




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 45-56.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0059
陈宜新1( ), 杨秀波1, 田士军2, 王聪1, 白志英1,3, 李存东1(
), 杨秀波1, 田士军2, 王聪1, 白志英1,3, 李存东1( ), 张科1(
), 张科1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-21
接受日期:2024-03-08
出版日期:2025-04-15
发布日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
李存东,张科
作者简介:陈宜新 E-mail:cyx06060701@163.com
基金资助:
Yixin CHEN1( ), Xiubo YANG1, Shijun TIAN2, Cong WANG1, Zhiying BAI1,3, Cundong LI1(
), Xiubo YANG1, Shijun TIAN2, Cong WANG1, Zhiying BAI1,3, Cundong LI1( ), Ke ZHANG1(
), Ke ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-01-21
Accepted:2024-03-08
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Cundong LI,Ke ZHANG
摘要:
褪黑素作为一种吲哚胺类化合物,对调节植物生长发育及抵御逆境胁迫有广泛作用。COMT(caffeic acid O-methyltransferase)是一种O-甲基转移酶,在苯丙烷代谢途径中发挥重要作用,是褪黑素合成的关键酶。陆地棉中共有57个GhCOMT同源基因,其中GhCOMT28和GhCOMT55与拟南芥AtCOMT同源性最高,以GhCOMT28为例,对其生物学功能进行了解析,发现GhCOMT28和GhCOMT55在棉花根和茎的表达量最高,定位于细胞质。GhCOMT28受干旱胁迫诱导,沉默GhCOMT28(TRV2:GhCOMT28)导致叶片中褪黑素水平降低,超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase,POD)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)等抗氧化酶活性降低,自由基积累增加,植株耐旱性下降。在拟南芥中超表达GhCOMT28(35S:GhCOMT28-GFP)则显著提高植株耐旱性。揭示了GhCOMT28对于棉花幼苗抵御干旱有重要调控作用,在耐旱品种改良中具有利用潜力。
中图分类号:
陈宜新, 杨秀波, 田士军, 王聪, 白志英, 李存东, 张科. 陆地棉GhCOMT28对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 45-56.
Yixin CHEN, Xiubo YANG, Shijun TIAN, Cong WANG, Zhiying BAI, Cundong LI, Ke ZHANG. Response of GhCOMT28 to Drought Stress in Gossypium hirsutum[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 45-56.
| 药品名称 Name | 药品用量 Dosage/(g·L-1) |
|---|---|
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 118.075 |
| KNO3 | 50.550 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 49.294 |
| KH2PO4 | 13.609 |
| NH4H2PO4 | 51.764 |
| H3BO3 | 2.860 |
| MnSO4·H2O | 1.180 |
| ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.220 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.080 |
| (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O | 0.020 |
表1 霍格兰德营养液配方
Table 1 Hoagland nutrient solution formula
| 药品名称 Name | 药品用量 Dosage/(g·L-1) |
|---|---|
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 118.075 |
| KNO3 | 50.550 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 49.294 |
| KH2PO4 | 13.609 |
| NH4H2PO4 | 51.764 |
| H3BO3 | 2.860 |
| MnSO4·H2O | 1.180 |
| ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.220 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.080 |
| (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O | 0.020 |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| GhCOMT28-CDS-F | CGGGATCCATGGGTTCAATCGGTGAAACTCA | 转基因载体构建 Construct transgenic vector |
| GhCOMT28-CDS-R | GCTCTAGACAAACACTTTTGAGAAACTCCATG | |
| V-GhCOMT28-F | GGAATTCCGCCTCATGTCATTGAGGATGCT | 基因沉默载体构建 Construct gene silence vector |
| V-GhCOMT28-R | GGAATTCCGTCTGGCAAAGCTTCATAGCAG | |
| q-GhCOMT28-F | TTGAGGATGCTCCTAGCTGTCC | qRT-PCR |
| q-GhCOMT28-R | AATCACTTTCCCGTTGTCTGG | |
| q-GhACTIN7-F | ATCCTCCGTCTTGACCTTG | |
| q-GhACTIN7-R | TGTCCGTCAGGCAACTCAT | |
| q-GhNCED1-F | GCACGACTTCGCCATCACT | |
| q-GhNCED1-R | GGTTCTTCCCAAGCATTCCA | |
| q-GhCBF5-F | ACCACTGCGGTTATGGCTACT | |
| q-GhCBF5-R | CAGTTGGCAACGCGACATTTC | |
| q-GhHSFA2-F | GGGGATTGTAACAACGTCAGC | |
| q-GhHSFA2-R | GCGGTTAATGCTCCAGGAAAC | |
| q-GhNHX1-F | CCAGCATGCTCTCAGACCAA | |
| q-GhNHX1-R | GGAACGAAGGGCACAAAACC |
表2 本研究中所用引物序列
Table 2 Primer sequences used in this study
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 用途 Usage |
|---|---|---|
| GhCOMT28-CDS-F | CGGGATCCATGGGTTCAATCGGTGAAACTCA | 转基因载体构建 Construct transgenic vector |
| GhCOMT28-CDS-R | GCTCTAGACAAACACTTTTGAGAAACTCCATG | |
| V-GhCOMT28-F | GGAATTCCGCCTCATGTCATTGAGGATGCT | 基因沉默载体构建 Construct gene silence vector |
| V-GhCOMT28-R | GGAATTCCGTCTGGCAAAGCTTCATAGCAG | |
| q-GhCOMT28-F | TTGAGGATGCTCCTAGCTGTCC | qRT-PCR |
| q-GhCOMT28-R | AATCACTTTCCCGTTGTCTGG | |
| q-GhACTIN7-F | ATCCTCCGTCTTGACCTTG | |
| q-GhACTIN7-R | TGTCCGTCAGGCAACTCAT | |
| q-GhNCED1-F | GCACGACTTCGCCATCACT | |
| q-GhNCED1-R | GGTTCTTCCCAAGCATTCCA | |
| q-GhCBF5-F | ACCACTGCGGTTATGGCTACT | |
| q-GhCBF5-R | CAGTTGGCAACGCGACATTTC | |
| q-GhHSFA2-F | GGGGATTGTAACAACGTCAGC | |
| q-GhHSFA2-R | GCGGTTAATGCTCCAGGAAAC | |
| q-GhNHX1-F | CCAGCATGCTCTCAGACCAA | |
| q-GhNHX1-R | GGAACGAAGGGCACAAAACC |

图4 不同环境胁迫下GhCOMT28的表达模式分析A:干旱(PEG)胁迫;B:冷胁迫;C:高温胁迫;D:盐胁迫。不同小写字母表示不同处理时间基因的表达量之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig.4 Analysis of expression patterns of GhCOMT28 under different environmental stressA: Drought(PEG) stress; B: Cold stress; C: Heat stress; D: Salt stress. Different lowercase letters indicate that the difference in gene expression between different treatment times is significant at the P<0.05 level.
