




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 80-95.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0156
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xianguo LI1,2( ), Qi DAI1, Zepeng WANG1,2, Zhaolong CHEN1,2, Huizhuan YAN2, Ning LI1(
), Qi DAI1, Zepeng WANG1,2, Zhaolong CHEN1,2, Huizhuan YAN2, Ning LI1( )
)
Received:2023-03-06
Accepted:2023-06-14
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Ning LI
李贤国1,2( ), 戴麒1, 王泽鹏1,2, 陈兆龙1,2, 闫会转2, 李宁1(
), 戴麒1, 王泽鹏1,2, 陈兆龙1,2, 闫会转2, 李宁1( )
)
通讯作者:
李宁
作者简介:李贤国 E-mail:15099198840@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xianguo LI, Qi DAI, Zepeng WANG, Zhaolong CHEN, Huizhuan YAN, Ning LI. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tomato CCCH-like Zinc Finger Protein Family[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 80-95.
李贤国, 戴麒, 王泽鹏, 陈兆龙, 闫会转, 李宁. 番茄CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 80-95.
基因 Gene | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1 | TGGGTTTCAGTCTTCACCAGTT | TCCACTCGGACTCATAACCG |
| SlC3H2 | TGGCAATGGTGGATTCAAG | ACCAAGCATCTGAGTCACAGC |
| SlC3H3 | GCAGTCTCCTTCTGTTCAATCC | CGGATAAGGAGTCCAACCTGGT |
| SlC3H4 | CTTTCGGTAGCAGTGGAGGCAT | CATAGCAGTGTAGCCAGGAACA |
| SlC3H5 | TTCTGCTATTGATGAGGTGGG | TGGACCACAAGCACGGTTA |
| SlC3H6 | TGGTTCGCTCCACAGACTTT | TGGAACTTTCTTTGCCACTGC |
| SlC3H7 | CTGCGATTACTGCGATAAGGA | GCAGACTCCTTTACCGAACGA |
| SlC3H8 | GATTATGAATGGGCGGACTTG | GATGCCAGCGTCTTGTAGGA |
| SlC3H9 | CAGAGACAACGCCATCCAA | CCTTGATGTTGCTGTTGCG |
| SlC3H10 | GCAAGACAGGTGGTGATGACA | GCTGAAACTCTGATGTGAGCAG |
| SlC3H11 | GCAACAAATGGCAGGAGACT | GAAGTGGCAACGGTGACCATA |
| SlC3H12 | ACGATAAAGGTCTGGGCTGC | GGCAAATCATAGACACGAATGG |
| SlC3H13 | GGAAGCAAATCAAAGCCGT | TGGGAATAGGTGATGCTGGA |
| SlC3H14 | GATGATGAGATGGCGATGC | TCCCTTCAACATTTCCAAGC |
| SlC3H15 | GCAGTTATGGTGAAAGGTGCC | CACTTCATTTCCACCAGACACA |
| SlC3H16 | — | — |
| SlC3H17 | GAAGGGAAGAGGGTATTGGGCT | CTGGTCCTAAACTTGTCCCGT |
| SlC3H18 | GGAAGTAAGAAGGAAGAGGAACCA | CGGCATACCTCAGTCTTGTAACG |
| SlC3H19 | AGAATCAATGAGGAGGTTGGG | ACAGCACAGCACCAACAGAG |
| SlC3H20 | AGTTGCCGCTTTGAAGAGC | ACCGCAAATCTCCTTGGCTG |
| SlC3H21 | AGGGAGAGGAATCACCAAGC | ATAAGTGGCTGGCGGTGGAA |
| SlC3H22 | TTTGGTTACCCGTTGCGA | AACAACCGCTGGCAAAGGA |
| SlC3H23 | TCGGAAAGTGATAGCGACTACG | CCTTAGAAACATTCCGCCTGA |
| SlC3H24 | AATGAGAAGGCTGGTGACGC | GGGTAACTCAACCTCCTCCCAT |
| SlC3H25 | TTCTGACCAGGCAGTTTGGG | TGCGAGCATCTGAATCCTGC |
| SlC3H26 | AATGAGGTGGGCTTATGGTATG | TAGCCCTATCCGAACCACAAGC |
| SlC3H27 | CGATTAGCGTTTAGTCCCGAA | CCAACTTGATGGTTCGTAAAGG |
| SlC3H28 | CCACGATTGGACGGATTGT | AAGCCAACACTCAAACACCC |
| SlC3H29 | TTGCGAGGGAGATTATGTGC | GGGCTACTGAACACTGGATTTG |
| SlC3H30 | CTACACCCTGCTCGCTATCGTA | CCATCAAACGAATCAGACGAC |
| SlC3H31 | TGGCTCCACCAGTTGTCTCT | TCCAACTTCACTCTCACAAGGC |
| SlC3H32 | AACCTGCTGGTATGTCTGTGCC | GAAGCAACACTGGACCATAAGC |
| SlC3H33 | CTCAGTCTTCAGCACAACCTCA | TGATTGGCTGGAAGCGTCA |
| SlC3H34 | TCAGAACTTCATAGGACGAGGC | GGTGCTTTGGAGAATCGCT |
| SlC3H35 | GCTCCAGCATCAAGAAATGTG | GGCACAATCGGCTTACCAAT |
| SlC3H36 | CCTATGGTTATCGCCCTCTTGA | TCCAAGAGAAGGCGAAAGTG |
| SlC3H37 | GAACTTGCTGCCAACGATG | CGTAGCAGCAACCATCAAAGG |
| SlC3H38 | CAGCACCGCCTTATTCCAA | TCTTGTGAAGGAATGGTAGGCT |
| SlC3H39 | CGCAGTCATAGTAGAAGCCGA | TGTGTCCACTCCTTCGTCCA |
| SlC3H40 | TTATCCTGTCCGTGAAGGTGA | GGCATTCGGGTTGTCCTATTC |
| SlC3H41 | GGATTTCTTGAGGATGAAGGC | CCCATCATAAATGTCGCAGC |
| SlC3H42 | GCTATGAAGACCGCTCTCACA | CTGCCATCCCTAACTGGACTT |
| SlC3H43 | ATCCTGCCGTTACGCTCAT | AACGCCTCAGTCATCATAACG |
