




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 43-53.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.1090
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jingying JIA( ), Yahui LI, Bingzhe FU, Yun MA, Xiaoyan CAI(
), Yahui LI, Bingzhe FU, Yun MA, Xiaoyan CAI( )
)
Received:2021-12-23
Accepted:2022-05-06
Online:2023-07-15
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Xiaoyan CAI
通讯作者:
蔡小艳
作者简介:贾晶莹 E-mail:jiajingying176@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jingying JIA, Yahui LI, Bingzhe FU, Yun MA, Xiaoyan CAI. Analysis on miRs Expression Profiles of Alfalfa and Screening of Trans-border Potential miRs[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 43-53.
贾晶莹, 李雅辉, 伏兵哲, 马云, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿miRs表达谱分析及跨界潜力miRs初步筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 43-53.
miRs名称 miRs name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| 5s | F:GCAGACGAAGTCCTTGTGTTG R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| miR156b-5p | F:CGCAGACAGTTGACAGAAGAGA |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTCAC | |
| miR166a | F:CACAGTTCGGACCAGGCTT |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGGAATG | |
| miR167a | F:AAGCTTTGAAGCTGCCAGC |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTAGATCAT | |
| miR168a | F:CATGTGTCGCTTGGTGCAG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTTCCCGAC | |
| miR319a-3p | F:CGAACGTTTTGGACTGAAGG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGAGCTC |
Table 1 Primer information
miRs名称 miRs name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| 5s | F:GCAGACGAAGTCCTTGTGTTG R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| miR156b-5p | F:CGCAGACAGTTGACAGAAGAGA |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTCAC | |
| miR166a | F:CACAGTTCGGACCAGGCTT |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGGAATG | |
| miR167a | F:AAGCTTTGAAGCTGCCAGC |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTAGATCAT | |
| miR168a | F:CATGTGTCGCTTGGTGCAG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTTCCCGAC | |
| miR319a-3p | F:CGAACGTTTTGGACTGAAGG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGAGCTC |
| 组分Component | 体积Volume/μL |
|---|---|
预混液 TB Green Premix Ex Taq Ⅱ (Tli RNaseH Plus) (2×) | 10.0 |
PCR上游引物 PCR forward primer (10 μmol·L-1) | 0.4 |
PCR下游引物 PCR reverse primer (10 μmol·L-1) | 0.4 |
| DNA (100 ng·μL-1) | 2.0 |
| 灭菌水dd H2O | 7.2 |
| 总计Total | 20.0 |
Table 2 Fluorescence quantitative reaction system
| 组分Component | 体积Volume/μL |
|---|---|
预混液 TB Green Premix Ex Taq Ⅱ (Tli RNaseH Plus) (2×) | 10.0 |
PCR上游引物 PCR forward primer (10 μmol·L-1) | 0.4 |
PCR下游引物 PCR reverse primer (10 μmol·L-1) | 0.4 |
| DNA (100 ng·μL-1) | 2.0 |
| 灭菌水dd H2O | 7.2 |
