




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 154-160.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0115
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Ruiqi JIA1( ), Ziang GUO1, Chen YAO1, Pu LI2, Guixiao LA3, Xiazi LU1, Hongyu GUO1, Xuanzhen LI1(
), Ziang GUO1, Chen YAO1, Pu LI2, Guixiao LA3, Xiazi LU1, Hongyu GUO1, Xuanzhen LI1( )
)
Received:2022-02-21
Accepted:2022-04-12
Online:2022-08-15
Published:2022-08-22
Contact:
Xuanzhen LI
贾睿琪1( ), 郭子昂1, 姚晨1, 李璞2, 腊贵晓3, 陆夏梓1, 郭虹妤1, 李烜桢1(
), 郭子昂1, 姚晨1, 李璞2, 腊贵晓3, 陆夏梓1, 郭虹妤1, 李烜桢1( )
)
通讯作者:
李烜桢
作者简介:贾睿琪 E-mail:jiaruiqi96@outlook.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Ruiqi JIA, Ziang GUO, Chen YAO, Pu LI, Guixiao LA, Xiazi LU, Hongyu GUO, Xuanzhen LI. Effect of Low Phosphorus Stress on Cadmium Uptake in Wheat[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 154-160.
贾睿琪, 郭子昂, 姚晨, 李璞, 腊贵晓, 陆夏梓, 郭虹妤, 李烜桢. 低磷胁迫对小麦镉吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 154-160.
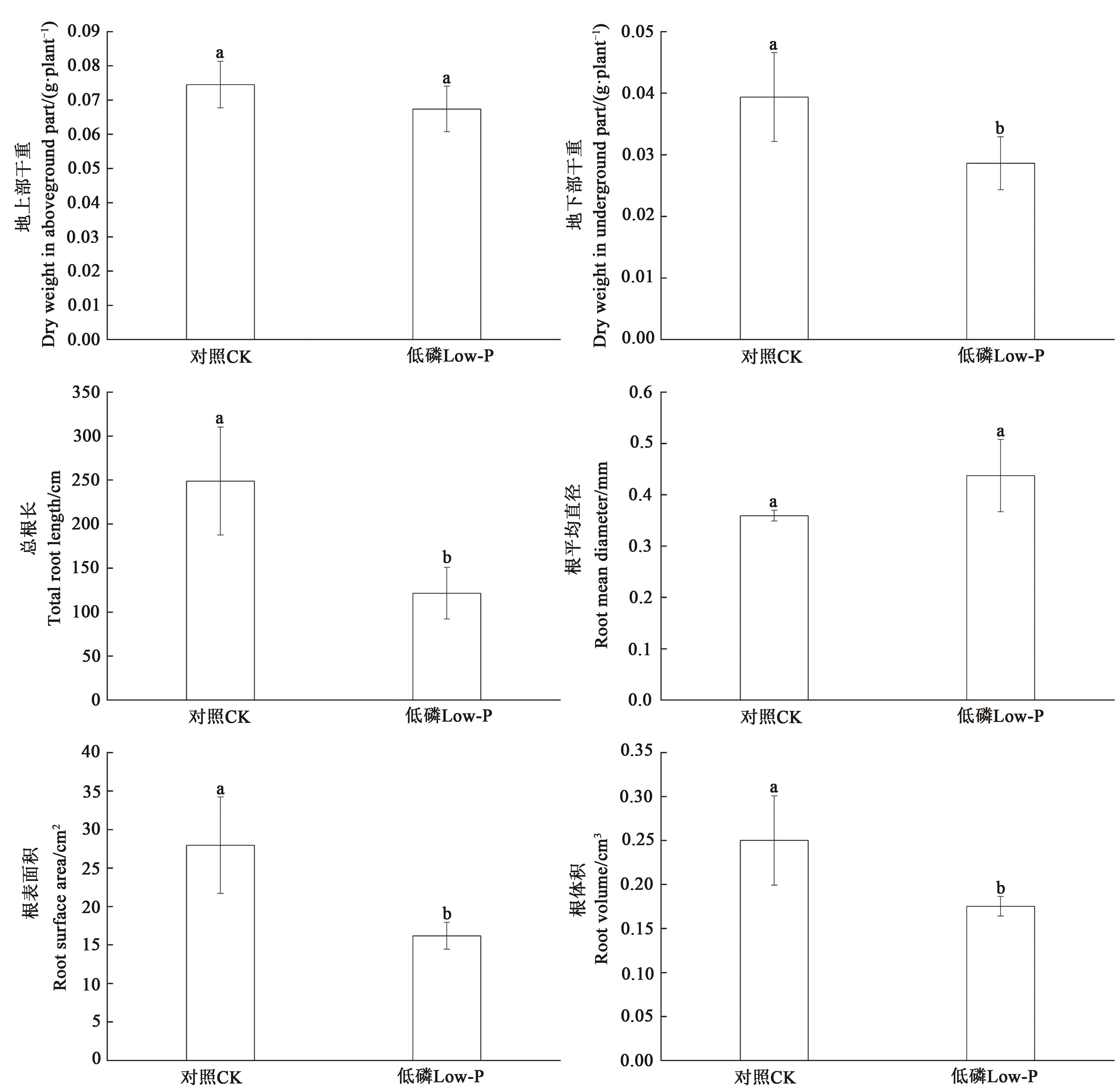
Fig. 1 Effects of low phosphorus stress on wheat biomass and root morphological indicatorsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
