




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 156-163.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0826
田甜1( ), 杨振奇2,3, 郭建英2,3(
), 杨振奇2,3, 郭建英2,3( ), 要振宇2,3, 赵天启2,3, 刘心宇2,3, 王子薇1
), 要振宇2,3, 赵天启2,3, 刘心宇2,3, 王子薇1
收稿日期:2023-11-10
接受日期:2024-03-11
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
郭建英
作者简介:田甜 E-mail:710773053@qq.com;
基金资助:
Tian TIAN1( ), Zhenqi YANG2,3, Jianying GUO2,3(
), Zhenqi YANG2,3, Jianying GUO2,3( ), Zhenyu YAO2,3, Tianqi ZHAO2,3, Xinyu LIU2,3, Ziwei WANG1
), Zhenyu YAO2,3, Tianqi ZHAO2,3, Xinyu LIU2,3, Ziwei WANG1
Received:2023-11-10
Accepted:2024-03-11
Online:2025-05-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Jianying GUO
摘要:
为探究不同放牧强度对土壤团聚体稳定性的影响,选取在内蒙古包头市达茂旗希拉穆仁建立的荒漠草原长期放牧试验平台(禁牧、轻度、中度、重度放牧强度)为研究对象,通过测定0—40 cm土层的土壤水稳定性团聚体,分析不同放牧强度下土壤团聚体组成、稳定性及抗蚀性特征。结果表明,放牧强度对土壤水稳定性大团聚体含量影响较大,各放牧处理的大团聚体质量百分比为73.00%~89.93%,且随放牧强度的增加,水稳定性大团聚体含量呈先增加后降低的趋势。轻度、中度放牧下土壤的平均重量直径、几何平均直径数均高于禁牧。相关性分析表明,水稳性大团聚体含量、平均重量直径、几何平均直径与土壤可蚀性因子均呈显著负相关。综上所述,适度放牧可以增强土壤团聚体的稳定性,提升土壤抗侵蚀性能,维护草原长期可持续发展。
中图分类号:
田甜, 杨振奇, 郭建英, 要振宇, 赵天启, 刘心宇, 王子薇. 放牧强度对荒漠草原土壤团聚体稳定性及可蚀性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 156-163.
Tian TIAN, Zhenqi YANG, Jianying GUO, Zhenyu YAO, Tianqi ZHAO, Xinyu LIU, Ziwei WANG. Effects of Grazing Intensity on Stability and Anti-erodibility of Soil Aggregates in Desert Steppe[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 156-163.
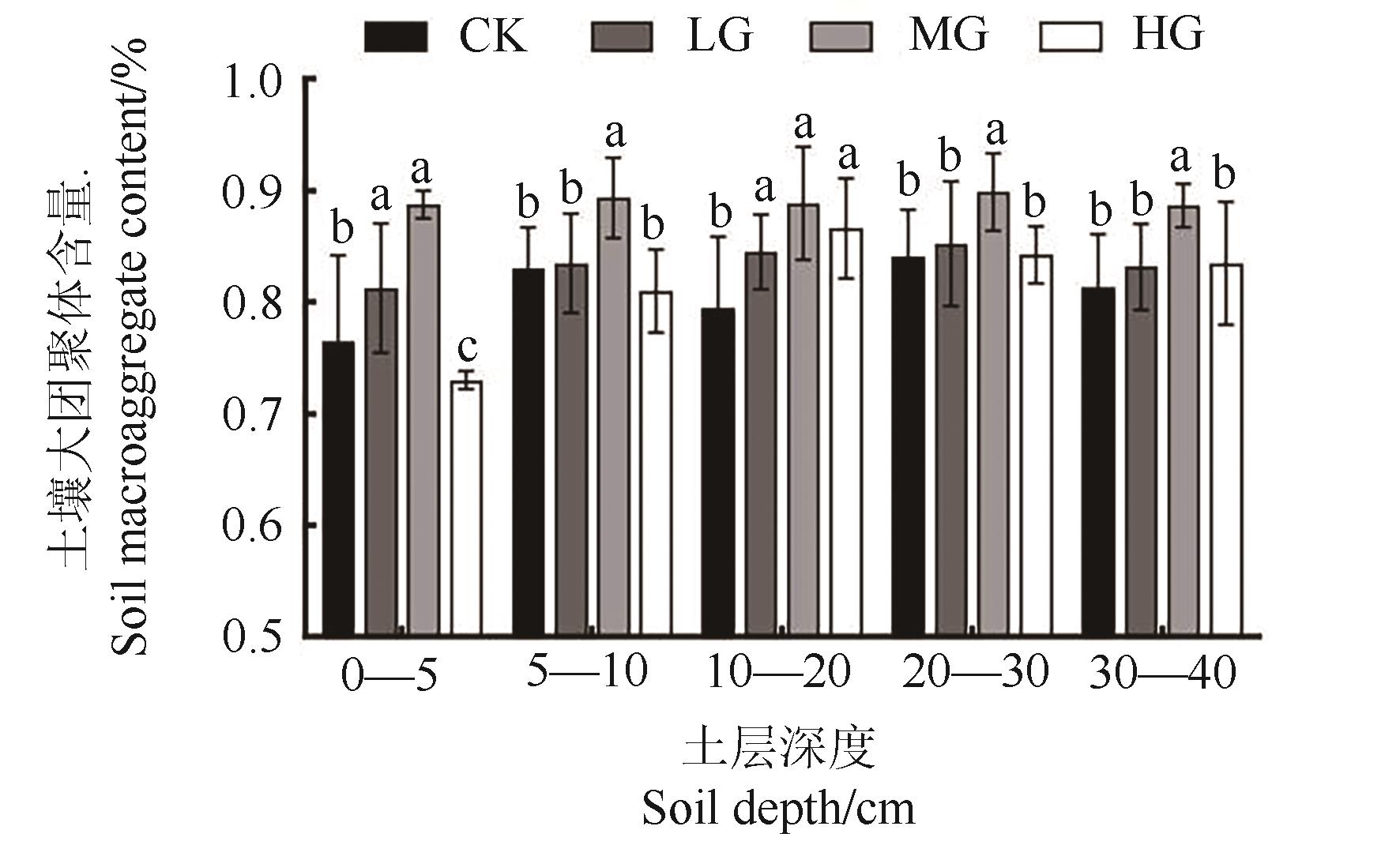
图1 不同放牧强度土壤大团聚体含量注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Soil macroaggregate content under different grazing intensitiesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
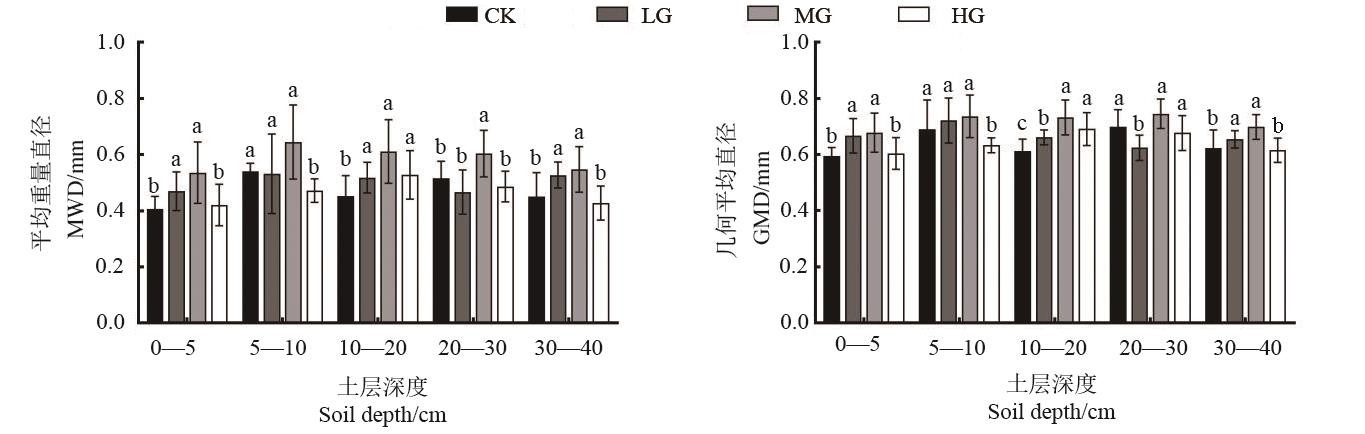
图2 不同放牧强度土壤团聚体平均重量直径和几何平均直径注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 MWD and GMD of soil aggregates under different grazing intensitiesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 处理 Treatment | 团聚体破坏率 PAD | 可蚀性因子K Erodibility factor K |
|---|---|---|---|
0—5 | CK | 0.322±0.108 αa | 0.021 5±0.000 8 αa |
| LG | 0.273±0.128 αa | 0.019 6±0.001 9 αb | |
| MG | 0.247±0.115 αa | 0.019 1±0.001 9 αc | |