| 总计Total | 20.0 |
miRs名称 miRs name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| miR5754 | F:TATTGCACTCATCTTCCATGGC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGCCATG | |
| miR156f | F:CCGTTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTC | |
| miR5743a | F:TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAAGGTG | |
| Novel-miR54 | F:CCAAGTCCTTGTGTTGCATCTC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAGATG | |
| Novel-miR158 | F:GCGCAAAGGATCATTGGATAAGTTc |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAACTT |
Table 1 Primer information
miRs名称 miRs name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| miR5754 | F:TATTGCACTCATCTTCCATGGC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGCCATG | |
| miR156f | F:CCGTTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTC | |
| miR5743a | F:TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAAGGTG | |
| Novel-miR54 | F:CCAAGTCCTTGTGTTGCATCTC |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAGATG | |
| Novel-miR158 | F:GCGCAAAGGATCATTGGATAAGTTc |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAACTT |
| 品种Variety | miRs数量Number of miRs | 优势表达miRNA(miRs TPM占总TPM百分比) Advantage expressed known miRs (miRs TPM/all miRs TPM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已知Known | 新预测Novel | ||
中苜1号 Zhongmu 1 | 433 | 223 | mtr-miR5213-5p(25.82%), mtr-miR159a(22.40%), mtr-miR396a-5p(11.72%), mtr-miR166e-3p(5.22%) |
新盐52号 Xinyan 52 | 480 | 223 | mtr-miR159a(27.27%), mtr-miR5213-5p(20.07%), mtr-miR396a-5p(14.19%), mtr-miR166e-3p(3.89%) |
Table 3 Advantage expression miRs in Zhongmu 1 andXinyan 52
| 品种Variety | miRs数量Number of miRs | 优势表达miRNA(miRs TPM占总TPM百分比) Advantage expressed known miRs (miRs TPM/all miRs TPM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已知Known | 新预测Novel | ||
中苜1号 Zhongmu 1 | 433 | 223 | mtr-miR5213-5p(25.82%), mtr-miR159a(22.40%), mtr-miR396a-5p(11.72%), mtr-miR166e-3p(5.22%) |
新盐52号 Xinyan 52 | 480 | 223 | mtr-miR159a(27.27%), mtr-miR5213-5p(20.07%), mtr-miR396a-5p(14.19%), mtr-miR166e-3p(3.89%) |
| miRs名称miRs name | 序列Sequence(5’-3’) | TPM值TPM value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中苜1号Zhongmu1 | 新盐52号Xinyan52 | ||
| miR5743a | TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT | 6 019.360 539 | 61.234 256 |
| miR5743b | TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT | 6 019.360 539 | 61.234 256 |
| novel-miR158 | AAAGGAUCAUUGGAUAAGUUC | 1 034.191 978 | 57.554 978 |
| miR5754 | TATTGCACTCATCTTCCATGGC | 904.998 534 | 6.803 806 |
| novel-miR54 | AAGUCCUUGUGUUGCAUCUC | 645.517 630 | 1 877.094 533 |
| miR156f | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
| miR156e | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
