




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 183-192.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0113
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Danyi SHI( ), Yu QIU, Chengzhen HUANG, Juan WANG(
), Yu QIU, Chengzhen HUANG, Juan WANG( )
)
Received:2023-02-20
Accepted:2023-07-27
Online:2024-09-15
Published:2024-09-13
Contact:
Juan WANG
通讯作者:
王娟
作者简介:史丹一 E-mail:1315390047@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Danyi SHI, Yu QIU, Chengzhen HUANG, Juan WANG. Effect of Acid Modified Biochar on Infiltration Characteristics of Coastal Saline Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 183-192.
史丹一, 邱禹, 黄成真, 王娟. 酸改性生物炭对滨海盐渍土壤水分入渗特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 183-192.

Fig. 1 Variation curve of cumulative infiltration with time under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
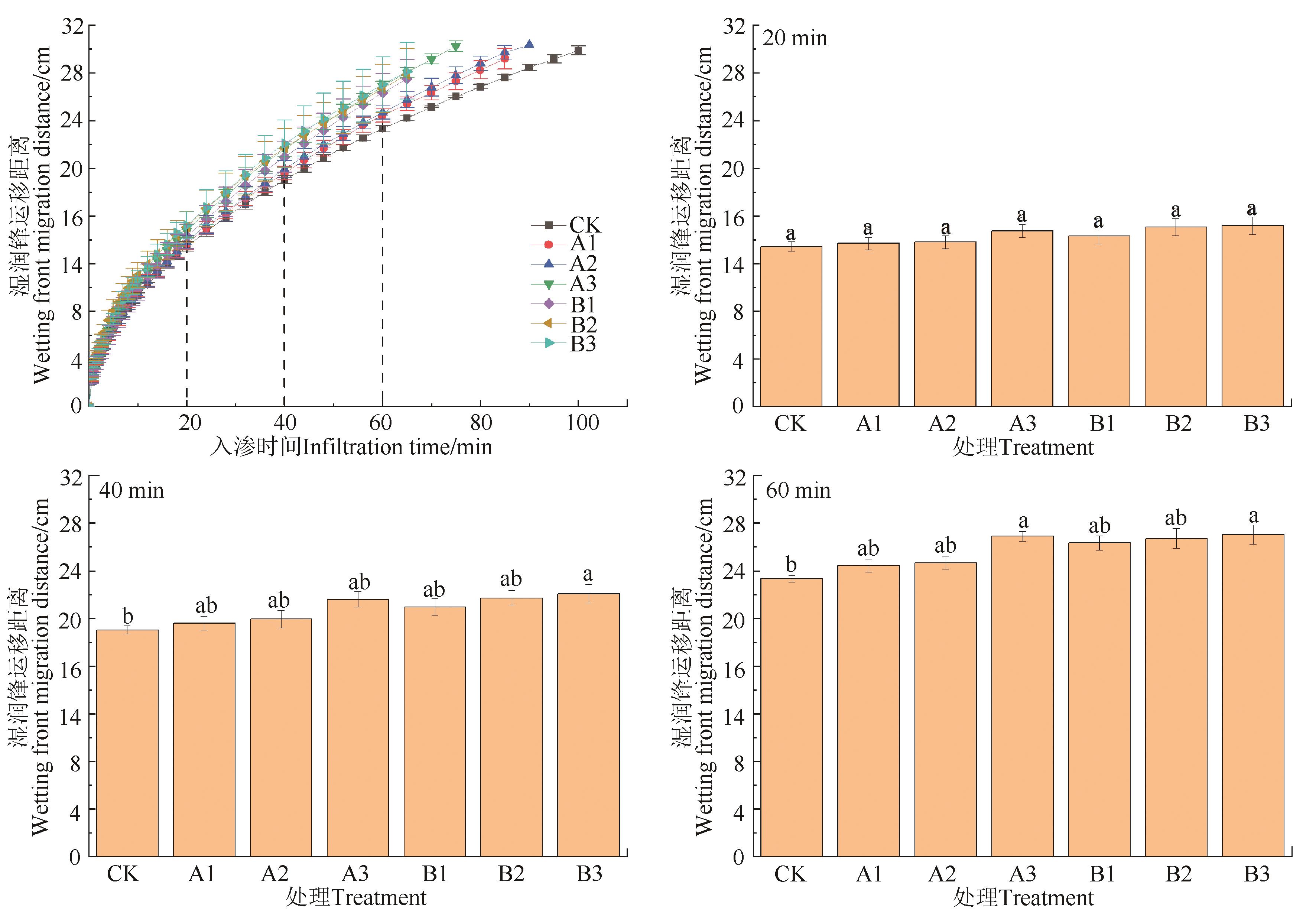
Fig. 2 Variation curve of wetting front migration distance with time under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 拟合参数n | 0.350 | 0.357 | 0.358 | 0.359 | 0.349 | 0.345 | 0.349 |
| 决定系数R² | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
Table 1 Fitting coefficient of the relationship between cumulative infiltration volume and wetting front depth
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 拟合参数n | 0.350 | 0.357 | 0.358 | 0.359 | 0.349 | 0.345 | 0.349 |
| 决定系数R² | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |

Fig.3 Variation curve of soil infiltration rate with time under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 经验系数K | 0.600 | 0.690 | 0.631 | 0.743 | 0.609 | 0.970 | 0.934 |
| 经验系数N | 0.525 | 0.520 | 0.536 | 0.528 | 0.552 | 0.434 | 0.463 |
| 决定系数R² | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
Table 2 Simulation parameters of the Kostiakov infiltration model
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 经验系数K | 0.600 | 0.690 | 0.631 | 0.743 | 0.609 | 0.970 | 0.934 |
| 经验系数N | 0.525 | 0.520 | 0.536 | 0.528 | 0.552 | 0.434 | 0.463 |
| 决定系数R² | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 0—5 | 11.65±3.21 b | 13.92±3.11 ab | 13.76±4.64 ab | 13.26±5.82 ab | 13.98±4.41 a | 12.11±5.89 ab |
| 5—10 | 6.00±5.51 b | 5.77±1.41 b | 7.01±5.26 ab | 7.73±4.50 ab | 8.94±3.55 ab | 9.20±8.50 a |
| 10—15 | 3.11±2.54 b | 3.43±2.54 b | 5.14±2.69 ab | 4.90±2.40 ab | 8.81±5.82 a | 8.27±4.43 a |
Table 3 Soil water holding efficiency of 0—15 cm shallow soil under different biochar addition
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 0—5 | 11.65±3.21 b | 13.92±3.11 ab | 13.76±4.64 ab | 13.26±5.82 ab | 13.98±4.41 a | 12.11±5.89 ab |
| 5—10 | 6.00±5.51 b | 5.77±1.41 b | 7.01±5.26 ab | 7.73±4.50 ab | 8.94±3.55 ab | 9.20±8.50 a |
| 10—15 | 3.11±2.54 b | 3.43±2.54 b | 5.14±2.69 ab | 4.90±2.40 ab | 8.81±5.82 a | 8.27±4.43 a |
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 拟合参数n | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.358 | 0.359 | 0.349 | 0.345 | 0.349 |
| 综合性状系数α | 0.262 | 0.405 | 0.323 | 0.272 | 0.279 | 0.422 | 0.469 |
