




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 201-210.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0321
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
马振华( ), 时倩茹, 宁欣杰, 魏宏杨, 王璨, 张静静, 张彪(
), 时倩茹, 宁欣杰, 魏宏杨, 王璨, 张静静, 张彪( ), 杨素勤(
), 杨素勤( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-24
接受日期:2023-05-14
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-02-14
通讯作者:
张彪,杨素勤
作者简介:马振华 E-mail:mzh9423@126.com
基金资助:
Zhenhua MA( ), Qianru SHI, Xinjie NING, Hongyang WEI, Can WANG, Jingjing ZHANG, Biao ZHANG(
), Qianru SHI, Xinjie NING, Hongyang WEI, Can WANG, Jingjing ZHANG, Biao ZHANG( ), Suqin YANG(
), Suqin YANG( )
)
Received:2023-04-24
Accepted:2023-05-14
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
Biao ZHANG,Suqin YANG
摘要:
为研究连续施用改性生物质炭对农田镉铅污染土壤修复及线虫群落的影响,以改性生物质炭为材料,开展连施改性生物质炭2、3、4和5年的定位试验。通过测定小麦籽粒和土壤有效态镉铅含量,探究改性生物质炭持续钝化土壤镉铅的能力,并利用高通量测序技术,探究改性生物质炭对土壤线虫群落的影响。结果表明,改性生物质炭能显著降低小麦籽粒和土壤有效态镉铅含量,其中,小麦籽粒镉含量降幅为21%~35%,小麦籽粒铅含量降幅为27%~39%;土壤有效态镉铅含量降幅分别为21%~43%和15%~28%。施用改性生物质炭降低食真菌土壤线虫滑刃属(Aphelenchoides)丰度,而植物寄生性土壤线虫默林属(Merlinius)、针属(Paratylenchus)等占比均增至40%以上。土壤中线虫c-p2类群的比例大幅降低,而c-p3类群占比增加;自由生活线虫成熟指数减少,植物寄生类线虫成熟指数增加,表明不同营养类群、不同生活史的土壤线虫对重金属污染的反应特性不同。整体而言,连施不同年限处理间线虫群落变化不明显。以上表明,小麦籽粒镉含量在连续施用改性生物质炭4年达到最低,小麦籽粒铅含量施用改性生物质炭2年即可低于GB 2762—2017限值0.2 mg·kg-1。施入改性生物质炭可调节线虫群落结构,从而影响土壤环境,在重金属污染土壤综合利用与修复方面具有较强的应用价值。
中图分类号:
马振华, 时倩茹, 宁欣杰, 魏宏杨, 王璨, 张静静, 张彪, 杨素勤. 生物质炭对镉铅污染土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 201-210.
Zhenhua MA, Qianru SHI, Xinjie NING, Hongyang WEI, Can WANG, Jingjing ZHANG, Biao ZHANG, Suqin YANG. Effects of Modified Biochar on Soil Nematode Community in Cadmium and Lead Contaminated Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 201-210.
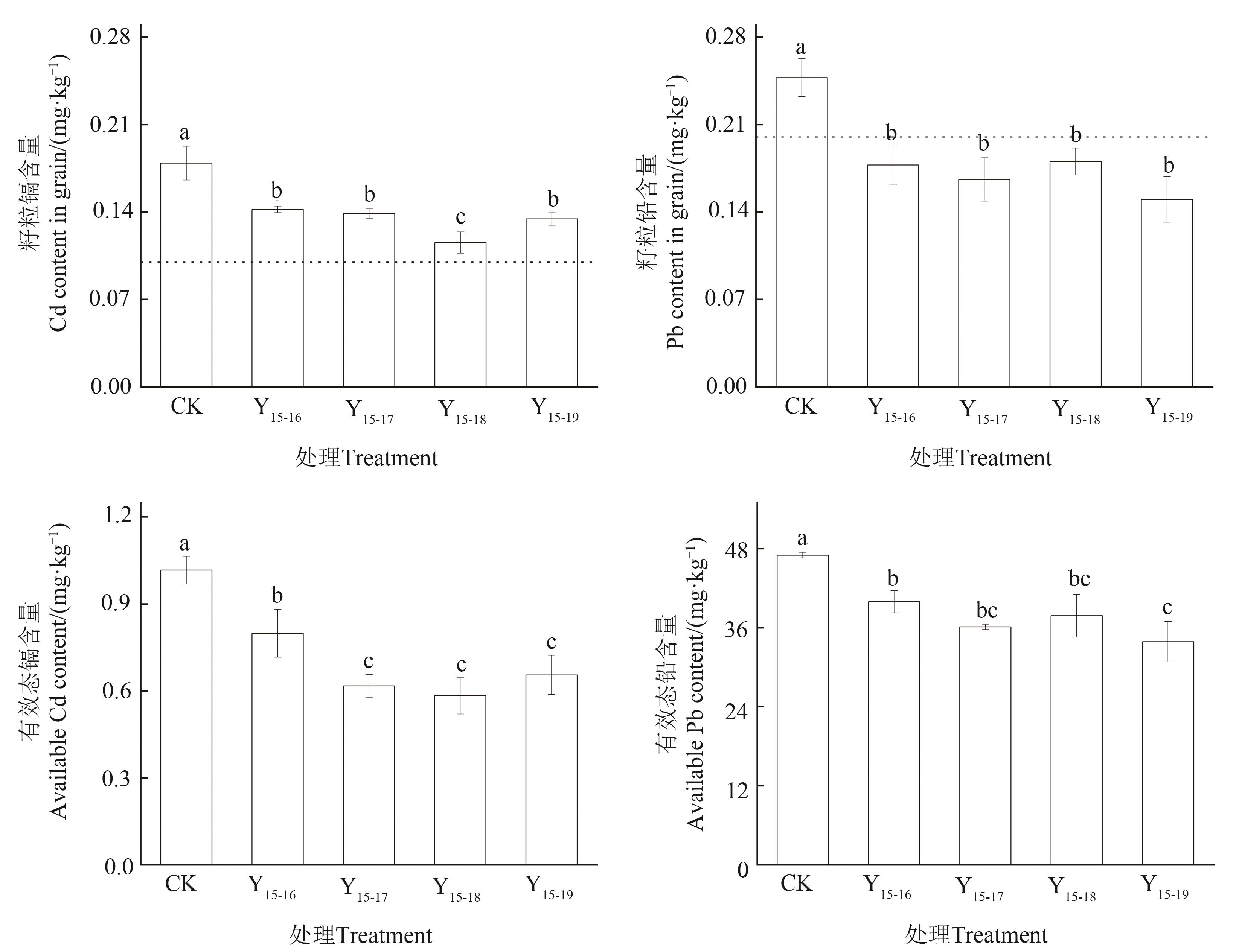