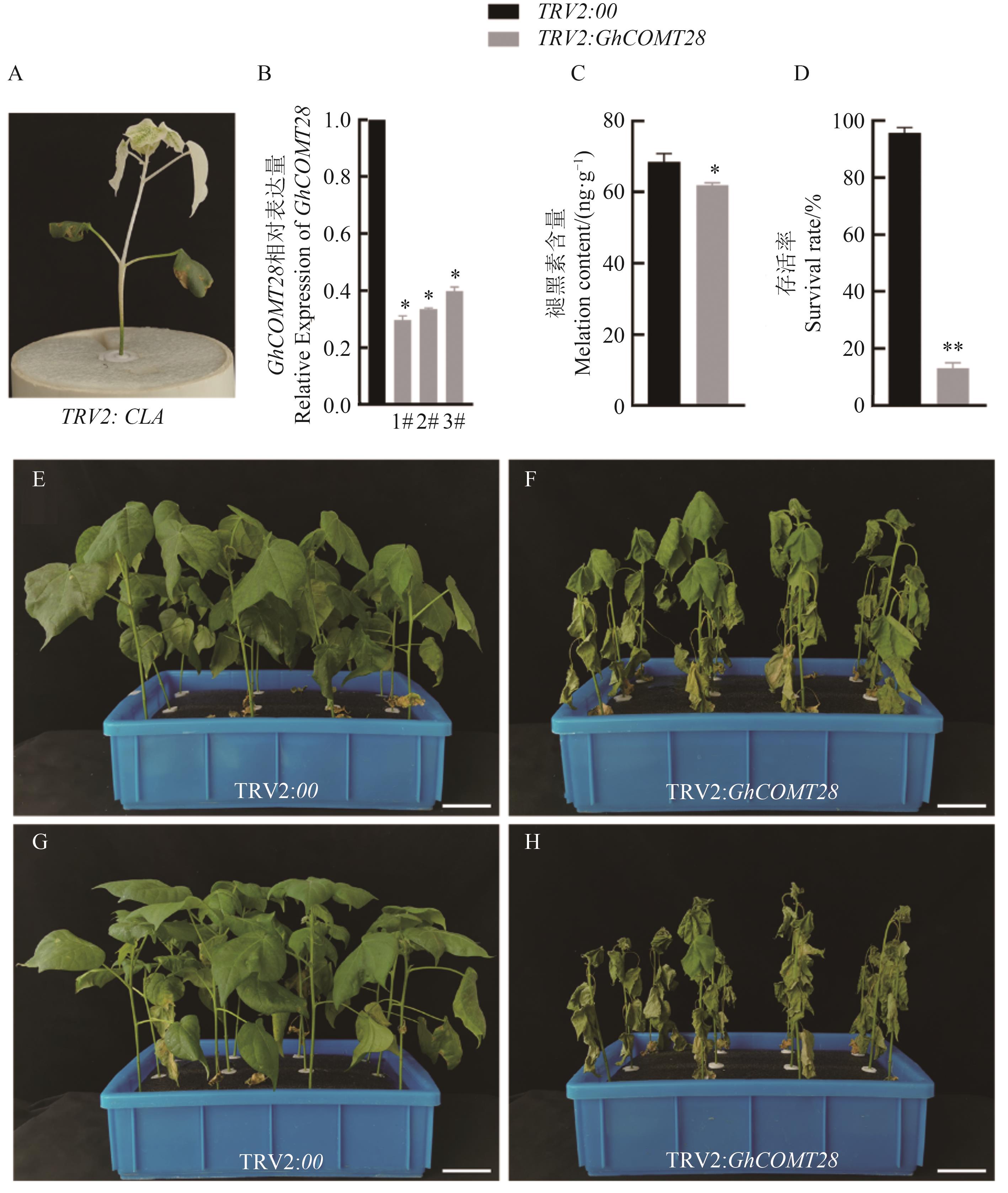
图5 TRV2:GhCOMT28的耐旱性分析A:TRV2:CLA白化表型;B:GhCOMT28沉默效率检测;C:褪黑素含量检测;D:干旱胁迫7 d后,TRV2:00和TRV2:GhCOMT28存活率统计;E~F:干旱胁迫14 d棉花幼苗的表型; G~H:复水7 d棉花幼苗的表型;*和**分别表示TRV2:GhCOMT28和TRV2:00之间的差异在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著;标尺为5 cm
Fig. 5 Drought tolerance analysis of TRV2:GhCOMT28A: TRV2: CLA albino phenotype; B: GhCOMT28 silencing efficiency detection; C: Melatonin content detection; D: Survival rate of TRV2: 00 and TRV2: GhCOMT28 after 7 d drought stress; E~F: Phenotype of cotton seedlings after 14 d of drought stress; G~H: Phenotype of cotton seedlings after 7 d of recovery water; * and ** indicate that the difference between the TRV2:GhCOMT28 and TRV2:00 is significant at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; the scale is 5 cm

图6 TRV2:GhCOMT28对叶片抗氧化体系的影响注:CK—正常生长;DS—6% PEG6000模拟干旱胁迫;不同小写字母表示不同样本之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig.6 TRV2:GhCOMT28 affects the antioxidant system of cotton.Note: CK—Normal growth; DS—6% PEG6000 simulated drought stress; different lowercase letters indicate that the difference between different samples is significant at the P<0.05 level.
