




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 23-33.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0172
收稿日期:2022-03-07
接受日期:2022-05-06
出版日期:2023-09-15
发布日期:2023-09-28
作者简介:单莉莉 E-mail:sdszfm@163.com
基金资助:Received:2022-03-07
Accepted:2022-05-06
Online:2023-09-15
Published:2023-09-28
摘要:
为探明孕穗期低温胁迫对不同品种水稻叶片生理特性和结实率的影响差异及外源褪黑素(melatonin,MT)对低温胁迫的缓解效应,以2个耐冷性不同的水稻品种龙粳11(LJ11,冷敏型)和龙稻5(LD5,耐冷型)为材料进行盆栽试验,于孕穗期分别进行低温(16 ℃)以及喷施100 μmol·L-1的MT处理,以室外温度、喷施清水为对照,探讨低温和外源MT对水稻叶片膜质过氧化、渗透调节、抗氧化酶活性等生理指标和结实率的影响。结果表明,低温胁迫下,耐冷型品种龙稻5的结实率变化较小,冷敏型品种龙粳11的结实率显著降低了5.96%~45.26%;龙稻5和龙粳11叶片中丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)和过氧化氢(hydrogen peroxide, H2O2)含量均显著提高,超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase,POD)活性均显著提高。同时低温胁迫也导致渗透调节物质含量增加,龙稻5和龙粳11叶片中可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖和脯氨酸含量均显著提高。叶面喷施外源MT能够有效缓解低温对水稻的伤害,对冷敏品种效果更为明显,可显著降低龙粳11叶片内MDA和H2O2含量;显著提高SOD和POD活性;可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸含量也显著增加。叶面喷施外源MT也可减轻低温对结实率的影响,龙粳11结实率极显著提高了3.13%~16.64%。综上,低温胁迫下MT能够诱导水稻叶片内抗氧化酶活性提高、渗透调节物质显著增加,有效地清除活性氧,进而提高了水稻的抗寒性。
中图分类号:
单莉莉. 孕穗期低温对水稻叶片生理、产量的影响及外源褪黑素缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 23-33.
Lili SHAN. Effects of Low Temperature During Booting Stage on Rice Physiology and Alleviating Effect of Exogenous Melatonin[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 23-33.
处理 Treatment | 药剂 Pesticide | 温度 Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 喷施MT Spray MT | 恒定16 ℃ Constant 16 ℃ |
