




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 182-192.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0674
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Jingjie GUO1( ), Xiaomeng REN2, Zhongju MENG1(
), Xiaomeng REN2, Zhongju MENG1( ), Tao WANG1, Shuai QI1, Jiajia SONG3, Baomengkenashun3, Shengli HAN4
), Tao WANG1, Shuai QI1, Jiajia SONG3, Baomengkenashun3, Shengli HAN4
Received:2022-08-16
Accepted:2022-09-14
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Zhongju MENG
郭靖捷1( ), 任晓萌2, 蒙仲举1(
), 任晓萌2, 蒙仲举1( ), 王涛1, 祁帅1, 宋佳佳3, 宝孟克那顺3, 韩胜利4
), 王涛1, 祁帅1, 宋佳佳3, 宝孟克那顺3, 韩胜利4
通讯作者:
蒙仲举
作者简介:郭靖捷 E-mail:1063646151@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jingjie GUO, Xiaomeng REN, Zhongju MENG, Tao WANG, Shuai QI, Jiajia SONG, Baomengkenashun, Shengli HAN. Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties of Plant Protection System for Salt Lake in Semi-arid Wind-sand Grassland Area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 182-192.
郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192.
样地 Experimental plot | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 地貌状况 Geographic condition | 植被特征 Vegetation characteristics | 植被盖度 Vegetation coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
干涸湖心 DLC | 43°24′3.56″N、 114°51′24.64″E | 地势平坦,地表覆盖盐结皮,部分 盐结皮被活化 Land is flat and covered with salt crust, some of which is activated | 无植被覆盖 No vegetation cover | 0 |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 43°23′13.35″N、114°52′17.51″E | 地势平坦,地表具有少量盐结皮 Terrain is flat with a small amount of salt crust on the surface | 碱蓬、盐爪爪 Suaeda glauca, Kalidium foliatum | 70~80 |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 43°22′45.19″N、114°52′46.93″E | 地势起伏较小,地表盐结皮发育 Small relief, salt crust surface development | 芨芨草、碱蓬、碱蒿 Achnatherum splendens, Suaeda glauca, Artemisia anethifolia | 40~50 |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 43°22′26.27″N、114°53′7.02″E | 地势起伏较大,灌丛沙包高度0.5~2.0 m,半固定 Relief is larger, shrub sandbag height 0.5~2.0 m, semi-fixed | 白刺为主,灌丛间有少量西伯利亚蓼、芨芨草 Nitraria tangutorum is dominant, with a small amount of Polygonum sibiricum and Achnatherum splendens among shrubs | 20~30 |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 43°21′21.86″N、114°54′14.20″E | 流沙,沙丘高度5~10 m,沙面结构松散 Quicksand, dune height 5~10 m, sand surface structure is loose | 沙丘上部无植被覆盖,丘间有少量白刺 Upper part of dune is not covered by vegetation, and there is a small amount of Nitraria tangutorum | 0~5 |
Table 1 Site location, landform and vegetation characteristics
样地 Experimental plot | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 地貌状况 Geographic condition | 植被特征 Vegetation characteristics | 植被盖度 Vegetation coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
