




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 59-70.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0986
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yilong ZHANG( ), Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI(
), Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI( ), Zongjiu SUN
), Zongjiu SUN
Received:2021-11-20
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-06-01
Published:2023-07-28
Contact:
Peiying LI
通讯作者:
李培英
作者简介:张一龙 E-mail:871298780@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yilong ZHANG, Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI, Zongjiu SUN. Physiological Response of Different Drought-resistant Cynodon dactylon Germplasm to Drought[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 59-70.
张一龙, 孙晓梵, 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根种质的抗旱生理响应差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 59-70.
| 编号Code | 采集地点 Collection location | 抗旱类型 Drought resistance type |
|---|---|---|
| C10 | 莎车县Shache county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C32 | 托克逊县Tuokexun county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C118 | 莎车县Shache county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
| C138 | 疏勒县Shule county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
Table 1 Origins and drought resistances of test materials
| 编号Code | 采集地点 Collection location | 抗旱类型 Drought resistance type |
|---|---|---|
| C10 | 莎车县Shache county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C32 | 托克逊县Tuokexun county | 敏旱型Drought sensitive |
| C118 | 莎车县Shache county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |
| C138 | 疏勒县Shule county | 抗旱型Drought resistant |

Fig. 1 Soil water content and relative leaf water content of different bermudagrass under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
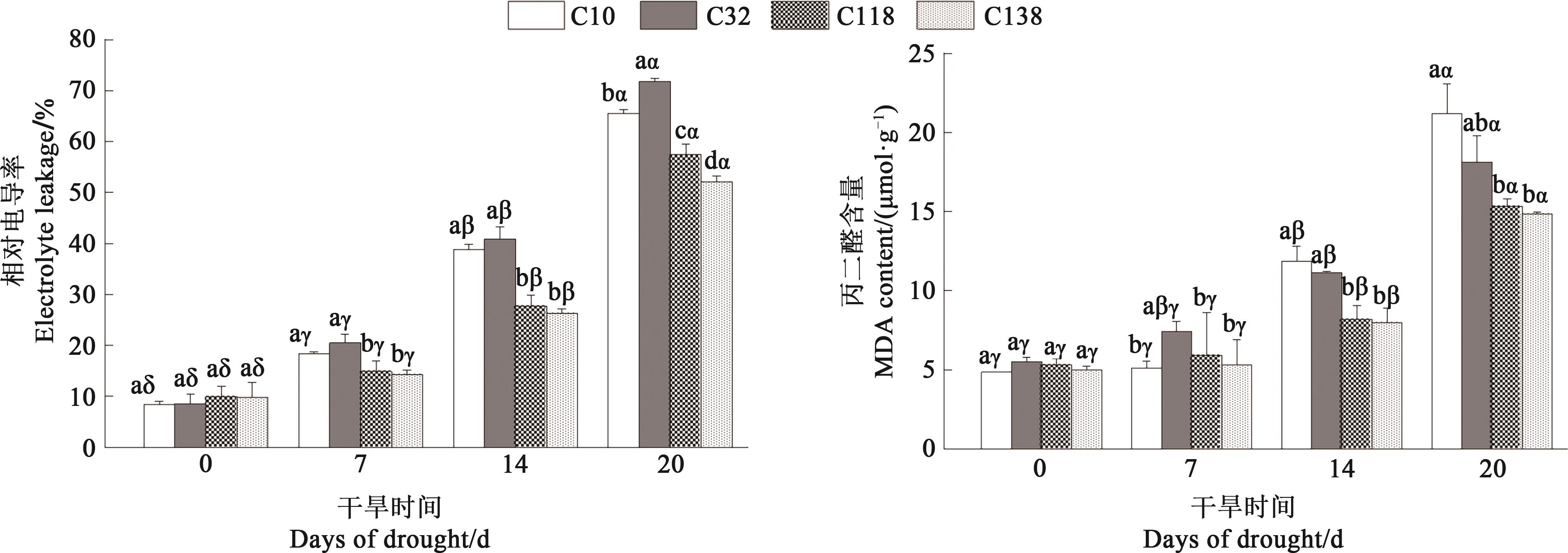
Fig. 2 Relative electrical conductivity and malondialdehyde content of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
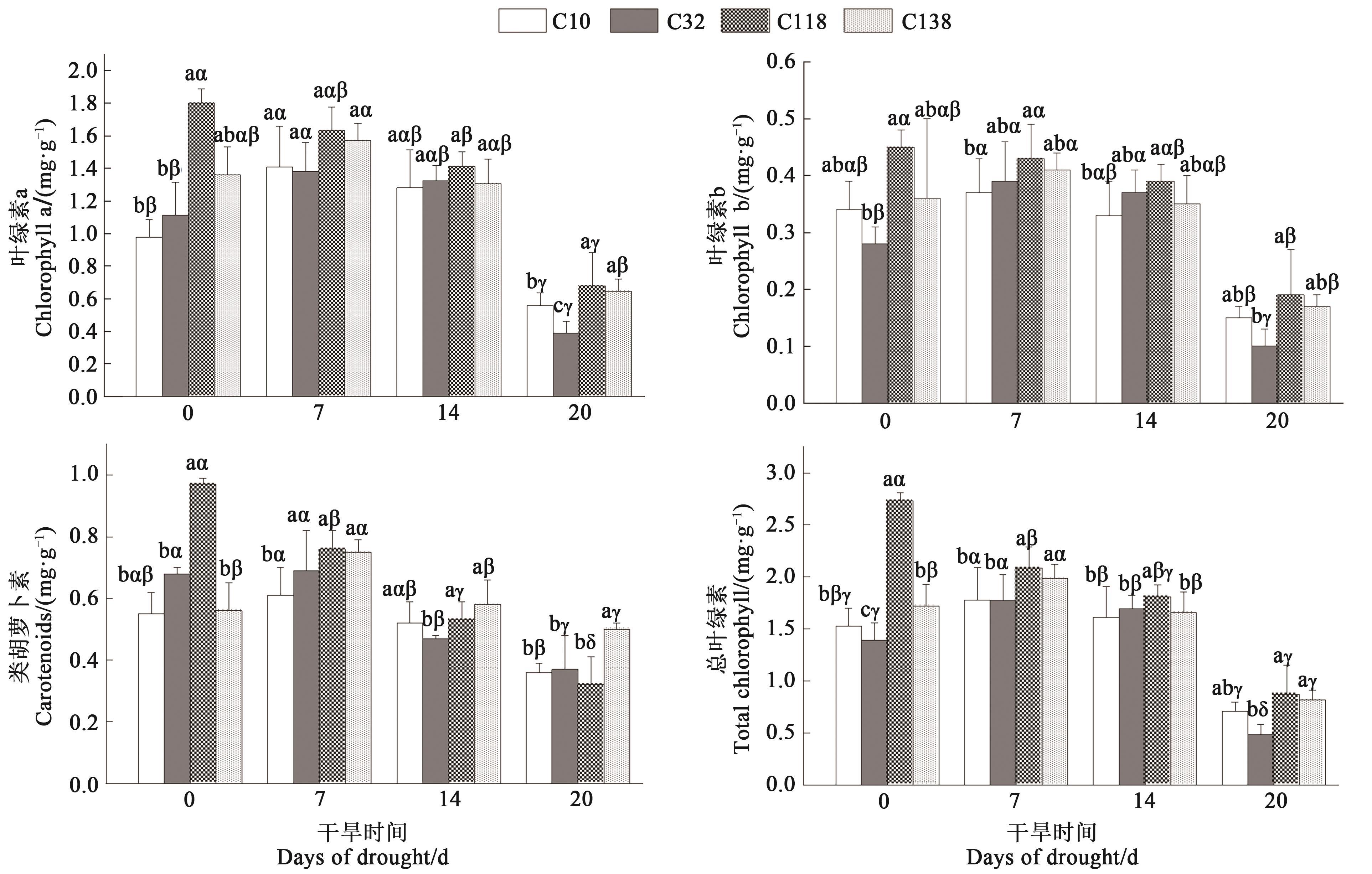
Fig. 3 Photosynthetic pigment content of different bermudagrass under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
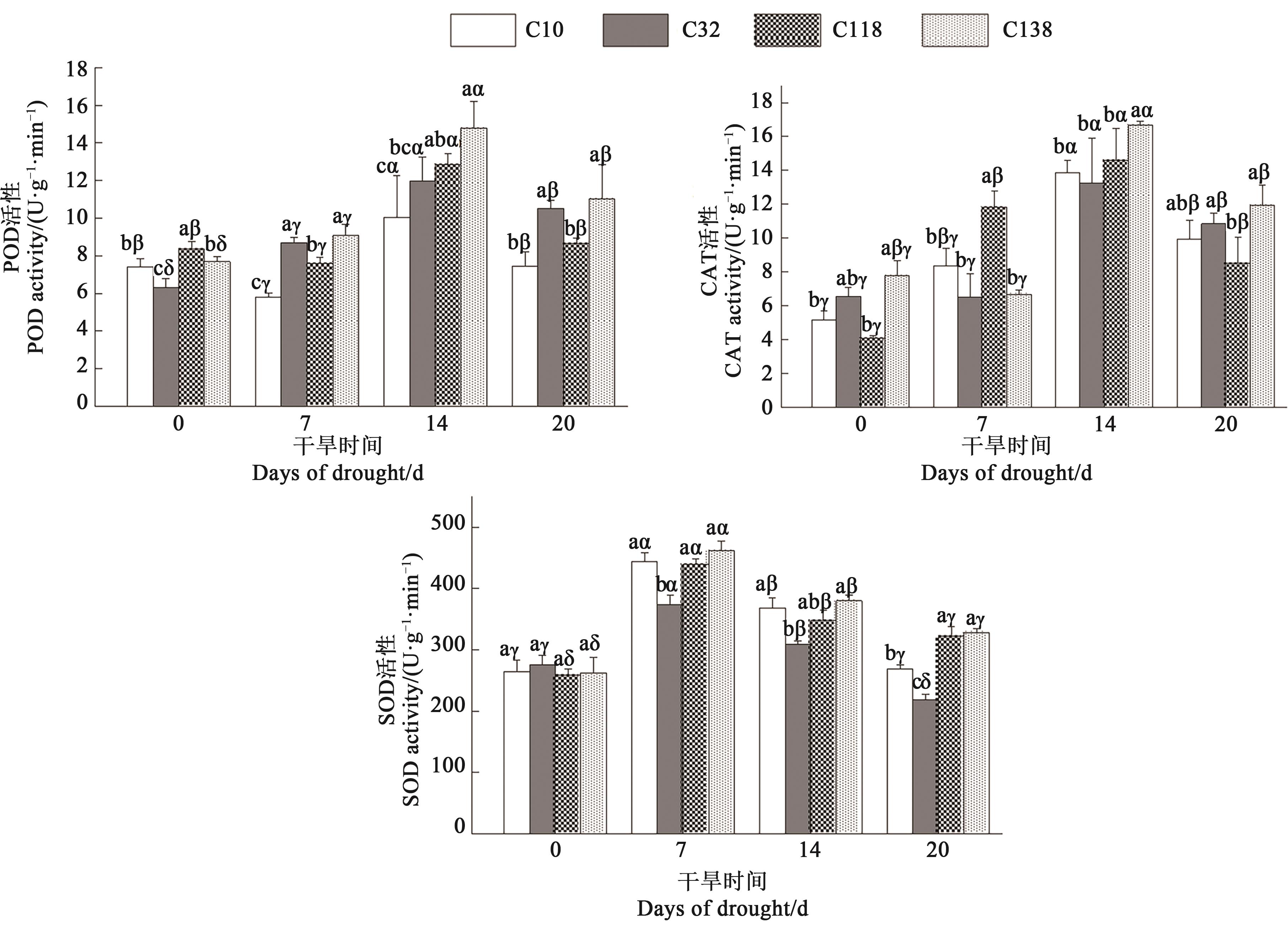
Fig. 4 Antioxidant enzyme activities of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 5 Soluble protein and proline content of different bermudagrass leaves under drought stressNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between different materials under same treatment time at P<0.05 level; different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of same material at P<0.05 level.
