




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 202-214.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0100
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Wei KOU1( ), Jiayue LIU1, Kexin HU1, Yiyao GAO1, Shiqi XU1, Yanzhen HE1, Xudong WANG1,2(
), Jiayue LIU1, Kexin HU1, Yiyao GAO1, Shiqi XU1, Yanzhen HE1, Xudong WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-02-04
Accepted:2024-04-24
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
Xudong WANG
寇威1( ), 刘佳月1, 户可欣1, 高铱遥1, 许世奇1, 何彦臻1, 王旭东1,2(
), 刘佳月1, 户可欣1, 高铱遥1, 许世奇1, 何彦臻1, 王旭东1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
王旭东
作者简介:寇威 E-mail:m15133377545@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Wei KOU, Jiayue LIU, Kexin HU, Yiyao GAO, Shiqi XU, Yanzhen HE, Xudong WANG. Effect of Organic Fertilizer with Rhamnolipid and Choline Chloride on Properties of Saline Soils and Salt Tolerance of Tomato[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 202-214.
寇威, 刘佳月, 户可欣, 高铱遥, 许世奇, 何彦臻, 王旭东. 有机肥与鼠李糖脂和氯化胆碱配施对盐渍土性质和番茄耐盐性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 202-214.
处理 Treatment | 施用量Dosage/(kg·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
化肥 Fertilizer (N+P2O5+K2O) | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 氯化胆碱 Choline chloride | 20%鼠李糖脂 20% rhamnolipid | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CF | 975 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CFM | 975 | 15 000 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CFMC1 | 975 | 15 000 | 6 | 0.00 |
| CFMC2 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.00 |
| CFMC3 | 975 | 15 000 | 15 | 0.00 |
| CFMS1 | 975 | 15 000 | 0 | 0.24 |
| CFMC2S1 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.24 |
| CFMC2S2 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.48 |
| CFMC2S3 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.72 |
Table 1 Application rates of chemical fertilizers, organic fertilizers, choline chloride and rhamnolipid in different treatments
处理 Treatment | 施用量Dosage/(kg·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
化肥 Fertilizer (N+P2O5+K2O) | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 氯化胆碱 Choline chloride | 20%鼠李糖脂 20% rhamnolipid | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CF | 975 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CFM | 975 | 15 000 | 0 | 0.00 |