| HG | 0.189±0.113 αa | 0.022 4±0.001 2 αa | |
5—10 | CK | 0.188±0.096 αa | 0.020 4±0.001 8 αa |
| LG | 0.216±0.097 αa | 0.017 5±0.001 3 αb | |
| MG | 0.124±0.076 αa | 0.018 1±0.002 9 αb | |
| HG | 0.152±0.103 αa | 0.020 9±0.001 3 αa | |
10—20 | CK | 0.192±0.109 αa | 0.019 9±0.001 7 αa |
| LG | 0.089±0.045 βa | 0.019 3±0.001 5 αa | |
| MG | 0.102±0.026 αa | 0.017 1±0.001 5 αb | |
| HG | 0.081±0.063 αa | 0.020 8±0.001 8 αa | |
20—30 | CK | 0.139±0.083 βa | 0.020 1±0.001 7 αa |
| LG | 0.131±0.066 βa | 0.019 4±0.002 1 αa | |
| MG | 0.072±0.089 βa | 0.016 8±0.001 6 αb | |
| HG | 0.154±0.119 αa | 0.020 4±0.001 5 βa | |
30—40 | CK | 0.189±0.113 βa | 0.020 9±0.000 8 βa |
| LG | 0.152±0.103 βa | 0.019 5±0.001 1 βb | |
| MG | 0.154±0.119 βa | 0.018 3±0.001 6 βb | |
| HG | 0.139±0.128 βa | 0.021 3±0.000 5 βa |
表1 不同放牧强度土壤团聚体破坏率和可蚀性因子差异分析
Table 1 Difference analysis of soil aggregate destruction rate and erodibility factor under different grazing intensities
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 处理 Treatment | 团聚体破坏率 PAD | 可蚀性因子K Erodibility factor K |
|---|---|---|---|
0—5 | CK | 0.322±0.108 αa | 0.021 5±0.000 8 αa |
| LG | 0.273±0.128 αa | 0.019 6±0.001 9 αb | |
| MG | 0.247±0.115 αa | 0.019 1±0.001 9 αc | |
| HG | 0.189±0.113 αa | 0.022 4±0.001 2 αa | |
5—10 | CK | 0.188±0.096 αa | 0.020 4±0.001 8 αa |
| LG | 0.216±0.097 αa | 0.017 5±0.001 3 αb | |
| MG | 0.124±0.076 αa | 0.018 1±0.002 9 αb | |
| HG | 0.152±0.103 αa | 0.020 9±0.001 3 αa | |
10—20 | CK | 0.192±0.109 αa | 0.019 9±0.001 7 αa |
| LG | 0.089±0.045 βa | 0.019 3±0.001 5 αa | |
| MG | 0.102±0.026 αa | 0.017 1±0.001 5 αb | |
| HG | 0.081±0.063 αa | 0.020 8±0.001 8 αa | |
20—30 | CK | 0.139±0.083 βa | 0.020 1±0.001 7 αa |
| LG | 0.131±0.066 βa | 0.019 4±0.002 1 αa | |
| MG | 0.072±0.089 βa | 0.016 8±0.001 6 αb | |
| HG | 0.154±0.119 αa | 0.020 4±0.001 5 βa | |
30—40 | CK | 0.189±0.113 βa | 0.020 9±0.000 8 βa |
| LG | 0.152±0.103 βa | 0.019 5±0.001 1 βb | |
| MG | 0.154±0.119 βa | 0.018 3±0.001 6 βb | |
| HG | 0.139±0.128 βa | 0.021 3±0.000 5 βa |