干涸湖心 DLC | 43°24′3.56″N、 114°51′24.64″E | 地势平坦,地表覆盖盐结皮,部分 盐结皮被活化 Land is flat and covered with salt crust, some of which is activated | 无植被覆盖 No vegetation cover | 0 |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 43°23′13.35″N、114°52′17.51″E | 地势平坦,地表具有少量盐结皮 Terrain is flat with a small amount of salt crust on the surface | 碱蓬、盐爪爪 Suaeda glauca, Kalidium foliatum | 70~80 |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 43°22′45.19″N、114°52′46.93″E | 地势起伏较小,地表盐结皮发育 Small relief, salt crust surface development | 芨芨草、碱蓬、碱蒿 Achnatherum splendens, Suaeda glauca, Artemisia anethifolia | 40~50 |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 43°22′26.27″N、114°53′7.02″E | 地势起伏较大,灌丛沙包高度0.5~2.0 m,半固定 Relief is larger, shrub sandbag height 0.5~2.0 m, semi-fixed | 白刺为主,灌丛间有少量西伯利亚蓼、芨芨草 Nitraria tangutorum is dominant, with a small amount of Polygonum sibiricum and Achnatherum splendens among shrubs | 20~30 |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 43°21′21.86″N、114°54′14.20″E | 流沙,沙丘高度5~10 m,沙面结构松散 Quicksand, dune height 5~10 m, sand surface structure is loose | 沙丘上部无植被覆盖,丘间有少量白刺 Upper part of dune is not covered by vegetation, and there is a small amount of Nitraria tangutorum | 0~5 |
土层 深度 Soil depth/cm | 样地 Sampling location | 粘粒 Clay/% | 粉粒 Silt/% | 极细砂 Very fine sand/% | 细砂 Fine sand/% | 中砂 Medium sand/% | 粗砂 Coarse sand/% | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 17.17±1.02 b | 36.36±5.16 b | 0.05±0.03 d | 0.00±0.00 c | 3.52±0.17 d | 33.39±4.20 b | 9.51±1.13 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 26.03±2.15 a | 44.41±3.41 a | 4.41±0.31 a | 4.62±0.75 b | 9.43±1.74 c | 9.33±6.21 c | 1.75±2.45 d | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 3.57±0.78 c | 11.68±0.51 c | 3.57±0.26 b | 5.59±0.11 b | 26.37±0.85 b | 44.01±1.47 b | 5.22±0.69 c | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 1.69±0.20 c | 6.83±0.15 cd | 1.19±0.03 c | 23.45±1.27 a | 53.73±1.22 a | 11.47±2.15 c | 1.64±0.17 d | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 2.70±1.52 c | 5.03±2.54 d | 0.00±0.00 d | 0.37±0.21 c | 2.43±0.27 d | 71.38±4.05 a | 18.08±0.26 a | |
| 10—20 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 27.26±6.86 a | 59.72±1.50 b | 0.45±0.19 c | 0.03±0.03 c | 0.53±5.27 c | 11.12±7.74 b | 1.89±3.28 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 35.84±5.30 a | 61.26±3.92 a | 0.46±0.09 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 1.45±1.29 d | 0.99±1.08 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 7.27±1.18 b | 29.76±1.39 b | 15.51±0.12 a | 21.83±1.67 b | 13.56±1.63 b | 12.07±0.11 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 2.05±0.22 b | 11.15±0.14 a | 2.03±0.05 b | 33.04±0.74 a | 38.80±0.60 a | 10.87±1.32 b | 2.05±0.50 b | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 5.47±0.75 b | 10.19±0.31 a | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 51.40±1.47 a | 32.93±0.44 a | |
| 20—30 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 25.14±4.94 a | 55.56±5.02 a | 5.30±0.08 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 32.27±4.76 a | 60.60±4.82 a | 7.13±0.07 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 1.94±0.23 b | 9.35±0.71 b | 8.38±0.49 a | 24.97±1.58 a | 20.65±2.60 b | 29.37±4.32 b | 5.34±1.06 b | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 1.76±0.15 b | 5.34±0.20 bc | 1.30±0.07 b | 13.16±0.44 b | 49.59±1.06 a | 26.59±1.61 b | 2.26±0.54 b | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 0.86±0.16 b | 1.93±0.12 c | 0.17±0.04 c | 2.64±0.06 c | 11.24±0.48 c | 69.86±0.63 a | 13.28±1.01 a |
Table 2 Soil mechanical composition with different underlying surfaces
