




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 168-175.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0850
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
刘宏元1( ), 周志花2, 赵光昕3, 王艳君1, 王娜娜1(
), 周志花2, 赵光昕3, 王艳君1, 王娜娜1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-30
接受日期:2021-11-22
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
王娜娜
作者简介:刘宏元 E-mail:saasliuhongyuan@163.com;
基金资助:
Hongyuan LIU1( ), Zhihua ZHOU2, Guangxin ZHAO3, Yanjun WANG1, Nana WANG1(
), Zhihua ZHOU2, Guangxin ZHAO3, Yanjun WANG1, Nana WANG1( )
)
Received:2021-09-30
Accepted:2021-11-22
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Nana WANG
摘要:
水资源短缺和养分利用率低一直是制约我国旱地农业发展的重要因素,而改性纤维素能够有效固持土壤水分和养分,同时还具有缓释作用促进作物生长。探究了羧甲基纤维素(Carboxymethyl cellulose,CMC)对旱地土壤性质的影响及其在植株生长过程中的实际应用效果,为羧甲基纤维素在旱地土壤中施用量、施用方法提供科学依据。通过旱稻盆栽试验,研究CMC-NH4、CMC-Na和CMC-K施加量为0.05%、0.10%、0.30%和0.50%时对旱稻萌发、土壤水分、物理性质、养分的影响。结果表明,与对照组相比,施加0.05%的3种改性纤维素均可以促进旱稻萌发和增加地上部生物量,达214.29%~316.33%。施加改性纤维素能降低培养前期土壤水分流失量,但对土壤累积水分流失量无显著性影响;其对土壤物理性质影响较大,尤其是CMC-NH4和CMC-Na可以增加土壤硬度以及土壤紧实度。施加CMC-NH4有降低土壤pH的趋势,而施加CMC-Na和CMC-K有增加土壤pH的趋势。施加CMC-NH4可以增加土壤硝态氮和铵态氮含量,分别达202.45%~1 017.79%和48.20%~172.60%;3种改性纤维素均在不同程度上提高了土壤速效磷含量;仅施加CMC-K可以显著增加土壤速效钾含量,达344.94%~1 458.73%。因此,3种改性纤维素施加量为0.05%时有利于作物生长和土壤养分的增加,可以作为旱地土壤改良剂应用。
中图分类号:
刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 王艳君, 王娜娜. 改性纤维素对旱稻萌发和旱地土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 168-175.
Hongyuan LIU, Zhihua ZHOU, Guangxin ZHAO, Yanjun WANG, Nana WANG. Effects of Modified Cellulose on Germination and Dryland Soil Physicochemical Properties of Upland Rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 168-175.
处理 Treatment | 纤维素类型 Cellulose type | 施加比例 Proportion/% | 处理 Treatment | 纤维素类型 Cellulose type | 施加比例 Proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | — | 0.00 | B3 | CMC-Na | 0.30 |
| A1 | CMC-NH4 | 0.05 | B4 | CMC-Na | 0.50 |
| A2 | CMC-NH4 | 0.10 | C1 | CMC-K | 0.05 |
| A3 | CMC-NH4 | 0.30 | C2 | CMC-K | 0.10 |
| A4 | CMC-NH4 | 0.50 | C3 | CMC-K | 0.30 |
| B1 | CMC-Na | 0.05 | C4 | CMC-K | 0.50 |
| B2 | CMC-Na | 0.10 |
表1 盆栽试验各处理设置
Table 1 Treatment of pot experiment
处理 Treatment | 纤维素类型 Cellulose type | 施加比例 Proportion/% | 处理 Treatment | 纤维素类型 Cellulose type | 施加比例 Proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | — | 0.00 | B3 | CMC-Na | 0.30 |
| A1 | CMC-NH4 | 0.05 | B4 | CMC-Na | 0.50 |
| A2 | CMC-NH4 | 0.10 | C1 | CMC-K | 0.05 |
| A3 | CMC-NH4 | 0.30 | C2 | CMC-K | 0.10 |
| A4 | CMC-NH4 | 0.50 | C3 | CMC-K | 0.30 |
| B1 | CMC-Na | 0.05 | C4 | CMC-K | 0.50 |
| B2 | CMC-Na | 0.10 |
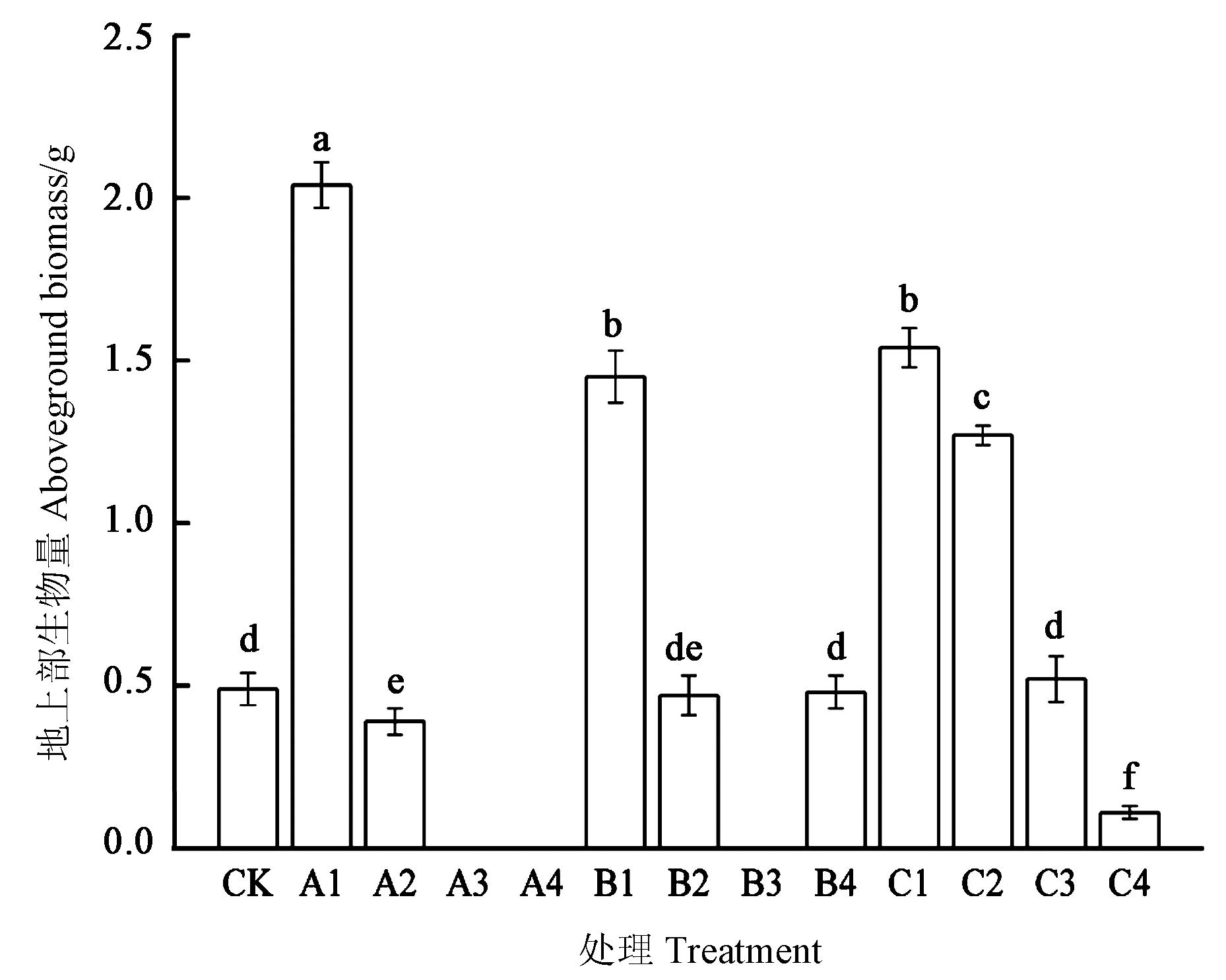
