




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 1-16.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0210
• 农业创新论坛 •
收稿日期:2023-03-20
接受日期:2024-01-04
出版日期:2025-01-15
发布日期:2025-01-21
作者简介:蒋雪松 E-mail:xsjiang@126.com
Xuesong JIANG( ), Zifan RONG, Linfeng HUANG, Qing CHEN, Zhicheng JIA, Jinpeng WANG
), Zifan RONG, Linfeng HUANG, Qing CHEN, Zhicheng JIA, Jinpeng WANG
Received:2023-03-20
Accepted:2024-01-04
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
摘要:
森林对生态环境的保护和经济的发展起重要作用,然而病虫害的侵染严重制约了森林资源的可持续发展。近年来,遥感、机器视觉、生物传感器、物联网等现代化监测技术迅速发展,为森林大面积病虫害的精准监测与快速预警奠定了坚实基础。因此,就现代化技术在森林病虫害监测和预警方面的应用进行综合评述,旨在为相关从业者提供技术参考及辅助决策依据。在遥感方面,介绍了基于光谱响应监测森林病虫害的机理,从近地、地块及区域3个尺度对森林病虫害遥感监测的研究现状进行总结和讨论;在机器视觉方面,对比传统图像处理方法与深度学习的优缺点,从迁移学习、轻量化模型等方面分析提高监测效率的可行性;在生物学方面,阐述了如何基于虫类的生物学特征以及植物的生物学变化实现对病虫害的监测。此外,对物联网、5G等网络技术与现代监测技术相结合的方法进行探讨,以期达到对森林病虫害进行远程监控与预警的目的。最后,针对现阶段森林病虫害监测不及时、演变不清晰、预警不准确、防治不精准等问题,提出今后亟需以物联网技术为核心,建立地面、空中立体化病虫害监测网络,构建完备的病虫害数据库,建立多终端在线实时信息显示的监测和预警系统。
中图分类号:
蒋雪松, 戎子凡, 黄林峰, 陈青, 贾志成, 王金鹏. 现代化技术在森林病虫害监测与预警中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 1-16.
Xuesong JIANG, Zifan RONG, Linfeng HUANG, Qing CHEN, Zhicheng JIA, Jinpeng WANG. Research Progress on Monitoring and Early Warning Technology of Forestry Pests and Diseases[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 1-16.
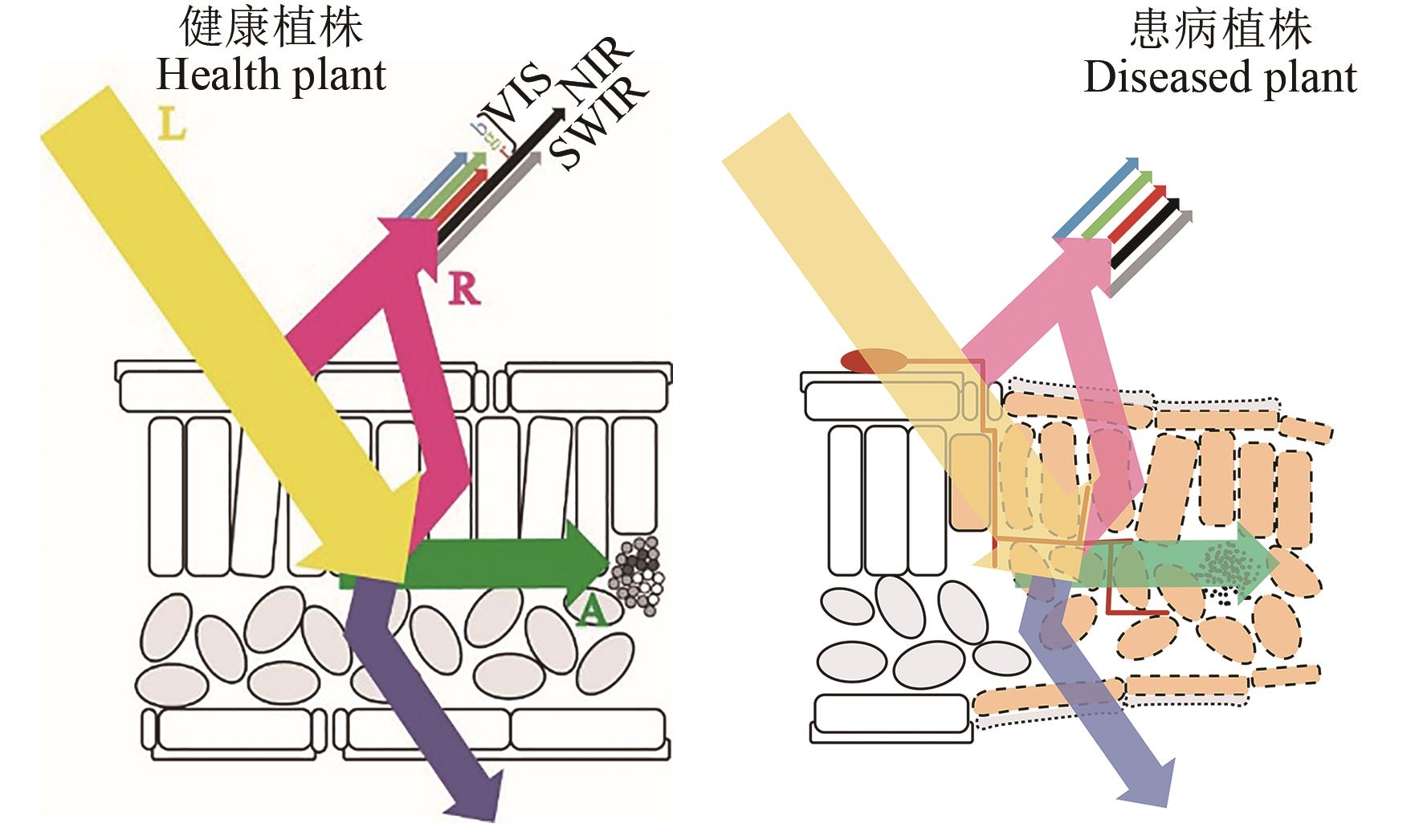
图1 健康植株和患病植株的反射光谱注:L—光;R—反射;A—吸收;VIS—可见光;NIR—近红外光;SWIR—短波红外光。
Fig. 1 Reflectance spectra of healthy plants and diseased plantsNote: L—Light; R—Reflect; A—Absorb; VIS—Visible light; NIR—Near-infrared; SWIR—Short wave infrared.