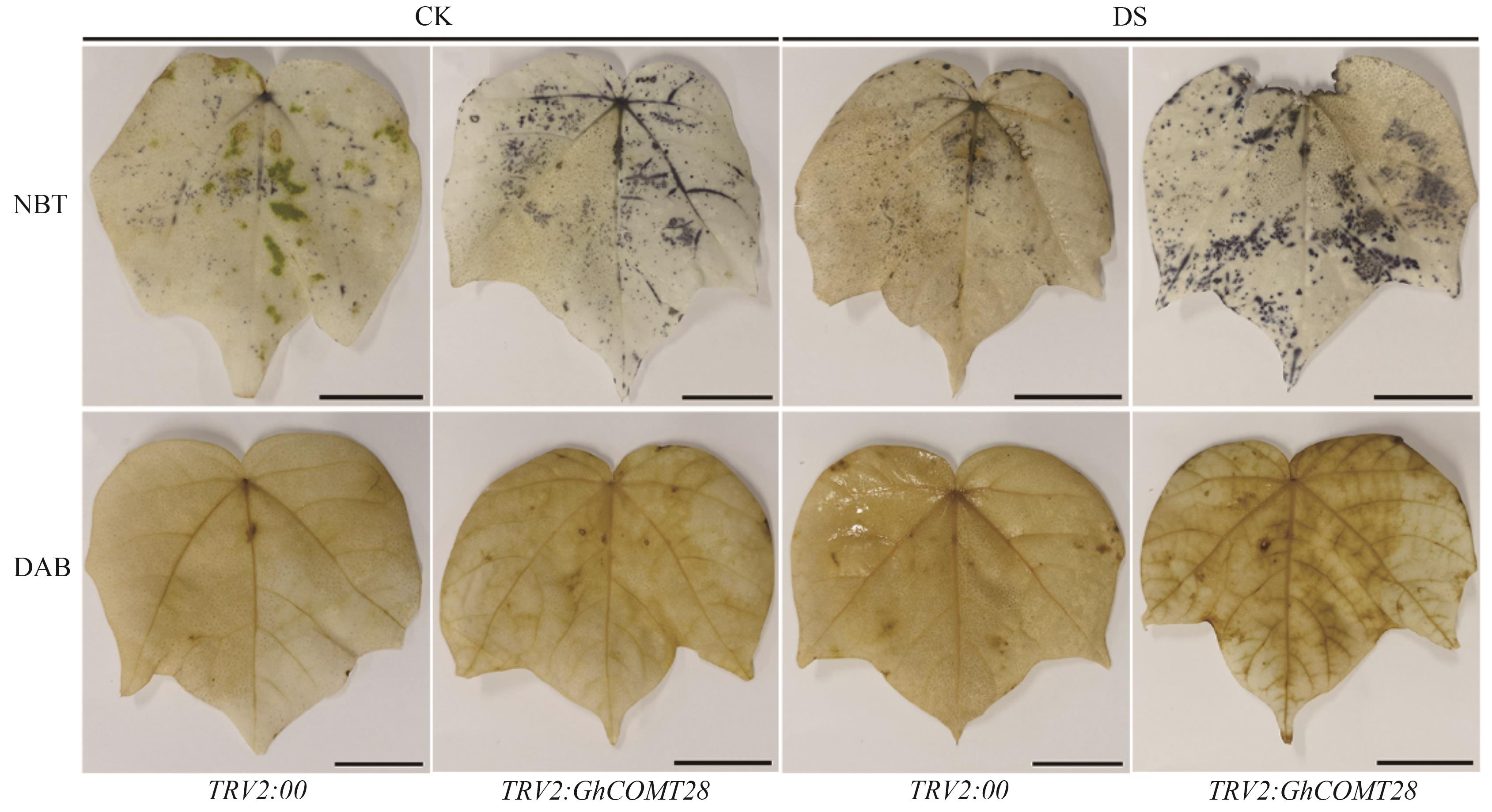
图7 棉花叶片的NBT和DAB染色注:CK—正常生长;DS—6% PEG6000模拟干旱胁迫。标尺为2 cm。
Fig. 7 NBT and DAB staining of cotton leavesNote: CK—Normal growth; DS—6% PEG6000 simulated drought stress. Bar is 2 cm.