图2 各处理地上部生物量注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Aboveground biomass in each treatmentNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 失水量 Water loss/kg | 处理 Treatment | 失水量 Water loss/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.67±0.02 | B3 | 0.65±0.02 |
| A1 | 0.70±0.02 | B4 | 0.65±0.09 |
| A2 | 0.67±0.02 | C1 | 0.72±0.04 |
| A3 | 0.66±0.03 | C2 | 0.72±0.01 |
| A4 | 0.69±0.03 | C3 | 0.70±0.01 |
| B1 | 0.70±0.03 | C4 | 0.68±0.01 |
| B2 | 0.67±0.03 |
表2 各处理累积失水量
Table 2 Cumulative water loss in each treatment
处理 Treatment | 失水量 Water loss/kg | 处理 Treatment | 失水量 Water loss/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.67±0.02 | B3 | 0.65±0.02 |
| A1 | 0.70±0.02 | B4 | 0.65±0.09 |
| A2 | 0.67±0.02 | C1 | 0.72±0.04 |
| A3 | 0.66±0.03 | C2 | 0.72±0.01 |
| A4 | 0.69±0.03 | C3 | 0.70±0.01 |
| B1 | 0.70±0.03 | C4 | 0.68±0.01 |
| B2 | 0.67±0.03 |
处理 Treatment | pH | 土壤紧实度 Soil compaction/kPa | 硬度与土壤成块性 Hardness and fragmentation | 表面结皮厚度 Surface crust thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.06±0.14 de | 905.96±12.69 fg | 土壤松软,未结块 Soil is loose, no agglomeration | 0.00±0.00 d |
| A1 | 7.95±0.15 ef | 1 035.82±12.36 ef | 土壤较硬,未结块 Soil is hard, no agglomeration | 1.77±0.42 bc |
| A2 | 7.94±0.08 ef | 1 053.53±50.74 e | 土壤较硬,少许板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a small amount of soil caking | 2.73±0.64 bc |
| A3 | 7.90±0.13 ef | 1 146.94±21.43 e | 土壤较硬,较多板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a large amount of soil caking | 2.90±0.17 bc |
| A4 | 7.77±0.17 f | 1 286.14±59.10 d | 土壤硬,较多板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a large amount of soil caking | 3.07±0.23 b |
| B1 | 8.33±0.12 bc | 1 781.54±107.12 c | 土壤坚硬,形成小结块 Soil agglomerate hardness is slightly harder | 1.53±0.21 c |
| B2 | 8.42±0.14 b | 1 905.46±111.02 c | 土壤坚硬,形成小结块 Soil agglomerate hardness is slightly harder | 2.50±0.26 c |
| B3 | 8.50±0.16 b | 2 119.97±96.21 b | 土壤非常坚硬,形成大结块 Soil is very hard and forms thick caking | 3.83±0.06 bc |
| B4 | 8.84±0.10 a | 2 313.36±202.74 a | 土壤非常坚硬,形成大结块 Soil is very hard and forms thick caking | 3.93±0.15 bc |
| C1 | 8.09±0.12 de | 874.30±15.37 g | 表层较硬,下层松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is loose | 1.57±0.06 c |
| C2 | 8.19±0.18 cd | 900.87±23.26 g | 表层较硬,下层松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is loose | 1.83±0.21 bc |
| C3 | 8.45±0.17 b | 930.75±31.05 fg | 表层较硬,下层较为松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is a little loose | 2.03±0.15 b |
| C4 | 8.47±0.09 b | 927.75±7.88 fg | 表层较硬,下层较为松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is a little loose | 2.57±0.12 a |
表3 各处理培养后土壤理化性质