图1 小麦籽粒及土壤有效态镉铅含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。虚线为GB 2762—2017限值。
Fig. 1 Cd and Pb in wheat grain and their available contents in soilNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05 level. The dotted line is the limit value of GB 2762—2017.
营养类型 Nutritional type | 属名 Genus name | c-p值 c-p value | 比例Proportion/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Y15-16 | Y15-17 | Y15-18 | Y15-19 | |||
食细菌线虫 Ba | 丽突属Acrobeles | 2 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| 拟丽突属Acrobeloides | 2 | 9.69 | 13.86 | 8.46 | 5.36 | 10.99 | |
| 无咽属Alaimus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| 头叶属Cephalobus | 2 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 真头叶属Eucephalobus | 2 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.05 | |
| 真单宫属Eumonhystera | 2 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| Oscheius | 1 | 0.61 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.00 | |
| 盆咽属Panagrolaimus | 1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| 绕线属Plectus | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 棱咽属Prismatolaimus | 3 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| 食真菌线虫Fu | 滑刃属Aphelenchoides | 2 | 72.54 | 10.31 | 0.23 | 2.08 | 6.34 |
| 茎属Ditylenchus | 2 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.56 | |
| 丝尾垫刃属Filenchus | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 细齿属Leptonchus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 捕食/杂食性线虫Om | Allodorylaimus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 孔咽属Aporcelaimellus | 5 | 2.37 | 5.28 | 5.60 | 5.47 | 5.74 | |
| 狭咽属Discolaimium | 5 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 盘咽属Discolaimus | 5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 锯齿属Prionchulus | 4 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | |
