




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (4): 184-194.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0029
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
高丽敏1( ), 顾泽辰2,3(
), 顾泽辰2,3( ), 贡雪菲2, 崔联明1, 郭东森1, 周影1, 王琳4, 魏启舜1(
), 贡雪菲2, 崔联明1, 郭东森1, 周影1, 王琳4, 魏启舜1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-11
接受日期:2024-03-09
出版日期:2024-04-15
发布日期:2024-04-23
通讯作者:
魏启舜
作者简介:高丽敏 E-mail: limingao1990@163.com
Limin GAO1( ), Zechen GU2,3(
), Zechen GU2,3( ), Xuefei GONG2, Lianming CUI1, Dongsen GUO1, Ying ZHOU1, Lin WANG4, Qishun WEI1(
), Xuefei GONG2, Lianming CUI1, Dongsen GUO1, Ying ZHOU1, Lin WANG4, Qishun WEI1( )
)
Received:2024-01-11
Accepted:2024-03-09
Online:2024-04-15
Published:2024-04-23
Contact:
Qishun WEI
摘要:
果园生草在改善果园环境、土壤生态、果树生理等方面具有重要作用。采用Meta分析方法,搜集2000—2022年669组数据,定量分析了果园生草对果实产量、果实品质、果园发病率、土壤理化性状及微生物多样性等的影响。结果表明,果园生草能显著提高果实产量(11.9%),但对处于低温区域(年均气温低于10 ℃)、土壤偏碱(pH>7)、有效磷含量较低(<5 mg·kg-1)或偏高(>40 mg·kg-1)及土壤速效钾含量较高(≥100 mg·kg-1)的果园无显著影响。草种类、土壤速效钾含量及果园类型是果园增产效应的关键影响因素,贡献率达到17.4%、9.8%、9.7%。果园生草提高了果实品质,显著降低了果园的发病率。果园生草显著提高了果园土壤的有机质、全氮、碱解氮、全磷、全钾、有效磷、速效钾、有效锌、有效铜、有效猛、有效镁含量。在果园0—20 cm土层,生草增加了土壤含水量、孔隙度,提升了土壤关键酶活性、微生物数量、碳氮量及群落多样性。结果表明,果园生草在改善果树-土壤系统生产性能中具有积极作用,是实现果园绿色可持续发展的有效措施。
中图分类号:
高丽敏, 顾泽辰, 贡雪菲, 崔联明, 郭东森, 周影, 王琳, 魏启舜. 果园生草对中国果树-土壤系统生产性能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 184-194.
Limin GAO, Zechen GU, Xuefei GONG, Lianming CUI, Dongsen GUO, Ying ZHOU, Lin WANG, Qishun WEI. Effects of Grass Growing on the Productivity of Orchard-Soil System in China: A Meta-Analysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 184-194.