土层 深度 Soil depth/cm | 样地 Sampling location | 粘粒 Clay/% | 粉粒 Silt/% | 极细砂 Very fine sand/% | 细砂 Fine sand/% | 中砂 Medium sand/% | 粗砂 Coarse sand/% | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 17.17±1.02 b | 36.36±5.16 b | 0.05±0.03 d | 0.00±0.00 c | 3.52±0.17 d | 33.39±4.20 b | 9.51±1.13 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 26.03±2.15 a | 44.41±3.41 a | 4.41±0.31 a | 4.62±0.75 b | 9.43±1.74 c | 9.33±6.21 c | 1.75±2.45 d | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 3.57±0.78 c | 11.68±0.51 c | 3.57±0.26 b | 5.59±0.11 b | 26.37±0.85 b | 44.01±1.47 b | 5.22±0.69 c | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 1.69±0.20 c | 6.83±0.15 cd | 1.19±0.03 c | 23.45±1.27 a | 53.73±1.22 a | 11.47±2.15 c | 1.64±0.17 d | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 2.70±1.52 c | 5.03±2.54 d | 0.00±0.00 d | 0.37±0.21 c | 2.43±0.27 d | 71.38±4.05 a | 18.08±0.26 a | |
| 10—20 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 27.26±6.86 a | 59.72±1.50 b | 0.45±0.19 c | 0.03±0.03 c | 0.53±5.27 c | 11.12±7.74 b | 1.89±3.28 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 35.84±5.30 a | 61.26±3.92 a | 0.46±0.09 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 1.45±1.29 d | 0.99±1.08 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 7.27±1.18 b | 29.76±1.39 b | 15.51±0.12 a | 21.83±1.67 b | 13.56±1.63 b | 12.07±0.11 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 2.05±0.22 b | 11.15±0.14 a | 2.03±0.05 b | 33.04±0.74 a | 38.80±0.60 a | 10.87±1.32 b | 2.05±0.50 b | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 5.47±0.75 b | 10.19±0.31 a | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 51.40±1.47 a | 32.93±0.44 a | |
| 20—30 | 干涸湖心 DLC | 25.14±4.94 a | 55.56±5.02 a | 5.30±0.08 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b |
碱蓬防护带 AS | 32.27±4.76 a | 60.60±4.82 a | 7.13±0.07 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 b | |
盐碱草滩地 SG | 1.94±0.23 b | 9.35±0.71 b | 8.38±0.49 a | 24.97±1.58 a | 20.65±2.60 b | 29.37±4.32 b | 5.34±1.06 b | |
白刺灌丛 WTB | 1.76±0.15 b | 5.34±0.20 bc | 1.30±0.07 b | 13.16±0.44 b | 49.59±1.06 a | 26.59±1.61 b | 2.26±0.54 b | |
沙地风蚀坑 SWEP | 0.86±0.16 b | 1.93±0.12 c | 0.17±0.04 c | 2.64±0.06 c | 11.24±0.48 c | 69.86±0.63 a | 13.28±1.01 a |

Fig. 4 Available nutrient contents in soils with different underlying surfacesNote:Different Greek letters indicate significant differences in each index between different sampling location in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different English letters indicate significant differencesin each index between different soil layer in the same sampling location at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 碱蓬防护带 AS/% | 盐碱草滩地 SG/% | 白刺灌丛 WTB/% | 沙地风蚀坑 SWEP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
速效氮 Available nitrogen | 0—10 | 8 | 11 | 28 | 6 |
| 10—20 | 18 | 25 | 63 | 14 | |
| 20—30 | 17 | 31 | 314 | 8 | |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0—10 | 86 | 79 | 42 | 13 |
| 10—20 | 90 | 67 | 25 | 8 | |
| 20—30 | 75 | 34 | 41 | 9 | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0—10 | 39 | 17 | 10 | 4 |
| 10—20 | 41 | 14 | 22 | 4 | |
| 20—30 | 56 | 17 | 10 | 6 |
Table 3 Enrichment of available nutrients in soils with different underlying surfaces