| Trischistoma | 3 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 植物寄生性线虫Pp | 刺属Belonolaimus | 5 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 环属Criconema | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 居中属Geocenamus | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 螺旋属Helicotylenchus | 3 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | |
| Irantylenchus | 2 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| 默林属Merlinius | 3 | 2.93 | 37.79 | 43.45 | 42.67 | 37.86 | |
| 针属Paratylenchus | 2 | 2.02 | 26.48 | 33.34 | 41.88 | 34.70 | |
| 短体属Pratylenchus | 3 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.06 | |
| Sakia | 2 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 矮化属Tylenchorhynchus | 3 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
表1 土壤线虫群落组成
Table 1 Community composition of soil nematodes
营养类型 Nutritional type | 属名 Genus name | c-p值 c-p value | 比例Proportion/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Y15-16 | Y15-17 | Y15-18 | Y15-19 | |||
食细菌线虫 Ba | 丽突属Acrobeles | 2 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| 拟丽突属Acrobeloides | 2 | 9.69 | 13.86 | 8.46 | 5.36 | 10.99 | |
| 无咽属Alaimus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| 头叶属Cephalobus | 2 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 真头叶属Eucephalobus | 2 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.05 | |
| 真单宫属Eumonhystera | 2 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| Oscheius | 1 | 0.61 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.00 | |
| 盆咽属Panagrolaimus | 1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| 绕线属Plectus | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 棱咽属Prismatolaimus | 3 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| 食真菌线虫Fu | 滑刃属Aphelenchoides | 2 | 72.54 | 10.31 | 0.23 | 2.08 | 6.34 |
