




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 122-128.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0871
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Shifeng MU1,2( ), Xiaolei WEN1,2(
), Xiaolei WEN1,2( ), Lina FENG1,2, Dexuan ZHAO1,2, Suhong GAO1,2, Peng GAO1,2, Huixia QI1,2(
), Lina FENG1,2, Dexuan ZHAO1,2, Suhong GAO1,2, Peng GAO1,2, Huixia QI1,2( )
)
Received:2023-11-28
Accepted:2024-01-03
Online:2024-09-15
Published:2024-09-13
Contact:
Huixia QI
母时风1,2( ), 温晓蕾1,2(
), 温晓蕾1,2( ), 冯丽娜1,2, 赵德轩1,2, 高素红1,2, 高朋1,2, 齐慧霞1,2(
), 冯丽娜1,2, 赵德轩1,2, 高素红1,2, 高朋1,2, 齐慧霞1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
齐慧霞
作者简介:母时风 E-mail:2786848750@qq.com基金资助:CLC Number:
Shifeng MU, Xiaolei WEN, Lina FENG, Dexuan ZHAO, Suhong GAO, Peng GAO, Huixia QI. Identification and Biological Characteristics of a Colletotrichum fructicola Causing Chestnut Internal Rot Disease[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 122-128.
母时风, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 赵德轩, 高素红, 高朋, 齐慧霞. 一种引起板栗内腐病的果生炭疽菌鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 122-128.
| 基因Gene | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| ITS | ITS1 | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |
| TUB2 | βt2a | GGTAACCAAATCGGTGCTGCTTTC |
| βt2b | ACCCTCAGTGTAGTGACCCTTGGC | |
| CAL | CL1 | GAATTCAAGGAGGCCTTCTC |
| CL2 | CTTCTGCATCATGAGCTGGAC |
Table 1 Primers sequence used
| 基因Gene | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| ITS | ITS1 | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |
| TUB2 | βt2a | GGTAACCAAATCGGTGCTGCTTTC |
| βt2b | ACCCTCAGTGTAGTGACCCTTGGC | |
| CAL | CL1 | GAATTCAAGGAGGCCTTCTC |
| CL2 | CTTCTGCATCATGAGCTGGAC |
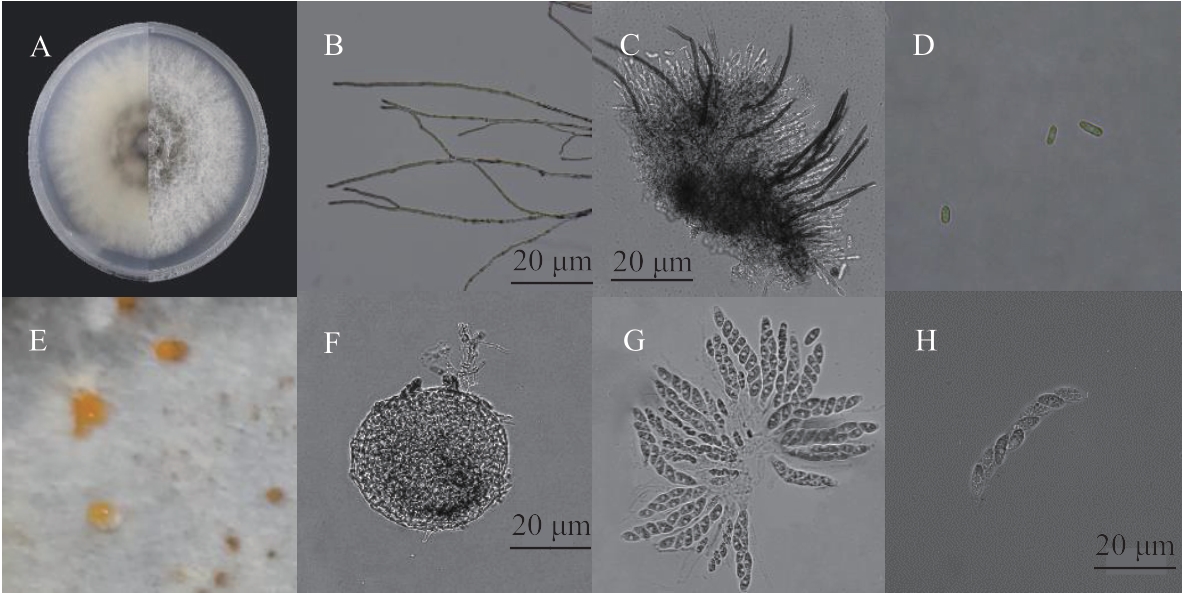

Fig. 1 Culture morphology of strain ZHZF21A: Colony on PDA; B: Mycelium; C: Ascus disc; D: Conidia; E: Conidia pile; F: Ascus shell; G: Ascus; H: Ascospores
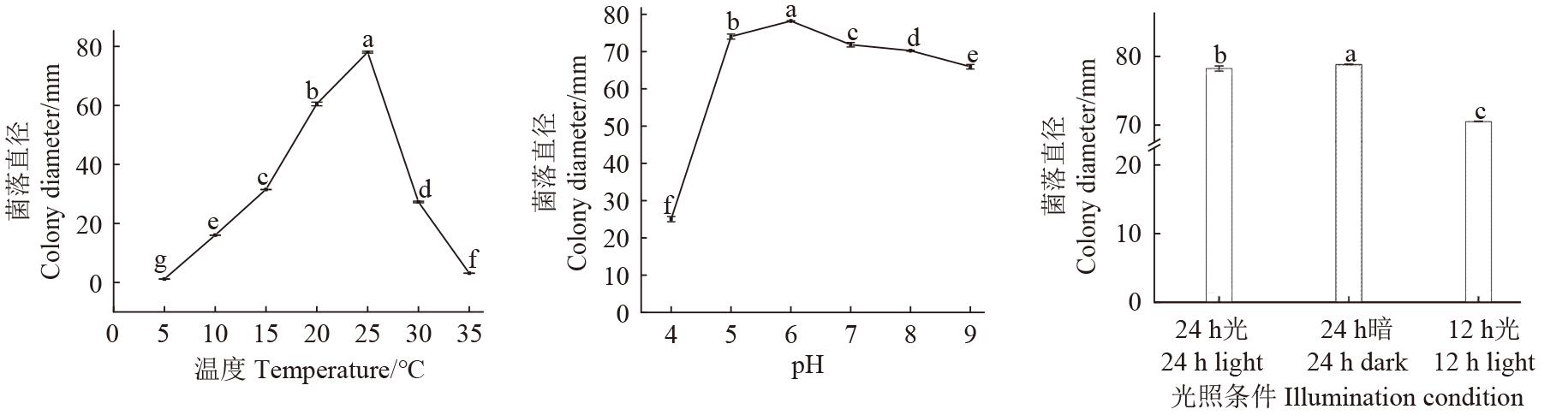
Fig. 4 Colony diameter of strain ZHZF21 under different temperaturesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
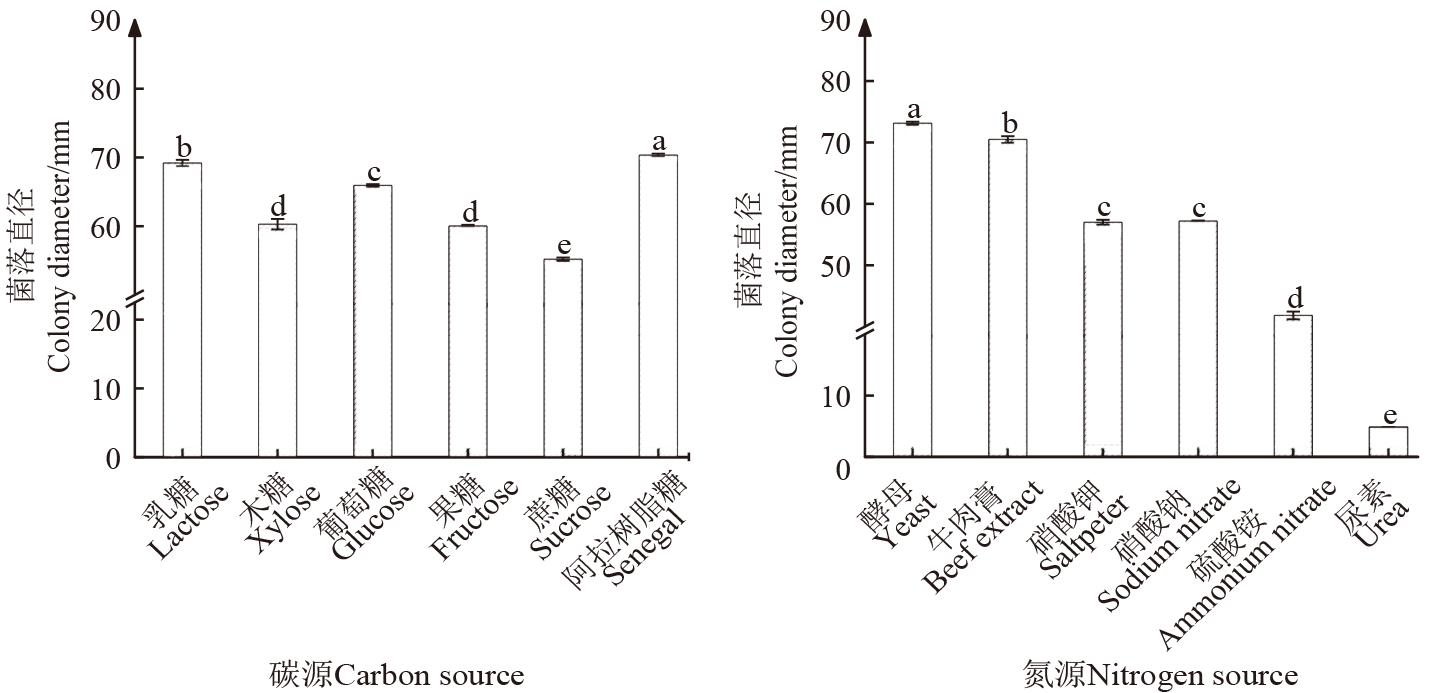
Fig. 5 Colony diameter of strain ZHZF21 under different carbon and nitrogen sourcesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 许凌云,杨倩,高磊,等.板栗贮藏保鲜方法研究进展[J].食品与发酵工业,2023,49(7):337-344. |