| SlC3H44 | CCTGTTCCCTCGCACTTTATG | TTCGGCGAGTTGCTATCAA |
| SlC3H45 | ACCACCTATGTCTCCGATGACG | CCGAATACAGGTGAACCCATT |
| SlC3H46 | GCAGCAGACAAAGTCCAACC | AGGCTGATTGTCGGTTTGC |
| SlC3H47 | CGGAATAGTAGCCGCCAATAC | AACACCAGGAGGTCCATAACC |
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
基因 Gene | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1 | TGGGTTTCAGTCTTCACCAGTT | TCCACTCGGACTCATAACCG |
| SlC3H2 | TGGCAATGGTGGATTCAAG | ACCAAGCATCTGAGTCACAGC |
| SlC3H3 | GCAGTCTCCTTCTGTTCAATCC | CGGATAAGGAGTCCAACCTGGT |
| SlC3H4 | CTTTCGGTAGCAGTGGAGGCAT | CATAGCAGTGTAGCCAGGAACA |
| SlC3H5 | TTCTGCTATTGATGAGGTGGG | TGGACCACAAGCACGGTTA |
| SlC3H6 | TGGTTCGCTCCACAGACTTT | TGGAACTTTCTTTGCCACTGC |
| SlC3H7 | CTGCGATTACTGCGATAAGGA | GCAGACTCCTTTACCGAACGA |
| SlC3H8 | GATTATGAATGGGCGGACTTG | GATGCCAGCGTCTTGTAGGA |
| SlC3H9 | CAGAGACAACGCCATCCAA | CCTTGATGTTGCTGTTGCG |
| SlC3H10 | GCAAGACAGGTGGTGATGACA | GCTGAAACTCTGATGTGAGCAG |
| SlC3H11 | GCAACAAATGGCAGGAGACT | GAAGTGGCAACGGTGACCATA |
| SlC3H12 | ACGATAAAGGTCTGGGCTGC | GGCAAATCATAGACACGAATGG |
| SlC3H13 | GGAAGCAAATCAAAGCCGT | TGGGAATAGGTGATGCTGGA |
| SlC3H14 | GATGATGAGATGGCGATGC | TCCCTTCAACATTTCCAAGC |
| SlC3H15 | GCAGTTATGGTGAAAGGTGCC | CACTTCATTTCCACCAGACACA |
| SlC3H16 | — | — |
| SlC3H17 | GAAGGGAAGAGGGTATTGGGCT | CTGGTCCTAAACTTGTCCCGT |
| SlC3H18 | GGAAGTAAGAAGGAAGAGGAACCA | CGGCATACCTCAGTCTTGTAACG |
| SlC3H19 | AGAATCAATGAGGAGGTTGGG | ACAGCACAGCACCAACAGAG |
| SlC3H20 | AGTTGCCGCTTTGAAGAGC | ACCGCAAATCTCCTTGGCTG |
| SlC3H21 | AGGGAGAGGAATCACCAAGC | ATAAGTGGCTGGCGGTGGAA |
| SlC3H22 | TTTGGTTACCCGTTGCGA | AACAACCGCTGGCAAAGGA |
| SlC3H23 | TCGGAAAGTGATAGCGACTACG | CCTTAGAAACATTCCGCCTGA |
| SlC3H24 | AATGAGAAGGCTGGTGACGC | GGGTAACTCAACCTCCTCCCAT |
| SlC3H25 | TTCTGACCAGGCAGTTTGGG | TGCGAGCATCTGAATCCTGC |
| SlC3H26 | AATGAGGTGGGCTTATGGTATG | TAGCCCTATCCGAACCACAAGC |
| SlC3H27 | CGATTAGCGTTTAGTCCCGAA | CCAACTTGATGGTTCGTAAAGG |
| SlC3H28 | CCACGATTGGACGGATTGT | AAGCCAACACTCAAACACCC |
| SlC3H29 | TTGCGAGGGAGATTATGTGC | GGGCTACTGAACACTGGATTTG |
| SlC3H30 | CTACACCCTGCTCGCTATCGTA | CCATCAAACGAATCAGACGAC |
| SlC3H31 | TGGCTCCACCAGTTGTCTCT | TCCAACTTCACTCTCACAAGGC |
| SlC3H32 | AACCTGCTGGTATGTCTGTGCC | GAAGCAACACTGGACCATAAGC |
| SlC3H33 | CTCAGTCTTCAGCACAACCTCA | TGATTGGCTGGAAGCGTCA |
| SlC3H34 | TCAGAACTTCATAGGACGAGGC | GGTGCTTTGGAGAATCGCT |
| SlC3H35 | GCTCCAGCATCAAGAAATGTG | GGCACAATCGGCTTACCAAT |
| SlC3H36 | CCTATGGTTATCGCCCTCTTGA | TCCAAGAGAAGGCGAAAGTG |
| SlC3H37 | GAACTTGCTGCCAACGATG | CGTAGCAGCAACCATCAAAGG |
| SlC3H38 | CAGCACCGCCTTATTCCAA | TCTTGTGAAGGAATGGTAGGCT |
| SlC3H39 | CGCAGTCATAGTAGAAGCCGA | TGTGTCCACTCCTTCGTCCA |
| SlC3H40 | TTATCCTGTCCGTGAAGGTGA | GGCATTCGGGTTGTCCTATTC |
| SlC3H41 | GGATTTCTTGAGGATGAAGGC | CCCATCATAAATGTCGCAGC |
| SlC3H42 | GCTATGAAGACCGCTCTCACA | CTGCCATCCCTAACTGGACTT |
| SlC3H43 | ATCCTGCCGTTACGCTCAT | AACGCCTCAGTCATCATAACG |
| SlC3H44 | CCTGTTCCCTCGCACTTTATG | TTCGGCGAGTTGCTATCAA |
| SlC3H45 | ACCACCTATGTCTCCGATGACG | CCGAATACAGGTGAACCCATT |
| SlC3H46 | GCAGCAGACAAAGTCCAACC | AGGCTGATTGTCGGTTTGC |