| miR156h-5p | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
Table 4 miRs sequence of differentially expressed
| miRs名称miRs name | 序列Sequence(5’-3’) | TPM值TPM value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中苜1号Zhongmu1 | 新盐52号Xinyan52 | ||
| miR5743a | TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT | 6 019.360 539 | 61.234 256 |
| miR5743b | TGAGAACTGTTTTCCGCACCTT | 6 019.360 539 | 61.234 256 |
| novel-miR158 | AAAGGAUCAUUGGAUAAGUUC | 1 034.191 978 | 57.554 978 |
| miR5754 | TATTGCACTCATCTTCCATGGC | 904.998 534 | 6.803 806 |
| novel-miR54 | AAGUCCUUGUGUUGCAUCUC | 645.517 630 | 1 877.094 533 |
| miR156f | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
| miR156e | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
| miR156h-5p | TTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC | 163.659 584 | 10.655 880 |
| GO编码 GO ID | 富集层面Enrichment level | 功能Function | 差异表达miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of differential expressed miR target genes enriched into pathway (Percentage/%) | 全部miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of all miR target genes enriched into the pathway (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006468 | 生物过程 Biological process | 蛋白质磷酸化Protein phosphorylation | 36(7.16) | 467(6.88) |
| GO:0055114 | 氧化还原过程Oxidation-reduction process | 29(5.77) | 440(6.49) | |
| GO:0006952 | 防御反应Defense response | 19(3.78) | 683(10.07) | |
| GO:0006508 | 蛋白水解作用Proteolysis | 18(3.58) | 169(2.49) | |
| GO:0006355 | 转录调控,DNA模板化 Regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 17(3.38) | 360(5.31) | |
| GO:0005975 | 碳水化合物代谢过程 Carbohydrate metabolic process | 15(2.98) | 116(1.71) | |
| GO:0055085 | 跨膜运输Transmembrane transport | 13(2.58) | 126(1.86) |
Table 5 GO functional enrichment analysis of miRs target genes
| GO编码 GO ID | 富集层面Enrichment level | 功能Function | 差异表达miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of differential expressed miR target genes enriched into pathway (Percentage/%) | 全部miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of all miR target genes enriched into the pathway (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006468 | 生物过程 Biological process | 蛋白质磷酸化Protein phosphorylation | 36(7.16) | 467(6.88) |
| GO:0055114 | 氧化还原过程Oxidation-reduction process | 29(5.77) | 440(6.49) | |
| GO:0006952 | 防御反应Defense response | 19(3.78) | 683(10.07) | |
| GO:0006508 | 蛋白水解作用Proteolysis | 18(3.58) | 169(2.49) | |
| GO:0006355 | 转录调控,DNA模板化 Regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 17(3.38) | 360(5.31) | |
| GO:0005975 | 碳水化合物代谢过程 Carbohydrate metabolic process | 15(2.98) | 116(1.71) | |
| GO:0055085 | 跨膜运输Transmembrane transport | 13(2.58) | 126(1.86) |