Table 3 Physical and chemical properties in each treatment
处理 Treatment | pH | 土壤紧实度 Soil compaction/kPa | 硬度与土壤成块性 Hardness and fragmentation | 表面结皮厚度 Surface crust thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.06±0.14 de | 905.96±12.69 fg | 土壤松软,未结块 Soil is loose, no agglomeration | 0.00±0.00 d |
| A1 | 7.95±0.15 ef | 1 035.82±12.36 ef | 土壤较硬,未结块 Soil is hard, no agglomeration | 1.77±0.42 bc |
| A2 | 7.94±0.08 ef | 1 053.53±50.74 e | 土壤较硬,少许板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a small amount of soil caking | 2.73±0.64 bc |
| A3 | 7.90±0.13 ef | 1 146.94±21.43 e | 土壤较硬,较多板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a large amount of soil caking | 2.90±0.17 bc |
| A4 | 7.77±0.17 f | 1 286.14±59.10 d | 土壤硬,较多板结、结块 Soil is hard, there is a large amount of soil caking | 3.07±0.23 b |
| B1 | 8.33±0.12 bc | 1 781.54±107.12 c | 土壤坚硬,形成小结块 Soil agglomerate hardness is slightly harder | 1.53±0.21 c |
| B2 | 8.42±0.14 b | 1 905.46±111.02 c | 土壤坚硬,形成小结块 Soil agglomerate hardness is slightly harder | 2.50±0.26 c |
| B3 | 8.50±0.16 b | 2 119.97±96.21 b | 土壤非常坚硬,形成大结块 Soil is very hard and forms thick caking | 3.83±0.06 bc |
| B4 | 8.84±0.10 a | 2 313.36±202.74 a | 土壤非常坚硬,形成大结块 Soil is very hard and forms thick caking | 3.93±0.15 bc |
| C1 | 8.09±0.12 de | 874.30±15.37 g | 表层较硬,下层松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is loose | 1.57±0.06 c |
| C2 | 8.19±0.18 cd | 900.87±23.26 g | 表层较硬,下层松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is loose | 1.83±0.21 bc |
| C3 | 8.45±0.17 b | 930.75±31.05 fg | 表层较硬,下层较为松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is a little loose | 2.03±0.15 b |
| C4 | 8.47±0.09 b | 927.75±7.88 fg | 表层较硬,下层较为松软 Surface is hard and the bottom soil is a little loose | 2.57±0.12 a |
处理 Treatment | 铵态氮 NH | 硝态氮 NO | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.63±0.23 de | 29.23±5.40 fg | 12.30±1.42 e | 161.67±7.02 e |
| A1 | 1.92±0.35 de | 31.51±0.60 efg | 15.47±2.89 cde | 197.00±56.35 e |
| A2 | 4.93±1.18 c | 43.32±1.55 cd | 14.17±0.49 de | 171.33±14.74 e |
| A3 | 15.40±0.59 b | 64.09±0.98 b | 19.26±2.21 b | 173.33±3.21 e |
| A4 | 18.22±1.09 a | 79.68±10.18 a | 19.06±1.63 b | 170.67±8.08 e |
| B1 | 1.16±0.34 ef | 43.51±3.43 cd | 18.60±3.16 bc | 157.33±5.13 e |
| B2 | 1.01±0.13 f | 37.01±3.28 de | 16.70±3.18 bcd | 162.33±6.03 e |
| B3 | 1.73±0.20 de | 27.20±1.66 g | 14.31±3.60 de | 156.33±5.77 e |
| B4 | 2.09±0.56 d | 12.82±1.14 h | 13.07±1.11 e | 158.33±4.51 e |
| C1 | 0.74±0.19 f | 48.37±5.03 c | 20.13±0.95 b | 719.33±24.01 d |
| C2 | 0.68±0.14 f | 34.54±5.68 efg | 19.43±0.40 b | 783.67±10.07 c |