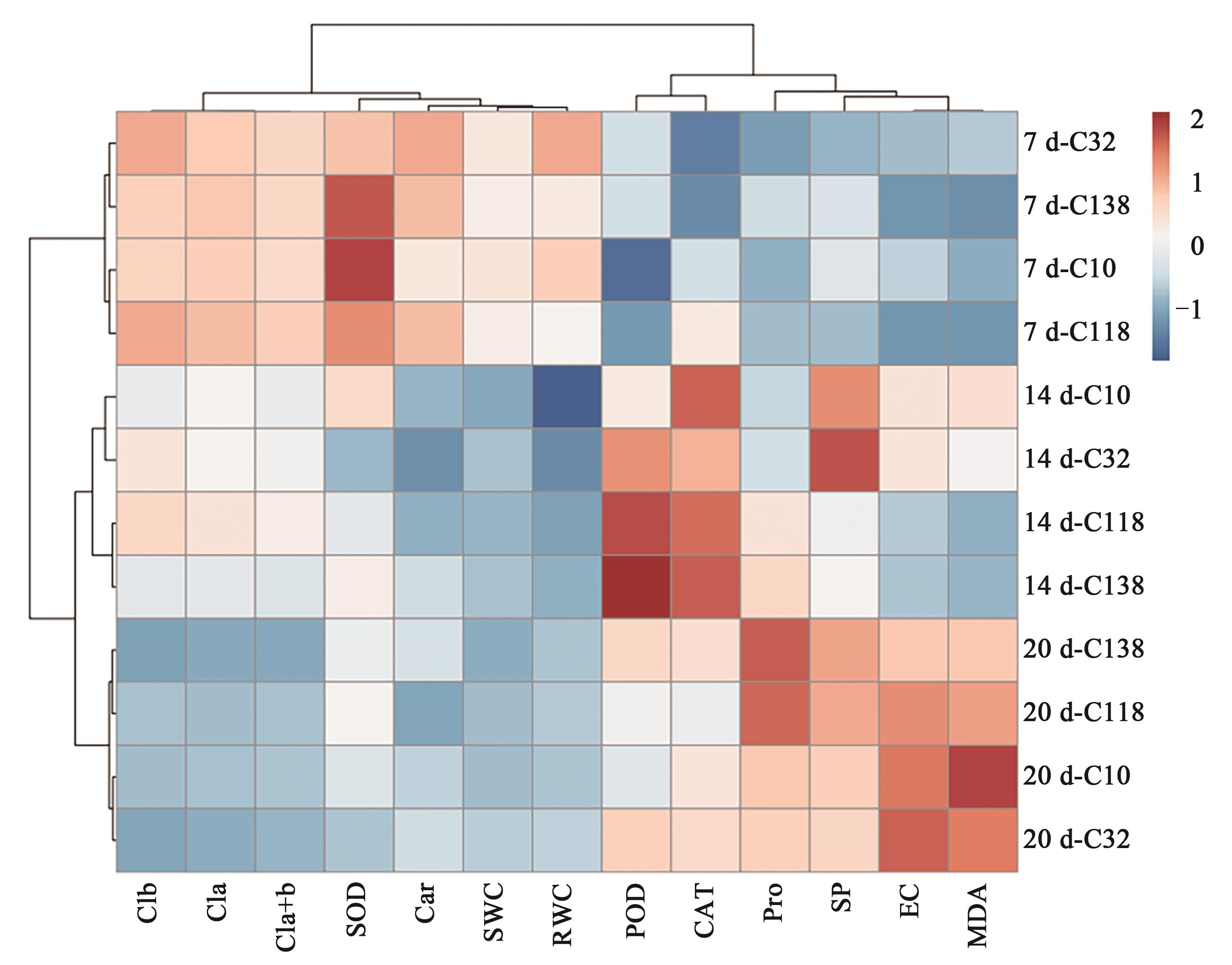
Fig. 6 Heat map cluster analysis of each index of 4 bermudagrass under drought treatment for 7~20 dNote: Clb—Chlorophyll b content;Cla—Chlorophyll a content;Cl(a+b)—Chlorophyll (a+b) content;SOD—Superoxide dismutase activity;Car—Carotenoid content;SWC—Soil water content;RWC—Relative water content in leaf;POD—Peroxidase activity;CAT—Catalase activity;Pro—Proline content;SP—Soluble protein content;EC—electrical conductivity;MDA—Malondialdehyde content; and 7 d, 14 d, 20 d represent the drought treatment time.
材料 Accession | 7 d | 14 d | 20 d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | |
| C10 | 0.482 2 | 4 | 0.435 9 | 3 | 0.268 4 | 4 |
| C32 | 0.575 7 | 1 | 0.372 3 | 4 | 0.396 6 | 3 |
| C118 | 0.483 5 | 3 | 0.510 5 | 2 | 0.538 6 | 2 |
| C138 | 0.562 6 | 2 | 0.677 2 | 1 | 0.807 2 | 1 |
Table 2 Membership function D value and ranking of bermudagrass under drought stress
材料 Accession | 7 d | 14 d | 20 d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | D值D value | 排序Ranking | |
| C10 | 0.482 2 | 4 | 0.435 9 | 3 | 0.268 4 | 4 |
| C32 | 0.575 7 | 1 | 0.372 3 | 4 | 0.396 6 | 3 |
| C118 | 0.483 5 | 3 | 0.510 5 | 2 | 0.538 6 | 2 |
| C138 | 0.562 6 | 2 | 0.677 2 | 1 | 0.807 2 | 1 |
干旱胁迫时间 Days after drought treatment/d | 特征向量 Eigen vector | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | ΨC10 | 0.624 0 | 0.514 5 | 0.516 6 | 0.508 5 | 0.648 0 | 0.520 7 | 0.569 8 | 0.754 3 | 0.577 8 | 0.839 2 | 0.614 4 | 0.512 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.620 0 | 0.510 3 | 0.734 0 | 0.624 1 | 0.550 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.749 1 | 0.500 2 | 0.972 4 | 0.729 6 | 0.571 6 | 0.748 5 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.644 0 | 0.710 8 | 0.734 1 | 0.551 8 | 0.589 4 | 0.677 2 | 0.563 3 | 0.667 2 | 0.345 7 | 0.893 1 | 0.654 5 | 0.504 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.635 1 | 0.787 5 | 0.520 9 | 0.834 0 | 0.564 7 | 0.653 7 | 0.583 1 | 0.569 4 | 0.555 0 | 0.785 0 | 0.597 0 | 0.559 0 | |
| 关联度Relevance | 0.630 8 | 0.630 8 | 0.626 4 | 0.629 6 | 0.588 0 | 0.614 1 | 0.616 3 | 0.622 8 | 0.612 7 | 0.811 7 | 0.609 4 | 0.580 9 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 12 | |
| 14 | ΨC10 | 0.606 9 | 0.409 4 | 0.428 3 | 0.369 4 | 0.498 0 | 0.357 1 | 0.663 0 | 0.615 3 | 0.488 5 | 0.396 0 | 0.530 1 | 0.729 2 |