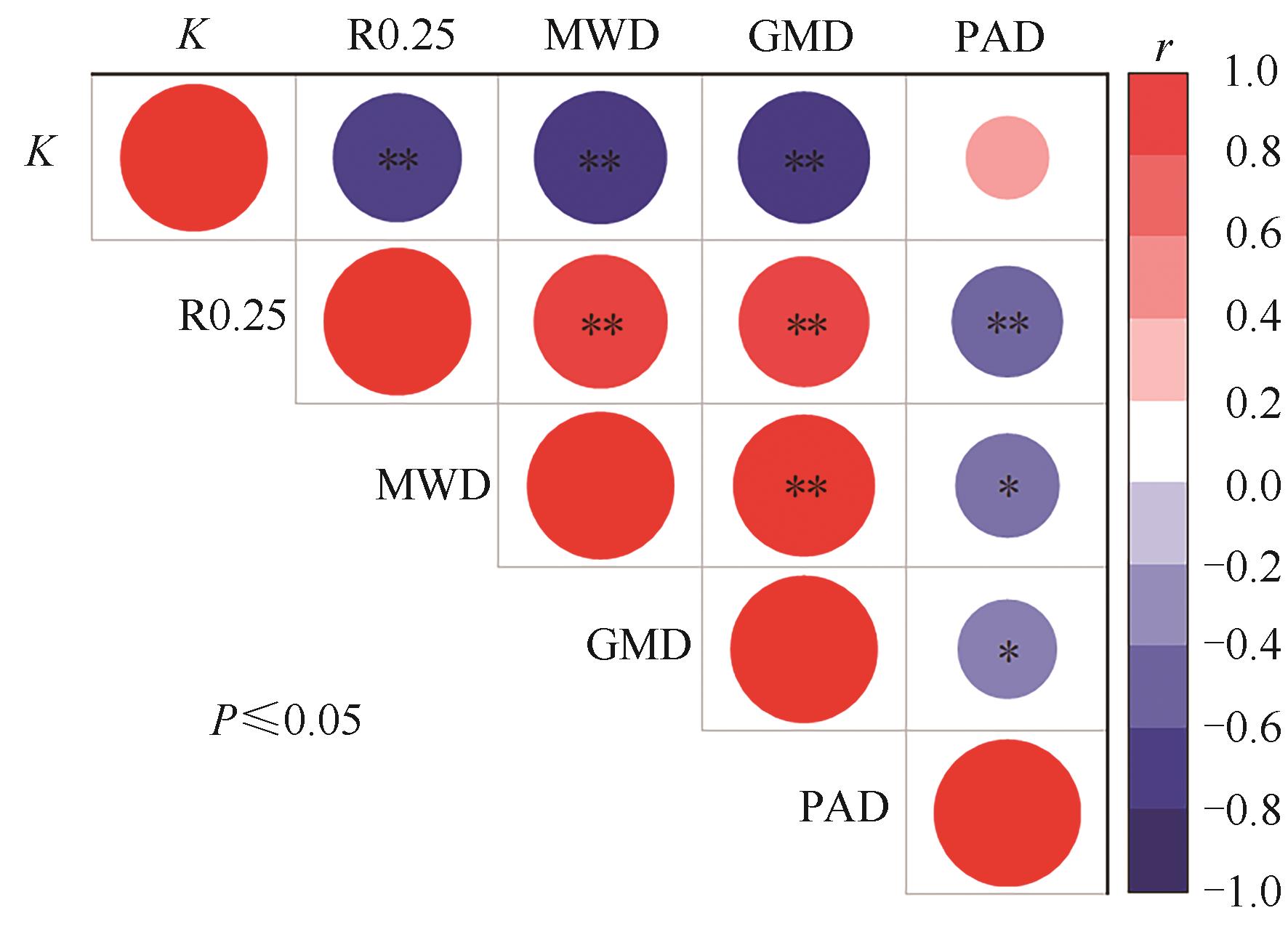
图3 不同放牧强度土壤团聚体与土壤稳定性的关系注:K—可蚀性因子;R0.25—土壤水稳性大团聚体含量;MWD—平均重量直径;GMD—几何平均直径;PAD—团聚体破坏率。*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平相关显著。
Fig. 3 Relationship between soil aggregates and soil stability under different grazing intensitiesNote:K—Erodibility factor;R0.25—Soil macroaggregate content;MWD—Mean weight diameter;GMD—Geometric mean diameter;PAD—Percentage of aggregate destruction. * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 任继周,草业大辞典[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2008:1-874. |
| 2 | LI X Y, SONG Z B, HU Y, et al.. Drought intensity and post-drought precipitation determine vegetation recovery in a desert steppe in Inner Mongolia,China [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2024,906:167449 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 3 | LIU S B, ZAMANIAN K, SCHLEUSS P M, et al.. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2018, 252:93-104. |
| 4 | REINERMANN S, ASAM S, KUENZER C. Remote sensing of grassland production and management: a review [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2020, 12:1949 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 5 | TIAN T, YANG Z Q, GUO J Y, et al.. Spatiotemporal evolution of soil erosion and its driving mechanism in the mongolian section of the Yellow River basin [J/OL]. Land, 2023, 12(4):801 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 6 | GAO W B, JIANG H T, ZHANG S, et al.. Vegetation characteristics and soil properties in grazing exclusion areas of the Inner Mongolia desert steppe [J/OL]. Inter. Soil. Water. Conser. Res., 2023, 11(3):005 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 7 | 朱凯,马茂华,李文娟,等.三峡水库消落带不同土地利用对土壤团聚体稳定性及其碳氮分布的影响[J].长江流域资源与环境,2022,31(7):1503-1513. |
| ZHU K, MA M H, LI W J, et al.. Effects of land-use types on soil aggregate stability and organic carbon and nitrogen in riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir [J].Resour.Environ.Yangtze Basin, 2022,31(7):1503-1513. | |