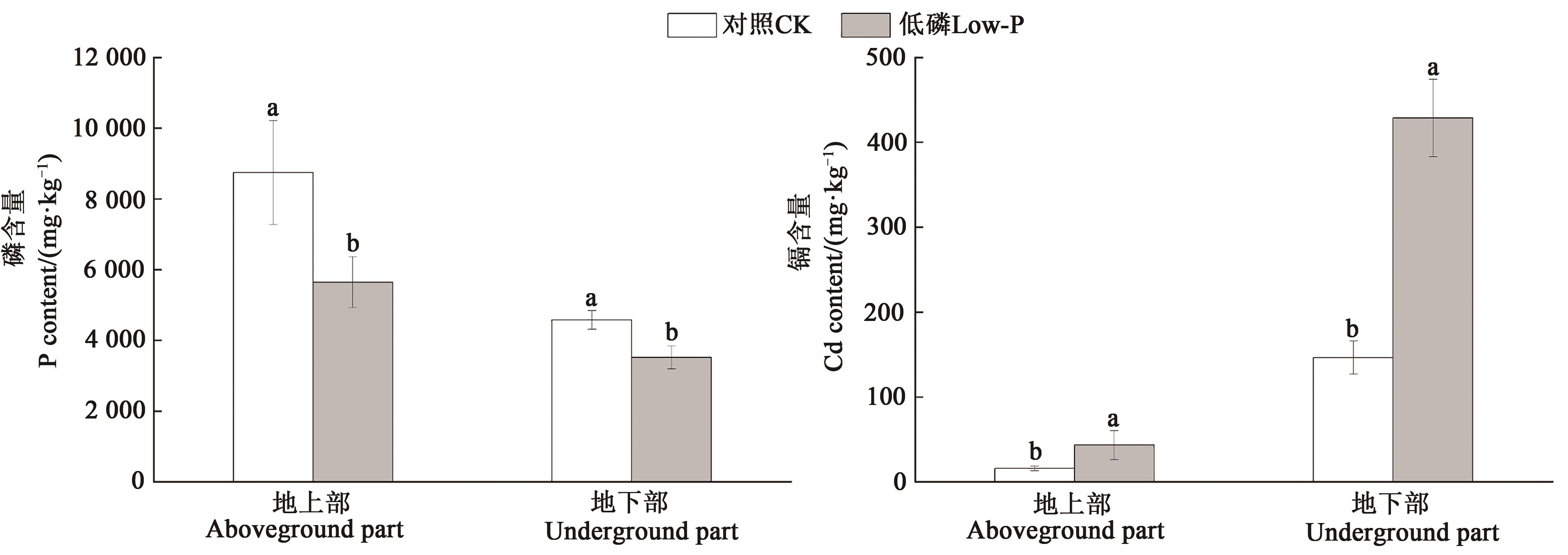
Fig. 2 Effect of low phosphorus stress on phosphorus and cadmium contents in wheatNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
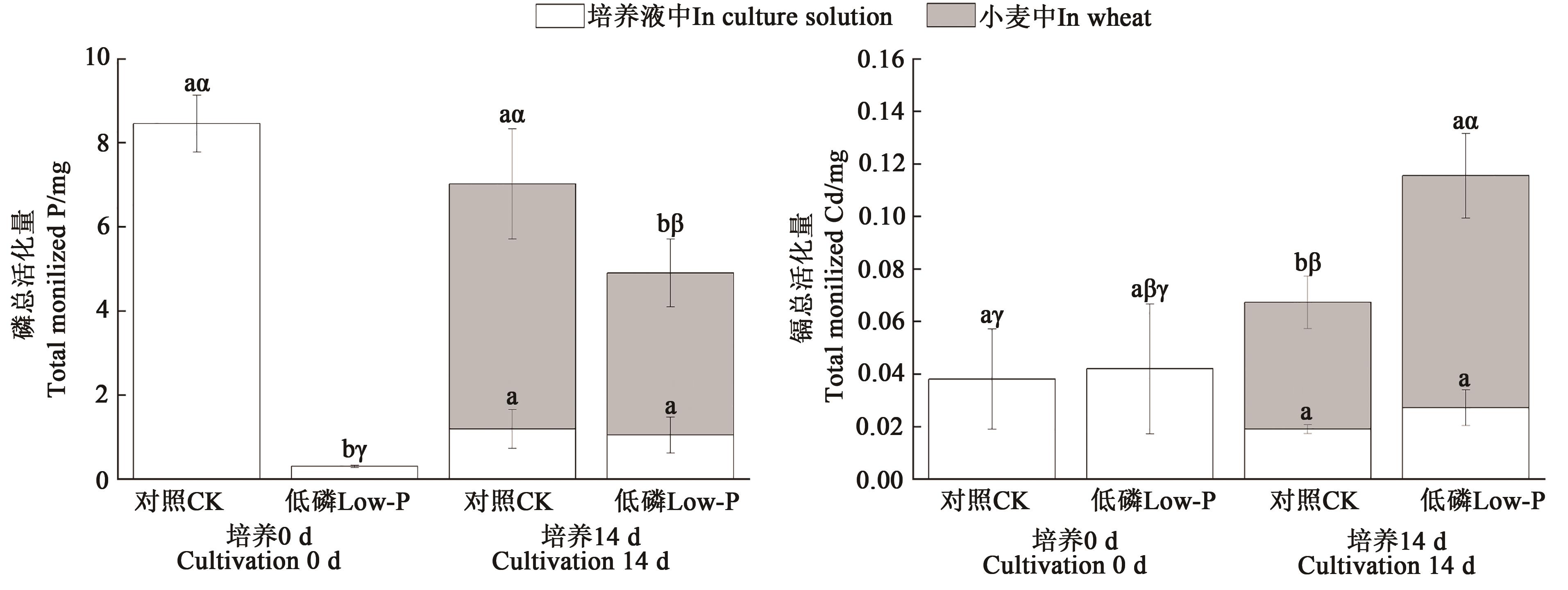
Fig. 3 Effect of low phosphorus stress on the distribution of phosphorus and cadmium in wheat-culture medium systemNote:Different English letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05),different Greek letters indicate significant differences between total activation (P<0.05).