| C3 | 0.86±0.19 f | 35.10±6.48 ef | 19.77±1.88 b | 1 073.33±85.20 b |
| C4 | 2.28±0.16 d | 36.63±2.46 def | 24.87±1.88 a | 2 520.00±233.88 a |
表4 各处理培养后土壤养分含量 (mg·kg-1)
Table 4 Soil nutrients in each treatment
处理 Treatment | 铵态氮 NH | 硝态氮 NO | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.63±0.23 de | 29.23±5.40 fg | 12.30±1.42 e | 161.67±7.02 e |
| A1 | 1.92±0.35 de | 31.51±0.60 efg | 15.47±2.89 cde | 197.00±56.35 e |
| A2 | 4.93±1.18 c | 43.32±1.55 cd | 14.17±0.49 de | 171.33±14.74 e |
| A3 | 15.40±0.59 b | 64.09±0.98 b | 19.26±2.21 b | 173.33±3.21 e |
| A4 | 18.22±1.09 a | 79.68±10.18 a | 19.06±1.63 b | 170.67±8.08 e |
| B1 | 1.16±0.34 ef | 43.51±3.43 cd | 18.60±3.16 bc | 157.33±5.13 e |
| B2 | 1.01±0.13 f | 37.01±3.28 de | 16.70±3.18 bcd | 162.33±6.03 e |
| B3 | 1.73±0.20 de | 27.20±1.66 g | 14.31±3.60 de | 156.33±5.77 e |
| B4 | 2.09±0.56 d | 12.82±1.14 h | 13.07±1.11 e | 158.33±4.51 e |
| C1 | 0.74±0.19 f | 48.37±5.03 c | 20.13±0.95 b | 719.33±24.01 d |
| C2 | 0.68±0.14 f | 34.54±5.68 efg | 19.43±0.40 b | 783.67±10.07 c |
| C3 | 0.86±0.19 f | 35.10±6.48 ef | 19.77±1.88 b | 1 073.33±85.20 b |
| C4 | 2.28±0.16 d | 36.63±2.46 def | 24.87±1.88 a | 2 520.00±233.88 a |
| 1 | CHIANG F, MAZDIYASNI O, AGHAKOUCHAK A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity [J]. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1): 1-10. |
| 2 | CAO Y, ZHANG W, REN J. Efficiency analysis of the input for water-saving agriculture in China [J]. Water, 2020, 12(1): 207. |
| 3 | WANG W S, YANG S Q, ZHANG A P, et al.. Synthesis of a slow-release fertilizer composite derived from waste straw that improves water retention and agricultural yield [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 768(1):144978 . |
| 4 | 杨世琦,邢磊,刘宏元,等.羧甲基纤维素铵对黄土高原新造耕地土壤性质的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(5):74-80. |
| YANG S Q, XING L, LIU H Y, et al.. Effects of applying ammonium carboxymethyl cellulose on soil properties of new cultivated farmland in Loess Plateau [J]. J. Northwest A & F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 49(5):74-80. | |
| 5 | 廖人宽,杨培岭,任树梅.高吸水树脂保水剂提高肥效及减少农业面源污染[J].农业工程学报, 2012, 28(17):1-10. |
| LIAO R K, YANG P L, REN S M. High water absorbing resin water retention agent improves fertilizer efficiency and reduces agricultural non-point source pollution [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2012, 28(17):1-10. | |
| 6 | 苟春林,王新爱,李永胜,等.保水剂与氮肥的相互影响及节水保肥效果[J].中国农业科学, 2011, 44(19):4015-4021. |
| GOU C L, WANG X A, LI Y S, et al.. Interaction between water retaining agent and nitrogen fertilizers and the effect of water and fertilizer conservation [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2011, 44(19):4015-4021. | |