| ΨC32 | 0.503 6 | 0.379 1 | 0.512 2 | 0.535 2 | 0.479 2 | 0.465 1 | 0.551 4 | 0.424 8 | 0.594 8 | 0.449 1 | 0.372 0 | 0.517 2 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.623 7 | 0.725 0 | 0.731 2 | 0.653 8 | 0.564 3 | 0.653 6 | 0.533 2 | 0.591 0 | 0.392 0 | 0.670 0 | 0.674 0 | 0.429 2 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.573 5 | 0.978 9 | 0.547 6 | 0.727 0 | 0.619 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.584 1 | 0.552 8 | 0.832 6 | 0.808 8 | 0.703 0 | 0.541 8 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.576 9 | 0.623 1 | 0.554 8 | 0.571 3 | 0.540 3 | 0.618 9 | 0.582 9 | 0.545 9 | 0.577 0 | 0.581 0 | 0.569 8 | 0.554 3 | |
| 排序Ranking | 6 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 10 | |
| 20 | ΨC10 | 0.658 0 | 0.666 0 | 0.369 5 | 0.376 1 | 0.448 5 | 0.490 2 | 0.453 9 | 0.525 1 | 0.409 3 | 0.350 4 | 0.611 1 | 0.657 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.563 9 | 0.400 6 | 0.734 5 | 0.504 1 | 0.472 0 | 0.466 7 | 0.633 7 | 0.381 3 | 0.522 0 | 0.494 4 | 0.645 0 | 0.562 8 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.649 0 | 0.657 6 | 0.664 6 | 0.637 9 | 0.573 2 | 0.591 6 | 0.475 7 | 0.591 0 | 0.474 8 | 0.651 0 | 0.606 7 | 0.687 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.582 7 | 0.668 0 | 0.519 4 | 0.776 7 | 0.711 7 | 0.615 5 | 0.619 4 | 0.655 6 | 0.569 0 | 0.921 2 | 0.672 7 | 0.643 6 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.613 4 | 0.598 0 | 0.572 0 | 0.573 7 | 0.551 3 | 0.541 0 | 0.545 7 | 0.538 3 | 0.493 7 | 0.604 2 | 0.633 9 | 0.637 6 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
Table 3 Correlations between various indicators and bermudagrass drought resistance under different drought times
干旱胁迫时间 Days after drought treatment/d | 特征向量 Eigen vector | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | ΨC10 | 0.624 0 | 0.514 5 | 0.516 6 | 0.508 5 | 0.648 0 | 0.520 7 | 0.569 8 | 0.754 3 | 0.577 8 | 0.839 2 | 0.614 4 | 0.512 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.620 0 | 0.510 3 | 0.734 0 | 0.624 1 | 0.550 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.749 1 | 0.500 2 | 0.972 4 | 0.729 6 | 0.571 6 | 0.748 5 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.644 0 | 0.710 8 | 0.734 1 | 0.551 8 | 0.589 4 | 0.677 2 | 0.563 3 | 0.667 2 | 0.345 7 | 0.893 1 | 0.654 5 | 0.504 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.635 1 | 0.787 5 | 0.520 9 | 0.834 0 | 0.564 7 | 0.653 7 | 0.583 1 | 0.569 4 | 0.555 0 | 0.785 0 | 0.597 0 | 0.559 0 | |
| 关联度Relevance | 0.630 8 | 0.630 8 | 0.626 4 | 0.629 6 | 0.588 0 | 0.614 1 | 0.616 3 | 0.622 8 | 0.612 7 | 0.811 7 | 0.609 4 | 0.580 9 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 12 | |
| 14 | ΨC10 | 0.606 9 | 0.409 4 | 0.428 3 | 0.369 4 | 0.498 0 | 0.357 1 | 0.663 0 | 0.615 3 | 0.488 5 | 0.396 0 | 0.530 1 | 0.729 2 |