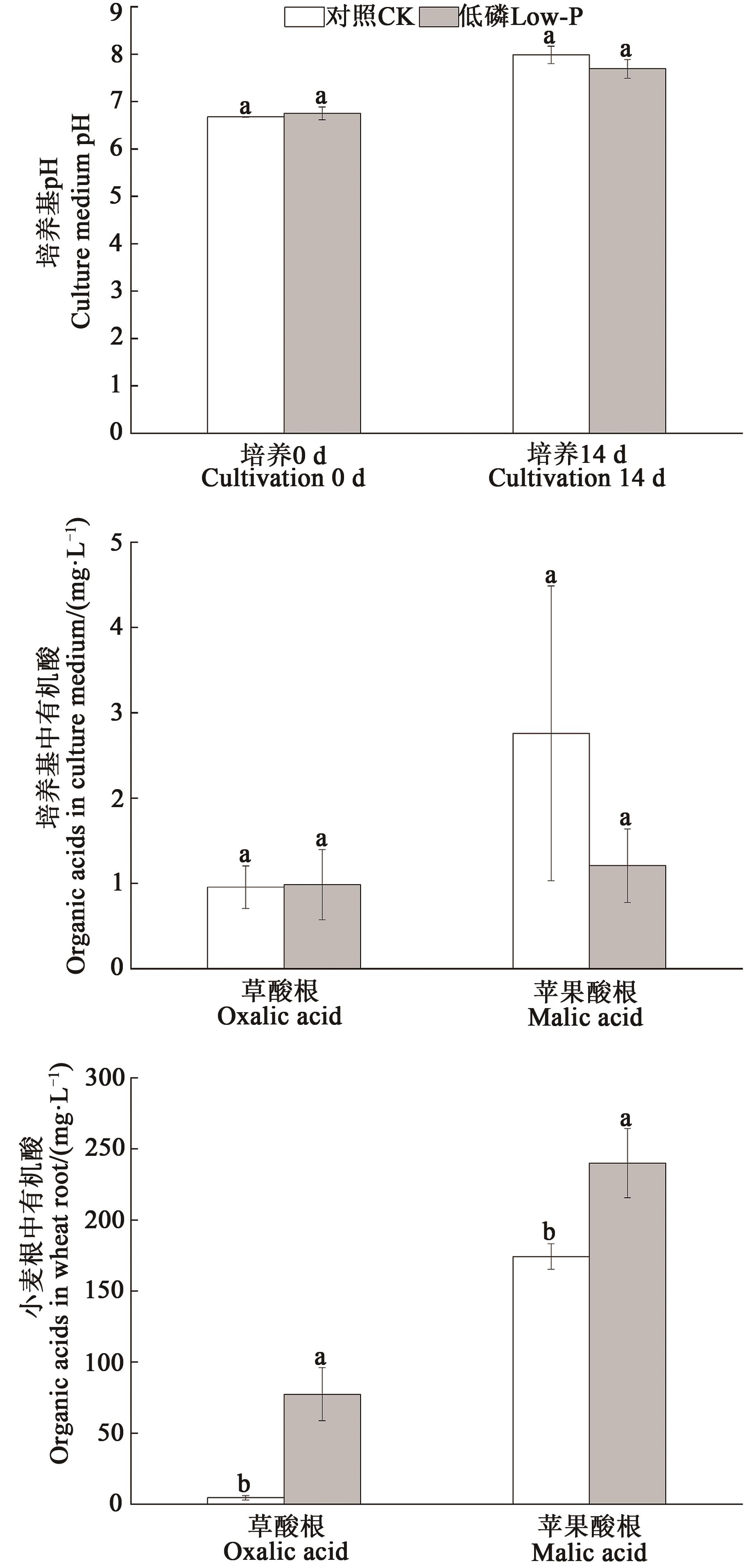
Fig. 4 Effect of low phosphorus stress on medium pH, organic acid and organic acids in wheat rootsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
| 1 | HUSSAIN B, ASHRAF M N, SHAFEEQ UR R, et al.. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ. , 2021, 754: 142188 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 2 | ZHAO F J, MA Y, ZHU Y G, et al.. Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(2): 750-759. |
| 3 | SUN Y, XU Y, XU Y, et al.. Reliability and stability of immobilization remediation of Cd polluted soils using sepiolite under pot and field trials [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2016, 208: 739-746. |
| 4 | SHI T, MA J, WU X, et al.. Inventories of heavy metal inputs and outputs to and from agricultural soils: a review [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2018, 164: 118-124. |
| 5 | QIAO K, WANG F, LIANG S, et al.. New biofortification tool: wheat TaCNR5 enhances zinc and manganese tolerance and increases zinc and manganese accumulation in rice grains [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2019, 67(35): 9877-9884. |
| 6 | ZHANG L, ZHANG C, DU B, et al.. Effects of node restriction on cadmium accumulation in eight Chinese wheat (Triticum turgidum) cultivars [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ. , 2020, 725: 138358[2022-02-20]. . |
| 7 | LIANG X, STRAWN D G, CHEN J, et al.. Variation in cadmium accumulation in spring wheat cultivars: uptake and redistribution to grain [J]. Plant Soil, 2017, 421(1-2): 219-231. |
| 8 | LIU N, HUANG X, SUN L, et al.. Screening stably low cadmium and moderately high micronutrients wheat cultivars under three different agricultural environments of China [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125065 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 9 | RIZWAN M, ALI S, ABBAS T, et al.. Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2016, 130: 43-53. |
| 10 | GRUTER R, COSTEROUSSE B, MAYER J, et al.. Long-term organic matter application reduces cadmium but not zinc concentrations in wheat [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 669: 608-620. |
| 11 | ROMANYA J, BLANCO-MORENO J M, SANS F X. Phosphorus mobilization in low-P arable soils may involve soil organic C depletion [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 113: 250-259. |
| 12 | WEYERS E, STRAWN D G, PEAK D, et al.. Phosphorus speciation in calcareous soils following annual dairy manure amendments [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2016, 80(6): 1531-1542. |
| 13 | OBURGER E, LEITNER D, JONES D L, et al.. Adsorption and desorption dynamics of citric acid anions in soil [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 62(5): 733-742. |
| 14 | HU Y, GAO Z, HUANG Y, et al.. Impact of poplar-based phytomanagement on metal bioavailability in low-phosphorus calcareous soil with multi-metal contamination [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 686: 848-855. |
| 15 | CONG W F, SURIYAGODA L D B, LAMBERS H. Tightening the phosphorus cycle through phosphorus-efficient crop genotypes [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2020, 25(10): 967-975. |
| 16 | VANCE C P, UHDE-STONE C, ALLAN D L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource [J]. New Phytol., 2003, 157(3): 423-447. |