| T2 | 喷施清水 Spray water | 恒定16 ℃ Constant 16 ℃ |
| CK | 喷施清水 Spray water | 常温 Normal temperature |
表1 试验设计
Table 1 Test design scheme
处理 Treatment | 药剂 Pesticide | 温度 Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 喷施MT Spray MT | 恒定16 ℃ Constant 16 ℃ |
| T2 | 喷施清水 Spray water | 恒定16 ℃ Constant 16 ℃ |
| CK | 喷施清水 Spray water | 常温 Normal temperature |
| 材料 Material | 处理Treatment | 处理天数 Days after treating/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 龙稻5 LD5 | T1 | 99.24±0.04 Aa | 99.25±0.04 Aa | 99.27±0.06 Aa | 99.22±0.11 Aa | 99.24±0.07 Aa |
| T2 | 99.34±0.05 Aa | 99.31±0.04 Aa | 99.22±0.05 Aa | 99.22±0.11 Aa | 99.21±0.07 Aa | |
| CK | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.05 Aa | 99.41±0.01 Aa | |
| 龙粳11 LJ11 | T1 | 62.95±0.08 Bb | 60.89±0.08 Bb | 56.71±0.41 Bb | 51.44±0.64 Bb | 38.74±0.45 Bb |
| T2 | 61.04±0.09 Cc | 56.48±0.07 Cc | 50.76±0.48 Cc | 44.10±0.36 Cc | 35.53±0.35 Cc | |
| CK | 64.91±0.15 Aa | 64.91±0.07 Aa | 64.91±0.26 Aa | 64.91±0.35 Aa | 64.91±0.21 Aa | |
表2 不同处理下水稻的结实率 (%)
Table 2 Seed-setting of rice under different treatments
| 材料 Material | 处理Treatment | 处理天数 Days after treating/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 龙稻5 LD5 | T1 | 99.24±0.04 Aa | 99.25±0.04 Aa | 99.27±0.06 Aa | 99.22±0.11 Aa | 99.24±0.07 Aa |
| T2 | 99.34±0.05 Aa | 99.31±0.04 Aa | 99.22±0.05 Aa | 99.22±0.11 Aa | 99.21±0.07 Aa | |