| GO编码 GO ID | 富集层面Enrichment level | 功能Function | 差异表达miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of differential expressed miR target genes enriched into pathway (Percentage/%) | 全部miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of all miR target genes enriched into the pathway (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0043161 | 蛋白酶体介导的泛素依赖性蛋白分解代谢过程Proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | 12(2.39) | 26(0.38) | |
| GO:0016021 | 细胞组分 Cellular component | 膜的组成部分 Integral component of membrane | 160(31.81) | 2 454(36.18) |
| GO:0005634 | 核Nucleus | 85(16.90) | 591(8.71) | |
| GO:0005886 | 质膜Plasma membrane | 24(4.77) | 294(4.33) | |
| GO:0009506 | 胞间连丝Plasmodesma | 16(3.18) | 122(1.80) | |
| GO:0005829 | 胞浆Cytosol | 13(2.58) | 159(2.34) | |
| GO:0005622 | 胞内Intracellular | 12(2.39) | 102(1.50) | |
| GO:0005737 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 12(2.39) | 255(3.76) | |
| GO:0005524 | 分子功能Molecular function | ATP结合ATP binding | 97(19.28) | 1 227(18.09) |
| GO:0003677 | DNA结合DNA binding | 84(16.70) | 502(7.40) | |
| GO:0008270 | 锌离子结合Zinc ion binding | 34(6.76) | 317(4.67) | |
| GO:0004674 | 蛋白质丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 Protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 34(6.76) | 394(5.81) | |
| GO:0043531 | ADP结合ADP binding | 14(2.78) | 658(9.70) | |
| GO:0046872 | 金属离子结合Metal ion binding | 14(2.78) | 267(3.94) | |
| GO:0016887 | ATP酶活性ATPase activity | 11(2.19) | 44(0.65) |
Table 5 GO functional enrichment analysis of miRs target genes
| GO编码 GO ID | 富集层面Enrichment level | 功能Function | 差异表达miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of differential expressed miR target genes enriched into pathway (Percentage/%) | 全部miR靶基因富集到该通路的数量(百分比/%) Number of all miR target genes enriched into the pathway (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0043161 | 蛋白酶体介导的泛素依赖性蛋白分解代谢过程Proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | 12(2.39) | 26(0.38) | |
| GO:0016021 | 细胞组分 Cellular component | 膜的组成部分 Integral component of membrane | 160(31.81) | 2 454(36.18) |
| GO:0005634 | 核Nucleus | 85(16.90) | 591(8.71) | |
| GO:0005886 | 质膜Plasma membrane | 24(4.77) | 294(4.33) | |
| GO:0009506 | 胞间连丝Plasmodesma | 16(3.18) | 122(1.80) | |
| GO:0005829 | 胞浆Cytosol | 13(2.58) | 159(2.34) | |
| GO:0005622 | 胞内Intracellular | 12(2.39) | 102(1.50) | |
| GO:0005737 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | 12(2.39) | 255(3.76) | |
| GO:0005524 | 分子功能Molecular function | ATP结合ATP binding | 97(19.28) | 1 227(18.09) |
| GO:0003677 | DNA结合DNA binding | 84(16.70) | 502(7.40) | |
| GO:0008270 | 锌离子结合Zinc ion binding | 34(6.76) | 317(4.67) | |
| GO:0004674 | 蛋白质丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 Protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 34(6.76) | 394(5.81) | |