| XU L Y, YANG Q, GAO L, et al.. Research progress on preservation of chestnut during storage [J]. Food Ferm. Ind., 2023, 49(7):337-344. | |
| 2 | 易善军.我国板栗产业发展现状及策略[J].西部林业科学,2017,46(5):132-134. |
| YI S J. Situation and development strategy of chestnut industry in China [J]. J. West China For. Sci., 2017, 46(5):132-134. | |
| 3 | 华娟,李淋玲,程华,等.罗田栗实致腐真菌的分离鉴定及拮抗菌筛选[J].中国农学通报,2013,29(25):102-107. |
| HUA J, LI L L, CHENG H, et al.. Isolation, identification and screening of antagonistic bacteria of the pathogenic fungi in Chinese chestnut from Luotian county [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2013, 29(25):102-107. | |
| 4 | 朱祎一,文安燕,王琴,等.贵州望谟板栗冷藏期致腐真菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J].食品与发酵工业,2023,49(8):113-120. |
| ZHU Y Y, WEN A Y, WANG Q, et al.. Identification and biological characteristics of pathogenic fungi of refrigerated chestnut from Wangmo, Guizhou province [J]. Food Ferm. Ind., 2023, 49(8):113-120. | |
| 5 | 张娜娜,温晓蕾,李双民,等.三种镰刀菌引起的板栗内腐病病原菌鉴定[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(7):117-122. |
| ZHANG N N, WEN X L, LI S M, et al.. Pathogens identification of Fusarium causing seed rot of chestnut [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(7):117-122. | |
| 6 | 何利钦,王丽华,李明章,等.四川省猕猴桃溃疡病调查及病原菌株型鉴定[J].中国南方果树,2019,48(4):73-78. |
| HE L Q, WANG L H, LI M Z, et al.. Investigation of kiwi fruit canker in Sichuan province and identification of its pathogen strain [J]. South China Fruits, 2019, 48(4):73-78. | |
| 7 | 贡长怡,刘姣姣,邓强,等.茶树炭疽病病原菌鉴定及其致病性分析[J].园艺学报,2022,49(5):1092-1101. |
| GONG C Y, LIU J J, DENG Q, et al.. Identification and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species causing anthracnose on camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2022, 49(5):1092-1101. | |
| 8 | 李文欣,朱德全,吴云飞,等.红阳猕猴桃致腐真菌的分离与鉴定[J].佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版),2022,40(2):109-111. |
| LI W X, ZHU D Q, WU Y F, et al.. Isolation and identification of red kiwi fruit rot fungi [J]. J. Jiamusi Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2022, 40(2):109-111. | |