| ΨC32 | 0.503 6 | 0.379 1 | 0.512 2 | 0.535 2 | 0.479 2 | 0.465 1 | 0.551 4 | 0.424 8 | 0.594 8 | 0.449 1 | 0.372 0 | 0.517 2 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.623 7 | 0.725 0 | 0.731 2 | 0.653 8 | 0.564 3 | 0.653 6 | 0.533 2 | 0.591 0 | 0.392 0 | 0.670 0 | 0.674 0 | 0.429 2 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.573 5 | 0.978 9 | 0.547 6 | 0.727 0 | 0.619 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.584 1 | 0.552 8 | 0.832 6 | 0.808 8 | 0.703 0 | 0.541 8 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.576 9 | 0.623 1 | 0.554 8 | 0.571 3 | 0.540 3 | 0.618 9 | 0.582 9 | 0.545 9 | 0.577 0 | 0.581 0 | 0.569 8 | 0.554 3 | |
| 排序Ranking | 6 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 10 | |
| 20 | ΨC10 | 0.658 0 | 0.666 0 | 0.369 5 | 0.376 1 | 0.448 5 | 0.490 2 | 0.453 9 | 0.525 1 | 0.409 3 | 0.350 4 | 0.611 1 | 0.657 0 |
| ΨC32 | 0.563 9 | 0.400 6 | 0.734 5 | 0.504 1 | 0.472 0 | 0.466 7 | 0.633 7 | 0.381 3 | 0.522 0 | 0.494 4 | 0.645 0 | 0.562 8 | |
| ΨC118 | 0.649 0 | 0.657 6 | 0.664 6 | 0.637 9 | 0.573 2 | 0.591 6 | 0.475 7 | 0.591 0 | 0.474 8 | 0.651 0 | 0.606 7 | 0.687 0 | |
| ΨC138 | 0.582 7 | 0.668 0 | 0.519 4 | 0.776 7 | 0.711 7 | 0.615 5 | 0.619 4 | 0.655 6 | 0.569 0 | 0.921 2 | 0.672 7 | 0.643 6 | |
关联度 Relevance | 0.613 4 | 0.598 0 | 0.572 0 | 0.573 7 | 0.551 3 | 0.541 0 | 0.545 7 | 0.538 3 | 0.493 7 | 0.604 2 | 0.633 9 | 0.637 6 | |
| 排序Ranking | 3 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | FENG Q, SHINOZAKIKAZUO, KAZUKO Y S. Achievements and challenges in understanding plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2011, 52(9):1569-1582. |
| 2 | 朱烨,刘懿,王文,等.基于土壤含水率的骤发干旱和缓慢干旱时空特征分析[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(2):114-122. |
| ZHU Y, LIU Y, WANG W, et al.. Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics of flash drought and slowly-evolving drought using soil moisture percentile [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2021, 37(2):114-122. | |
| 3 | 温琦,赵文博,张幽静,等.植物干旱胁迫响应的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(12):11-15. |
| WEN Q, ZHAO W B, ZHANG Y J, et al.. Research progress of plant response to drought stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(12):11-15. | |
| 4 | ANJUM S A, XIE Y. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress [J]. AFR JAGR Res., 2011, 6(9):2026-2032. |
| 5 | 宋娅丽,王莎,王克勤,等.3种冷季型草坪草苗期对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J].草原与草坪,2018,38(3):9-16. |
| SONG Y L, WANG S, WANG K Q, et al.. Physiological and ecological responses of three cool-season turfgrasses to drought stress at seedling stage [J]. Grassland Turf, 2018, 38(3): 9-16. | |
| 6 | 孙明伟,徐月乔,王贵,等.松嫩草地两种生态型羊草根际效应和光合生理对干旱胁迫的响应[J].中国草地学报, 2021,43(5):8-17. |