| CK | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.03 Aa | 99.41±0.05 Aa | 99.41±0.01 Aa | |
| 龙粳11 LJ11 | T1 | 62.95±0.08 Bb | 60.89±0.08 Bb | 56.71±0.41 Bb | 51.44±0.64 Bb | 38.74±0.45 Bb |
| T2 | 61.04±0.09 Cc | 56.48±0.07 Cc | 50.76±0.48 Cc | 44.10±0.36 Cc | 35.53±0.35 Cc | |
| CK | 64.91±0.15 Aa | 64.91±0.07 Aa | 64.91±0.26 Aa | 64.91±0.35 Aa | 64.91±0.21 Aa | |
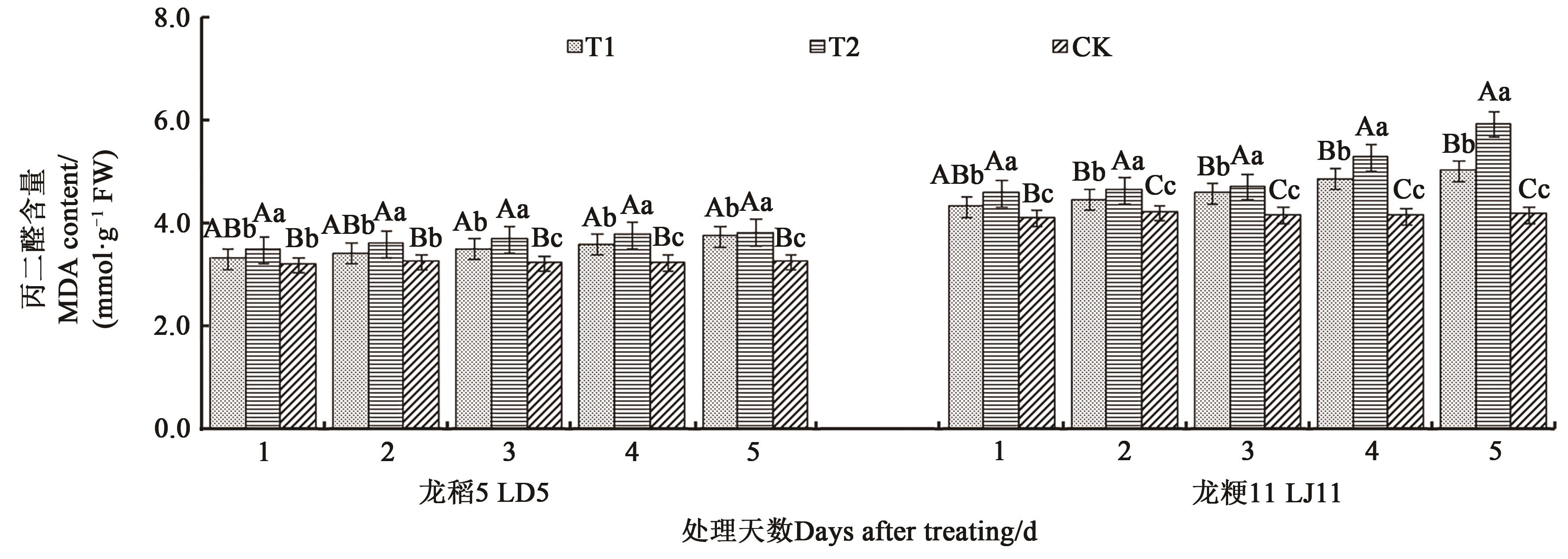
图1 不同处理下水稻叶片的丙二醛含量注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 MDA content in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
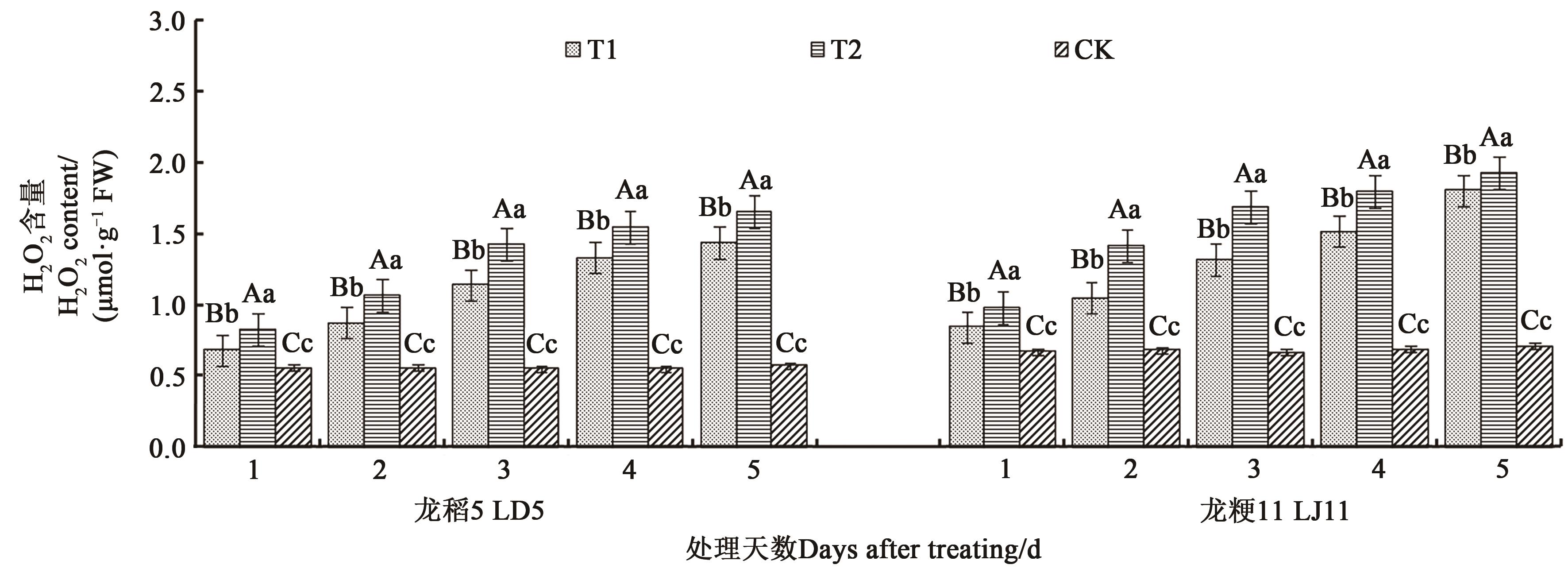
图2 不同处理下水稻叶片的过氧化氢含量注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 H2O2 content in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between differnet treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
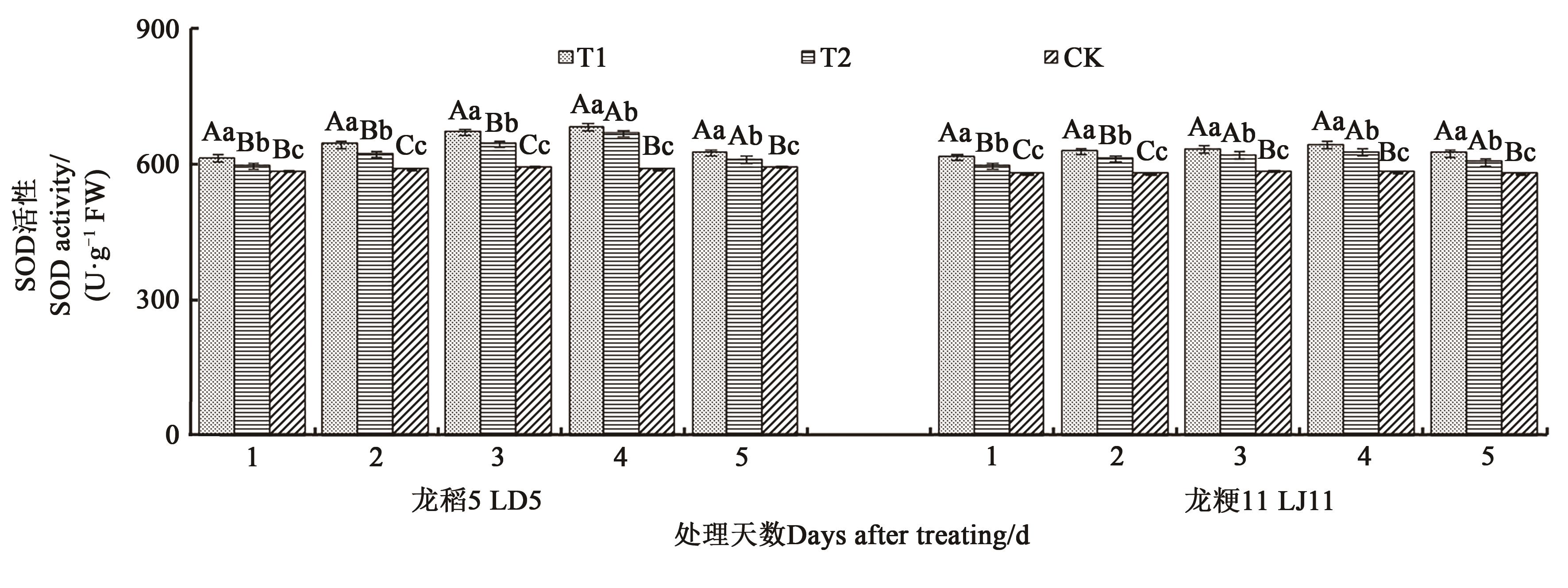
图3 不同处理下水稻叶片的超氧化物歧化酶活性注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 SOD activity in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
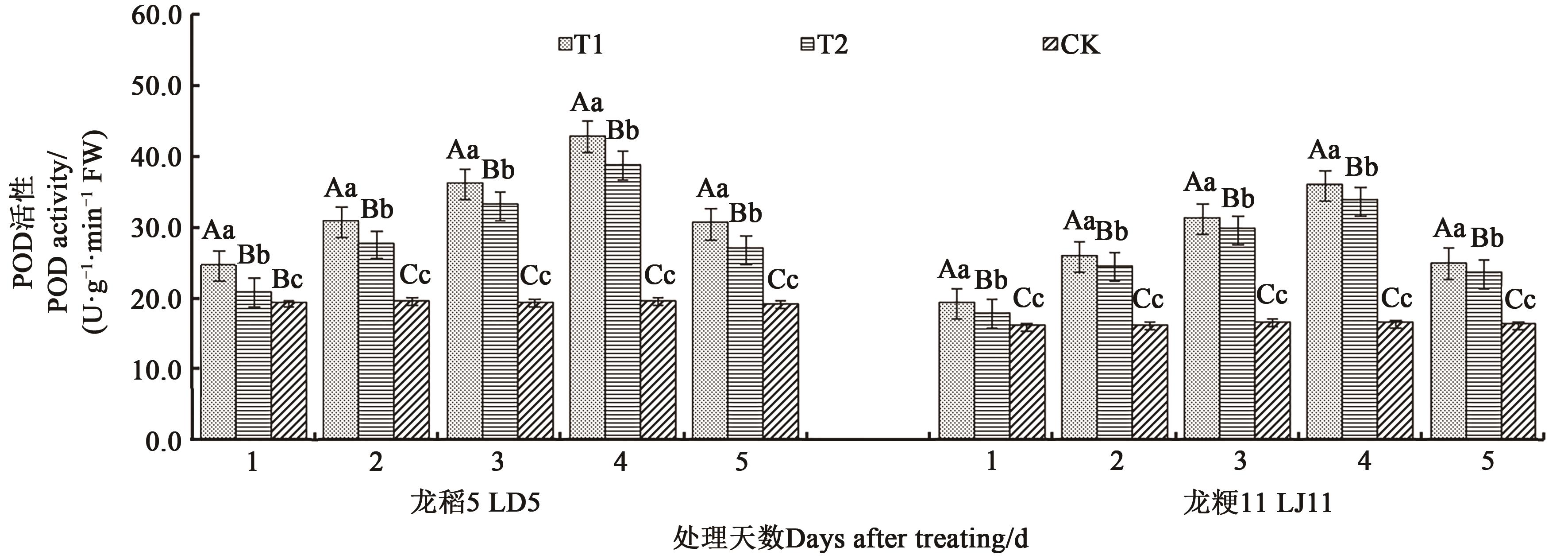
图4 不同处理下水稻叶片的过氧化物酶活性注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 POD activity in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between differnet treatments in same variety column at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | 处理天数Days after treating/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 龙稻5 LD5 | T1 | 25.01±0.26 Bc | 20.96±0.12 Cc | 18.62±0.13 Bc | 15.94±0.13 Cc | 20.49±0.12 Cc |
