




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 201-212.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0932
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
王兴松1( ), 王娜1(
), 王娜1( ), 杜宇1, 周鹏1, 王戈1, 贾孟1, 徐照丽2(
), 杜宇1, 周鹏1, 王戈1, 贾孟1, 徐照丽2( ), 白羽祥1(
), 白羽祥1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-29
接受日期:2023-01-12
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-12
通讯作者:
徐照丽,白羽祥
作者简介:王兴松 E-mail:2962435088@qq.com基金资助:
Xingsong WANG1( ), Na WANG1(
), Na WANG1( ), Yu DU1, Peng ZHOU1, Ge WANG1, Meng JIA1, Zhaoli XU2(
), Yu DU1, Peng ZHOU1, Ge WANG1, Meng JIA1, Zhaoli XU2( ), Yuxiang BAI1(
), Yuxiang BAI1( )
)
Received:2022-10-29
Accepted:2023-01-12
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-12
Contact:
Zhaoli XU,Yuxiang BAI
摘要:
为进一步明确有机肥增施对植烟土壤微生态环境的影响及其内在相互作用,通过田间试验,在常规化学肥料基础上分别增施0、3 000、6 000和12 000 kg·hm-2有机肥,研究其对土壤有机质组分、理化性质及微生物群落特征的影响。结果表明,增施有机肥显著提升了植烟土壤pH及有机质和速效养分含量;随着有机肥施入量的增加,土壤颗粒有机质、水溶性有机碳、微生物量碳氮及轻组有机质含量均呈现增加趋势,其中有机质含量提升7%~28%,速效钾含量提升10%~61%,微生物量碳提升14%~20%,微生物量氮提升24%以上。增施有机肥处理提高植烟土壤细菌与真菌的ACE指数,土壤中变形菌门、担子菌门、枝顶孢霉属、假单胞菌属等有益菌群的丰度明显增加;Bryobacter、Haliangium等菌群丰度明显降低,且其丰度与土壤活性有机质含量呈负相关。综上所述,增施有机肥刺激了土壤有益微生物菌群的生长和繁殖,提高了植烟土壤活性有机质组分含量,改善了土壤理化性状。
中图分类号:
王兴松, 王娜, 杜宇, 周鹏, 王戈, 贾孟, 徐照丽, 白羽祥. 有机肥对玉溪植烟土壤有机质组分和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 201-212.
Xingsong WANG, Na WANG, Yu DU, Peng ZHOU, Ge WANG, Meng JIA, Zhaoli XU, Yuxiang BAI. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on Organic Matter Composition and Microbial Community Structure of Tobacco-Growing Soil in Yuxi[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 201-212.
pH pH | 有机质 OM/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP/(g·kg-1) | 全钾 TK/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 AN/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.28 | 19.37 | 0.98 | 0.27 | 6.02 | 85.26 | 8.68 | 249.13 |
表1 供试土壤基本养分性状
Table 1 Basic nutrient properties of tested soil
pH pH | 有机质 OM/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP/(g·kg-1) | 全钾 TK/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 AN/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.28 | 19.37 | 0.98 | 0.27 | 6.02 | 85.26 | 8.68 | 249.13 |