| GO:0043531 | ADP结合ADP binding | 14(2.78) | 658(9.70) | |
| GO:0046872 | 金属离子结合Metal ion binding | 14(2.78) | 267(3.94) | |
| GO:0016887 | ATP酶活性ATPase activity | 11(2.19) | 44(0.65) |
富集通路 Enrichment Pathway | 富集通路类型 Enrichment pathway type | 富集基因数量(百分比/%) Enrichment gene number (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|
| 内吞作用Endocytosis | 细胞过程Cellular processes | 6(6.74) |
| ABC转运蛋白ABC transporters | 环境信息处理 Environmental information processing | 5(5.62) |
植物激素信号转运体 Plant hormone signal transporters | 3(3.37) | |
| RNA转运RNA Transport | 遗传信息处理 Genetic information processing | 6(6.74) |
泛素介导的蛋白质水解作用 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 5(5.62) | |
| 蛋白酶体Proteasome | 4(4.49) | |
| RNA聚合酶RNA polymerase | 4(4.49) | |
| 核糖体Ribosome | 3(3.37) | |
氨基酸的生物合成 Biosynthesis of amino acids | 新陈代谢 Metabolism | 4(4.49) |
氨基糖和核苷酸糖的代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 4(4.49) | |
淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 4(4.49) | |
GPI锚生物合成 Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | 3(3.37) | |
谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | 3(3.37) | |
植物-病原互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 有机系统 Organismal system | 3(3.37) |
Table 6 Target gene KEGG pathway enrichment of differential expressed miRs
富集通路 Enrichment Pathway | 富集通路类型 Enrichment pathway type | 富集基因数量(百分比/%) Enrichment gene number (Percentage/%) |
|---|---|---|
| 内吞作用Endocytosis | 细胞过程Cellular processes | 6(6.74) |
| ABC转运蛋白ABC transporters | 环境信息处理 Environmental information processing | 5(5.62) |
植物激素信号转运体 Plant hormone signal transporters | 3(3.37) | |
| RNA转运RNA Transport | 遗传信息处理 Genetic information processing | 6(6.74) |
泛素介导的蛋白质水解作用 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 5(5.62) | |
| 蛋白酶体Proteasome | 4(4.49) | |
| RNA聚合酶RNA polymerase | 4(4.49) | |
| 核糖体Ribosome | 3(3.37) | |
氨基酸的生物合成 Biosynthesis of amino acids | 新陈代谢 Metabolism | 4(4.49) |
氨基糖和核苷酸糖的代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 4(4.49) | |
淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 4(4.49) | |
GPI锚生物合成 Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | 3(3.37) | |
谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | 3(3.37) | |
植物-病原互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 有机系统 Organismal system | 3(3.37) |
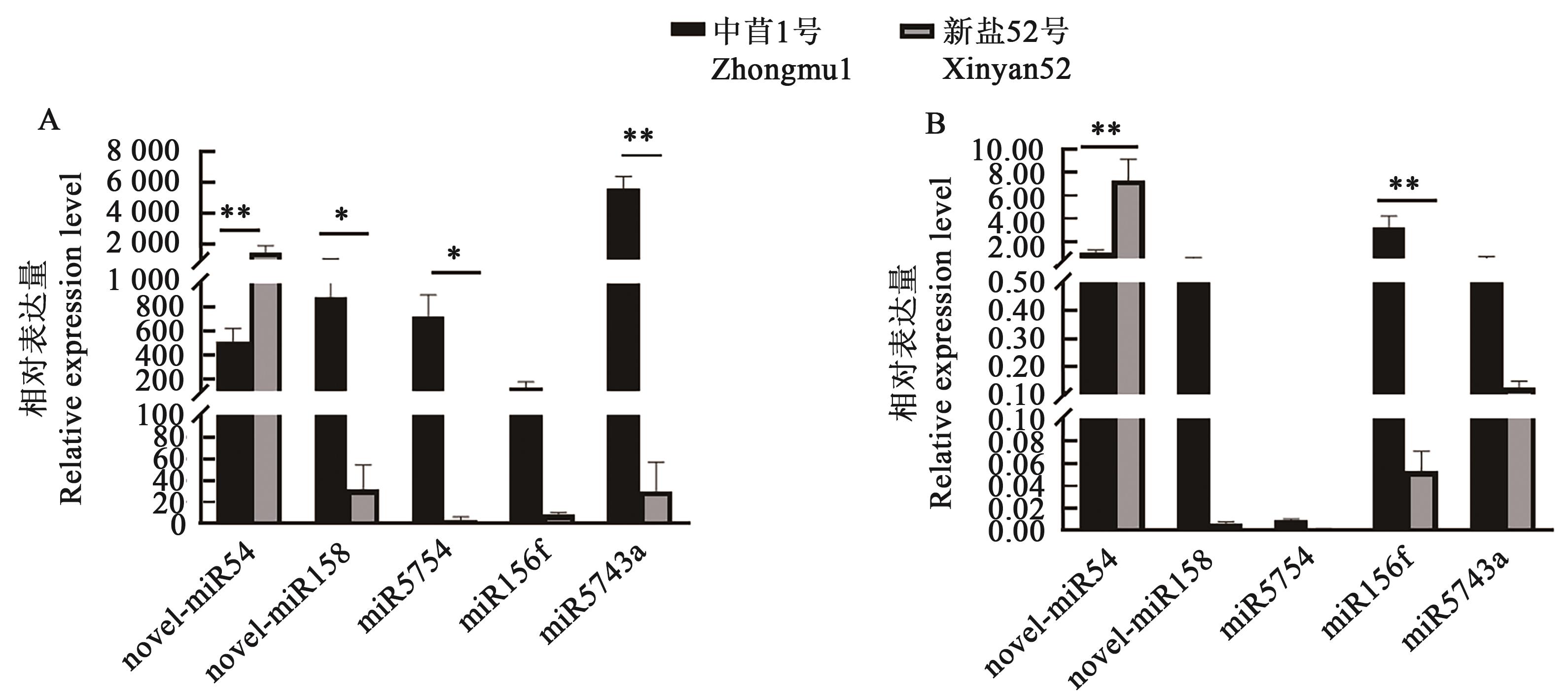
Fig. 4 Relative expression level of differentially expressed miRsA: Base on RNA-Seq; B: Bsae on RT-qPCR;* and ** indicate signifiant differences between different varieties at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively
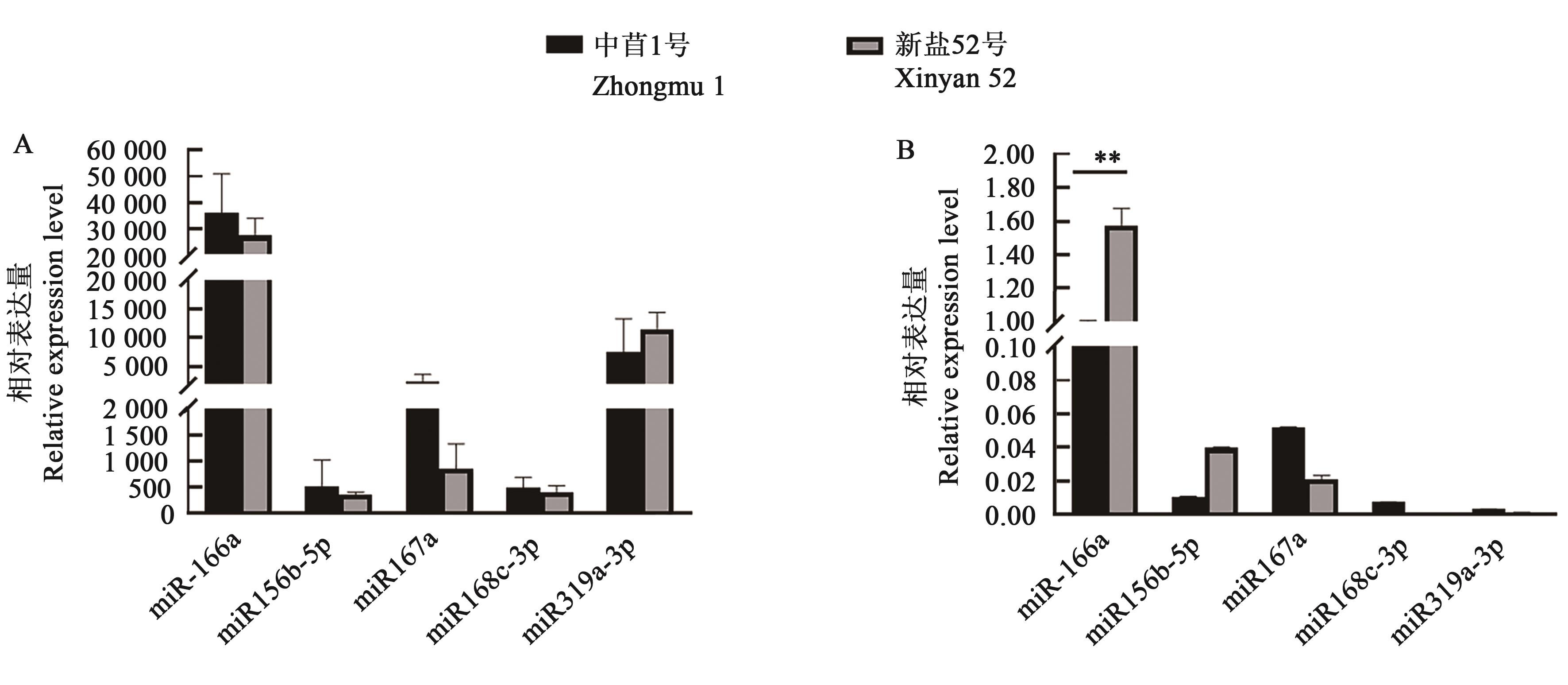