| 茎属Ditylenchus | 2 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.56 | |
| 丝尾垫刃属Filenchus | 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 细齿属Leptonchus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 捕食/杂食性线虫Om | Allodorylaimus | 4 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 孔咽属Aporcelaimellus | 5 | 2.37 | 5.28 | 5.60 | 5.47 | 5.74 | |
| 狭咽属Discolaimium | 5 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 盘咽属Discolaimus | 5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 锯齿属Prionchulus | 4 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | |
| Trischistoma | 3 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 植物寄生性线虫Pp | 刺属Belonolaimus | 5 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 环属Criconema | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 居中属Geocenamus | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 螺旋属Helicotylenchus | 3 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | |
| Irantylenchus | 2 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| 默林属Merlinius | 3 | 2.93 | 37.79 | 43.45 | 42.67 | 37.86 | |
| 针属Paratylenchus | 2 | 2.02 | 26.48 | 33.34 | 41.88 | 34.70 | |
| 短体属Pratylenchus | 3 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.06 | |
| Sakia | 2 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 矮化属Tylenchorhynchus | 3 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
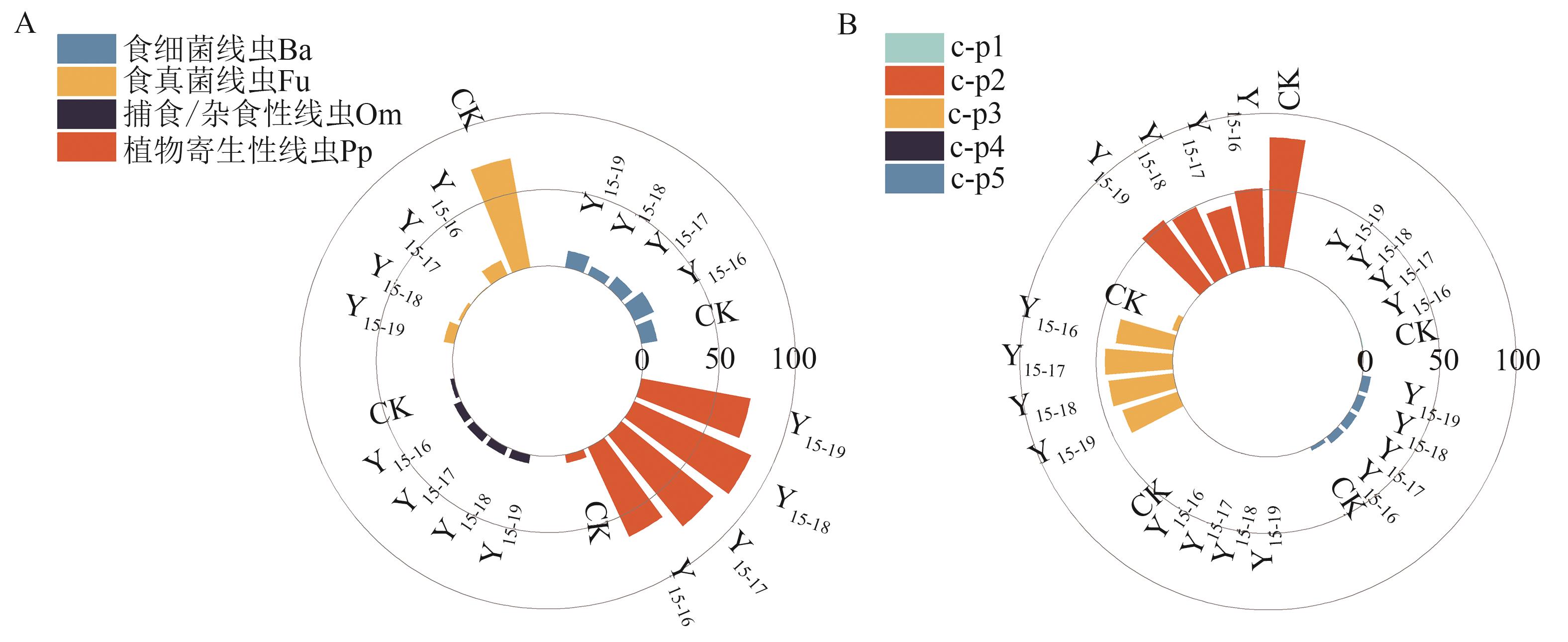
图2 属水平土壤线虫营养类群和生活史策略A:土壤线虫营养类群; B:土壤线虫生活史策略
Fig. 2 Vegetative groups and life history strategies of soil nematodes at the level of genusA:Vegetative groups of soil nematodes; B: Life history strategies of soil nematodes