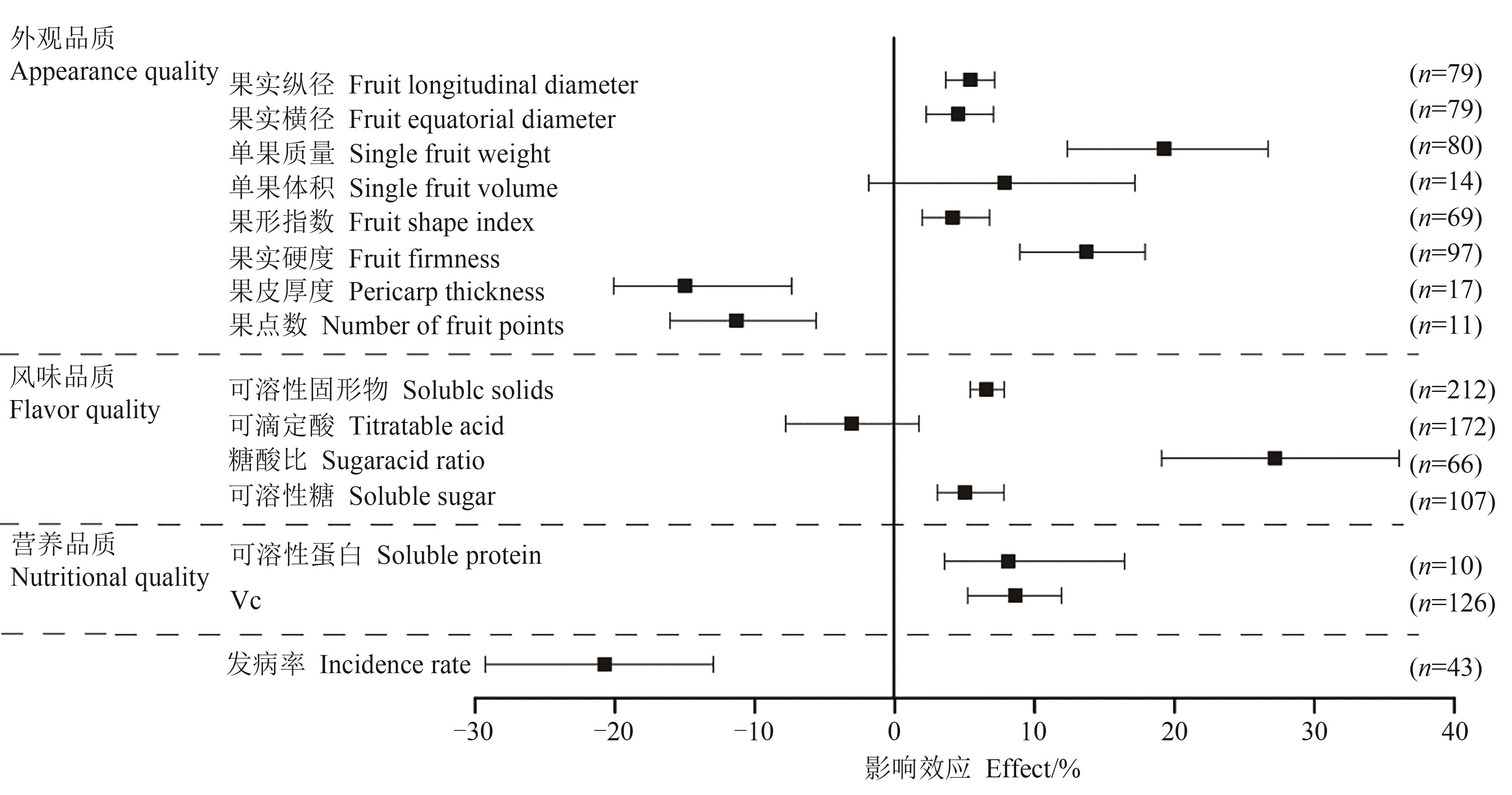
图3 果园生草对果实品质及发病率的影响效应注:n为观察样本量。
Fig. 3 Effect of orchard grass growing on fruit quality and incidence rateNote:n is numbers of experimental observation.