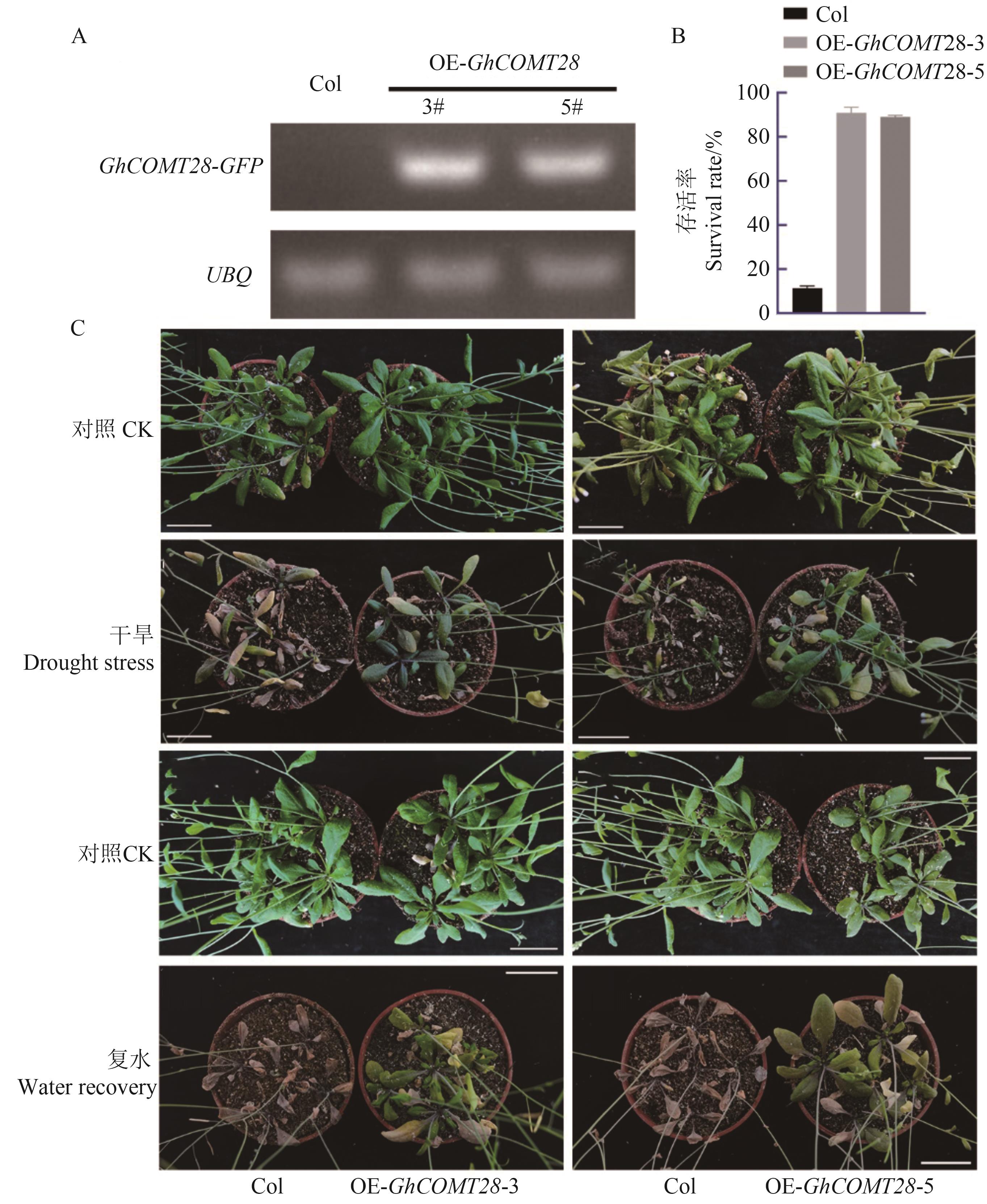
图8 超表达GhCOMT28增强拟南芥耐旱性A:转基因拟南芥中GhCOMT28-GFP转录水平检测; B:拟南芥植株的存活率统计; C:不同条件下拟南芥的耐旱表型;标尺为5 cm
Fig. 8 Overexpression of GhCOMT28 enhances drought resistance in Arabidopsis thalianaA: Detection of GhCOMT28-GFP transcription level in transgenic Arabidopsis; B: Statistics of survival rate of Arabidopsis plants under drought stress; C:Drought tolerance phenotype of transgenic Arabidopsis under different conditions; the scale is 5 cm
| 1 | 雷亚平, 魏晓文, 刘志红. 中国棉花产业发展现状及展望 [J]. 农业展望, 2014,10(9):43-47. |
| LEI Y P, WEI X W, LIU Z H. Present status and outlook of cotton industtry development in China [J].Agric. Outlook,2014,10(9):43-47. | |
| 2 | ARNAO M B, CANO A, HERNANDEZ-RUIZ J. Phytomelatonin:an unexpected molecule with amazing performances in plants [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2022,73(17): 5779-5800. |
| 3 | LEE H Y, BYEON Y, BACK K. Melatonin as a signal molecule triggering defense responses against pathogen attack in Arabidopsis and tobacco [J]. J. Pineal Res., 2014, 57(3): 262-268. |
| 4 | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 等. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| LIU D S, YAO L, XU W R,et al.. Research progress of melatonin in plant stress resistance [J].Chin. Bull. Bot., 2022, 57(1), 111-126. | |
| 5 | KE Q B, YE J, WANG B M, et al.. Melatonin mitigates salt stress in wheat seedlings by modulating polyamine metabolism [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2018, 9:914 [2024-04-08].. |
| 6 | LV Y, PAN J J, WANG H P, et al.. Melatonin inhibits seed germination by crosstalk with abscisic acid, gibberellin, and auxin in Arabidopsis [J/OL]. J. Pineal Res., 2021, 70(4): e12736[2024-04-08].. |
| 7 | LEE H Y, BACK K. Melatonin induction and its role in high light stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J/OL]. J. Pineal Res, 2018, 65(3): e12504 [2024-04-08]. . |
| 8 | 杨过, 聂圣松, 杭俊楠, 等. 褪黑素在植物生长发育和逆境响应中的研究进展[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2022, 41(6): 37-46. |
| YANG G, NIE S S, HANG J N, et al..Research progress of melatonin in plant growth and development and stress response [J]. J. Mountain Agric. Biol., 2022, 41(6), 37-46. | |