| SUN M W, XU Y Q, WANG G, et al.. Responses of the rhizosphere effect and photosynthetic physiology of two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis to drought stress in Songnen grassland [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2021, 43(5):8-17. | |
| 7 | 张娜.不同抗旱性燕麦品种对水分胁迫的生理响应机制研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2012. |
| ZHANG N. Drought resistance of different oat cultivars to water stress physiological response mechanism [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 8 | KATUWAL K B, SCHWARTZ B, JESPERSEN D. Desiccation avoidance and drought tolerance strategies in bermudagrasses [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2019, 171(10):39-47. |
| 9 | ZHOU Y, LAMBRIDES C J, FUKAI S. Drought resistance of bermudagrass (Cynodon spp) ecotypes collected from different climatic zones [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2013, 85:22-29. |
| 10 | 段敏敏,张向向,孙宗玖,等.水分胁迫下两种抗旱类型狗牙根种质的生理生态响应差异[J].中国草地学报,2018,40(3):8-13. |
| DUAN M M, ZHANG X X, SUN Z J, et al.. Response resistance difference in physiology and ecology of two drought resistance type Cynodon dactylon germplasm to water stress [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2018, 40(3):8-13. | |
| 11 | AJTAHED S S, REZAEI A, TAFRESHI S. Identifying superior drought-tolerant bermudagrass accessions and their defensive responses to mild and severe drought conditions [J]. Euphytica, 2021, 217(1):2-21. |
| 12 | 曾令霜,李培英,孙晓梵,等.新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J].草业学报,2020,29(8):155-169. |
| ZENG L S, LI P Y, SUN X F, et al.. A multi-trait evaluation of drought resistance of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) germplasm from different habitats in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(8):155-169. | |
| 13 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:1-275. |
| 14 | ALAN R W. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as will as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophoto meters of different resolution[J]. Plant Physiol., 1994, 144(3):307-313. |
| 15 | 王永军.超高产夏玉米群体质量与个体生理功能研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2008. |
| WANG Y J. Study on population quality and individual physiology function of super high-yielding maize (Zea mays) [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2008. | |
| 16 | 王燕凌.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2014:1-287. |
| 17 | 刘一明,郇恒福,丁西朋,等. 55份不同生态型假俭草的耐盐性评价[J].草业科学,2017,34(11):2261-2271. |
| LIU Y M, HUAN H F, DING X P,et al.. Evaluation of salinity tolerance of 55 centipedegrass ecotypes [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2017, 34(11):2261-2271. | |
