




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 93-103.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0010
呼斯乐( ), 包玉龙(
), 包玉龙( ), 图布新巴雅尔null, 陶际峰, 郭恩亮
), 图布新巴雅尔null, 陶际峰, 郭恩亮
收稿日期:2024-01-05
接受日期:2024-03-18
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-06-23
通讯作者:
包玉龙
作者简介:呼斯乐 E-mail:20214019048@mails.imnu.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Sile HU( ), Yulong BAO(
), Yulong BAO( ), Tubuxinbayaer, Jifeng TAO, Enliang GUO
), Tubuxinbayaer, Jifeng TAO, Enliang GUO
Received:2024-01-05
Accepted:2024-03-18
Online:2025-06-15
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Yulong BAO
摘要:
叶绿素含量是监测作物长势的关键指标,快速、有效、准确的估算对作物健康评估具有重要意义。通过采集3个生长期的无人机高光谱影像,结合地面叶绿素实测数据,选用多种机器学习和集成学习模型,反演春小麦叶绿素含量,并对比不同模型的反演精度。结果表明,春小麦不同生长期冠层反射率基本一致,但在770~900 nm 波长范围内显示出明显的光谱反射率强度差异。16种光谱指数均与叶绿素含量呈显著相关,其中优化植被指数1、植物生化指数和归一化差异红边指数在整个生长周期内均与叶绿素含量保持高相关性。Stacking和Voting集成学习模型的预测精度高于基础模型,其中Voting集成学习模型表现更突出,测试集中3个生长期的决定系数(R2)分别为0.78、0.77和0.73,均方根误差(root mean square error,RMSE)分别为8.70、11.36和16.17;与随机森林、支持向量机、K_近邻和岭回归相比,其R2平均分别提高约0.17、0.14和0.22,RMSE平均降低4.64、2.54和6.51,显示出良好的预测能力。研究结果可为精准农业和作物健康监测提供新的视角和方法。
中图分类号:
呼斯乐, 包玉龙, 图布新巴雅尔null, 陶际峰, 郭恩亮. 基于无人机高光谱和集成学习的春小麦叶绿素含量反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 93-103.
Sile HU, Yulong BAO, Tubuxinbayaer, Jifeng TAO, Enliang GUO. Chlorophyll Content Inversion of Spring Wheat Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral and Integrated Learning[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 93-103.
生长期 Growth stage | 平均值 Mean value | 最大值 Maximum value | 最小值 Minimum value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期Jointing stage | 155.85 | 218.00 | 72.00 | 22.22 | 14 |
| 抽穗期Heading stage | 160.53 | 218.00 | 104.00 | 23.36 | 15 |
| 灌浆期Filling stage | 125.47 | 180.00 | 53.00 | 33.59 | 27 |
表1 不同生长期春小麦LCC变化特征
Table 1 Characteristics of changes in LCC in spring wheat at different growth stages
生长期 Growth stage | 平均值 Mean value | 最大值 Maximum value | 最小值 Minimum value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期Jointing stage | 155.85 | 218.00 | 72.00 | 22.22 | 14 |
| 抽穗期Heading stage | 160.53 | 218.00 | 104.00 | 23.36 | 15 |
| 灌浆期Filling stage | 125.47 | 180.00 | 53.00 | 33.59 | 27 |
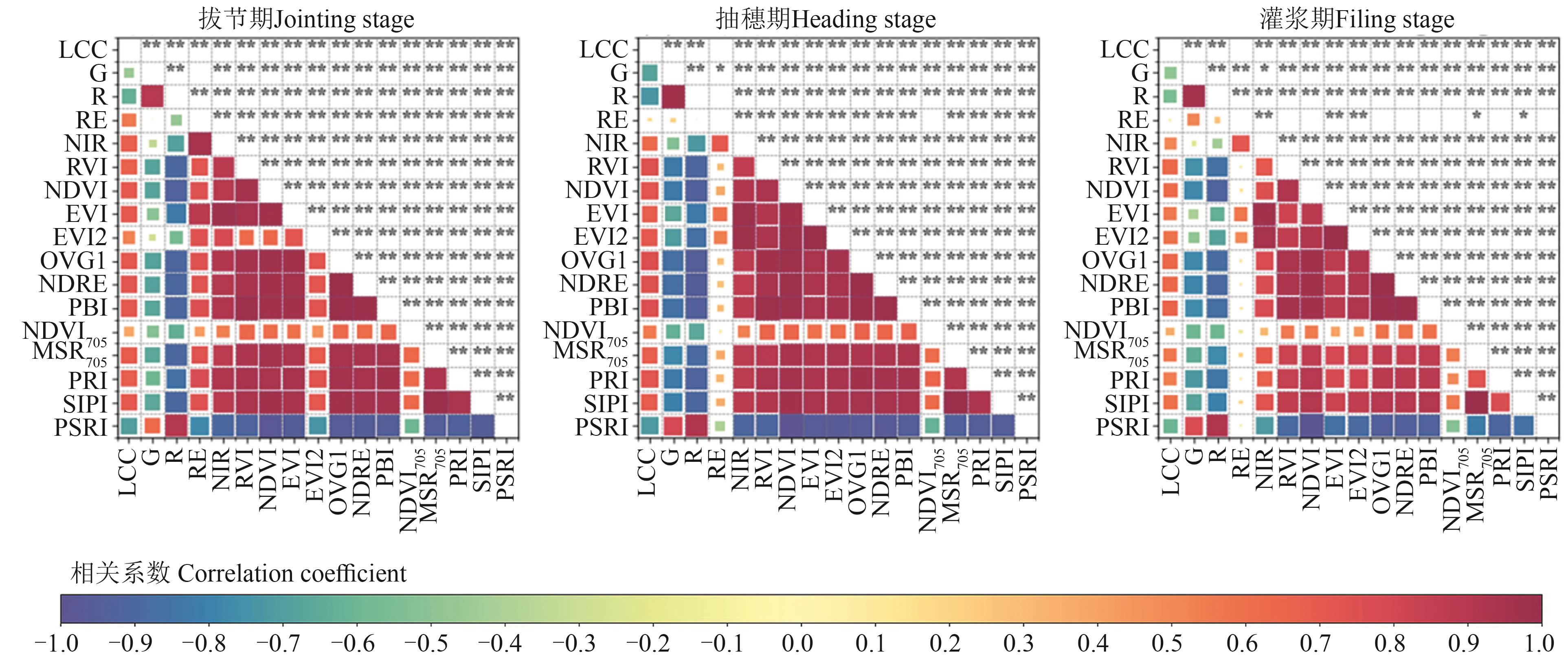
图5 光谱指数与LCC相关性热力图注:B—蓝光波段;G—绿光波段;R—红光波段;NIR—近红外波段;RVI—比值植被指数;NDVI—归一化差异植被指数;EVI—增强型植被指数;EVI 2—双波段增强型植被指数;OVG1—优化植被指数1;NDRE—归一化差异红边指数;PBI—植物生化指数;NDVI705—705 nm归一化差异植被指数;mSR705—705 nm比值植被指数;PRI—光化学反射指数;SIPI—结构不敏感色素指数;PSRI—植物衰老反射指数;LCC—叶绿素含量。