| 8 | LIU D D, JU W L, JIN X L,et al..Associated soil aggregate nutrients and controlling factors on aggregate stability in semiarid grassland under different grazing prohibition timeframes [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,777:146104 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 9 | AN S S, MENTLER A, MAYER H,et al..Soil aggregation,aggregate stability,organic carbon and nitrogen in different soil aggregate fractions under forest and shrub vegetation on the Loess Plateau,China [J]. CATENA, 2010,81(3):226-233. |
| 10 | MILCHUNAS D G, LAURENROTH W K. Quantitative effects of grazing on vegetation and soils over a global range of environments [J]. Ecol. Mono., 1993, 63:327-366. |
| 11 | 张成霞,南志标.放牧对草地土壤理化特性影响的研究进展[J].草业学报,2010,19(4):204-211. |
| ZHANG C X, NAN Z B. Research progress on effects of grazing on physical and chemical characteristics of grassland soil [J]. Acta. Pratac. Sin., 2010, 19(4):204-211. | |
| 12 | 史志华,宋长青.土壤水蚀过程研究回顾[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(5):1-10. |
| SHI Z H, SONG C Q.Water erosion processes:a historical review [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2016,30(5):1-10. | |
| 13 | 王永琪,杜保军,张树振,等.放牧对新疆天山山地草甸土壤团聚体和土壤呼吸潜力的影响[J].草地学报,2022,30(10):2729-2736. |
| WANG Y Q, DU B J, ZHANG S Z,et al..Effects of grazing on soil aggregates and soil respiration potential in Tianshan Mountain grassland,Xinjiang [J].Acta Agrestia Sin.,2022,30(10):2729-2736. | |
| 14 | YANG C, LIU N, ZHANG Y G. Soil aggregates regulate the impact of soil bacteria land fungal communities on soil respiration [J]. Geodeama, 2019, 337:444-452. |
| 15 | WANG J W, ZHAO C Z, ZHAO L C,et al..Effects of grazing on the allocation of mass of soil aggregates and aggregate-associated organic carbon in an alpine meadow [J/OL].PLoS One,2020,15(6):e0234477 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 16 | 张昊,李建平,王誉陶,等.封育与放牧对黄土高原天然草地土壤化学计量特征的影响[J].水土保持学报,2020,34(5):251-258. |
| ZHANG H, LI J P, WANG Y T, et al.. Effect of enclosure and grazing on the soil stoichiometry characteristics of natural grassland on the Loess Plateau [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2020,34(5):251-258. | |