| 18 | 伏兵哲,高雪芹,高永发,等. 21个苜蓿品种主要农艺性状关联分析与综合评价[J].草业学报,2015,24(11):174-182. |
| FU B Z, GAO X Q, GAO Y F, et al.. Correlation analysis of the main agronomic traits and performance of 21 alfalfa varieties [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2015, 24(11):174-182. | |
| 19 | CAUDLE K L, JOHNSON L C, BAER S G, et al.. A comparison of seasonal foliar chlorophyll change among ecotypes and cultivars of Andropogon gerardii (Poaceae) by using nondestructive and destructive methods [J]. Photosynthetica, 2014, 52(4):511-518. |
| 20 | 王平,王沛,孙万斌,等. 8份披碱草属牧草苗期抗旱性综合评价[J].草地学报,2020,28(2):109-116. |
| WANG P, WANG P, SUN W B, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of eight Elymus germplasms at seedling stage [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2020, 28(2): 397-404. | |
| 21 | 胡杨,李钢铁,李星,等.干旱胁迫对细穗柽柳幼苗生长和生理生化指标的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021, 23(6):43-50. |
| HU Y, LI G T, LI X, et al.. Growth and physiological index of tamarix leptostachys bunge seedlings under soil drought stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(6):43-50. | |
| 22 | 杨喜珍,杨利,覃亚,等.PEG-8000模拟干旱胁迫对马铃薯组培苗叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量的影响[J].中国马铃薯,2019,33(4):193-202. |
| YANG X Z, YANG L, QIN Y, et al.. Effects of PEG-8000 strees on carotenoid of potato contents of chlorophyll and plantlets in vitro [J]. Chin. Potato J., 2019, 33(4):193-202. | |
| 23 | 王凯悦, 陈芳泉, 黄五星. 植物干旱胁迫响应机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 19-25. |
| WANG K Y, CHEN F Q, HUANG W X. Research advance on drought stress response mechanism in plants [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(2):19-25. | |
| 24 | 张然,李佳缙,王铭,等. 11份草地早熟禾种质材料对PEG-6000胁迫的生理响应和耐旱性评价[J].草原与草坪,2021,41(2):113-121. |
| ZHANG R, LI J J, WANG M, et al.. Physiological kentucky responses to drought stress in 11 different bluegrass germplasm and the evaluation of their drought tolerance [J]. Grassland Turf, 2021, 41(2):113-121. | |
| 25 | 张翠梅,师尚礼,吴芳.干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系生长及生理特性影响[J].中国农业科学,2018,51(5):868-882. |
| ZHANG C M, SHI S L, WU F. Effects of drought stress on root and physiological responses of different drought-tolerant Alfalfa varieties [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2018, 51(5):868-882. | |
| 26 | 赵春程,李晓宁,张寅坤,等.4个多年生黑麦草品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J].草业科学,2020,37(4):669-677. |
| ZHAO C C, LI X N, ZHANG Y K, et al.. Physiological correspondence of four varieties of perennial ryegrass to drought stress [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2020, 37(4):669-677. | |