| CFMC1 | 975 | 15 000 | 6 | 0.00 |
| CFMC2 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.00 |
| CFMC3 | 975 | 15 000 | 15 | 0.00 |
| CFMS1 | 975 | 15 000 | 0 | 0.24 |
| CFMC2S1 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.24 |
| CFMC2S2 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.48 |
| CFMC2S3 | 975 | 15 000 | 9 | 0.72 |
| 处理Treatment | pH | 电导率EC/(mS·m-1) | 钠吸附比RSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.20±0.36 a | 153.00±6.49 b | 8.60±0.43 a |
| CF | 9.50±0.36 a | 226.00±9.59 a | 8.50±0.40 a |
| CFM | 8.30±0.47 a | 246.50±13.94 a | 8.30±0.47 b |
| CFMC1 | 8.20±0.35 a | 243.00±10.31 a | 8.30±0.35 b |
| CFMC2 | 8.10±0.24 a | 239.50±6.77 a | 8.40±0.23 b |
| CFMC3 | 8.10±0.35 a | 236.50±10.03 a | 8.30±0.34 b |
| CFMS1 | 8.20±0.23 a | 240.50±6.80 a | 8.20±0.23 b |
| CFMC2S1 | 8.10±0.35 a | 237.50±10.08 a | 8.20±0.34 b |
| CFMC2S2 | 7.90±0.46 a | 235.50±13.32 a | 8.10±0.45 b |
| CFMC2S3 | 7.60±0.34 a | 234.50±9.95 a | 8.00±0.32 b |
Table 2 pH, EC and SAR of organic fertilizers with choline chloride and rhamnolipid soils
| 处理Treatment | pH | 电导率EC/(mS·m-1) | 钠吸附比RSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.20±0.36 a | 153.00±6.49 b | 8.60±0.43 a |
| CF | 9.50±0.36 a | 226.00±9.59 a | 8.50±0.40 a |
| CFM | 8.30±0.47 a | 246.50±13.94 a | 8.30±0.47 b |
| CFMC1 | 8.20±0.35 a | 243.00±10.31 a | 8.30±0.35 b |
| CFMC2 | 8.10±0.24 a | 239.50±6.77 a | 8.40±0.23 b |
| CFMC3 | 8.10±0.35 a | 236.50±10.03 a | 8.30±0.34 b |
| CFMS1 | 8.20±0.23 a | 240.50±6.80 a | 8.20±0.23 b |
| CFMC2S1 | 8.10±0.35 a | 237.50±10.08 a | 8.20±0.34 b |
| CFMC2S2 | 7.90±0.46 a | 235.50±13.32 a | 8.10±0.45 b |
| CFMC2S3 | 7.60±0.34 a | 234.50±9.95 a | 8.00±0.32 b |
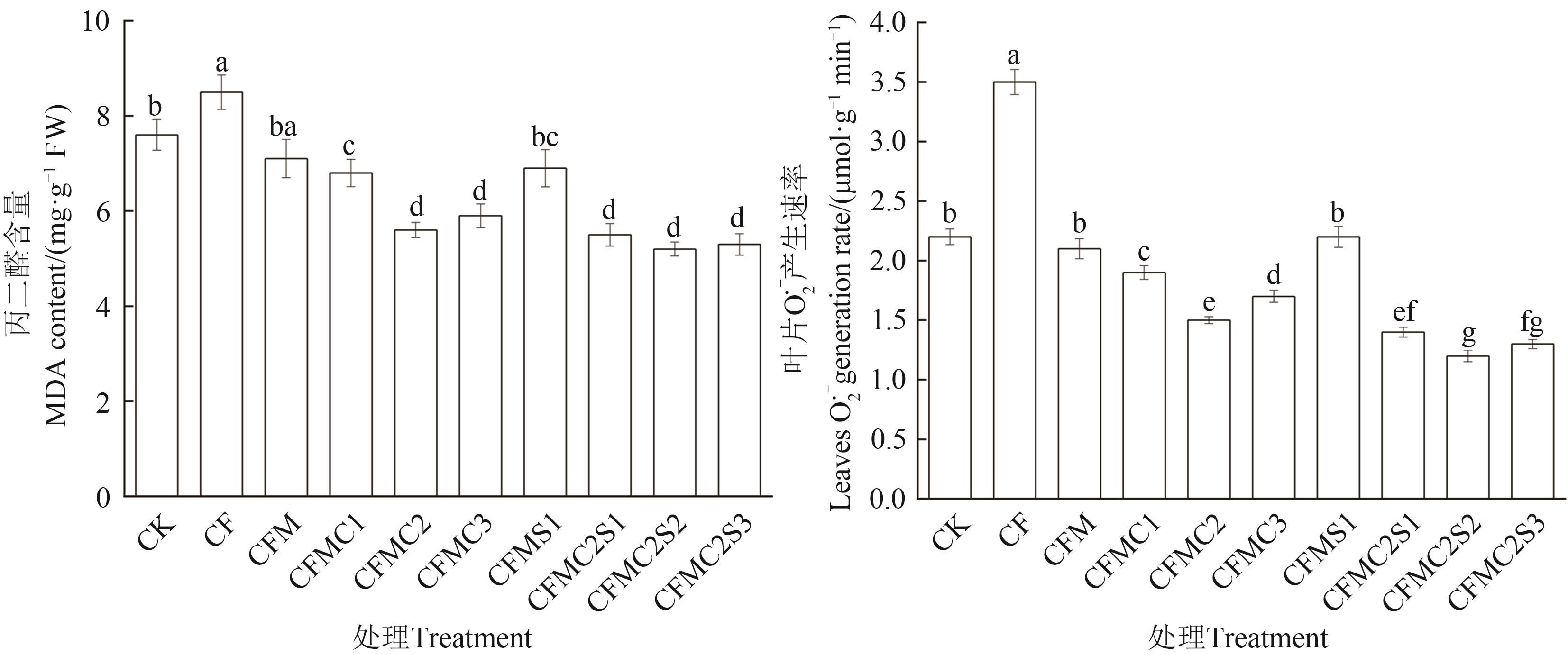
Fig. 1 MDA content and O2.- generation rate of tomatoes in organic fertilizers with choline chloride and rhamnolipidNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
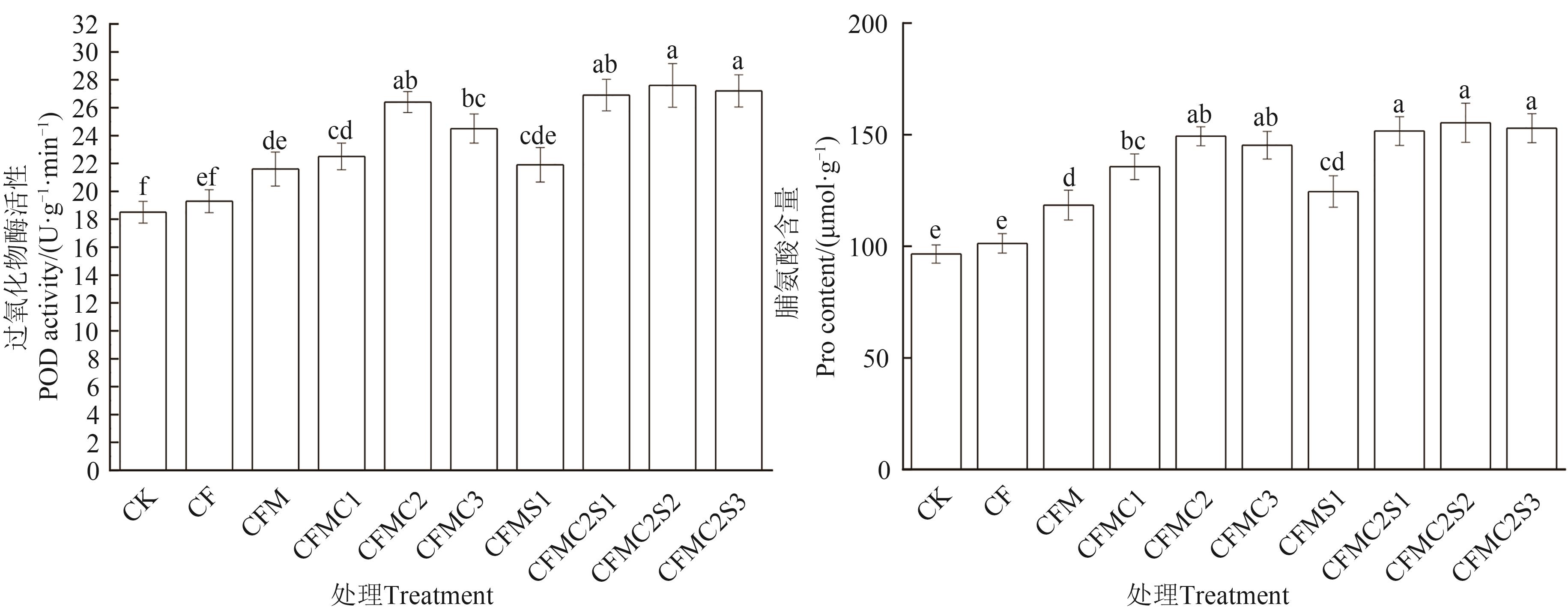
Fig. 2 POD activity and Pro content of tomatoes in organic fertilizers with choline chloride and rhamnolipidNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 3 Soluble sugars, VC content, yield and fresh weight of tomato in organic fertilizers with choline chloride and rhamnolipidNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
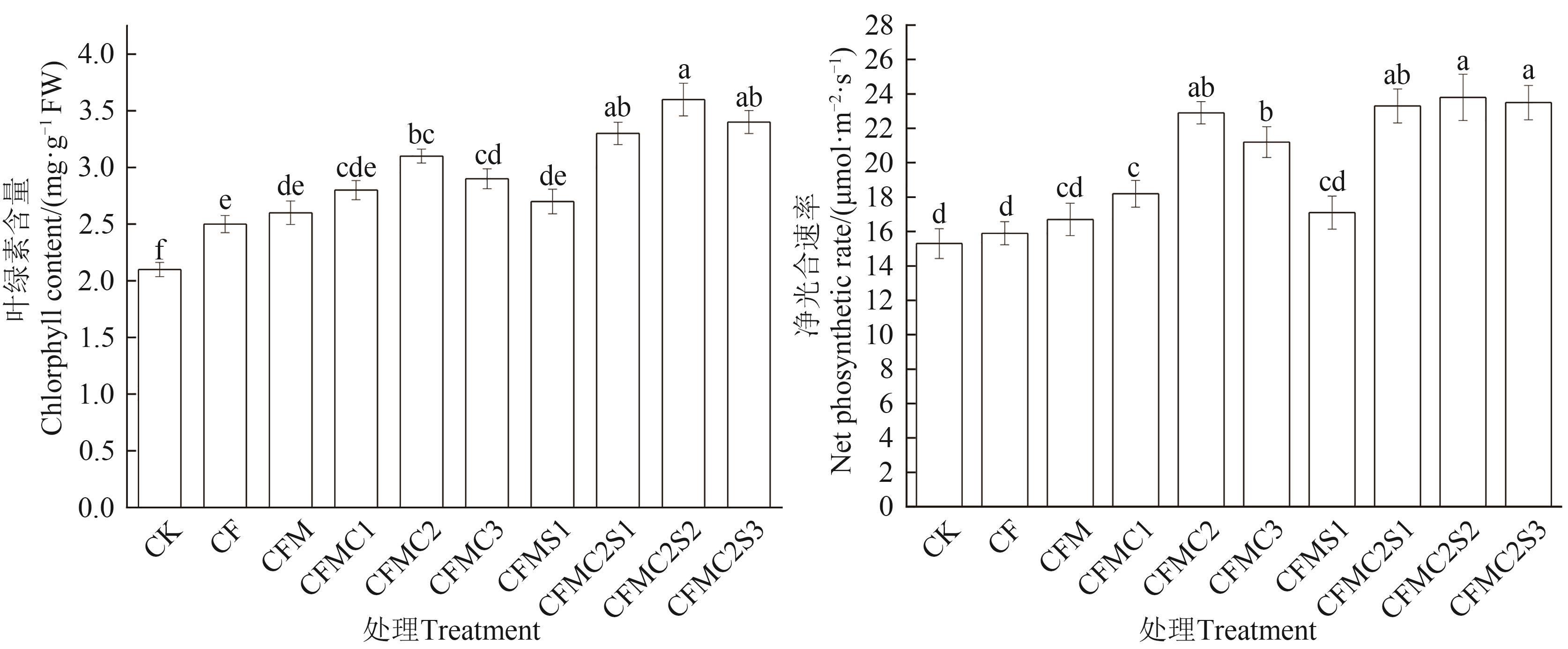