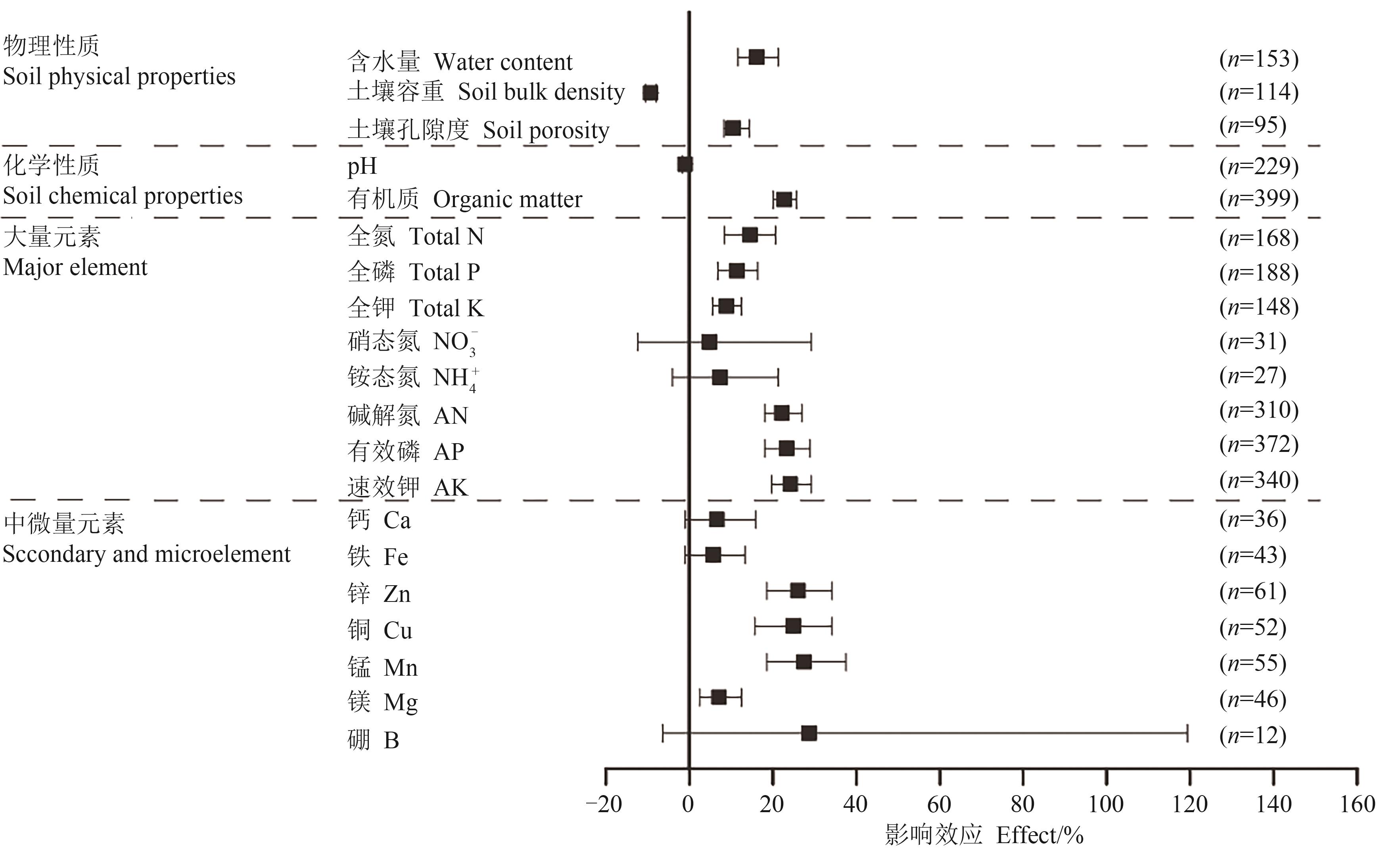
图4 果园生草对果园0—20 cm土壤理化性质的影响效应注:n为观察样本量。
Fig. 4 Effect of orchard grass growing on 0—20 cm soil physical and chemical propertiesNote:n is numbers of experimental observation.
