




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 11-21.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0172
鲍新跃1,2( ), 陈红敏3(
), 陈红敏3( ), 王伟伟2, 唐益苗2, 房兆峰2, 马锦绣2, 汪德州2(
), 王伟伟2, 唐益苗2, 房兆峰2, 马锦绣2, 汪德州2( ), 左静红2(
), 左静红2( ), 姚占军1(
), 姚占军1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-07
接受日期:2024-03-26
出版日期:2024-06-15
发布日期:2024-06-12
通讯作者:
汪德州,左静红,姚占军
作者简介:鲍新跃E-mail:1772145342@qq.com基金资助:
Xinyue BAO1,2( ), Hongmin CHEN3(
), Hongmin CHEN3( ), Weiwei WANG2, Yimiao TANG2, Zhaofeng FANG2, Jinxiu MA2, Dezhou WANG2(
), Weiwei WANG2, Yimiao TANG2, Zhaofeng FANG2, Jinxiu MA2, Dezhou WANG2( ), Jinghong ZUO2(
), Jinghong ZUO2( ), Zhanjun YAO1(
), Zhanjun YAO1( )
)
Received:2024-03-07
Accepted:2024-03-26
Online:2024-06-15
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
Dezhou WANG,Jinghong ZUO,Zhanjun YAO
摘要:
小麦产量关系我国粮食安全,干旱、低温、盐害和高温等非生物胁迫严重制约小麦产量增长。前期转录组分析发现小麦TaCOBL-5D在多种非生物胁迫下差异表达。克隆并获取TaCOBL-5D及其同源基因TaCOBL-5A、TaCOBL-5B,并对其生物信息学特性及表达模式进行了分析。结果显示,TaCOBL-5与其他物种的COBL基因在基因结构、蛋白三级结构、保守结构域以及启动子调控元件方面表现出明显的保守性。TaCOBL-5在根部表达量最高,并对各种非生物胁迫响应不同,尤其是在干旱胁迫下调控显著,表明其在干旱胁迫中的重要性,同时对低温、高温和盐胁迫也有不同响应。此外,TaCOBL-5D基因在不同干旱抗性及高温抗性材料中表达量差异显著,进一步暗示其在逆境胁迫中具有重要作用。这些研究结果有助于理解COBL基因在小麦中的功能,同时为小麦抗逆育种提供科学支持。
中图分类号:
鲍新跃, 陈红敏, 王伟伟, 唐益苗, 房兆峰, 马锦绣, 汪德州, 左静红, 姚占军. 小麦TaCOBL-5基因克隆及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 11-21.
Xinyue BAO, Hongmin CHEN, Weiwei WANG, Yimiao TANG, Zhaofeng FANG, Jinxiu MA, Dezhou WANG, Jinghong ZUO, Zhanjun YAO. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Wheat TaCOBL-5 Genes[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 11-21.