| 7 | 侯贤清,李荣,何文寿,等.保水剂施用量对旱作土壤理化性质及马铃薯生长的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5):325-330. |
| HOU X Q, LI R, HE W S, et al.. Effect of water-retaining agent application rate on soil physical and chemical properties and potato growth in dry farming [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2015, 29(5):325-330. | |
| 8 | SHI Z, ZHANG Y, PHILLIPS G, et al.. Utilization of bacterial cellulose in food [J]. Food Hydrocolloid., 2014, 35(1):539-545. |
| 9 | PRADO H J, MATULEWICZ M C. Cationization of polysaccharides: a path to greener derivatives with many industrial applications [J]. Eur. Polym. J., 2014, 52:53-75. |
| 10 | HOKKANEN S, BHATNAGAR A, SILLANPAA M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity [J]. Water Res., 2016, 91:156-173. |
| 11 | WANG W S, YANG S Q, ZHANG A P, et al.. Preparation and properties of novel corn straw cellulose-based superabsorbent with water-retaining and slow-release functions [J]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2020, 137(32): 48951. |
| 12 | 王惟帅,杨世琦.羧甲基纤维素钠制备及改性研究[J].合成纤维, 2018, 47(10):24-30. |
| WANG W S, YANG S Q. Study on the preparation and modification of carboxymethyl cellulose [J]. Synthetic Fiber, 2018, 47(10):24-30. | |
| 13 | LIU H Y, LI H B, ZHANG A P, et al.. Inhibited effect of biochar application on N2O emissions is amount and time-dependent by regulating denitrification in a wheat-maize rotation system in North China [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 721: 137636. |
| 14 | 王化琪.旱稻二十一世纪新粮源[J].中国农村小康科技, 1998(7):26-27. |
| 15 | 邢磊.改性纤维素对黄土高原农田土壤及作物的影响研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院, 2019. |
| XING L. Effects of modified cellulose on farmland soil and crops in Loess Plateau [D].Beijing :Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. | |
| 16 | 杨永辉,吴普特,武继承,等.保水剂对冬小麦不同生育阶段土壤水分及利用的影响[J].农业工程学报, 2010, 26(12):19-26. |
| YANG Y H, WU P T, WU J C, et al.. Impacts of water-retaining agent on soil moisture and water use in different growth stages of winter wheat [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2010, 26(12):19-26. | |
| 17 | 王琰,井大炜,付修勇,等.保水剂施用量对杨树苗土壤物理性状与微生物活性的影响[J].水土保持通报, 2017, 37(3):53-58. |
| WANG Y, JING D W, FU X Y, et al.. Effects of application amount of super-absorbent polymer on soil physical characteristics and microbial activity under poplar seedlings [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 37(3):53-58. | |
| 18 | 许紫峻,韩舒,师庆东.不同保水剂对土壤物理性质影响的探究[J].节水灌溉, 2016(10):10-14. |
| XU Z J, HAN S, SHI Q D. Effect of different super absorbent polymer on soil physical properties [J]. Water Sav. Irrig., 2016(10):10-14. | |