| 指标Index | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | 粗颗粒有机质 cPOM | 5.39±0.12 d | 8.63±0.15 c | 12.25±0.23 b | 14.71±0.56 a |
| 细颗粒有机质fPOM | 2.56±0.35 c | 3.10±0.03 b | 3.46±0.03 b | 3.74±0.10 a | |
| 矿物结合有机质MOM | 19.78±0.24 a | 18.04±0.18 b | 17.95±0.68 b | 16.98±0.24 c | |
| 占比Percentage/% | 矿物结合有机质 MOM | 71.33±2.51 a | 60.60±4.44 b | 53.33±0.78 c | 47.93±2.95 d |
| 粗颗粒有机质 cPOM | 19.44±0.11 d | 28.99±2.05 c | 36.40±0.31 b | 41.52±0.78 a | |
| 细颗粒有机质 fPOM | 9.23±0.13 b | 10.41±0.02 a | 10.27±1.02 a | 10.56±0.07 a | |
表2 不同处理下的植烟土壤颗粒有机质组成
Table 2 Organic matter composition of tobacco planting soil particles under different treatments
| 指标Index | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量Content/(g·kg-1) | 粗颗粒有机质 cPOM | 5.39±0.12 d | 8.63±0.15 c | 12.25±0.23 b | 14.71±0.56 a |
| 细颗粒有机质fPOM | 2.56±0.35 c | 3.10±0.03 b | 3.46±0.03 b | 3.74±0.10 a | |
| 矿物结合有机质MOM | 19.78±0.24 a | 18.04±0.18 b | 17.95±0.68 b | 16.98±0.24 c | |
| 占比Percentage/% | 矿物结合有机质 MOM | 71.33±2.51 a | 60.60±4.44 b | 53.33±0.78 c | 47.93±2.95 d |
| 粗颗粒有机质 cPOM | 19.44±0.11 d | 28.99±2.05 c | 36.40±0.31 b | 41.52±0.78 a | |
| 细颗粒有机质 fPOM | 9.23±0.13 b | 10.41±0.02 a | 10.27±1.02 a | 10.56±0.07 a | |
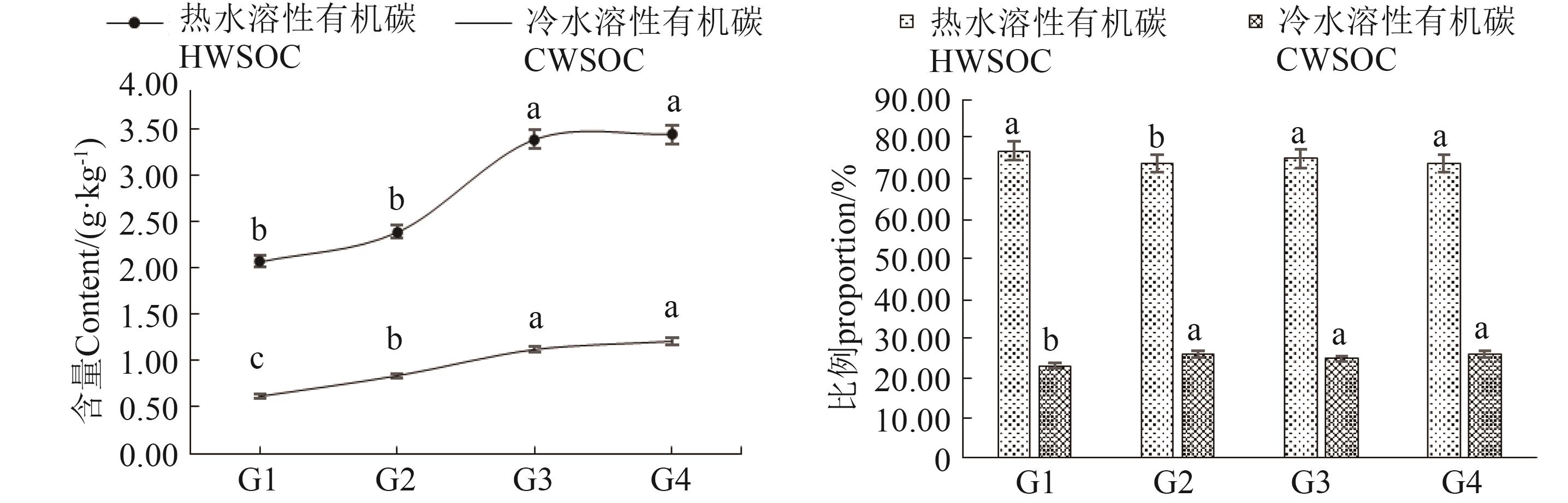
图1 不同处理下对植烟土壤水溶性有机碳组分与比例注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Composition and proportion of water-soluble organic carbon in tobacco-growing soil under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters of the same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
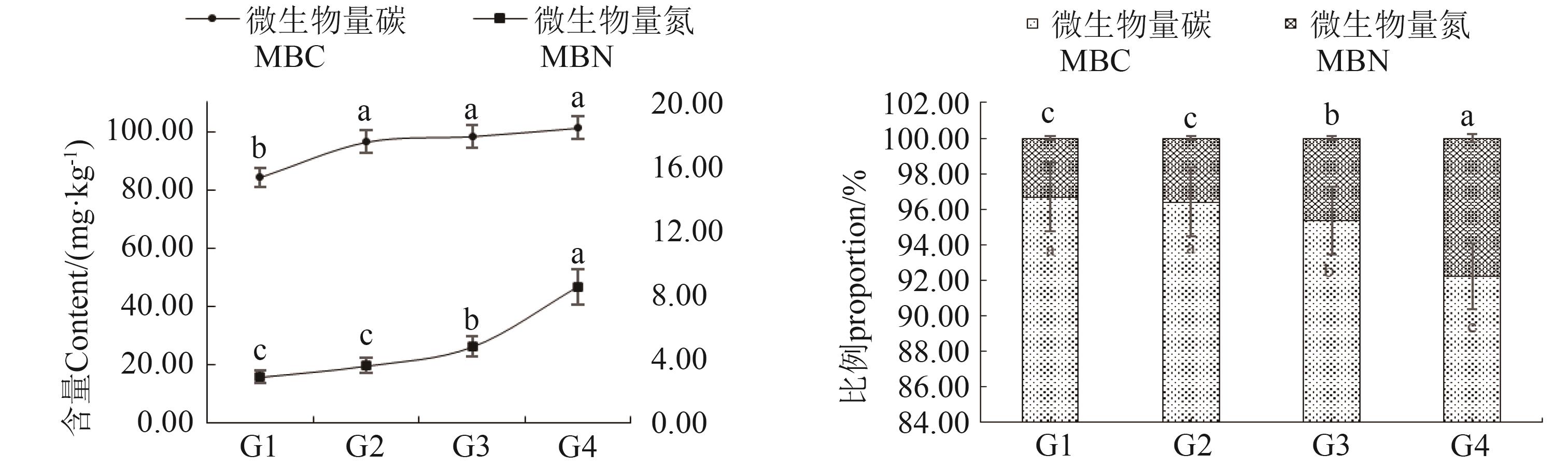
图2 不同处理下对植烟土壤微生物量碳、氮含量和比例注:同一指标不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 The content and proportion of carbon, nitrogen and nitrogen were treated differentlyNote: Different lowercase letters of the same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
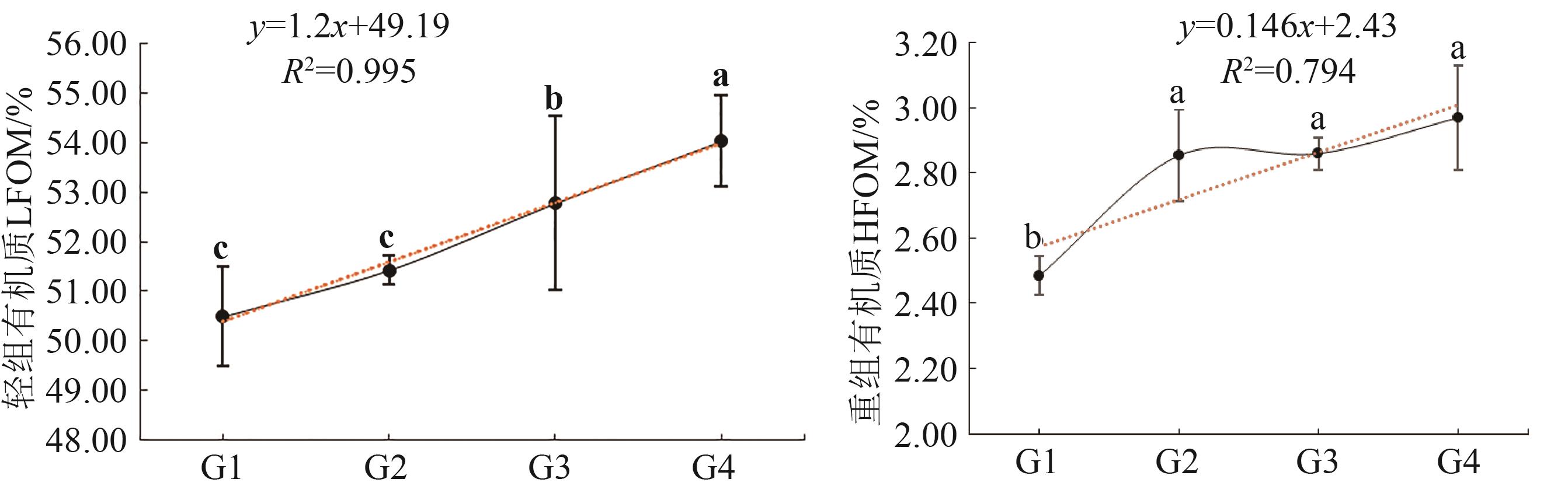
图3 不同处理下植烟土壤轻组有机质和土壤重组有机质组成注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Light organic matter and reconstituted organic matter in tobacco-growing soil under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | pH | 有机质OM/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮AN/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾AK/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 6.22±0.04 b | 27.73±1.10 c | 96.55±3.38 b | 16.09±0.03 b | 543.33±22.04 d |