处理 Treatment | 丰富度指数Abundance index | 均匀度指数 Evenness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 自由生活线虫成熟指数MI | 植物寄生性线虫成熟指数 PPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao指数Chao index | Ace指数 Ace index | Simpsoneven指数Simpsoneven index | Shannoneven指数Shannoneven index | Simpson指数Simpson index | Shannon指数Shannon index | |||
| CK | 22.8 a | 24.0 a | 0.085 b | 0.34 b | 0.55 a | 1.06 b | 1.79 a | 0.14 b |
| Y15-16 | 22.1 a | 22.8 a | 0.177 a | 0.51 a | 0.27 b | 1.55 a | 0.76 b | 1.67 a |
| Y15-17 | 21.5 a | 23.6 a | 0.149 a | 0.43 ab | 0.36 b | 1.29 ab | 0.47 b | 1.99 a |
| Y15-18 | 22.2 a | 22.4 a | 0.141 ab | 0.41 ab | 0.38 b | 1.21 ab | 0.43 b | 2.12 a |
| Y15-19 | 19.7 a | 20.5 a | 0.172 a | 0.48 a | 0.31 b | 1.43 ab | 0.65 b | 1.83 a |
表2 土壤线虫生态指数
Table 2 Ecological index of soil nematodes
处理 Treatment | 丰富度指数Abundance index | 均匀度指数 Evenness index | 多样性指数 Diversity index | 自由生活线虫成熟指数MI | 植物寄生性线虫成熟指数 PPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao指数Chao index | Ace指数 Ace index | Simpsoneven指数Simpsoneven index | Shannoneven指数Shannoneven index | Simpson指数Simpson index | Shannon指数Shannon index | |||
| CK | 22.8 a | 24.0 a | 0.085 b | 0.34 b | 0.55 a | 1.06 b | 1.79 a | 0.14 b |
| Y15-16 | 22.1 a | 22.8 a | 0.177 a | 0.51 a | 0.27 b | 1.55 a | 0.76 b | 1.67 a |
| Y15-17 | 21.5 a | 23.6 a | 0.149 a | 0.43 ab | 0.36 b | 1.29 ab | 0.47 b | 1.99 a |
| Y15-18 | 22.2 a | 22.4 a | 0.141 ab | 0.41 ab | 0.38 b | 1.21 ab | 0.43 b | 2.12 a |
| Y15-19 | 19.7 a | 20.5 a | 0.172 a | 0.48 a | 0.31 b | 1.43 ab | 0.65 b | 1.83 a |
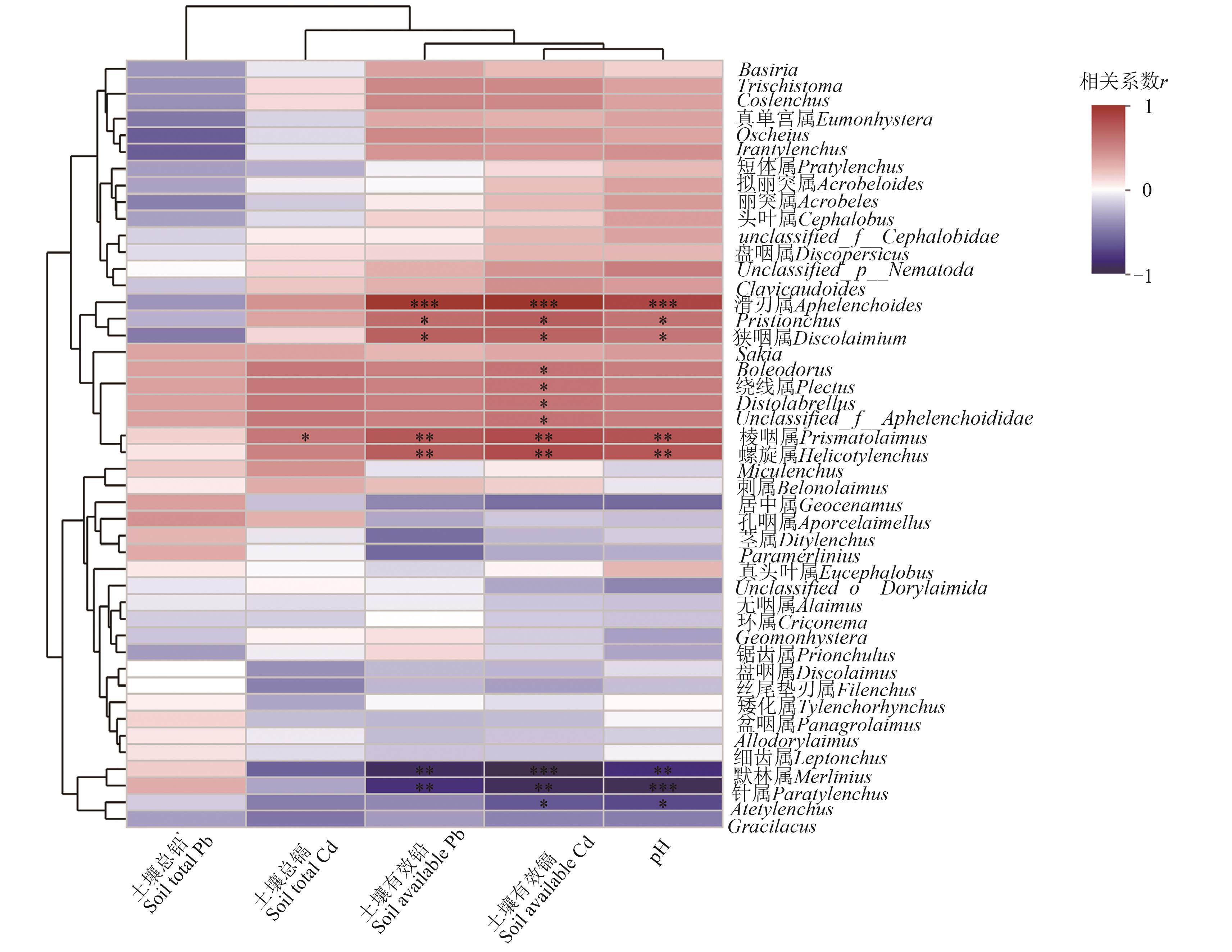
图5 属水平土壤线虫与环境因子相关性热图注:*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著相关。
Fig. 5 Heat map of correlation between soil nematodes at the level of genus and environmental factorsNote:*,** and *** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels,respectively.