*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 5 Heatmap of the correlation between spectral indices and LCCNote: B—Blue;G—Green;R—Red;NIR—Near infrared;RVI—Ratio vegetation index;NDVI—Normalized difference vegetation index;EVI—Enhanced vegetation index;EVI 2—Two-band enhanced vegetation index;OVG1—Optimized vegetation index 1;NDRE—Normalized difference red edge index;PBI—Plant biochemical index;NDVI705—Normalized difference vegetation index705;mSR705—Modified simple ratio705;PRI—Photochemical reflectance index;SIPI—Structure insensitive pigment index;PSRI—Plant senescence reflectance Index;LCC—Leaf chlorophyll content. * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
生长期 Growth stage | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 随机森林 RF | 支持向量机 SVR | K_近邻 K_NN | 岭回归 RR | Stacking | Voting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拔节期 Jointing stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 11.94 | 14.07 | 14.61 | 15.78 | 12.21 | 11.50 | |
抽穗期 Heading stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.80 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 12.52 | 14.50 | 17.29 | 15.11 | 12.25 | 10.77 | |
灌浆期 Filling stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.71 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 16.60 | 22.69 | 27.92 | 22.64 | 17.10 | 15.52 |
表2 春小麦不同生长期LCC反演模型训练集
Table 2 Training set for LCCinversion model of spring wheat at different growth stages
生长期 Growth stage | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 随机森林 RF | 支持向量机 SVR | K_近邻 K_NN | 岭回归 RR | Stacking | Voting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拔节期 Jointing stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 11.94 | 14.07 | 14.61 | 15.78 | 12.21 | 11.50 | |
抽穗期 Heading stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.80 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 12.52 | 14.50 | 17.29 | 15.11 | 12.25 | 10.77 | |
灌浆期 Filling stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.71 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 16.60 | 22.69 | 27.92 | 22.64 | 17.10 | 15.52 |
生长期 Growth stage | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 随机森林 RF | 支持向量机 SVR | K_近邻 K_NN | 岭回归 RR | Stacking | Voting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拔节期 Jointing stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.75 | 0.78 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 13.73 | 10.47 | 13.10 | 16.06 | 9.39 | 8.70 | |
抽穗期 Heading stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 13.24 | 13.19 | 14.00 | 15.20 | 13.13 | 11.36 | |
灌浆期 Filling stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.73 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 17.83 | 23.67 | 26.17 | 23.09 | 19.98 | 16.18 |
表3 春小麦不同生长期LCC反演模型测试集
Table 3 Test set for LCC inversion model of spring wheat at different growth stages
生长期 Growth stage | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 随机森林 RF | 支持向量机 SVR | K_近邻 K_NN | 岭回归 RR | Stacking | Voting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