| SlC3H47 | CGGAATAGTAGCCGCCAATAC | AACACCAGGAGGTCCATAACC |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1 | Solyc01G000285 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H2 | Solyc01G000732 | Chr1 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| SlC3H3 | Solyc01G001958 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H4 | Solyc01G002357 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H5 | Solyc01G002417 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H6 | Solyc01G002511 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H7 | Solyc01G003423 | Chr1 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| SlC3H8 | Solyc01G003523 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H9 | Solyc02G000685 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H10 | Solyc02G001874 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H11 | Solyc02G002224 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H12 | Solyc03G000439 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H13 | Solyc03G001290 | Chr3 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| SlC3H14 | Solyc03G002428 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H15 | Solyc03G002917 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H16 | Solyc03G003234 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H17 | Solyc04G002040 | Chr4 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H18 | Solyc05G000368 | Chr5 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| SlC3H19 | Solyc06G000257 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H20 | Solyc06G000284 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H21 | Solyc06G001227 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H22 | Solyc06G001228 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H23 | Solyc06G001444 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H24 | Solyc06G002030 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H25 | Solyc06G002122 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H26 | Solyc06G002533 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H27 | Solyc07G001794 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H28 | Solyc07G002095 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H29 | Solyc07G002693 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H30 | Solyc08G001378 | Chr8 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H31 | Solyc09G001678 | Chr9 | 细胞外基质Extracellular | ||||
| SlC3H32 | Solyc09G002209 | Chr9 | — | ||||
| SlC3H33 | Solyc10G000921 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H34 | Solyc10G001254 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H35 | Solyc10G002269 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H36 | Solyc10G002300 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H37 | Solyc10G002434 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H38 | Solyc10G002434 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H39 | Solyc10G002648 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H40 | Solyc11G000372 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| SlC3H41 | Solyc11G001986 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H42 | Solyc11G002140 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H43 | Solyc11G002291 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H44 | Solyc11G002364 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H45 | Solyc12G000277 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H46 | Solyc12G000350 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H47 | Solyc12G000810 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus |
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of amino acid sequences encoded by members of tomato SlC3H gene family