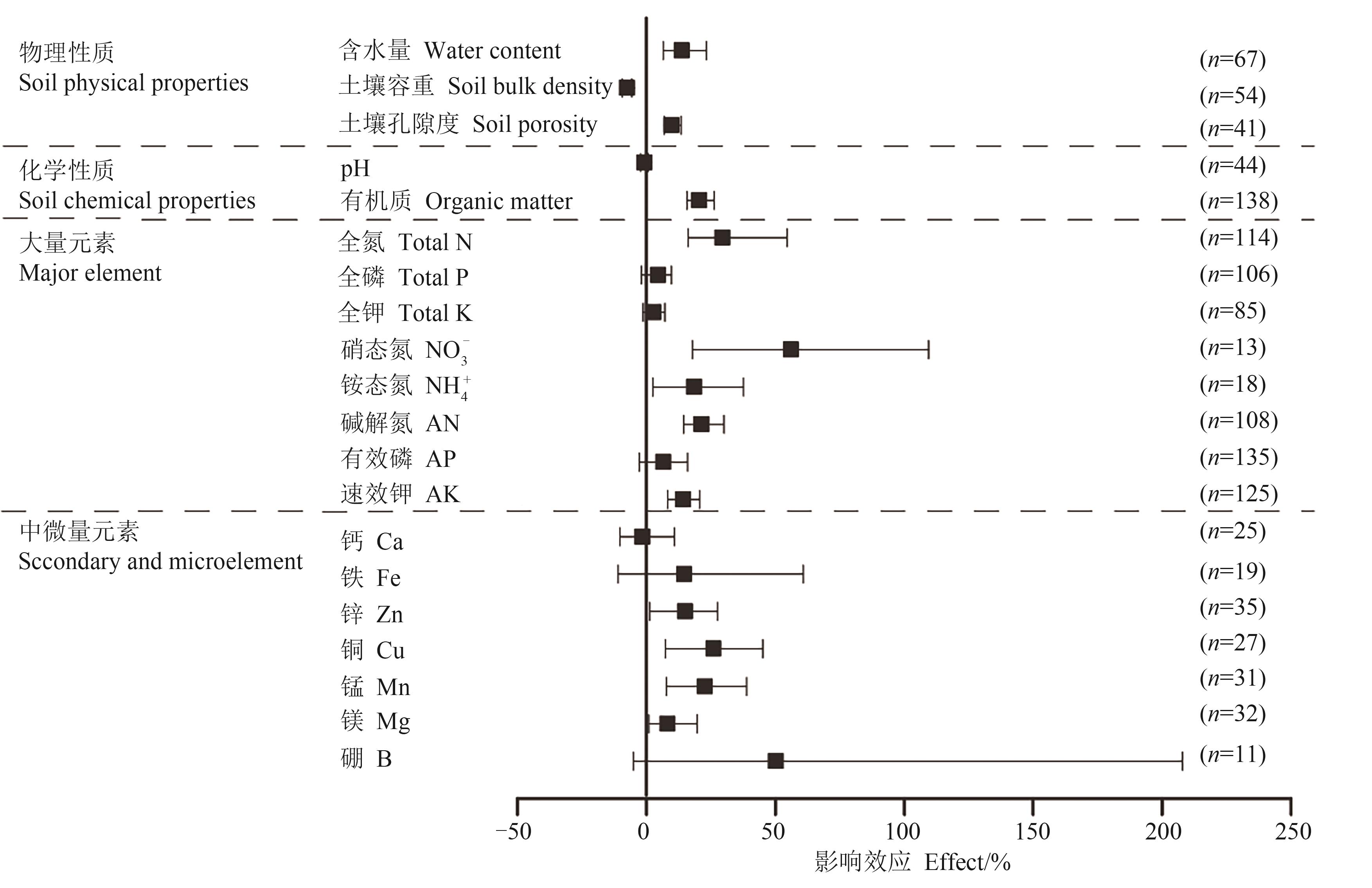
图5 果园生草对果园20—40 cm土壤理化性质的影响效应注:n为观察样本量。
Fig. 5 Effect of orchard grass growing on 20—40 cm soil physical and chemical propertiesNote:n is numbers of experimental observation.