| 19 | 纪冰祎,李娜,王云跃.保水剂对土壤物理性质影响的研究进展[J].水土保持应用技术, 2018(5):29-31. |
| JI B Y, LI N, WANG Y Y. Research progress on effects of water retaining agents on soil physical properties [J]. Technol. Soil Water Conserv., 2018(5):29-31. | |
| 20 | 邢磊,杨世琦.改性纤维素的吸附性能及应用研究进展[J].中国农学通报, 2020, 36(3):59-65. |
| XING L, YANG S Q. Adsorption properties and application of modified cellulose: a review [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2020, 36(3):59-65. | |
| 21 | 倪芳,蔡卫兵,蒲双双,等.保水剂对土壤含水量及黑麦草种子萌发的影响[J].安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(27):52-54. |
| NI F, CAI W B, PU S S, et al.. Effects of water retaining agent on total soil moisture content and seed germination of perennial rye-grass [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2016, 44(27):52-54. | |
| 22 | 黄志勇,赵春燕,倪佳东,等.吡啶酮改性纤维素吸附剂对金属离子的吸附性能[J].离子交换与吸附, 2016, 32(5):440-448. |
| HUANG Z Y, ZHAO C Y, NI J D, et al.. Metal cation adsorption properties of pyridone functionalized cellulosic adsorbent [J]. Ion. Exch. Adsorpt., 2016, 32(5):440-448. | |
| 23 | 杨世琦,邢磊,刘宏元,等.羧甲基纤维素钠对黄土高原新造耕地土壤改良效果[J].中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(4):185-191. |
| YANG S Q, XING L, LIU H Y, et al.. Effects of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose application on soil properties of new cultivating farmland in Loess Plateau [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2021, 26(4):185-191. | |
| 24 | 白文波,李茂松,赵虹瑞,等.保水剂对土壤积水入渗特征的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2010, 43(24):5055-5062. |
| BAI W B, LI M S, ZHAO H R, et al.. Effect of water retaining agent on infiltration characteristics of soil water accumulation [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2010, 43(24):5055-5062. | |
| 25 | 王惟帅,杨正礼,张爱平,等.玉米秸秆基纤维素保水缓释肥制备及应用[J].农业工程学报, 2020, 36(2):236-244. |
| WANG W S, YANG Z L, ZHANG A P, et al.. Preparation and application of corn straw cellulose-based fertilizer with integration of water-retaining and slow-release [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020, 36(2):236-244. | |
| 26 | KANMANI P, ARAVIND J, KAMARAJ M, et al.. Environmental applications of chitosan and cellulosic biopolymers: a comprehensive outlook [J]. Bioresource Technol., 2017(242):295-303. |
| 27 | OMER A M, ELGARHY G S, EL-SUB R UITI G M, et al.. Fabrication of novel iminodiacetic acid-functionalized carboxymethyl cellulose microbeads for efficient removal of cationic crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 148:1072-1083. |
| 28 | 邢磊,杨世琦.改性纤维素对盆栽小麦生长及土壤水分和养分的影响[J].西北农业学报, 2019, 28(4):536-545. |