| 尺度Scale | 优点Advantage | 缺点Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
叶片和冠层尺度 Leaf and canopy scale | 受环境干扰较少、监测的精度高 Less environmental interference, high monitoring accuracy | 只能满足单木监测 Only meet the monitoring of single wood |
地块尺度 Block scale | 通过无人机搭载光谱相机可以实现大范围的病虫害监测 A wide range of pest and disease monitoring can be achieved by carrying a spectral camera on UAV | 容易受到光照、风速等环境因素的影响 Easily affected by environmental factors such as light and wind speed |
区域尺度 Regional scale | 视域广、成本低、监测范围广 Wide visual range, low cost, wide monitoring range | 空间分辨率低且容易受到云层的干扰 Low spatial resolution and easily disturbed by clouds |
表1 不同监测尺度的优缺点
Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of different monitoring scale
| 尺度Scale | 优点Advantage | 缺点Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
叶片和冠层尺度 Leaf and canopy scale | 受环境干扰较少、监测的精度高 Less environmental interference, high monitoring accuracy | 只能满足单木监测 Only meet the monitoring of single wood |
地块尺度 Block scale | 通过无人机搭载光谱相机可以实现大范围的病虫害监测 A wide range of pest and disease monitoring can be achieved by carrying a spectral camera on UAV | 容易受到光照、风速等环境因素的影响 Easily affected by environmental factors such as light and wind speed |
区域尺度 Regional scale | 视域广、成本低、监测范围广 Wide visual range, low cost, wide monitoring range | 空间分辨率低且容易受到云层的干扰 Low spatial resolution and easily disturbed by clouds |
平台 Platform | 植被类型 Vegetational type | 病虫害名称 Name of pest and disease | 分类模型 Disaggregated model | 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
近地尺度 Near-earth scale | 梨 Pear | 火疫病 Fire blight disease | Fisher判别分析 fisher discrimination analysis | [ |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | 模糊聚类 Fuzzy clustering methods | [ | |
油棕榈树 Oil plam | 真菌病害 Fungal disease | 偏最小二乘和线性判别分析 Partial least squares and linear discriminant analysis | [ | |
刺五加 Acanthopanax root | 黑斑病 Black spot disease | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
地块尺度 Block scale | 柑橘 Citrus | 溃疡病 Canker disease | 径向基函数 Radial basis function | [ |
香蕉 Banana | 枯萎病 Blight disease | 贝叶斯线性回归 Bayesian linear regression | [ | |
松 Pine | 松甲虫虫害 Pine beetle infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
苹果 Apple | 火疫病 Fire blight disease | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
柑橘 Citrus | 黄龙病和红蜘蛛虫害Yellow dragon disease and red spider infestation | 逻辑回归和支持向量机 Logistic regression and support vector machine | [ | |
油棕榈 Oil plam | 基腐病 Basal rot disease | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
杨 Poplar | 锈病 Rust disease | K近邻和Fisher判别 K nearest neighbor and Fisher discriminant | [ | |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | BP神经网络 BP neural network | [ | |
松 Pine | 松枯萎病 Pine wilt disease | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
区域尺度 Regional scale | 槟榔 Areca catechu | 黄叶病 Chlorotic disorder | 随机森林 Random forest | [ |
红树林 Mangrove | 小斑螟虫害 Insect infestation of small spot borer | 多元逐步回归分析 Multiple stepwise regression analysis | [ | |
竹 Bamboo | 刚竹毒蛾虫害 Bamboo moth infestation | XGBoost | [ | |
桉 Eucalyptus | 切叶蚁虫害 Leaf cutter insect infestation | 偏最小二乘判别分析 Partial least squares-discriminant analysis | [ | |
松 Pine | 松甲虫虫害 Pine beetle infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
云杉 Spruce | 小蠹虫虫害 Silverfish infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ |
表2 病虫害遥感监测中典型的分类算法
Table 2 Typical classification algorithms in remote sensing monitoring of pests and diseases
平台 Platform | 植被类型 Vegetational type | 病虫害名称 Name of pest and disease | 分类模型 Disaggregated model | 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
近地尺度 Near-earth scale | 梨 Pear | 火疫病 Fire blight disease | Fisher判别分析 fisher discrimination analysis | [ |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | 模糊聚类 Fuzzy clustering methods | [ | |
油棕榈树 Oil plam | 真菌病害 Fungal disease | 偏最小二乘和线性判别分析 Partial least squares and linear discriminant analysis | [ | |
刺五加 Acanthopanax root | 黑斑病 Black spot disease | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
地块尺度 Block scale | 柑橘 Citrus | 溃疡病 Canker disease | 径向基函数 Radial basis function | [ |
香蕉 Banana | 枯萎病 Blight disease | 贝叶斯线性回归 Bayesian linear regression | [ | |
松 Pine | 松甲虫虫害 Pine beetle infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
苹果 Apple | 火疫病 Fire blight disease | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
柑橘 Citrus | 黄龙病和红蜘蛛虫害Yellow dragon disease and red spider infestation | 逻辑回归和支持向量机 Logistic regression and support vector machine | [ | |
油棕榈 Oil plam | 基腐病 Basal rot disease | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
杨 Poplar | 锈病 Rust disease | K近邻和Fisher判别 K nearest neighbor and Fisher discriminant | [ | |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