| 17 | YU Z, MIAO W, XU W, et al.. Grazing regulates changes in soil microbial communities in plant-soil systems [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2023, 13(3):708 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 18 | 张彧行,翁白莎,严登华.基于文献可视化分析的土壤团聚体研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2022,37(4):429-438. |
| ZHANG Y X, WENG B S, YAN D H. Research progress of soil aggregates based on literature visualization analysis [J].Adv.Earth Sci., 2022,37(4):429-438. | |
| 19 | 李柏桥,付玉,李光录,等.退耕年限与方式对土壤团聚体稳定性及有机碳分布的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2017,35(3):238-244. |
| LI B Q, FU Y, LI G L, et al.. Effects of age and type of conversion from cropland to forest land and qrassland on stability andorganic carbon in soil aggregates [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2017, 35(3):238-244. | |
| 20 | 张钦,于恩江,林海波,等.连续种植不同绿肥作物的土壤团聚体稳定性及可蚀性特征[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(2):9-16. |
| ZHANG Q, YU E J, LIN H B, et al.. Stability and erodibility of aggregate affected by different continuous green manureultivations [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 26(2):9-16. | |
| 21 | 杨振奇,郭建英,秦富仓,等.裸露砒砂岩区不同植被类型土壤团聚体稳定性与抗蚀性能[J].水土保持通报,2021,41(3):8-14. |
| YANG Z Q, GUO J Y, QIN F C, et al.. Soil aggregate stability and erodibility in different vegetation types of exposed feldspathic sandstone region [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2021,41(3):8-14. | |
| 22 | DENBOBA M A. Grazing management and carbon sequestration in the dry lowland rangelands of southern Ethiopia [J]. Sus. Environ., 2022, 8(1):2765-8511. |
| 23 | CHAPLOT V, COOPER M.Soil aggregate stability to predict organic carbon outputs from soils [J].Geoderma,2015,243:205-213. |
| 24 | 贾丽英,陈清,张洛梓,等.放牧和围封对内蒙古羊草草原土壤团聚体理化性质的影响[J].天津师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,41(6):40-45. |