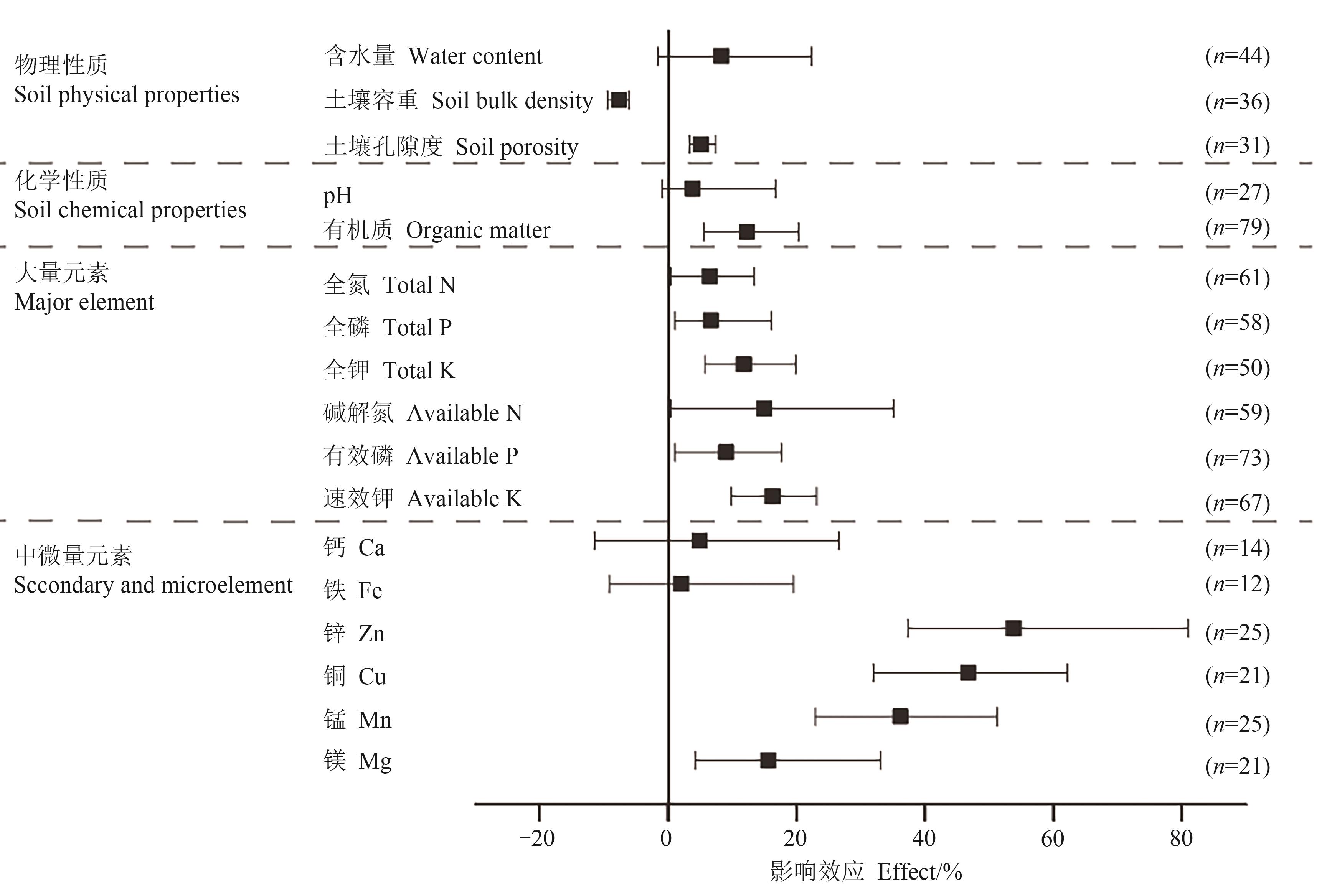
图6 果园生草对果树40—60 cm土壤理化性质的影响效应注:n为观察样本量。
Fig. 6 Effect of orchard grass growing on 40—60 cm soil physical and chemical propertiesNote:n is numbers of experimental observation.