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1 | Solyc01G000285 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H2 | Solyc01G000732 | Chr1 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| SlC3H3 | Solyc01G001958 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H4 | Solyc01G002357 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H5 | Solyc01G002417 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H6 | Solyc01G002511 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H7 | Solyc01G003423 | Chr1 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| SlC3H8 | Solyc01G003523 | Chr1 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H9 | Solyc02G000685 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H10 | Solyc02G001874 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H11 | Solyc02G002224 | Chr2 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H12 | Solyc03G000439 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H13 | Solyc03G001290 | Chr3 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| SlC3H14 | Solyc03G002428 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H15 | Solyc03G002917 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H16 | Solyc03G003234 | Chr3 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H17 | Solyc04G002040 | Chr4 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H18 | Solyc05G000368 | Chr5 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| SlC3H19 | Solyc06G000257 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H20 | Solyc06G000284 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H21 | Solyc06G001227 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H22 | Solyc06G001228 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H23 | Solyc06G001444 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H24 | Solyc06G002030 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H25 | Solyc06G002122 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H26 | Solyc06G002533 | Chr6 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H27 | Solyc07G001794 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H28 | Solyc07G002095 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H29 | Solyc07G002693 | Chr7 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H30 | Solyc08G001378 | Chr8 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H31 | Solyc09G001678 | Chr9 | 细胞外基质Extracellular | ||||
| SlC3H32 | Solyc09G002209 | Chr9 | — | ||||
| SlC3H33 | Solyc10G000921 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H34 | Solyc10G001254 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H35 | Solyc10G002269 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H36 | Solyc10G002300 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H37 | Solyc10G002434 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H38 | Solyc10G002434 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H39 | Solyc10G002648 | Chr10 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H40 | Solyc11G000372 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲疏水性 Gravy | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| SlC3H41 | Solyc11G001986 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H42 | Solyc11G002140 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H43 | Solyc11G002291 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H44 | Solyc11G002364 | Chr11 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H45 | Solyc12G000277 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H46 | Solyc12G000350 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus | ||||
| SlC3H47 | Solyc12G000810 | Chr12 | 细胞核Nucleus |
重复基因对 Duplicated gene pairs | 同义替换率 Ka | 非同义替换率 Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1/SlC3H41 | 0.177 401 | 0.647 337 | 0.274 048 |