引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (3’-5’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (3’-5’) |
|---|---|---|
| TaCOBL-5A | GCGGCACCCGTGTCTTCTAT | CGTCTCGTCTCGTCGCAGTA |
| TaCOBL-5B | GCGGCACCCATGTCTTCTAT | CGTCTCGTCTCGTCGCAGTA |
| TaCOBL-5D | ACGGCACCCGCGTCTTCTAT | TCTCGTCGCTGTAAAAACTG |
| qTaCOBL-5A | CGTTGGATCTCTCTTGCAGC | TGGGATGGTCATGGGCAAAG |
| qTaCOBL-5B | GATTACGTGCAGGTTACATTCC | TCTCAAGGCTCCAGGTCAGG |
| qTaCOBL-5D | CAGCGAATCATAAGCCTCTG | GAGTAGCGGGGCAGGAAATG |
| TaActin | GGAATCCATGAGACCACCTAC | GACCCAGACAACTCGCAAC |
表1 基因克隆和荧光定量的引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in this study for gene cloning and qPCR
引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (3’-5’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (3’-5’) |
|---|---|---|
| TaCOBL-5A | GCGGCACCCGTGTCTTCTAT | CGTCTCGTCTCGTCGCAGTA |
| TaCOBL-5B | GCGGCACCCATGTCTTCTAT | CGTCTCGTCTCGTCGCAGTA |
| TaCOBL-5D | ACGGCACCCGCGTCTTCTAT | TCTCGTCGCTGTAAAAACTG |
| qTaCOBL-5A | CGTTGGATCTCTCTTGCAGC | TGGGATGGTCATGGGCAAAG |
| qTaCOBL-5B | GATTACGTGCAGGTTACATTCC | TCTCAAGGCTCCAGGTCAGG |
| qTaCOBL-5D | CAGCGAATCATAAGCCTCTG | GAGTAGCGGGGCAGGAAATG |
| TaActin | GGAATCCATGAGACCACCTAC | GACCCAGACAACTCGCAAC |
基因 Gene | 基因号 Gene ID number | 物理位置 Physical position/bp | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 蛋白长度 Protein length/aa | 预测定位 Predicted location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaCOBL-5A | TraesCS5A02G392000 | 588 375 577~588 379 139 | 50 867.2 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |
| TaCOBL-5B | TraesCS5B02G396900 | 574 675 118~574 678 654 | 50 841.18 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |
| TaCOBL-5D | TraesCS5D02G401900 | 467 600 940~467 604 428 | 50 823.15 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |
表2 TaCOBL-5基因信息及其编码蛋白的理化性质分析
Table. 2 TaCOBL-5 gene information and physicochemical properties analysis
基因 Gene | 基因号 Gene ID number | 物理位置 Physical position/bp | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 蛋白长度 Protein length/aa | 预测定位 Predicted location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaCOBL-5A | TraesCS5A02G392000 | 588 375 577~588 379 139 | 50 867.2 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |
| TaCOBL-5B | TraesCS5B02G396900 | 574 675 118~574 678 654 | 50 841.18 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |
| TaCOBL-5D | TraesCS5D02G401900 | 467 600 940~467 604 428 | 50 823.15 | 8.98 | 457 | 细胞膜Cell membrane |

图1 TaCOBL-5基因结构、保守基序及启动子顺式作用元件分析A:基因结构;B:保守序列;C:启动子顺式作用元件
Fig. 1 Analysis of gene structure, conserved motif and cis-acting regulatory elements of TaCOBL-5A: Gene structure; B: Conserved motif; C: Cis-acting regulatory elements

图3 COBRA结构域及三级结构预测A: COBRA结构域;B:COBL蛋白三级结构
Fig. 3 Analysis of conserved COBRA domain and the tertiary structure of COBL proteinsA: COBRA domain; B: Tertiary structure of COBL protein
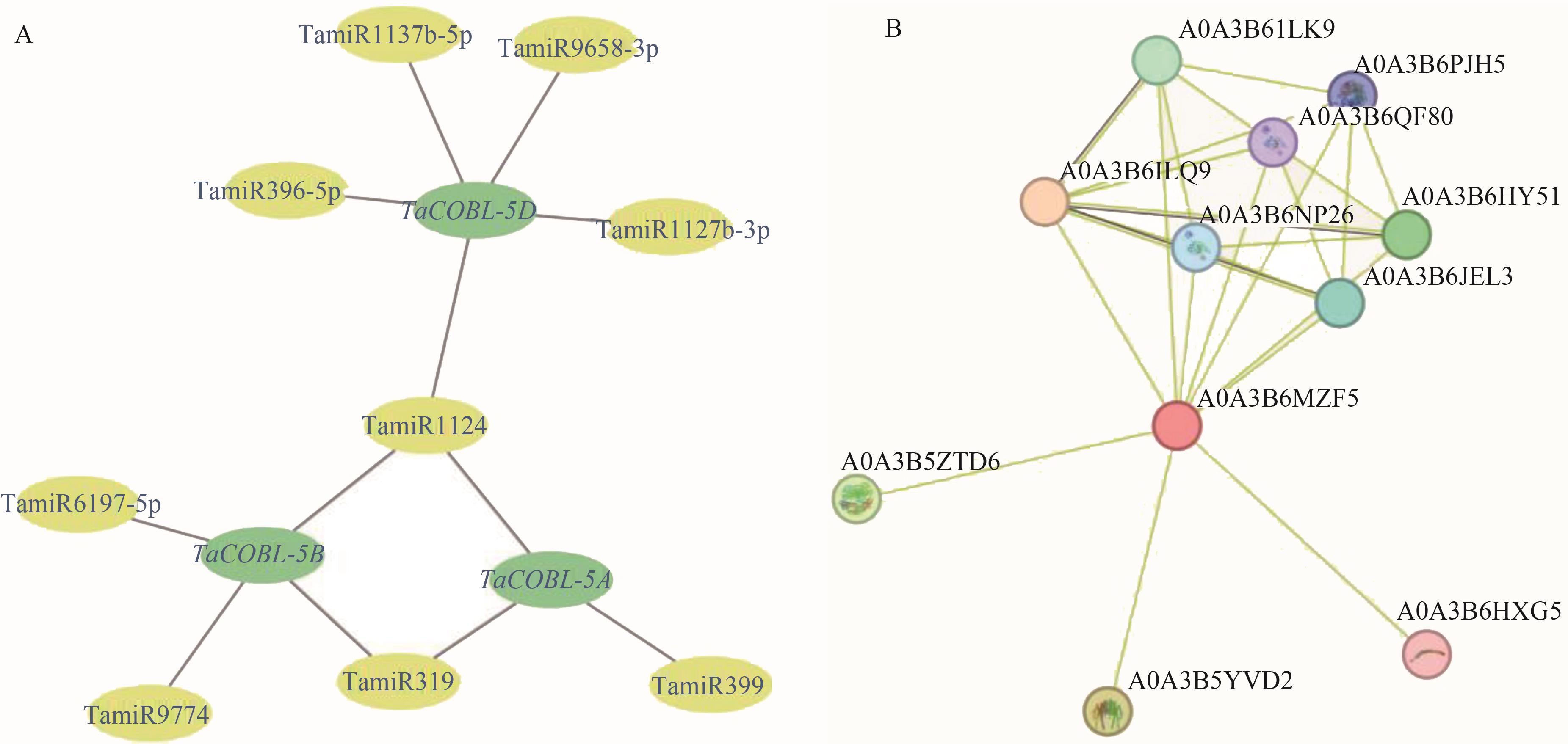
图5 小麦miRNA调控网络预测及互作蛋白预测A: miRNA调控网络;B:蛋白互作网络
Fig. 5 Prediction putative networks of wheat miRNAs and the interacting proteinsA: Putative network of wheat miRNAs; B: Network of interacting proteins
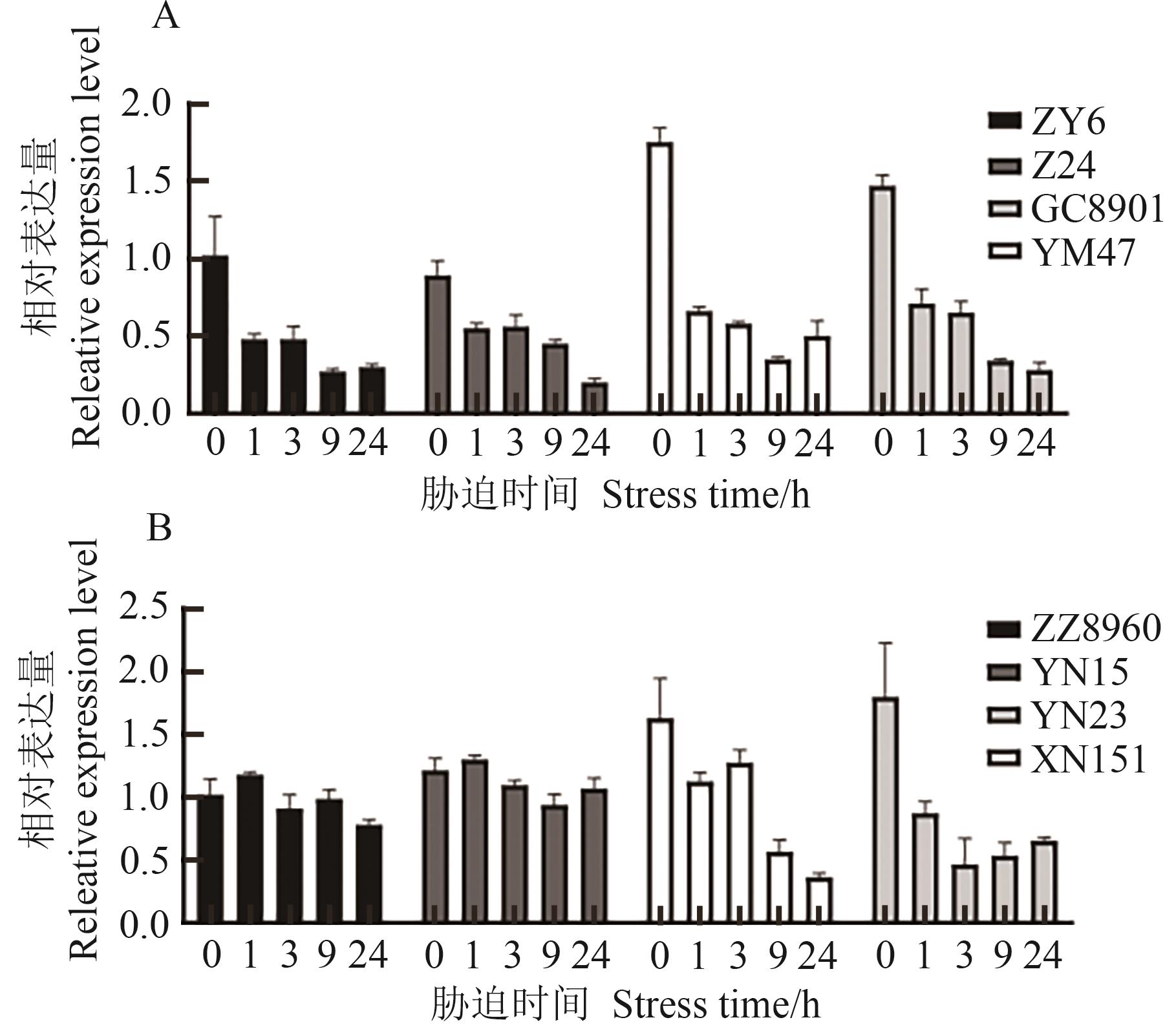
图8 不同抗性材料干旱胁迫、高温胁迫处理下TaCOBL-5D表达模式分析A: 干旱胁迫;B:高温胁迫
Fig. 8 Expression profiles of TaCOBL-5D among different resistant materials under drought and heat stressesA: Drought stress; B: Heat stress
| 1 | ZHU J K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2002, 53(1):247-273. |
| 2 | 陈翔,胡雨喆,陈甜甜,等.小麦抗低温逆境化控技术研究进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(8):1543-1555. |
| CHEN X, HU Y Z, CHEN T T, et al.. Progress of chemical regulation on wheat resistance to low temperature stress [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2023, 29(8):1543-1555. | |
| 3 | WINFIELD M O, LU C G, WILSON I D, et al.. Plant responses to cold: transcriptome analysis of wheat [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2010, 8(7):749-771. |
| 4 | MAO H D, JIAN C, CHENG X X, et al.. The wheat ABA receptor gene TaPYL1-1B contributes to drought tolerance and grain yield by increasing water-use efficiency [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2022, 20(5):846-861. |
| 5 | 温辉芹,程天灵,裴自友,等.山西中部区试小麦品种抗旱节水指标分析[J].山西农业科学,2020,48(10):1572-1575. |
| WEN H Q, CHENG T L, PEI Z Y, et al.. Analysis on drought resistance and water saving indexes of wheat varieties of regional trial in central Shanxi [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(10):1572-1575. | |
| 6 | 健康,倪建平.植物非生物胁迫信号转导及应答[J].中国稻米, 2016, 22(6):52-60. |
| ZHU J K, NI J P. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants [J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(6):52-60. | |
| 7 | 盛松柏,田菊,庞晓明.冬枣COBRA基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J].分子植物育种, 2018, 16(1):61-68. |