松 Pine | 松毛虫虫害 Pine caterpillar infestation | BP神经网络 BP neural network | [ | |
松 Pine | 松枯萎病 Pine wilt disease | 支持向量机 Support vector machine | [ | |
区域尺度 Regional scale | 槟榔 Areca catechu | 黄叶病 Chlorotic disorder | 随机森林 Random forest | [ |
红树林 Mangrove | 小斑螟虫害 Insect infestation of small spot borer | 多元逐步回归分析 Multiple stepwise regression analysis | [ | |
竹 Bamboo | 刚竹毒蛾虫害 Bamboo moth infestation | XGBoost | [ | |
桉 Eucalyptus | 切叶蚁虫害 Leaf cutter insect infestation | 偏最小二乘判别分析 Partial least squares-discriminant analysis | [ | |
松 Pine | 松甲虫虫害 Pine beetle infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ | |
云杉 Spruce | 小蠹虫虫害 Silverfish infestation | 随机森林 Random forest | [ |
病虫害 Plant disease and insect pest | 光谱指标 Spectral index | 公式 Equation | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
松枯萎病 Bursaphelenchus xylophilus nickle | 归一化植被指数NVDI | (RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+RR) | [ |
| 不同指数比Different index ratio CDIR | R760/R675 | ||
| 归一化绿红差异指数NGRDI | (RG-RR)/(RG+RR) | [ | |
| △NGRDI | NGRDI2-NGRDI1 | ||
火疫病 Fire blight disease | QF1 1450 | (R1600-R1450)/(R1600+R1450) | [ |
| QF2 1910 | (R1600-R1910)/(R1600+R1910) | ||
| 比值植被指数RVI | RNIR/RR | [ | |
| 花青素反射率指数ARI | (1/R550)-(1/R700) | ||
| 三角植被指数TVI | 0.5(120R750-R550)-200(R670-R550) | ||
黄叶病 Chlorotic disorder | 植物衰老反射指数PSRI | (R678-R550)/R750 | [ |
| 增强植被指数EVI | 2.5(RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+6R-7.5RB+1) | ||
小蠹虫虫害 Silverfish infestation | 增强湿度差值指数Enhanced humidity difference index (EWDI) | Wetness2-Wetness1 | [ |
| 温度植被干旱指数Temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) | (TS-TSMIN)/(TSMAX-TSMIN) | [ | |
| 归一化植被指数NVDI | (RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+RR) | [ |
表3 森林病虫害量化分析光谱指数
Table 3 Spectral index for quantitative analysis of forest pest and disease
病虫害 Plant disease and insect pest | 光谱指标 Spectral index | 公式 Equation | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
松枯萎病 Bursaphelenchus xylophilus nickle | 归一化植被指数NVDI | (RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+RR) | [ |
| 不同指数比Different index ratio CDIR | R760/R675 | ||
| 归一化绿红差异指数NGRDI | (RG-RR)/(RG+RR) | [ | |
| △NGRDI | NGRDI2-NGRDI1 | ||
火疫病 Fire blight disease | QF1 1450 | (R1600-R1450)/(R1600+R1450) | [ |
| QF2 1910 | (R1600-R1910)/(R1600+R1910) | ||
| 比值植被指数RVI | RNIR/RR | [ | |
| 花青素反射率指数ARI | (1/R550)-(1/R700) | ||
| 三角植被指数TVI | 0.5(120R750-R550)-200(R670-R550) | ||
黄叶病 Chlorotic disorder | 植物衰老反射指数PSRI | (R678-R550)/R750 | [ |
| 增强植被指数EVI | 2.5(RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+6R-7.5RB+1) | ||
小蠹虫虫害 Silverfish infestation | 增强湿度差值指数Enhanced humidity difference index (EWDI) | Wetness2-Wetness1 | [ |
| 温度植被干旱指数Temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) | (TS-TSMIN)/(TSMAX-TSMIN) | [ | |
| 归一化植被指数NVDI | (RNIR-RR)/(RNIR+RR) | [ |
| 1 | ZHANG J C, HUANG Y B, PU R L, et al.. Monitoring plant diseases and pests through remote sensing technology: a review [J/OL]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2019, 165:1835 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 2 | LUO Y Q, HUANG H G, ALAIN R, et al.. Early monitoring of forest wood-boring pests with remote sensing [J]. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 2023, 68:277-298. |
| 3 | THAKUR P, PRITTE K, TANUJA S, et al.. Trends in vision-based machine learning techniques for plant disease identification: a systematic review [J/OL]. Expert Syst. Appl., 2022, 208: 39252 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 4 | 郑蓓君.基于贝叶斯全卷积神经网络的胡杨林遥感提取[D].福州:福州大学,2021. |
| ZHENG B J. Remote sensing extraction of populus euphratica forest based on bayesian fully convolutional neural network [D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2021. | |
| 5 | 邢东兴,常庆瑞.基于光谱反射率的果树病虫害级别定量化测评——以红富士苹果树黄叶病害、红蜘蛛虫害为例[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(11):143-148. |
| XING D X, CHANG Q R. Quantitative evaluation of the degrees of diseases or insect pests based on spectral reflectance of canopies of fruit trees—yellow leaf disease and red mite insect pest of FuJi apple trees as samples [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2009, 37(11):143-148. | |
| 6 | BAGHERI N, HOSNA M, ASIAN A, et al.. Detection of fire blight disease in pear trees by hyperspectral data [J]. Eur. J. Remote Sens., 2018, 51(1):1-10. |
| 7 | SKONECZNY H, KUBIAK K, SPIRALSKI M, et al.. Fire blight disease detection for apple trees: hyperspectral analysis of healthy, infected and dry leaves [J]. Remote Sens., 2020, 12(13):2101 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 8 | JU Y W, PAN J, WANG X T, et al.. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus infection in Pinus massoniana from hyperspectral data [J]. Nematology, 2014, 16:1197-1207. |