| G2 | 6.41±0.04 a | 29.77±2.25 b | 98.52±0.28 b | 16.73±0.48 b | 598.47±11.33 c |
| G3 | 6.37±0.05 a | 33.65±0.51 a | 111.33±4.08 a | 17.92±0.68 a | 670.00±5.73 b |
| G4 | 6.34±0.05 a | 35.43±1.22 a | 113.42±2.34 a | 18.35±0.50 a | 873.33±27.35 a |
表3 不同处理下的植烟土壤理化性质
Table 3 Physicochemical properties of tobacco-growing soil under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | pH | 有机质OM/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮AN/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾AK/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 6.22±0.04 b | 27.73±1.10 c | 96.55±3.38 b | 16.09±0.03 b | 543.33±22.04 d |
| G2 | 6.41±0.04 a | 29.77±2.25 b | 98.52±0.28 b | 16.73±0.48 b | 598.47±11.33 c |
| G3 | 6.37±0.05 a | 33.65±0.51 a | 111.33±4.08 a | 17.92±0.68 a | 670.00±5.73 b |
| G4 | 6.34±0.05 a | 35.43±1.22 a | 113.42±2.34 a | 18.35±0.50 a | 873.33±27.35 a |
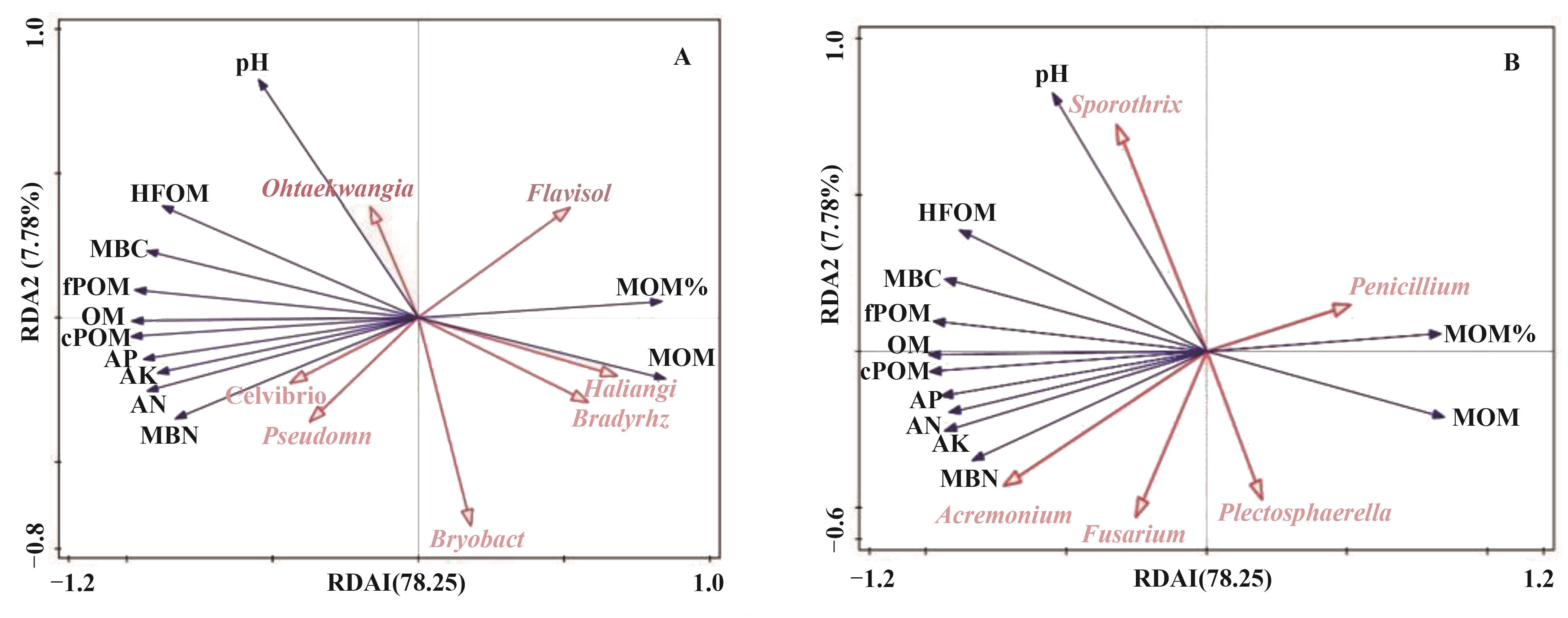
图9 优势菌属与理化性质、有机质组分的相关性分析注:HFOM—重组有机质;MBC—微生物量碳;MBN—微生物量氮;fPOM—细颗粒有机质;OM—有机质;cPOM—粗颗粒有机质;AP—有效磷;AK—速效钾;AN—碱解氮;MOM—矿物结合有机质。
Fig. 9 Correlation analysis of dominant bacteria genera with physicochemical properties and organic matter componentsNote: HFOM—Heavy fraction organic matter;MBC—Microbial biomass carbon;MBN—Microbial biomass nitrogen;fPOM—Fine organic matter; OM—Organic matter;cPOM—Coarse organic matter;AP—Available phosphorus;AK—Available potassium;AN—Hydrolyzed nitrogen;MOM—Minerals combine organic matter.
| 指标Index | 偏回归方程Partial regression equation | 标准化系数Normalization coefficient | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 微生物量氮MBN | Y=-6.311+0.17AK | 0.948 | 0.996** |
| 微生物量碳MBC | Y=33.576+1.845OM+0.139Sporothrix | 0.829; 0.298 | 0.914** |
| 粗颗粒占土壤百分比cPOM% | Y=-19.006+0.983OM | 0.952 | 0.906** |
| 矿物结合有机质MOM | Y=102.173-3.154AP+0.475Haliangium | -0.563; 0.475 | 0.838** |
| 土壤有机质OM | Y=-85.328+0.317AN+13.248pH | 0.796; 0.338 | 0.916** |
表4 土壤有机质组分与理化性状及微生物菌属逐步回归分析
Table 4 Stepwise regression analysis of soil organic matter components, physicochemical properties and microbial genera
| 指标Index | 偏回归方程Partial regression equation | 标准化系数Normalization coefficient | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 微生物量氮MBN | Y=-6.311+0.17AK | 0.948 | 0.996** |