指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 碱蓬防护带 AS/% | 盐碱草滩地 SG/% | 白刺灌丛 WTB/% | 沙地风蚀坑 SWEP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
速效氮 Available nitrogen | 0—10 | 8 | 11 | 28 | 6 |
| 10—20 | 18 | 25 | 63 | 14 | |
| 20—30 | 17 | 31 | 314 | 8 | |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0—10 | 86 | 79 | 42 | 13 |
| 10—20 | 90 | 67 | 25 | 8 | |
| 20—30 | 75 | 34 | 41 | 9 | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0—10 | 39 | 17 | 10 | 4 |
| 10—20 | 41 | 14 | 22 | 4 | |
| 20—30 | 56 | 17 | 10 | 6 |
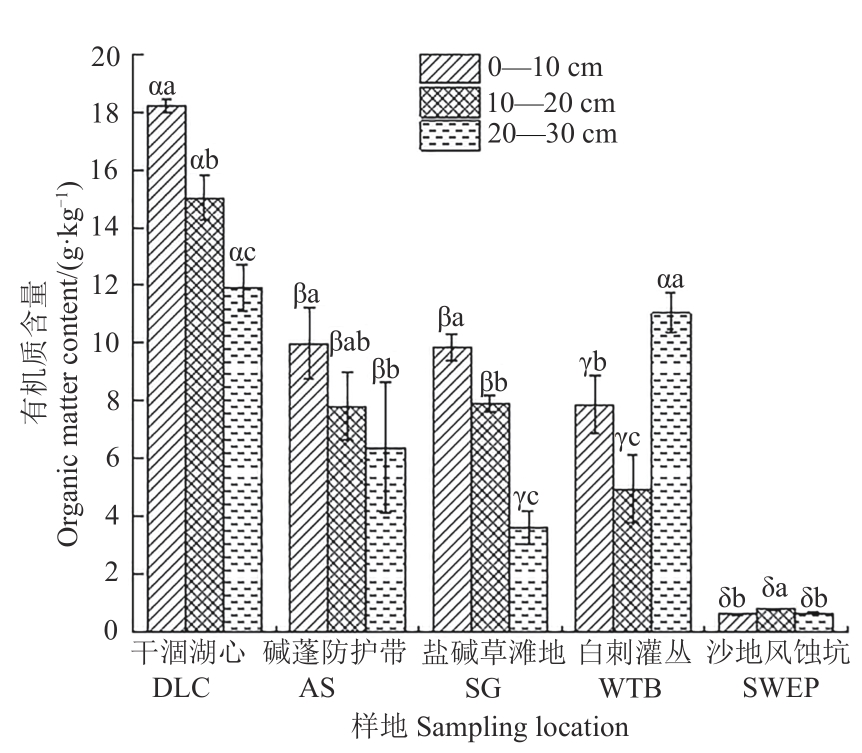
Fig. 5 Oganic matter content in soils with different underlying surfacesNote:Different Greek letters indicate significant differences between different sampling location in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different English letters indicate significant differences between different soil depth in the same sampling location at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 碱蓬防护带 AS/% | 盐碱草滩地 SG/% | 白刺灌丛 WTB/% | 沙地风蚀坑 SWEP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter | 0—10 | 55 | 54 | 43 | 3 |
| 10—20 | 52 | 53 | 33 | 5 | |
| 20—30 | 53 | 30 | 93 | 5 |
Table 4 Enrichment of organic matter in soils with different underlying surfaces
指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 碱蓬防护带 AS/% | 盐碱草滩地 SG/% | 白刺灌丛 WTB/% | 沙地风蚀坑 SWEP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter | 0—10 | 55 | 54 | 43 | 3 |
| 10—20 | 52 | 53 | 33 | 5 | |
| 20—30 | 53 | 30 | 93 | 5 |
指标 Index | 粘粒 Clay | 粉粒 Silt | 极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.69** | 0.76** | 0.28 | -0.36 | -0.62* | -0.42 | -0.38 |
速效氮 Available nitrogen | -0.05 | -0.08 | -0.23 | -0.02 | 0.28 | -0.03 | -0.10 |
速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.62* | 0.58* | -0.27 | -0.43 | -0.40 | -0.29 | -0.22 |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.82** | 0.86** | 0.03 | -0.36 | -0.33 | -0.67** | -0.62* |
有机质 Organic matter | 0.45 | 0.47 | -0.04 | -0.18 | 0.02 | -0.46 | -0.49 |
Table 5 Correlation analysis of soil nutrient content and soil mechanical composition
指标 Index | 粘粒 Clay | 粉粒 Silt | 极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.69** | 0.76** | 0.28 | -0.36 | -0.62* | -0.42 | -0.38 |
速效氮 Available nitrogen | -0.05 | -0.08 | -0.23 | -0.02 | 0.28 | -0.03 | -0.10 |
速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.62* | 0.58* | -0.27 | -0.43 | -0.40 | -0.29 | -0.22 |
速效钾 Available potassium | 0.82** | 0.86** | 0.03 | -0.36 | -0.33 | -0.67** | -0.62* |
有机质 Organic matter | 0.45 | 0.47 | -0.04 | -0.18 | 0.02 | -0.46 | -0.49 |
| 1 | 王亚俊,孙占东.中国干旱区的湖泊[J].干旱区研究,2007,24(4):422-427. |
| WANG Y J, SUN Z D. Lakes in the arid areas in China [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2007,24(4):422-427. | |
| 2 | 王瑾杰,丁建丽,张喆. 2008—2014年新疆艾比湖流域土壤水分时空分布特征[J].生态学报,2019,39(5):1784-1794. |
| WANG J J, DING J L, ZHANG Z. Temporal-spatial dynamic change characteristics of soil moisture in Ebinur Lake Basin from 2008—2014 [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(5):1784-1794. | |
| 3 | 郝帅,李发东.艾比湖流域典型荒漠植被水分利用来源研究[J].地理学报,2021,76(7):1649-1661. |
| HAO S, LI F D. Water sources of the typical desert vegetation in Ebinur Lake Basin [J]. Acta Geogr. Sin.,2021,76(7):1649-1661. | |