Fig. 4 Chlorophyll content and Pn of organic fertilizer with choline chloride and rhamnolipid tomatoNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
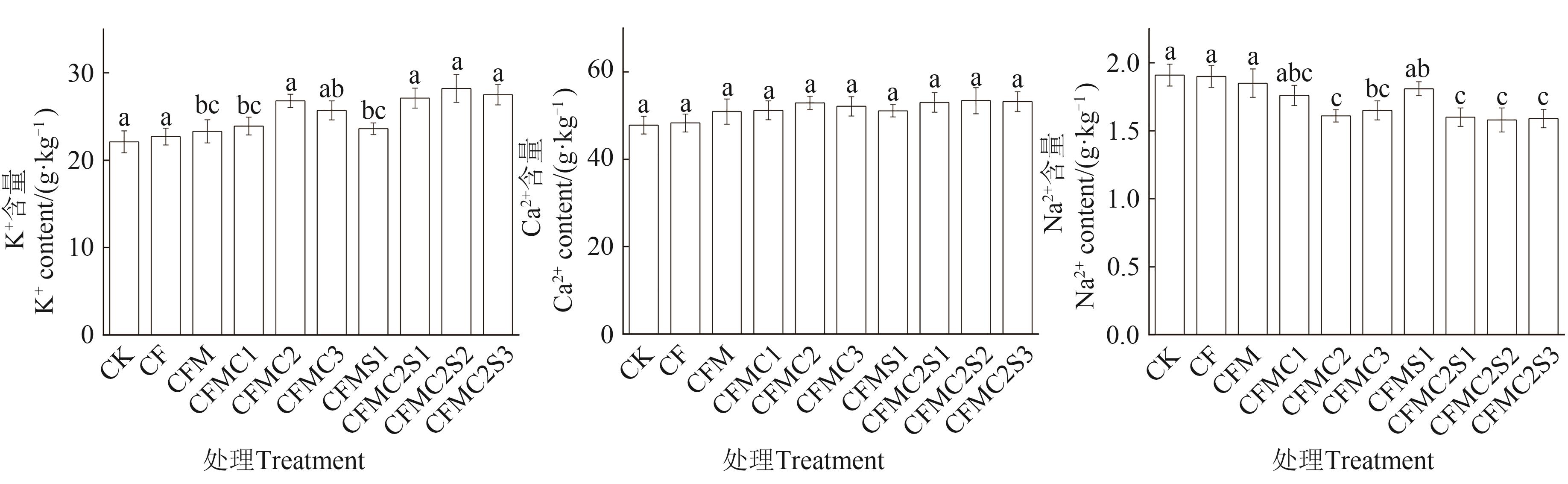
Fig. 5 K+, Ca2+ and Na+ contents of tomato leaves with organic fertilizers with choline chloride and rhamnolipidNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 6 Correlation analysis of tomato yield with various indicatorsNote: *,** and *** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels,respectively.
| [1] | KUMAWAT K C, NAGPAL S, SHARMA P. Potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria-plant interactions in mitigating salt stress for sustainable agriculture: a review [J]. Pedosphere, 2022, 32(2):223-245. |
| [2] | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Global Map of Salt-affected Soils (GSASmap) [R].FAO, 2021:1-20. |
| [3] | 杨劲松,姚荣江,王相平,等.中国盐渍土研究:历程、现状与展望[J].土壤学报, 2022,59(1):10-27. |
| YANG J S, YAO R J, WANG X P, et al.. Research on salt-affected soils in China: history,status quo and prospect [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2022, 59(1):10-27. | |
| [4] | ZHANG Q, DAI W. Stress Physiology of Woody Plants [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, 2019:155-173. |
| [5] | NAVADA S, VADSTEIN O, GAUMET F, et al.. Biofilms remember: Osmotic stress priming as a microbial management strategy for improving salinity acclimation in nitrifying biofilms [J/OL]. Water Res., 2020, 176:115732 [2024-01-06].. |
| [6] | PAN T, LIU M, KRESLAVSKI V D, et al.. Non-stomatal limitation of photosynthesis by soil salinity [J]. Critical Reviews Environ. Sci. Technol., 2021, 51(8): 791-825. |
| [7] | GHAZALI G E B E. Suaeda vermiculata Forssk. ex J. F. Gmel.: structural characteristics and adaptations to salinity and drought:a review [J]. Int. J. Sci., 2020, 9(2):28-33. |
| [8] | 邵孝候,张宇杰,常婷婷,等.生物有机肥对盐渍土壤水盐动态及番茄产量的影响[J].河海大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(2):153-160. |
| SHAO X H, ZHANG Y J, CHANG T T, et al.. Effects of different fertilizer treatments on soil water,salt and crop yield formation in saline soils [J]. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat.Sci.), 2018, 46(2):153-160. | |
| [9] | 荆恩恩,高翔,李宗震,等.氯化胆碱对小麦幼苗耐低温能力的生理调控效应[J].麦类作物学报,2018,38(6):748-755. |
| JING E E, GAO X, LI Z Z, et al.. Physiological regulation of choline chloride on tolerance of wheat seedling to low temperature [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(6):748-755. | |