| 1 | 黄卫, 庄荣浩, 刘辉, 等. 农田土壤镉污染现状与治理方法研究进展[J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2022, 45(1): 49-56. |
| HUANG W, ZHUANG R H, LIU H, et al.. Recent advances of the current situation and remediation methods of cadmium contamination in paddy soil [J]. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ., 2022, 45(1): 49-56. | |
| 2 | 杨莉, 付婧, 文子伟, 等. 6种低温生物质炭的制备及结构表征[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2021, 43(5): 565-573. |
| YANG L, FU J, WEN Z W, et al.. Preparation and structure characterization of six kinds of low temperature biochar [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2021, 43(5): 565-573. | |
| 3 | 孙宇龙, 张永利, 苏有健, 等. 生物质炭对土壤物理结构性状和水分特征影响的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(23): 25-32. |
| SUN Y L, ZHANG Y L, SU Y J, et al.. Effects of biochar on soil physical structure properties and hydrologic properties: a review [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2022, 50(23): 25-32. | |
| 4 | 杨文浩, 李佩, 周碧青, 等. 生物炭缓解污染土壤中植物的重金属胁迫研究进展[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(6): 695-705. |
| YANG W H, LI P, ZHOU B Q, et al.. Biochar-mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress in plants growing in contaminated soils: a review [J]. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ.(Nat. Sci.), 2019, 48(6): 695-705. | |
| 5 | 左静, 陈德, 郭虎, 等. 小麦秸秆生物质炭对旱地土壤铅镉有效性及小麦、玉米吸收的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(6): 1133-1140. |
| ZUO J, CHEN D, GUO H, et al.. Effects of biochar on Cd Pb availability and uptake by maize and wheat in upland soil [J]. J. Agric. Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(6): 1133-1140. | |
| 6 | 施琪, 鲁然英, 常德政, 等. 增施生物质炭对镉污染土壤的修复效果研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2019, 31(10): 83-87. |
| SHI Q, LU R Y, CHANG D Z, et al.. Effects of increasing biochar application on remediation of Cd contaminated soil [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2019, 31(10): 83-87. | |
| 7 | 肖和友, 朱伟, 王海军, 等. 连续施用不同生物质炭对植烟土壤特性和烤烟品质的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2021, 42(3): 19-25. |
| XIAO H Y, ZHU W, WANG H J, et al.. Effects of continuous application of different biochar on tobacco-planting soil, flue-cured tobacco leaf quality [J]. China Tob. Sci., 2021, 42(3): 19-25. | |
| 8 | 杨素勤, 魏森, 张彪, 等. 连续施用改性生物质炭对镉铅土壤修复效果及其对微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(7): 1460-1471. |
| YANG S Q, WEI S, ZHANG B, et al.. Remediation effect of continuous application of modified biochar on cadmium-and Lead-contaminated soil and its effect on microbial community structure [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(7): 1460-1471. | |
| 9 | 杜晓芳, 李英滨, 刘芳, 等. 土壤微食物网结构与生态功能[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(2): 403-411. |
| DU X F, LI Y B, LIU F, et al.. Structure and ecological function of soil micro-food web [J]. Acta Appl. Ecol., 2018, 29(2): 403-411. | |
| 10 | LU Q F, LIU T T, WANG N Q, et al.. A review of soil nematodes as biological indicators for the assessment of soil health [J]. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng., 2020, 7(3): 275-281. |
| 11 | ZHANG X K, LI Q, LIANG W J, et al.. Soil nematode response to biochar addition in a Chinese wheat field [J]. Pedosphere, 2013, 23(1): 98-103. |
| 12 | 杨贝贝, 朱新萍, 赵一, 等. 生物炭基肥施用对棉田土壤线虫群落结构的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(4): 66-71. |
| YANG B B, ZHU X P, ZHAO Y, et al.. Effect of biochar based application on soil nematode community structure in cotton field [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2020(4): 66-71. | |
| 13 | 牛亚茹. 施用生物质炭对日光温室黄瓜生长及土壤微生物和线虫群落结构的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. |
| NIU Y R. Effect of biochar on cucumber growth and soil microbial and nematode community structure in sunlight greenhouse [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 14 | DOMENE X, MATTANA S, SÁNCHEZ-MORENO S. Biochar addition rate determines contrasting shifts in soil nematode trophic groups in outdoor mesocosms: an appraisal of underlying mechanisms [J/OL]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2021, 158: 103788 [2023-03-23]. . |