| 决定系数R² | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 均方根误差RMSE/% | 0.013 | 0.166 | 0.035 | 0.016 | 0.529 | 0.602 | 0.242 |
| 符合度指数D | 0.983 | 0.885 | 0.964 | 0.978 | 0.765 | 0.765 | 0.854 |
Table 4 Parameters of one dimensional algebraic model and simulation accuracy analysis under different biochar addition
| 项目Item | 处理 Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| 拟合参数n | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.358 | 0.359 | 0.349 | 0.345 | 0.349 |
| 综合性状系数α | 0.262 | 0.405 | 0.323 | 0.272 | 0.279 | 0.422 | 0.469 |
| 决定系数R² | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 均方根误差RMSE/% | 0.013 | 0.166 | 0.035 | 0.016 | 0.529 | 0.602 | 0.242 |
| 符合度指数D | 0.983 | 0.885 | 0.964 | 0.978 | 0.765 | 0.765 | 0.854 |
| 1 | 国务院第三次全国国土调查领导小组办公室,自然资源部,国家统计局. 第三次全国国土调查主要数据成果公报[EB/OL]. (2021-08-25)[2023-01-20]. . |
| 2 | 自然资源部,国家统计局,国务院第二次全国国土调查领导小组办公室. 第二次全国国土调查主要数据成果公报[EB/OL]. (2013-12-30) [2023-01-20]. . |
| 3 | 杨劲松,姚荣江,王相平,等.中国盐渍土研究: 历程、现状与展望[J].土壤学报,2022,59(1):10-27. |
| YANG J S, YAO R J, WANG X P, et al.. Research on salt-affected soils in China: history, status quo and prospect [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2022, 59(1): 10-27. | |
| 4 | 赵秀芳,杨劲松,姚荣江. 苏北典型滩涂区土壤盐分动态与水平衡要素之间的关系[J].农业工程学报, 2010,26(3):52-57. |
| ZHAO X F, YANG J S, YAO R J. Relationship between soil salt dynamics and factors of water balance in the typical coastal area of Northern Jiangsu province [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2010, 26(3): 52-57. | |
| 5 | 张翼夫,李问盈,胡红,等.盐碱地改良研究现状及展望[J].江苏农业科学,2017,45(18):7-10. |
| 6 | GLASER B, HAUMAIER L, GUGGENBERGER G, et al.. Black carbon in soils: the use of benzenecarboxylic acids as specific markers [J]. Organic Geochem., 1998, 29(4): 811-819. |
| 7 | ZHENG H, WANG X, CHEN L, et al.. Enhanced growth of halophyte plants in biochar amended coastal soil: roles of nutrient availability and rhizosphere microbial modulation [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2018, 41(3):517-532. |
| 8 | 张进红,吴波,王国良,等.生物炭对盐渍土理化性质和紫花苜蓿生长的影响[J].农业机械学报,2020,51(8):285-294. |
| ZHANG J H, WU B, WANG G L, et al.. Effects and evaluation of biochar on physical-chemical properties of coastal saline soil and alfalfa growth [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2020, 51(8): 285-294. | |
| 9 | 简敏菲,高凯芳,余厚平,等.不同温度生物炭酸化前后的表面特性及镉溶液吸附能力比较[J].生态环境学报,2015,24(8):1375-1380. |
| JIAN M F, GAO K F, YU H P, et al.. Comparison of surface characteristics and cadmium solution adsorption capacity of un-acidified or acidified biochars prepared from rice straw under different temperatures [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2015, 24(8): 1375-1380. | |
| 10 | 段曼莉,李志健,刘国欢,等.改性生物炭对土壤中Cu2+吸附和分布的影响[J].环境污染与防治,2021,43(2):150-155, 160. |
| DUAN M L, LI Z J, LIU G H, et al.. Effects of modified biochar on adsorption and distribution of Cu2+ in soil [J]. Environ. Pollut. Control, 2021, 43(2): 150-155, 160. | |
| 11 | GAO Y, SHAO G C, YANG Z, et al.. Influences of soil and biochar properties and amount of biochar and fertilizer on the performance of biochar in improving plant photosynthetic rate: a meta-analysis [J/OL]. Eur. J. Agron., 2021, 130:126345 [2023-01-20]. . |