| JIA L Y, CHEN Q, ZHANG L Z, et al.. Effects of grazing and enclosure on physicochemical properties of soil aggregates in Leymuschinensis steppe, Inner Mongolia [J]. J. Tianjin Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 41(6):40-45. | |
| 25 | 刘文亭,王天乐,张爽,等.放牧对短花针茅荒漠草原建群种与土壤团聚体特征的影响[J].生态环境学报,2017,26(6):978-984. |
| LIU W T, WANG T L, ZHANG S, et al.. Effects of grazing on edificators and soil aggregate characteristics in Stipa breviflora desert steppe [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2017, 26(6):978-984. | |
| 26 | 严方晨,焦菊英,曹斌挺,等.黄土丘陵沟壑区撂荒地不同演替阶段植物群落的土壤抗蚀性:以坊塌流域为例[J].应用生态学报,2016,27(1):64-72. |
| YAN F C, JIAO J Y, CAO B T, et al.. Soil anti-erodibility of abandoned lands during different succession stages of plant community in hilly-gullied region of the Loess Plateau:take Fangta small watershed as an example [J].Chin.J. Appl. Ecol., 2016,27(1):64-72. | |
| 27 | 张彬,赵天启,贺启珅,等.放牧对短花针茅荒漠草原土壤团聚体组成及稳定性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(12):3263-3270. |
| ZHANG B, ZHAO T Q, HE Q S, et al.. Effects of grazing on soil aggregate composition and stability in Stipa breviflora desert steppe [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2022,33(12):3263-3270. | |
| 28 | 郭建英,董智,李锦荣,等.放牧强度对荒漠草原土壤物理性质及其侵蚀产沙的影响[J].中国草地学报,2019,41(3):74-82. |
| GUO J Y, DONG Z, LI J R, et al.. Effects of grazing intensity on soil physical properties and soil erosion and sediment yield in desert steppe [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2019,41(3):74-82. | |
| 29 | 张娜.不同放牧强度对典型草原植被群落特征及土壤理化性状的影响[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2020. |
| ZHANG N. Effects of grazing intensity on vegetation communitycharacteristies and soil physical and chemical properties of typical steppe [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. | |
| 30 | 杨雅楠,杨振奇,郭建英.放牧强度对荒漠草原植被、土壤及其侵蚀特征的影响[J].水土保持通报,2022,42(4):66-73. |
| YANG Y N, YANG Z Q, GUO J Y. Effects of grazing intensity on features of vegetation, soil and its erosion in a steppe desert [J]. Bull. Soil. Water. Conser., 2022, 42(4):66-73. | |
| 31 | CAGNA C P, CALABRIA Z K P, GUEDES O, et al.. Structural properties of soil in maize and forage grass intercropping under no-tillage in the Brazilian Cerrado [J]. Eng. Agric., 2019, 39:512-517. |