Fig. 5 Relative expression level of cross-kingdom regulated miRsA: Base on RNA-Seq; B: Bsae on RT-qPCR; ** indicates significant differences between different varieties at P<0.01 level
| 1 | AMBROS V, BARTEL B, BARTEL D P, et al.. A uniform system for microRNA annotation [J] . RNA (Cambridge), 2003, 9(3):277-279. |
| 2 | CUI J, YOU C, CHEN X. The evolution of microRNAs in plants [J]. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2017, 35(1):61-67. |
| 3 | FILIPOWICA W, BHATTACHARYYA S N, SOENBERG N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? [J]. Nat. Rev. Genet., 2008, 9(2):102-114. |
| 4 | ZHANG L, HOU D, CHEN X, et al.. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA [J]. Cell Res., 2012, 22(1):107-126. |
| 5 | CHIN A R, FONG M Y, SOMLO G, et al..Cross-kingdom inhibition of breast cancer growth by plant miR159 [J]. Cell Res., 2016, 26(2):217-228. |
| 6 | ZHOU L K, ZHOU Z, JIANG X M, et al.. Absorbed plant MIR2911 in honeysuckle decoction inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and accelerates the negative conversion of infected patients [J/OL]. Cell Discov., 2020, 6:54 [2021-11-10]. . |
| 7 | ZHOU Z, LI X, LIU J, et al.. Honeysuckle-encoded atypical microRNA2911 directly targets influenza A viruses [J]. Cell Res., 2015, 25(1):39-49. |
| 8 | LUO Y, WANG P, WANG X, et al.. Detection of dietetically absorbed maize-derived microRNAs in pigs [J/OL]. Sci. Rep.Uk., 2017, 7(1):645 [2021-11-10]. . |
| 9 | MARZANO F, CARATOZZOLO M F, CONSIGLIO A, et al.. Plant miRNAs reduce cancer cell proliferation by targeting MALAT1 and NEAT1: a beneficial cross-Kingdom interaction [J/OL]. Front. Genet., 2020, 11:552490 [2021-11-10]. . |
| 10 | DAVALOS A, PINILLA L, LOPEZ D L H M C, et al.. Dietary microRNAs and cancer: a new therapeutic approach? [J]. Seminars Cancer Biol., 2021, 73(1):19-29. |
| 11 | WANG D, LIANG G, WANG B, et al.. Systematic microRNAome profiling reveals the roles of microRNAs in milk protein metabolism and quality: insights on low-quality forage utilization [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2016,6: 21194 [2021-11-10]. . |
| 12 | 李跃.紫花苜蓿对干旱的响应:形态、生理以及miRNA组学研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2017. |
| LI Y. Drought response of alfalfa: morphologic, physiological, and miRNA omics studies [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2017. | |
| 13 | 何芳芳.植物MIR156a通过下调JAM-A抑制内皮细胞对单核细胞的黏附[D].南京:南京大学,2019. |
| HE F F. Plant MIR156a inhibits adhension of monocyte to endothelial cells by down-regulating JAM-A [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019. | |
| 14 | 彭朦媛.人参水煎剂及其microRNA对气虚疲劳小鼠的干预和跨界调控作用研究[D].广州:广东药科大学,2020. |
| PENG M Y. Intervention of ginseng decoction and its microRNAs on qi-deficient fatigue mice and study on cross-kingdom regulation of ginseng microRNAs [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2020. | |