| 17 | POSTMA J A, DATHE A, LYNCH J P. The optimal lateral root branching density for maize depends on nitrogen and phosphorus availability [J]. Plant Physiol., 2014, 166(2): 590-602. |
| 18 | HALING R E, BROWN L K, STEFANSKI A, et al.. Differences in nutrient foraging among Trifolium subterraneum cultivars deliver improved P-acquisition efficiency [J]. Plant Soil, 2018, 424(1): 539-554. |
| 19 | HINSINGER P, PLASSARD C, TANG C X, et al.. Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review [J]. Plant Soil, 2003, 248(1): 43-59. |
| 20 | RICHARDSON A E, LYNCH J P, RYAN P R, et al.. Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture [J]. Plant Soil, 2011, 349(1): 121-156. |
| 21 | PANG J, BANSAL R, ZHAO H, et al.. The carboxylate-releasing phosphorus-mobilizing strategy can be proxied by foliar manganese concentration in a large set of chickpea germplasm under low phosphorus supply [J]. New Phytol., 2018, 219(2): 518-529. |
| 22 | 邢维芹, 张红毅, SCHECKEL Kirk G., 等. 铅冶炼污染区小麦籽粒镉含量及低积累品种筛选 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(10): 2039-2040. |
| XING W Q, ZHANG H Y, SCHECKEL K G, et al.. Grain Cd concentrations of 100 wheat(Triticum aestivum L.) varieties and strains grown on lead-smelting contaminated soils and screening for low Cd varieties [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(10): 2039-2040. | |
| 23 | MA S, NAN Z, HU Y, et al.. Phosphorus supply level is more important than wheat variety in safe utilization of cadmium-contaminated calcareous soil [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2022, 424: 127224 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 24 | LUO L, MA Y, SANDERS R L, et al.. Phosphorus speciation and transformation in long-term fertilized soil: evidence from chemical fractionation and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy [J]. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems, 2017, 107(2): 215-226. |
| 25 | 屈锋,牟世芬,侯小平,等. 小麦根系中有机酸的离子色谱法分析研究 [J]. 色谱, 1995(5): 395-397. |
| QU F, MOU S F, HOU X P, et al.. Determination of organic acids in wheat-root by lon chromatography [J]. Chin. J. Chromatography, 1995(5): 395-397. | |
| 26 | LAMBERS H, SHANE M W, CRAMER M D, et al.. Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits [J]. Ann. Bot., 2006, 98(4): 693-713. |
| 27 | SHEN J, YUAN L, ZHANG J, et al.. Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant [J]. Plant Physiol., 2011, 156(3): 997-1005. |
| 28 | MANSKE G, ORTIZ-MONASTERIO J, MVAN GINKEL, et al.. Traits associated with improved P-uptake efficiency in CIMMYT’s semidwarf spring bread wheat grown on an acid Andisol in Mexico [J]. Plant Soil, 2000, 221(2): 189-204. |
| 29 | TENG W, DENG Y, CHEN X P, et al.. Characterization of root response to phosphorus supply from morphology to gene analysis in field-grown wheat [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2013, 64(5): 1403-1411. |
| 30 | SHEN Q, WEN Z, DONG Y, et al.. The responses of root morphology and phosphorus-mobilizing exudations in wheat to increasing shoot phosphorus concentration [J/OL]. Aob Plants, 2018, 10(5): ply054 [2022-02-20]. . |
| 31 | LIU D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| 32 | LIU B, LI H, ZHU B, et al.. Complementarity in nutrient foraging strategies of absorptive fine roots and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi across 14 coexisting subtropical tree species [J]. New Phytol., 2015, 208(1): 125-136. |