| 9 | 黄晓君.落叶松针叶虫害地面高光谱识别及遥感监测方法研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| HUANG X J. Remote sensing identification and monitoring of larch needle pests based on ground hyperspectral data [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. | |
| 10 | ROLLIN G, LASSALLE G, ELGER A, et al.. Mapping plant species in a former industrial site using airborne hyperspectral and time series of sentinel-2 data sets [J]. Remote Sens., 2022, 14(15):368-377. |
| 11 | LELONG C, ROGER J, SIMON B, et al.. Evaluation of oil-palm fungal disease infestation with canopy hyperspectral reflectance data [J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(1):734-747. |
| 12 | 李军,杨秋珍,黄敬峰,等.杨扇舟蛾和杨小舟蛾危害对意大利214杨高光谱特征的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2007,29(6):148-155. |
| LI J, YANG Q Z, HUANG J F, et al.. Impact of Clostera anachoreta and Micromelalopha troglodyta insect-induced damage on the hyperspectral features of Populus×Canadesis cv.‘I-214’ [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2007, 29(6):148-155. | |
| 13 | 许章华,刘健,余坤勇,等.松毛虫危害马尾松光谱特征分析与等级检测[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2013,33(2):428-433. |
| XU Z H, LIU J, YU K Y, et al.. Spectral features analysis of Pinus massoniana with pest of Dendrolimus punctatus walker and levels detrctio [J]. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal., 2013, 33(2):428-433. | |
| 14 | 赵森,付芸,崔江南,等.高光谱的刺五加黑斑病的早期检测研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(6):1898-1904. |
| ZHAO S, FU Y, CUI J N, et al.. Application of hyperspectral imaging in the diagnosis of Acanthopanax senticosus black spot disease [J]. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal., 2021, 41(6):1898-1904. | |
| 15 | CHANG A J, YEOM J, JUNG J, et al.. Comparison of canopy shape and vegetation indices of citrus trees derived from UAV multispectral images for characterization of citrus greening disease [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2020, 12(24):4122 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 16 | ABDULRIDHA J, BATUMAN O, AMPATZIDIS Y. UAV-based remote sensing technique to detect citrus canker disease utilizing hyperspectral imaging and machine learning [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2019, 11(11):1373 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 17 | YE H, HUANG W, HUANG S, et al.. Recognition of banana Fusarium wilt based on UAV remote sensing [J]. Remote Sens., 2020, 13(3):136-144. |
| 18 | 马书英,郭增长,王双亭,等.板栗树红蜘蛛虫害无人机高光谱遥感监测研究[J].农业机械学报,2021,52(4):171-180. |
| MA S Y, GUO Z Z, WANG S T, et al.. Hyperspectral remote sensing monitoring of Chinese chestnut red mite insect pests in UAV [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2021, 52(4):171-180. | |
| 19 | XIAO D Q, PAN Y Q, FENG J Z, et al.. Remote sensing detection algorithm for apple fire blight based on UAV multispectral image [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2022, 19(9):268-278. |
| 20 | 马云强,李宇宸,刘梦盈,等.基于无人机多光谱影像的云南切梢小蠹危害监测反演研究[J].西南农业学报,2021,34(9):1878-1884. |
| MA Y Q, LI Z C, LIU M Y, et al.. Harm monitoring and inversion study on Tomicus yunnanensis based on multi-spectral image of unmanned aerial vehicle [J]. Southwest Chin. J. Agric. Sci., 2021, 34(9):1878-1884.. | |
| 21 | LIU Y, ZHAN Z, REN L, et al.. Hyperspectral evidence of early-stage pine shoot beetle attack in Yunnan pine [J/OL]. For. Ecol. Manage., 2021, 497:119505 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 22 | HUO L, PERSSON H, LINDBERG E. Early detection of forest stress from European spruce bark beetle attack, and a new vegetation index: normalized distance red & SWIR (NDRS) [J/OL]. Remote Sens. Environ., 2021, 255(7):112240 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 23 | SMIGAJ M, GAULTON R, SUÁREZ J, et al.. Canopy temperature from an unmanned aerial vehicle as an indicator of tree stress associated with red band needle blight severity [J]. For. Ecol. Manage., 2019, 433:699-708. |
| 24 | LIN Q, HUANG H, WANG J, et al.. Detection of pine shoot beetle (PSB) stress on pine forests at individual tree level using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and lidar [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2019, 11(21):2540 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 25 | 卢京,陈玖英,李伟,等.基于高光谱激光雷达的林木病虫害样本分类研究[J].激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(16):519-525. |
| LU J, CHEN J Y, LI W, et al.. Research on classification of pest and disease tree samples based on hyperspectral lidar [J] Laser Optoelectron. Prog., 2021, 58(16):519-525. | |
| 26 | CAO K K, TAN W X, LI X W, et al.. Monitoring broadleaf forest pest based on L-band SAR tomography [C]// Proceedings of 4th international conference on advances in energy resources and environment engineering (ICAESEE), 2019. |