拔节期 Jointing stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.75 | 0.78 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 13.73 | 10.47 | 13.10 | 16.06 | 9.39 | 8.70 | |
抽穗期 Heading stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 13.24 | 13.19 | 14.00 | 15.20 | 13.13 | 11.36 | |
灌浆期 Filling stage | 决定系数R2 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.73 |
| 均方根误差RMSE | 17.83 | 23.67 | 26.17 | 23.09 | 19.98 | 16.18 |
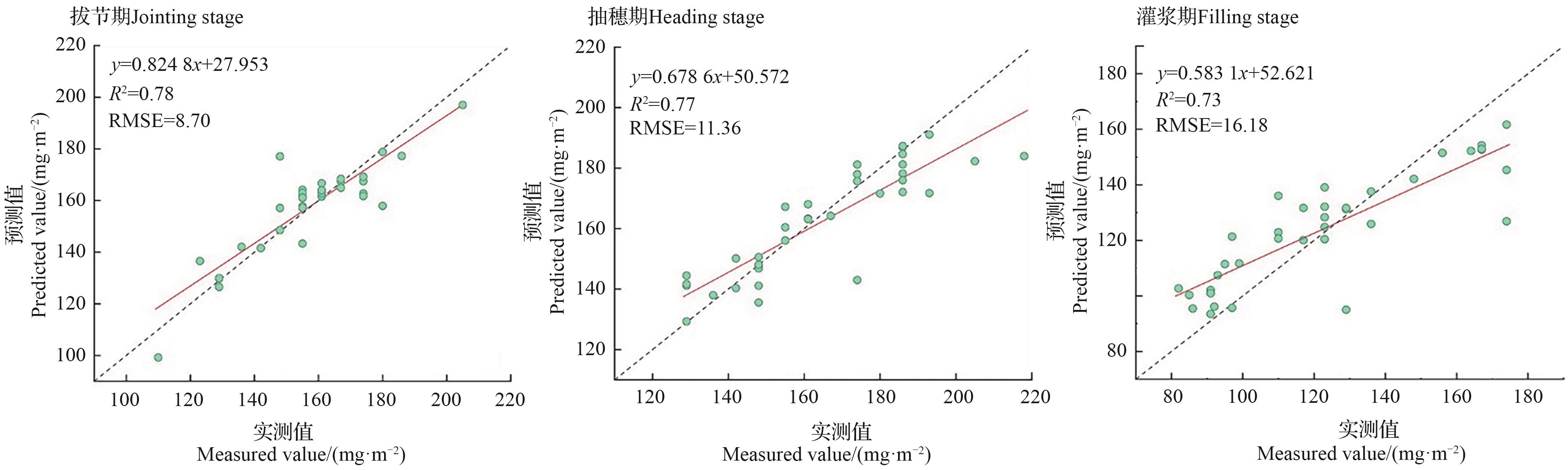
图6 基于Voting集成学习模型的不同生长期春小麦LCC反演散点图
Fig. 6 Scatter plots of LCC inversion in spring wheat at different growth stages based on the Voting ensemble learning model
| 1 | WIJESINGHA J, DAYANANDA S, WACHENDORF M, et al.. Comparison of spaceborne and UAV-borne remote sensing spectral data for estimating monsoon crop vegetation parameters [J/OL]. Sensors,2021,21(8):2886 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 2 | BOHMAN B J, ROSEN C J, MULLA D J. Evaluation of variable rate nitrogen and reduced irrigation management for potato production [J]. Agron. J., 2019, 111(4): 2005-2017. |
| 3 | LI X Q, LI L, LIU X N. Collaborative inversion heavy metal stress in rice by using two-dimensional spectral feature space based on HJ-1 A HSI and radarsat-2 SAR remote sensing data [J]. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf., 2019, 78: 39-52. |
| 4 | PUTRA B T W.New low-cost portable sensing system integrated with on-the-go fertilizer application system for plantation crops [J/OL]. Measurement, 2020, 155: 107562 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 5 | 刘涛,张寰,王志业,等.利用无人机多光谱估算小麦叶面积指数和叶绿素含量[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(19):65-72. |
| LIU T, ZHANG H, WANG Z Y, et al.. Estimation of the leaf area index and chlorophyll content of wheat using UAV multi-spectrum images [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2021,37(19): 65-72. | |
| 6 | 赵春江.农业遥感研究与应用进展[J].农业机械学报,2014,45(12): 277-293. |
| ZHAO C J. Advances of research and application in remote sensing for agriculture [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2014,45(12): 277-293. | |
| 7 | 杨贵军,李长春,于海洋,等.农用无人机多传感器遥感辅助小麦育种信息获取[J].农业工程学报, 2015, 31(21): 184-190. |
| YANG G J, LI C C, YU H Y, et al.. UAV based multi-load remote sensing technologies for wheat breeding information acquirement [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2015, 31(21):184-190. | |
| 8 | 刘建刚,赵春江,杨贵军,等.无人机遥感解析田间作物表型信息研究进展[J].农业工程学报, 2016, 32(24): 98-106. |
| LIU J G, ZHAO C J, YANG G J, et al.. Review of field-based phenotyping by unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing platform [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(24): 98-106. | |
