红宝,孔佳君,等.梨幼果多酚的纯化及其抗氧化性[J].食品科学,2017,38(5):14-20. |
| ZHU J, WANG H B, KONG J J, et al.. Purification of polyphenols from young pear fruits and their antioxidant properties [J]. Food Sci., 2017, 38(5):14-20. | |
| 5 | KOLNIAK J, KLOPOTOWSKA D, RUTKOWSKI K P, et al.. Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of pear (Pyrus communis L.) fruits [J/OL]. Molecules, 2020, 25(19):4444 [2023-09-20]. . |
| 6 | LI X, WANG T T, ZHOU B, et al.. Chemical composition and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of peels and flesh from 10 different pear varieties (Pyrus spp.) [J]. Food Chem., 2014, 152(4):531-538. |
| 7 | LI X, ZHANG J Y, GAO W Y, et al.. Chemical compositionand anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of eight pear cultivars [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2012, 60(35):8738-8744. |
| 8 | LIN L Z, HARNLY J M. Phenolic compounds and chromatographic profiles of pear skins (Pyrus spp.) [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2008, 56(19):9094-9101. |
| 9 | 李静,聂继云,曹玉芬,等.砀山酥梨和秋白梨酚类物质UPLC-PDA-MS/MS-ESI分析[J].园艺学报,2016, 43(4):752-762. |
| LI J, NIE J Y, CAO Y F, et al.. UPLC-PDA-MS/MS-ESI analysis of phenolic compounds in fruits of Dangshan Suli and Qiubaili pears (Pyrus bretschneideri) [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2016, 43(4):752-762. | |
| 10 | 黄怡,高春丽,毕阳,等.低温贮藏期间梨果皮酚类物质及抗氧化性变化[J].食品与发酵工业,2019,45(19):219-226. |
| HUANG Y, GAO C L, BI Y, et al.. Changes in phenolic substances and antioxidant properties of pear pericarp during low temperature storage [J]. Food Ferment. Ind., 2019, 45(19):219-226. | |
| 11 | 安景舒,关晔晴,程玉豆,等.5个梨品种果实不同部位的总酚、黄酮含量及其抗氧化能力分析[J].保鲜与加工,2020,20(3):162-166. |
| AN J S, GUAN Y Q, CHENG Y D, et al.. Analysis of total phenolics and flavonoids contents and their antioxidant capacity in different parts of five pear varieties [J]. Storage Process., 2020, 20(3):162-166. | |
| 12 | 张小双,郑迎春,曹玉芬,等.‘早酥’和‘南果梨’16个部位多酚物质组成及含量分析[J].中国农业科学,2017,50(3):545-555. |
| ZHANG X S, ZHENG Y C, CAO Y F, et al.. The composition and content of polyphenols in 16 parts of ‘Zaosu’ and ‘Nanguoli’ [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2017, 50(3):545-555. | |
| 13 | 李丽梅,赵哲,何近刚,等.不同品种梨果实酚类物质和抗氧化性能分析[J].食品科学,2014,35(17): 83-88. |
| LI L M, ZHAO Z, HE J G, et al.. Analysis of phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in fruits from different pear cultivars [J]. Food Sci., 2014, 35(17):83-88. | |
| 14 | 曾少敏.梨果实主要酚类物质含量及抗氧化活性研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院, 2013. |
| ZENG S M. Study on the major phenolic content and antioxidant activities in pear fruits [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. | |
| 15 | ANDREOTTI C, COSTA G, TREUTTER D. Composition of phenolic compounds in pear leaves as affected by genetics, ontogenesis and the environment [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2006, 109(2):130-137. |
| 16 | 姜喜,唐章虎,吴翠云,等.3种梨果实发育过程中酚类物质及其抗氧化能力分析[J].食品科学,2021,42(23):99-105. |
| JIANG X, TANG Z H, WU C Y, et al.. Phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of developing pear fruit from three cultivars [J]. Food Sci., 2021, 42(23):99-105. | |
| 17 | PU Y F, DING T, WANG W J, et al.. Effect of harvest, drying and storage on the bitterness, moisture, sugars, free amino acids and phenolic compounds of jujube fruit (Zizyphus jujuba cv. Junzao) [J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2018, 98(2):628-634. |
| 18 | 王玲平,周生茂,戴丹丽,等.植物酚类物质研究进展[J].浙江农业学报,2010,22(5):696-701. |
| WANG L P, ZHOU S M, DAI D L, et al.. Progress in plant phenolic compounds [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2010, 22(5):696-701. | |
| 19 | BLOKHINA O. Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review [J]. Ann. Bot., 2003, 91(2):179-194. |
| 20 | 刘旭,杨丽,张芳芳,等.酿酒葡萄成熟期间果实质地特性和花色背含量变化[J]食品科学,2015,36(2):105-109. |
| LIU X, YANG L, ZHANG F F, et al.. Changes in textural properties and anthocyanins content of wine grape during maturation [J]. Food Sci., 2015, 36(2):105-109. | |
