




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 215-226.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0145
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Can WANG1( ), Qiang CUI2, Qianru SHI1, Hao TANG3, Xinjie NING4, Jingjing ZHANG1, Suqin YANG1(
), Qiang CUI2, Qianru SHI1, Hao TANG3, Xinjie NING4, Jingjing ZHANG1, Suqin YANG1( ), Biao ZHANG1(
), Biao ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-02-28
Accepted:2024-05-12
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
Suqin YANG,Biao ZHANG
王璨1( ), 崔强2, 时倩茹1, 唐浩3, 宁欣杰4, 张静静1, 杨素勤1(
), 崔强2, 时倩茹1, 唐浩3, 宁欣杰4, 张静静1, 杨素勤1( ), 张彪1(
), 张彪1( )
)
通讯作者:
杨素勤,张彪
作者简介:王璨 E-mail:wangc_116@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Can WANG, Qiang CUI, Qianru SHI, Hao TANG, Xinjie NING, Jingjing ZHANG, Suqin YANG, Biao ZHANG. Deactivation of 3 Amendments and Their Effects on Microbial Coummunity in Different Contaminated Soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 215-226.
王璨, 崔强, 时倩茹, 唐浩, 宁欣杰, 张静静, 杨素勤, 张彪. 3种调理剂对不同镉污染土壤钝化效果及微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 215-226.
试验点 Experimental site | 土壤类型 Soil type | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 全量Cd Total Cd/(mg·kg-1) | 有效态Cd Available Cd/(mg·kg-1) | 风险筛选值 Risk screening value/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