| 27 | GUO J W, YU J, YE H C, et al.. Recognition of areca leaf yellow disease based on planetscope satellite imagery [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(1):14 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 28 | 曹庆先.基于遥感影像的红树林虫害监测模型[J].广西科学,2017, 24(2):144-149. |
| CAO Q X. Mangrove pests monitoring model based on the remote sensing image [J]. Guangxi Sci., 2017, 24(2):144-149. | |
| 29 | 许章华,周鑫,姚雄,等.基于Sentinel-2A MSI特征的毛竹林刚竹毒蛾危害检测[J].农业机械学报,2022,53(5):191-200. |
| XU Z H, ZHOU X, YAO X, et al.. Severity detecting of pantana phyllistachysae chao infestation of moso bamboo by selecting optimal sentinel-2A MSI features [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2022, 53(5):191-200. | |
| 30 | SILVA N D, SANTOS A D, SANTOS I, et al.. Mapping defoliation by leaf-cutting ants Atta species in Eucalyptus plantations using the sentinel-2 sensor [J]. Int. J. Remote Sens., 2020, 41(4):1542-1554. |
| 31 | OUMAR Z, ONISIMO M. Using WorldView-2 bands and indices to predict bronze bug (Thaumastocoris peregrinus) damage in plantation forests [J]. Int. J. Remote Sens., 2013, 34(6):2236-2249. |
| 32 | LI X H, LEE W, LI M Z, et al.. Feasibility study on Huanglongbing (Citrus greening) detection based on WorldView-2 satellite imagery [J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2015, 132:28-38. |
| 33 | IMMITZER M, CLEMENT A. Early detection of bark beetle infestation in norway spruce (Picea abies L.) using WorldView-2 data [J]. Photogramm Fernerkun., 2014(5):351-367. |
| 34 | 朱程浩,瞿帅,张晓丽.油松毛虫灾害遥感监测及其影响因子分析[J].遥感学报,2016, 20(4):653-664. |
| ZHU C H, QU S, ZHANG X L. Dendrolimus tabulaeformis disaster monitoring and analysis of its fluencing factors through remote sensing technology [J]. J. Remote Sens., 2016, 20(4):653-664. | |
| 35 | 马慧琴,黄文江,景元书.遥感与气象数据结合预测小麦灌浆期白粉病[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(9):165-172. |
| MA H Q, HUANG W J, JING Y S. Wheat powdery mildew forecasting in filling stage based on remote sensing and meteorological data [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(9):165-172. | |
| 36 | 亓兴兰,肖丰庆,刘健,等.基于SPOT-5影像的马尾松毛虫虫害遥感监测研究[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2019,39(4):59-65. |
| QI X L, XIAO F Q, LIU J, et al.. Study on monitoring Dendrolimus punctatus damage based on SPOT-5 remote sensing image [J]. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol., 2019, 39(4):59-65. | |
| 37 | 沈亲,邓槿,刘旭升,等.基于遥感温度植被干旱指数的小蠹虫害预警[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(9):167-174. |
| SHEN Q, DENG J, LIU X S, et al.. Prediction of bark beetles pest based on temperature vegetation dryness index [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2018, 34(9):167-174. | |
| 38 | 马望,房磊,方国飞,等.基于最大熵模型的神农架林区华山松大小蠹灾害遥感监测[J].生态学杂志,2016, 35(8):2122-2131. |
| MA W, FANG L, FANG G F, et al.. Mapping the infestation of Dendroctonus aramandi in Shennongjia forested region using Landsat and MaxEnt model [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2016, 35(8):2122-2131. | |
| 39 | MENG R, GAO R, ZHAO F, et al.. Landsat-based monitoring of southern pine beetle infestation severity and severity change in a temperate mixed forest [J]. Remote Sens. Environ., 2022, 269:112847 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 40 | ZHANG B, YE H, LU W, et al.. A spatiotemporal change detection method for monitoring pine wilt disease in a complex landscape using high-resolution remote sensing imagery [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2021, 13(11):2083 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 41 | 包云轩,李玉婷,王琳,等.基于多时相HJ卫星遥感影像的稻纵卷叶螟发生情况监测[J].中国农业气象,2016, 37(4):464-470. |
| BAO Y X, LI Y T, WANG L, et al.. Monitoring on occurrence of Canphalocrocis medinalis based on multi-temporal HJ satellites remote sensing image [J]. Chin. J. Agrometeorol., 2016, 37(4):464-470. | |
| 42 | SU J Y, LIU C J, HU X P, et al.. Spatio-temporal monitoring of wheat yellow rust using UAV multispectral imagery [J/OL]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2019, 167:105035 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 43 | XIAO D Q, PAN Y Q, FENG J Z, et al.. Remote sensing detection algorithm for apple fire blight based on UAV multispectral image [J/OL]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2022, 199: 106358 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 44 | 邓小玲,曾国亮,朱梓豪,等.基于无人机高光谱遥感的柑橘患病植株分类与特征波段提取[J].华南农业大学学报,2020,41(6):100-108. |
| DENG X L, ZENG G L, ZHU Z H, et al.. Classification and feature band extraction of diseased citrus plants based on UAV hyperspectral remote sensing [J]. J. South China Agric. Univ., 2020, 41(6):100-108. | |