| SlC3H35/SlC3H38 | 0.113 408 | 0.685 379 | 0.165 467 |
| SlC3H36/SlC3H37 | 0.152 286 | 0.535 449 | 0.284 408 |
| SlC3H45/SlC3H30 | 0.298 310 | 1.423 712 | 0.209 530 |
| SlC3H14/SlC3H24 | 0.283 640 | 0.744 457 | 0.381 003 |
| SlC3H19/SlC3H32 | 0.204 448 | 0.524 756 | 0.389 606 |
Table 3 Ka/Ks analysis of tomato SlC3H genes
重复基因对 Duplicated gene pairs | 同义替换率 Ka | 非同义替换率 Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| SlC3H1/SlC3H41 | 0.177 401 | 0.647 337 | 0.274 048 |
| SlC3H35/SlC3H38 | 0.113 408 | 0.685 379 | 0.165 467 |
| SlC3H36/SlC3H37 | 0.152 286 | 0.535 449 | 0.284 408 |
| SlC3H45/SlC3H30 | 0.298 310 | 1.423 712 | 0.209 530 |
| SlC3H14/SlC3H24 | 0.283 640 | 0.744 457 | 0.381 003 |
| SlC3H19/SlC3H32 | 0.204 448 | 0.524 756 | 0.389 606 |
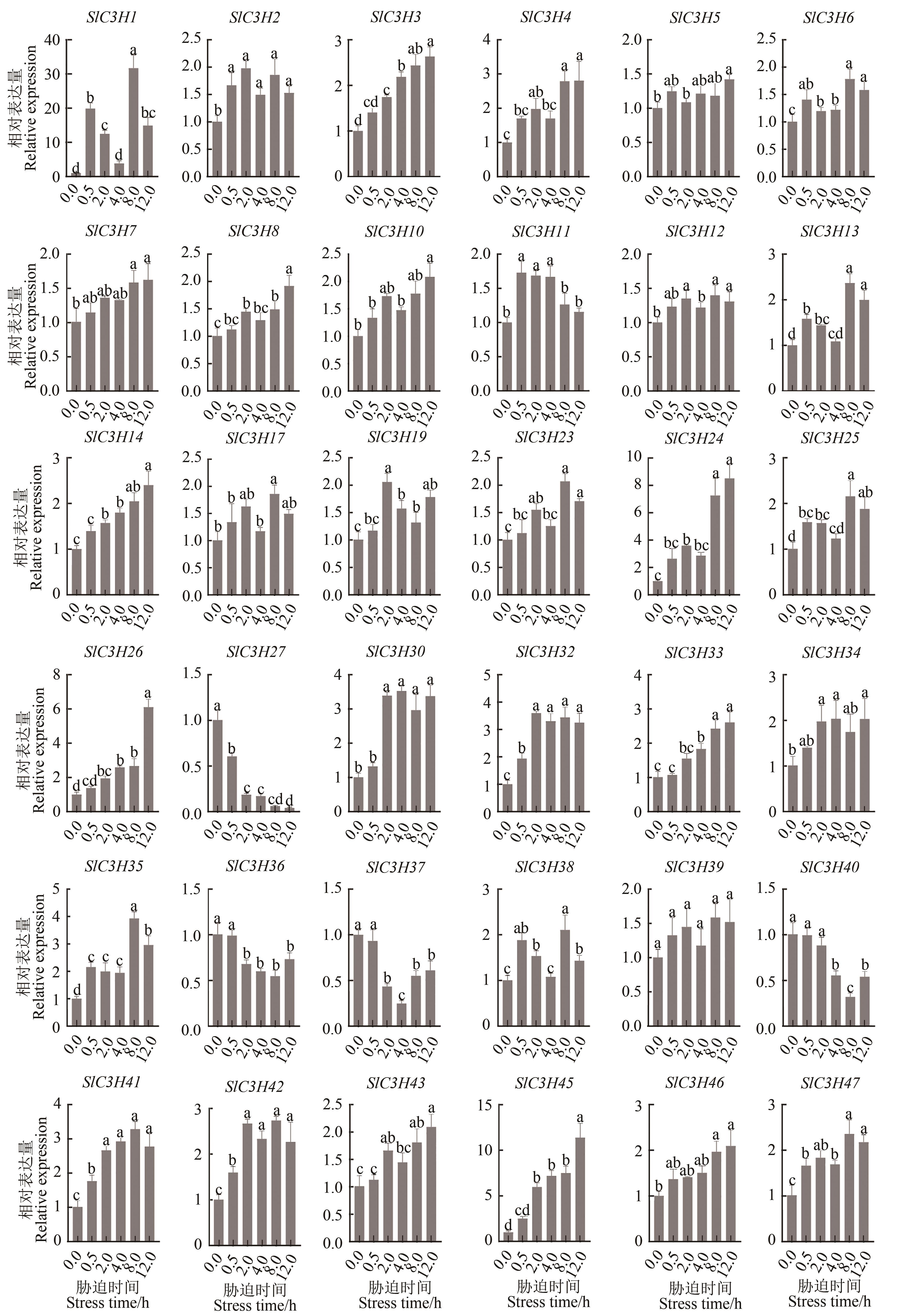
Fig. 7 Expression of tomato SlC3H family genes in response to salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different stress times at P<0.05 level.
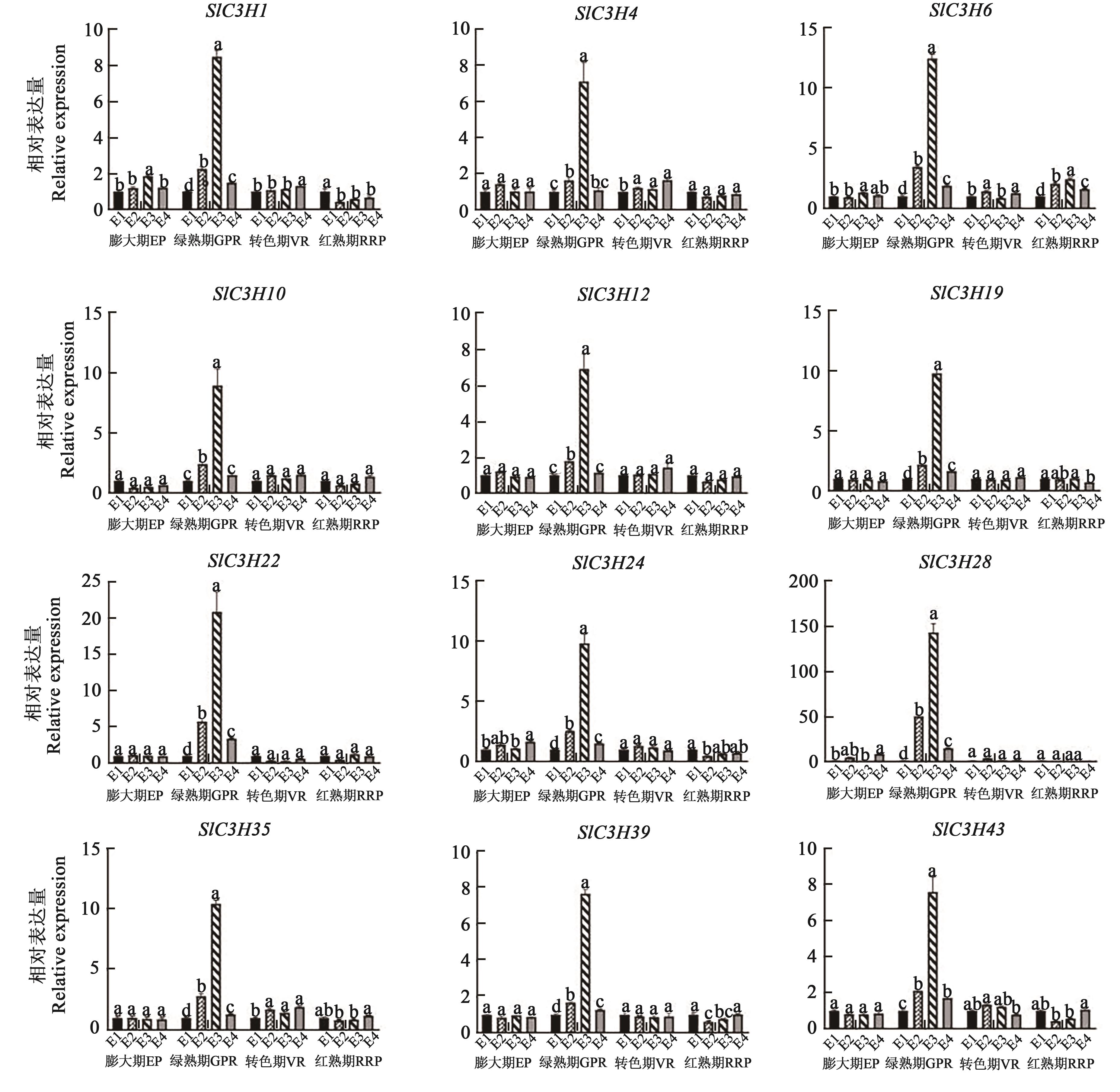
Fig. 8 Expression analysis of tomato SlC3H family genes under hormonal stress during fruit developmentNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same period at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | GAO G, GUO X, GOFF S P, et al.. Inhibition of retroviral RNA production by ZAP, a CCCH-type zinc finger protein [J]. Science, 2002, 297(5587):1703-1706. |
| 2 | MAZUMDAR P, LAU S E, WEE W Y, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of the CCCH zinc-finger gene family in banana (Musa acuminata): an insight in to motif and gene structure arrangement, evolution and salt stress responses [J]. Trop. Plant Biol., 2017, 10(11):177-193. |
| 3 | DRÖGE-LASER W, SNOEK B L, SNEL B, et al.. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family-an update [J]. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2018, 45(PtA):36-49. |
| 4 | SU L Y, XIAO X C, JIANG M Q, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of the CCCH zinc finger family in longan: characteristic identification and expression profiles in Dimocarpus longan Lour [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2022, 21(1):113-130. |
| 5 | DELANEY K J, XU R, ZHANG J, et al.. Calmodulin interacts with and regulates the RNA-binding activity of an Arabidopsis polyadenylation factor subunit [J]. Plant Physiol., 2006, 140 (4):1507-1521. |
| 6 | CARRICK D M, LAI W S, BLACKSHEAR P J. The tandem CCCH zinc finger protein tristetraprolin and its relevance to cytokine mRNA turnover and arthritis [J]. Arthritis Res. Ther., 2004, 6 (6):248-264. |
| 7 | DE J, LAI W S, THORN J M, et al.. Identification of four CCCH zinc finger proteins in Xenopus, including a novel vertebrate protein with four zinc fingers and severely restricted expression [J]. Gene, 1999, 228(1-2):133-145. |
| 8 | BOGAMUWA S P, JANG J C. Tandem CCCH zinc finger proteins in plant growth, development and stress response [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2014, 55(8):1367‐1375. |
| 9 | ZHANG L Y, BAI M Y, WU J, et al.. Antagonistic HLH/bHLH transcription factors mediate brassinosteroid regulation of cell elongation and plant development in rice and Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(12):3767-3780. |
| 10 | ZHANG H, GAO X, ZHI Y, et al.. A non‐tandem CCCH‐type zinc-finger protein, IbC3H18, functions as a nuclear transcriptional activator and enhances abiotic stress tolerance in sweet potato [J]. New Phytol., 2019, 223(4):1918‐1936. |