| 12 | HERATH H M S K, CAMPS-ARBESTAIN M, HEDLEY M. Effect of biochar on soil physical properties in two contrasting soils: an alfisol and an andisol [J]. Geoderma, 2013, 209-210(3):188-197. |
| 13 | 王艳阳,魏永霞,孙继鹏,等.不同生物炭施加量的土壤水分入渗及其分布特性[J].农业工程学报,2016, 32(8):113-119. |
| WANG Y Y, WEI Y X, SUN J P, et al.. Soil water infiltration and distribution characteristics under different biochar addition amount [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(8): 113-119. | |
| 14 | 黄明逸,张展羽,徐辉,等. 咸淡轮灌和生物炭对滨海盐渍土水盐运移特征的影响[J].农业机械学报,2021,52(1):238-247. |
| HUANG M Y, ZHANG Z Y, XU H, et al.. Effects of cycle irrigation with brackish and fresh water and biochar on water and salt transports of coastal saline soil [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2021, 52(1): 238-247. | |
| 15 | 王娟,陈安全,宋文瑾,等.生物炭种类与施量对新复垦区土壤水分入渗过程的影响[J].农业机械学报,2022,53(11):388-394. |
| WANG J, CHEN A Q, SONG W J, et al.. Effect of biochar species and application amounts on soil water infiltration of newly reclaimed area [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2022, 53(11): 388-394. | |
| 16 | 王春霞,王全九,吕廷波,等.添加化学改良剂的砂质盐碱土入渗特征试验研究[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(1):31-35. |
| WANG C X, WANG Q J, LYU T B, et al.. The studies of infiltration characteristics on sandy saline alkali soil by chemical amelioration [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2014, 28(1): 31-35. | |
| 17 | 王全九,邵明安,郑继勇.土壤中水分运动与溶质迁移[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2007:20-21. |
| 18 | 赵连东,高佩玲,王乃江,等.一维代数模型在重度盐碱土微咸水灌溉中的适用性[J].排灌机械工程学报,2017,35(3):248-255. |
| ZHAO L D, GAO P L, WANG N J, et al.. Applicability of one dimensional algebraic model in brackish water irrigation of severe saline-alkali soil [J]. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng., 2017, 35(3): 248-255. | |
| 19 | 王幼奇,阮晓晗,白一茹,等.不同种植年限压砂地土壤水分入渗过程及模型分析[J].排灌机械工程学报,2022,40(10):1048-1055. |
| WANG Y Q, RUAN X H, BAI Y R, et al.. Process of soil moisture infiltration and model analysis of gravel-mulched land with different planting years [J]. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng., 2022, 40(10): 1048-1055. | |
| 20 | 吴克宁,赵瑞.土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨[J].土壤学报,2019,56(1):227-241. |
| WU K N, ZHAO R. Soil texture classification and its application in China [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2019,56(1):227-241. | |
| 21 | 邵明安,王全九,黄明斌. 土壤物理学[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2006:126-156. |
| 22 | WANG Q J, ROBERT H, SHAO M A. Algebraic model for one-dimensional infiltration and soil water distribution [J]. Soil Sci.,2003,168(10):671-676. |
| 23 | WILLMOTT C J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance [J]. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 1982, 63:1309-1313. |
| 24 | 孙燕,王春宏,王全九,等.生化黄腐酸对盐碱土水盐运移特征及盐基离子组成的影响[J].水土保持学报,2022,36(4):228-235. |