| 微生物量碳MBC | Y=33.576+1.845OM+0.139Sporothrix | 0.829; 0.298 | 0.914** |
| 粗颗粒占土壤百分比cPOM% | Y=-19.006+0.983OM | 0.952 | 0.906** |
| 矿物结合有机质MOM | Y=102.173-3.154AP+0.475Haliangium | -0.563; 0.475 | 0.838** |
| 土壤有机质OM | Y=-85.328+0.317AN+13.248pH | 0.796; 0.338 | 0.916** |
| 1 | 马文富,邓小鹏,杜杏蓉,等.连作年限对植烟土壤化学特性及烟叶产质量的影响[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2021,36(6):993-999. |
| MA W F, DENG X P, DU X R, et al.. Effects of continuous cropping years on the chemical characteristics of tobacco-planted soil, yield and quality of tobacco leaves [J]. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 36(6):993-999. | |
| 2 | 马瑞萍,戴相林,刘国一,等.施肥模式对青稞田土壤潜在固氮速率和自生固氮微生物群落结构的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2021,29(10):1692-1703. |
| MA R P, DAI X L, LIU G Y, et al.. Effects of fertilizer patterns on the potential nitrogen fixation rate and community structure of Asymbiotic diazotroph in highland barley fields on the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2021, 29(10):1692-1703. | |
| 3 | 王源,朱毓蓉,欧阳铖人,等.有机肥施用对植烟农田土壤肥力及烟叶质量的影响研究进展[J].土壤通报,2020,51(4):1003-1009. |
| WANG Y, ZHU Y R, OUYANG C R, et al.. A review of effect of organic fertilizer on soil fertility and quality of flue-cured tobacco [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2020, 51(4):1003-1009. | |
| 4 | 费裕翀,刘丽,陈钢,等.不同有机肥处理对紫色土油茶林土壤微生物碳源利用的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2020(5):101-108. |
| FEI Y C, LIU L, CHEN G, et al.. Effects of different organic fertilizer treatments on carbon source utilization of soil microbial communities of Camellia oleifera plantation in purple soil area [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2020(5):101-108. | |
| 5 | 许跃奇,阎海涛,王晓强,等.生物碳与有机肥配施对褐土烟田微生物功能多样性的影响[J].中国烟草科学,2020,41(5):55-59, 67. |
| XU Y Q, YAN H T, WANG X Q, et al.. Effects of mixed application of biochar and organic fertilizers on microbial functional diversity in tobacco growing cinnamon soil [J]. Chin. Tobacco Sci., 2020, 41(5):55-59, 67. | |
| 6 | 黄龙,包维楷,李芳兰,等.土壤结构和植被对土壤微生物群落的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报,2021,27(6):1725-1731. |