| 33 | CHEN W, KOIDE R T, ADAMS T S, et al.. Root morphology and mycorrhizal symbioses together shape nutrient foraging strategies of temperate trees [J]. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, 113(31): 8741-8746. |
| 34 | LI H, LIU B, MCCORMACK M L, et al.. Diverse belowground resource strategies underlie plant species coexistence and spatial distribution in three grasslands along a precipitation gradient [J]. New Phytol., 2017, 216(4): 1140-1150. |
| 35 | MA Z, GUO D, XU X, et al.. Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits [J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7694): 94-97. |
| 36 | LAMBERS H, HAYES P E, LALIBERTE E, et al.. Leaf manganese accumulation and phosphorus-acquisition efficiency [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2015, 20(2): 83-90. |
| 37 | WANG Y, LAMBERS H. Root-released organic anions in response to low phosphorus availability: recent progress, challenges and future perspectives [J]. Plant Soil, 2020, 447(1): 135-156. |
| 38 | 刘胜亮, 朱舒亮, 李静, 等. 不同有机酸对磷酸三钙溶解能力的研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2017, 39(5): 1010-1016. |
| LIU S L, ZHU S L, LI J, et al.. A study on the ability of different organic acids to dissolve tricalcium phosphate [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2017, 39(5): 1010-1016. | |
| 39 | ROBIN A L, SANKHLA D. Essential Guide to Food Additives. [M]. 4th Ed n. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013: 44-64. |
| 40 | YANG P, CHEN H J, FAN H Y, et al.. Phosphorus supply alters the root metabolism of Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. varchinensis. utilis Tsen et Lee) and the mobilization of Cd bound to lepidocrocite in soil [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2019, 167: 103827 [2020-02-20]. . |
| 41 | EDAYILAM N, MONTGOMERY D, FERGUSON B, et al.. Phosphorus stress-induced changes in plant root exudation could potentially facilitate uranium mobilization from stable mineral forms [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52(14): 7652-7662. |
| 42 | MAGDZIAK Z, MLECZEK M, RUTKOWSKI P, et al.. Diversity of low-molecular weight organic acids synthesized by salix growing in soils characterized by different Cu, Pb and Zn concentrations [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2017, 39(6): 1-15. |
| 43 | 刘桂华, 敖明, 柴冠群, 等. 低分子有机酸对贵州黄壤中镉释放及形态的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(6): 1473-1479. |
| LIU G H, AO M, CHAI G Q, et al.. Effects of organic acids with low molecular weight on the extraction and fractionations of cadmium in yellow soil of Guizhou [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2018, 49(6): 1473-1479. | |
| 44 | 胡浩, 潘杰, 曾清如, 等. 低分子有机酸淋溶对土壤中重金属Pb Cd Cu和Zn的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008 (4): 1611-1616. |
| HU H, PAN J, ZENG Q R, et al.. The effects of soil leaching with low molecular weight organic acids on Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2008(4): 1611-1616. | |
| 45 | 魏佳, 李取生, 徐智敏, 等. 多种有机酸对土壤中碳酸镉的活化效应[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(9): 5298-5306. |
| WEI J, LI Q S, XU Z M, et al.. Mobilization effects of various organic acids on cadmium carbonate in soil [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2017, 11(9): 5298-5306. |
| [1] | Xuejing LIU, Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN. Dynamics of Soil Water Content and Yield Formation Characteristics of Winter Wheat Under Water Limited Irrigation in Spring in Haihe Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 167-176. |