| 45 | KURIHARA J, KOO V C, GUEY C W, et al.. Early detection of basal stem rot disease in oil palm tree using unmanned aerial vehicle-based hyperspectral imaging [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2022, 14(3):2101 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 46 | 丁锐.基于无人机光谱遥感的杨树锈病早期检测研究[D].南京:南京林业大学,2019. |
| DING R. Early detection of poplar rust based on UAV spectral remote sensing [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2019. | |
| 47 | 张凝,杨贵军,赵春江,等.作物病虫害高光谱遥感进展与展望[J].遥感学报,2021,25(1):403-422. |
| ZHANG N, YANG G J, ZHAO C J, et al.. Progress and prospect of hyperspectral remote sensing technology for crop diseases and pests [J]. J. Remote Sens., 2021, 25(1):403-422. | |
| 48 | 张军国,韩欢庆,胡春鹤,等.基于无人机多光谱图像的云南松虫害区域识别方法[J].农业机械学报,2018,49(5):249-255. |
| ZHANG J G, HAN H Q, HU C H, et al.. Identification method of Pinus yunnanensis pest area based on UAV multispectral image [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2018, 49(5):249-255. | |
| 49 | SYIFA M, PARK S J, LEE C W. Detection of the pine wilt disease tree candidates for drone remote sensing using artificial intelligence techniques [J]. Engineering, 2020, 6(8):919-926. |
| 50 | LONCAN L, ALMEIDA L B, BIOUCASDIAS J M, et al.. Hyperspectral pansharpening: a review [J]. IEEE Geosci. Rem. Sen., 2015, 3(3):27-46. |
| 51 | 王维枫.山杏常见叶部病虫害图像识别技术研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2008. |
| WANG W F. Study on image recognition technology of common leaf diseases and insect pests of Apricot [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2008. | |
| 52 | 李宗儒,何东健.基于手机拍摄图像分析的苹果病害识别技术研究[J].计算机工程与设计,2010, 31(13):3051-3055, 3095. |
| LI Z R, HE D J. Research on identify technologies of apple’s disease based on mobile photograph image analysis [J]. Comput. Eng. Des., 2010, 31(13):3051-3055, 3095. | |
| 53 | JIANG P, CHEN Y, LIU B, et al.. Real-time detection of apple leaf diseases using deep learning approach based on improved convolutional neural networks [J/OL]. IEEE Access., 2019,99. 2914929:1 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 54 | 吴建伟,黄杰,熊晓菲,等.基于AI的桃树病害智能识别方法研究与应用[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(5):111-118. |
| WU J W, HUANG J, XIONG X F, et al.. Research and application of peach disease intelligent recognition method based on AI [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(5):111-118. | |
| 55 | 黄平,吕庆闭,莫燕斌,等.基于多尺度特征融合的柑橘病虫害图像识别方法[J].无线电工程,2022,52(3):407-416. |
| HUANG P, LYU Q B, MO Y B, et al.. Image recognition method of citrus diseases and pests based on multi-scale feature fusion [J]. Radio Eng., 2022, 52(3):407-416. | |
| 56 | FAISAL M, LEU J S, TDARMAWAN J. Model selection of hybrid feature fusion for coffee leaf disease classification [J]. IEEE Access., 2023, 11: 62281-62291. |
| 57 | LU X Y, YANG R, ZHOU J, et al.. A hybrid model of ghost-convolution enlightened transformer for effective diagnosis of grape leaf disease and pest [J]. J. King. Saud. Univ-Com., 2022, 34(5):1755-1767. |
| 58 | 龙满生,欧阳春娟,刘欢,等.基于卷积神经网络与迁移学习的油茶病害图像识别[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(18):194-201. |
| LONG M S, OUYANG C J, LIU H, et al.. Image recognition of Camellia oleifera diseases based on convolutional neural network & transfer learning [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2018, 34(18):194-201. | |
| 59 | SINGH P, ABHISHEK V, ALEX J R. Disease and pest infection detection in coconut tree through deep learning techniques [J]. Comput. Electron Agric., 2021, 182: 264-271. |
| 60 | 万军杰,祁力钧,卢中奥,等.基于迁移学习的GoogLeNet果园病虫害识别与分级[J].中国农业大学学报,2021,26(11):209-221. |
| WAN J J, QI L J, LU Z A, et al.. Recognition and grading of diseases and pests in orchard by GoogLeNet based on transfer learning [J]. J. Chin. Agric. Univ., 2021, 26(11):209-221. | |
| 61 | 刘斌,贾润昌,朱先语,等.面向移动端的苹果叶部病虫害轻量级识别模型[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(6):130-139. |
| LIU B, JIA R C, ZHU X Y, et al.. Lightweight identification model of apple leaf diseases and pests based on mobile terminal [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2022, 38(6):130-139. | |
| 62 | CHAO X F, XIAO H, FENG J Z, et al.. Construction of apple leaf diseases identification networks based on xception fused by SE module [J/OL]. Appl. Sci., 2021, 11(10):4614 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 63 | ZHENG T F, YANG X T, LYU J W, et al.. An efficient mobile model for insect image classification in the field pest management [J]. Eng. Sci. Technol., 2023, 39:268-275. |
| 64 | YANG L, LI X M, BAI N, et al.. Transcriptomic analysis reveals that Rho GTPases regulate trap development and lifestyle transition of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora [J/OL]. Microbiol. Spectr., 2022, 10(1):21 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 65 | WANG H N, YANG L, PAN Y F, et al.. Pan trapping is an effective method to trap adults of the jujube gall midge, Dasineura jujubifolia (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) [J]. Environ. Entomol., 2023, 156(5):289-296. |