| 4 | 邓廷飞,刘彦,颜秋晓,等.贵州典型山银花土壤机械组成与养分特性及其关系[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(5):209-214. |
| DENG T F, LIU Y, YAN Q X, et al.. Soil mechanical composition and nutrient characteristics of lonicera japonica in typical mountain of Guizhou and their relationship [J]. Soil Water conserv., 2014,28(5):209-214. | |
| 5 | 李学斌,张义凡,陈林,等.荒漠草原典型群落土壤粒径和养分的分布特征及其关系研究[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(8):1635-1644. |
| LI X B, ZHANG Y F, CHEN L, et al.. Distribution characteristics and relationship between soil particle size and nutrients in typical community of desert steppe [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin.,2017,37(8):1635-1644. | |
| 6 | 刘东伟,吉力力·阿不都外力,雷加强,等.盐尘暴及其生态效应[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(1):168-173. |
| LIU D W, Abuduwaili Jilili, LEI J Q, et al.. Saline dust storm and its ecological effects [J]. J. Desert Res.,2011,31(1):168-173. | |
| 7 | 何玉惠,刘新平,谢忠奎.红砂灌丛对土壤盐分和养分的富集作用[J].干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(3):115-119. |
| HE Y H, LIU X P, XIE Z K. Enrichment of soil salinity and nutrients under desertification shrub Reaumuria soongorica [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2015,29(3):115-119. | |
| 8 | 刘涛涛,王勇辉,阿迪拉·阿布力米提.艾比湖湿地不同厚度盐结皮与土壤物理性质的相互关系及其影响因素[J].中山大学学报(自然科学版),2021,60(6):91-101. |
| LIU T T, WANG Y H, Abulimiti Adila. The relationship between different salt crust thickness and soil physical properties in Ebinur Lake wetland and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni,2021,60(6):91-101. | |
| 9 | 邓怀敏,吉力力·阿不都外力,葛拥晓.艾比湖干涸湖底盐漠土壤环境特征分析[J].水土保持研究,2013,20(6):14-18. |
| DENG H M, Abuduwaili Jilili, GE Y X. Analysis on the characteristics of dry lakebed sedimentary soil in Ebinur [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2013,20(6):14-18. | |
| 10 | 刘东伟,吉力力·阿不都外力,王立新.新疆艾比湖地区盐尘的沉积通量及其物质组成[J].冰川冻土,2014,36(2):352-359. |
| LIU D W, Abuduwaili Jilili, WANG L X. Sediment fluxes and material composition of the salt dust in Ebinur lake region, Xinjiang [J]. J. Glaciol. Geocry., 2014,36(2):352-359. | |
| 11 | 鄢雪英,丁建丽,李鑫,等.艾比湖湿地退化对盐尘暴发生及运移路径的影响[J].生态学报,2015,35(17):5856-5865. |
| YAN X Y, DING J L, LI X, et al.. Effects of salt dust storm migration pathways on degradation of Ebinur lake wetland [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin.,2015,35(17):5856-5865. | |
| 12 | 刘宏宇,宁小莉,海全胜,等.浑善达克沙地蒸散发时空变化及植被和气候响应[J].干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(8):110-118. |
| LIU H Y, NING X L, HAI Q S, et al.. Spatial-temporal variability of evapotranspiration and its response to vegetation and climate in Hunshandake sandy land [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ.,2022,36(8):110-118. | |
| 13 | 江南,王永,董进,等.内蒙古查干淖尔湖2000a以来气候环境演变的沉积记录[J].地质通报,2016,35(6):953-962. |
| JIANG N, WANG Y, DONG J, et al.. Sedimentary record of climate and environmental evolution since 2000a in Chaganzhuer lake, Inner Mongolia [J]. Geol. Bull. China, 2016,35(6):953-962. | |
| 14 | 周玲美,王世航,权玲.基于遥感和地理信息系统的内蒙古呼日查干淖尔地区生态脆弱性评价[J].生态与农村环境学报,2021,37(4):484-491. |
| ZHOU L M, WANG S H, QUAN L. Ecological vulnerability assessment in Huri Chagannoor of Inner Mongolia based on RS and GIS technology [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ.,2021,37(4):484-491. | |