| [2] | Lijuan ZHANG, Yukun QIN, Huihuang CHENG, Yongqi LI, Haihua LUO. Research on Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss from Surface Runoff of Cotton Field in Northern Jiangxi Province of Poyang Lake Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 166-175. |
| [3] | Yuan YI, Huiyun ZHANG, Liwei LIU, Jing WANG, Xuecheng ZHU, Na ZHAO, Guohua FENG. Effects of Slow-released Fertilizer Compound Humic Acid Instead of Urea on Grain Yield and Population Quality in Xumai New Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 144-153. |
| [4] | Xiaoqing ZHANG, Zhuangzhuang LI, Shibao CHEN, Yu MENG, Dajun REN, Shuqing ZHANG. Sensitivity Differences of Shrub Seedlings to Cadmium Toxicity [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 173-184. |
| [5] | Yinyan GAO, Yi SUN, Baochun LI. Estimating of Wheat Ears Number in Field Based on RGB Images Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 103-110. |
| [6] | Linlin DONG, Jinfang ZHA, Mingxing SHEN, Haihou WANG, Linlin SHI, Yueyue TAO, Xinwei ZHOU, Changying LU. Effect of Long-term Straw Returning on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions Composition in Rice-Wheat Rotation Ecosystem [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 166-175. |
| [7] | Chenchen SUN, Lan MA, Yonghong WU, Yuanchun YU. Effects and Mechanism of Indoleacetic Acid on the Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Water by Peripheral Organisms [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 204-209. |
| [8] | Jun XU, Ting LI, Minjun HU, Yugen JIANG, Huili YAN, Wenxiu XU, Yijun YU, Zhenyan HE. Development and Utilization of KASP Marker LCd-38 for Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 40-47. |
| [9] | Xin XU, Zhaowu MA, Shuping XIONG, Xinming MA, Tao CHENG, Haiyang LI, Jinpeng ZHAO. Wheat Yield Forecast in Henan Province Based on Climate Year Type [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 136-144. |
| [10] | Jian WANG, Ailing XU, Xiaodong WEI, Jilong XI, Na YANG, Ke WANG, Tianyuan XI, Jiancheng ZHANG. Risk Assessment of Spring Freezing Injury of Wheat at Different Sowing Dates in Yuncheng Basin [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 137-147. |
| [11] | Shuwei ZHANG, Lili ZHAO, Chao CHEN, Jingchen TAN, Li ZHANG, Yi XI. Growth and Physiological Response of 3 Different Provenances of Pueraria lobate Under Low Phosphorus Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 71-82. |
| [12] | JIANG Yun, ZHANG Lili, XUE Ping, WANG Xiudong. Development Status of Wheat Industry in China and International Experience for Reference [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 1-10. |
| [13] | LI Junjie, DU Pufang, SHI Tingrui, HOU Peijia, CHAI Xinyu, ZHAO Rui, WANG Yu, LI Hongxia. LI Junjie, DU Pufang, SHI Tingrui, HOU Peijia, CHAI Xinyu, ZHAO Rui, WANG Yu, LI Hongxia* [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 21-32. |
| [14] | JIAN Tiancai, KANG Jianhong, WU Hongliang, LIU Genhong, GAO Di, MA Xueying, LI Xin. Antioxidative Characteristics Study of Nitrogen in Alleviating Premature Senescence of Spring Wheat at High Temperature after Anthesis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 33-44. |
| [15] | YE Linwei, TANG Rongnian, LI Chuang. Qualitative Study on Phosphorus Content in Rubber Leaves Based on AE-FFNN Neural Network [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 117-124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号