| 15 | RENČO M, ČEREVKOVÁ A, HLAVA J, et al.. Life in a contaminated environment: how soil nematodes can indicate long-term heavy-metal pollution [J/OL]. J. Nematol., 2022, 54(1): 20220053 [2023-03-23]. . |
| 16 | 邓普荣, 姚志, 刘勇波. 基于线虫生物多样性的稻田镉污染土壤修复成效研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(10): 2378-2387. |
| DENG P R, YAO Z, LIU Y B. Effects of cadmium contamination remediation on the biodiversity of soil nematodes in paddy fields [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2022, 35(10): 2378-2387. | |
| 17 | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行): [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| 18 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第三版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 163-165. |
| 19 | 刘凤枝,刘铭,蔡彦明,等. 土壤质量 有效态铅和镉的测定 原子吸收法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. |
| 20 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品中镉的测定: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. |
| 21 | 李琪, 梁文举, 姜勇. 农田土壤线虫多样性研究现状及展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(2): 134-141. |
| LI Q, LIANG W J, JIANG Y. Present situation and prospect of soil nematode diversity in farmland ecosystems [J]. Biodiversity Sci., 2007,15(2): 134-141. | |
| 22 | YEATES G W, BONGERS T, DE GOEDE R G M, et al.. Feeding habits in nematode families and genera:an outline for soil ecologists [J]. J. Nematol., 1993, 25(3): 315-331. |
| 23 | BONGERS T. The maturity index:an ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition [J]. Oecologia, 1990, 83(1): 4-19. |
| 24 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. |
| 25 | 汪鹏, 王静, 陈宏坪, 等. 我国稻田系统镉污染风险与阻控[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1409-1417. |
| WANG P, WANG J, CHEN H P, et al.. Cadmium risk and mitigation in paddy systems in China [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2018, 37(7): 1409-1417. | |
| 26 | ZHAO F J, WANG P. Arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice and mitigation strategies [J]. Plant Soil, 2020, 446(1): 1-21. |
| 27 | CLEMENS S, AARTS M G M, THOMINE S, et al.. Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning [J].Trends Plant Sci.,2013, 18(2): 92-99. |
| 28 | 周志云. 磷酸改性生物炭和氯化物混施对小麦吸收铅镉的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHOU Z Y. Effects of phosphoric-acid modified biochar combined with chlorine on lead and cadmium absorption in wheat [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 29 | 景鑫鑫. 几种钝化剂修复铅镉污染石灰性土壤的效果研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2015. |
| JING X X. Effects of different stabilizers on the remediation for heavy metal contaminated alkaline soil [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 30 | 付煜恒, 张惠灵, 王宇, 等. 磷酸盐对铅镉复合污染土壤的钝化修复研究[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(9): 176-180. |
| FU Y H, ZHANG H L, WANG Y, et al.. Immobilization of soil contaminated by lead and cadmium using phosphate [J]. Environ. Eng., 2017, 35(9): 176-180. | |
| 31 | 孙新, 李琪, 姚海凤, 等. 土壤动物与土壤健康[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(5): 1073-1083. |
| SUN X, LI Q, YAO H F, et al.. Soil fauna and soil health [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2021, 58(5): 1073-1083. | |
| 32 | 张晓珂, 梁文举, 李琪. 我国土壤线虫生态学研究进展和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(10): 1060-1073. |
| ZHANG X K, LIANG W J, LI Q. Recent progress and future directions of soil nematode ecology in China [J]. Biodiversity Sci., 2018, 26 (10): 1060-1073. | |
| 33 | NEHER D A. Role of nematodes in soil health and their use as indicators [J]. J. Nematol., 2001, 33(4): 161-168. |
| 34 | HAN D C, ZHANG X K, TOMAR V V S, et al.. Effects of heavy metal pollution of highway origin on soil nematode guilds in North Shenyang, China [J]. J. Environ. Sci., 2009, 21(2): 193-198. |
| 35 | LI H X, HU F. Effect of bacterial-feeding nematode inoculation on wheat growth and N and P uptake [J]. Pedosphere, 2001, 11(1): 57-62. |
| 36 | XIAO H F, GRIFFITHS B, CHEN X Y, et al.. Influence of bacterial-feeding nematodes on nitrification and the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) community composition [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2010, 45(3): 131-137. |
| 37 | 王赢利, 王宏洪, 廖金铃, 等. 电子垃圾拆解地重金属污染对稻田土壤线虫群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 874-881. |