| 1 | 付凌晖,刘爱华.中国统计年鉴[M].北京:中国统计出版社,2021:385-414. |
| FU L H, LIU A H. China Statistical Yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021: 385-414. | |
| 2 | 李燕青,车升国,李壮,等.土壤管理制度对果园土壤水热、微生物及养分的影响研究进展[J].中国果树,2018,5:66-72. |
| LI Y Q, CHE S G, LI Z, et al.. Research progress on the effects of soil management systems on soil water, heat, microorganisms and nutrients in orchards [J]. China Fruits, 2018, 5: 66-72. | |
| 3 | 周维杰,李钟淏,李婷玉,等.协同作物提质增效和土壤地力提升的最佳氮素有机替代比例探索——以攀枝花芒果为例[J].热带作物学报,2022,43(5):1032-1044. |
| ZHOU W J, LI Z H, LI T Y, et al.. Optimal nitrogen organic replacement ratio for synergistic crop quality and efficiency enhancement and soil fertility enhancement-taking panzhihua mango as an example [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2022, 43(5): 1032-1044. | |
| 4 | 罗自威,陶晶霞,侯凯捷,等.养分优化管理实现蜜柚高产高效和降低碳排放[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(4):688-700. |
| LUO Z W, TAO J X, HOU K J, et al.. Optimized nutrient management improves fruit yield and fertilizer use efficiency and reduces carbon emissions in pomelo production [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2022, 28(4): 688-700. | |
| 5 | 王树桐,王亚南,曹克强.近年我国重要苹果病害发生概况及研究进展[J].植物保护,2018,44(5):13-25. |
| WANG S T, WANG Y N, CAO K Q. Occurrence of and research progress in important apple diseases in China in recent years [J]. Plant Protection, 2018, 44(5): 13-25. | |
| 6 | 丁婷婷,段廷玉.果园绿肥对果树-土壤-微生物系统影响研究进展[J].果树学报,2021,38(12):2196-2208. |
| DING T T, DUAN T Y. Research progress on the influence of orchard green manure on fruit treesoil-microbe system [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2021, 38(12): 2196-2208. | |
| 7 | 吕德国,秦嗣军,杜国栋,等.果园生草的生理生态效应研究与应用[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2012,43(2):131-136. |
| LYU D G, QIN S J, DU G D, et al.. The research on eco-physiological effects and application of orchard sod culture [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2012, 43(2): 131-136. | |
| 8 | 焦润安,张舒涵,李毅,等.生草影响果树生长发育及果园环境的研究进展[J].果树学报,2017,34(12):1610-1623. |
| JIAO R A, ZHANG S H, LI Y, et al.. Research progress about the effect of sod-culture on the growth and development of fruit and orchard environment [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2017, 34(12): 1610-1623. | |
| 9 | 侯启昌.黄河故道地区梨园生草栽培的生态效应[J].果树学报,2009,26(5):739-743. |
| HOU Q C. Study on the ecological effects of inter-planting herbage in pear orchards in the old flooded area of Yellow River [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2009, 26(5): 739-743. | |
| 10 | 秦秦,宋科,孙丽娟,等.猕猴桃园行间生草对土壤养分的影响及有效性评价[J].果树学报,2020,37(1):68-76. |
| QIN Q, SONG K, SUN L J, et al.. Effect of inter-row sod system on the contents and availability of soil nutrients in a kiwifruit orchard [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2020, 37(1): 68-76. | |
| 11 | 肖力婷,杨慧林,黄文新,等.生草栽培对南丰蜜橘园土壤微生物群落结构与功能特征的影响[J].核农学报,2022,36(1):190~200. |
| XIAO L T, YANG H L, HUANG W X, et al.. Effects of grass cultivation on soil microbial community structure and functional characteristics in Nanfeng tangerine orchard [J]. J. Nuclear Agric. Sci., 2022, 36(1): 190-200. | |
| 12 | 段志龙,王晨光,宋云.陕北苹果园绿肥种植模式对土壤物理性质及果实品质和产量的影响[J].中国果树,2022,1:24-28. |
| DUAN Z L, WANG C G, SONG Y. Effects of different green manure cultivation models on soil physical properties, apple quality and yield in fruit regions of Northern Shaanxi [J]. China Fruits, 2022, 1: 24-28. | |