| HUANG L, BAO W K, LI F L, et al.. Effects of soil structure and vegetation on soil microbial community [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2021, 27(6):1725-1731. | |
| 7 | 吕睿,常帆,张兴昌,等.黄土高原土壤细菌和真菌群落结构及其多样性对菌糠有机肥响应机制研究[J].环境生态学, 2022, 4(Z1):40-49. |
| LYU R, CHANG F, ZHANG X C, et al.. Responses of soil bacterial and fungal community structure and diversity to microbial bran organic manure in the Loess Plateau [J]. Chin. Environ. Biol., 2022, 4(Z1):40-49. | |
| 8 | 李秀英,赵秉强,李絮花,等.不同施肥制度对土壤微生物的影响及其与土壤肥力的关系[J].中国农业科学,2005(8):1591-1599. |
| LI X Y, ZHAO B Q, LI X H, et al.. Effects of different fertilization systems on soil microbe and its relation to soil fertility [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci., 2005(8):1591-1599. | |
| 9 | 苗彤.高通量测序技术在土壤微生物方面的应用研究进展[J].现代农业科技,2020(18):155-156, 162. |
| MIAO T. Research progress on the application of high-thoughput sequencing techonlogy in soil microbial diversity [J]. J. Modern Tech., 2020, (18):155-156, 162. | |
| 10 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| 11 | CAMBARDELLA C A, ELLIOTT E T. Particulate soil organic-matter changes across a grassland cultivation sequence [J/OL]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 1992, 56(3):17 [2022-09-20]. . |
| 12 | 姬强,孙汉印,王勇,等.土壤颗粒有机碳和矿质结合有机碳对4种耕作措施的响应[].水土保持学报,2012,26(2):134-139. |
| JI Q, SUN H Y, WANG Y, et al.. Response of soil particulate organic carbon and mineral-bound organic carbon to four kinds of tillage pratices [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2012, 26(2):134-139. | |
| 13 | 吴宪,王蕊,胡菏,等.潮土细菌及真菌群落对化肥减量配施有机肥和秸秆的响应[J].环境科学,2020,41(10):4669-4681. |
| WU X, WANG R, HU H, et al.. Response of bacterial and fungal communities to chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer and straw in fluvo-aquic soil [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Sci., 2021, 41(10):4669-4681. | |
| 14 | 周东兴,李欣,宁玉翠,等.蚯蚓粪配施化肥对稻田土壤性状和酶活的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2021,52(2):25-35. |
| ZHOU D X, LI X, NING Y C, et al.. Effect of chemical fertilizer combined with vermicompost on soil characters and enzyme activity in paddy fields [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2021, 52(2):25-35. | |
| 15 | 渠晨晨,任稳燕,李秀秀,等.重新认识土壤有机质[J].科学通报, 2022,67(10):913-923. |