豫北 Northern Henan | 褐土Cinnamon soil | 8.4 | 14.3 | 0.6 | 15.5 | 74.2 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
豫东 Eastern Henan | 潮土Alluvial soil | 8.0 | 11.8 | 0.5 | 11.6 | 107.6 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
豫南 Southern Henan | 砂姜黑土Shajiang black soil | 4.6 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 13.9 | 122.2 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties and heavy metal content of soil at experimental sites
试验点 Experimental site | 土壤类型 Soil type | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 全量Cd Total Cd/(mg·kg-1) | 有效态Cd Available Cd/(mg·kg-1) | 风险筛选值 Risk screening value/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
豫北 Northern Henan | 褐土Cinnamon soil | 8.4 | 14.3 | 0.6 | 15.5 | 74.2 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
豫东 Eastern Henan | 潮土Alluvial soil | 8.0 | 11.8 | 0.5 | 11.6 | 107.6 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
豫南 Southern Henan | 砂姜黑土Shajiang black soil | 4.6 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 13.9 | 122.2 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
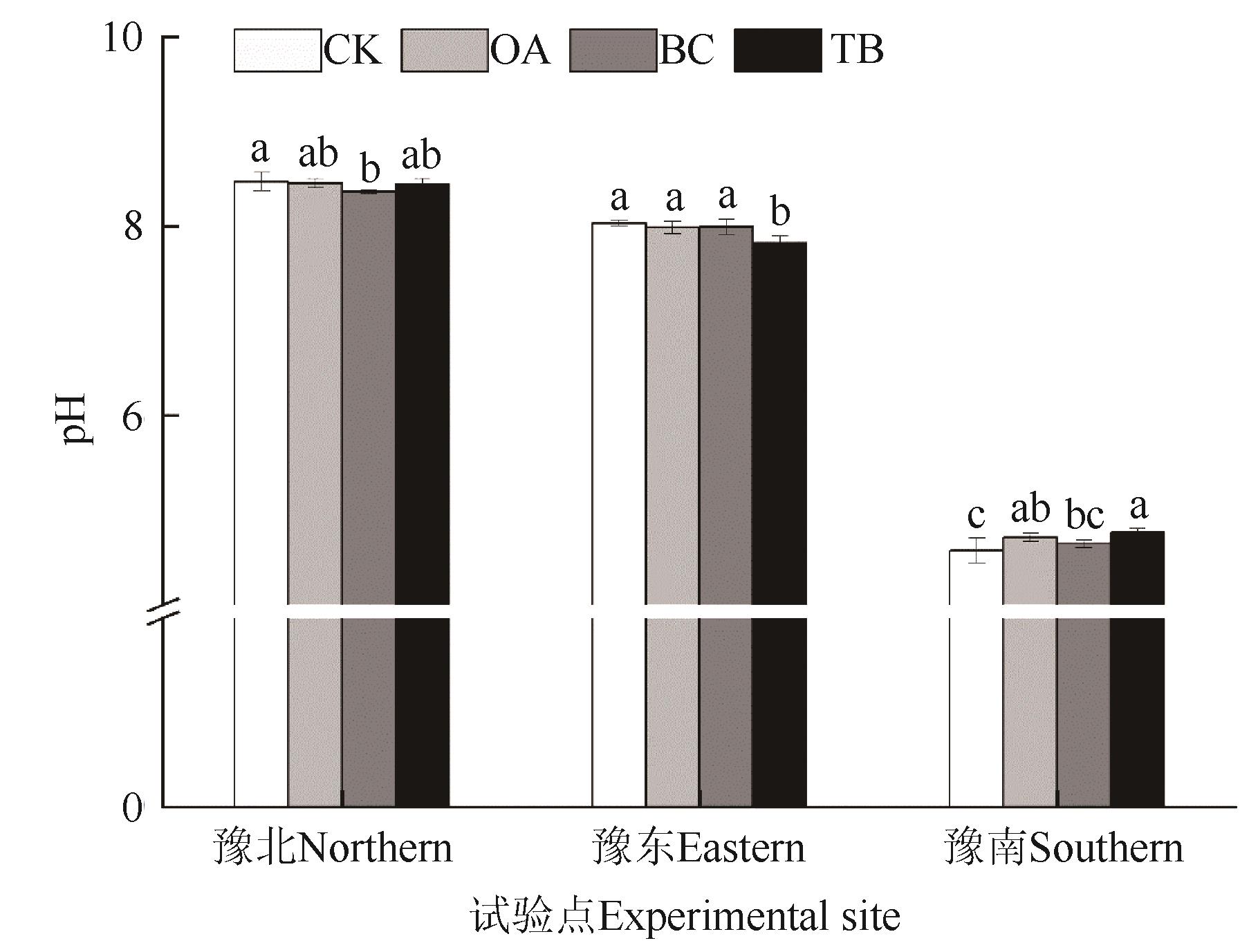
Fig. 1 Soil pH of different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same site at P<0.05 level.
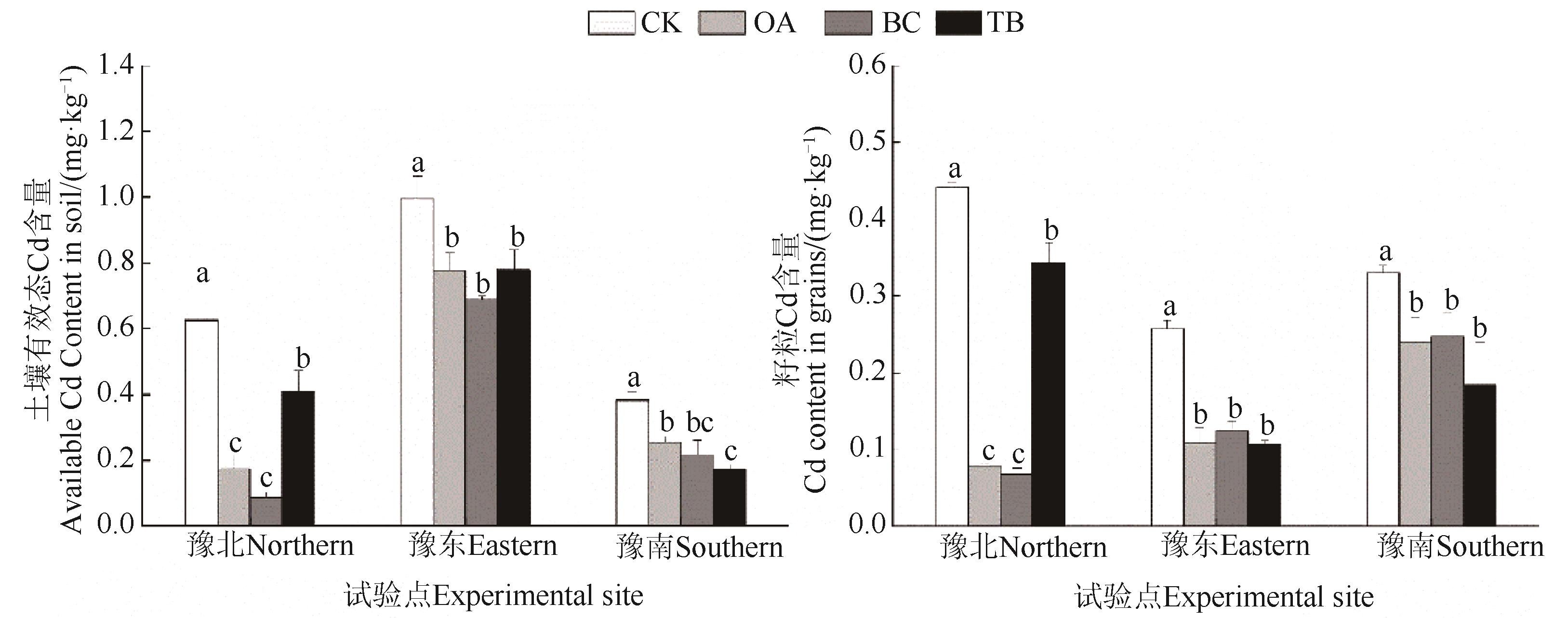
Fig. 2 Contents of soil available Cd and Cd in grains under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same site at P<0.05 level.