| 32 | 王海茹,张卫青,卢晓霞,等.放牧强度对典型草原土壤团聚体机械稳定性的影响——以内蒙古阿巴嘎旗草原为例[J].干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(6):164-170. |
| WANG H R, ZHANG W Q, LU X X, et al.. Effects of grazing intensity on mechanical stability of soil aggregates in typical grassland [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2022,36(6):164-170. | |
| 33 | 董全民,赵新全,李世雄,等.草地放牧系统中土壤-植被系统各因子对放牧响应的研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2014,33(8):2255-2265. |
| DONG Q M, ZHAO X Q, LI S X, et al.. A review on the responses of various factors within soil-vegetation system to grazing in grassland grazing systems [J].Chin.J.Ecol.,2014,33(8):2255-2265. | |
| 34 | 王合云,郭建英,李红丽,等.短花针茅荒漠草原不同退化程度的植被特征[J].中国草地学报,2015,37(3):74-79. |
| WANG H Y, GUO J Y, LI H L, et al.. Vegetation characteristics of Stipa breviflora desert steppe in different degradation degree [J].Chin. J. Grassland, 2015,37(3):74-79. | |
| 35 | 张扬建,朱军涛,沈若楠,等.放牧对草地生态系统影响的研究进展[J].植物生态学报,2020,44(5):553-564. |
| ZHANG Y J, ZHU J T, SHEN R N, et al.. Research progress on the effects of grazing on grassland ecosystem [J].Chin. J. Plant Ecol.,2020,44(5):553-564. | |
| 36 | 冯嘉仪,储双双,王婧,等.华南地区几种典型人工林土壤有机碳密度及其与土壤物理性质的关系[J].华南农业大学学报,2018,39(1):85-92. |
| FENG J Y, CHU S S, WANG J,et al.. Soil organic carbon density and its relationship with soil physical properties of typical plantations in South China [J]. J. South China Agric.Univ.,2018,39(1):85-92. | |
| 37 | 刘亚龙,王萍,汪景宽.土壤团聚体的形成和稳定机制:研究进展与展望[J].土壤学报,2023,60(3):627-643. |
| LIU Y L, WANG P, WANG J K.Formation and stability mechanism of soil aggregates:progress and prospect [J].Acta Pedol. Sin., 2023,60(3):627-643. | |
| 38 | RILLIG M C, MULLER L A, LEHMANN A.Soil aggregates as massively concurrent evolutionary incubators [J]. ISME J., 2017,11(9):1943-1948. |
| 39 | ZHANG C, SONG Z L, ZHUANG D H, et al.. Urea fertilization decreases soil bacterial diversity,but improves microbial biomass,respiration,and N-cycling potential in a semiarid grassland [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2019,55(3):229-242. |