| QU C C, REN W Y, LI X X, et al.. Revisit soil organic matter [J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2022, 67(10):913-923. | |
| 16 | CHAO L, CHENG G, DEVINE L, et al.. An absorbing markov chain approach to understanding the microbial role in soil carbon stabilization [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2011, 106(3):303-309. |
| 17 | 周萌,肖扬,刘晓冰.土壤活性有机质组分的分类方法及其研究进展[J].土壤与作物, 2019,8(4):349-360. |
| ZHOU M, XIAO Y, LIU X B. Soil labile organic matter components and research progress [J]. Soils Crops, 2019, 8(4):349-360. | |
| 18 | 张久明,匡恩俊,刘亦丹,等.有机肥替代不同比例化肥对土壤有机碳组分的影响[J].麦类作物学报, 2021,41(12):1534-1540. |
| ZHANG J M, KUANG EN J, LIU Y D, et al.. Effect of different proportions of labile organic fertilizer substituted by nitrogen fertilizer on components of soil organic carbon [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(12):1534-1540. | |
| 19 | 宁川川,王建武,蔡昆争.有机肥对土壤肥力和土壤环境质量的影响研究进展[J].生态环境学报,2016,25(1):175-181. |
| NING C C, WANG J W, CAI K Z. The effects of organic fertilizers on soil fertility and soil environmental quality: a review [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2016, 25(1):175-181. | |
| 20 | 李潇潇,师桂英,张立彭,等.荧光假单胞菌(Pseudomonas fluorescens)在植物病害生物防治中的研究及展望[J].草原与草坪, 2021,41(5):148-156. |
| LI X X, SHI G X, ZHANG L P, et al.. Identification and characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens for biological control of plant diseases [J]. Grassl. Turf, 2021, 41(5):148-156. | |
| 21 | 王利利,董民,张璐,等.不同碳氮比有机肥对有机农业土壤微生物生物量的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2013,21(9):1073-1077. |
| WANG L L, DONG M, ZHANG L, et al.. Effects of organic manures with different carbon-to-nitrogen ratios on soil microbial biomass of organic agriculture [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2013, 21(9):1073-1077. | |
| 22 | 李婧,迟凤琴,魏丹,等.不同有机物料还田对黑土活性有机碳组分含量的影响[J].大豆科学,2016,35(6):975-980. |
| LI Q, CHI F Q, WEI D, et al.. Effects of different organic materials returning to field on active organic carbon components in black soil [J]. Soybean Sci., 2016, 5(6):975-980. | |
| 23 | 周东兴,李欣,宁玉翠,等.蚯蚓粪配施化肥对稻田土壤性状和酶活的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2021,52(2):25-35. |