| 因素Factor | F值F value | 贡献率Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 试验点Experimental site | 61.92*** | 14.49 |
| 调理剂Amendment | 138.85*** | 48.86 |
试验点×调理剂 Experimental site×amendment | 47.86** | 33.75 |
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA of grains Cd content
| 因素Factor | F值F value | 贡献率Contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 试验点Experimental site | 61.92*** | 14.49 |
| 调理剂Amendment | 138.85*** | 48.86 |
试验点×调理剂 Experimental site×amendment | 47.86** | 33.75 |
试验点 Experimental site | 处理 Treatment | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
多样性指数 Diversity index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | ||||||
| Shannon | Simpson | Chao | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | Chao | Ace | ||
豫北 Northern Henan | CK | 6.79 a | 0.002 6 c | 3 912.6 a | 3 936.7 a | 4.32 a | 0.043 a | 711.5 a | 718.5 a |
| OA | 6.44 c | 0.003 9 a | 3 191.3 b | 3 184.1 b | 4.20 a | 0.041 a | 568.2 b | 569.2 b | |
| BC | 6.60 b | 0.003 1 b | 3 431.3 b | 3 431.1 b | 4.59 a | 0.023 a | 730.4 a | 726.8 a | |
| TB | 6.45 c | 0.004 0 a | 3 386.9 b | 3 329.4 b | 4.45 a | 0.032 a | 692.7 a | 694.5 a | |
豫东 Eastern Henan | CK | 6.92 a | 0.002 6 a | 4 728.5 a | 4 759.6 a | 4.13 a | 0.049 a | 781.1 a | 793.2 a |
| OA | 6.92 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 773.9 a | 4 995.0 a | 4.34 a | 0.034 a | 800.9 a | 847.7 a | |
| BC | 6.91 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 698.0 a | 5 125.5 a | 4.50 a | 0.030 a | 809.4 a | 821.3 a | |
| TB | 6.91 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 624.7 a | 4 673.0 a | 4.43 a | 0.029 a | 830.1 a | 813.8 a | |
豫南 Southern Henan | CK | 5.55 b | 0.010 6 a | 1 773.4 b | 1 778.9 b | 4.20 a | 0.037 a | 569.8 a | 570.6 a |
| OA | 5.72 ab | 0.009 7 ab | 2 048.6 ab | 2 037.0 ab | 4.39 a | 0.026 a | 629.5 a | 627.9 a | |
| BC | 5.70 ab | 0.009 7 ab | 1 989.8 ab | 1 963.6 ab | 4.30 a | 0.034 a | 616.0 a | 618.3 a | |
| TB | 5.83 a | 0.008 5 b | 2 207.8 a | 2 205.3 a | 4.10 a | 0.049 a | 630.3 a | 644.2 a | |
Table 3 Alpha diversity of bacteria and fungi under different treatments
试验点 Experimental site | 处理 Treatment | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
多样性指数 Diversity index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 丰富度指数 Richness index | ||||||
| Shannon | Simpson | Chao | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | Chao | Ace | ||
豫北 Northern Henan | CK | 6.79 a | 0.002 6 c | 3 912.6 a | 3 936.7 a | 4.32 a | 0.043 a | 711.5 a | 718.5 a |
| OA | 6.44 c | 0.003 9 a | 3 191.3 b | 3 184.1 b | 4.20 a | 0.041 a | 568.2 b | 569.2 b | |
| BC | 6.60 b | 0.003 1 b | 3 431.3 b | 3 431.1 b | 4.59 a | 0.023 a | 730.4 a | 726.8 a | |
| TB | 6.45 c | 0.004 0 a | 3 386.9 b | 3 329.4 b | 4.45 a | 0.032 a | 692.7 a | 694.5 a | |
豫东 Eastern Henan | CK | 6.92 a | 0.002 6 a | 4 728.5 a | 4 759.6 a | 4.13 a | 0.049 a | 781.1 a | 793.2 a |
| OA | 6.92 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 773.9 a | 4 995.0 a | 4.34 a | 0.034 a | 800.9 a | 847.7 a | |
| BC | 6.91 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 698.0 a | 5 125.5 a | 4.50 a | 0.030 a | 809.4 a | 821.3 a | |
| TB | 6.91 a | 0.002 5 a | 4 624.7 a | 4 673.0 a | 4.43 a | 0.029 a | 830.1 a | 813.8 a | |
豫南 Southern Henan | CK | 5.55 b | 0.010 6 a | 1 773.4 b | 1 778.9 b | 4.20 a | 0.037 a | 569.8 a | 570.6 a |
| OA | 5.72 ab | 0.009 7 ab | 2 048.6 ab | 2 037.0 ab | 4.39 a | 0.026 a | 629.5 a | 627.9 a | |
| BC | 5.70 ab | 0.009 7 ab | 1 989.8 ab | 1 963.6 ab | 4.30 a | 0.034 a | 616.0 a | 618.3 a | |
| TB | 5.83 a | 0.008 5 b | 2 207.8 a | 2 205.3 a | 4.10 a | 0.049 a | 630.3 a | 644.2 a | |