| [10] | UNWIN N. Structure of a cholinergic cell membrane [J/OL]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2022, 119(34): e2207641119 [2024-01-06]. . |
| [11] | SALAMA K H A, MANSOUR M M F, HASSAN N S. Choline priming improves salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. Australian J. Basic Appl. Sci., 2011, 5(11): 26-132. |
| [12] | WANG J F, BAO H Y, PAN G D, et al.. Combined application of rhamnolipid and agricultural wastes enhances PAHs degradation via increasing their bioavailability and changing microbial community in contaminated soil [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manag., 2021, 294:112998 [2024-01-06].. |
| [13] | 王敏鸽,刘艺文,张丹丹,等.鼠李糖脂改性生物炭对盐渍土小白菜抗性及氮素吸收的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2022,40(5):81-87. |
| WANG M G, LIU Y W, ZHANG D D, et al.. Effects of rhamnolipid modified biochar on resistance and nitrogen absorption of Chinese cabbage in saline soil [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2022, 40(5): 81-87. | |
| [14] | 彭奥翔. 鼠李糖脂改土效果及对平邑甜茶生长影响的研究 [D].泰安:山东农业大学,2022. |
| PENG A X. Effects of rhamnolipid on soil amelioration and growth of Malus hupehensis [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [15] | 张丹丹. 鼠李糖脂对基质栽培小白菜抗盐性的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2022. |
| ZHANG D D. Effect of rhamnosin on salt resistance of chinesecabbage in matrix cultivation [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. | |
| [16] | 黄炳川. 鼠李糖脂和纳米硅肥对棉花耐盐特性的影响[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2022. |
| HUANG B C. Effects of rhamnolipid and nano silicon fertilizeron salt tolerance of cotton [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2022. | |
| [17] | HU K X, XU S Q, GAO Y Y, et al.. Choline chloride and rhamnolipid combined with organic manures improve salinity tolerance, yield,and quality of tomato [J]. J. Plant Growth Regul., 2023, 42(7):4118-4130. |
| [18] | 咸敬甜,陈小兵,王上,等.盐渍土磷有效性研究进展与展望[J].土壤, 2023,55(3):474-486. |
| XIAN J T, CHEN X B, WANG S, et al.. Phosphorus availability in saline soil:a review [J]. Soils, 2023, 55(3): 474-486. | |
| [19] | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:116-261. |