| 9 | 边明博,马彦鹏,樊意广,等.融合无人机多源传感器的马铃薯叶绿素含量估算[J].农业机械学报,2023,54(8):240-248. |
| BIAN M B, MA Y P, FAN Y G, et al.. Estimation of potato chlorophyll content based on UAV multi-source sensor [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2023, 54(8): 240-248. | |
| 10 | QIAO L, TANG W J, GAO D H, et al.. UAV-based chlorophyll content estimation by evaluating vegetation index responses under different crop coverages [J/OL]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2022, 196:106775 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 11 | BEHMANN J, MAHLEIN A K, RUMPF T, et al.. A review of advanced machine learning methods for the detection of biotic stress in precision crop protection [J]. Precis. Agric., 2015,16(3): 239-260. |
| 12 | SHU M Y, SHEN M Y, ZUO J Y, et al.. The application of UAV-based hyperspectral imaging to estimate crop traits in maize inbred lines [J/OL]. Plant Phenomics,2021,2021: 9890745 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 13 | 刘楠,李斐,杨海波,等.优化光谱指数助力机器学习提高马铃薯叶绿素含量反演精度[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2023,29(8):1531-1542. |
| LIU N, LI F, YANG H B, et al.. Machine learning models fed with optimized spectral indices to improve inversion accuracy of potato chlorophyll content [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2023,29(8):1531-1542. | |
| 14 | QI H X, WU Z Y, ZHANG L, et al.. Monitoring of peanut leaves chlorophyll content based on drone-based multispectral image feature extraction [J/OL]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2021,187: 106292 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 15 | 张卓然,常庆瑞,张廷龙,等.基于支持向量机的棉花冠层叶片叶绿素含量高光谱遥感估算[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(11): 39-45. |
| ZHANG Z R, CHANG Q R, ZHANG T L, et al.. Hyperspectral estimation of chlorophyll content of cotton canopy leaves based on support vector machine [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat.Sci.), 2018, 46(11): 39-45. | |
| 16 | JIAO Q J, SUN Q, ZHANG B, et al.. A random forest algorithm for retrieving canopy chlorophyll content of wheat and soybean trained with PROSAIL simulations using adjusted average leaf angle [J/OL]. Remote. Sens., 2021, 14(1):98 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 17 | 罗丹,常庆瑞,齐雁冰.基于红边参数和人工神经网络的苹果叶片叶绿素含量估算[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(1):107-115. |
| LUO D, CHANG Q R, QI Y B. Estimation of chlorophyll content in apple leaves based on red edge parameters and artificial neural network [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2019, 47(1): 107-115. | |