| 27 | 李州,彭燕,苏星源.不同叶型白三叶抗氧化保护及渗透调节生理对干旱胁迫的响应[J].草业学报,2013,22(2):257-263. |
| LI Z, PENG Y, SU X Y. Physiological responses of white clover by different leaf types associated with anti-oxidative enzyme protection and osmotic adjustment under drought stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2013, 22(2):257-263. | |
| 28 | 赵福庚,孙诚,刘友良.盐胁迫激活大麦幼苗脯氨酸合成的鸟氨酸途径[J].植物学报,2001,43(1):36-40. |
| ZHAO F G, SUN C, LIU Y L. Ornithine pathway in proline biosynthesis activated by salt stress in barley seedlings [J]. J. Acta Bot. Sin., 2001, 43(1):36-40. | |
| 29 | 郭郁频,米福贵,闫利军,等.不同早熟禾品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价[J].草业学报,2014,23(4):220-228. |
| GU Y P, MI F G, YAN L J, et al.. Physiological response to drought stresses and drought resistances evaluation of different Kentucky bluegrass varieties [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2014, 23(4):220-228. | |
| 30 | 李江艳,张鲜花,袁小强.鸭茅种质资源苗期抗旱指标筛选及抗旱评价[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,11(1):215-226. |
| LI J Y, ZHANG X H, YUAN X Q. Drought resistance index screening and drought resistance evaluation of Dactylis glomerata germplasm resources during seedling [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 11(1):215-226. | |
| 31 | 田小霞,许明爽,郑明利,等.黄花草木樨苗期抗旱性鉴定及抗旱指标筛选[J].干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(10):120-127. |
| TIAN X X, XU M S, ZHENG M L, et al.. Drought resistance identification and drought resistance index screening of melilotus officinalis seedling [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, 35(10):120-127. |
| [1] | Shuang WANG, Yixing HOU, Linjiao FENG, Qianqian LU, Long ZHOU. Effect of Drought Stress on Anatomical Structure of Leaves in Table Grape Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [2] | Qing LU, Ting LIANG, Weiwei WANG, Dezhou WANG, Xian WU, Xiaoyan WANG, Yimiao TANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Wheat Heat Shock Protein Gene TaHSP90-1 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [3] | Lili WANG, Congpei YIN, Feng LI, Zhimin YANG, Fangming LIU, Baisong LIN, Xiaojing LIU, Haijun LIU, Jing SUN, Dongdong SHAN, Jianghui CUI, Zhenqing ZHANG. Microbial Community Structure of Potato Rhizosphere Soil and Its Response to Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 58-69. |
| [4] | Fangling WANG, Mingyue ZHANG, Yaru ZHOU, Qinglin GUAN, Xinyan LI, Qiu ZHONG, Mingqin ZHAO. Effect of TS-PAA Water Retaining Agent on Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cigar under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [5] | Jiangyan LI, Xianhua ZHANG, Xiaoqiang YUAN. Drought Resistance Index Screening and Drought Resistance Evaluation of Dactylisglomerata Germplasm Resources During Seedling [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 84-94. |