| [20] | LIU J B, ZHU K C, ZHANG C, et al.. Microscale spatiotemporal variation and generation mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in the rhizosphere of ryegrass:coupled biotic-abiotic processes [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2022, 56(22): 16483-16493. |
| [21] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:8-29. |
| [22] | AMINI S, GHADIRI H, CHEN C R, et al.. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: a review [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2016, 16(3): 939-953. |
| [23] | XU X, WANG J H, TANG Y M, et al.. Mitigating soil salinity stress with titanium gypsum and biochar composite materials: improvement effects and mechanism [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2023, 321:138127 [2024-01-06].. |
| [24] | CHEN X D, OPOKU-KWANOWAA Y, LI J M, et al.. Application of organic wastes to primary saline-alkali soil in Northeast China: effects on soil available nutrients and salt ions [J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Analysis, 2020, 51(9): 1238-1252. |
| [25] | 王晟强.植茶年限对土壤团聚体养分含量变化的影响[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2014. |
| WANG S Q. Effects of ages of tea plantations on changes of nutrientcontents in soil aggregates [D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| [26] | 罗玲,潘宏兵,钟奇,等.石灰和有机肥对芒果园酸性土壤的改良效果及对芒果品质的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2021(3):169-177. |
| LUO L, PAN H B, ZHONG Q, et al.. Effects of lime and organic fertilizer on acid soil of mango plantation and mango quality [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(3):169-177. | |
| [27] | YIN S, HU W, CHEN Y, et al.. Chinese consumer preferences for fresh produce: interaction between food safety labels and brands [J]. Agribusiness, 2019, 35(1): 53-68. |
| [28] | CHEN T X, SHABALA S, NIU Y N, et al.. Molecular mechanisms of salinity tolerance in rice [J]. Crop J., 2021, 9(3):506-520. |
| [29] | DING F, QIANG X, JIA Z Q, et al.. Knockout of a novel salt responsive gene SlABIG1 enhance salinity tolerance in tomato [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2022,200: 104903 [2024-01-06]. . |
| [30] | 郭光光,杨俐苹,曹磊.关于化肥对土壤的污染及有效治理举措阐述[J].环境与发展,2020,32(1):78-79. |
| GUO G G, YANG L P, CAO L. Explanation of soil pollution by chemical fertilizers and effective control measures [J]. Environ. Dev., 2020, 32(1):78-79. | |