| 40 | FAN J L, JIN H, ZHANG C H, et al.. Grazing intensity induced alternations of soil microbial community composition in aggregates drive soil organic carbon turnover in a desert steppe [J/OL].Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2021, 313:107387 [2023-10-01]. . |
| 41 | 兰瑞君,郭建英,尹忠东,等.不同放牧强度下土壤侵蚀对典型草原土壤有机碳的影响[J].水土保持学报,2017,31(4):172-177. |
| LAN R J, GUO J Y, YIN Z D, et al.. Effects of soil erosion on the soil organic carbon of typical steep under different grazing intensities [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 31(4):172-177. | |
| 42 | 杨泽宇.不同放牧强度对典型草原土壤团聚体稳定性的影响[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2021. |
| YANG Z Y. Effects of different grazing intensitieson soil aggregate stability in typical steppe [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2021. | |
| 43 | 张天宇,宝音陶格涛,高若凡 等.长期不同刈割制度对典型草原土壤团聚体稳定性的影响[J].中国草地学报,2021,43(11):26-36. |
| ZHANG T Y, Baoyintaogetao, GAO R F, et al.. Effects of long-term different mowing regimes on soil aggregate stability in steppe grassland [J]. Chin. J. Grassland,2021,43(11):26-36. | |
| 44 | 张钦弟,刘剑荣,杨磊,等.半干旱黄土区植被恢复对土壤团聚体稳定性及抗侵蚀能力的影响[J].生态学报,2022,42(22):9057-9068. |
| ZHANG Q D, LIU J R, YANG L, et al.. Effect of vegetation restoration on stability and erosion resistance of soil aggregates in semi-arid loess region [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2022,42(22):9057-9068. |
| [1] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [2] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 天山北坡典型草地土壤呼吸特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 189-199. |
| [3] | 胡旭凯,陈居田,朱利霞*,李俐俐*. 干湿交替对土壤团聚体特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 141-149. |
| [4] | 王进,刘子琦*,张国,李渊,鲍恩俣. 石漠化区林草恢复与传统农耕对土壤团聚体和有机碳含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(11): 133-143. |
| [5] | 林杰1,张阳1,朱艳芳1,董波1,潘颖1,丁鸣鸣2. 淮北土石山区不同土地利用方式对土壤团聚体组成的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(4): 133-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号