| 15 | LUKASIK A, ZIELENKIEWICZ P. In silico identification of plant miRNAs in mammalian breast milk exosomes—a small step forward? [J/OL]. PloS One, 2014, 9:e99963 [2021-11-10]. . |
| 16 | 母治平.猪体内食物源性植物miRNAs的鉴定[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2013. |
| MU Z P. Identification of food-derived exogenous plant miRNAs in swine [D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| 17 | ARSHAD M, FEYISSA B A, AMYOT L, et al.. MicroRNA156 improves drought stress tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by silencing SPL13 [J]. Plant Sci., 2017, 258(1):122-136. |
| 18 | 孙铭优,吴照晨,王斌,等. ABC转运蛋白及其相关的多药抗性研究现状[J].植物保护学报,2022, 49(1): 374-382. |
| SUN M Y, WU Z C, WANG B, et al.. Research status of ABC transporter and its related multidurg resistance [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2022, 49(1):374-382. | |
| 19 | LOCHER K P. Mechanistic diversity in ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters [J]. Nat. Structural Mol. Biol., 2016, 23(6):487-493. |
| 20 | HIGGINS C F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man [J]. Annual Rev. Cell Biol., 1992, 8(1):67-113. |
| 21 | 王依纯,李佳赟,马进.南方型紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa‘Millenium’)耐盐相关miRNAs及靶基因预测[J].分子植物育种,2019,17(24):8072-8081. |
| WANG Y C, LI J Y, MA J. Identification and analysis of microRNAs and targets involved in salt stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa‘Millenium’) [J]. Mole. Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(24):8072-8081. | |
| 22 | KAMMES K L, HEEMINK G B, ALBRENCHT K A, et al.. Utilization of kura clover-reed canarygrass silage versus alfalfa silage by lactating dairy cows [J]. J. Dairy Sci., 2008, 91(8):3138-3144. |
| 23 | SUN H Z, WANG D M, WANG B, et al.. Metabolomics of four biofluids from dairy cows: potential biomarkers for milk production and quality [J]. J. Proteome Res., 2015,14(2): 1287-1298. |
| 24 | WANG B, MAO S Y, YANG H J, et al.. Effects of alfalfa and cereal straw as a forage source on nutrient digestibility and lactation performance in lactating dairy cows [J]. J. Dairy Sci., 2014, 97(12):7706-7715. |
| 25 | 王莹,宋响文. miRNAs在不同物种进化中序列保守性的研究[J].辽宁师范大学学报(自然科学版),2009,32(3):351-355. |
| WANG Y, SONG X W. Conservation of miRNAs sequences in the process of evolution of different species[J]. J. Liaoning Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2009, 32(3):351-355. | |
| 26 | 王鹏俊.猪体内玉米miRNAs的检测及其潜在靶基因的预测和鉴定[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2017. |
| WANG P J. Detection of maize-derived microRNAs and prediction and validation of their potential target genes in pigs [D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 27 | 贾凌.桑树miRNA的鉴定及其在蚕桑互作中的功能研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2015. |