| 15 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2020:1-495. |
| 16 | 谭明东,王振华,王越,等.长期滴灌棉田非灌溉季节土壤盐分累积特征[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(2):485-492. |
| TAN M D, WANG Z H, WANG Y, et al.. Characteristics of soil salt accumulation in non-irrigated cotton field under long-term drip irrigation [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2022,39(2):485-492. | |
| 17 | 雷斯越,赵文慧,杨亚辉,等.不同坡位植被生长状况与土壤养分空间分布特征[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(1):86-91. |
| LEI S Y, ZHAO W H, YANG Y H, et al.. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrients and vegetation growth status in different slope [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv.,2019,26(1):86-91. | |
| 18 | 王晓芬,马源,张格非,等.高寒草甸退化阶段植物群落多样性与系统多功能性的联系[J].草地学报,2021,29(5):1053-1060. |
| WANG X F, MA Y, ZHANG G F, et al.. Relationship between plant community diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality during alpine meadow degradation [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin.,2021,29(5):1053-1060. | |
| 19 | 冯亚亚,汪季,党晓宏,等.土壤水盐因子对盐湖防护林体系植被群落分布的影响[J].水土保持通报,2021,41(2):43-50. |
| FENG Y Y, WANG J, DANG X H, et al.. Effects of soil water and salt factors on distribution of vegetation community in salt lake shelterbelt system [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv.,2021,41(2):43-50. | |
| 20 | 袁媛,张鹤,武杼华,等.植被恢复对毛乌素沙地土壤pH和养分含量的影响[J].土壤通报,2021,52(1):148-156. |
| YUAN Y, ZHANG H, WU Z H, et al.. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil pH and nutrient contents in the Mu Us sandland [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2021,52(1):148-156. | |
| 21 | 奚萨茹拉. 查干淖尔盐碱化土壤化学组成分析及其对碱蓬生物学特性的影响[D].呼和浩特 :内蒙古师范大学,2011. |
| Xisarula. Analysis of chemical composition of saline-alkali soil and its effect on biological characteristics of Suaeda suaeda [D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Normal University,2011. | |
| 22 | 王遵亲,祝寿泉,尤文瑞,等.中国盐渍土[M].北京:科学出版社,1993:1-573. |
| 23 | 刘进辉,王雪芹,马洋.沙漠绿洲过渡带柽柳灌丛沙堆-丘间地系统土壤养分空间异质性[J].生态学报,2016,36(4):979-990. |
| LIU J H, WANG X Q, MA Y. Spatial variation of soil nutrients of Tamarix ramosissima nebkhas and interdune areas in a desert-oasis ecotone [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2016,36(4):979-990. | |
| 24 | 董雷. 查干淖尔退化湖盆湿地植被分布特征与生态恢复效果评价[D].呼和浩特 :内蒙古农业大学,2014. |
| DONG L. Vegetation distribution characteristics and ecological restoration effect evaluation of degraded lake basin wetland in Chaganuoer [D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 25 | 雷学明,段洪浪,刘文飞,等.鄱阳湖湿地碟形湖泊沿高程梯度土壤养分及化学计量研究[J].土壤,2017,49(1):40-48. |
| LEI X M, DUAN H L, LIU W F, et al.. Soil nutrients and stoichiometry along elevation gradients in shallow-lakes of Poyang lake wetland [J]. Soils, 2017,49(1):40-48. | |
| 26 | 徐涛,蒙仲举,斯庆毕力格,等.吉兰泰盐湖周边不同沙化程度植被群落与土壤养分特征研究[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(4):95-100. |
| XU T, MENG Z J, Siqingbilige, et al.. Vegetation communities and soil nutrient characteristics of the regions with different desertification degrees around the Jartai saline lake [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2018,32(4):95-100. | |