| 66 | WILSON A D. Diverse applications of electronic-nose technologies in agriculture and forestry [J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(2):2295-2348. |
| 67 | MORRIS C A, JOHNSON S A, WAAL J Y, et al.. A review of Trimen’s false tiger moth, Agoma trimenii (Lepidoptera: Agaristidae): seasonal biology, potential monitoring and control techniques [J]. South African J. Enol. Vitic., 2020, 41(2):128-132. |
| 68 | BIAN L, CAI X M, LUO Z X, et al.. Decreased capture of natural enemies of pests in light traps with light-emitting diode technology [J]. Ann. Appl. Biol., 2018, 173(3):251-260. |
| 69 | KURIHARA K, TOSHIAKI I, YUKIHISA S, et al.. Management of nuisance macromoths in expressways through academic-industrial collaboration: light trap designed on the basis of moths’ preferences for light attributes [J]. Zool. Sci., 2022, 39(4):307-319. |
| 70 | POHE S, M-JWINTERBOURN, HARDING JON S. Comparison of fluorescent lights with differing spectral properties on catches of adult aquatic and terrestrial insects [J]. Nz. Entomol., 2018, 41(1):1-11. |
| 71 | SUKOVATA L, ALEKSANDER D, PARRATT M, et al.. The importance of trap type, trap colour and capture liquid for catching Dendrolimus pini and their impact on by-catch of beneficial insects [J]. Agric. For. Entomol., 2020, 22(4):319-327. |
| 72 | FEZZA E, MROBERTS J, ABRUCE T J, et al.. Optimising vine weevil, Otiorhynchus sulcatus F. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), monitoring tool design [J]. Insects., 2022, 13(1):158-165. |
| 73 | BATISTA E S, AREDAK R, CBUSOLI A, et al.. Trapping for sirex woodwasp in brazilian pine plantations: lure, trap type and height of deployment [J]. J Insect Behav., 2018, 31(2):210-221. |
| 74 | RAJUS S, S-GBHAGAVAN, KHARVA H, et al.. Behavioral ecology of the coffee white stem borer: toward ecology-based pest management of India’s coffee plantations [J]. Front. Ecol. Evol., 2021, 9(2):369-378. |
| 75 | AKINCI H A, GENC C, AKINCI H. Susceptibility assessment and mapping of Ips typographus (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in oriental spruce forests in Artvin, Turkey [J]. J. Appl. Entomol., 2022, 146(9):1185-1199. |
| 76 | OLIVEIRA L, VIEIRA V, A-OSOARES, et al.. Abundance of Epiphyas postvittana (Walker, 1863) in forestry nurseries of Sao Miguel Island (Azores, Portugal) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) [J]. Shilap Rev. Lepidopt., 2022, 50(9):425-433. |
| 77 | NOETH K P, VERLEUR P M, BOUWER M C, et al.. Mass trapping of Coryphodema tristis (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) using a sex pheromone in Eucalyptus nitens compartments in Mpumalanga, South Africa [J]. South For., 2020, 82(3):271-279. |
| 78 | 孙仲享,宋圆圆,曾任森.植物挥发物介导的种内与种间关系研究进展[J].华南农业大学学报,2019,40(5):166-174. |
| SUN Z X, SONG Y Y, CENG R S. Advances in studies on intraspecific and interspecific relationships mediated by plant volatiles [J]. J. South Chin. Agric. Univ., 2019, 40(5):166-174. | |
| 79 | BOROWIK P, ADAMOWICZ L, TARAKOWSKI R, et al.. Application of a low-cost electronic nose for differentiation between pathogenic oomycetes Pythium intermedium and Phytophthora plurivora [J/OL]. Molecules, 2021, 26(17):5272 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 80 | TKACZYK M, SLUSARSKI S, SKRZECZ I. Use of an electronic nose for the detection of volatile organic compounds produced by plants pathogenic fungi [J]. Sylwan, 2019, 163(7):551-555. |
| 81 | BAIETTO M, POZZI L, WILSON A D, et al.. Evaluation of a portable MOS electronic nose to detect root rots in shade tree species [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2013, 96:117-125. |
| 82 | SAMANTHA M, BAYANSAL F, AHMADI A. Emerging methods of monitoring volatile organic compounds for detection of plant pests and disease [J/OL]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(4):239 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 83 | CUI S Q, LING P, ZHU H P, et al.. Plant pest detection using an Artificial nose system: a review [J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2):258-269. |
| 84 | 潘洁,廖振峰,张衡,等.基于高光谱数据与网络GIS应用的森林病虫害监测系统研究[J].世界林业研究,2015,28(3):47-52. |
| PAN J, LIAO Z F, ZHANG H, et al.. Hyperspectral data and WebGIS based monitoring system for forest pests and diseases [J]. World For. Res., 2015, 28(3):47-52. | |
| 85 | DONG Y Y, XU F, LIU L Y, et al.. Monitoring and forecasting for disease and pest in crop based on WebGIS system [C]// Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), 2019. |