| T2 | 28.74±0.40 Ab | 22.54±0.06 Bb | 19.56±0.06 Bb | 17.19±0.09 Bb | 22.68±0.06 Bb | |
| CK | 30.35±0.15 Aa | 30.04±0.06 Aa | 30.68±0.18 Aa | 30.24±0.19 Aa | 31.03±0.17 Aa | |
| 龙粳11 LJ11 | T1 | 32.06±0.14 Cc | 24.25±0.18 Bc | 20.28±0.04 Bc | 17.92±0.18 Bb | 25.09±0.21 Bb |
| T2 | 33.52±0.17 Bb | 25.13±0.07 Bb | 20.95±0.12 Bb | 18.60±0.10 Bb | 25.73±0.33 Bb | |
| CK | 36.18±0.05 Aa | 35.83±0.24 Aa | 35.26±0.16 Aa | 35.46±0.28 Aa | 35.72±0.50 Aa | |
表3 不同处理下水稻叶片的SOD/POD比值
Table 3 SOD/POD ratio in leaves of rice under different treatments
材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | 处理天数Days after treating/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 龙稻5 LD5 | T1 | 25.01±0.26 Bc | 20.96±0.12 Cc | 18.62±0.13 Bc | 15.94±0.13 Cc | 20.49±0.12 Cc |
| T2 | 28.74±0.40 Ab | 22.54±0.06 Bb | 19.56±0.06 Bb | 17.19±0.09 Bb | 22.68±0.06 Bb | |
| CK | 30.35±0.15 Aa | 30.04±0.06 Aa | 30.68±0.18 Aa | 30.24±0.19 Aa | 31.03±0.17 Aa | |
| 龙粳11 LJ11 | T1 | 32.06±0.14 Cc | 24.25±0.18 Bc | 20.28±0.04 Bc | 17.92±0.18 Bb | 25.09±0.21 Bb |
| T2 | 33.52±0.17 Bb | 25.13±0.07 Bb | 20.95±0.12 Bb | 18.60±0.10 Bb | 25.73±0.33 Bb | |
| CK | 36.18±0.05 Aa | 35.83±0.24 Aa | 35.26±0.16 Aa | 35.46±0.28 Aa | 35.72±0.50 Aa | |
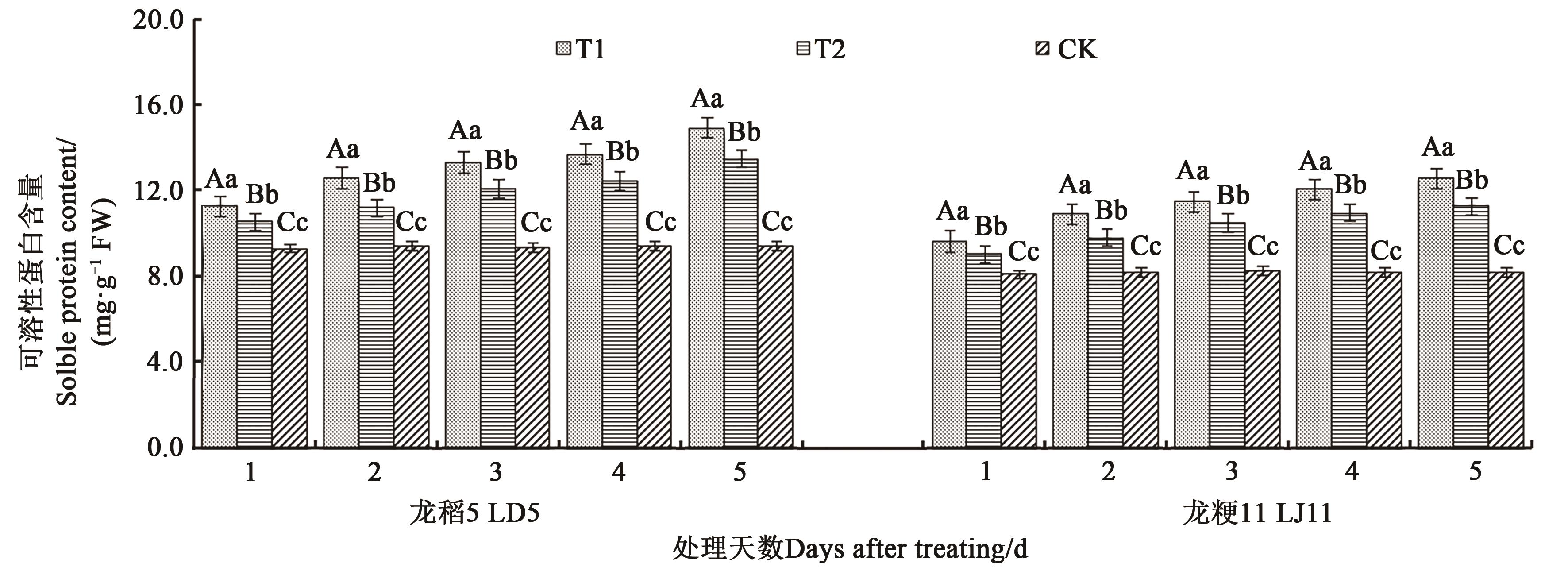
图5 不同处理下水稻叶片的可溶性蛋白的含量注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Soluble protein content in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.