| 9 | SUN C L, LIU L J, WANG L X, et al.. Melatonin: a master regulator of plant development and stress responses [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2021, 63(1): 126-145. |
| 10 | LIU Y, WANG X Y, LV H M, et al.. Anabolism and signaling pathways of phytomelatonin [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2022, 73(17): 5801-5817. |
| 11 | BACK K. Melatonin metabolism, signaling and possible roles in plants [J]. Plant J., 2021, 105(2): 376-391. |
| 12 | BYEON Y, LEE H Y, LEE K, et al.. Caffeic acid O‐methyltransferase is involved in the synthesis of melatonin by methylating N‐acetylserotonin in Arabidopsis [J]. J. Pineal Res., 2014,57(2): 219-227. |
| 13 | BYEON Y, G-HCHOI, LEE H Y, et al.. Melatonin biosynthesis requires N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase activity of caffeic acid O-methyltransferase in rice [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2015, 66(21): 6917-6925. |
| 14 | YAO Z P, ZHANG X, LIANG Y C, et al.. NtCOMT1 responsible for phytomelatonin biosynthesis confers drought tolerance in Nicotiana tabacum [J/OL]. Phytochem., 2022, 202:113306 [2024-04-08].. |
| 15 | LIU D D, SUN X S, LIU L, et al.. Overexpression of the melatonin synthesis-related gene SlCOMT1 improves the resistance of tomato to salt stress [J/OL].Molecules, 2019, 24(8):1514 [2024-04-08].. |
| 16 | YANG W J, DU Y T, ZHOU Y B, et al.. Overexpression of TaCOMT improves melatonin production and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20(3):652 [2024-04-08].. |
| 17 | HUANGFU L X, CHEN R J, LU Y, et al.. OsCOMT, encoding a caffeic acid O-methyltransferase in melatonin biosynthesis, increases rice grain yield through dual regulation of leaf senescence and vascular development [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2022, 20(6): 1122-1139. |
| 18 | TAN K X, ZHENG J Z, LIU C, et al.. Heterologous expression of the melatonin-related gene HIOMT improves salt tolerance in Malus domestica [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(22):12425[2024-04-08]. . |
| 19 | LEE H Y, BYEON Y, LEE K, et al.. Cloning of Arabidopsis serotonin N-acetyltransferase and its role with caffeic acid O-methyltransferase in the biosynthesis of melatonin in vitro despite their different subcellular localizations [J]. J. Pineal Res., 2014, 57(4): 418-426. |