| WANG Y L, WANG H H, LIAO J L, et al.. Effects of heavy metal contamination on nematode communities in paddy soils of an e-waste recycling area [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(5): 874-881. | |
| 38 | 成碧君, 刘良坡, 张红梅, 等. 重金属对煤矿区土壤线虫群落结构的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2022, 50(12): 1680-1688. |
| CHENG B J, LIU L P, ZHANG H M, et al.. Effects of heavy metals on soil nematode community structure in coal mine areas [J]. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2022, 50(12): 1680-1688. | |
| 39 | 吕莹. 线虫群落对大连滨海石油与土壤重金属污染及绿地生态系统恢复的指示作用研究[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2012. |
| LYU Y. The study of responses of nematode communites to crude oil contamination, soil heavy metal pollution and recovery of urban greenland in Dalian [D]. Dalian: Liaoning Normal University, 2012. | |
| 40 | NAGY P, BAKONYI G, BONGERS T, et al.. Effects of microelements on soil nematode assemblages seven years after contaminating an agricultural field [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2003, 320(2): 131-143. |
| 41 | ZHANG W D, XIAO Y, WANG X F, et al.. Soil nematode community characteristics around the Gangue hill of Fushun West Open-pit mine [J]. Helminthologia, 2011, 48(2): 116-123. |
| 42 | DOROSZUK A. Populations under stress:analysis on the interface between ecology and evolutionary genetics in nematodes [D]. Wageningen: Wageningen University, 2007. |
| 43 | 李孟洁. 小麦-玉米轮作体系中长期施肥对土壤线虫群落结构的影响[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018. |
| LI M J. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil nematode community structure in wheat-maize rotation system [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2018. | |
| 44 | 杨盼盼,黄菁华,张欣玥,等.长期施肥对渭北旱塬麦田土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2022, 40(5): 242-251. |
| YANG P P, HUANG J H, ZHANG X Y, et al.. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil nematode community of wheat field in Weibei dryland, China [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2022, 40(5):242-251. | |
| 45 | 金娜, 刘倩, 简恒. 植物寄生线虫生物防治研究新进展[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2015, 31(5): 789-800. |
| JIN N, LIU Q, JIAN H. Advances on biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Control, 2015, 31(5): 789-800. | |
| 46 | 段玉玺. 植物线虫学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 52-53. |
| 47 | JORÉ A R M, CARMEN G, MIGUEL E, et al.. Effect of mine tailing on the spatial variability of soil nematodes from lead pollution in La Union (Spain) [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 473-474:518-529. |
| [1] | 刘霏霏, 何万荣, 孙强, 席琳乔, 廖结安, 韩路. 苜蓿绿肥对塔里木盆地苹果园土壤细菌多样性和功能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 223-233. |
| [2] | 付彦博, 冷冰冰, 扁青永, 董志多, 刘国宏, 李海峰, 温云梦, 郭文博, 张万旭. 生物炭和油菜幼苗对土壤重金属镉污染的钝化效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 183-190. |
| [3] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [4] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [5] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [6] | 贾晶莹, 李雅辉, 伏兵哲, 马云, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿miRs表达谱分析及跨界潜力miRs初步筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 43-53. |
| [7] | 赵柏霞, 闫建芳. 高通量技术分析‘砂蜜豆’甜樱桃不同组织内生细菌多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 66-77. |
| [8] | 闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [9] | 李洁, 林莹, 徐美玉, 王飞, 徐凌川. 泰山白首乌根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 70-81. |
| [10] | 赵宏岩, 谭君伟, 张杰, 陈浩楠, 王春旭, 赵地, 李海鹏, 朱李霞, 韩毅强. 小豆和绿豆茎基感病部位真菌群落结构研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 129-136. |
| [11] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [12] | 范鹤龄, 朱清, 孙雪冰, 张丽, 李长江, 陈萍, 黄小龙, 张荣萍. 不同农用酵素的微生物多样性和群落结构[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 179-189. |
| [13] | 苏雨萌§,张旭婷§,特日格乐,田敏,尚晓蕊,李国婧,王瑞刚*. 高通量测序鉴定中间锦鸡儿干旱条件下的microRNA[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 51-57. |
| [14] | 刘璐1,名晓东1,张晓艳2,郝俊杰2,付丽平1,王乾坤1,吕鑫1,陈旺1,刘全兰1*. 高通量测序分析蚕豆种子内生细菌的多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 73-80. |
| [15] | 杨晶晶,张青青*,吐尔逊娜依·热依木,阿马努拉·依明尼亚孜,雪热提江·麦提努日. 游牧和定居对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤真菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号