图6 不同处理下水稻叶片的可溶性糖的含量注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Soluble sugar content in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
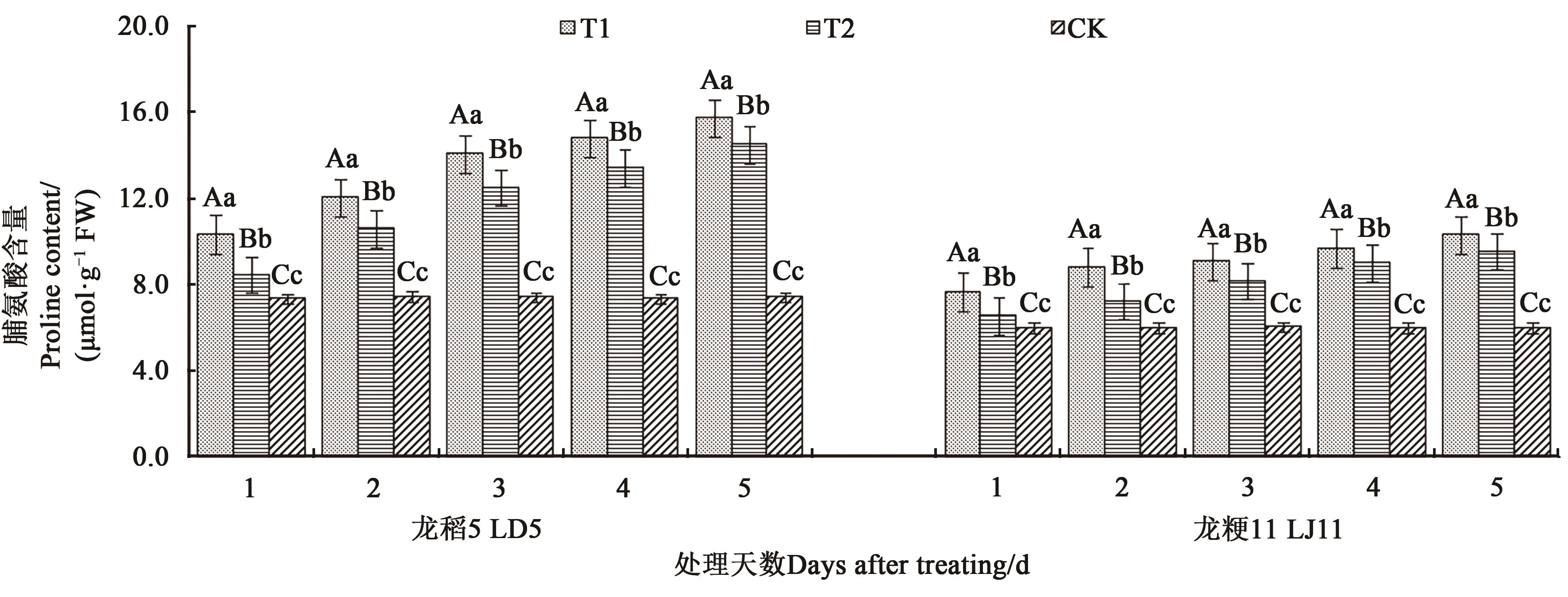
图7 不同处理下水稻叶片的脯氨酸的含量注:不同大、小写字母分别表示同一品种不同处理间在P<0.01和P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 Proline content in leaves of rice under different treatmentsNote:Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between differnet treatments in same variety at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 梁琴, 周泽弘, 马雪清, 等. 绿肥翻压与氮肥减施对水稻产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021,23(10): 124-130. |
| LIANG Q, ZHOU Z H, MA X Q, et al.. Effects of green manure turning over and nitrogen reducing on rice yield, quality and soil fertility [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021,23(10): 124-130. | |
| 2 | 杨文飞, 杜永林, 顾大路, 等. 4种调节物质对水稻耐低温能力的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2017,33(4): 739-746. |
| YANG W F, DU Y L, GU D L, et al.. Effects of four kinds of regulatory agents on cold-tolerance of rice [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2017,33(4): 739-746. | |
| 3 | 项洪涛, 王彤彤, 郑殿峰, 等. 孕穗期低温条件下ABA对水稻结实率及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016,32(36): 16-23. |
| XIANG H T, WANG T T, ZHENG D F, et al.. Effect of ABA seed-setting rate and physiological characteristics of rice leaves under low temperature stress at booting stage [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016,32(36): 16-23. | |
| 4 | CRUA R P, SPEROTTO R A, CARGNELUTTI D, et al.. Avoiding damage and achieving cold tolerance in rice plants [J]. Food Energy Secur., 2013, 2(2): 96-119. |
| 5 | 蔡志欢, 张桂莲. 水稻低温冷害研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2018,32(3): 249-255. |
| CAI Z H, ZHANG G L. Research progress on low temperature and chilling injury of rice [J]. Crop Res., 2018,32(3): 249-255. | |
| 6 | OLIVER S N, DENNIS E S, DOLFERUS R. ABA regulates apoplastic sugar transport and is a potential signal for cold-induced pollen sterility in rice [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2007, 48(9):1319-1330. |
| 7 | RUDLGER H. Melatonin and the theories of aging: a critical appraisal of melatonin’s role in antiaging mechanisms [J]. J. Pineal Res., 2013,55(4): 325-356. |
| 8 | 柯希望, 徐鹏, 殷丽华, 等. 褪黑素延缓红小豆叶片衰老的作用研究[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2015,27(5): 52-55. |
| KE X W, XU P, YIN L H, et al.. Exogenous application of melatonin delays leaf senescence in adzuki bean [J]. J. Heilongjiang Bayi Agric. Univ., 2015,27(5): 52-55. | |
| 9 | 李贺, 姜欣悦, 陈忠诚, 等. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下大豆V1期幼苗光合荧光及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020,42(4): 640-648. |
| LI H, JIANG X Y, CHEN Z C, et al.. Effect of exogenous melatonin on photosynthetic fluorescence and antioxidant system of soybean V1 seedlings under low temperature [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2020,42(4): 640-648. | |
| 10 | 张嘉雯, 卢绍浩, 赵喆, 等. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下烟草幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020,22 (9): 78-86. |
| ZHANG J W, LU S H, ZHAO Z, et al.. Influences of exogenous melatonin on physiological properties of tobacco seedlings under low temperature stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020,22(9): 78-86. | |
| 11 | 史中飞, 梁娟红, 张小花, 等. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下油菜幼苗抗寒性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2019,37(4): 163-170. |
| SHI Z F, LIANG J H, ZHANG X H, et al.. Effect of exogenous melatonin on cold resistance of Brassica rapa seedlings under low temperature stress [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2019,37(4): 163-170. | |
| 12 | 黄益宗, 蒋航, 王农, 等. 外源褪黑素对砷胁迫下水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018,37(6): 1738-1743. |
| HUANG Y Z, JIANG H, WANG N, et al.. Effect of exogenous melatonin on the growth of rice seedlings under as stress [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2018,37(6): 1738-1743. | |