| SUN Y, WANG C H, WANG Q J, et al.. Effects of biochemical fulvic acid application on water and salt transport characteristics and basic ion composition of saline-alkaline soil [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2022, 36(4): 228-235. | |
| 25 | 吕振豫,刘珊珊,秦天玲,等.土壤入渗研究进展及方向评述[J].中国农村水利水电,2019(7):1-5. |
| LYU Z Y, LIU S S, QIN T L, et al.. Comment on the progress and major direction of soil infiltration research [J]. China Rural Water Hydropower, 2019(7):1-5. | |
| 26 | 黄成真,王娟,仲昭易,等.普通生物炭和酸改性生物炭对盐渍土入渗、蒸发过程的影响[J].中国农村水利水电,2020(11):138-142, 150. |
| HUANG C Z, WANG J, ZHONG Z Y, et al.. Effect of common biochar and acid modified biochar on infiltration andevaporation of saline soil [J]. China Rural Water Hydropower, 2020(11): 138-142, 150. | |
| 27 | 刘淙琮,董心亮,郭凯,等.柽柳生物炭对滨海盐渍土咸水入渗特征的影响研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2022,30(7):1194-1202. |
| LIU C Z, DONG X L, GUO K, et al.. Effect of tamarix ramosissima biochar on infiltration characteristics of saline water in coastal saline soil [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(7): 1194-1202. | |
| 28 | 杨玲,张富仓,孙鑫, 等. 生物炭施用量和滴灌量对陕北榆林沙土性质和马铃薯生长的影响[J].中国农业科技导报, 2023,25(3):221-233.. |
| YANG L, ZHANG F C, SUN X, et al.. Effects of biochar and drip irrigation amounts on soil properties and growth of potato in blown-sand region of Northern Yulin, Shaanxi province [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(3): 221-233. | |
| 29 | 蒋慧,郝雅琼,王荔霄,等.改性小麦秸秆生物炭对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(7):250-255. |
| JIANG H, HAO Y Q, WANG L X, et al.. Adsorption properties of modified wheat straw biochar for Cr (VI) in water [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(7): 250-255. | |
| 30 | 刘国欢.改性生物炭对盐碱地改良及冬小麦生长特征影响的研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2021. |
| LIU G H. Effects of modified biochar on saline alkali soil improvement and growth characteristics of winter wheat [D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 31 | 吴雨晴,郑春莲,李科江,等.咸水灌溉对麦-玉两熟制农田土壤水稳性团聚体的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2021,35(2):288-294, 308. |
| WU Y Q, ZHENG C L, LI K J, et al.. Effect of saline water irrigation on soil water-stable aggregates in wheat-maize crop double cropping system [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2021, 35(2): 288-294, 308. | |
| 32 | 刘月,李孟钊,徐志杰,等.不同改良方法对盐碱土壤水盐运移效果的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(6):183-191. |
| LIU Y, LI M Z, XU Z J, et al.. Effects of different improvers on water and salt migration in saline-alkali soil [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2020, 38(6): 183-191. |
| [1] | Jidong ZHANG, Yaxiong ZHANG, Wei CHENG, Li PU, Luhang LIU, Yaming WANG. Effects of Combined Application of Biochar and Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Characteristics in Apple Recropping Field [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 213-222. |
| [2] | Hao WANG, Pengjie JIN, Shan GAO, Mingxuan ZHAO, Changai ZHANG, Shengdao SHAN. Effect of Additives on Stability Immersed in Water of Biochar Based Long-acting Fertilizer [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 174-182. |