| 20 | WU C C, ZUO D Y, XIAO S P, et al.. Genome-wide identification and characterization of GhCOMT gene family during fiber development and verticillium wilt resistance in cotton [J/OL]. Plants, 2021, 10(12):2756 [2024-04-08]. . |
| 21 | GE C W, WANG L, YANG Y F, et al.. Genome-wide association study identifies variants of GhSAD1 conferring cold tolerance in cotton [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2022, 73(7): 2222-2237. |
| 22 | GUO Y P, CHEN Q, QU Y Y, et al.. Development and identification of molecular markers of GhHSP70-26 related to heat tolerance in cotton [J/OL]. Gene, 2023, 874:147486 [2024-04-08]. . |
| 23 | 穆春, 周琳, 李茂营, 等. 水培条件下病毒诱导棉花基因沉默体系的建立及优化[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(6): 844-849. |
| MU C, ZHOU L, LI M Y,et al.. Establishment and optimisation of virus-induced gene silencing in system hydroponic cotton [J].Acta Agron. Sin., 2016, 42(6), 844-849. | |
| 24 | LIU R, SHEN Y, WANG M, et al.. GhMYB102 promotes drought resistance by regulating drought-responsive genes and ABA biosynthesis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) [J/OL]. Plant Sci., 2023,329:111608 [2024-04-08]. . |
| 25 | JIANG B C, SHI Y T, PENG Y, et al.. Cold-induced CBF-PIF3 interaction enhances freezing tolerance by stabilizing the phyB thermosensor in Arabidopsis [J]. Mol. Plant, 2020,13(6): 894-906. |
| 26 | WANG N, QIAO W Q, LIU X H, et al.. Relative contribution of Na+/K+ homeostasis, photochemical efficiency and antioxidant defense system to differential salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2017,119:121-131. |
| 27 | ZHANG Y X, FAN Y P, RUI C, et al.. Melatonin improves cotton salt tolerance by regulating ROS scavenging system and Ca2+ signal transduction [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2021,12:693690 [2024-04-08]. . |
| 28 | YU Y, LV Y, SHI Y, et al.. The role of phyto-melatonin and related metabolites in response to stress [J/OL]. Molecules, 2018, 23(8):1887 [2024-04-08].. |
| 29 | LAM L P Y, LUI A C W, BARTLEY L E, et al.. Multifunctional 5-hydroxyconiferaldehyde O-methyltransferase (CAldOMTs) in plant metabolism [J]. J. Exp. Bot.,2024,75(6):1671-1695. |
| 30 | LIU Q Q, LUO L, ZHENG L Q.Lignins:biosynthesis and biological functions in plants [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2018,19(2):335[2024-04-08].. |