| 13 | 宋雪飞, 甘淳丹, 赵海燕, 等. 叶面喷施褪黑素调控水稻幼苗耐盐性的浓度效应研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2018,55(2): 455-466. |
| SONG X F, GAN C D, ZHAO H Y, et al.. Concentration-dependent effect of foliar spraying of melatonin on salt tolerance of rice [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2018,55(2): 455-466. | |
| 14 | 陈东, 李强, 彭彦, 等. 淹水胁迫下褪黑素浸种对水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019,34(3): 129-136. |
| CHEN D, LI Q, PENG Y, et al.. Effect of melatonin on rice seedling growth under submergence stress [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2019,34(3): 129-136. | |
| 15 | 石光达, 康鹏, 潘雅清, 等. 干旱复水条件下外源褪黑素对玉米幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021,49(24): 60-66. |
| SHI G D, KANG P, PANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on plant growth and physiology characteristics of maize seedling under drought-rewater treatment [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2021,49(24): 60-66. | |
| 16 | 高安静, 刘婷婷, 周美亮, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下苦荞幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021,52(11): 3003-3012. |
| GAO A J, LIU T T, ZHOU M L, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth and physiological characteristics of tartary buckwheat seedlings under drought stress [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2021,52(11): 3003-3012. | |
| 17 | 吴燕, 乔晓燕, 葛伟强, 等. 高温强光下外源褪黑素对栝楼雌花生理生化特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020,32(3): 421-429. |
| WU Y, QIAO X Y, GE W Q, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on physiological and biochemical characteristics in female flowers of trichosanthes kirilowii under high temperature and strong light [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2020,32(3): 421-429. | |
| 18 | 段文静, 孟妍君, 江丹, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗形态及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(1): 92-104. |
| DUAN W J, MENG Y J, JIANG D, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the morphology and antioxidant enzyme activities of cotton seedlings under salt stress [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022, 30(1): 92-104. | |
| 19 | 赵丽娟, 麻冬梅, 王文静, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗抗氧化能力以及光合作用效率的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021,41(8): 1355-1363. |
| ZHAO L J, MA D M, WANG W J, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on antioxidant capacity and photosynthetic efficiency of Alfalfa seedling under salt stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2021,41(8): 1355-1363. | |
| 20 | 项洪涛,王立志,王彤彤,等. 孕穗期低温胁迫对水稻结实率及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 农学学报,2016,32(11): 1-7. |
| XIANG H T, WANG L Z, WANG T T, et al.. Effect of low temperature stress on seed-setting rate and physiological characteristics of rice leaves at booting stage [J]. J. Agric., 2016,32(11): 1-7. | |
| 21 | 李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰. 植物生理生化试验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000:167-169, 184-185. |
| 22 | CHAKRABARTY D, DATTA S K. Micropropagation of gerbera: lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities during acclimatization process [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant,2008,30(3), 325-331. |
| 23 | 张宪政. 作物生理研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1992:201-202. |
| 24 | 路正禹,李任任,於丽华,等.低温胁迫下秸秆覆盖对甜菜子叶期幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 中国糖料,2021,43(1): 29-35. |
| LU Z Y, LI R R, YU L H, et al.. Effects of straw covering on physiological indexes of sugar beet seedlings in cotyledon stage under low temperature stress [J]. Sugar Crop Chin., 2021,43(1): 29-35. | |
| 25 | 余燕, 张雅婷, 赵雪, 等. H2O2浸种对低温胁迫下花生种子萌发的调控作用[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020,42(5): 860-868. |
| YU Y, ZHANG Y T, ZHAO X, et al.. Effects of seed soaking with H2O2 on seed germination of peanut under low temperature conditions [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2020,42(5): 860-868. | |