| 86 | LI F, LIU Z, SHEN W, et al.. A remote sensing and airborne edge-computing based detection system for pine wilt disease [J/OL]. IEEE Access., 2021, 99. 3073929 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 87 | 赵小娟,叶云,冉耀虎.基于物联网的茶树病虫害监测预警系统设计与实现[J].中国农业信息,2019,31(6):107-115. |
| ZHAO X J, YE Y, RAN Y H. Design and implementation of tea tree pests and diseases monitoring and early warning system based on internet of things [J]. Chin. Agric. Inform., 2019, 31(6):107-115. | |
| 88 | 邓梦怡,俞龙,周波,等.茶园虫情远程监测装备的系统设计[J].现代农业装备,2021,42(5): 23-27. |
| DENG M Y, YU L, ZHOU B, et al.. System design of remote pest monitoring equipment [J]. Mod. Agric. Equip., 2021, 42(5):23-27. | |
| 89 | WELSH T, BENTALL D, CONNOR K, et al.. Automated surveillance of Lepidopteran pests with smart optoelectronic sensor traps [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(15):789-796. |
| 90 | 齐建东,蒋禧,赵燕东.基于无线多媒体传感器网络的森林病虫害监测系统[J].北京林业大学学报,2010,32(4):186-190. |
| QI J D, JIANG X, ZHAO Y D. A forest pest and disease monitoring system based on wireless multimedia sensor network [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2010, 32(4):186-190. | |
| 91 | XUE X, QIU Y, HU L, et al.. Cloud-based video monitoring system applied in control of diseases and pests in orchards [C]// Proceedings of 9th IFIP WG 5.14 International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture (CCTA), 2016:275-284. |
| 92 | HU F H, LI Z, YAN L P. CNN and Raspberry PI for fruit tree disease detection [C]// Proceedings of Conference on Intelligent Computing, Information and Control Systems (ICICCS), 2020:1-8. |
| 93 | 李震,洪添胜,文韬,等.基于物联网的果园实蝇监测系统的设计与实现[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2015,41(1):89-93. |
| LI Z, HONG T S, WEN T, et al.. Design and development of orchard fruit fly monitoring system based on internet of things [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2015, 41(1):89-93. | |
| 94 | RIGAKIS I I, VARIKOU K N, NIKOLAKAKIS A E, et al.. The E-funnel trap: automatic monitoring of Lepidoptera; a case study of tomato leaf miner [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2021, 185(4):367-377. |
| 95 | MDHAFFAR A, ZALILA B, MOALLA R, et al.. A smart trap for counting olive moths based on the internet of things and deep learning [C]// Proceedings of 19th IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), 2022. |
| 96 | MEHMET T, GOKOZAN H. Real-time monitoring of indoor air quality with internet of things-based E-nose [J/OL]. Appl. Sci., 2019, 9(16):3435 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 97 | LIU C C, CHU Z J, WENG S Z, et al.. Fusion of electronic nose and hyperspectral imaging for mutton freshness detection using input-modified convolution neural network [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2022, 385:132651 [2023-02-20]. . |
| [1] | 胡国玉, 董娅兰, 古丽巴哈尔·托乎提, 刘广, 周建平. 基于机器视觉的葡萄藤结构分割方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 105-111. |
| [2] | 母时风, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 赵德轩, 高素红, 高朋, 齐慧霞. 一种引起板栗内腐病的果生炭疽菌鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 122-128. |
| [3] | 蒋沛含, 杨晓楠, 杨晨旭, 张爱军. 基于偏最小二乘回归的谷子冠层氮素含量高光谱估测研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 91-101. |
| [4] | 卢登洋, 童盼盼, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 刘鸣哲, 夏怡蕾, 吴翠云. 库尔勒香梨大果芽变的鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [5] | 李锐风, 杨云福, 杨永发, 于永顺. 基于机器视觉的玫瑰花检测与特征提取[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 106-113. |
| [6] | 丁亚会, 陈诚, 乔晓军, 沈剑波, 林森, 张云鹤, 冯思思. 基于物联网的病虫害绿色防控系统研发与应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 77-86. |
| [7] | 张彦, 王来刚, 贺佳, 郭燕, 杨秀忠, 张红利, 刘婷. 基于多源遥感数据的茶叶种植面积时空变化研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(12): 107-114. |
| [8] | 刘佳浩, 高军伟. 基于机器视觉与BA-BP的苹果分级系统研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 117-125. |
| [9] | 唐天君, 陈洋, 胡军, 江浩田. 基于无人机影像数据的烟草精准识别方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 145-157. |
| [10] | 周世莹, 刘晏辰, 张洋, 杨雪松, 关伟军, 高扬. 大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养与生物学鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 96-105. |
| [11] | 刘朝阳, 王永强, 周聪玲, 强斯祺. 室外池塘养殖投饵系统智能控制方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 123-130. |
| [12] | 王鑫慈, 李军乔, 李晨芹, 田甜, 曲俊儒. 一株乳突赤壳属蕨麻致病菌的鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 87-95. |
| [13] | 许鑫, 孟昆, 蔡红英, 杨培龙, 蒋显仁. 乳酸菌在猪生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 19-26. |
| [14] | 杨小虎, 张曼玉, 杨海昌, 张凤华, 江宜霖, 易小兰. 基于组合模型的玛纳斯河流域农田土壤盐分反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 134-141. |
| [15] | 胡灵炆, 周忠发, 尹林江, 朱孟, 黄登红. 基于无人机RGB影像的苗期油菜识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 116-128. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号