| ZHOU D X, LI X, NING Y C, et al.. Effect of chemical fertilizer combined with vermicompost on soil characters and enzyme activity in paddy fields [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2021, 52(2):25-35. | |
| 24 | 付海丽.牛粪与化肥配施对侧柏根际土壤微生物数量和酶活性的影响[J].生物灾害科学,2014,37(2):134-139. |
| FU H L. Effect of cattle manure co-applied with inorganic fertilizer on microorganism population and enzyme activtiy in the rhizosphere soil of Platycladus orientalis [J]. Bio. Disaster Sci., 2014, 37(2):134-139. | |
| 25 | 谭骏,黄河,汤薇,等.蚯蚓粪有机肥对土壤微生物群落的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2021,49(20):228-233. |
| TAN J, HUANG H, TANG W, et al.. Effects of earthworm manure on soil microbial community [J]. J. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(20): 228-233. | |
| 26 | 王珏,杜琴,彭双,等.不同施肥处理对植烟土壤细菌群落的影响[J].土壤,2021,53(5):998-1007. |
| WANG J, DU Q, PENG S, et al.. Effects of different fertilization treatments on bacterial community in tobacco-planting soil [J]. Soils, 2022, 53(5):998-1007. | |
| 27 | FIERER N, LAUBER C L, RAMIREZ K S, et al.. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients [J]. ISME J., 2012, 6(5):1007-1017. |
| 28 | 王天乐,王晓娟,刘恩科,等.甘蓝、菜豆和玉米不同轮作组合对淡褐土细菌群落和作物产量的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2022,41(2):375-386. |
| WANG T L, WANG X J, LIU EN K, et al.. Effects of different crop rotation combinations of cabbage, kidney bean, and maize on bacterial community and crop yield in light brown soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(2):375-386. | |
| 29 | ZHAO S C, QIU S J, XU X P, et al.. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2019, 138:123-123. |
| 30 | 柴晓虹,姚拓,李录山,等.12株植物根际促生菌促生功能稳定性评价及鉴定[J].草原与草坪,2020,40(5):68-75. |
| CHAI X H, YAO T, LI L S, et al.. Stability evaluation of growth promoting function and identification of 12 PGPR strains [J]. Grassl. Turf, 2020, 40(5):68-75. | |
| 31 | KANAE O S, WHITELAW-WECKERT M, KADAM T A, et al.. Phosphate solubilization by stress-tolerant soil fungus talaromyces funiculosus SLS8 isolated from the neem rhizosphere [J]. Ann. Microbiol., 2015, 65(1):85-93. |
| 32 | 赵雅姣,刘晓静,吴勇,等.西北半干旱区紫花苜蓿-小黑麦间作对根际土壤养分和细菌群落的影响[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(5):1645-1652. |