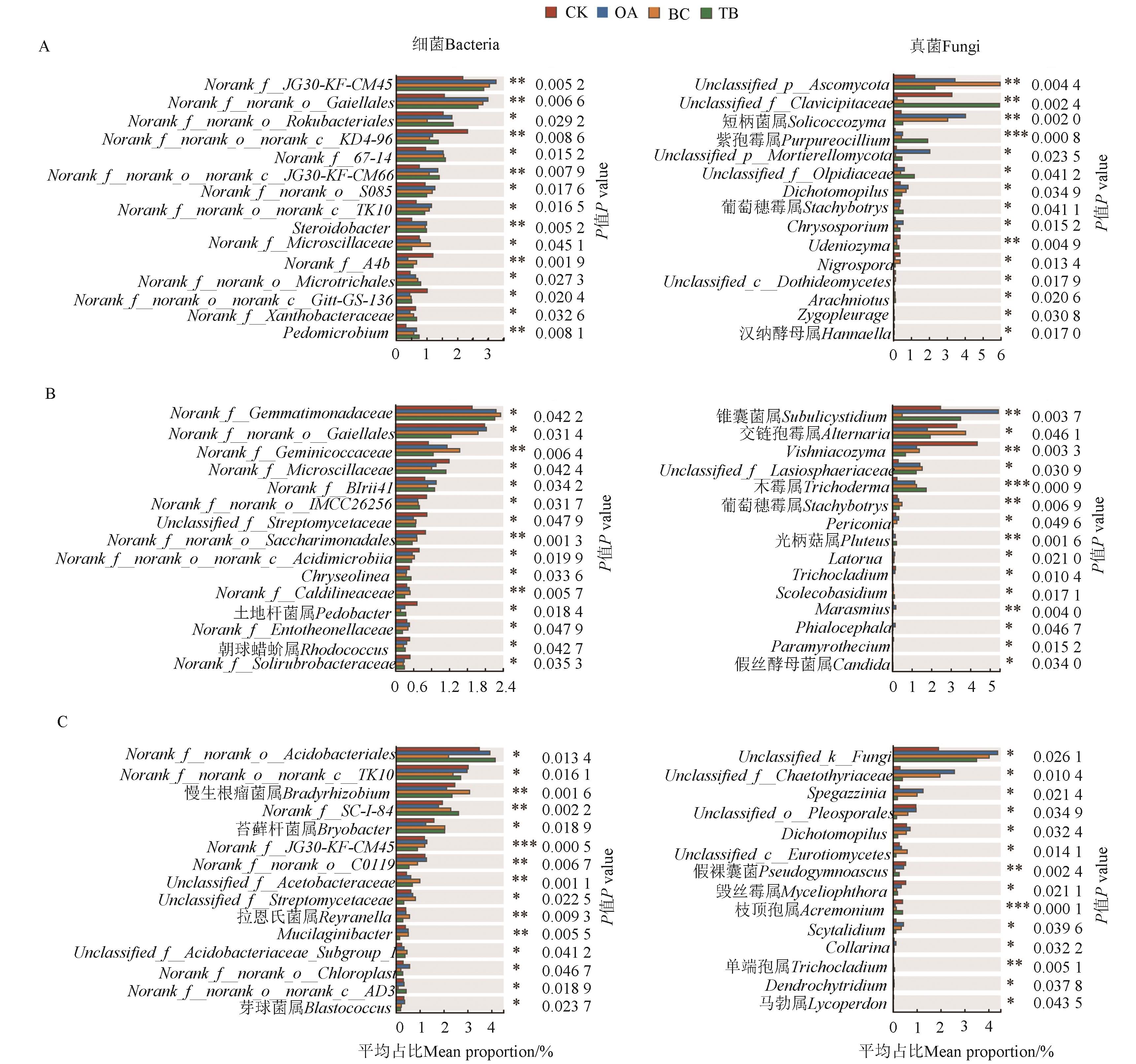
Fig. 5 Species with significant differences in bacteria and fungi of different treatmentsA:Northern Henan;B:Easthern Henan;C:Southern Henan;*, ** and *** indicate significant at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively
类别 Type | 属 Genus | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 有效态Cd Available Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | Norank_f__norank_o__Vicinamibactera | 0.738*** | 0.383** | 0.384** |
| Candidatus_Solibacter | -0.586*** | -0.661*** | -0.498*** | |
| 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus | 0.084 | 0.020 | -0.031 | |
| Gaiella | 0.581*** | 0.720*** | 0.690*** | |
| 类诺卡氏属Nocardioides | 0.705*** | 0.510*** | 0.376** | |
真菌 Fungi | 被孢霉属Mortierella | 0.431** | -0.304 | -0.097 |
| 枝孢菌属Cladosporium | 0.608*** | 0.680*** | 0.255 | |
| 篮状菌属Talaromyces | -0.212 | 0.104 | -0.069 | |
| 毛壳菌属Chaetomium | -0.809*** | -0.567*** | -0.428** | |
| Solicoccozyma | -0.815*** | -0.571*** | -0.589*** |
Table 4 Correlation analysis between dominant microflora and environmental factors
类别 Type | 属 Genus | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 有效态Cd Available Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | Norank_f__norank_o__Vicinamibactera | 0.738*** | 0.383** | 0.384** |
| Candidatus_Solibacter | -0.586*** | -0.661*** | -0.498*** | |
| 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus | 0.084 | 0.020 | -0.031 | |
| Gaiella | 0.581*** | 0.720*** | 0.690*** | |
| 类诺卡氏属Nocardioides | 0.705*** | 0.510*** | 0.376** | |
真菌 Fungi | 被孢霉属Mortierella | 0.431** | -0.304 | -0.097 |
| 枝孢菌属Cladosporium | 0.608*** | 0.680*** | 0.255 | |
| 篮状菌属Talaromyces | -0.212 | 0.104 | -0.069 | |
| 毛壳菌属Chaetomium | -0.809*** | -0.567*** | -0.428** | |
| Solicoccozyma | -0.815*** | -0.571*** | -0.589*** |
| [1] | JIA X L, HU B F, MARCHANT B P,et al..A methodological framework for identifying potential sources of soil heavy metal pollution based on machine learning:a case study in the Yangtze Delta, China [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2019,250:601-609. |
| [2] | ANDERSON S N, STITZER M C, BROHAMMER A B,et al..Transposable elements contribute to dynamic genome content in maize [J]. Plant J., 2019,100(5):1052-1065. |
| [3] | GOMES H I, DIAS-FERREIRA C, RIBEIRO A B.Overview of in situ and ex situ remediation technologies for PCB-contaminated soils and sediments and obstacles for full-scale application [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2013,445:237-260. |
| [4] | SONG B, ZENG G M, GONG J L,et al..Evaluation methods for assessing effectiveness of in situ remediation of soil and sediment contaminated with organic pollutants and heavy metals [J]. Environ. Int., 2017,105:43-55. |
| [5] | 陈鸿鹄,蔡润.探究矿山地质环境现状与生态修复技术的应用[J].中国金属通报,2022(8):204-206. |
| [6] | LIU L W, LI W, SONG W P,et al..Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils:principles and applicability [J].Sci. Total Environ., 2018,633:206-219. |
| [7] | HUSSAIN B, ASHRAF M N,SHAFEEQ-UR-RAHMAN,et al..Cadmium stress in paddy fields:effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,754:142188 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [8] | ALBUQUERQUE A R L, ANGELICA R S, MERINO A, et al.. Chemical and mineralogical characterization and potential use of ash from Amazonian biomasses as an agricultural fertilizer and for soil amendment [J/OL]. J. Clean, 2021, 295(5):126472 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [9] | 韩云昌,张乃明.施用钝化剂对土壤重金属污染修复的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(10):52-56. |
| [10] | 张小凯,何丽芝,陆扣萍,等.生物质炭修复重金属及有机物污染土壤的研究进展[J].土壤,2013,45(6):970-977. |