| [3] | Zitian PU, Hong WANG, Bin ZHAO, Xinxin WANG. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Growth of Scutellaria baicalensis and Soil Enzyme Activities in Continuous Cropping [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(7): 189-198. |
| [4] | Yanbo FU, Bingbing LENG, Qingyong BIAN, Zhiduo DONG, Guohong LIU, Haifeng LI, Yunmeng WEN, Wenbo GUO, Wanxu ZHANG. Passivation Effect of Biochar on Soil Cadmium Pollution and Rape Growth [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 183-190. |
| [5] | Yuxin CHEN, Hongmei ZHAO, Weijun YANG, Mei YANG, Song GUO, Shilong SONG, Chao HUI. Effects of Biochar on Soil Microbial Carbon Source Utilization and Spring Wheat Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 174-183. |
| [6] | Ling LIN, Yujie ZHU, Lei FENG, Guangmu TANG, Yunshu ZHANG, Wanli XU. Effects of Aged Cotton Straw Biochars on Soil Properties and Nitrogen Utilization of Wheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 184-191. |
| [7] | Yahong ZHAO, Qianyu HU, Rong XIA, Zhijiang WANG, Yonghui XIE, Xianwen YE, Lei YU, Ying QI, Shaowu YANG, Zhiqin XUE, Zhixing WU, Feiyan HUANG, Tianhua HAN. Effects of Biochar Fertilizer on Rhizosphere Flora and Physicochemical Properties of Flue-cured Tobacco Susceptible to Root Knot Nematode [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 206-214. |
| [8] | Huijun LI, Weijian ZHANG, Weijian WU, Gaoyang LI, Yijie CHEN, Fengcheng HUANG, Yongxiang HUANG, Zhong LIN, Zhen ZHEN. Effects of Sea Rice on Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Coastal Solonchaks [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [9] | Jing GAO, Minggang XU, Ran LI, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Lei ZHENG. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 186-196. |
| [10] | Hongyuan LIU, Zhihua ZHOU, Guangxin ZHAO, Qinrui SHEN. Effects of Long-term Biochar Application on Greenhouse Gas Emission and Its Temporal Effect in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [11] | Xudong WANG, Xuebing REN, Shu TANG, Qin GUO, Mengyao XUE, Peng JIN, Yunhua ZHANG. Application of Sludge Biochar in Soil Improvement [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 165-173. |
| [12] | Jia YAO, Jiaxin LIU, Yan SU, Xiaojuan SU. Effects of Combined Application of Tobacco Stem Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizers on Corn Growth and Soil Properties in Seeding Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [13] | Yunfei LIU, Fengjie WEI, Maolin XIA, Zhaojin YU, Hao XIA, Chunyu YI, Jianbo CHANG, Xiaoming JI. Alleviative Effect of New Composite Hydrogels on Cadmium Stress Tobacco Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 188-197. |
| [14] | Ling YANG, Fucang ZHANG, Xin SUN, Shaohui ZHANG, Haidong WANG, Ahmed Elsayed ABDELGHANY, Zhanfei CHEN, Yuchuan FANG. Effects of Biochar and Drip Irrigation Amounts on Soil Properties and Growth of Potato in Blown-sand Region of Northern Yulin, Shaanxi Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 221-233. |
| [15] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号