| 13 | 王燕,白岗栓.自然生草对土壤和树体矿质营养及苹果树生理病害的影响[J].草地学报,2021,29(10):2309-2322. |
| WANG Y, BAI G S. Effects of natural grass on mineral nutrition of soil and apple tree and physiological disease of apple tree [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(10): 2309-2322. | |
| 14 | 胡斌,张瀚曰,潘宏兵,等.间种绿肥及其还田对攀枝花地区芒果园土壤养分和芒果产量的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报,2021,27(2): 251-260. |
| HU B, ZHANG H Y, PAN H B, et al.. Effects of green manure planting and its return on soil nutrients and yield of mango orchards in Panzhihua, China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2021, 27(2): 251-260. | |
| 15 | 樊巍,孔令省,阴三军,等.干旱丘陵区苹果-紫花苜蓿复合系统对苹果生长,产量和品质的影响[J].河南农业大学学报,2004,38(4):423-426. |
| FAN W, KONG L S, YIN S J, et al.. Effects of apple-alfalfa system on growth, fruit yield and quality of apple tree in the drought hilly regions of Taihang mountain [J]. J. Henan Agric. Univ., 2004, 38(4): 423-426. | |
| 16 | REED-JONES N L, MARINE S C, EVERTS K L, et al.. Effects of cover crop species and season on population dynamics of Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua in soil [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2016, 82(6): 1767-1777. |
| 17 | 呼盼,高晓东,赵西宁,等.生草对果园生态系统服务功能的影响:全球数据整合分析研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2022,30(8):1238-1248. |
| HU P, GAO X D, ZHAO X N, et al.. Effects of grassing on orchard ecosystem services function: a global Meta analysis [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(8): 1238-1248. | |
| 18 | BAH A R, ZAHARAH A R, HUSSIN A. Phosphorus uptake from green manures and phosphate fertilizers applied in an acid tropical soil [J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal, 2006, 37(13-14): 2077-2093. |
| 19 | MO X H, LIU G X, ZHANG Z Y, et al.. Mechanisms underlying soybean response to phosphorus deficiency through integration of omics analysis [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(9): 4592 [2024-03-05]. . |
| 20 | Yu G H, Liu P C, Lu G L, et al.. Millet (Brassica napus L.) rotation model promoted the yield of millet by improving the fungal community structure in drylands in China [J]. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res., 2022, 20(3): 2565-2576. |
| 21 | WANG X D, MA H, GUAN C Y, et al.. Germplasm screening of green manure rapeseed through the effects of short-term decomposition on soil nutrients and microorganisms [J/OL]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(12): 1219 [2024-03-05]. . |
| 22 | HO G C, HYEON J S, MOHAMMAD S I B, et al.. Unexpected high suppression of ammonia volatilization loss by plastic film mulching in Korean maize cropping system [J/OL]. Agric. Ecosys. Environ., 2022, 335: 108022 [2024-03-05]. . |
| 23 | MA D K, YIN L N, JU W L, et al.. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China [J/OL]. Field Crops Res., 2021, 266: 108146 [2024-03-05]. . |
| 24 | Antoine C, Lionel A, Hélène T, et al.. Cover crop crucifer-legume mixtures provide effective nitrate catch crop and nitrogen green manure ecosystem services [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2018, 254: 50-59. |
| 25 | QIAN X, GU J, PAN H J, et al.. Effects of living mulches on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and bacterial community diversities of apple orchard soils [J]. Eur. J. Soil Biol., 2015, 70: 23-30. |