| 9 | 陈亭妤,李聪,周国英,等.海南台农芒采后果实炭疽病病原鉴定[J].热带作物学报,2018,39(7):1396-1401. |
| CHEN T Y, LI C, ZHOU G Y, et al.. Colletotrichum species responsible for anthracnose disease of postharvest fruits of Tai Nong Mango [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2018, 39(7):1396-1401. | |
| 10 | 汪筱雪. 广西西北部核桃真菌性病害调查及核桃炭疽菌防治研究[D].南宁:广西大学,2019. |
| WANG X X. Investigation on walunt fungal disease in northwest Guangxi and control of walnut anthracnose [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2018. | |
| 11 | 刘婉蓉. 广东省桑树上七种真菌性病害病原鉴定[D].广州:仲恺农业工程学院,2020. |
| LIU W R. Identification of pathogens of seven fungal mulberry diseases in Guangdong province [D].Guangzhou: Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2020. | |
| 12 | 姚令,吴石平,陈小均,等.贵州芒果炭疽菌种类鉴定及表型特征分析[J].现代园艺,2023,46(16):1-3. |
| 13 | 李河,李杨,蒋仕强,等.湖南省油茶炭疽病病原鉴定[J].林业科学,2017,53(8):43-53. |
| LI H, LI Y, JIANG S Q, et al.. Pathogen of oil-tea trees anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum spp. in Hunan province [J]. For. Sci., 2017, 53(8):43-53. | |
| 14 | 朱辉,宋薇薇,余凤玉,等.海南槟榔炭疽病病原菌的鉴定[J].江西农业学报,2015,27(1):28-31. |
| ZHU H, SONG W W, YU F Y, et al.. Identification of pathogen of arecanut anthracnose in Hainan [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2015, 27(1):28-31. | |
| 15 | 秦瑞凤. 陕西省苹果和葡萄炭疽病病原鉴定[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2015. |
| QIN R F. Identification of pathogens causing apple bitter botand grape ripe rot in Shaanxi province [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2011. | |
| 16 | 王树和,张佳正,何金鹤.河南省臭椿炭疽病病原鉴定[J].林业科学研究,2021,34(5):186-192. |
| WANG S H, ZHANG J Z, HE J H. Identification of the pathogen causing anthracnose on ailanthus altissima in Henan province, China [J]. For. Res., 2021, 34(5):186-192. | |
| 17 | 周嫒婷,王芳,尹加笔,等.德宏州油茶炭疽病病原鉴定及其生物学特性[J].经济林研究,2021,39(4):203-211. |
| ZHOU Y T, WANG F, YIN J B, et al.. Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen of anthracnose on Camellia oleifera in Dehong prefecture [J]. Non-wood For. Res., 2021, 39(4):203-211. | |
| 18 | 任立超,谢昀烨,施鹏程,等.甜柿炭疽病病原种类及生物学特性比较[J].果树学报,2023,40(2):340-349. |
| REN L C, XIE Y Y, SHI P C, et al.. Pathogen identification and biological characteristics of sweet persimmon anthracnose causing by Colletotrichum species [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2023, 40(2):340-349. | |