| 18 | FEI S P, HASSAN M A, HE Z H, et al.. Assessment of ensemble learning to predict wheat grain yield based on UAV-multispectral reflectance [J/OL]. Remote. Sens., 2021, 13(12): 2338 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 19 | ZHANG Z, PASOLLI E, CRAWFORD M M. An adaptive multiview active learning approach for spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images [J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens., 2020, 58(4):2557-2570. |
| 20 | 符欣彤,常庆瑞,张佑铭,等.基于Stacking集成学习的猕猴桃叶片叶绿素含量估算[J].干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(4):247-256. |
| FU X T, CHANG Q R, ZHANG Y M, et al.. Estimation of kiwifruit leaf chlorophyll content based on Stacking ensemble learning [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2023,41(4):247-256. | |
| 21 | PEPPES N, DASKALAKIS E, ALEXAKIS T, et al.. Performance of machine learning-based multi-model voting ensemble methods for network threat detection in agriculture 4.0 [J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(22): 7475 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 22 | LIANG L, DI L P, ZHANG L P, et al.. Estimation of crop LAI using hyperspectral vegetation indices and a hybrid inversion method [J]. Remote. Sens. Environ., 2015, 165:123-134. |
| 23 | RABIDEAU S W, LEMONS J F. The potential of the Pu(Ⅲ)—Pu(IV) couple and the equilibrium constants for some complex ions of Pu(IV)1 [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1951, 73(6): 2895-2899. |
| 24 | DEFRIES R S, TOWNSHEND J R G. NDVI-derived land cover classifications at a global scale [J]. Int. J. Remote. Sens., 1994,15(17): 3567-3586. |
| 25 | HUETE A, DIDAN K, LEEUWEN L W, et al.. MODIS vegetation indices [J/OL]. Land Remote Sens. Glob. Environ. Change, 2010:579-602 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 26 | JIANG Z Y, HUETE A R, DIDAN K, et al.. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band [J].Remote. Sens. Environ., 2008, 112(10):3833-3845. |
| 27 | VOGELMANN J E, ROCK B N, MOSS D M. Red edge spectral measurements from sugar maple leaves [J]. Int. J. Remote.Sens.,1993, 14(8):1563-1575. |
| 28 | FITZGERALD G J, RODRIGUEZ D, CHRISTENSEN L K, et al..Spectral and thermal sensing for nitrogen and water status in rainfed and irrigated wheat environments [J]. Precis. Agric., 2006, 7(4): 233-248. |
| 29 | RAO N R, GARG P K, GHOSH S K, et al.. Estimation of leaf total chlorophyll and nitrogen concentrations using hyperspectral satellite imagery [J]. J. Agric. Sci., 2008, 146(1):65-75. |
| 30 | WU C Y, NIU Z, TANG Q, et al.. Estimating chlorophyll content from hyperspectral vegetation indices:modeling and validation [J]. Agric. For. Meteor., 2008, 148:1230-1241. |
| 31 | DROLET G G, HUEMMRICH K F, HALL F G, et al.. A MODIS-derived photochemical reflectance index to detect inter-annual variations in the photosynthetic light-use efficiency of a boreal deciduous forest [J]. Remote. Sens. Environ., 2005, 98(2): 212-224. |