| SHENG S B, TIAN J, PANG X M. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of COBRA gene family in Ziziphus jujuba [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(1):61-68. | |
| 8 | SUN X M, XIONG H Y, JIANG C H, et al.. Natural variation of DROT1 confers drought adaptation in upland rice [J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1):4265 [2024-04-03].. |
| 9 | LI Y H, QIAN O, ZHOU Y H, et al.. BRITTLE CULM1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein, affects the mechanical properties of rice plants [J]. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(9):2020-2031. |
| 10 | BRADY S M, SONG S, DHUGGA K S, et al.. Combining expression and comparative evolutionary analysis. The COBRA gene family [J]. Plant Physiol., 2007, 143(1):172-187. |
| 11 | JULIUS B T, MCCUBBIN T J, MERTZ R A, et al.. Maize Brittle Stalk2-Like3, encoding a COBRA protein, functions in cell wall formation and carbohydrate partitioning [J]. Plant Cell, 2021, 33(10):3348-3366. |
| 12 | AHMED M Z, ALQAHTANI A S, NASR F A, et al.. Comprehensive analysis of the COBRA-like (COBL) gene family through whole-genome analysis of land plants [J]. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol., 2024, 71(1):863-872. |
| 13 | QIU C, CHEN J H, WU W H, et al.. Genome-wide analysis and abiotic stress-responsive patterns of COBRA-like gene family in Liriodendron chinense [J/OL]. Plants-Basel, 2023, 12(8):1616 [2024-04-03]. . |
| 14 | BEN-TOV D, ABRAHAM Y, STAV S, et al.. COBRA-LIKE2, a member of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored COBRA-LIKE family, plays a role in cellulose deposition in Arabidopsis seed coat mucilage secretory cells [J]. Plant Physiol., 2015, 167(3):711-724. |
| 15 | LIU F F, WAN Y X, CAO W X, et al.. Novel function of a putative TaCOBL ortholog associated with cold response [J]. Mol. Biol. Rep., 2023, 50(5):4375-4384. |
| 16 | LIU L F, SHANG-GUAN K K, ZHANG B C, et al.. Brittle Culm1, a COBRA-Like protein, functions in cellulose assembly through binding cellulose microfibrils [J/OL]. PLoS Genet., 2013, 9(8):e1003704 [2024-04-03]. . |
| 17 | YE X, KANG B G, OSBURN D L, et al.. The COBRA gene family in Populus and gene expression in vegetative organs and in response to hormones and environmental stresses [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2009, 58(2):211-223. |