| ZHANG X K, HE L Z, LU K P,et al..Use of biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants: a review [J]. Soils, 2013, 45(6):970-977. | |
| [11] | HODSON M E, VALSAMI-JONES É, COTTER-HOWELLS J D.Bonemeal additions as a remediation treatment for metal contaminated soil [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000,34(16):3501-3507. |
| [12] | OK Y S, OH S E, AHMAD M,et al..Effects of natural and calcined oyster shells on Cd and Pb immobilization in contaminated soils [J].Environ.Earth Sci., 2010,61(6):1301-1308. |
| [13] | SOARES M A R, QUINA M J, QUINTA-FERREIRA R M.Immobilisation of lead and zinc in contaminated soil using compost derived from industrial eggshell [J].J.Environ. Manage., 2015,164:137-145. |
| [14] | HRISTOZKOVA M, GIGOVA L, GENEVA M, et al.. Mycorrhizal fungi and microalgae modulate antioxidant capacity of basil plants [J]. J. Plant Prot. Res., 2018, 57(4):417-426. |
| [15] | BEATTIE R E, HENKE W, CAMPA M F,et al..Variation in microbial community structure correlates with heavy-metal contamination in soils decades after mining ceased [J].Soil Biol. Biochem., 2018,126:57-63. |
| [16] | JANKAIT E, VASAREVICIUS S A. Remediation technologies for soils contaminated with heavy metals [J] Environ. Eng. Landsc. J., 2005, 13(2):109-113. |
| [17] | ZHAO Y F, GAO J F, WANG Z Q, et al.. Responses of bacterial communities and resistance genes on microplastics to antibiotics and heavy metals in sewage environment [J/OL].J.Hazard. Mater., 2020,402:123550 [2024-01-20]. . |
| [18] | NADEEM N, ASIF R, AYYUB S, et al.. Role of rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metals [J]. Biol. Clin. Sci. Res. J., 2020, 2020(1):220-232. |
| [19] | CHEN Q L, CUI H L, SU J Q,et al..Antibiotic resistomes in plant microbiomes [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2019, 24(6):530-541. |
| [20] | 刘沙沙,付建平,蔡信德,等.重金属污染对土壤微生物生态特征的影响研究进展[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(6):1173-1178. |
| LIU S S, FU J P, CAI X D, et al.. Effect of heavy metals pollution on ecological characteristics of soil microbes:a review [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2018, 27(6):1173-1178. | |
| [21] | 刘香香,王琳,江棋,等.调理剂对Cd污染农田土壤环境质量的影响及修复效果评价[J].农产品质量与安全,2021(2):25-29. |
| [22] | LI L J, WANG S T, LI X Z,et al..Effects of Pseudomonas chenduensis and biochar on cadmium availability and microbial community in the paddy soil [J]. Sci.Total Environ., 2018, 640:1034-1043. |
| [23] | 武琳,林小兵,刘晖,等.土壤调理剂对Cd污染农田土壤生物因子、有效态Cd及糙米Cd的影响[J].环境生态学,2020,2(4):78-84, 100. |
| WU L, LIN X B, LIU H,et al..Soil biological factors,available Cd and brown rice Cd under different soil conditioners in Cd-contaminated farmland [J]. Environ. Ecol., 2020, 2(4):78-84, 100. | |
| [24] | 陈兆进,李英军,邵洋,等.新乡市镉污染土壤细菌群落组成及其对镉固定效果[J].环境科学,2020,41(6):2889-2897. |
| CHEN Z J, LI Y J, SHAO Y,et al..Bacterial community composition in cadmium-contaminated soils in Xinxiang city and its ability to reduce cadmium bioaccumulation in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(6):2889-2897. | |
| [25] | XU C R, HE S B, LIU Y M,et al..Bioadsorption and biostabilization of cadmium by Enterobacter cloacae TU [J].Chemosphere, 2017, 173:622-629. |
| [26] | 生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2018. |
| [27] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第2版.北京:中国农业出版社,1999:34-108. |
| [28] | 宋正国,唐世荣,丁永祯,等.田间条件下不同钝化材料对玉米吸收镉的影响研究[J].农业环境科学学报,2011,30(11):2152-2159. |
| SONG Z G, TANG S R, DING Y Z,et al..Effects of different amendments on cadmium uptake by maize under field conditions [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2011, 30(11):2152-2159. | |