| 32 | SIMS D A, GAMON J A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species,leaf structures and developmental stages [J]. Remote. Sens. Environ., 2002, 81(3):337-354. |
| 33 | ANDEREGG J, YU K, AASEN H, et al.. Spectral vegetation indices to track senescence dynamics in diverse wheat germplasm [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019,10:1749 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 34 | 张东彦,韩宣宣,林芬芳,等.基于多源无人机影像特征融合的冬小麦LAI估算[J].农业工程学报,2022,38(9):171-179. |
| ZHANG D Y, HAN X X, LIN F F, et al.. Estimation of winter wheat leaf area index using multi-source UAV image feature fusion [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2022, 38(9):171-179. | |
| 35 | 刘京,常庆瑞,刘淼,等.基于SVR算法的苹果叶片叶绿素含量高光谱反演[J].农业机械学报,2016,47(8):260-265, 272. |
| LIU J, CHANG Q R, LIU M, et al.. Chlorophyll content inversion with hyperspectral technology for apple leaves based on support vector regression algorithm [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2016, 47(8): 260-265, 272. | |
| 36 | COSENZA DIOGO N, LAURI K, MATTI M, et al.. Comparison of linear regression, k-nearest neighbour and random forest methods in airborne laser-scanning-based prediction of growing stock [J]. For. Int. J. For. Res., 2021, 94(2):311-323. |
| 37 | JI S, GU C, XI X B, et al.. Quantitative monitoring of leaf area index in rice based on hyperspectral feature bands and ridge regression algorithm [J/OL]. Remote Sens., 2022, 14(12): 2777 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 38 | 杨红云,郭紫微,郭高飞,等.基于Stacking集成卷积神经网络的水稻氮素营养诊断[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2023,29(3):573-581. |
| YANG H Y, GUO Z W, GUO G F, et al.. Rice nitrogen nutrition diagnosis based on Stacking integrated convolutional neural network [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2023, 29(3):573-581. | |
| 39 | MAIRE G L, FRANÇOIS C, DUFRÊNE E. Towards universal broad leaf chlorophyll indices using PROSPECT simulated database and hyperspectral reflectance measurements [J]. Remote. Sens. Environ., 2004, 89(1):1-28. |
| 40 | 汪旭,邓裕帅,练雪萌,等.基于无人机多光谱技术的甜菜冠层叶绿素含量反演[J].中国糖料,2022,44(4):36-42. |
| WANG X, DENG Y S, LIAN X M, et al.. Inversion of chlorophyll content in sugar beet canopy based on UAV multispectral technique [J]. Sugar Crops China, 2022, 44(4): 36-42. | |
| 41 | CHLINGARYAN A, SUKKARIEH S, WHELAN B. Machine learning approaches for crop yield prediction and nitrogen status estimation in precision agriculture:a review [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2018, 151:61-69. |