| [31] | SYEED S, SEHAR Z, MASOOD A, et al.. Control of elevated ion accumulation,oxidative stress,and lipid peroxidation with salicylic acid-induced accumulation of Glycine betaine in salinity-exposed Vigna radiata L. [J]. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2021, 193(10): 3301-3320. |
| [32] | HAO S, WANG Y, YAN Y, et al.. A Review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance [J/OL]. Horticulturae, 2021, 7(6): 132 [2024-01-06]. . |
| [33] | HUSSAIN I, SALEEM M H, MUMTAZ S, et al. Choline chloride mediates chromium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by restricting its uptake in relation to Morpho-physio-biochemical attributes [J]. J. Plant Growth Regul., 2022, 41(4):1594-1614. |
| [34] | ZHAO Y, HE Y, WANG X, et al.. Proline metabolism regulation in Spartina alterniflora and SaP5CS2 gene positively regulates salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. J. Plant Interactions, 2022, 17(1): 632-642. |
| [35] | YAO W S, XU T T, FAROOQ S U, et al.. Glycine betaine treatment alleviates chilling injury in zucchini fruit (Cucurbita pepo L.) by modulating antioxidant enzymes and membrane fatty acid metabolism [J]. Postharvest Biol. Technol., 2018, 144: 20-28. |
| [36] | SALINAS R, SANCHEZ E, RUIZ J M, et al.. Proline, betaine, and choline responses to different phosphorus levels in green bean [J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Analysis, 2013, 44(1-4): 465-472. |
| [37] | SOFY M R, ELHAWAT N, TAREK ALSHAAL. Glycine betaine counters salinity stress by maintaining high K+/Na+ ratio and antioxidant defense via limiting Na+ uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020, 200:110732 [2024-01-06]. . |
| [38] | 刘雅,蔡光容,于伟,等.生物表面活性剂鼠李糖脂对大豆叶面肥喷施效果的影响[J].大豆科学,2018,37(3):378-384. |
| LIU Y, CAI G R, YU W, et al.. Effect of biosurfactant rhamnolipid on the spraying efficiency of soybean foliar fertilizer [J]. Soybean Sci., 2018, 37(3):378-384. | |
| [39] | HAMEED A, AHMED M Z, HUSSAIN T, et al.. Effects of salinity stress on chloroplast structure and function [J/OL]. Cells, 2021, 10(8):2023 [2024-01-06].. |
| [40] | GULZAR S, HUSSAIN T, GUL B, et al. Handbook of Halophytes: From Molecules to Ecosystems towards Biosaline Agriculture [M]. Berlin:Springer International Publishing, 2020: 1-31. |
| [41] | XUE F, LIU W, CAO H, et al.. Stomatal conductance of tomato leaves is regulated by both abscisic acid and leaf water potential under combined water and salt stress [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 172(4): 2070-2078. |