| [29] | 孙国红,李剑睿,徐应明,等.不同水分管理下镉污染红壤钝化修复稳定性及其对氮磷有效性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2015,34(11):2105-2113. |
| SUN G H, LI J R, XU Y M, et al.. Effects of water management on cadmium stability and nitrogen and phosphorus availability in cadmium polluted red soil after immobilization remediation [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(11):2105-2113. | |
| [30] | 贺前锋,桂娟,刘代欢,等.淹水稻田中土壤性质的变化及其对土壤镉活性影响的研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(12):2260-2268. |
| HE Q F, GUI J, LIU D H,et al..Research progress of soil property’s changes and its impacts on soil cadmium activity in flooded paddy field [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2016,35(12):2260-2268. | |
| [31] | 王林,徐应明,孙国红,等.海泡石和磷酸盐对镉铅污染稻田土壤的钝化修复效应与机理研究[J].生态环境学报,2012,21(2):314-320. |
| WANG L, XU Y M, SUN G H,et al..Effect and mechanism of immobilization of paddy soil contaminated by cadmium and lead using sepiolite and phosphate [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2012, 21(2):314-320. | |
| [32] | 张倩茹,冀琳宇,高程程,等.改性生物炭的制备及其在环境修复中的应用[J].农业环境科学学报,2021,40(5):913-925. |
| ZHANG Q R, JI L Y, GAO C C,et al..Preparation of modified biochar and its application in environmental remediation [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2021, 40(5):913-925. | |
| [33] | HOODA P S, ALLOWAY B J.Cadmium and lead sorption behaviour of selected English and Indian soils [J].Geoderma, 1998, 84(1/2/3):121-134. |
| [34] | 张剑,孔繁艺,卢升高.无机钝化剂对镉污染酸性水稻土的修复效果及其机制[J].环境科学,2022,43(10):4679-4686. |
| ZHANG J, KONG F Y, LU S G.Remediation effect and mechanism of inorganic passivators on cadmium contaminated acidic paddy soil [J]. Environ. Sci., 2022, 43(10):4679-4686. | |
| [35] | KUBIER A, PICHLER T.Cadmium in groundwater-A synopsis based on a large hydrogeochemical data set [J].Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 689:831-842. |
| [36] | 孙花,谭长银,黄道友,等.土壤有机质对土壤重金属积累、有效性及形态的影响[J].湖南师范大学自然科学学报,2011,34(4):82-87. |
| SUN H, TAN C Y, HUANG D Y,et al..Effects of soil organic matter on the accumulation availability and chemical speciation of heavy metal [J].J.Nat.Sci.Hunan Norm.Univ., 2011, 34(4):82-87. | |
| [37] | 杜明阳,赵秀兰.土壤有机质与重金属迁移转化关系文献综述[J].南方农业,2016,10(17):3. |
| [38] | 徐龙君,袁智.土壤重金属污染及修复技术[J].环境科学与管理,2006,31(8):67-69. |
| XU L J, YUAN Z.The soil pollution of heavymetal and remediation techniques [J]. Environ. Sci. Manage., 2006, 31(8):67-69. | |
| [39] | UCHIMIYA M, CHANG S, KLASSON K T.Screening biochars for heavy metal retention in soil:role of oxygen functional groups [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 190(1/2/3):432-441. |
| [40] | 杨素勤,魏森,张彪,等.连续施用改性生物质炭对镉铅土壤修复效果及其对微生物群落结构的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2022,41(7):1460-1471. |
| YANG S Q, WEI S, ZHANG B,et al..Remediation effect of continuous application of modified biochar on cadmium-and lead-contaminated soil and its effect on microbial community structure [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(7):1460-1471. | |
| [41] | 国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2022. |
| [42] | 程金金,宋静,陈文超,等.镉污染对红壤和潮土微生物的生态毒理效应[J].生态毒理学报,2013,8(4):577-586. |
| CHENG J J, SONG J, CHEN W C, et al.. The ecotoxicity effects of cadmium on microorganism in udic-ferrosols and aquic-cambosols [J]. Asian J. Ecotoxicol., 2013, 8(4):577-586. | |
| [43] | LAUBER C L, HAMADY M, KNIGHT R,et al..Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, 75(15):5111-5120. |
| [44] | 张丽丽,李继蕊,毕焕改,等.不同土壤pH和磷水平下黄腐酸对番茄产量和根际土壤微生态的影响[J].中国蔬菜,2021(11):45-52. |
| ZHANG L L, LI J R, BI H G,et al..Effects of fulvic acid on tomato yield and hizosphere soil microecology under different soil pH and phosphorus levels [J]. China Veg., 2021(11):45-52. | |