| 26 | ZHONG Z M, HUANG X S, FENG D Q, et al.. Long-term effects of legume mulching on soil chemical properties and bacterial community composition and structure [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2018, 268: 24-33. |
| 27 | 钱雅丽,梁志婷,曹铨,等.陇东旱作果园生草对土壤细菌群落组成的影响[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(10):3010-3017. |
| QIAN Y L, LIANG Z T, CAO Q, et al.. Effects of grass-planting on soil bacterial community composition of apple orchard in Longdong arid region [J]. Chin. J Ecol., 2018, 37(10): 3010-3017. | |
| 28 | 郭新送,张娟,巩有才,等.生草不同条件还田对桃园土壤微生物,酶活性及养分供应的影响[J].水土保持学报,2021,35(4):307-320. |
| GUO X S, ZHANG J, GONG Y C, et al.. Effect of grass return under different conditions on soil microorganism, enzyme activities and nutrients supply in peach orchard [J]. J. Soil Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 307-320. | |
| 29 | CURTRIGHT A J, TIEMANN L K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: a meta-analysis [J/OL]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2021, 319: 107489 [2024-03-05]. |
| 30 | 邓丽娟,郭晓睿,焦小强,等.果园生草对中国果园土壤肥力和生产力影响的整合分析[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(11):4021-4028. |
| DENG L J, GUO X R, JIAO X Q, et al.. Effects of grass growing on soil fertility and productivity of orchards in China: A meta-analysis [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2021, 32(11): 4021-4028. | |
| 31 | 舒然,尹显慧,李磊,等.伴生植物对根结线虫的调控及对猕猴桃品质和产量的影响[J].中国植保导刊,2021,7:63-70. |
| SHU R, YIN X H, LI L, et al.. Regulation of companion plants on Actinidiaheterodera glycines and their effects on the quality and yield of kiwifruit [J]. China Plant Protection, 2021, 7: 63-70. | |
| 32 | PAUDEL B R, CARPENTER-BOGGS L, HIGGINS S. Influence of brassicaceous soil amendments on potentially beneficial and pathogenic soil microorganisms and seedling growth in Douglasfir nurseries [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2016, 105: 91-100. |
| [1] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [2] | 陈芙蓉, 熊伟仡, 尹娇, 张小卓, 韩宇, 邓毅书. 微生物菌剂对叶菜废弃物堆肥过程的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 146-154. |
| [3] | 阿什日轨, 张荣萍, 周宁宁, 冯婷煜, 周林, 马鹏, 阿尔力色, 廖雪环, 张坷塬. 硅钙钾镁肥和密度对水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 155-163. |
| [4] | 赵刚, 王淑英, 李尚中, 张建军, 党翼, 王磊, 李兴茂, 程万莉, 周刚, 倪胜利, 樊廷录. 黄土旱塬区近40年降水对冬小麦耗水和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 164-173. |
| [5] | 周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187. |
| [6] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [7] | 表达特征分析, 姚亮伟, 沙玉柱, 郭新羽, 蒲小宁, 徐英, 王继卿, 李少斌, 郝志云, 刘秀. 不同海拔藏绵羊肉品质、营养成分及肉质相关基因[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 66-75. |
| [8] | 李忠义, 唐红琴, 董文斌, 韦彩会, 何铁光. 稻秸-紫云英联合还田对水稻光合特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 171-180. |
| [9] | 刘峰峰, 吴明, 周迎辉, 吴勇, 田嘉树, 许嘉阳, 许自成, 何结望. 生长素与钼配施对烤烟上部叶生理代谢及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 208-215. |
| [10] | 金艳, 宋全昊, 宋佳静, 陈亮, 赵立尚, 陈杰, 白冬, 朱统泉. 69份小麦种质资源的综合性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 33-45. |
| [11] | 王辉, 付虹雨, 岳云开, 崔国贤, 佘玮. 基于气候变量的苎麻产量SSA-BP预测模型[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 110-118. |
| [12] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [13] | 郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192. |
| [14] | 张海军, 张娟, 贾毅男, 王江龙, 冯丽. 不同架式对‘南太湖特早’葡萄果实香气成分及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 201-213. |
| [15] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号