| 42 | LIAKOS K G, BUSATO P, MOSHOU D, et al.. Machine learning in agriculture:a review [J/OL]. Sensors, 2018,18(8):2674 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 43 | FENG L W, ZHANG Z, MA Y C, et al.. Alfalfa yield prediction using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and ensemble learning [J/OL]. Remote. Sens., 2020, 12(12): 2028 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 44 | GE H X, MA F, LI Z W, et al.. Improved accuracy of phenological detection in rice breeding by using ensemble models of machine learning based on UAV-RGB imagery [J/OL]. Remote. Sens., 2021, 13(14):2678 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 45 | PRAGATHI K. Crop yield prediction and fertilizer recommendation using voting based ensemble classifier [J]. Int. J. Innovat. Res. Technol., 2021, 8(6): 510-516. |
| [1] | 郑舒元, 刀剑, 张学林, 刘珊珊, 王建雄. 基于可见光波段的绿色植被提取方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 107-117. |
| [2] | 蒋沛含, 杨晓楠, 杨晨旭, 张爱军. 基于偏最小二乘回归的谷子冠层氮素含量高光谱估测研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 91-101. |
| [3] | 王薇, 付虹雨, 卢建宁, 岳云开, 杨瑞芳, 崔国贤, 佘玮. 基于无人机航拍的苎麻倒伏信息解译研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 91-97. |
| [4] | 唐天君, 陈洋, 胡军, 江浩田. 基于无人机影像数据的烟草精准识别方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 145-157. |
| [5] | 房彦飞, 罗晓颖, 唐江华, 孙婷婷, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 徐文修. 播种方式对旱地春小麦产量、干物质及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 173-181. |
| [6] | 田蕊, 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆抗旱遗传位点及候选基因发掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 69-82. |
| [7] | 王建华, 温晓蕾, 栗佳宁, 郭思柔, 赵春明, 母时风, 赵德轩, 齐慧霞. 不同施药方式对板栗红蜘蛛田间防效和效益分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 139-146. |
| [8] | 尹林江, 李威, 赵卫权, 赵祖伦, 吕思思, 孙小琼. 水稻多时相植被指数特征及覆盖度提取研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 83-98. |
| [9] | 郭倩, 魏嘉豪, 张健, 叶章熙, 张厚喜, 赖正清, 邓辉. 基于无人机多光谱影像和随机森林的蔬菜识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 99-110. |
| [10] | 卢闯, 胡海棠, 覃苑, 淮贺举, 李存军. 基于无人机多光谱影像的春玉米田管理分区研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 106-115. |
| [11] | 胡灵炆, 周忠发, 尹林江, 朱孟, 黄登红. 基于无人机RGB影像的苗期油菜识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 116-128. |
| [12] | 张静, 郭思梦, 韩迎春, 雷亚平, 邢芳芳, 杜文丽, 李亚兵, 冯璐. 基于无人机RGB图像的棉花产量估算[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 112-120. |
| [13] | 坚天才, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 刘根红, 高娣, 马雪莹, 李鑫. 氮素缓解春小麦花后高温早衰的抗氧化特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 33-44. |
| [14] | 张冠宏, 王新军, 徐晓龙, 闫立男, 常梦迪, 李永康, . 基于面向对象的无人机遥感影像荒漠植被分类[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 69-77. |
| [15] | 伏荣桃,陈诚,王剑,陈雪娟,卢代华*. 植保无人机对水稻病虫害防治条件与防效的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 103-109. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号