| [45] | 钟珍梅.圆叶决明对果园红壤可溶性氮及细菌群落动态变化的影响[D].福州:福建农林大学, 2019. |
| ZHONG Z M. Effects of chamaecrista rotundifolia on dynamic changes of soil soluble nitrogen and bacterial communities in orchard red earth [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. | |
| [46] | YONEYAMA T, TERAKADO T, MINAMISAWA K. Exploration of bacterial N2-fixation systems in association with soil-grown sugarcane, sweet potato, and paddy rice: a review and synthesis [J]. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2017, 63(6):578-590. |
| [47] | 李巧玲,李爱博,黄志远,等.解磷微生物在林业土壤生态修复中的应用进展[J].世界林业研究,2022, 35(1):15-20. |
| LI Q L, LI AB, HUANG Z Y, et al.. Application of phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms in forestry soil ecological restoration [J]. World For. Res., 2022, 35(1):15-20. | |
| [48] | 陈志谊,刘永峰,刘邮洲,等.植物病害生防芽孢杆菌研究进展[J].江苏农业学报,2012, 28(5):999-1006. |
| CHEN Z Y, LIU Y F, LIU Y Z,et al..Research progress in biocontrol of Bacillus spp. against plant diseases [J]. Jiangsu J.Agric. Sci., 2012, 28(5):999-1006. | |
| [49] | YANG F C, CHEN Y L, TANG S L, et al.. Integrated multi-omics analyses reveal the biochemical mechanisms and phylogenetic relevance of anaerobic androgen biodegradation in the environment [J]. ISME J., 2016, 10(8):1967-1983. |
| [50] | SAKAI M, HOSODA A, OGURA K,et al..The growth of Steroidobacter agariperforans sp.nov.,a novel agar-degrading bacterium isolated from soil,is enhanced by the diffusible metabolites produced by bacteria belonging to rhizobiales [J]. Microbes Environ., 2014, 29(1):89-95. |
| [51] | GEBERS R, BEESE M. Pedomicrobium americanum sp. nov. and pedomicrobium australicum sp. nov. from aquatic habitats, pedomicrobium gen. emend, and Pedomicrobium ferrugineum sp. emend. [J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 1988, 38(3):303-315. |
| [52] | COX T L, SLY L I.Phylogenetic relationships and uncertain taxonomy of Pedomicrobium species [J].Polymers,1997,47(2):377-380. |
| [53] | 商鸿生.现代植物免疫学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2013 1-433. |
| [54] | LEHMANN J, RILLIG M C, THIES J, et al.. Biochar effects on soil biota-a review [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2011, 43(9):1812-1836. |
| [55] | ZHU X M, CHEN B L, ZHU L Z,et al.. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation:a review [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2017, 227:98-115. |
| [56] | 殷全玉,刘健豪,刘国顺,等.连续4年施用生物炭对植烟褐土微生物群落结构的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(1):176-185. |
| YIN Q Y, LIU J H, LIU G S, et al.. Effects of biochar application for four consecutive years on microbial community structure of tobacco cinnamon soil [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(1):176-185. | |
| [57] | 张英英,魏玉杰,吴之涛,等.不同种植年限对特殊药材土壤化学性质和微生物多样性的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(1):150-159. |
| ZHANG Y Y, WEI Y J, WU Z T,et al..Effects of different cropping years on soil chemical properties of special medicine source plant [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2023, 41(1):150-159. | |
| [58] | 刘峰.高效解磷真菌的筛选鉴定及促进玉米磷吸收的机制[D].青岛:青岛农业大学,2022. |
| LIU F. Screening and identification of high-efficiency phosphate-solubilizing fungus and the mechanism of promoting phosphorus absorption in maize [D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [59] | SARABIA M, CAZARES S, GONZÁLEZ-RODRÍGUEZ A, et al.. Plant growth promotion traits of rhizosphere yeasts and their response to soil characteristics and crop cycle in maize agroecosystems [J]. Rhizosphere, 2018, 6:67-73. |