| ZHAO Y J, LIU X J, WU Y, et al.. Effects of medicago sativa-triticale wittmack intercropping system on rhizosphere soil nutrients and bacterial community in semi-arid region of Northwest China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, 31(5):1645-1652. | |
| 33 | 蓝贤瑾,刘益仁,侯红乾,等.长期有机无机肥配施对红壤性水稻土微生物生物量和有机质结构的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(5):810-819. |
| LAN X J, LIU Y R, HOU H Q, et al.. Effect of long-term organic manure application combined with chemical fertilizers on soil microbial biomass and organic matter structure in red paddy [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2021, 38(5):810-819. |
| [1] | 杨娅琳, 吴峰婧琳, 陈健鑫, 武自强, 刘丽, 张东华, 马焕成, 伍建榕. 油茶根腐病根际土壤、根系内真菌群落结构和多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 121-135. |
| [2] | 王世芳, 宋海燕. 土壤有机质可见-近红外反射光谱特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 183-188. |
| [3] | 姜坤宏, 许祯莹, 郭真真, 白林, 郝晓霞, 姜冬梅, 邱时秀. 微生物电化学技术原理及其在畜禽废弃物资源化领域的应用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 210-222. |
| [4] | 王子凡, 李燕, 张庆银, 王丹丹, 师建华, 耿晓彬, 田东良, 钟增明, 赵晓明, 齐连芬. 微生物菌剂对设施番茄主要病害及土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [5] | 强敬雯, 王晚晴, 唐曼玉, 张娜, 武双, 华威, 邵恒煊, 程艳玲. 厨余垃圾厌氧消化对沼气微生物及环境的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 159-169. |
| [6] | 赵鸿硕, 曹红雨, 高广磊, 孙哲, 张英, 丁国栋. 微生物诱导碳酸钙沉淀固沙对典型沙生植物叶片性状和生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 170-182. |
| [7] | 陈雨欣, 赵红梅, 杨卫君, 杨梅, 郭颂, 宋世龙, 惠超. 生物质炭对土壤微生物碳源利用及春小麦产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 174-183. |
| [8] | 杜洋洋, 包媛媛, 刘项宇, 张新永. 荞麦轮作对云南栽培马铃薯根际土壤酶活和微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 192-200. |
| [9] | 张昱, 张洪波, 张瑜瑜, 陈丽娟, 赵明方, 夏云. 玫瑰秸秆与牲畜粪污厌氧消化特性及微生物群落研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 201-211. |
| [10] | 高丽敏, 顾泽辰, 贡雪菲, 崔联明, 郭东森, 周影, 王琳, 魏启舜. 果园生草对中国果树-土壤系统生产性能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 184-194. |
| [11] | 韩秀丽, 李嘉伟, 张杰, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥替代化肥对葡萄生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 195-205. |
| [12] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [13] | 陈芙蓉, 熊伟仡, 尹娇, 张小卓, 韩宇, 邓毅书. 微生物菌剂对叶菜废弃物堆肥过程的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 146-154. |
| [14] | 周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187. |
| [15] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号