| [42] | RIAZ S, HUSSAIN I, IBRAHIM M, et al.. holine chloride mediates salinity tolerance in cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) by improving growth, oxidative defense, and secondary metabolism [J]. Dose-response, 2021, 19(4):55026[2024-01-06]. . |
| [43] | 陈文志,邬梦晞,罗巧,等.两种表面活性剂对镉胁迫下龙葵生理特性的影响[J].北方园艺,2017(11):1-7. |
| CHEN W Z, WU M X, LUO Q, et al.. Effects of two surfactants on growth of Solanum nigrum L. under cadmium stress [J]. Northern Hortic., 2017(11):1-7. | |
| [44] | WEI L, ZHANG J, WEI S, et al.. Nitric oxide enhanced salt stress tolerance in tomato seedlings,involving phytohormone equilibrium and photosynthesis [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(9):4539 [2024-01-06].. |
| [45] | 张培苹.鼠李糖脂水溶肥料对苹果农艺性状及产量的影响[J].农业科技通讯,2014(10):137-139. |
| [46] | KHEDR R A, SOROUR S G R, ABOUKHADRAH S H, et al.. Alleviation of salinity stress effects on agro-physiological traits of wheat by auxin, Glycine betaine, and soil additives [J]. Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2022, 29(1):534-540. |
| [1] | Qi ZHOU, Qiang LIU, Jing ZHANG, Chaochao DENG, Zhenlong WANG, Yang LIU, Fang WU, Hao CHANG, Yanfang ZHOU, Cuicui SU, Zhiguo SHI, Zhengrui GAO, Fengjie MA. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Replacing Chemical Fertilizer on Yield and Soil Biological Characteristics of Pumpkin [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 190-203. |
| [2] | Xiyu ZHANG, Xing SHEN, Wei LI, Wenge XIE, Jie LI, Changhao YANG, Zhongping CHAI. Influence of Reduced Nitrogen Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Korla Pear Orchards [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 217-228. |
| [3] | Yaxin WANG, Yangcheng LYU, Wenqi WANG, Qi LIU, Jie YANG, Guihong REN, Wuping ZHANG, Fuzhong LI. Nondestructive Segmentation and Extraction of Stem and Leaf Phenotypes During Tomato Plant Growth [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 90-100. |
| [4] | Jianglin LAN, Rongfeng XIAO, Jieping WANG, Haifeng ZHANG, Bo LIU. Effects of Integrated Microbiome Agent on Tomato Plant Growth and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Diversity [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 173-181. |