| [60] | NOORMOHAMADI H R, FAT'HI M R, GHAEDI M,et al..Potentiality of white-rot fungi in biosorption of nickel and cadmium:modeling optimization and kinetics study [J].Chemosphere, 2019, 216:124-130. |
| [61] | MENDES GD, DE FREITAS ALM, PEREIRA OL, et al.. Mechanisms of phosphate solubilization by fungal isolates when exposed to different P sources [J]. Ann. Microbiol., 2014, 64(1):239-249. |
| [62] | ADAMS P, DE-LEIJ F A A M, LYNCH J M. Trichoderma harzianum rifai 1295-22 mediates growth promotion of crack willow (Salix fragilis) saplings in both clean and metal-contaminated soil [J]. Microb. Ecol., 2007, 54(2):306-313. |
| [63] | SIDDIQUEE S, ROVINA K, AZAD S A. Heavy metal contaminants removal from wastewater using the potential filamentous fungi biomass: a review [J]. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol., 2015, 6:384-393. |
| [64] | MAZROU Y S, NEHA B, KANDOLIYA U K, et al.. Selection and characterization of novel zinc-tolerant Trichoderma strains obtained by protoplast fusion [J]. J. Environ. Biol., 2020, 41(4):718-726. |
| [65] | 蔚杰.河北峰峰矿区DSE真菌物种多样性和耐重金属性研究[D].保定:河北大学,2019. |
| WEI J. Species diversity and heavy metal tolerance of DSE fungi in Fengfeng mining area, Hebei province [D]. Baoding: Hebei University. 2019. |
| [1] | Xiaoyu QI, Yanjie GUO, Lu LIU, Zitao ZHANG, Lijuan ZHANG, Yanzhi JI. Effects of Planting Years on Soil Salinization and Microbial Community in Facility Vineyards [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 218-228. |
| [2] | Taijun FANG, Lu HOU, Luchao BAI. Soil Microbial Diversity in the Rhizosphere of Lycium barbarum Infected with Root Rot Disease in the Qaidam Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [3] | Rui XIAO, Lu TAN, Liang WU, Hao ZHANG, Jiayuan GUO, Haijun YANG. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil of Kochia scoparia Under Cd Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [4] | PANG Zhe, WANG Qilong, LI Juan. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties, Rice Yield and Economic Benefits in Low-lying Saline Alkali Land in Northern Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [5] | Haiyu SHEN, Hao ZHANG, Zilong WU, Chao HAN, Wei SONG, Xiaofei MA. Effect of Addition Several Kinds of Amendment on the Water-retaining Properties of Gangue Matrix and the Germination of Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 161-168. |
| [6] | Heling FAN, Qing ZHU, Xuebing SUN, Li ZHANG, Changjiang LI, Ping CHEN, Xiaolong HUANG, Rongping ZHANG. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure of Different Agricultural Jiaosu [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 179-189. |
| [7] | ZHANG Lei, LUO Zehua, YANG Mingchuan, LI Shigui, XIN Yuhua, CAI Bin, LIU Haobao, CENG Dailong, GU Jingang, DUAN Bihua. Diversity of Fermentation Microbes and Changes of Hydrolytic Enzyme Activities of Cigar Leaf Raw Materials [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(10): 171-180. |
| [8] | LIU Qian1,2, LI Jichao1, ZUO Yingmei1, YANG Tianmei1, YANG Meiquan1, ZHANG Jinyu1*. Influences of Organic Mulching on Soil Nutrient and Microbial Diversity of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [9] | LIN Lihua, ZHI Huyu. Influence of Silkworm Excrement Soil Amendments on Acidic Soil and Growth of Vigna unguiculata [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(4): 108-114. |
| [10] | PAN Jinhua1, ZHUANG Shunyao1*, SHI Xuezheng1, CAO Zhihong1, CAI Xianjie2, CHENG Sen2. Combined Effects of Bamboo Biochar and T20 Amendment on Dryland Flue-cured Tobacco Ecology, Yield and Quality at South Anhui Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(4): 73-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号