| 11 | KIM D H, YAMAGUCHI S, LIM S, et al.. SOMNUS, a CCCH-type zinc finger protein in Arabidopsis, negatively regulates light-dependent seed germination downstream of PIL5 [J]. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(5):1260-1277. |
| 12 | LI J, JIA D, CHEN X. HUA1, a regulator of stamen and carpel identities in Arabidopsis, codes for a nuclear RNA binding protein [J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(10):2269-2281. |
| 13 | JIANG M, JIANG J J, MIAO L X, et al.. Over-expression of a C3H-type zinc finger gene contributes to salt stress tolerance in transgenic broccoli plants [J]. Plant Cell, 2017, 130(2):239-254. |
| 14 | PRADHAN S, KANT C, VERMA S, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of the CCCH zinc finger family identifies tissue specific and stress responsive candidates in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) [J/OL]. PloS One, 2017, 12(7):e0180469 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 15 | GUO Y H, YU YP, WANG D, et al.. GhZFP1, a novel CCCH-type zinc fifinger protein from cotton, enhances salt stress tolerance and fungal disease resistance in transgenic tobacco by interacting with GZIRD21A and GZIPR5 [J]. New Phytol., 2009,183(1):62-75. |
| 16 | 刘雨轩.番茄WRKY基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2020. |
| LIU Y X. Identification and expression analysis of tomato WRKY gene family members [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 17 | WANG D, GUO Y, WU C, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of CCCH zinc finger family in Arabidopsis and rice [J]. BMC Genomics, 2008, 9(1):44-64. |
| 18 | PENG X, ZHAO Y, CAO J, et al.. CCCH-type zinc finger family in maize: genome-wide identification, classification and expression profiling under abscisic acid and drought treatments [J/OL]. PloS One, 2012, 7(7): e40120 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 19 | LI C, FANG Q, ZHANG W, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the CCCH gene family in rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.) reveals its potential functions [J]. Biotechnol. Equip., 2021, 35(1):517-526. |
| 20 | 唐春闺,邓兆龙,刘琼,等.普通烟草CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的全基因组鉴定和表达分析[J]. 河南农业科学, 2022, 51(4): 48-58. |
| TANG C G, DENG Z L, LIU Q, et al.. Genome wide identification and expression analysis of CCCH zinc finger like protein family in tobacco [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2022, 51(4):48-58. | |
| 21 | XU R. Genome-wide analysis and identification of stress-responsive genes of the CCCH zinc finger family in Solanum lycopersicum [J]. Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2014, 289(5):965-979. |
| 22 | PI B, HE X, RUAN Y, et al.. Genome-wide analysis and stress-responsive expression of CCCH zinc finger family genes in Brassica rapa [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2018, 18(1):7 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 23 | PI B, PAN J, XIAO M, et al.. Systematic analysis of CCCH zinc finger family in Brassica napus showed that BnRR-TZFs are involved in stress resistance [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2021, 21(1):8 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 24 | LIU S, KHAN M R G, LI Y, et al.. Comprehensive analysis of CCCH-type zinc finger gene family in citrus (Clementine mandarin) by genome-wide characterization [J]. Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2014, 289(5): 855-872. |