| JIA L. Identification of mulberry miRNA and its function in silkworm mulberry interaction [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2015. | |
| 28 | LUKASIK A, BRZOZOWSKA I, ZIZELENKIEWICZ U, et al.. Detection of plant miRNAs abundance in human breast milk [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 19(1):37 [2021-11-10].. |
| [1] | Baixia ZHAO, Jianfang YAN. Diversity Analysis of Endophytic Bacterial Community in Different Tissues of ‘Summit’ Sweet Cherry Using High-throughput Sequencing [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 66-77. |
| [2] | Ning YAN, Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI. Effects of Reductive Soil Disinfestation on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Enzyme Activity in Continuous Cropping of Ginseng [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [3] | Hongyan ZHAO, Junwei TAN, Jie ZHANG, Haonan CHEN, Chunxu WANG, Di ZHAO, Haipeng LI, Lixia ZHU, Yiqiang HAN. Community Structure of Stem-based Fungi Infected with Adzuki Bean and Mung Bean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 129-136. |
| [4] | Yanchen WEI, Jixiang CHEN, Yonggang WANG, Tongtong MENG, Yalong HAN, Mei LI. Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in the Rhizosphere Soil of Salsolapasserina and Its Correlation with the Soil Physical and Chemical Properties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [5] | Heling FAN, Qing ZHU, Xuebing SUN, Li ZHANG, Changjiang LI, Ping CHEN, Xiaolong HUANG, Rongping ZHANG. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure of Different Agricultural Jiaosu [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 179-189. |
| [6] | LIU Lu1, MING Xiaodong1, ZHANG Xiaoyan2, HAO Junjie2, FU Liping1, WANG Qiankun1, LYU Xin1, CHEN Wang1, LIU Quanlan1*. Diversity of Endophytic Bacteria in Faba Bean Seeds by High-Throughput Sequencing [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 73-80. |
| [7] | YANG Jingjing, ZHANG Qingqing*, Tuerxunnayi·Reyimu, Amanula·Yimingniyazi, Xueretijiang·Maitinuri. Effects of Nomadic Grazing and Settled Grazing on the Diversity of Fungi Community in Seriphidium transiliense Desert Grassland [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yijie, SHAO Huifang*, ZHANG Ke, JIA Hongfang, HUANG Wuxing, HAN Dan. Influences of Fertilization on Soil Environment and Microorganism in Continuous Cropping Based on High-Throughput Sequencing [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(5): 16-25. |
| [9] | QU Meng-nan1,2§, JIANG Bing-jun2§, LIU Wei2, MA Li-ming2, LIN Kang-xue2, HAN T F. New Approaches to Molecular Breeding of Soybean [J]. , 2014, 16(3): 8-13. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号