| 18 | ZHANG D Q, YANG X H, ZHANG Z Y, et al.. Expression and nucleotide diversity of the poplar COBL gene [J]. Tree Genet. Genomes, 2010, 6(2):331-344. |
| 19 | YILAN E, XIN G, JING X, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the COBRA-like gene family in Pinus tabuliformis and the role of PtCOBL12 in the regulation of cellulose biosynthesis [J]. Ind. Crop Prod., 2023, 203. |
| 20 | YANG Q, WANG S, CHEN H, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the COBRA-like genes reveal likely roles in stem strength in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2021,16(11):e0260268 [2024-04-03]. . |
| 21 | NIU E L, SHANG X G, CHENG C Z, et al.. Comprehensive analysis of the COBRA-Like (COBL) gene family in Gossypium identifies two COBLs potentially associated with fiber quality [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12):e014572 [2024-04-03]. . |
| 22 | SANGI S, ARAÚJO PAULA M, COELHO F S, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of the COBRA-Like gene family supports gene expansion through whole-genome duplication in soybean (Glycine max) [J]. Plants, 2021, 10 (1):167-167. |
| 23 | XU L, WANG D Z, LIU S, et al.. Comprehensive atlas of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR expression during male reproductive development and abiotic stress [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11:586144 [2024-04-03]. . |
| 24 | 吴凯铭.337份小麦品种(系)萌发期抗旱性鉴定及生理响应[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2022. |
| WU K M. Identification of drought resistance and physiological response during germination in 337 wheat varieties (lines) [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. | |
| 25 | 史冰新.黄淮和长江中下游冬麦区小麦耐热种质资源筛选[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2023. |
| SHI B X. Screened for heat tolerance of wheat germplasm resources in the Yellow and Huai River valley winter wheat zone and the middle and lower Yangtze valley winter wheat zone [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2023. | |
| 26 | KESAWAT M S, KHERAWAT B S, SINGH A, et al.. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the Brassinazole-resistant (BZR) gene family and its expression in the various developmental stage and stress conditions in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(16):8743-8743. |