| 25 | WANG X L, ZHONG Y, CHENG Z M. Evolution and expression analysis of the CCCH zinc finger gene family in Vitis vinifera [J]. Plant Genome, 2014, 7(3):16-25. |
| 26 | PRAKASH A, JEFFRYES M, BATEMAN A, et al.. The HMMER web server for protein sequence similarity search [J]. Curr. Prot. Bioinf., 2017, 60:15-23. |
| 27 | GASTEIGER E, GATTIKER A, HOOGLAND C, et al.. ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2003, 31(13):3784-3788. |
| 28 | HORTON P, PARK K J, OBAYASHI T, et al.. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2007, 35:585-587. |
| 29 | KUMAR S, STECHER G, LI M, et al.. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms [J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2018, 35(6):1547-1579. |
| 30 | BAILEY T L, BODEN M, BUSKE F A, et al.. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2009, 37:202-208. |
| 31 | CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al.. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Mol. Plant, 2020, 13(8):1191-1202. |
| 32 | WANG Y P, TANG H B, DEBARRY J D, et al.. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity [J/OL]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2012, 40(7):e49 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 33 | KRZYWINSKI M, SCHEIN J, BIROL I, et al.. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics [J]. Genome Res., 2009, 19(9):1639-1645. |
| 34 | WANG D, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al.. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies [J]. Genom Proteom. Bioinf., 2010, 8(1):77-80. |
| 35 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔ CT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408. |
| 36 | YAO Q, BAI Y, KUMAR S, et al.. Minimal residual disease detection by next-generation sequencing in multiple myeloma: A omparison with real-time quantitative PCR [J/OL]. Front. Oncol., 2020, 10: 611021 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 37 | CHAI G, HU R, ZHANG D, et al.. Comprehensive analysis of CCCH zinc finger family in poplar (Populus trichocarpa ) [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2012, 13(1):253 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 38 | JOUFFREY V, LEONARD A S, AHNERT S E. Gene duplication and subsequent diversification strongly affect phenotypic evolvability and robustness [J]. Roy Soc. Open Sci., 2021, 8(6):1636-1642. |
| 39 | WANG W, JIANG W, LIU J G, et al.. Genome-wide characterization of the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene superfamily in soybean and its potential role in drought stress response [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1):518 [2023-02-05]. . |
| 40 | 魏梦园,刘爱丽,黎冬华,等.芝麻CCCH锌指蛋白基因SiC3H1的克隆及表达分析[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(24):7982-7988. |
| WEI M Y, LIU A L, LI D H, et al.. Cloning and expression analysis of CCCH zinc finger protein gene SiC3H1 from sesame [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2020, 18(24):7982-7988. | |
| 41 | 刘小艳,孙艳侠,王亚男,等.水稻CCCH型锌指蛋白亚家族Ⅰ基因的表达分析[J]. 山东农业科学,2015,47(2):7-11. |
| LIU X Y, SUN Y X, WANG Y N, et al.. Expression analysis of CCCH zinc finger protein subfamily Ⅰ genes in rice [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2015, 47(2):7-11. | |
| 42 | VERMA V, RAVINDRAN P, KUMAR P P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2016, 16:1-10. |
| 43 | LIN P C, POMERANZ M C, JIKUMARU Y, et al.. The Arabidopsis tandem zinc finger protein AtTZF1 affects ABA‐and GA‐mediated growth, stress and gene expression responses [J]. Plant J., 2011, 65(2):253-268. |