| 19 | 李沛利,刘丹,陈诗瑶,等.四川省成都市狭叶十大功劳炭疽病病原菌的鉴定与生物学特性研究[J].植物保护,2018,44(3):61-66. |
| LI P L, LIU D, CHEN S Y, et al.. Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen causing anthracnose on mahonia fortunei in Chengdu, Sichuan [J]. Plant Prot., 2018, 44(3):61-66. | |
| 20 | 宋丽丽,张丽勍,高清华,等.草莓果生刺盘孢菌的生物学特性及致病性测定[J].上海农业学报,2019,35(6):88-96. |
| SONG L L, ZHANG L Q, GAO Q H, et al.. Biological characteristics and pathogenicity of strawberry Colletotrichum fructicola [J]. Acta Agric. Shanghai, 2019, 35(6):88-96. |
| [1] | Dengyang LU, Panpan TONG, Min YAN, Jingkai BAO, Mingzhe LIU, Yilei XIA, Cuiyun WU. Identification and Evaluation of Korla Pear Bud Sport with Larger Fruit Size [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [2] | Mengting JI, Changjiang CHEN, Liuhe LUO, Zhijian LIN, Menglin ZHAN, Bingye YANG, Fangping HU, Xueqing CAI. Pathogen Identification of Kiwi Bacterial Wilt in Fujian [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 144-152. |
| [3] | Pengsheng LI, Qingtai HUANG, Yongmei FAN, Meng WANG, Ye YANG. Identification of Pathogen Causing Bacterial Fruit Blotch of Melon in Hainan [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 117-123. |
| [4] | Shiying ZHOU, Yanchen LIU, Yang ZHANG, Xuesong YANG, Weijun GUAN, Yang GAO. Isolational Culture and Biological Identification of Japanese Large Ear White Rabbit Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 96-105. |
| [5] | Xinci WANG, Junqiao LI, Chenqin LI, Tian TIAN, Junru QU. Identification and Biological Characteristics of a Thelonectria Pathogenic Fungi of Potentilla anserina L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 87-95. |
| [6] | Xin XU, Kun MENG, Hongying CAI, Peilong YANG, Xianren JIANG. Research Progress on Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Pig Production [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 19-26. |
| [7] | Yuping SHI, Yixian LIU, Guowei LI, Yi TANG, Liming DAI, Lanlan LI, Zhiying CAI. Isolation and Identification of Pathogen of Rubber Tree Phytophthora Leaf Fall Disease and Screening of Control Fungicides [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 114-122. |