| 21 | SOTO-VACA A, GUTIERREZ A, LOSSO J N, et al.. Evolution of phenolic compounds from color and flavor problems to health benefits [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2012, 60(27):6658-6677. |
| 22 | SANTIN M, RANIERI A, HANSER M T, et al.. The outer influences the inner: postharvest UV-B irradiation modulates peach flesh metabolome although shielded by the skin [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2021, 338:127782 [2023-09-20]. . |
| 23 | ZHANG X, LI X, SU M, et al.. A comparative UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based metabolomics approach for distinguishing peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) fruit cultivars with varying antioxidant activity [J/OL]. Food Res. Int., 2020, 137:109531 [2023-09-20]. . |
| 24 | CUI T, NAKAMURA K, MA L, et al.. Analyses of arbutin and chlorogenic acid, the major phenolic constituents in oriental pear [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2005, 53(10):3882-3887. |
| 25 | 袁江,张绍铃,曹玉芬,等.梨果实酚类物质与酶促褐变底物的研究[J].园艺学报,2011,38(1):7-14. |
| YUAN J, ZHANG S L, CAO Y F, et al.. Polyphenolic compound and substances determination of enzymatic browning in pear [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2011, 38(1):7-14. | |
| 26 | 邹丽红,张玉星.砂梨果肉褐变与酚类物质及相关酶活性的相关分析[J].果树学报,2012,29 (6):1022-1026. |
| ZOU L H, ZHANG Y X. Correlation analysis of flesh browning between phenolic compound and relavent enzymatic activity in fruit of Pyrus pyrifolia [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2012, 29(6):1022-1026. | |
| 27 | BRAHERM M, RENARD C M, EDER S, et al.. Characterization and quantification of fruit phenolic compounds of European and Tunisian pear cultivars [J]. Food Res. Int., 2017, 95(3):125-133. |
| 28 | PENG Y B, ZHANG D P. Ultrastructure of epidermis and flesh ofthe developing apple fruit [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2000, 42(8):794-802. |
| 29 | FAUST M. Physiology of Temperate Zone Fruit Trees [M]. New York: Wiley, 1989:200-221. |
| 30 | GILLASPY G, BEN-DAVID H, GRUISSEM W. Fruits: a developmental perspective [J]. Plant Cell, 1993, 5(10):1439-1451. |
| [1] | 刘锦霖, 陈莹莹, 蓝晓妹, 陈海永, 李鹏声, 覃碧, 杨叶. 哈斯油梨果实炭疽病病原鉴定及杀菌剂敏感性测定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 138-146. |
| [2] | 卢登洋, 童盼盼, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 刘鸣哲, 夏怡蕾, 吴翠云. 库尔勒香梨大果芽变的鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [3] | 卢登洋, 王鑫, 唐章虎, 吴翠云, 蒲云峰, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 姜喜. 梨果实发育过程中酚类物质组成及抗氧化活性比较[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 97-104. |
| [4] | 李志元, 江虹, 马艳, 姜秀梅, 张力方, 梁志国, 王泽鹏, 唐亮, 梁肖, 秦勇. 氮水平对雪菊幼苗中黄酮类化合物和矿质营养累积的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 208-216. |
| [5] | 陈昌婕, 马琳, 苗玉焕, 郭兰萍, 刘大会. 施用钾肥对蕲春蕲艾产量、出绒率及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 201-209. |
| [6] | 罗立娜1,韩树全1*,王代谷1,李茂富2,马蔚红3,张正学1,刘小翠1. 油梨果实品质的差异分析与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 105-113. |
| [7] | 郁帆, 冯莹, 韩剑, 盛强, 孙丽英, 罗明, . 农用植物酵素液中梨树腐烂病菌拮抗细菌的筛选和防病效果[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 125-135. |
| [8] | 金敏, 张倩, 张天正, 包建平, 吴翠云, 张锐, 陶书田. 库尔勒香梨短果枝花序维管束与萼片脱落关系研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 55-61. |
| [9] | 吴婕1,2,宫江宁3. 大孔树脂纯化金银花总黄酮及其对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 89-97. |
| [10] | 颜仕龙1§,蔡波2,3§,唐华玲4,袁洋5,敖苏2,3*. 苦瓜不同部位化感作用研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(8): 100-107. |
| [11] | 曹慧方,李新新,张玥琦,石鹏君,柏映国*,姚斌*. 来源于脂环酸芽孢杆菌的GH1家族β-葡萄糖苷酶的葡萄糖耐受性分子改造[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(5): 26-33. |
| [12] | 李彬彬,侯智霞*,杨俊枫,陈露,万如萌. ‘北陆’蓝莓叶片变色过程中类黄酮和糖的变化特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(3): 20-29. |
| [13] | 魏娜,次顿,张唐伟. 西藏高原地理与气候因子对青稞功能性成分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(12): 115-121. |
| [14] | 黄娟,邓娇,陈庆富*. 荞麦根的转录组学分析及黄酮合成基因的鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(2): 9-19. |
| [15] | 梁霞丽,赵亚周,张红城,彭文君*. 蜂胶中4种黄酮对HepG2细胞胰岛素抵抗的改善作用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(11): 74-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号