| [1] | Chunjiao MI, Hongren SUN, Jiping ZHANG, Yucai LYU, Yandi ZHANG. Abundance-deficiency Index of Soil Available Phosphorus and Recommended Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rates for Tomato in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [2] | Junlei ZHANG, Xiaotong GE, Zhengting ZHAO, Di LIU, Jinfeng WANG, Ning JIANG, Yating LIU. Establishment and Optimization of RT-LAMP Assay System for Tobacco Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [3] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [4] | Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [5] | Mingbo LI, Yule LIU, Zhimin MU, Junwang GUO, Yong WEI, Dongyue REN, Jishen JIA, Zezhong WEI, Yuhong LI. Tomato Fruit Recognition Based on YOLOX-L-TN Model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 97-105. |
| [6] | Daye HUANG, Zhibin YU, Zhongyi WAN, Dan YANG, Jinping LI, Chunxia CAO. Study on Control Effect of Streptomyces phaeoluteichromatogenes HEBRC45958 Strain on Corynespora Leaf Spot of Tomato [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(11): 136-142. |
| [7] | Zhenwei ZHANG, Xiangshu DONG, Jing YANG, Xuejun LI, Meijun QI, Kuaile JIANG, Yonglin YANG, Butian WANG, Xuedong SHI, Junchao QIU, Zhihua CHEN, Yu GE. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Key Chlorophyll Synthesis Related Gene CaPOR in Coffea arabica [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 83-97. |
| [8] | Yurong DENG, Lian HAN, Jinlong WANG, Xinghan WEI, Xudong WANG, Ying ZHAO, Xiaohong WEI, Chaozhou LI. Identification of SOD Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa and Their Response to Mixed Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [9] | Xiubo XIA, Tao LI, Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG. Effect of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Partial Replacing Chemical Fertilizer on Bacterial Community in Greenhouse Tomato Root Zone [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 187-196. |
| [10] | Jinfeng ZHAO, Aili YU, Yanfang LI, Yanwei DU, Gaohong WANG, Zhenhua WANG. Response Characteristics of SiCBL3 to Abiotic Stresses in Foxtail Millet [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| [11] | LIU Zhengwen, WANG Xingfen, MENG Chengsheng, ZHANG Yan, SUN Zhengwen, WU Liqiang, MA Zhiying, ZHANG Guiyin. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of GH9 Gene Family in Gossypium barbadense L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(9): 30-45. |
| [12] | PU Quanming, YANG Peng, YONG Lei, DENG Yuchuan, HE Zihan, LIN Bangmin, SHI Songmei, XIANG Chengyong, FANG Fang. Studies on Pigment Content and Photosyntheic Characteristics of Purple-red Leaf Color Mutant in Radish [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| [13] | CUI Jianghui§, YANG Puyuan§, CHANG Jinhua*. Identification and Expression Analysis Under Abiotic Stress of GRF Gene Family in Sorghum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 37-46. |
| [14] | LIU Qianjie, CHENG Yunxia, JIA Kai, SHI Zhenyu, ZHANG Jing, WEI Shaowei, WU Hui*. Influences of Nitrogen Application on Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes Activities, Yield and Quality of Tomato in Composite Sand Culture [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 183-191. |
| [15] | GU Huimin1, CHEN Bolang1*, SUN Jin2. Influences of Mycorrhizal Seedling on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Processing Tomato Under Salt Stress#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号