| 31 | KANWAR M K, YU J Q, ZHOU J. Phytomelatonin: recent advances and future prospects [J/OL]. J. Pineal. Res.,2018,65(4):e12526 [2024-04-08]. . |
| [1] | 秦岭, 王艳珂, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张梦媛, 管延安. ABA缓解谷子幼苗干旱胁迫生理特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 36-44. |
| [2] | 彭梓程, 杜洪力, 王铭, 张凤华, 杨海昌. 丛枝菌根真菌调控盐碱胁迫下棉花生长及离子平衡的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 33-41. |
| [3] | 王宁宁, 罗雪梅, 陈明媛, 郭睿, 刘建国. 外源褪黑素对盐旱复合胁迫下油莎豆种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 51-61. |
| [4] | 薛振宇, 张康康, 张元元, 闫强强, 姚立蓉, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 司二静, 李葆春, 马小乐, 王化俊, 汪军成. 优质抗旱小麦种质的筛选及功能基因检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 35-49. |
| [5] | 翁慧婷, 刘海洋, 郭惠明, 程红梅, 李君, 张超, 苏晓峰. 棉花抗黄萎病相关基因GhERF020功能的初步分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 112-121. |
| [6] | 李紫琴, 王家强, 李贞, 邹德秋, 张小功, 罗霄玉, 柳维扬. 基于光谱指数的棉花叶片叶绿素密度估算研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 103-111. |
| [7] | 庞博, 李生梅, 李彦霖, 杨涛, 梁维维, 张茹, 黄雅婕, 任丹, 崔进鑫, 李静, 马晶晶, 高文伟. 192份陆地棉杂交种的遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 34-50. |
| [8] | 桂意云, 李海碧, 梁强, 杨荣仲, 韦金菊, 韦德斌, 李文教, 刘昔辉, 周会. 基于人为控水和自然水分胁迫下的甘蔗茎节生长变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 25-36. |
| [9] | 鲍新跃, 陈红敏, 王伟伟, 唐益苗, 房兆峰, 马锦绣, 汪德州, 左静红, 姚占军. 小麦TaCOBL-5基因克隆及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 11-21. |
| [10] | 秦宇坤, 陈俊英, 张丽娟. 赣北棉区棉花干物质积累特征和产量对减氮措施的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 191-199. |
| [11] | 魏茜雅, 林欣琪, 梁腊梅, 秦中维, 李映志. 褪黑素引发对干旱胁迫下辣椒种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 46-57. |
| [12] | 李江博, 高文举, 运晓东, 赵杰银, 耿世伟, 韩春斌, 陈全家, 陈琴. 不同水分胁迫处理对陆地棉核心种质资源的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 26-39. |
| [13] | 李丽花, 孙正文, 柯会锋, 谷淇深, 吴立强, 张艳, 张桂寅, 王省芬. 陆地棉纤维强度KASP-SNP标记的开发及效应评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 46-55. |
| [14] | 翟梦华, 孙明辉, 李雪瑞, 徐新龙, 高海洲, 张巨松. 不同株行距配置下缩节胺对棉花株型塑造的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(12): 145-156. |
| [15] | 程珍, 牛建龙, 马玉婷, 柳维扬, 蒋学玮, 梁雪齐, 董红强. 1990—2020年南疆阿拉尔垦区棉花物候期的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 206-214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号