| 27 | FANG Y J, ZHENG Y Q, LU W, et al.. Roles of miR319-regulated TCPs in plant development and response to abiotic stress [J]. Crop J., 2021, 9(1):17-28. |
| 28 | JIAN C, HAO P A, HAO C Y, et al.. The miR319/TaGAMYB3 module regulates plant architecture and improves grain yield in common wheat (Triticum aestivum) [J]. New Phytol., 2022, 235(4):1515-1530. |
| 29 | 梁婷,左静红,陆青,等.小麦IQM基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达分析[J].中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2):27-37. |
| LIANG T, LU Q, ZUO J Het al.. Identification and expression analysis under abiotic stress of IQM gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(2):27-37. | |
| 30 | 陆青,梁婷,汪德州,等.小麦热激蛋白基因TaHSP90-1的克隆与表达分析[J].中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8):44-54. |
| LU Q, LIANG T, WANG D Zet al.. Cloning and expression analysis of wheat heat shock protein gene TaHSP90-1 [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(8):44-54. |
| [1] | 陈明迪, 胡桂花, 张海文, 王旺田. 水稻RR基因家族生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 20-29. |
| [2] | 赵刚, 王淑英, 李尚中, 张建军, 党翼, 王磊, 李兴茂, 程万莉, 周刚, 倪胜利, 樊廷录. 黄土旱塬区近40年降水对冬小麦耗水和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 164-173. |
| [3] | 张宏, 李卫国, 张晓东, 卢必慧, 张琤琤, 李伟, 马廷淮. 基于HJ-1星和GF-1号影像融合特征提取冬小麦种植面积[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 109-119. |
| [4] | 张景云, 关峰, 石博, 万新建. 小麦根系分泌物对苦瓜幼苗生长及土壤生物学环境的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 181-190. |
| [5] | 李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [6] | 刘博, 王旺田, 马骊, 武军艳, 蒲媛媛, 刘丽君, 方彦, 孙万仓, 张岩, 刘睿敏, 曾秀存. 白菜型油菜IPT基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 56-66. |
| [7] | 王韵弘, 苗琪, 李俊超, 王红叶, 张济世, 崔振岭. 田间管理措施对滨海盐渍地区中低产田生产力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 163-172. |
| [8] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [9] | 邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [10] | 姜雪敏, 陈向前, 李红燕, 姜奇彦. 小麦盐胁迫响应的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [11] | 赵明宇, 贾浩, 石晓宇, 潘义, 黄妤韵, 王凯澄, 褚庆全. 近30年黄淮海农作区冬小麦水足迹分布变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 138-147. |
| [12] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [13] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [14] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [15] | 刘盼, 高珊, 李浩宇, 王翼, 尹宝重, 郭进考, 甄文超. 缩行匀株对小麦分蘖的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 32-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号