| [6] | Xiaochun SUN, Wenjing HUANG, Bo LI. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Physiological and Biochemical Indexes and Related Gene Expression in Platycodongrandiflorus Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 63-70. |
| [7] | LIU Yuan, ZHANG Xiuyan, XU Miaoyun, ZHENG Hongyan, ZOU Junjie, ZHANG Lan, WANG Lei. Global Small RNA Transcriptome Profiling of Rice Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 23-32. |
| [8] | HU Yang, LI Gangtie, LI Xing, JIA Shouyi. Growth and Physiological Index of Tamarix leptostachys Bunge Seedlings Under Soil Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 43-50. |
| [9] | ZHANG Haoyang, JIN Yinan, SUN Yanxin, LI Ziwei, GUO Xiaoheng, XU Zicheng*. Research Progress of Plant microRNAs in Drought Stress Response [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 27-36. |
| [10] | WANG Deyun1,2, LIU Peipei1, CHEN Yunting1, XU Yueying1, ZHOU Li1, LUO Guangming1*. Effect of Drought Stress on Endogenous Hormone Content of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 58-63. |
| [11] | ZHANG Mao, XU Yanhong, XI Yi*, PEI Yingjie, HUANG Benyong, YANG Kechao, LI Jinmeng. Effects of Pb2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ on Growth, Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Perennial Ryegrass [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 41-50. |
| [12] | SU Yumeng§, ZHANG Xuting§, Terigele, TIAN Min, SHANG Xiaorui, LI Guojing, WANG Ruigang*. Identification of microRNAs in Caragana intermedia Kuang by High Throughput Sequencing Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 51-57. |
| [13] | ZHANG Luxiang1, CHEN Simeng1, ZHENG Cong2, JIN Yinan1, HAN Yi3, XU Zicheng1, HUANG Wuxing1, SHAO Huifang1*. Influences of Different Deacclimation Duration on Drought Resistance of Tobacco Seedlings#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 57-64. |
| [14] | YANG Ruiping1, LIU Ruixiang1, MA Yingmei1*, Guo Zhanbin2, ZHANG Hongwu2, BAI Yu1, ZHAO Xinyu1. Evaluation of Different Chenopodium quinoa Resources and Effects of Osmotic Regulators on Their Drought Resistance [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| [15] | SONG Jinhui, WENG Qiaoyun, LYU Aizhi, YUAN Jincheng, LIU Yinghui*. Influence of Drought Stress on Growth and Quality of Silage Corn at Jointing Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(6): 161-167. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号