| [5] | Jing XU, Han LI, Pinglu CHEN, Jiangni LUO, Chenglu TANG, Muhua LIU. Calibration and Validation of Discrete Element Model for Camelliaoleifera Seed Meal [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 112-121. |
| [6] | Darong LI, Xiaoling LI, Wuxian ZHOU, Meide ZHANG, Xiaogang JIANG, Jinwen YOU, Hua WANG. Effects of Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Growth and Soil Properties of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 216-226. |
| [7] | Jincheng LUO, Xiaolin ZHU, Xiaohong WEI, Xian WANG, Baoqiang WANG, Xuefen DU. Effect of Exogenous NO on Expression of Tomato Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Under Tomato Yellowing Leaf Curl Virus Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 125-135. |
| [8] | Chunjiao MI, Hongren SUN, Jiping ZHANG, Yucai LYU, Yandi ZHANG. Abundance-deficiency Index of Soil Available Phosphorus and Recommended Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rates for Tomato in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [9] | Xianguo LI, Qi DAI, Zepeng WANG, Zhaolong CHEN, Huizhuan YAN, Ning LI. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tomato CCCH-like Zinc Finger Protein Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [10] | Danyi SHI, Yu QIU, Chengzhen HUANG, Juan WANG. Effect of Acid Modified Biochar on Infiltration Characteristics of Coastal Saline Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 183-192. |
| [11] | Junlei ZHANG, Xiaotong GE, Zhengting ZHAO, Di LIU, Jinfeng WANG, Ning JIANG, Yating LIU. Establishment and Optimization of RT-LAMP Assay System for Tobacco Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [12] | Xingsong WANG, Na WANG, Yu DU, Peng ZHOU, Ge WANG, Meng JIA, Zhaoli XU, Yuxiang BAI. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on Organic Matter Composition and Microbial Community Structure of Tobacco-Growing Soil in Yuxi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 201-212. |
| [13] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [14] | Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [15] | Xiuli HAN, Jiawei LI, Jie ZHANG, Yanjie GUO, Lijuan ZHANG, Yanzhi JI. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer Replacing Part of Chemical Fertilizer on Grape Growth and Soil Fertility [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 195-205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号