| 27 | 吴晓妮,付登高,刘兴祝,等.柴河流域典型景观类型土壤氮磷含量的空间变异特征[J].土壤,2016,48(6):1209-1214. |
| WU X N, FU D G, LIU X Z, et al.. Spatial variability of soil nitrogen and phosphorus in the typical landscape units in Chaihe catchment [J]. Soils, 2016,48(6):1209-1214. | |
| 28 | YAN Y C, XIN X P, XU X L, et al.. Quantitative effects of wind erosion on the soil texture and soil nutrients under different vegetation coverage in a semiarid steppe of Northern China [J]. Plant Soil, 2013,369(1/2) :585-598. |
| 29 | 李昂,高天鹏,张鸣,等.西北风蚀区植被覆盖对土壤风蚀动态的影响[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(6):120-123. |
| LI A, GAO T P, ZHANG M, et al.. Effects of vegetation cover on dynamics of soil wind erosion in northwest China [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv.,2014,28(6):120-123. | |
| 30 | 周永维,葛瑶,艾宁,等.南泥湾湿地不同植被类型土壤养分变化规律与肥力评价[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(5):76-80. |
| ZHOU Y W, GE Y, AI N, et al.. Soil nutrient variation patterns and fertility evaluation in different vegetation types in Nanniwan wetland [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2021,28(5):76-80. | |
| 31 | 黄娟,邓羽松,韦慧,等.喀斯特峰丛洼地不同植被类型土壤微生物量碳氮磷和养分特征[J].土壤通报,2022,53(3):605-612. |
| HUANG J, DENG Y S, WEI H, et al.. Characteristics of soil microbial biomass C, N, P and nutrients in different vegetation types in karst peak cluster depression [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci.,2022,53(3):605-612. | |
| 32 | 管雪薇,汪季,丁延龙,等.吉兰泰盐湖防风固沙林体系土壤理化性状特征[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(5):114-120. |
| GUAN X W, WANG J, DING Y L, et al.. Characteristics of soil physical and chemical properties in the wind-breaking and sand-fixing forest system in Jilantai salt lake [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2019,33(5):114-120. | |
| 33 | 李静鹏,徐明锋,苏志尧,等.不同植被恢复类型的土壤肥力质量评价[J].生态学报,2014,34(9):2297-2307. |
| LI J P, XU M F, SU Z Y, et al.. Soil fertility quality assessment under different vegetation restoration patterns [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2014,34(9):2297-2307. |
| [1] | Rui XIAO, Lu TAN, Liang WU, Hao ZHANG, Jiayuan GUO, Haijun YANG. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil of Kochia scoparia Under Cd Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [2] | Lu MENG, Jingwen FAN, Xinyu SAI, Lusheng ZENG, Xiangyun SONG, Dejie CUI. Effects of Lime on Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Apple Orchards [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [3] | Min LI, Gangtie LI, Hongwu ZHANG, Jiahuan CHEN. Effects of Stubble on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties of Three Kinds of Protein Mulberry Forest [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 172-182. |
| [4] | YANG Jingjing, ZHANG Qingqing*, Tuerxunnayi·Reyimu, Amanula·Yimingniyazi, Xueretijiang·Maitinuri. Effects of Nomadic Grazing and Settled Grazing on the Diversity of Fungi Community in Seriphidium transiliense Desert Grassland [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| [5] | YE Xie-feng1, LING Ai-fen2, LIU Qing-hua3, HAO Wei-hong4, LI Yan-tao4, XUE Qing-. Effect of Humic Acid on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Tobacco Field [J]. , 2010, 12(6): 120-125. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号