| 26 | 王芳,王淇,赵曦阳.低温胁迫下植物的表型及生理响应机制研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种,2019,17(15): 5144-5153. |
| WANG F, WANG Q, ZHAO X Y. Research progress of phenotype and physiological response mechanism of plants under low temperature stress [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding,2019,17(15): 5144-5153. | |
| 27 | 马俊丽,吉乃喆,陈洪菲.低温胁迫对月季生理生化指标的影响试验初报[J]. 南方农业,2020,14(34): 64-68, 77. |
| MA J L, JI N Z, CHEN H F. Preliminary report on the effect of low temperature stress on the physiological and biochemical indexes of Chinese rose [J]. South Chin. Agric.,2020,14(34): 64-68, 77. | |
| 28 | 周伟江, 吴旺嫔, 唐才宝, 等. 外源油菜素内酯对低温胁迫下水稻幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2020,29 (9): 1410-1416. |
| ZHOU W J, WU W P, TANG C B, et al.. Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on germination and physiological characteristics of rice seedling under chilling stress [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2020,29 (9): 1410-1416. | |
| 29 | 刘琪, 栾春晶, 李修平. 寒地水稻耐冷性研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021,49 (12): 5-7, 12. |
| LIU Q, LUAN C J, LI X P. Research progress on cold tolerance of rice in cold region [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2021,49 (12): 5-7, 12. | |
| 30 | 罗秋红, 吴俊, 柏斌, 等. 孕穗期低温灌溉对水稻剑叶和颖花生理特征的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2020,35 (3): 111-118. |
| LUO Q H, WU J, BAI B, et al.. Effects of low temperature irrigation at booting stage on physiological characteristics of sword leaves and spikelets in rice [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2020,35 (3): 111-118. | |
| 31 | 王立志, 项洪涛, 王连敏, 等. 不同水稻品种对孕穗期低温的敏感性分析[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014(9): 14-17. |
| WANG L Z, XIANG H T, WANG L M, et al.. Analysis on susceptibility to chilling injury of different rice cultivars at booting stage [J]. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci., 2014(9): 14-17. | |
| 32 | 曾宪国, 项洪涛, 王立志, 等. 孕穗期不同低温对水稻空壳率的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014(6): 19-21. |
| ZENG X G, XIANG H T, WANG L Z, et al.. Effect of different low temperature on the percentage of rice unfilled grains in booting stage [J]. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci., 2014(6): 19-21. | |
| 33 | KLINGLER J P, BATELLI G, ZHU J K. ABA receptors: the START of a new paradigm in phytohormone signaling [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2010,61(12): 3199-3210. |
| 34 | 尉欣荣, 张智伟, 周雨, 等. 褪黑素对低温和干旱胁迫下多年生黑麦草幼苗生长和抗氧化系统的调节作用[J]. 草地学报, 2020,28 (5): 1337-1345. |
| YU X R, ZHANG Z W, ZHOU Y, et al.. Effects of melatonin on growth and antioxidant system of perennial ryegrass seedlings under cold and drought stress [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin.,2020,28(5): 1337-1345. | |
| 35 | 叶君, 于美玲, 曹梦龙, 等. 水分亏缺条件下褪黑素对春小麦光合特性及产量性状的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2021,49 (2): 24-30. |
| YE J, YU M L, CAO M L, et al.. Effects of melatonin on photosynthetic characteristics and yield traits of spring wheat under water deficit [J]. J. Northern Agric., 2021,49 (2): 24-30. | |
| 36 | 张桂莲, 张顺堂, 肖浪涛, 等. 抽穗开花期高温胁迫对水稻花药、花粉粒及柱头生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014,28(2): 155-166. |
| ZHANG G L, ZHANG S T, XIAO L T, et al.. Effects of high temperature stress on physiological characteristics of anther, pollen and stigma of rice during heading-flowering stage [J]. Chin J. Rice Sci., 2014,28(2): 155-166. | |
| 37 | 陈莉, 刘连涛, 马彤彤, 等. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花种子抗氧化酶活性及萌发的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2019,31(5): 438-447. |
| CHEN L, LIU L T, MA T T, et al.. Effects of melatonin on the antioxidant enzyme activities and seed germination of cotton (gossypium hirsutum L.) under salt-stress conditions [J]. Cotton Sci., 2019,31(5): 438-447. | |
| 38 | 娄慧, 赵曾强, 朱金成, 等. 褪黑素对低温胁迫下棉花种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021,37(35): 13-19. |