| XING L, YANG S Q. Effects of modified cellulose on growth of potted wheat and soil moisture and nutrients [J]. Acta. Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2019, 28(4):536-545. | |
| 29 | 杨静静,王秀峰,魏珉,等.保水剂吸水、释水及吸肥特性研究[J].山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(5):696-700. |
| YANG J J, WANG X F, WEI M, et al.. Study on characteristics of absorption,release and fertilizer absorption of water retaining agent [J]. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 47(5):696-700. | |
| 30 | LU S, LIU W, WANG Y, et al.. An adsorbent based on humic acid and carboxymethyl cellulose for efficient dye removal from aqueous solution [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 134:790-797. |
| 31 | UGAWA S, INAGAKI Y, KARIBU F, et al.. Effects of soil compaction by a forestry machine and slash dispersal on soil N mineralization in Cryptomeria japonica plantations under high precipitation [J]. New For., 2020, 51(5):1-21. |
| [1] | 姚佳, 刘加欣, 苏焱, 苏小娟. 烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [2] | 聂婷婷, 董乙强, 杨合龙, 阿斯太肯·居力海提, 周时杰, 安沙舟. 围栏封育对蒿类荒漠植物-土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 178-187. |
| [3] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [4] | 卢闯, 胡海棠, 覃苑, 淮贺举, 李存军. 基于无人机多光谱影像的春玉米田管理分区研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 106-115. |
| [5] | 陈奎元, 刘卉, 丁伟. 草甘膦对大豆田土壤养分及其功能酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 180-188. |
| [6] | 何振嘉, 范王涛, 杜宜春, 王启龙. 基于土体有机重构的水肥耦合对土壤理化性质和水稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [7] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [8] | 刘著文, 杨龙飞, 刘茂林, 贾国涛, 姚倩, 马一琼, 崔廷, 杨欣玲, 陈洋, 程良琨. 不同土壤改良剂对土壤养分及烤烟内在品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 190-198. |
| [9] | 高日平, §, 刘小月, §, 杜二小, 韩云飞, 任永峰, 高宇, 赵沛义, 李焕春, 张鹏, . 垄膜沟播与秸秆还田对内蒙古黄土高原玉米农田土壤水分、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 181-190. |
| [10] | 刘倩1,2,李纪潮1,左应梅1,杨天梅1,杨美权1,张金渝*. 有机覆盖三七对土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [11] | 蒲全明1,杨鹏1*,邓榆川2,向承勇1,林邦民1,刘莉莎1,施松梅3,何泽民1,雍磊1. 不同施肥方式对冬春茬甘蓝根际土壤酶活性、土壤养分及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 130-139. |
| [12] | 秦富仓,牛晓乐,杨振奇,马鑫,任小同. 冒山小流域不同地形和土地利用下的土壤养分空间变异特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 138-148. |
| [13] | 刘岑薇,叶菁,李艳春,林怡,王义祥*. 生物炭对茶园酸性红壤氮素养分淋溶的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 181-186. |
| [14] | 朱国龙,王转,龙怀玉*,张认连,喻科凡. 负压供水下土壤水分对樱桃萝卜生长及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(12): 127-136. |
| [15] | 王转,朱国龙,龙怀玉*,张认连,申哲,曲潇琳,喻科凡. 土壤水分时间变异对玉米生长及水分效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(11): 153-164. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号