| [8] | Keze YANG, Fang WU, Yujie WEI, Liangfang WANG, Hao CHANG, Zhitao WU, Xianzhong YANG. Pathogen Identification and Laboratory Drug Screening of Peony Root Rot in Cold and Cool Region of Hexi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 144-151. |
| [9] | Nana ZHANG, Xiaolei WEN, Shuangmin LI, Lina FENG, Jiahuan HUO, Shuhui LAN, Jianing LI, Sirou GUO, Jianhua WANG, Huixia QI. Identification of Pathogens of Three Kinds of Fusarium Causing Seed Rot of Chestnut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 117-122. |
| [10] | Jiahuan HUO, Xiaolei WEN, Shuangmin LI, Lina FENG, Shuhui LAN, Lixin DONG, Sirou GUO, Jianing LI, Jianhua WANG, Huixia QI. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Root Rot of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 137-144. |
| [11] | Wenjie YANG, Xiaolei WEN, Lina FENG, Nana ZHANG, Weiming SUN, Huixia QI. Identification of the Pathogen of Chinese Chestnut Yellow Crinkle and Its Control [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 148-156. |
| [12] | Hua SUN, Ning GUO, Xiaojuan ZHENG, Jie SHI, Lirong ZHANG, Hongfei YAN. Identification and Biological Characteristics Analysis of Fusarium andiyazi Causing Maize Ear Rot [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [13] | ZHANG Nana§, LI Shuangmin§, WEN Xiaolei, FENG Lina, WANG Junfeng, YANG Wenjie, HUO Jiahuan, LAN Shuhui, SUN Weiming, QI Huixia. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Pink Disease of Chestnut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [14] | WEN Xiaolei1,2, QI Huixia1*, SUN Weiming1, LIU Yijian1, FENG Lina1, MENG Tongyao2, HAN Zhiling1, CAO Jia1, WANG Junfeng1. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen (Fusarium equiseti) Causing Shoot Blight of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(5): 115-121. |
| [15] | WANG Junfeng1§, WEN Xiaolei1§, SUN Weiming1, LIU Yijian1, SHI Luting2, ZHANG Nana1, YANG Wenjie1, CHEN Weidong3, QI Huixia1*. Study on Cultural Conditions of Penicillium spinulosum Causing Chestnut Rot and Fungicides Screening [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 79-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号