| LOU H, ZHAO Z Q, ZHU J C, et al.. Melatonin under low temperature stress: effects on germination characteristics of cotton seeds [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021,37(35): 13-19. | |
| 39 | 苏如奇, 徐志荣, 韩瑞才, 等. NO对低温胁迫下水稻幼苗生理生化特性的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2020,42(2): 213-218. |
| SU R Q, XU Z R, HAN R C, et al.. Effect of exogenous NO on physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice under low temperature stress at seedling stage [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2020,42(2): 213-218. | |
| 40 | 余小芬, 线罕英, 邱学礼, 等.低温与氮肥耦合对水稻生理指标的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020,33(10): 2190-2197. |
| YU X F, XIAN H Y, QIU X L, et al.. Coupling effect of low temperature and nitrogen on physiological indexes of rice [J]. Southwest Chin. J. Agric. Sci., 2020,33(10): 2190-2197. | |
| 41 | 项洪涛, 郑殿峰, 何宁, 等. 植物对低温胁迫的生理响应及外源脱落酸缓解胁迫效应的研究进展[J]. 草业学报,2021,30(1): 208-219. |
| XIANG H T, ZHENG D F, HE N, et al.. Coupling effect of low temperature and nitrogen on physiological indexes of rice [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin.,2021,30(1): 208-219. | |
| 42 | 朱春权, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 等.不同属性特征基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021,35(5): 503-512. |
| ZHU C Q, XU Q S, CAO X C, et al.. Effects of substrates with different properties on chilling tolerance of early rice seedlings [J].Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2021,35(5): 503-512. | |
| 43 | 于奇, 曹亮, 金喜军, 等. 低温胁迫下褪黑素对大豆种子萌发的影响[J]. 大豆科学, 2019, 38 (1): 56-62. |
| YU Q, CAO L, JIN X J, et al.. Effects of melatonin on seed germination of soybean under low temperature stress [J]. Soybean Sci., 2020,33(10): 2190-2197. | |
| 44 | 潘红艳, 张晓庆, 李婕, 等. 褪黑素对低温胁迫后菘蓝种子苗抗氧化性影响[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(2): 238-242. |
| PAN H Y, ZHANG X Q, LI J, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatonin on antioxidant activities in isatis indigotica fort. seedlings after low temperature stress [J]. J. Northwest Univ.(Nat. Sci.), 2013, 43(2): 238-242. |
| [1] | 钱政, 杨孙哲, 张国卿, 郭紫微, 张林朋, 万家兴, 杨红云. 基于卷积神经网络的水稻氮素营养诊断[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 113-121. |
| [2] | 李慧君, 张伟健, 吴伟健, 李高洋, 陈艺杰, 黄枫城, 黄永相, 蔺中, 甄珍. 种植海水稻对滨海盐土化学性质和微生物群落影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [3] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [4] | 张冬梦, 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 罗秋红, 庄文, 刘雄伦, 邓启云, 柏斌. 灌浆期田间自然低温对稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 144-153. |
| [5] | 肖芬芳, 张从合, 王慧, 叶亚峰, 张道林, 汪和廷, 李波, 吴跃进, 刘斌美. 杂交水稻花粉收集装置气力输送系统仿真优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 110-122. |
| [6] | 尹林江, 李威, 赵卫权, 赵祖伦, 吕思思, 孙小琼. 水稻多时相植被指数特征及覆盖度提取研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 83-98. |
| [7] | 曲宗普尺, 毛光锋, 吴敏, 吴洪恺. 水稻种子浸泡液电导率与种子活力的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 35-41. |
| [8] | 王巍, 谢莉娟, 肖东芽, 陈根生, 谢靓, 吴自明, 石绪根, 李辉婕. 江西省双季稻病虫害绿色防控技术模式探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 129-138. |
| [9] | 金辉, 王伟, 颜尘栋, 王薇, 李熙英. 水稻纹枯病生防木霉菌分离鉴定及适应性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 139-148. |
| [10] | 文双雅, 石楠, 陈崇怡, 胡海燕, 高志强. 基于涡度相关法的水稻光能利用率研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 159-166. |
| [11] | 李琼华, 张琳, 韩昕儒, 宋莉莉. 我国双季稻全要素生产率的时空分析及对策建议[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 15-23. |
| [12] | 唐楠锐, 周勇, 张国忠, 梁方, 柯烩彬. 搅种型孔式水稻穴播排种器的性能模拟与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 107-115. |
| [13] | 杨涛, 马小倩, 张全, 张洪亮. 组蛋白修饰在水稻中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 11-20. |
| [14] | 何振嘉, 范王涛, 杜宜春, 王启龙. 基于土体有机重构的水肥耦合对土壤理化性质和水稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [15] | 徐君, 李婷, 胡敏骏, 蒋玉根, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 虞轶俊, 何振艳. 水稻籽粒镉积累KASP分子标记LCd-38的开发与利用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 40-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号 